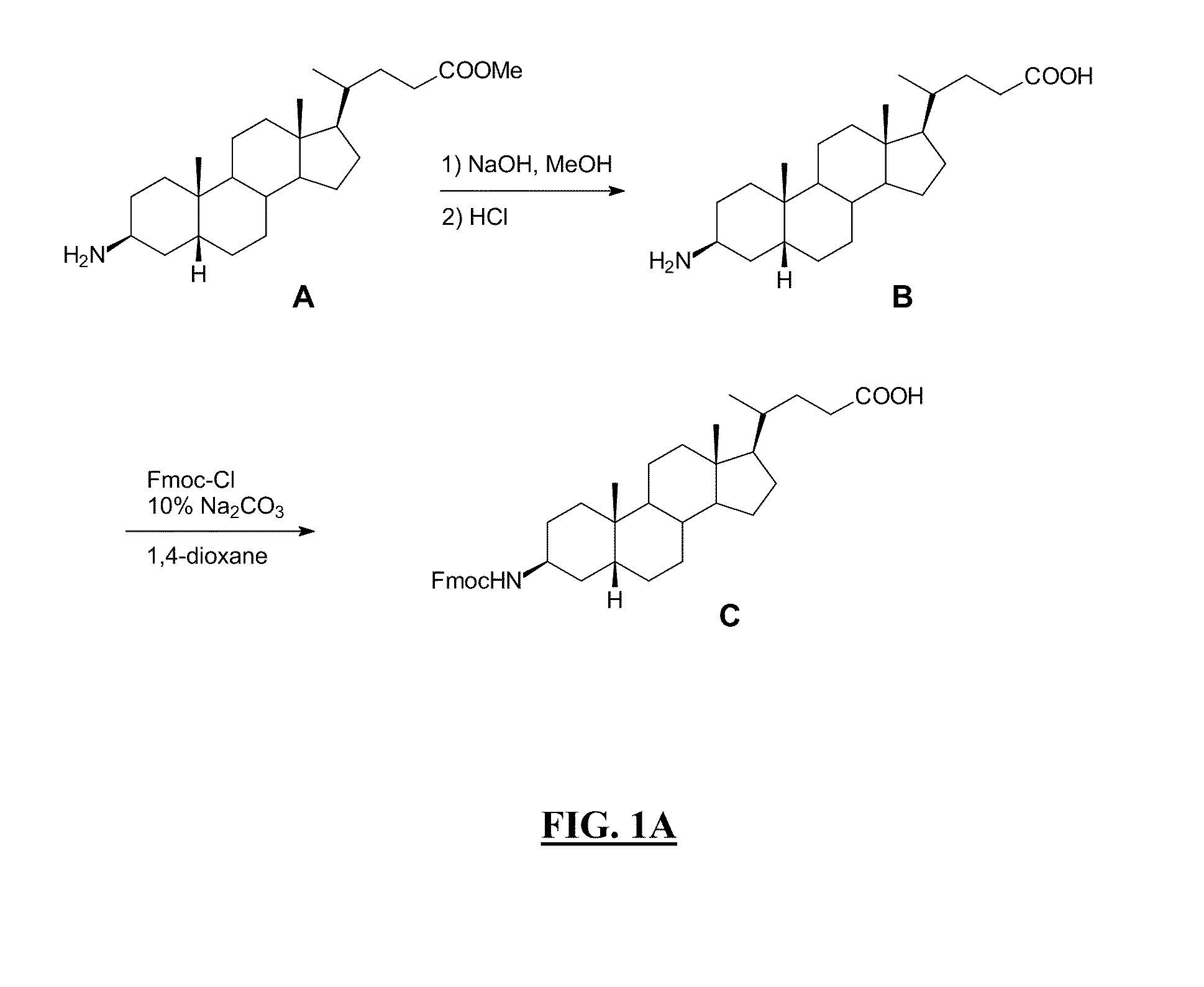
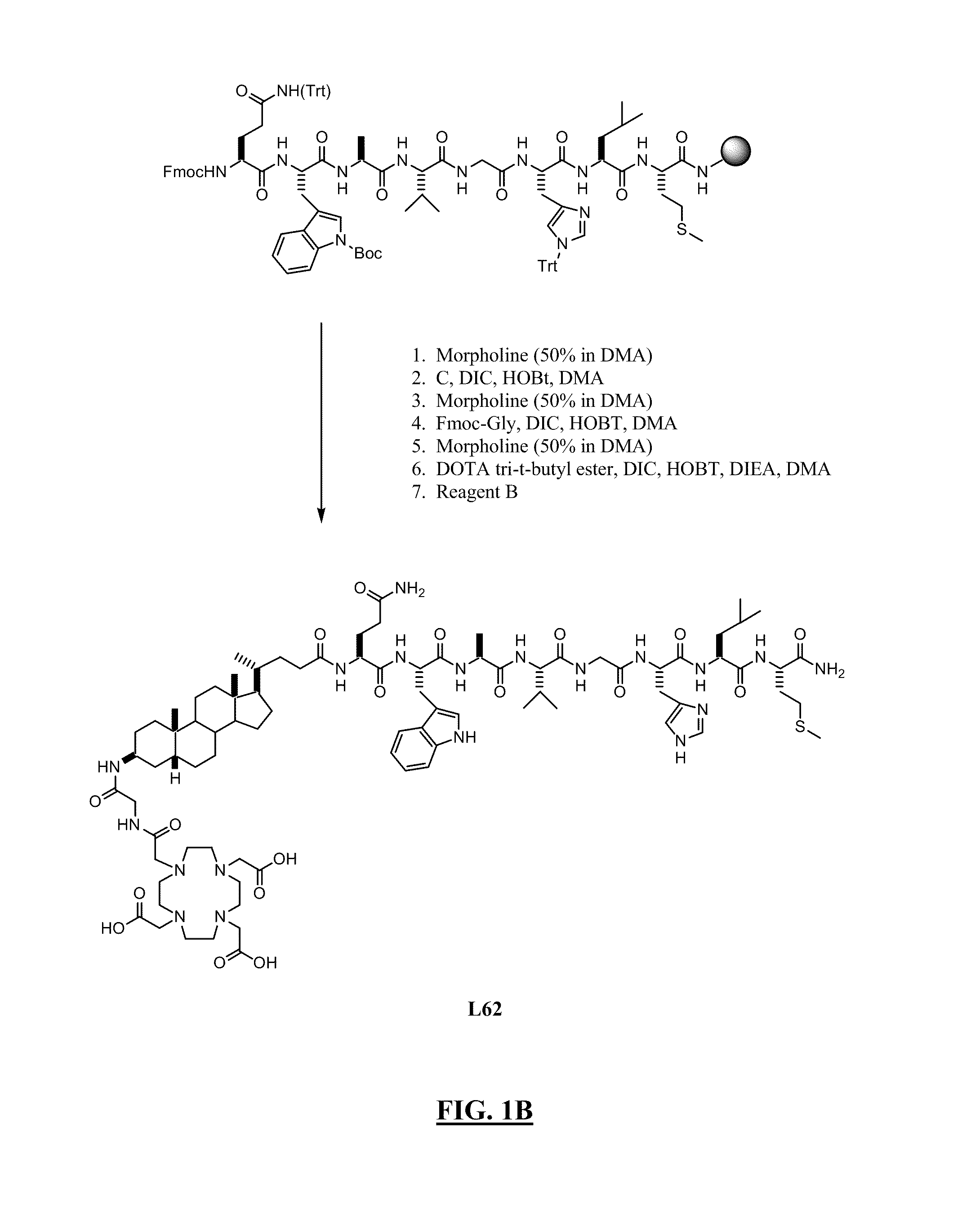
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Receptorome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
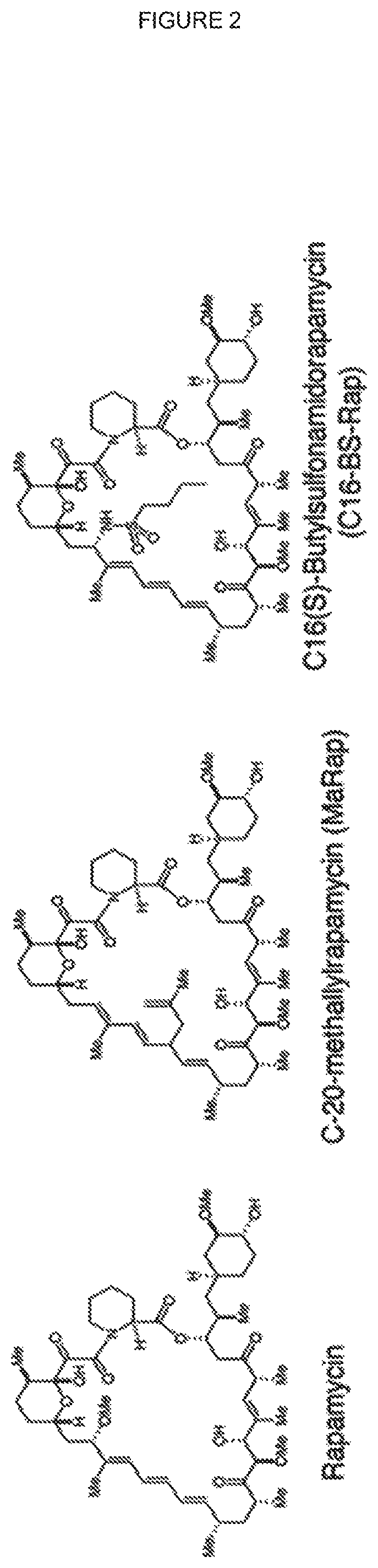
The receptorome is a concept analogue to the genome and proteome but also to other sets of structural or functional units such as the proteasome and connectome. In analogy with the genome, where the genome is the total set of genes, the receptorome can be considered the total set of genes giving rise to receptors or receptor molecules. It could also be seen as the total number of receptor proteins in a certain organism.
Method and composition for treatment of renal failure with antibodies and their equivalents as partial or complete replacement for dialysis
InactiveUS7504106B2Lower Level RequirementsSlow onsetBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInterleukin 6Creatinine rise
A method for treating patients with renal failure includes administering to them an effective amount of antibody or of a functional equivalent thereof to at least two of urea, creatinine, tumor necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma, interleukin 6 and interleukin 1 beta. Soluble cytokine receptors also can be employed. The method can be used as a supplement to or as partial or complete replacement for dialysis. A pharmaceutical composition includes antibody or functional equivalent thereof to urea, creatinine, or both; antibody, functional equivalent or soluble cytokine receptor to tumor necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma, interleukin 6, interleukin 1 beta or any combination thereof The composition can be included in a kit.
Owner:SKURKOVICH BORIS +2
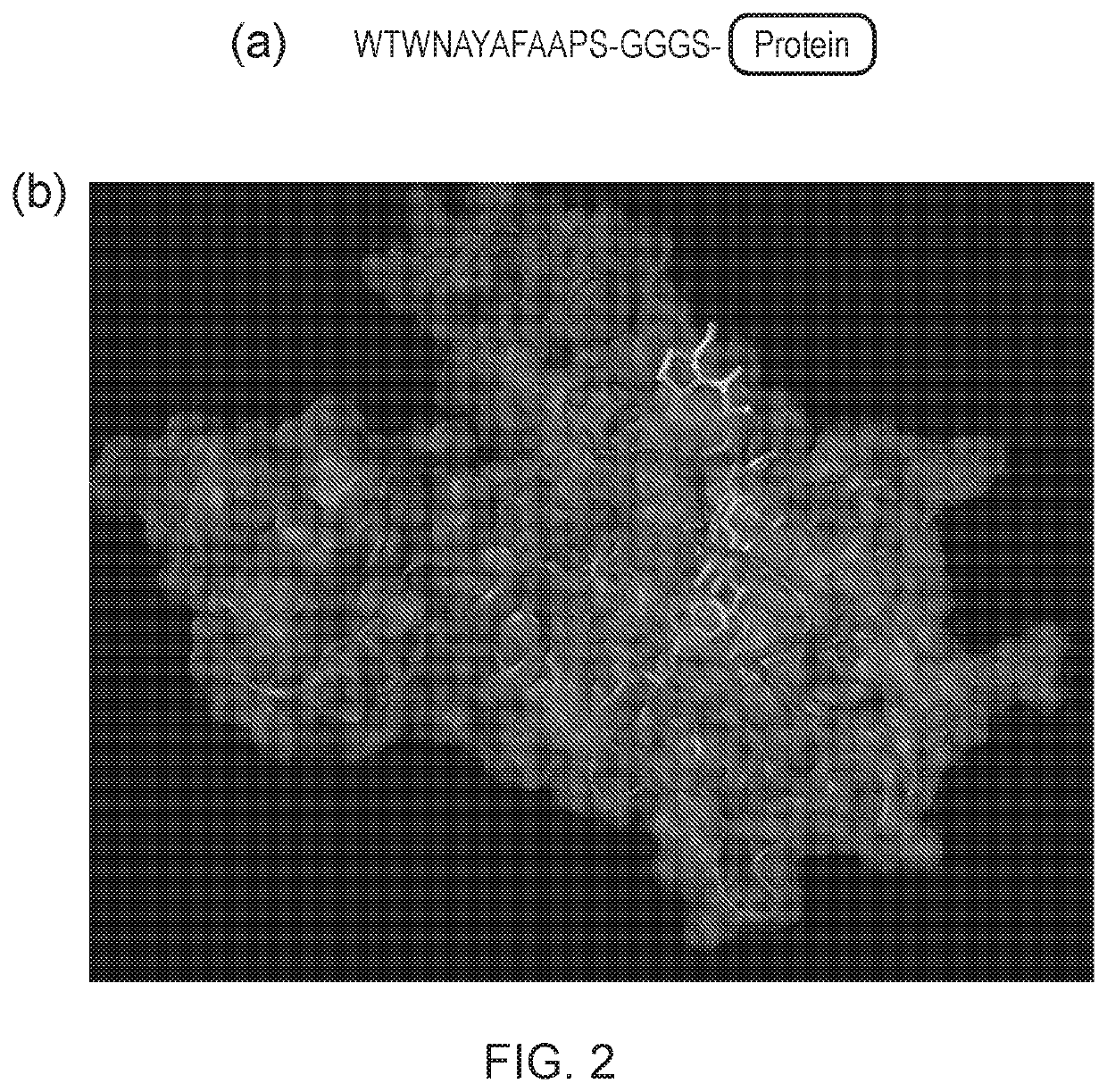
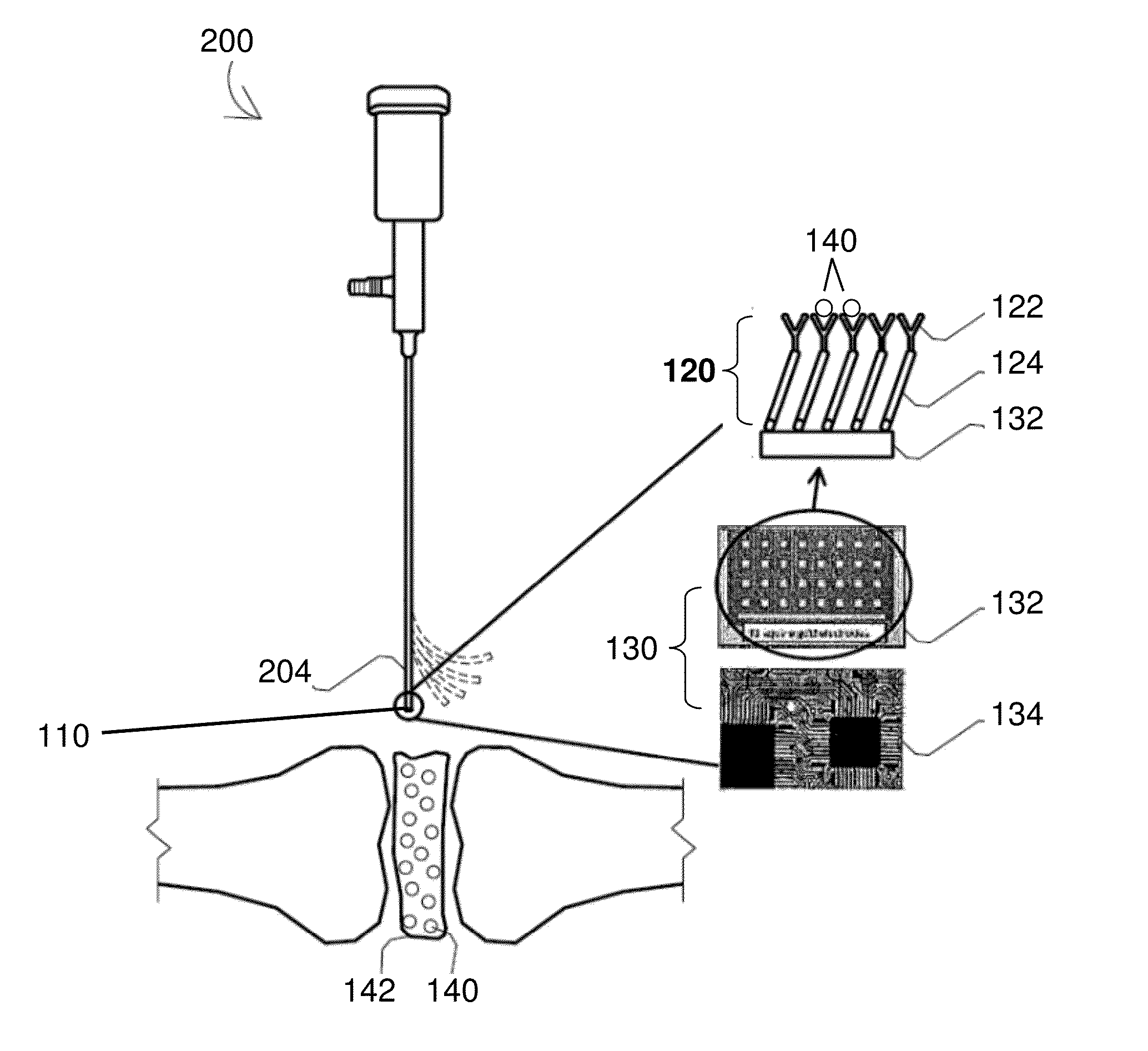
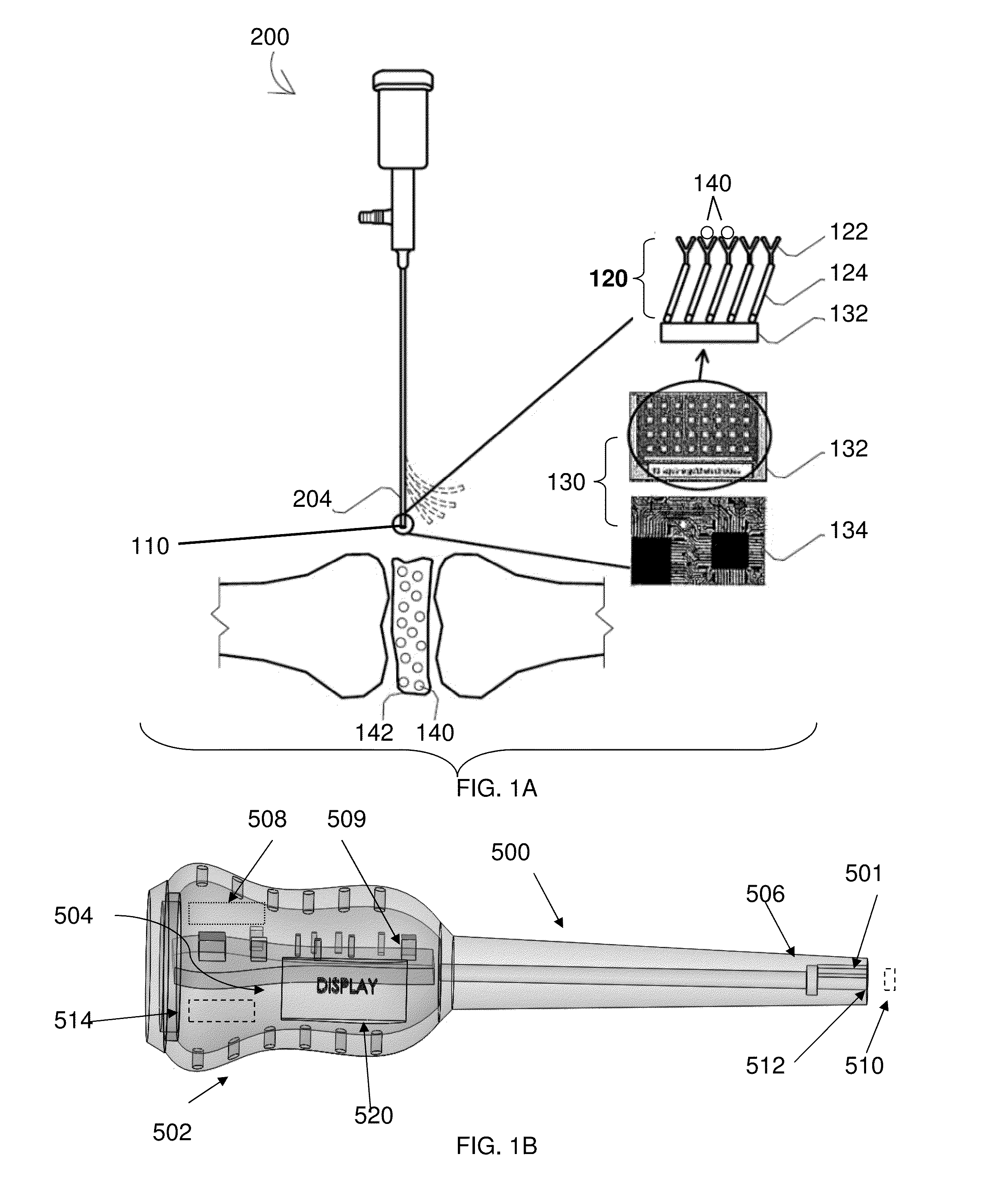
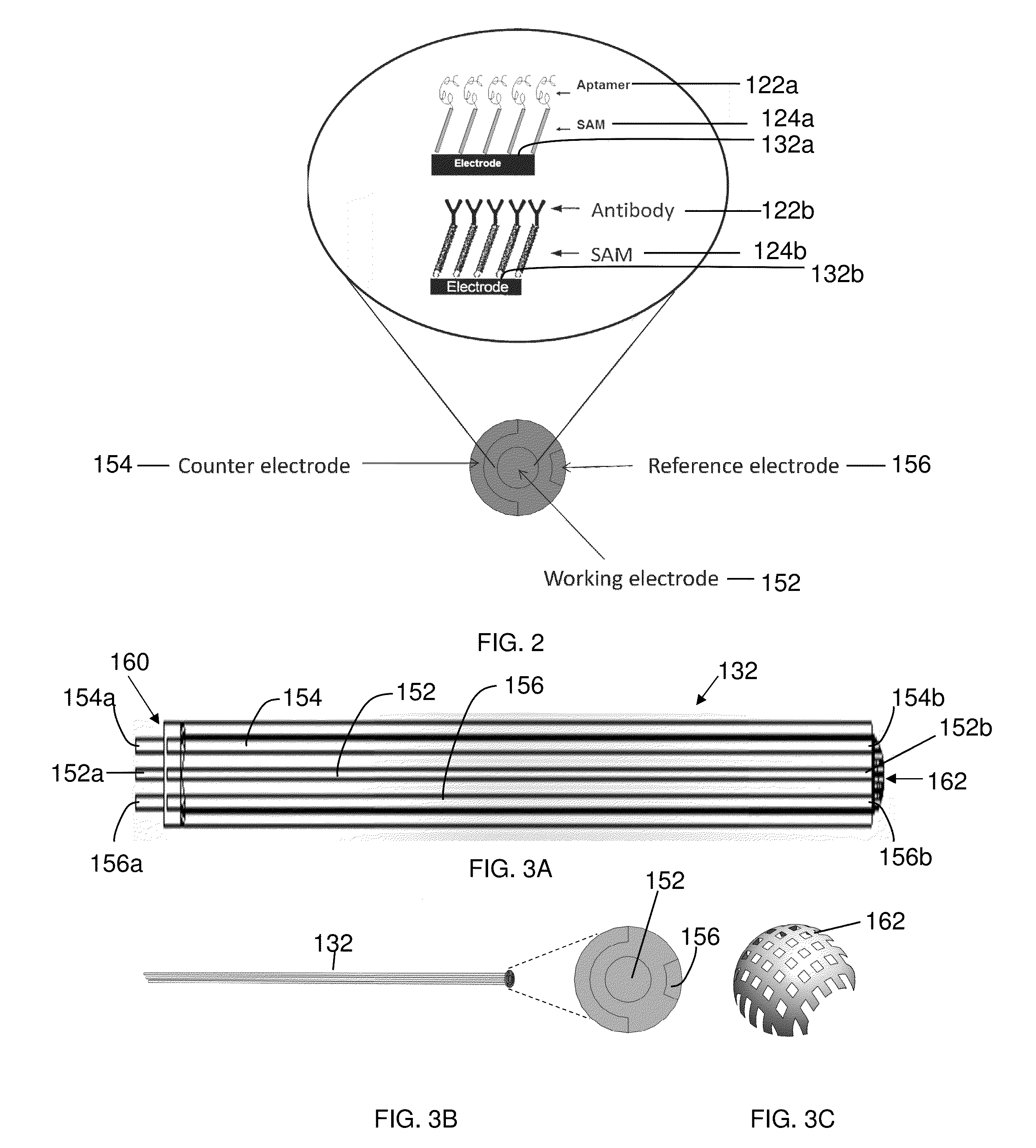
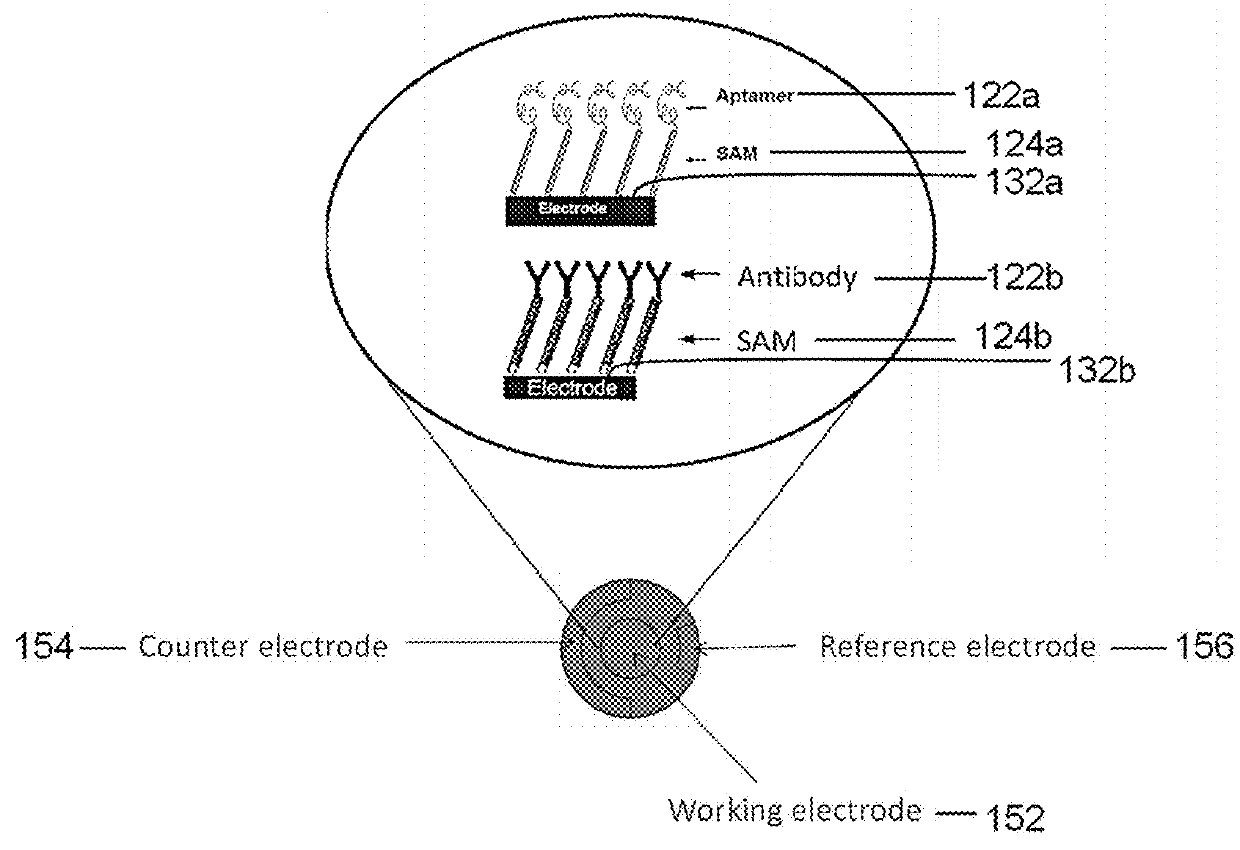
A Biosensor Device to Target Analytes in Situ, in Vivo, and/or in Real Time, and Methods of Making and Using the Same
