Chimeric cytokine receptors including TGFB binding domains
A technology for binding domains and cytokines, applied in the field of chimeric cytokine receptors including TGFβ binding domains, which can solve the problems of accelerating the rejection of CAR-T cells, affecting the therapeutic effect, toxicity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0215] Example 1: Creation of Chimeric Cytokine Receptor-CAR Constructs with Dominant Negative Truncations of TGFβR1 or TGFβR2 build and test
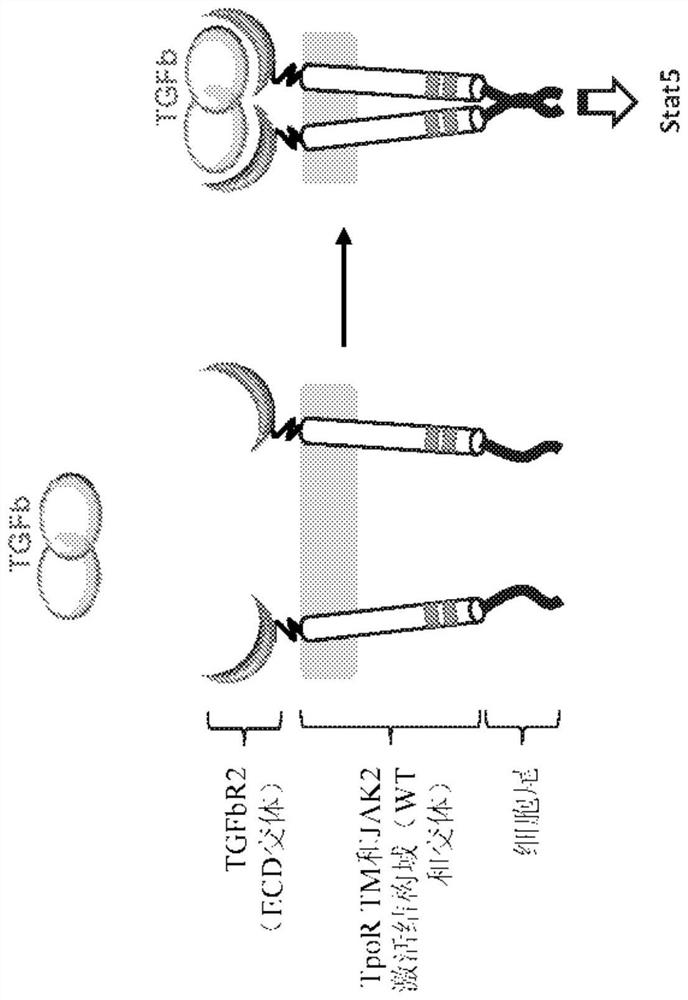
[0216] figure 1 A schematic diagram of an inducible chimeric cytokine receptor of the present disclosure is shown. To couple simultaneous TGF-β binding to cytokine signaling, chimeric cytokine receptors were constructed consisting of: (i) a binding domain comprising the extracellular domain of the TGF-β receptor part or TGF-beta antigen binding domain; (ii) transmembrane domain, said transmembrane domain has intracellular portion, said intracellular portion has JAK2 activation domain; and (iii) STAT recruitment domain, so The STAT recruitment domains include the Stat recruitment (Stat activation) domain from the cytokine receptor tail (cell tail). Such as figure 1 As shown by way of example in , the binding domain includes the extracellular domain of TGFβR2.
[0217] Using a HEK293T cell reporter gene assay, the inducibility ...
example 2
[0221] Example 2: Design and testing of inducible chimeric cytokine receptors using TGFβR2
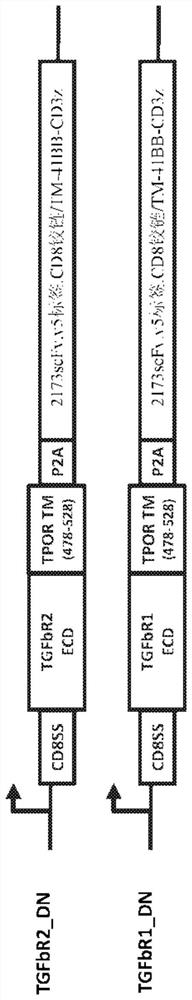
[0222] as reference figure 1 Briefly described, a chimeric cytokine receptor having a binding domain derived from TGFβR2 (“TGFβR2 chimeric cytokine receptor”) was constructed. To investigate the utility of the TGFβR2 chimeric cytokine receptor in the context of CAR-T cells, variants of the extracellular domain (ECD) of TGFβR2 and variants of the transmembrane (TM) domain of TPOR were constructed. Fusions of each TGFβR2 ECD variant, each TPOR™ domain variant, and the intracellular domain (ICD) of the desired cytokine receptor were cloned into a lentiviral vector encoding a second-generation EGFRvIII-specific CAR ( 2173 scFv; described in Sci Transl Med, 2015 Feb 18;7(275):275ra22), and these receptor variants were tested for activity. To allow stoichiometric co-expression of the chimeric cytokine receptor and CAR, the two genes were linked via the P2A peptide ("chimeric cytokine re...
