Millimeter wave anti-blocking multi-unmanned aerial vehicle deployment method based on building geometric analysis
A geometric analysis, multi-UAV technology, applied in baseband system components, wireless communications, radio transmission systems, etc., can solve the problem of greed, millimeter wave signal line-of-sight and non-line-of-sight transmission path loss is very different, not given. UAV location deployment plan and other issues, to achieve the effect of small path loss and large path loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0055] The specific content of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the specific embodiments:
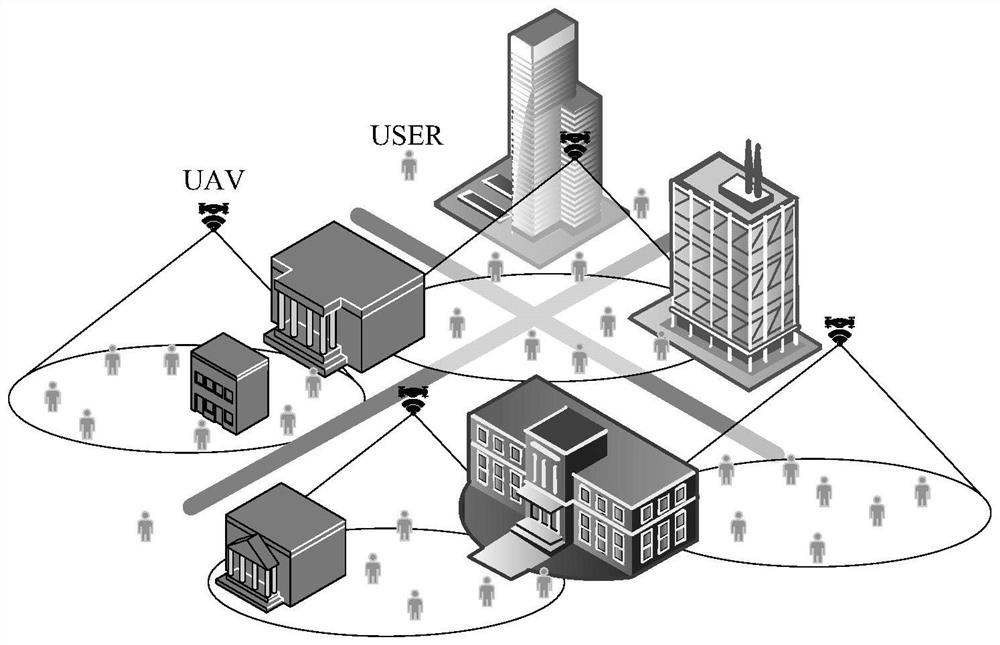
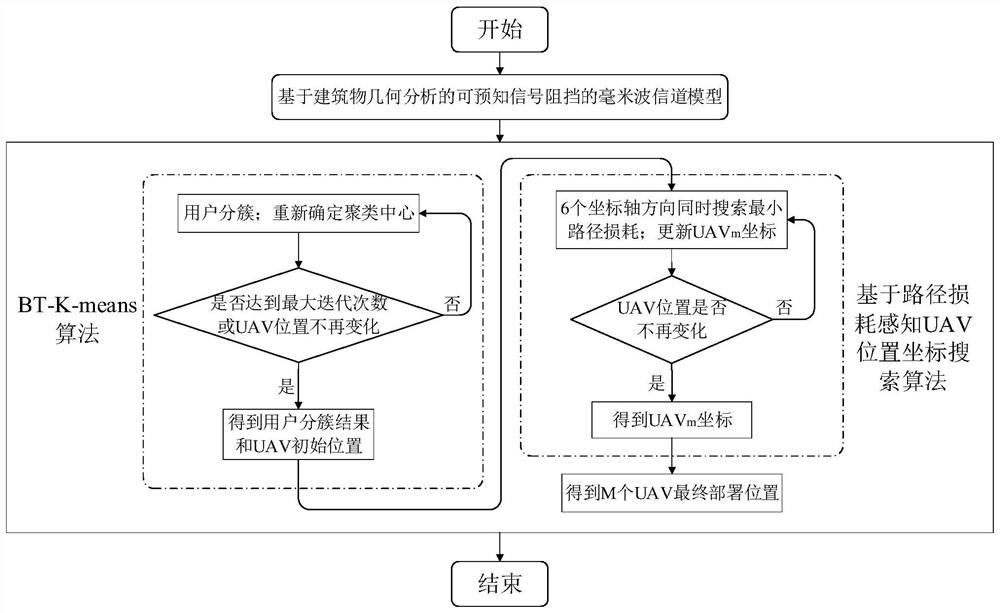
[0056] For figure 1 The urban environmental communication system, which is disclosed in the present invention, a millimeter wave anti-blocking multi-drone deployment method based on building geometric analysis, see figure 2 The following steps are specifically included.
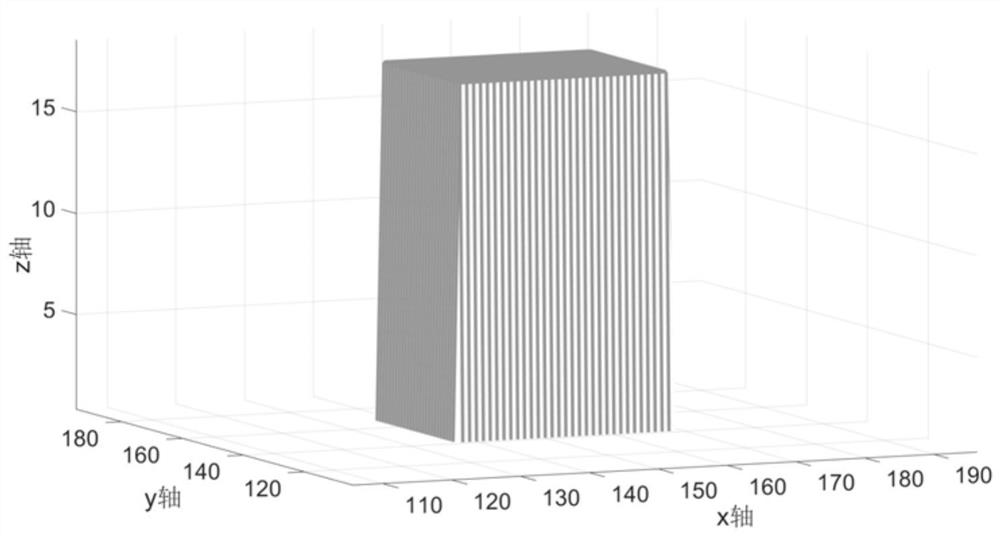
[0057] Step 1. Set a MR frame drone, the urban environmental communication system of K users, the position of the kth user is δ k = (X k Y k ,z k ), X k Y k ,z k The X, Y, Z axial coordinate of the kth user, respectively; the position of the March drone is ξ m = (X m Y m ,z m ), X m Y m ,z m The X, Y, Z axis coordinate of the March Machine; urban building height information is a matrix H; the user is randomly distributed around the building, each drone can serve multiple users at the same time. Millimeter waves are communicated with millimeters between drones and users. Suppose the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com