A biosensor device for the real-time detection of a target analyte includes a receptor component operatively connected to a transducer component which is adapted to interpret and transmit a detectable signal. The receptor component includes a sensing element capable of detecting and binding to at least one target analyte, and a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) layer. The SAM layer is positioned between and in contact with the sensing element and an electrode such that the sensing element, in the presence of the target analyte, causes a detectable signal capable of being transmitted to the electrode. The transducer component includes the electrode and microprocessor configured to screen noise and to pick up impedance change at a very low frequency range.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
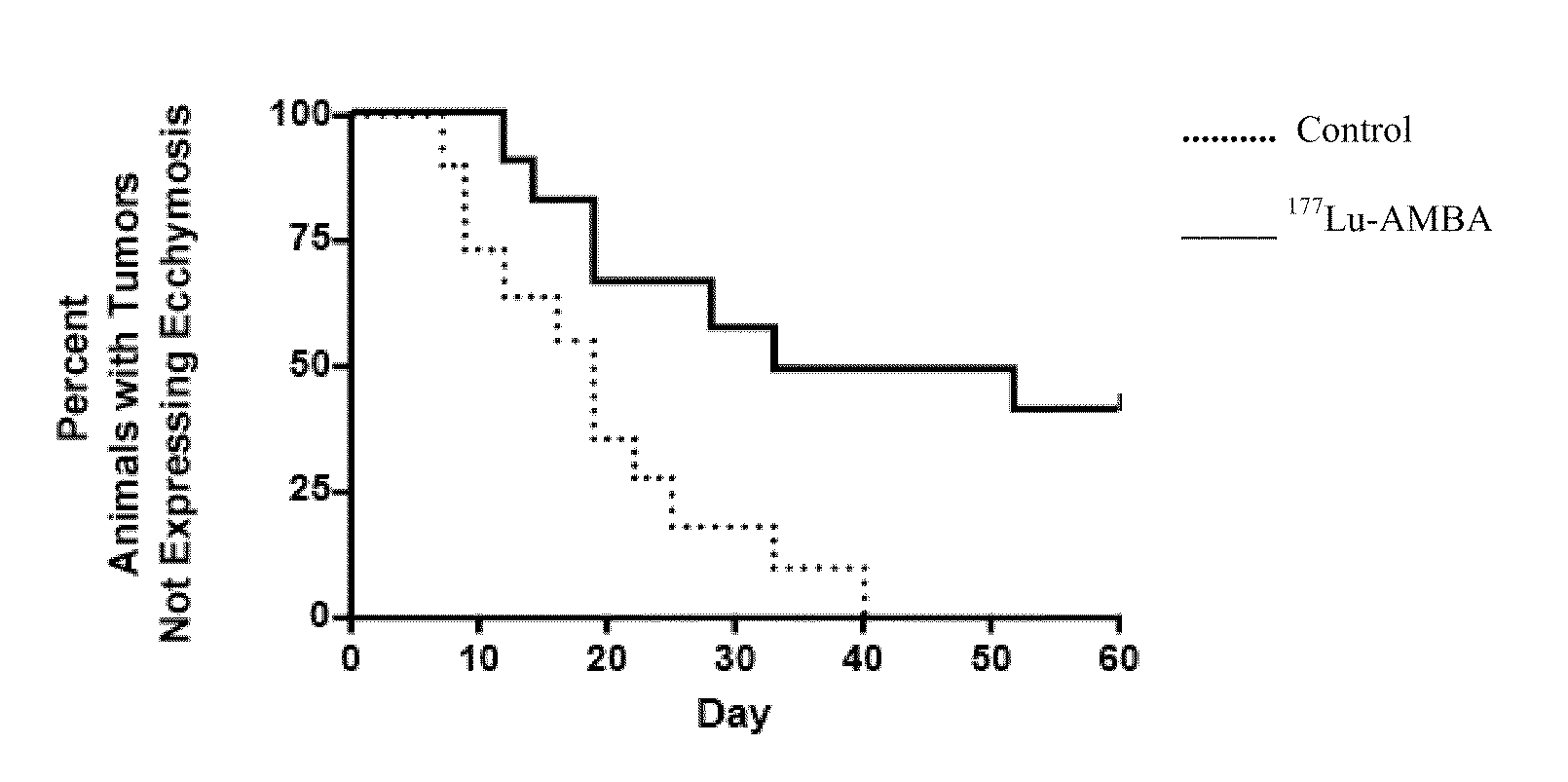
Gastrin releasing peptide compounds
InactiveUS20110250133A1Improve targetingPeptide/protein ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersNuclear medicineDisease
Methods and compositions for diagnosing, staging disease, monitoring therapeutic effect of drugs and imaging a patient are provided, including radiopharmaceutical formulations. Compositions comprising Ga-AMBA complexed with a radioactive isotope are provided; as are methods of imaging Gastrin Releasing Peptide receptor (GRP-R) bearing tissue and methods of diagnosing or staging disease in patients suspected of having disease associated with aberrant GRP-R function. Further, methods of monitoring therapeutic effect of a drug targeted to a receptor that crosstalks with GRP-R are provided; as are methods of pre-dosing / co-dosing non-target tissues containing GRP-R. Particularly, methods of monitoring activity of receptors and receptor pathways in vivo / in vitro by using a ligand that binds to the GRP-R are provided; as are methods of measuring the activity of a receptor or group of receptors and their associated pathways that exhibit crosstalk with the GRP-R by using such a ligand which is also detectable by external means.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