example 3
[0227] Example 3: Modification of Chimeric Cytokine Receptor Binding Domain and Measurement of Constructed Chimeric Cytokine Receptors try
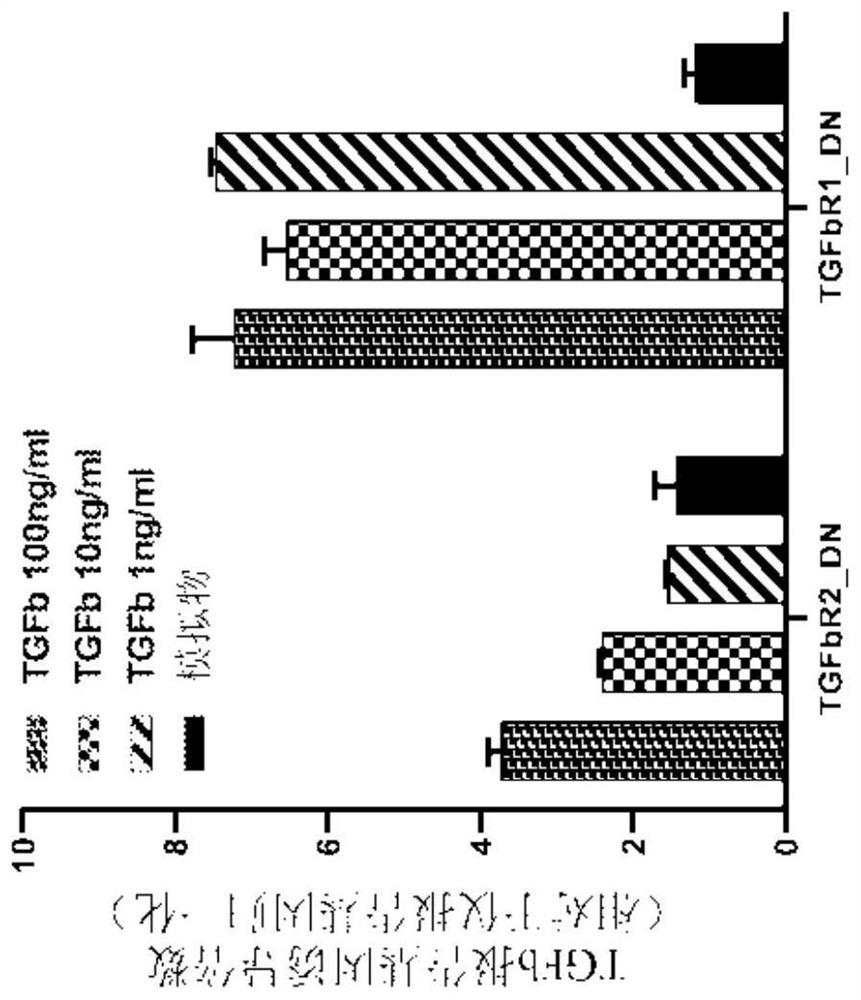
[0228] In the absence of TGFβR2, TGFβR1 interacts with TGF-β ligands with very low affinity. Once the ECD of TGFβR2 binds the TGF-β ligand, the binary complex has an extended interface to efficiently recruit TGFβR1, thereby forming a ternary complex. Engineered TGFβR2 chimeric cytokine receptors can also bind to endogenous TGFβR1, which can sterically interfere with intended signaling through the cytokine receptor ICD. To eliminate the interaction between the TGFβR2 chimeric cytokine receptor and TGFβR1, several variants of the TGFβR1 cassette were designed and modifications that could enhance cytokine signaling while inhibiting TGF-β signaling were identified.
[0229] Figures 6A-6C Inhibition of TGF-β signaling by expression of chimeric cytokine receptors constructed from TGFβR2 with modifications is shown. Figure 6A A schemati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com