Asymmetric flowing gas stimulated Raman scattering frequency conversion device
A technology of stimulated Raman scattering and flowing gas. It is applied in the direction of laser scattering effect, laser, electrical components, etc. It can solve the problems of uneven gas density, beam drift, low repetition frequency, etc., and improve the frequency conversion effect and stability. , The effect of reducing uneven airflow and simplifying the overall structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Based on high pressure CO 2 Stimulated Raman scattering frequency conversion device.
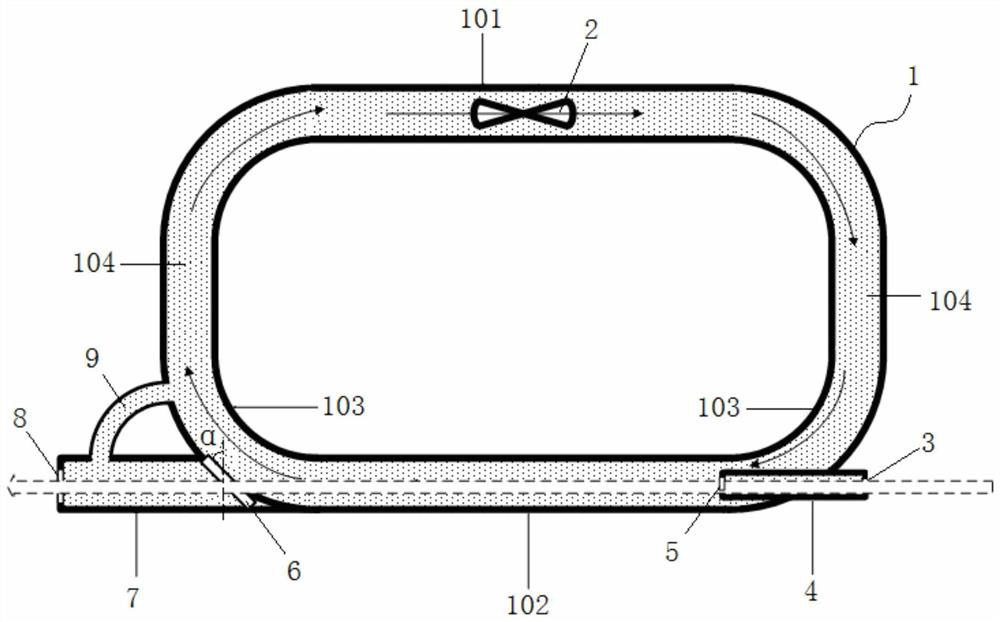
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, put CO at a pressure of 10atm 2 The gas is filled into the closed main gas circulation pipeline 1, and the airflow drive device 2 is controlled to drive the high-pressure CO 2 The gas flows clockwise, and the air flow enters the light-transmitting section 102 through the connecting section 104 on one side, is output from the light-passing section 102, and then enters the air-flow driving section 101 from the connecting section 104 on the other side, forming a circular flow. In this embodiment, the gas flow rate is controlled by controlling the speed of the airflow driving device 2 (fan), so as to adapt to different heat dissipation requirements. The flow guide balance tube 9 connects the output light guide arm 7 with the main gas circulation pipeline 1 to ensure output isolation. The air pressure on both sides of the optical window 6 is ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2, based on high pressure N 2 Stimulated Raman scattering frequency conversion device.
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, put the pressure at 10atm of N 2 The gas is filled into the closed main gas circulation pipeline 1, and the air flow driving device 2 is controlled to drive the high pressure N 2 The gas flows clockwise, and the air flow enters the light-transmitting section 102 through the connecting section 104 on one side, is output from the light-passing section 102, and then enters the air-flow driving section 101 from the connecting section 104 on the other side, forming a circular flow. In this embodiment, the gas flow rate is controlled by controlling the speed of the airflow driving device 2 (fan), so as to adapt to different heat dissipation requirements. The flow guide balance tube 9 connects the output light guide arm 7 with the main gas circulation pipeline 1 to ensure output isolation. The air pressure on both sides of the optical window ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment three, based on high pressure N 2 Stimulated Raman scattering frequency conversion device.
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, put the pressure at 10atm of N 2 The gas is filled into the closed main gas circulation pipeline 1, and the air flow driving device 2 is controlled to drive the high pressure N 2 The gas flows clockwise, and the air flow enters the light-transmitting section 102 through the connecting section 104 on one side, is output from the light-passing section 102, and then enters the air-flow driving section 101 from the connecting section 104 on the other side, forming a circular flow. In this embodiment, the gas flow rate is controlled by controlling the speed of the airflow driving device 2 (fan), so as to adapt to different heat dissipation requirements. The flow guide balance tube 9 connects the output light guide arm 7 with the main gas circulation pipeline 1 to ensure output isolation. The air pressure on both sides of the optical win...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com