A biosensor device to detect target analytes in situ, in vivo, and/or in real time, and methods of making and using the same
A biosensor device for the real-time detection of a target analyte includes a receptor component operatively connected to a transducer component which is adapted to interpret and transmit a detectable signal. The receptor component includes a sensing element capable of detecting and binding to at least one target analyte, and a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) layer. The SAM layer is positioned between and in contact with the sensing element and an electrode such that the sensing element, in the presence of the target analyte, causes a detectable signal capable of being transmitted to the electrode. The SAM layer may include an anti-fouling agent. The transducer component includes an electrode (or set of electrodes that includes a working electrode) and microprocessor configured to screen noise and to pick up a detectable signal, such as impedance change at a very low frequency range.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
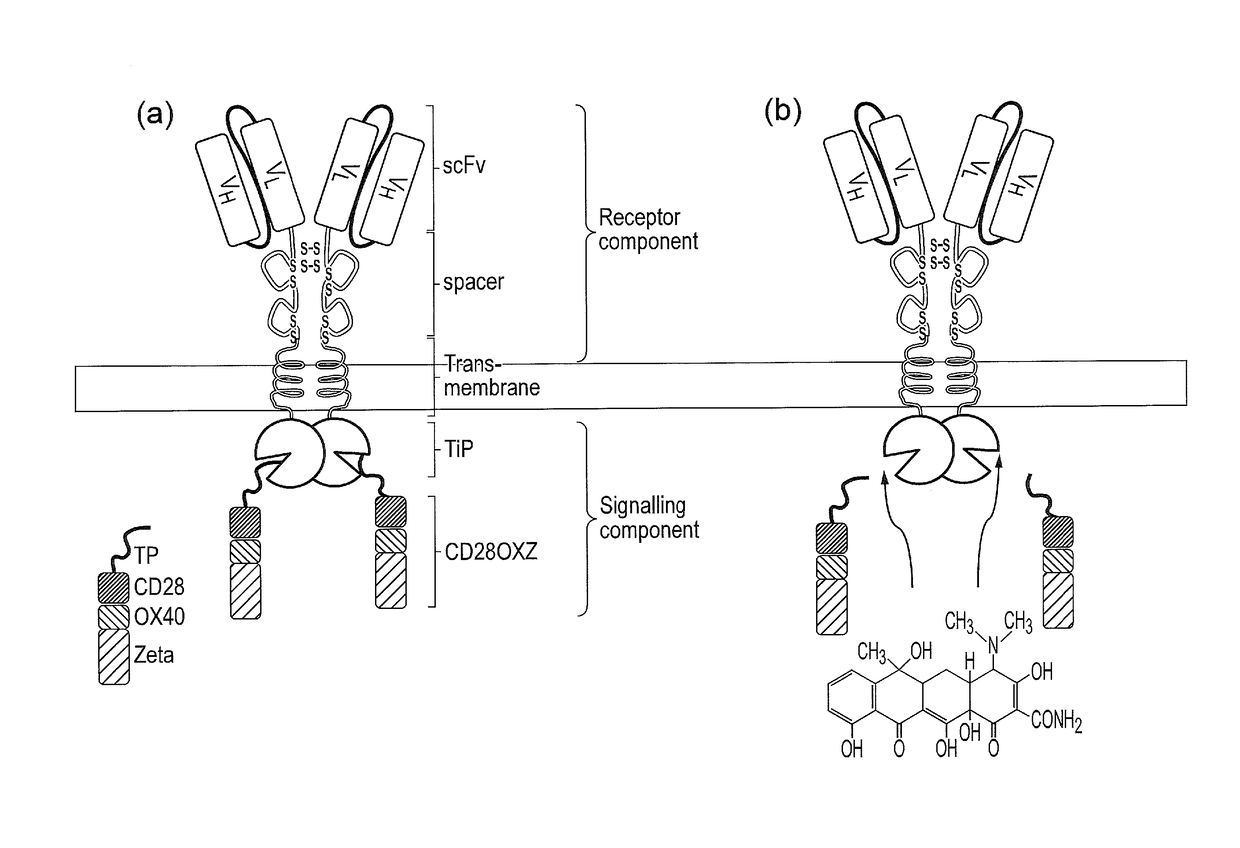
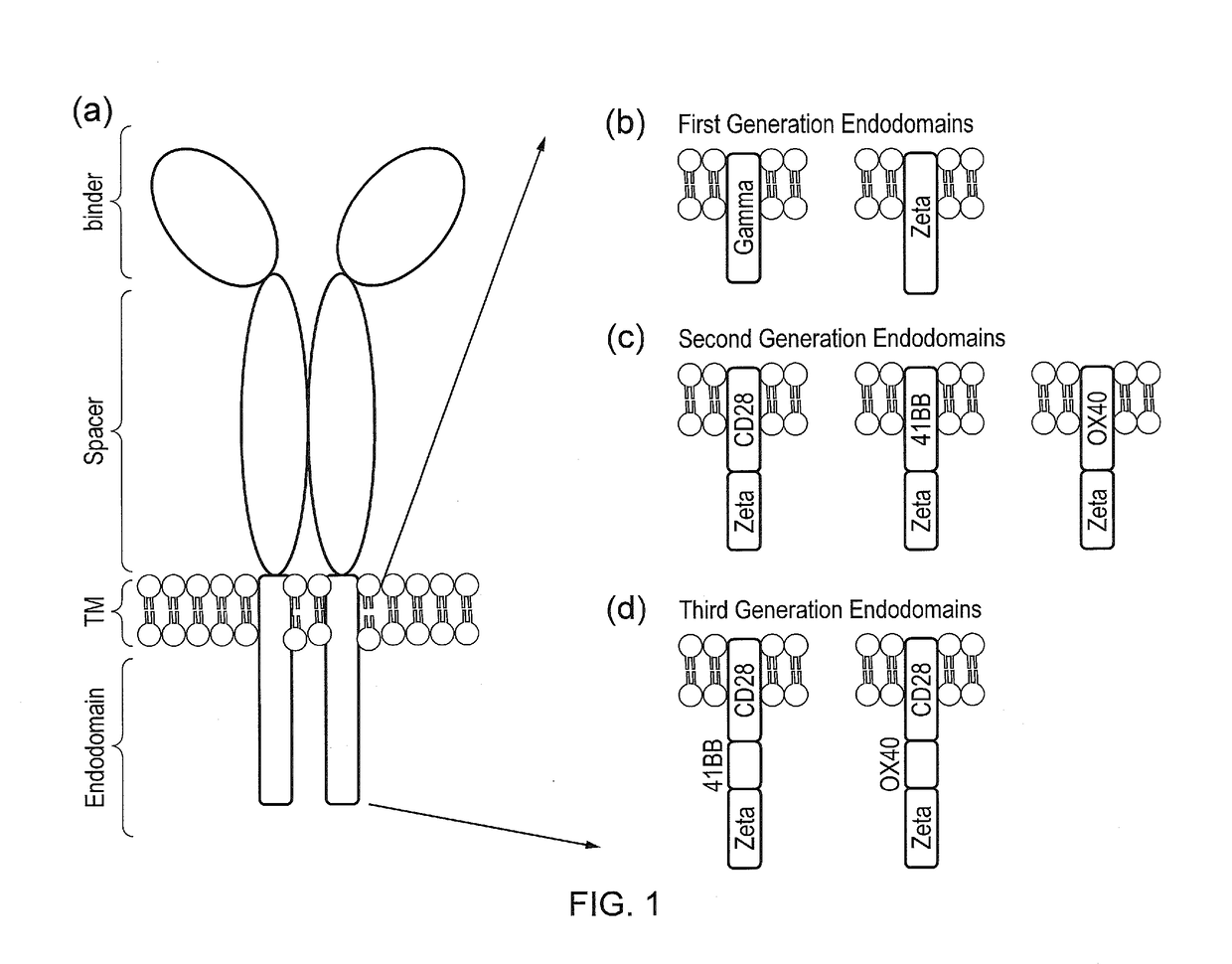
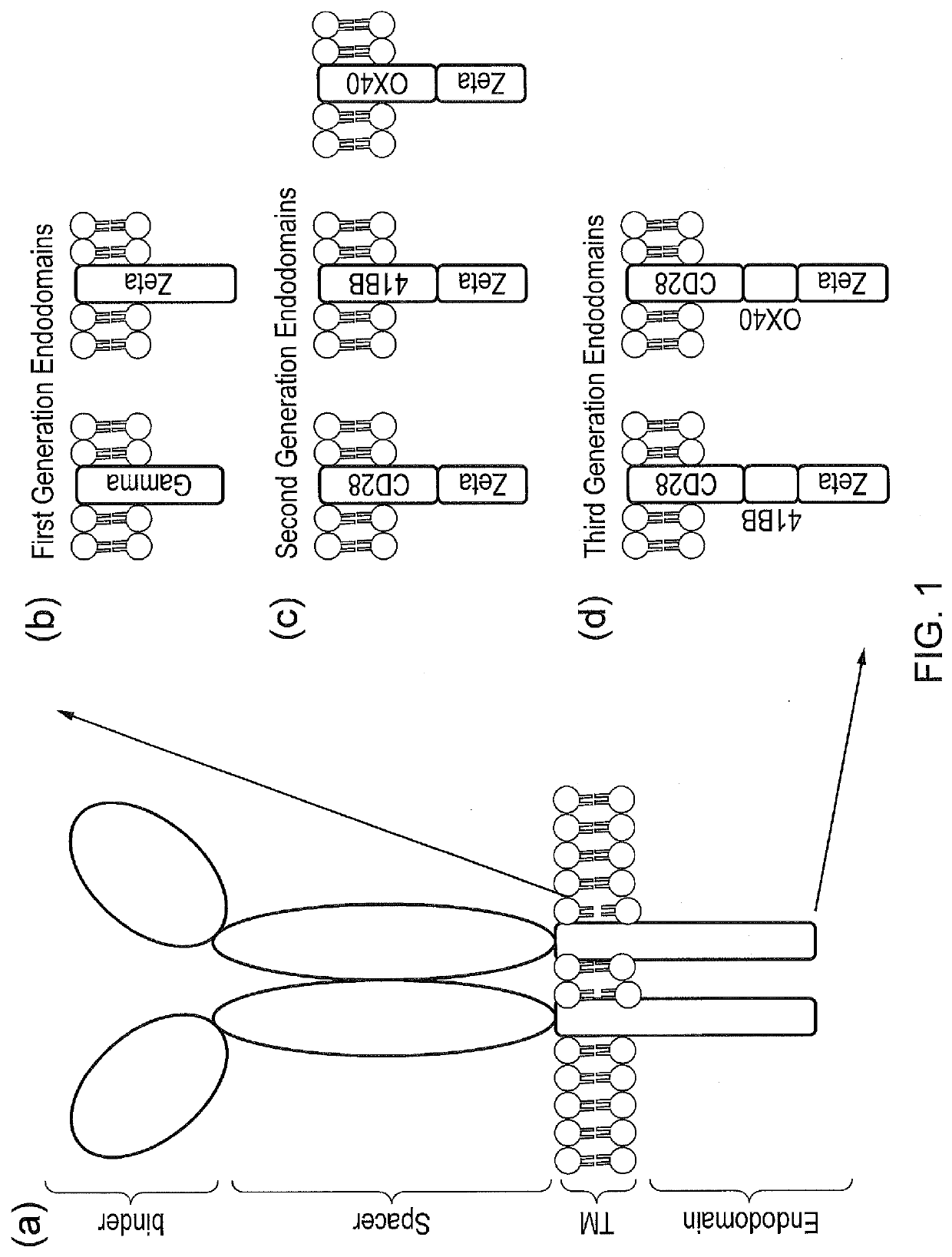
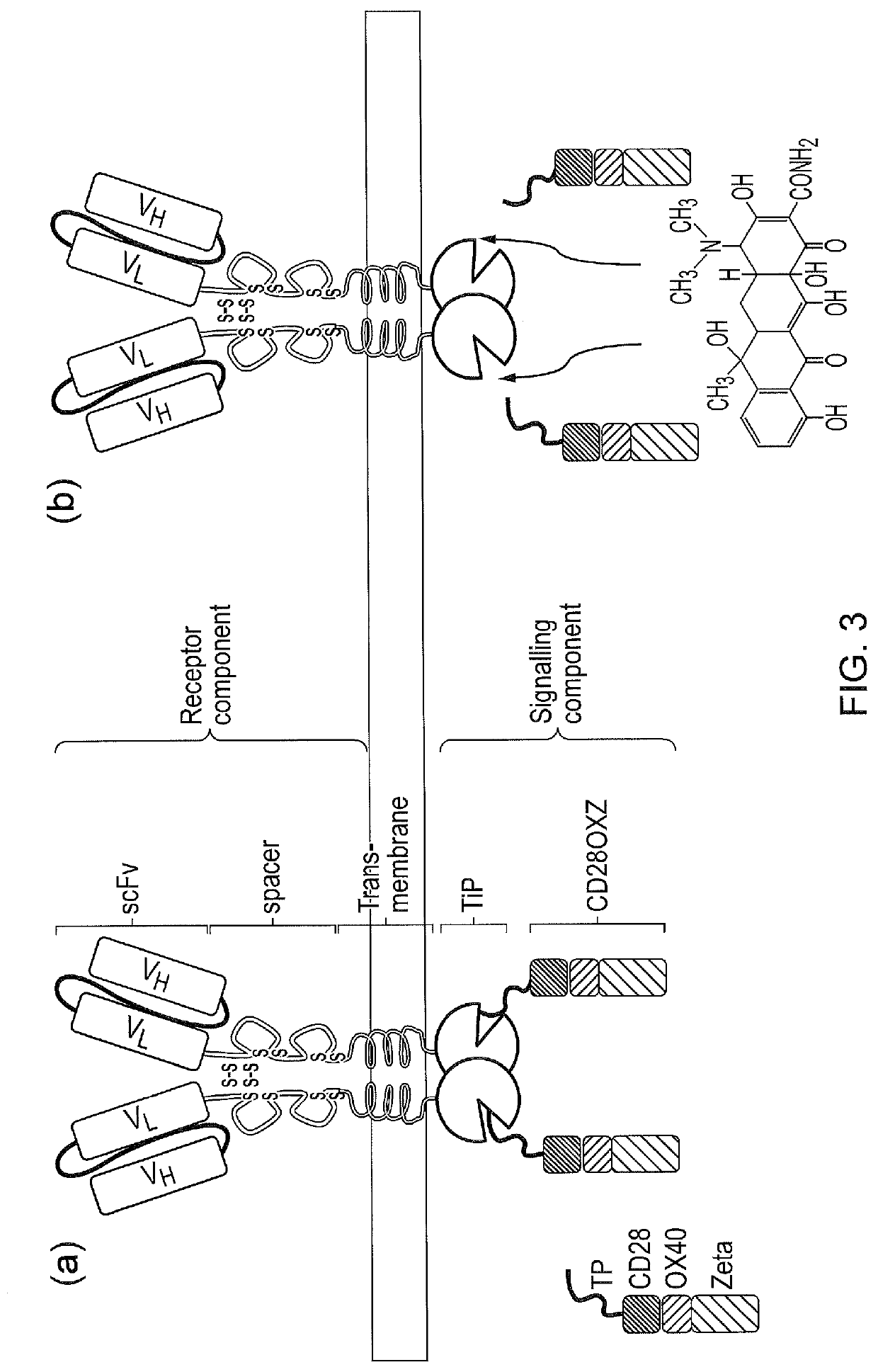
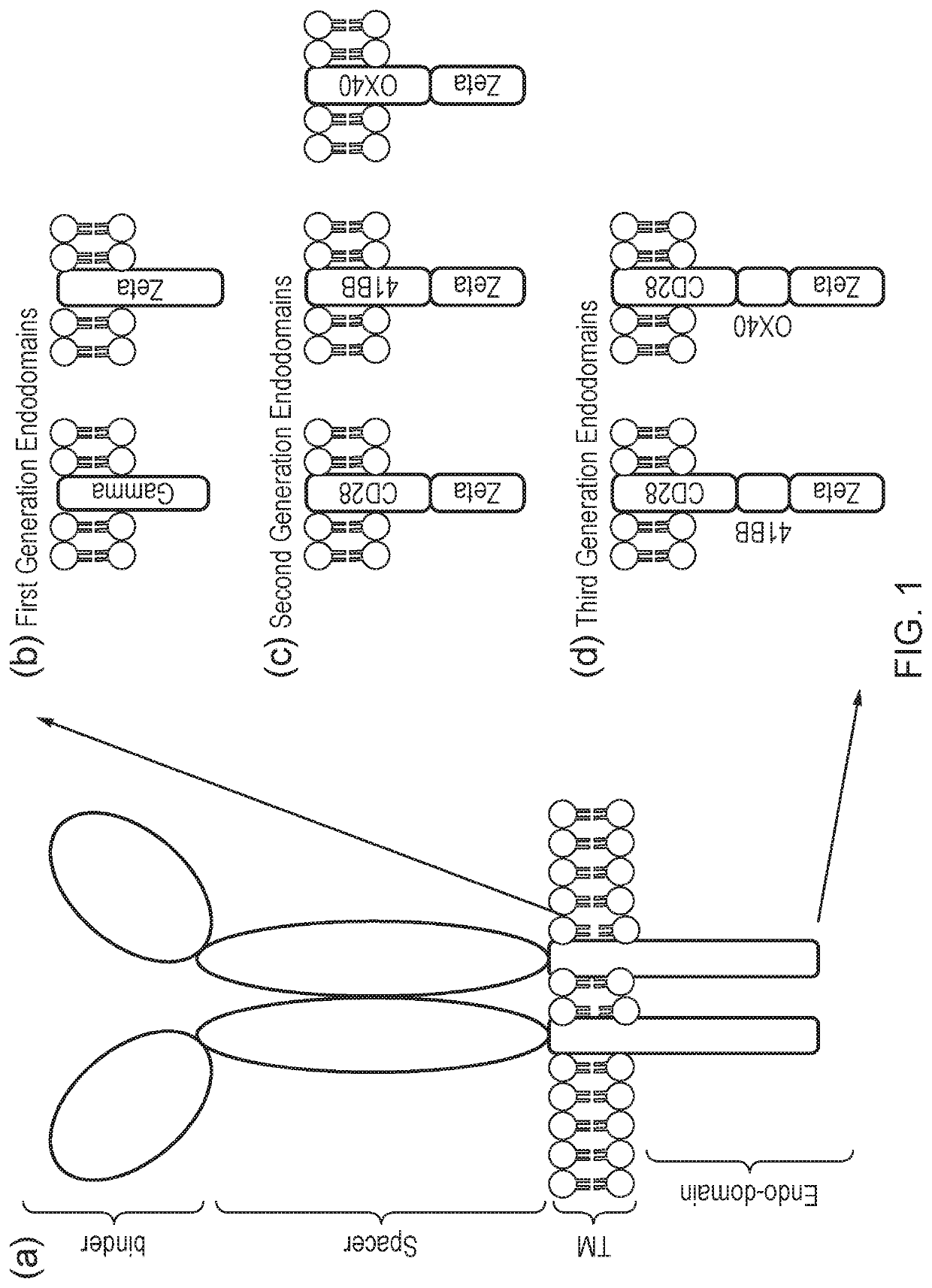
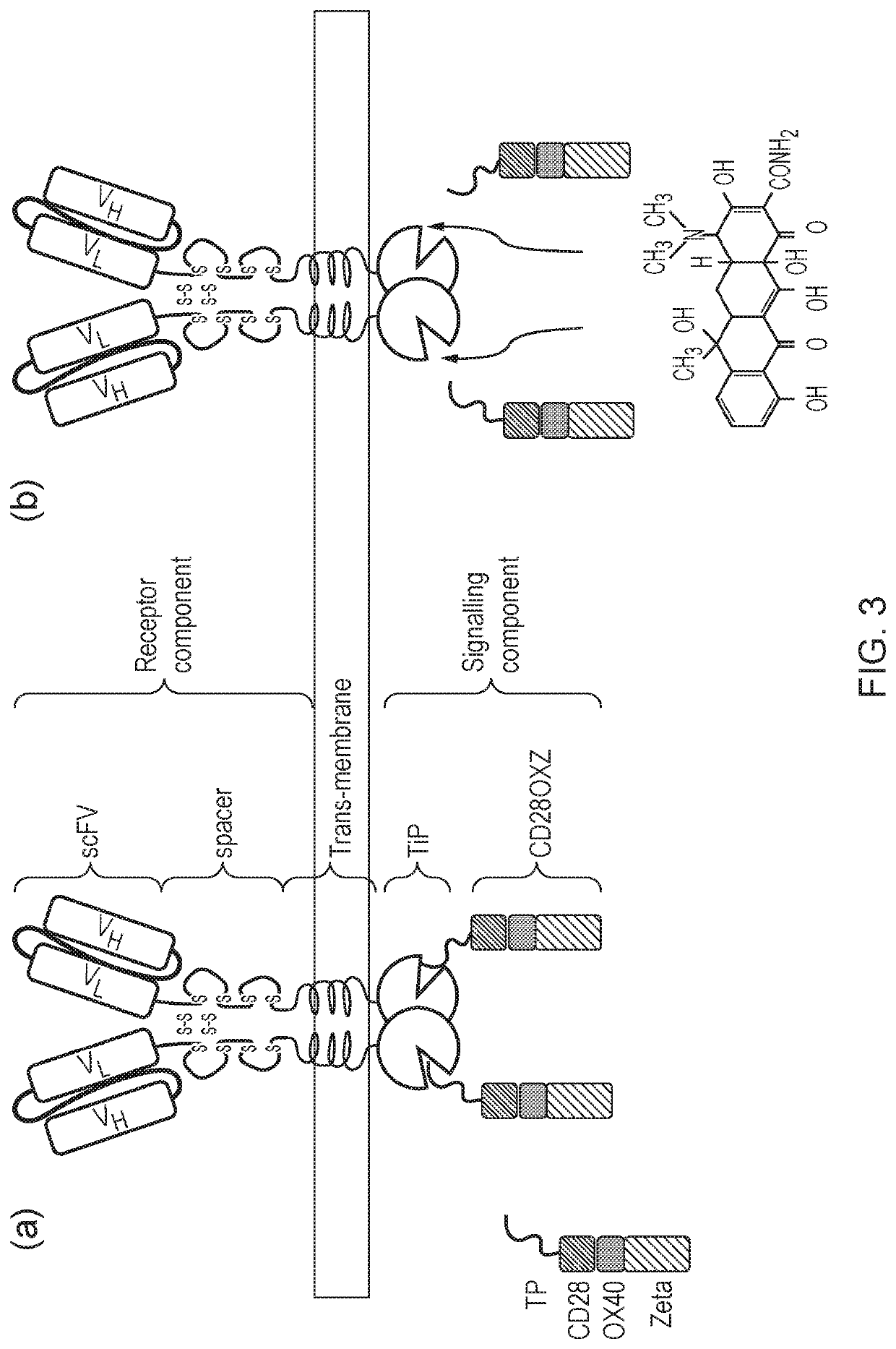
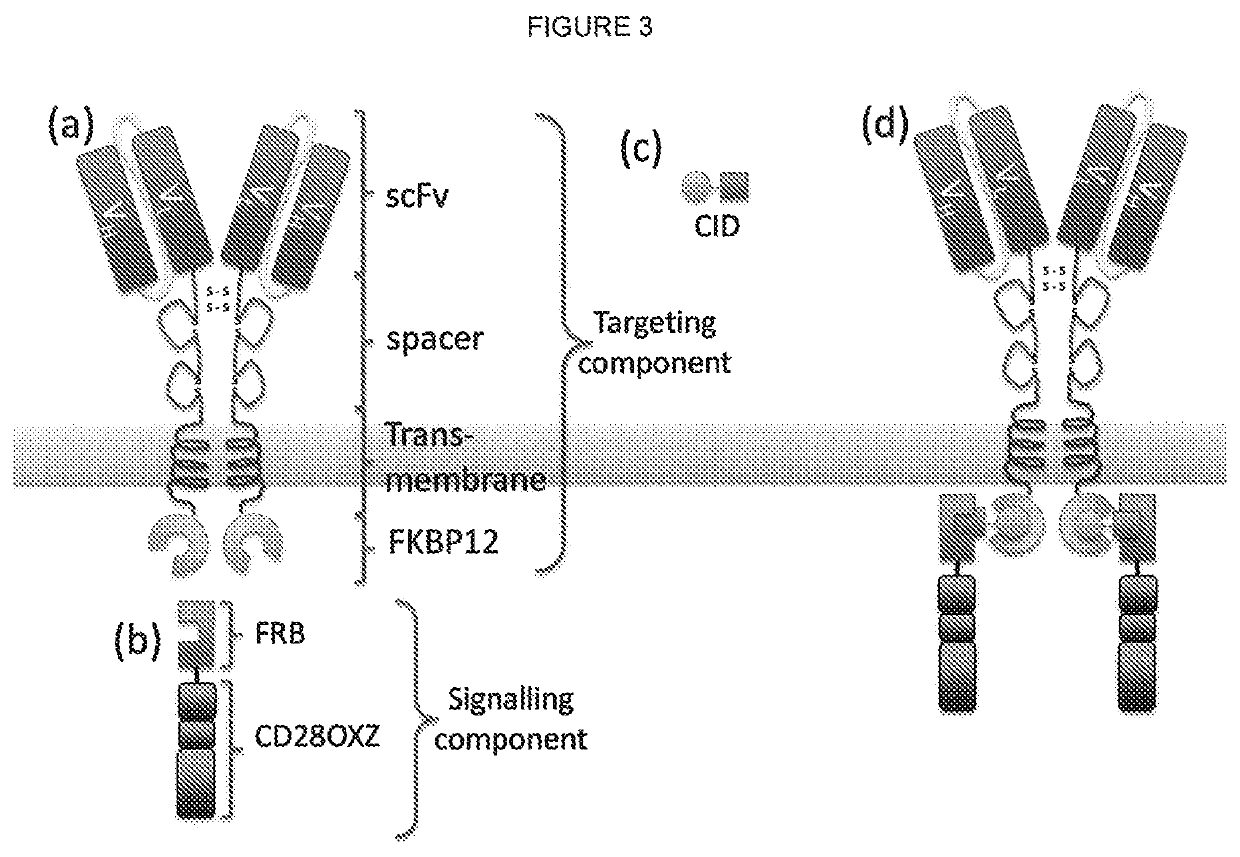
Signalling system
ActiveUS20170260269A1Reduce adverse toxic effectRapidly inhibited/terminatedPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyIntracellular signallingAntigen binding
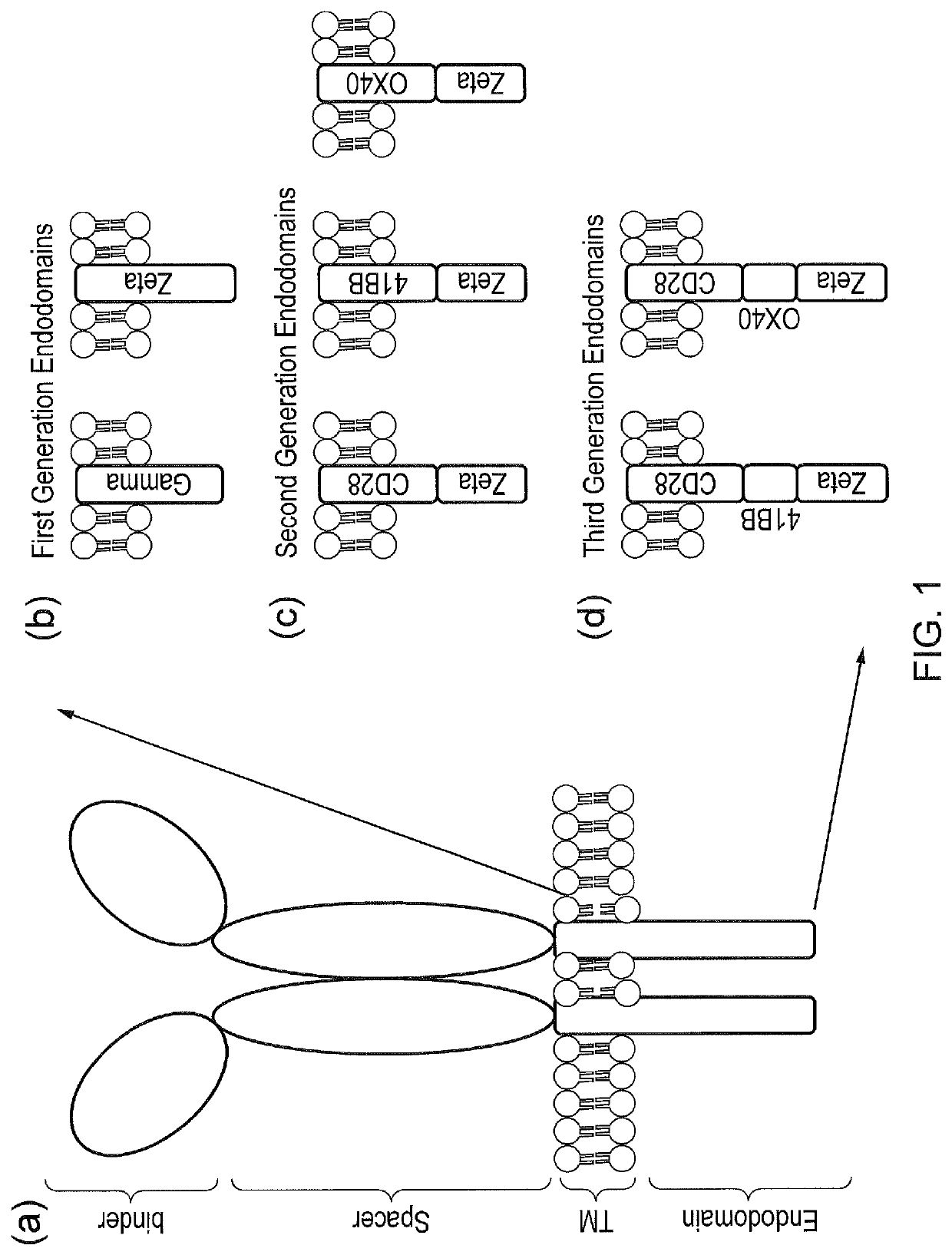
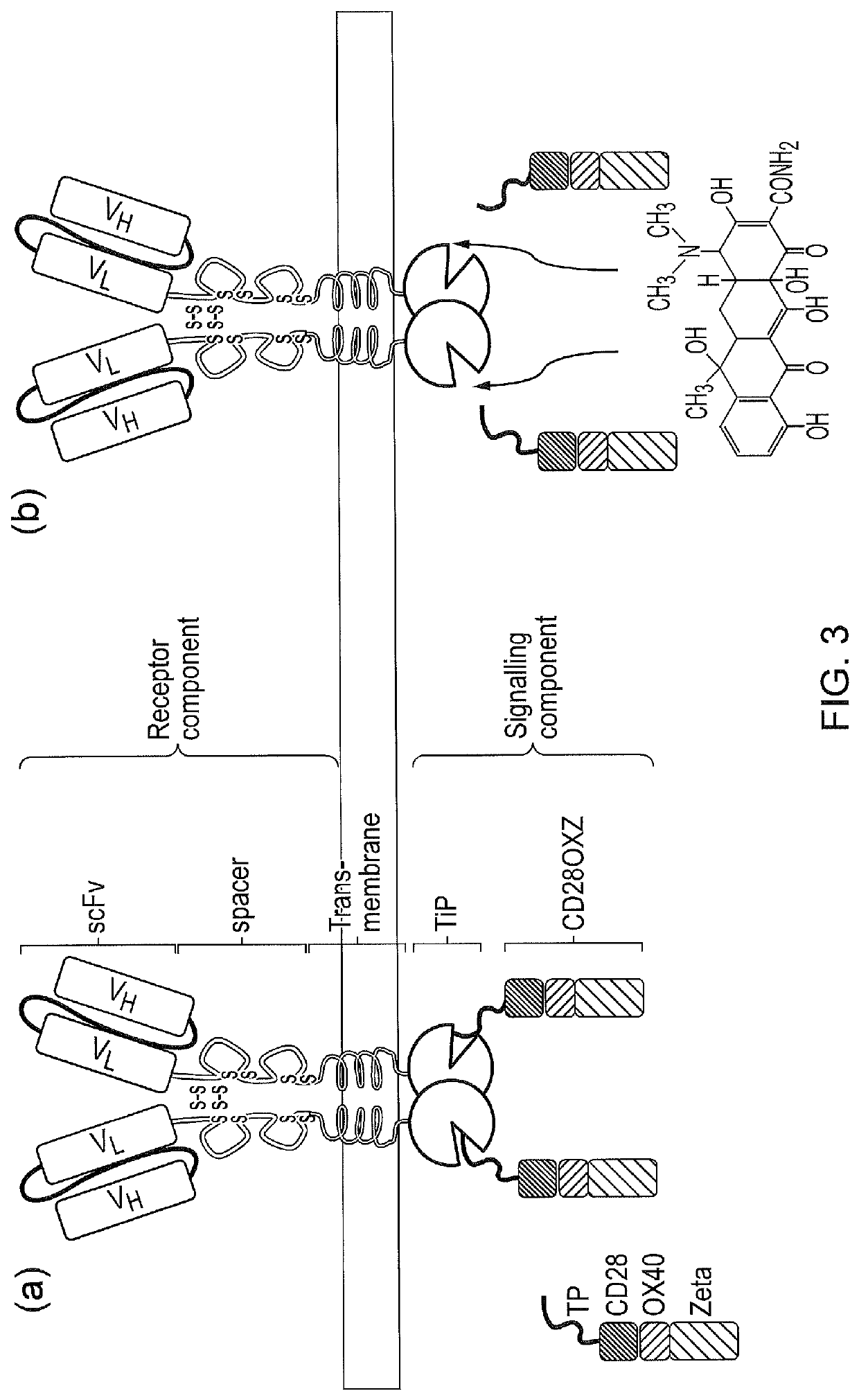
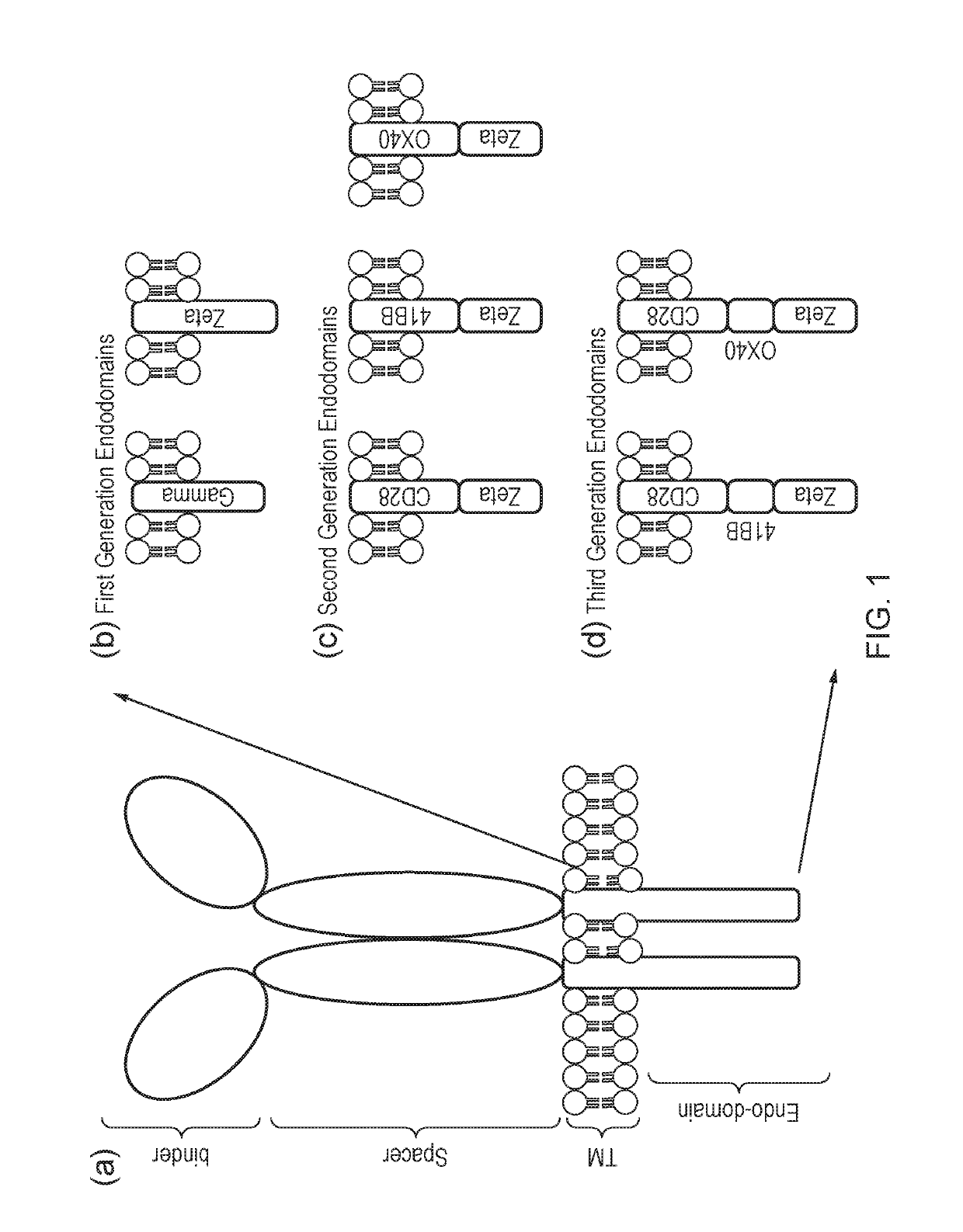
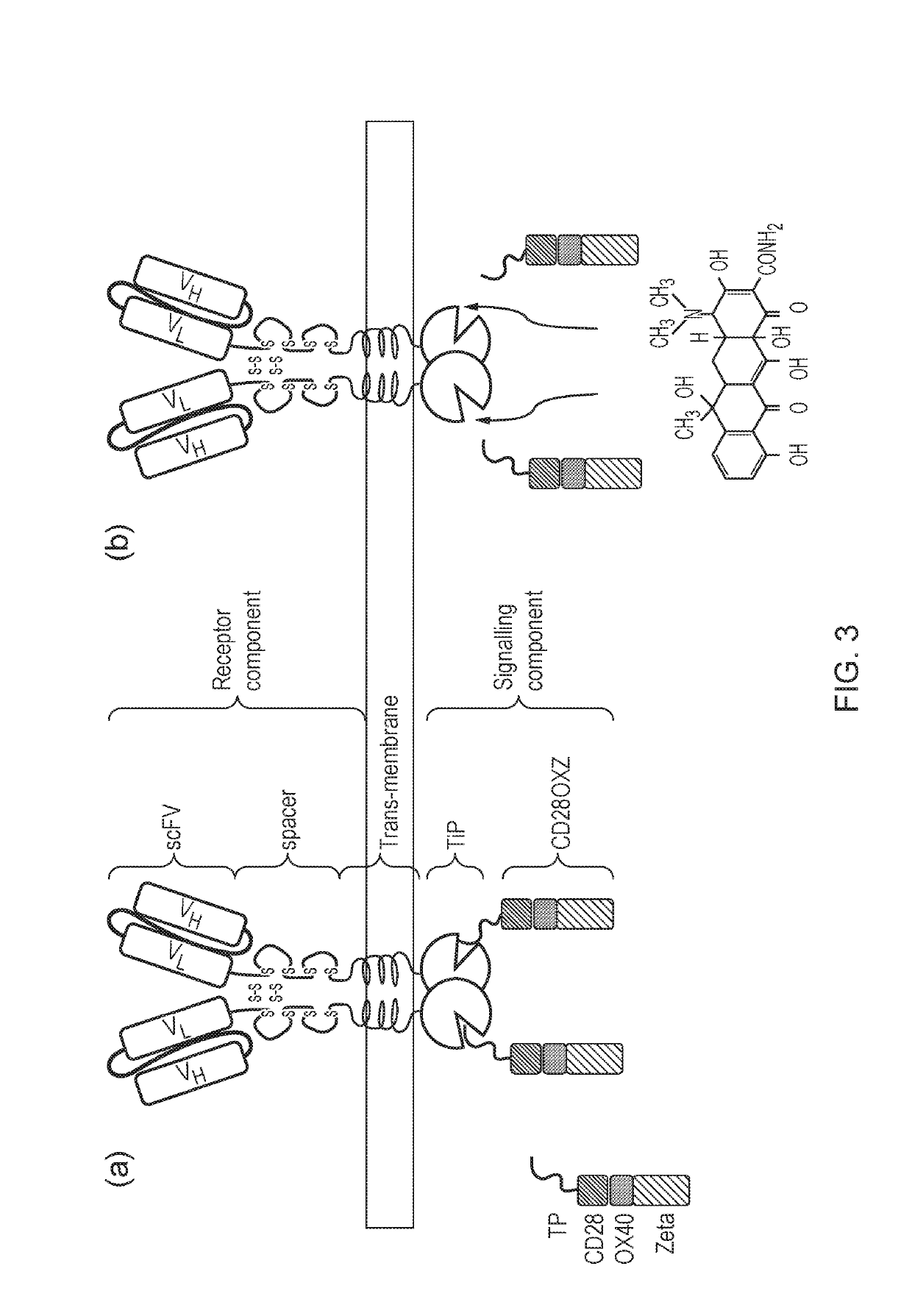
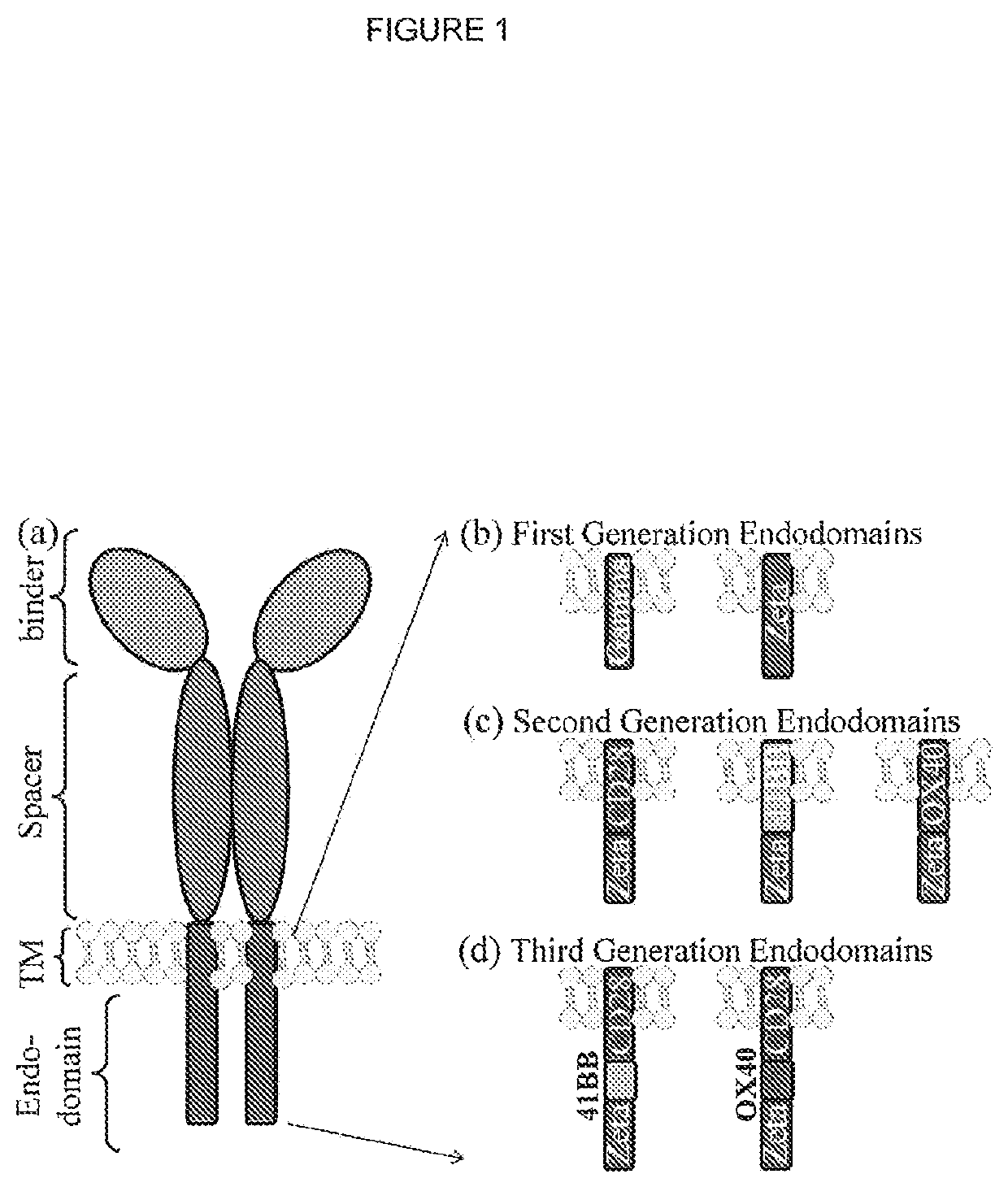
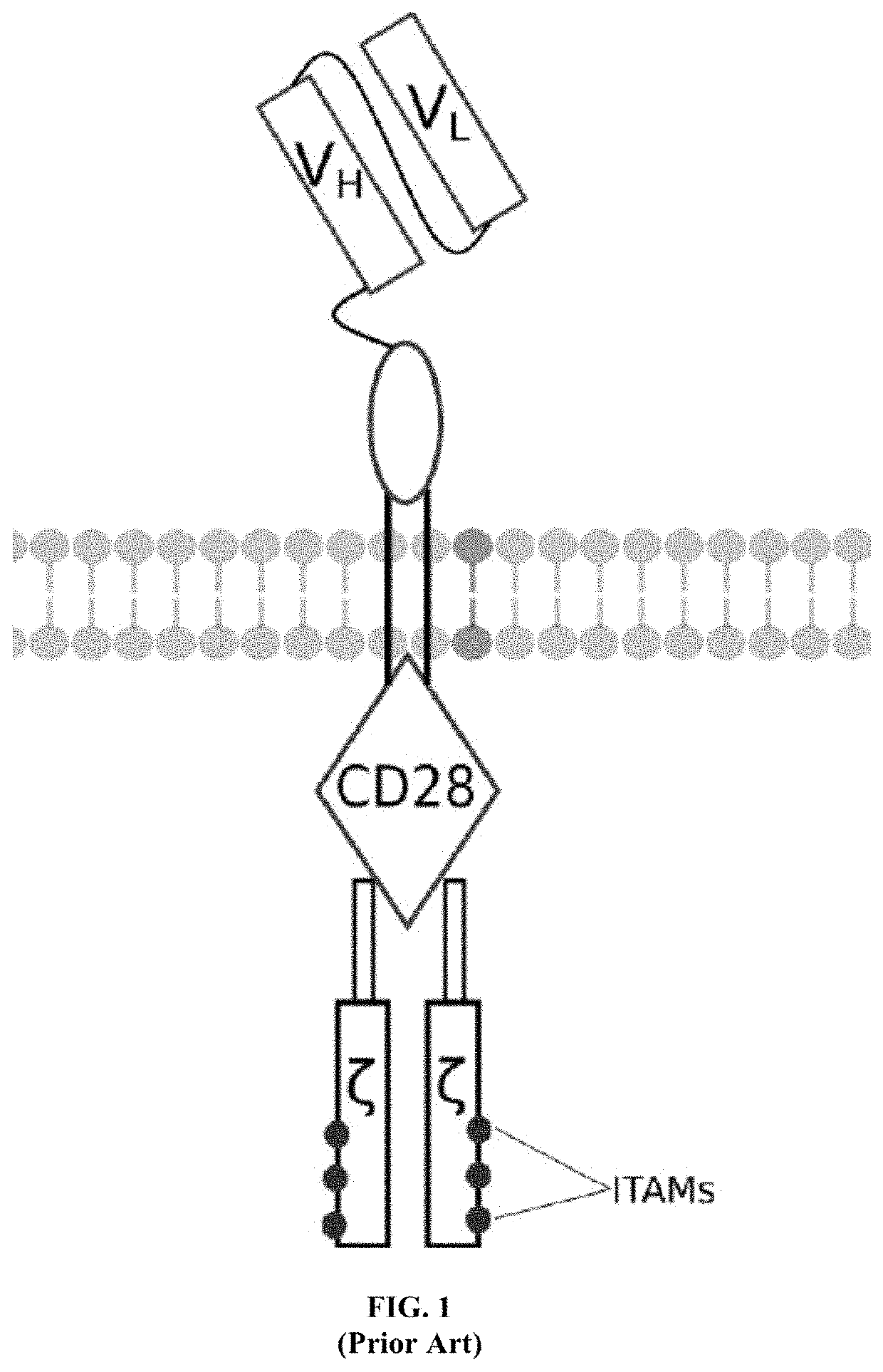
The present invention provides a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) signalling system comprising; (i) a receptor component comprising an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain and a first binding domain; and (ii) an intracellular signalling component comprising a signalling domain and a second binding domain which specifically binds the first binding domain of the receptor component; wherein, binding of the first and second binding domains is disrupted by the presence of an agent, such that in the absence of the agent the receptor component and the signalling component heterodimerize and binding of the antigen binding domain to antigen results in signalling through the signalling domain, whereas in the presence of the agent the receptor component and the signalling component do not heterodimerize and binding of the antigen binding domain to antigen does not result in signalling through the signalling domain.
Owner:AUTOLUS LIMIED
Exponential pattern recognition based cellular targeting, compositions, methods and anticancer applications
InactiveUS20030031677A1High target affinityLow cytotoxicityAntibody ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEnzymeTherapeutic intent
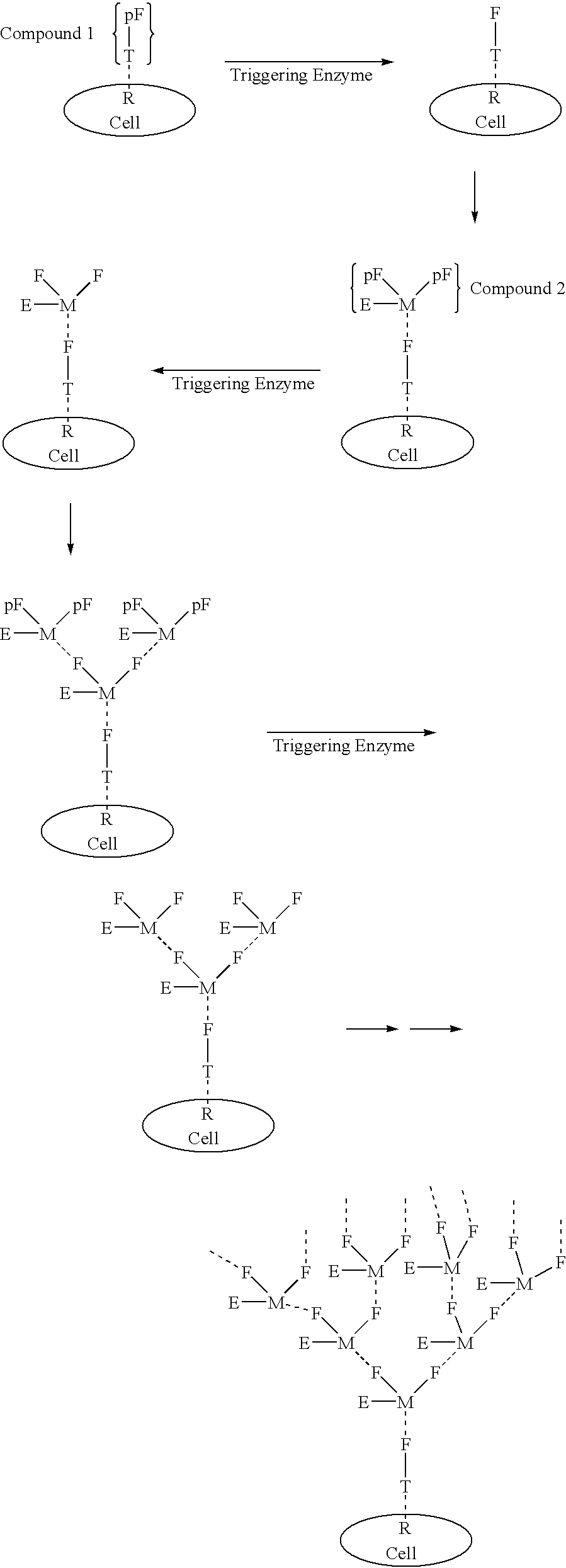
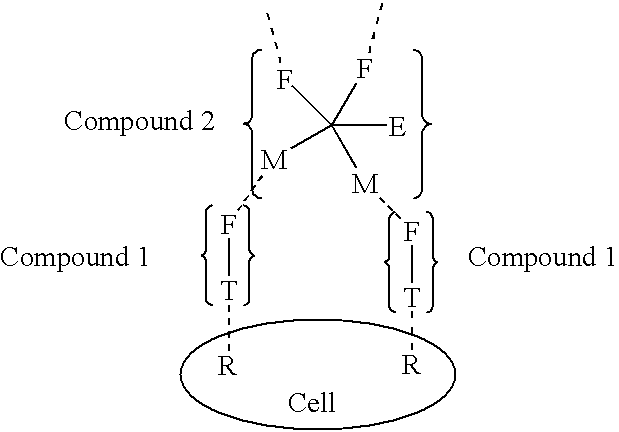
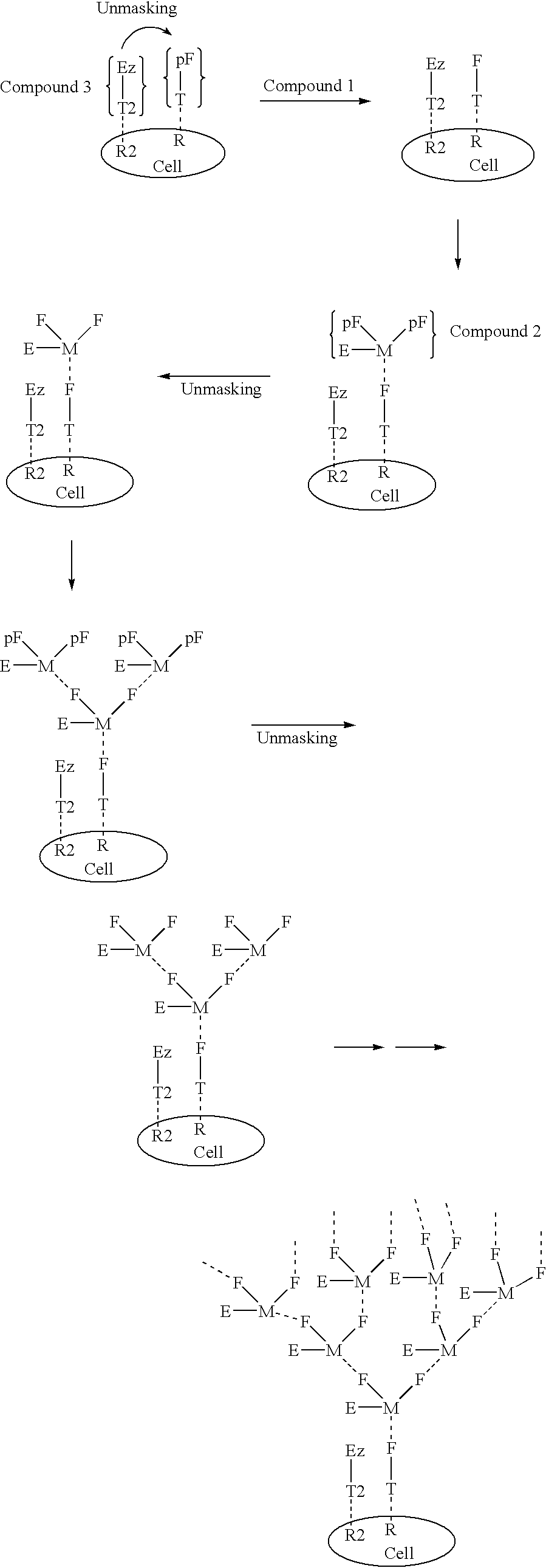
The present invention relates to the compositions, methods, and applications of a new approach to pattern recognition based targeting by which an exponential amplification of effector response can be specifically obtained at a targeted cells. The purpose of this invention is to enable the selective delivery of large quantities of an array of effector molecules to target cells for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. The invention is comprised of two components designated as "Compound 1" and "Compound 2": Compound 1 is comprised of a cell binding agent and a masked female adaptor. Compound 2 is comprised of a male ligand, an effector agent, and two or more masked female receptors. The male ligand is selected to bind with high affinity to the female adaptor. Compound 1 can bind with high affinity to the target cell and the female receptor can then be unmasked by an enzyme enriched at the tumor cell. The male ligand of Compound 2 can then bind to the unmasked female adaptor bound to the target cell. The masked female adaptor on the bound Compound 2 can then be specifically unmasked. One receptor has in effect become two. Two new molecules of Compound 2 can bind to the unmasked adaptors receptors. After unmasking two receptors in effect become four. The process can continue in an explosive exponential like fashion resulting in enormous amplification of the number of effector molecules specifically deposited at the target cell.
Owner:DRUG INNOVATION & DESIGN
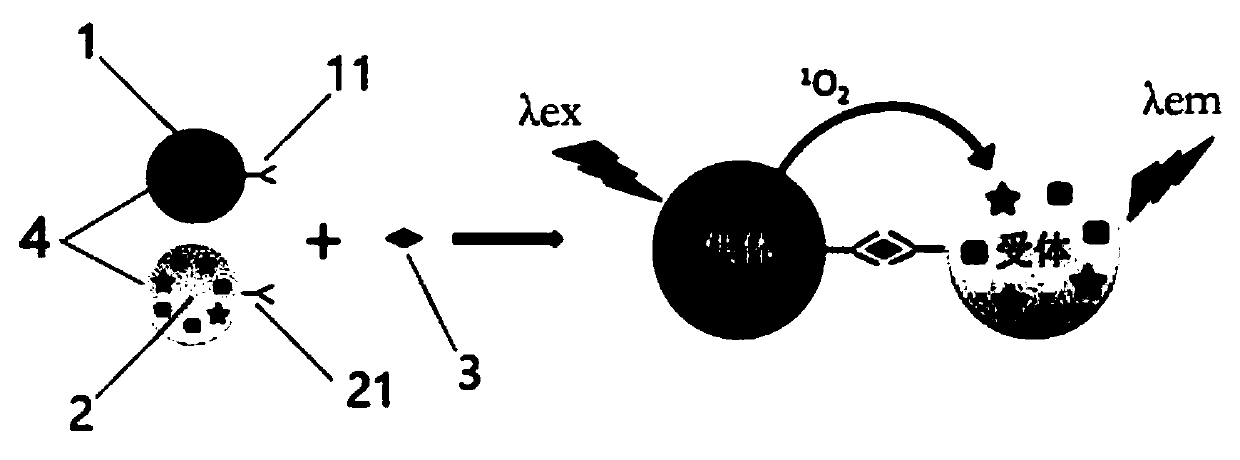
Homogeneous joint detection reagent and method based on immunoturbidimetry and afterglow luminescence
PendingCN111474341AEnhanced Change SensitivityHigh detection sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsMicrosphereLight excitation
The invention relates to a homogeneous joint detection reagent composition. The composition comprises a turbidity reagent I and a luminescent reagent II, wherein the turbidity reagent I comprises a carrier microsphere connected with a counterpart capable of being specifically binding to a turbidimetric biomarker, and the turbidity reagent I and the turbidimetric biomarker are subjected to an immune reaction to increase the turbidity; and the luminescent reagent II comprises a donor component II-1 and an acceptor component II-2, wherein the donor component II-1 comprises a donor microsphere connected with a counterpart specifically binding to an afterglow biomarker, the donor microsphere generates singlet oxygen under light excitation, and the acceptor component II-2 comprises an acceptor microsphere connected with a counterpart specifically binding to the afterglow biomarker, and the acceptor microsphere reacts with the singlet oxygen to generate an afterglow luminescence signal. In addition, the invention also relates to a homogeneous joint detection method and a kit containing the reagent composition.
Owner:SHANGHAI TAYWELL BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +2
CD1D-restricted NKT cells as a platform for off-the-shelf cancer immunotherapy
PendingCN111094555APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAllogeneic cellCD1D
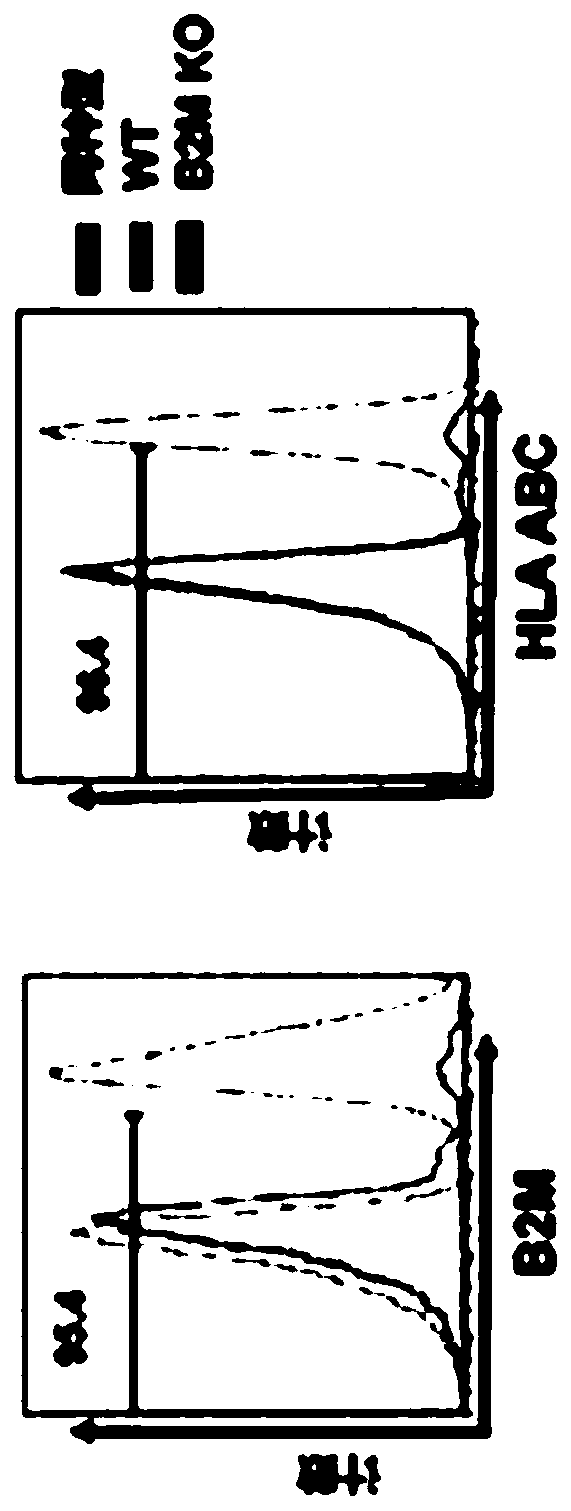
Embodiments of the disclosure include methods and compositions for immunotherapy that comprise allogeneic cells that are able to be universally tolerated in host individuals. In specific embodiments the cells have reduced expression of endogenous beta2-microglobulin (B2M) and / or MHC class II-associated invariant chain (Ii), and in particular cases the cells are NKT cells that lack the ability to damage host tissues, have much reduced recognition by host immune cells, and surprisingly avoid destruction by host NK cells. In some embodiments, B2M- and / or Ii-targeting molecules are engineered to be expressed in combination (including within a single construct) with recombinantly engineered receptors, for example, for a one-hit generation of universally tolerated off-the-shelf immunotherapy.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Signalling system
ActiveUS10654927B2Rapidly inhibited/terminatedAdverse toxic effectFusion with DNA-binding domainNGF/TNF-superfamilyIntracellular signallingAntigen receptor
The present invention provides a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) signalling system comprising; (i) a receptor component comprising an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain and a first binding domain; and (ii) an intracellular signalling component comprising a signalling domain and a second binding domain which specifically binds the first binding domain of the receptor component; wherein, binding of the first and second binding domains is disrupted by the presence of an agent, such that in the absence of the agent the receptor component and the signalling component heterodimerize and binding of the antigen binding domain to antigen results in signalling through the signalling domain, whereas in the presence of the agent the receptor component and the signalling component do not heterodimerize and binding of the antigen binding domain to antigen does not result in signalling through the signalling domain.
Owner:AUTOLUS LIMIED
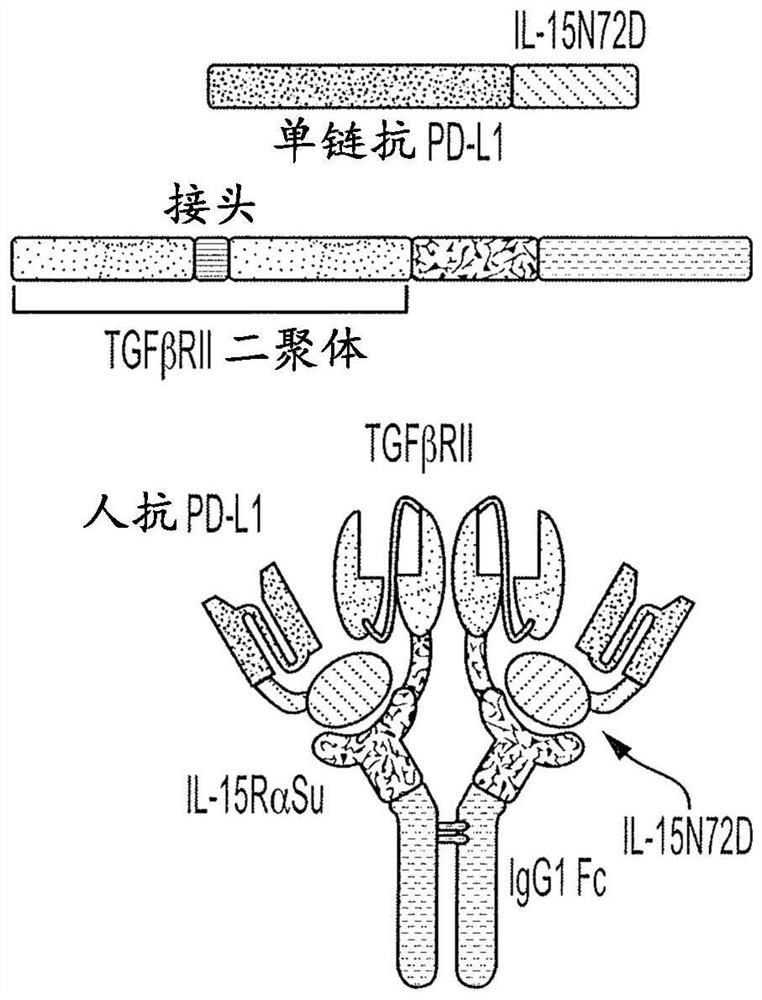
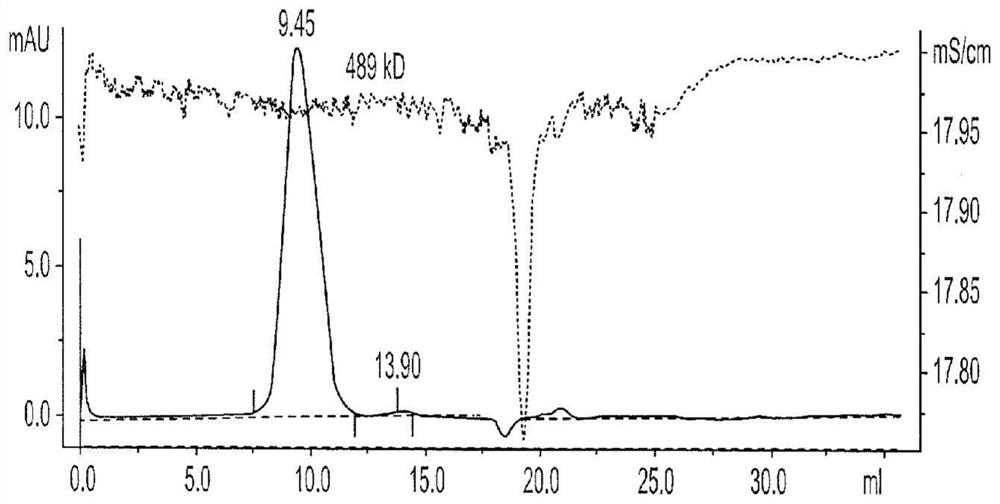
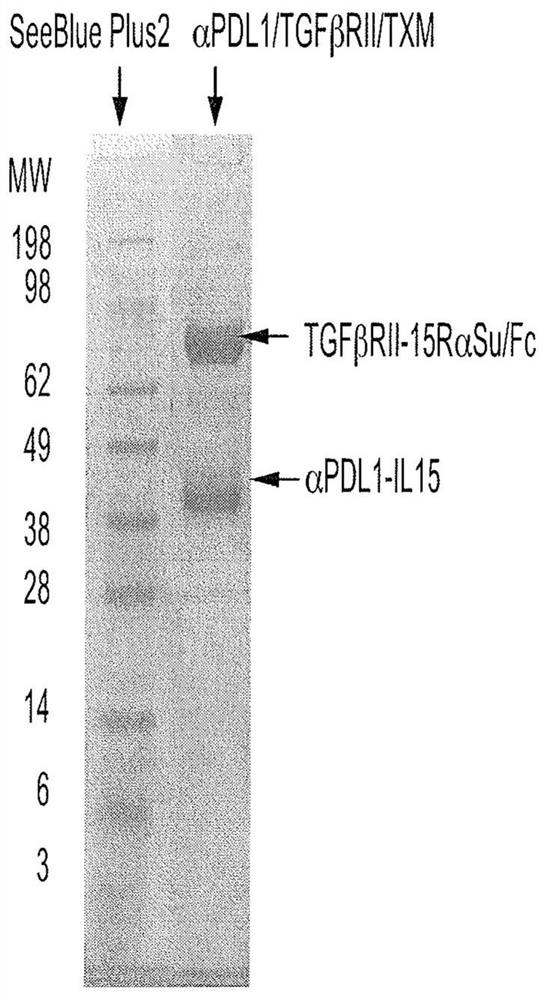
Anti-pdl1, il-15 and tgf-beta receptor combination molecules
The invention features multi- specific protein complexes with one domain comprising IL-15 or a functional variant, a cytokine receptor or cytokine ligand, and a binding domain specific to a disease antigen, immune checkpoint or signaling molecule.
Owner:阿尔托生物科学有限责任公司
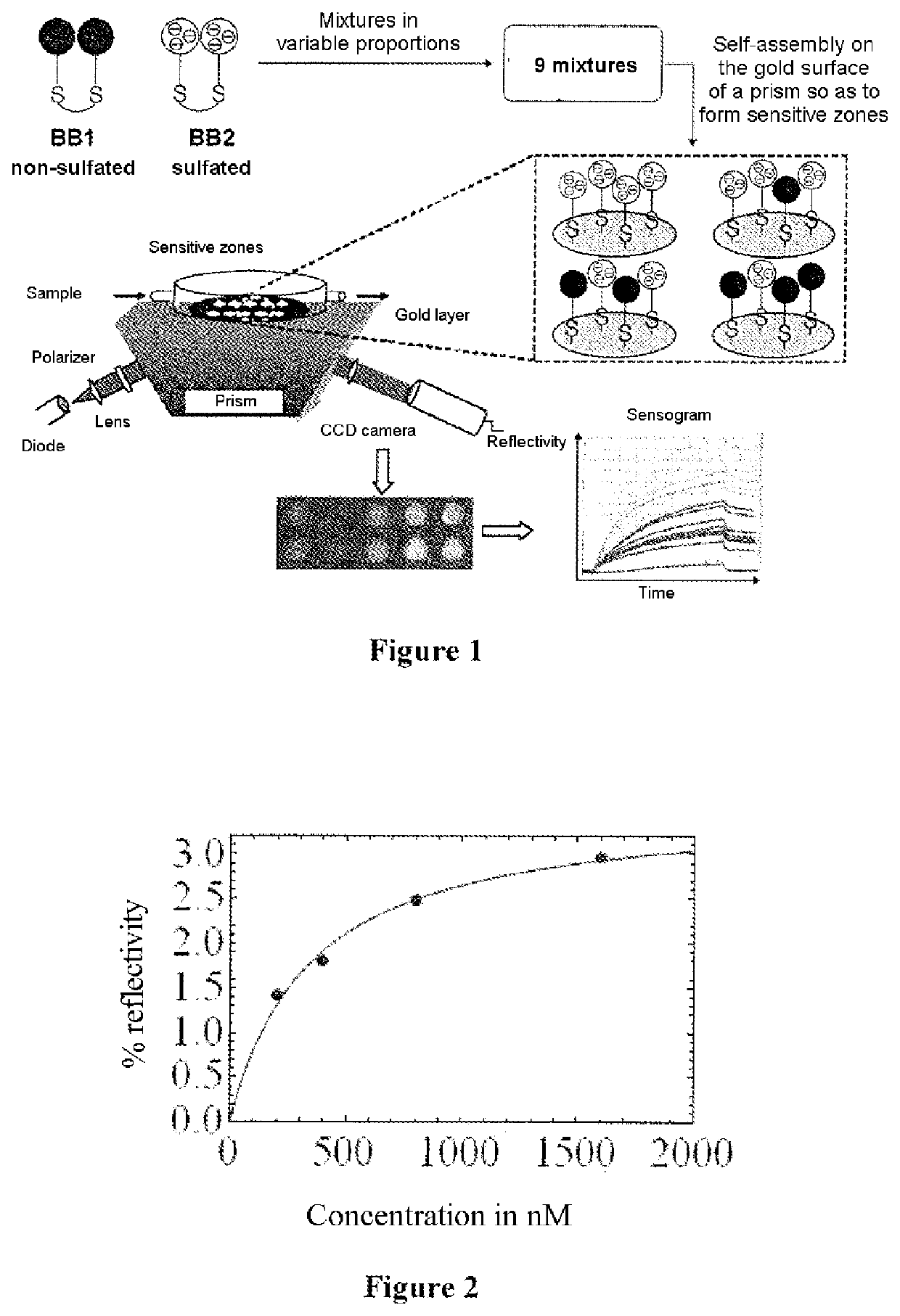
Electronic nose or tongue sensors
The present invention relates to a sensor for an electronic tongue or nose for analysing a sample or detecting a target. The sensor comprises a support, on one surface of which a plurality of sensitive areas are located, each sensitive area comprising at least one receptor and being capable of transmitting a measurable signal generated by the interaction of at least one constituent of the sample or one target with at least one receptor. The sensor is characterised in that it comprises at least three sensitive areas that differ from one another in terms of their respective receptor compositions, at least one of the sensitive areas comprising a mixture of at least two different receptors, while the two other sensitive areas each comprise at least one of the two receptors.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +2
Method and system for differential drug discovery
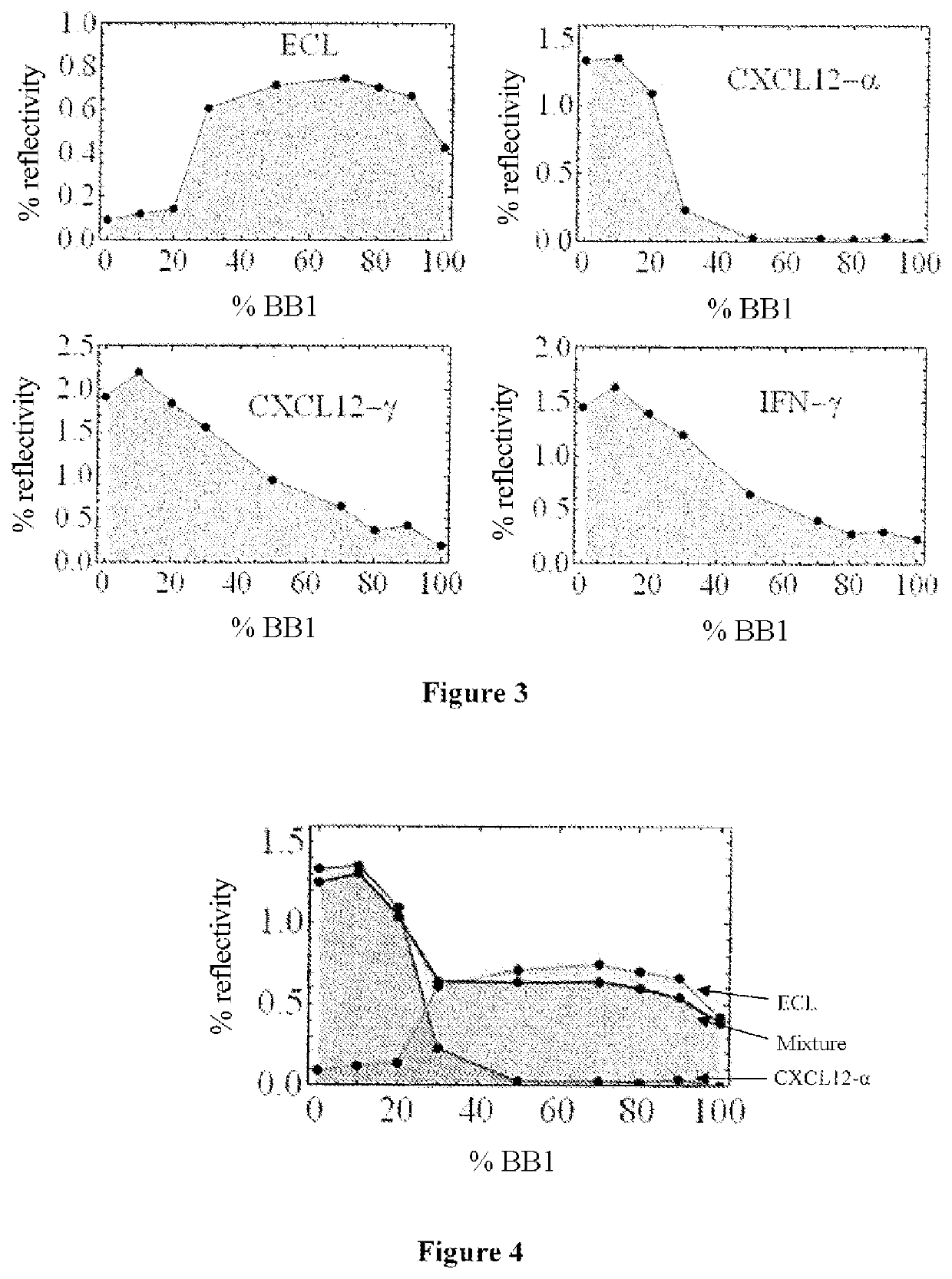
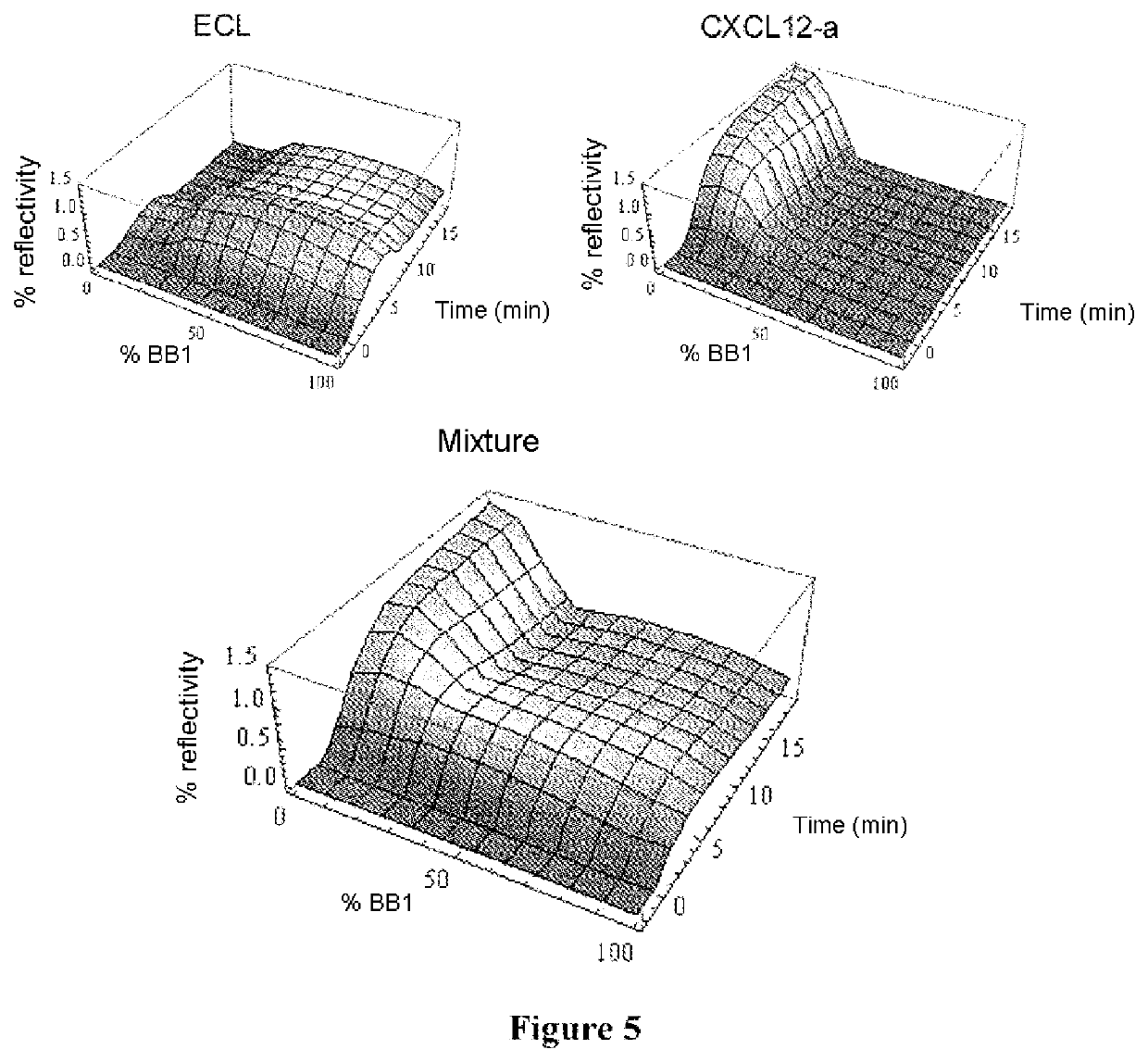
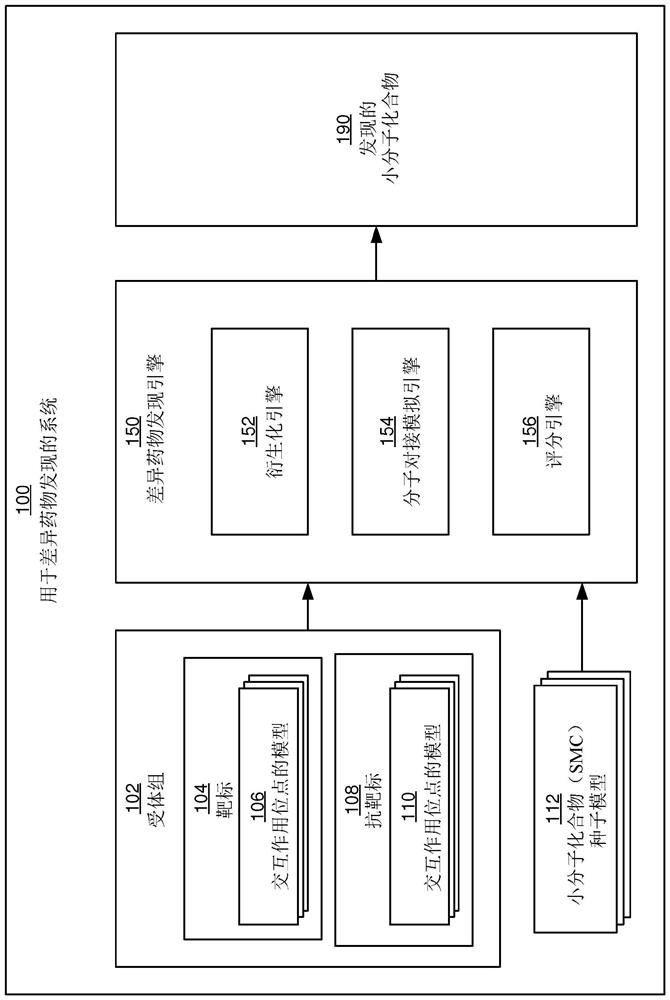
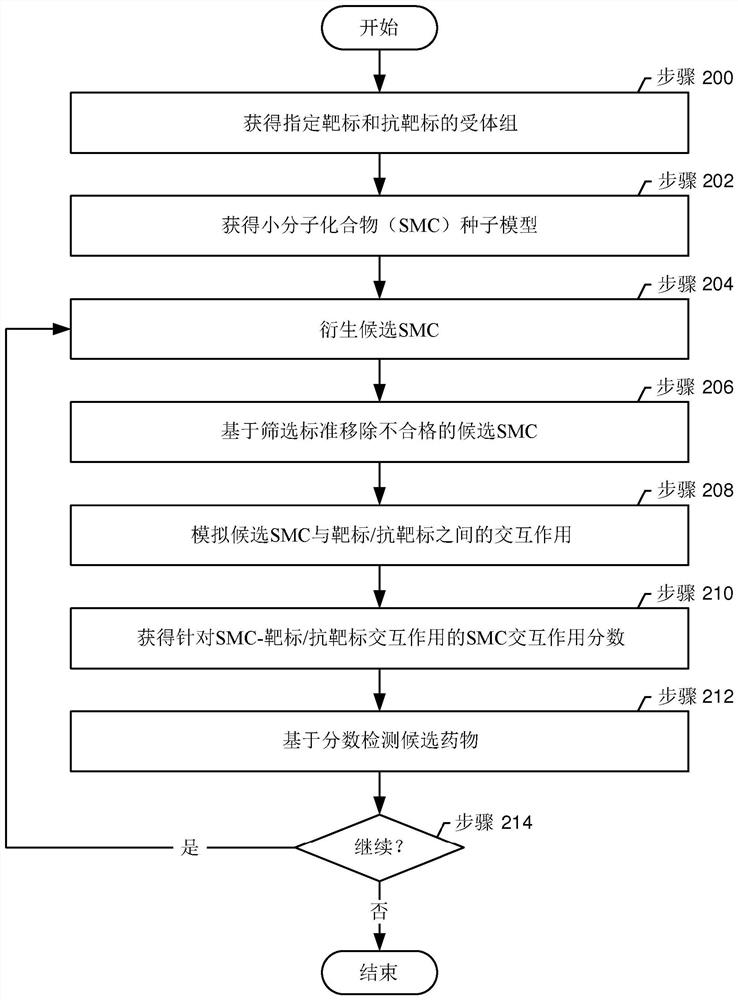
A method for differential drug discovery involves obtaining a receptor panel. The receptor panel specifies a multitude of targets and a multitude of anti- targets. The method further involves obtaining a small molecule compound (SMC) seed model and derivatizing a first multitude of candidate SMCs from the SMC seed model. For each of the candidate SMCs in the first multitude of candidate SMCs, first desired interactions between the candidate SMC and each of the multitude of targets are simulated. Further, for each of the candidate SMCs in the first multitude of candidate SMCs, first undesired interactions between the candidate SMC and each of the multitude of anti-targets are simulated. The method also involves obtaining a first SMC interaction score for each of the candidate SMCs in the first multitude of candidate SMCs based on the first desired interactions and based on the first undesired interactions, and based on the first SMC interaction score, determining whether at least a minimum score for a drug is reached.
Owner:CYCLICA INC
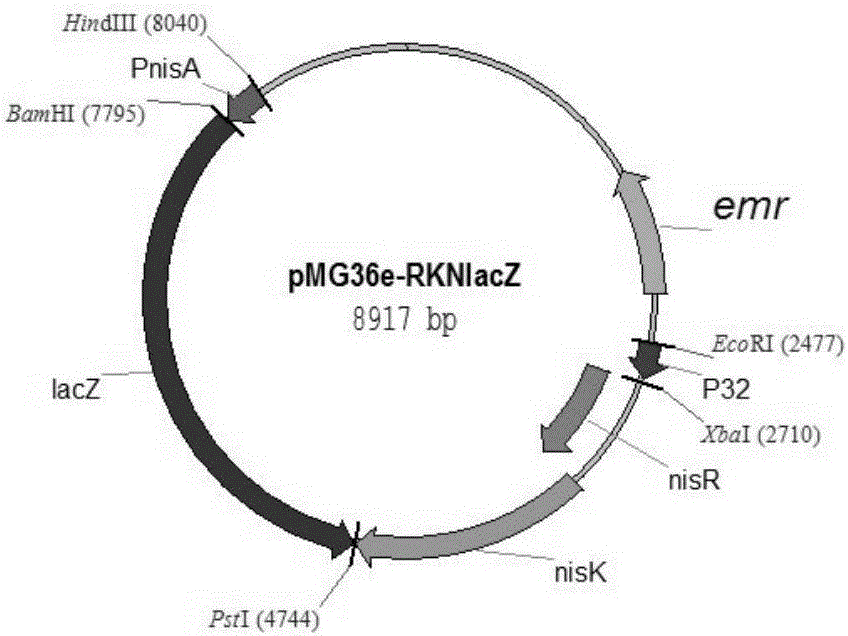
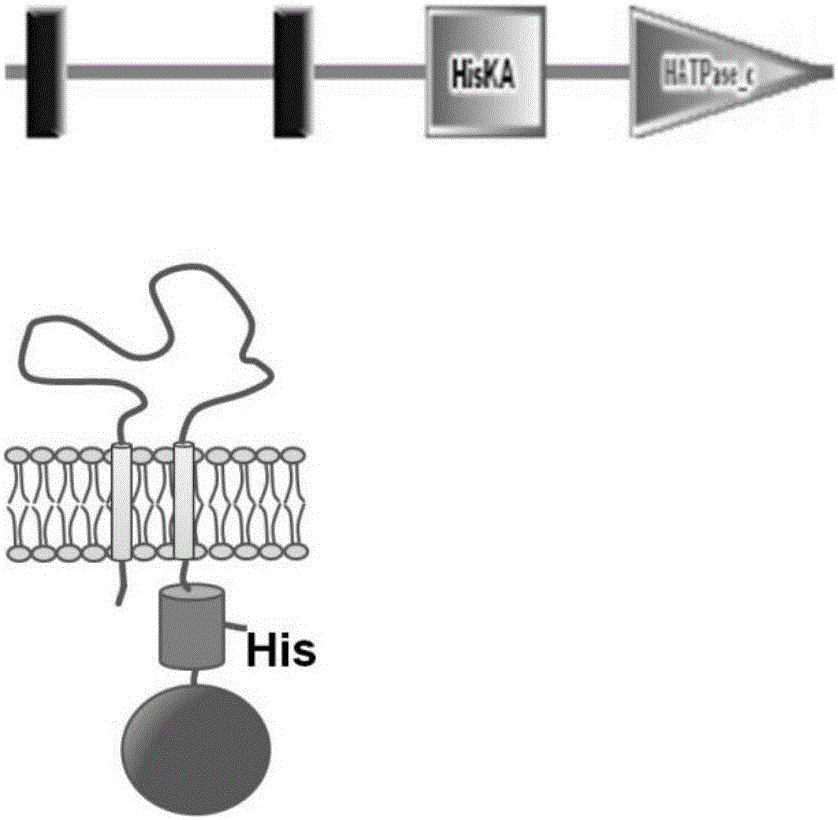
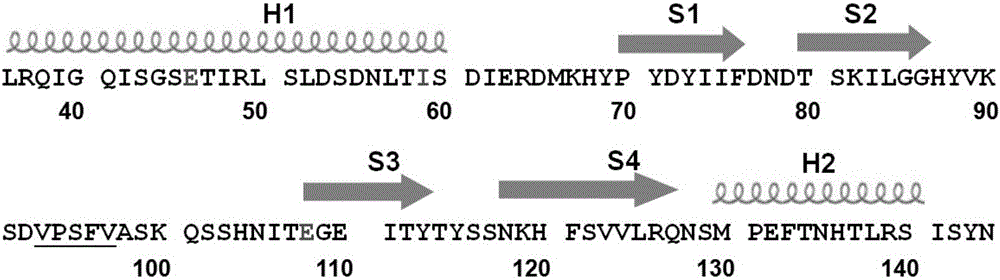
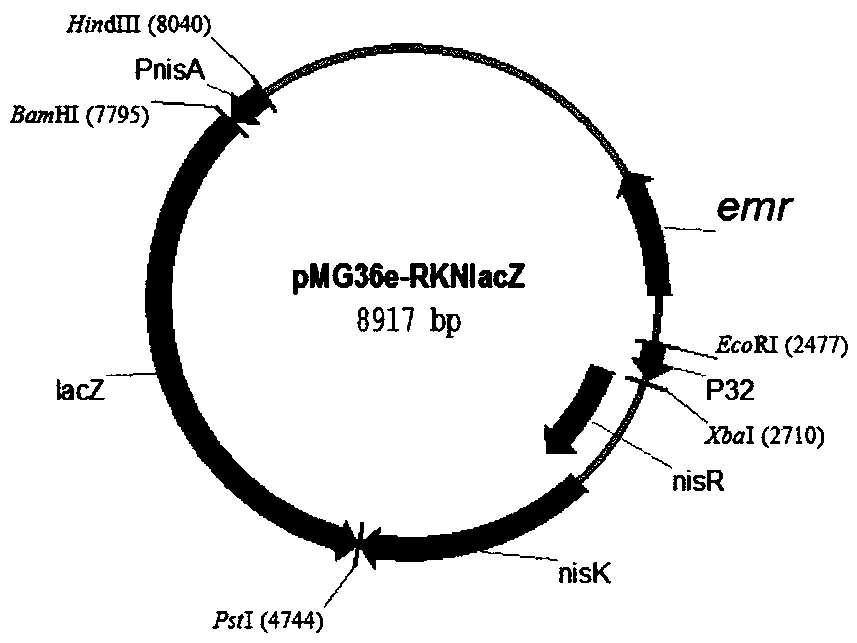
Method for improving nisin induction efficiency in lactic acid bacteria NICE expression system
The invention discloses a method for improving a nisin induction efficiency in a lactic acid bacteria NICE expression system. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the sensing activity of nisin is enhanced by conducting mutation transformation on receptor histidine kinase NisK of nisin molecules of an inducer. Experiments prove that through nisin induction of a same concentration, the expression amount of reporter protein is obviously increased and the nisin induction efficiency is remarkably enhanced after the NisK mutation transformation; therefore, the method disclosed by the invention has a quite important significance for improving the expression amount of heterologous protein, declining the concentration of the inducer and reducing the complexity of constructing the system by virtue of the NICE system.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Signalling system
InactiveUS20210032332A1Rapidly inhibited/terminatedAdverse toxic effectFusion with DNA-binding domainNGF/TNF-superfamilyIntracellular signallingAntigen receptor
The present invention provides a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) signalling system comprising; (i) a receptor component comprising an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain and a first binding domain; and (ii) an intracellular signalling component comprising a signalling domain and a second binding domain which specifically binds the first binding domain of the receptor component; wherein, binding of the first and second binding domains is disrupted by the presence of an agent, such that in the absence of the agent the receptor component and the signalling component heterodimerize and binding of the antigen binding domain to antigen results in signalling through the signalling domain, whereas in the presence of the agent the receptor component and the signalling component do not heterodimerize and binding of the antigen binding domain to antigen does not result in signalling through the signalling domain.
Owner:AUTOLUS LIMIED
A method for improving nisin induction efficiency in lactic acid bacteria nice expression system
ActiveCN105950582BIncrease concentrationHigh expressionBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyLactic acid bacterium
The invention discloses a method for improving a nisin induction efficiency in a lactic acid bacteria NICE expression system. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the sensing activity of nisin is enhanced by conducting mutation transformation on receptor histidine kinase NisK of nisin molecules of an inducer. Experiments prove that through nisin induction of a same concentration, the expression amount of reporter protein is obviously increased and the nisin induction efficiency is remarkably enhanced after the NisK mutation transformation; therefore, the method disclosed by the invention has a quite important significance for improving the expression amount of heterologous protein, declining the concentration of the inducer and reducing the complexity of constructing the system by virtue of the NICE system.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adjuvant compositions
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the stimulation of immune responses. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions for enhancing an immune response to one or more antigens. Compositions and methods of the invention are useful for the treatment and / or prevention of microbial infections, such as infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites, as well as the treatment and / or prevention of cancer and malignant diseases. Compositions and methods of the invention include one or more antigens / immunogens together with an adjuvant formulation comprising an emulsion delivery system in combination with one or more immunostimulatory compounds (e.g., a compound that stimulates the innate immune system (e.g., a toll-like receptor antagonist (e.g., synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides (ODN)))) that enhance immune responses to the one or more antigens / immunogens when administered to a subject. Compositions and methods of the invention find use in, among other things, clinical (e.g. therapeutic and preventative medicine (e.g., vaccination)) and research applications.
Owner:NANOBIO CORP +1
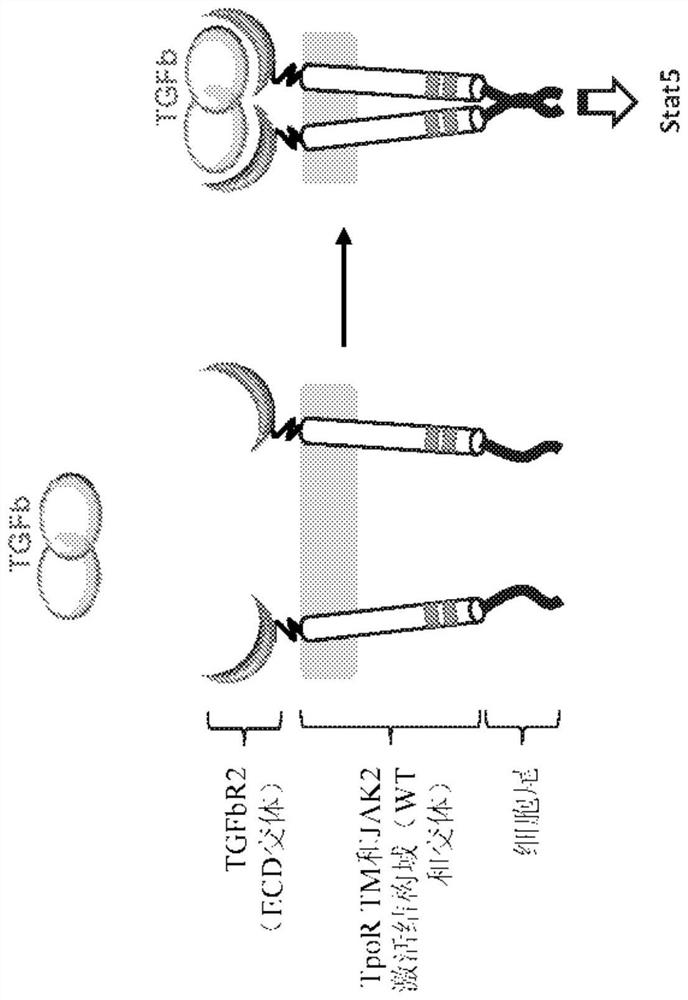
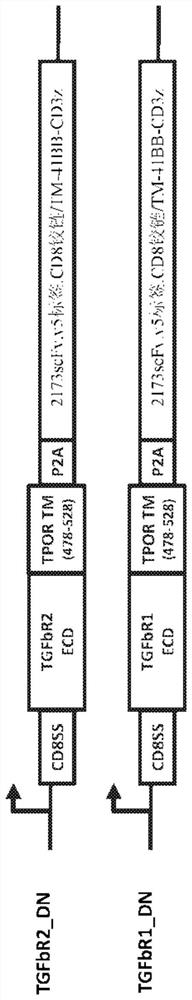
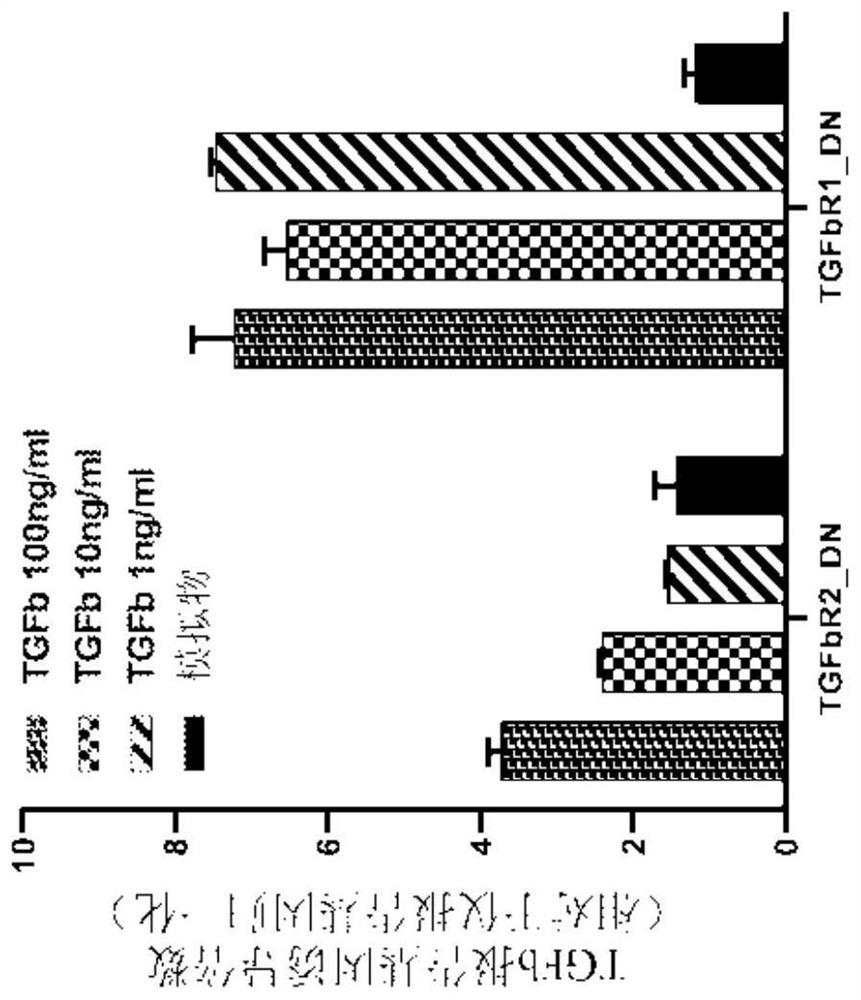
Chimeric cytokine receptors including TGFB binding domains
PendingCN114341193AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntigen receptorsReceptorome
Provided herein are chimeric cytokine receptors having a binding domain capable of binding to a TGF-beta ligand or a TGF-beta receptor antibody. When such receptors are present on immune cells (CAR-T cells) with chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), such receptors constitutively and / or by binding of TGF-beta ligands or TGF-beta receptor antibodies increase the expansion, activity and persistence of the CAR-T cells. The invention also provides methods of making and using the chimeric cytokine receptors described herein.
Owner:ALLOGENE THERAPEUTICS INC
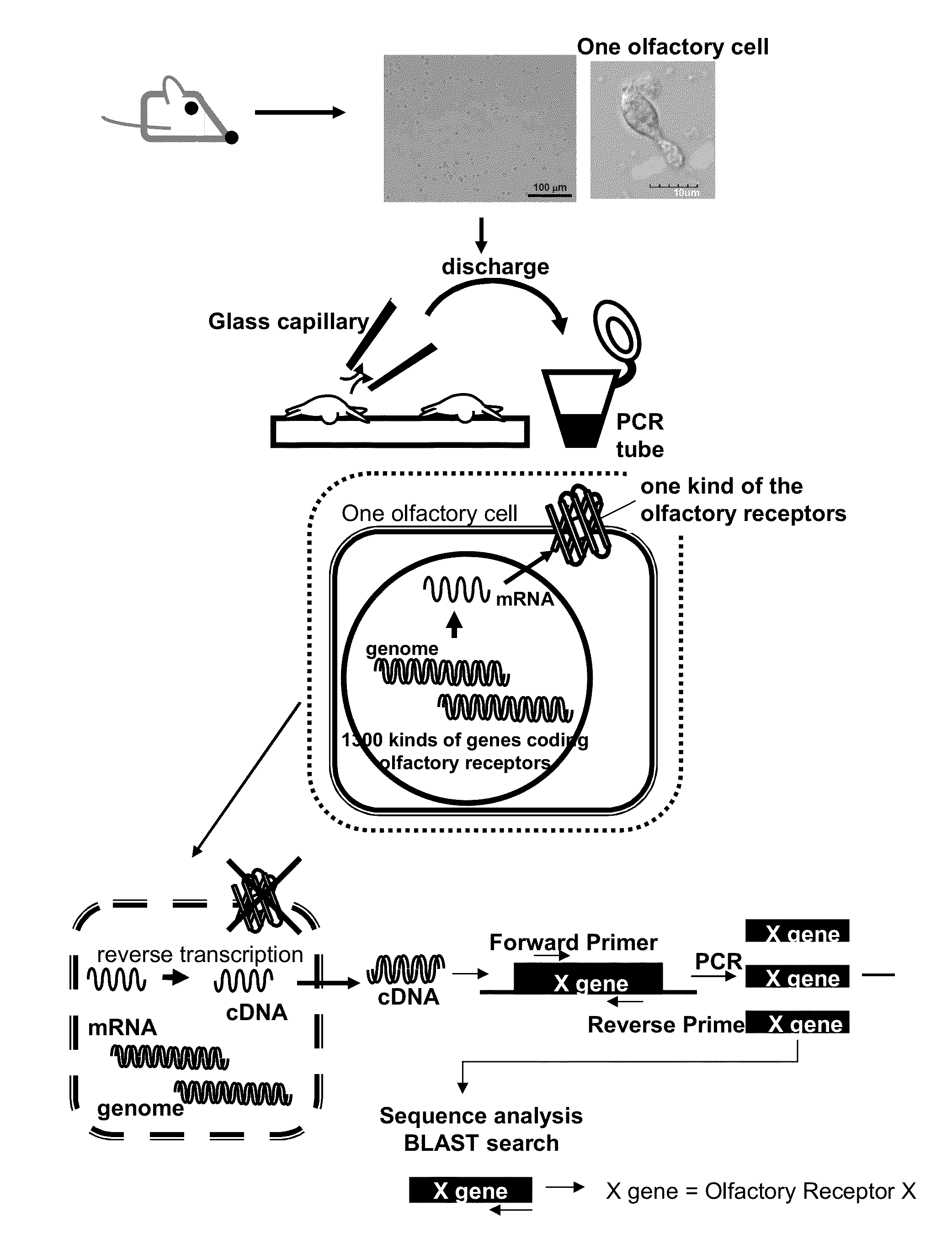
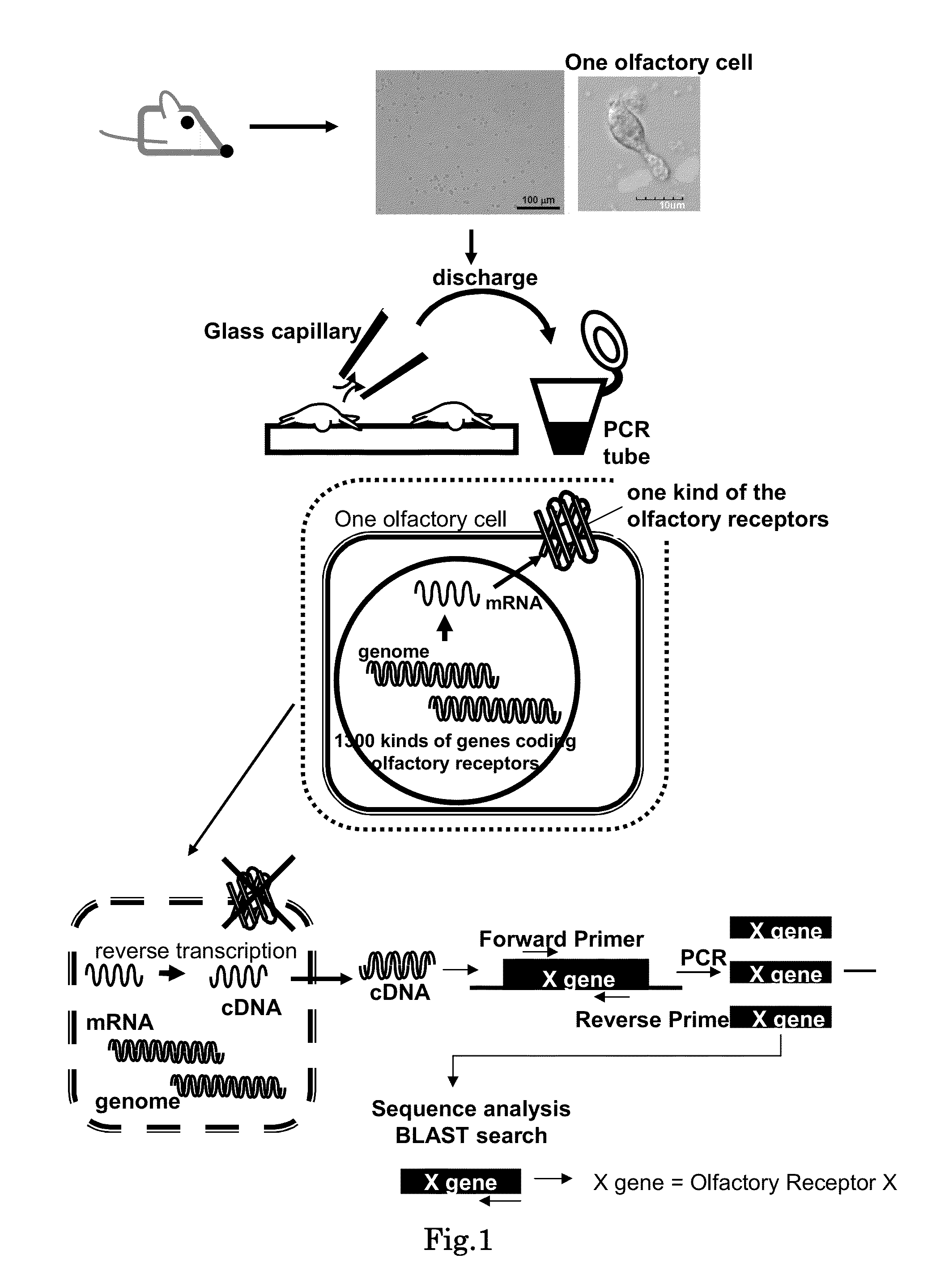
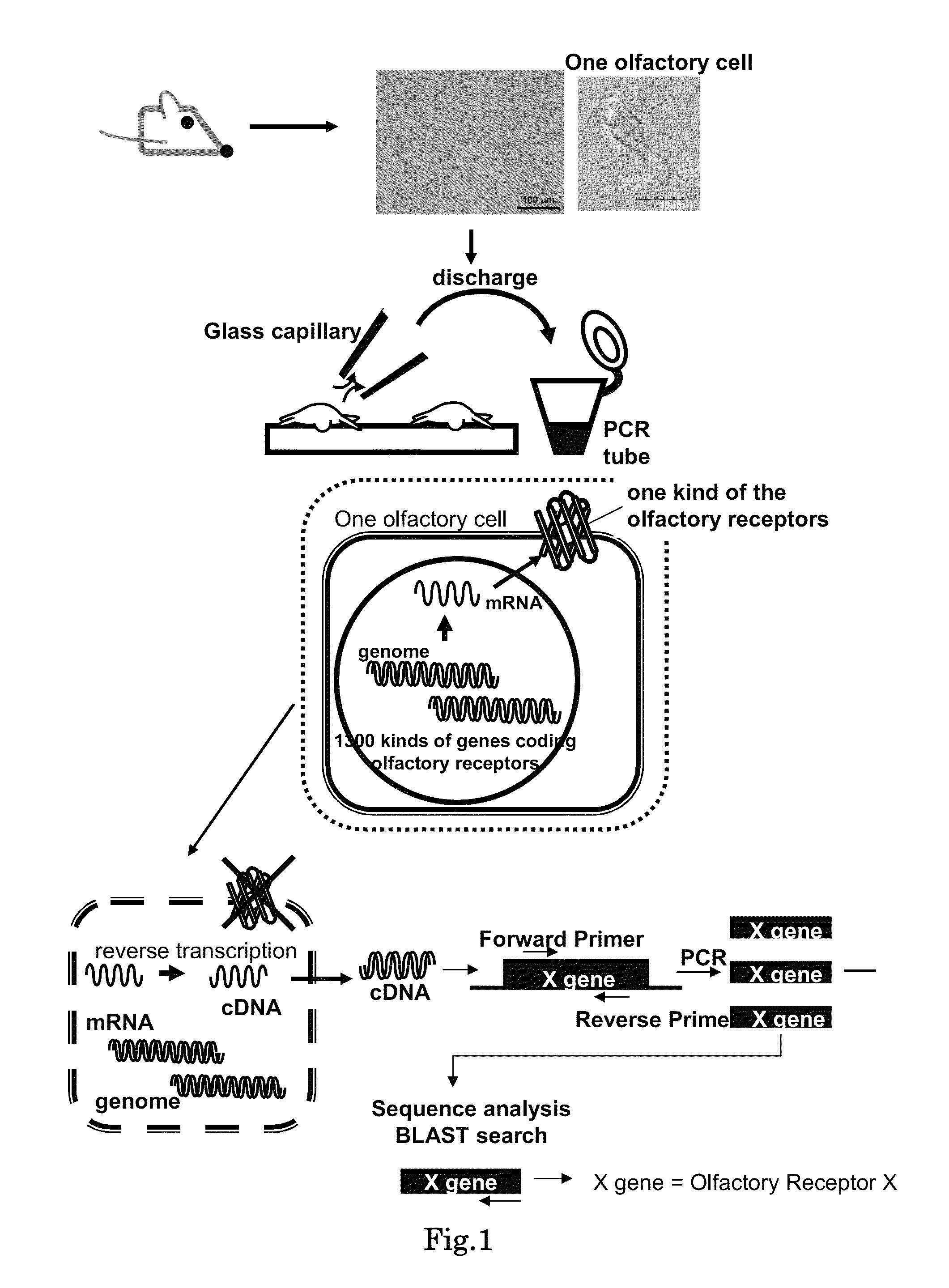
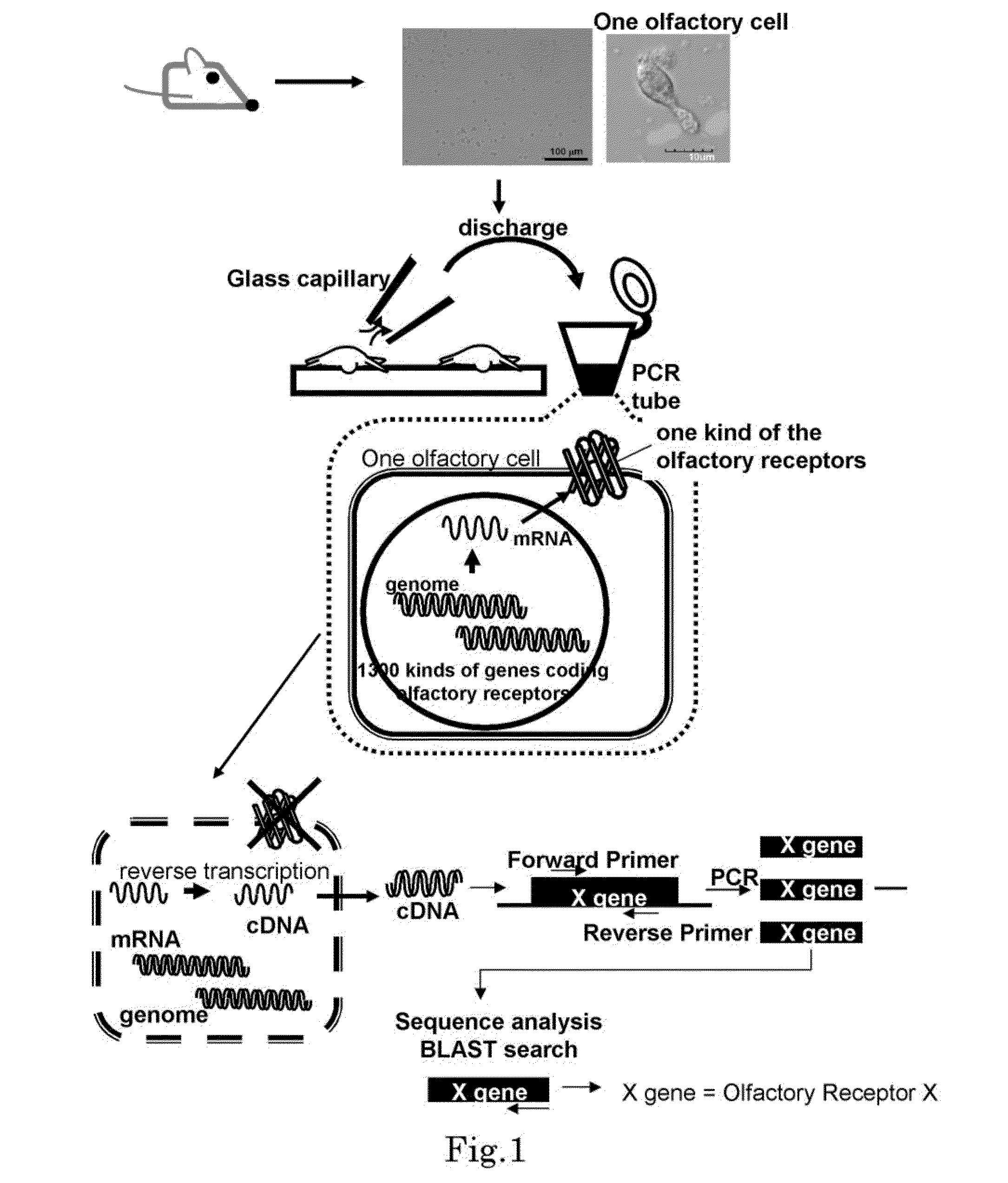
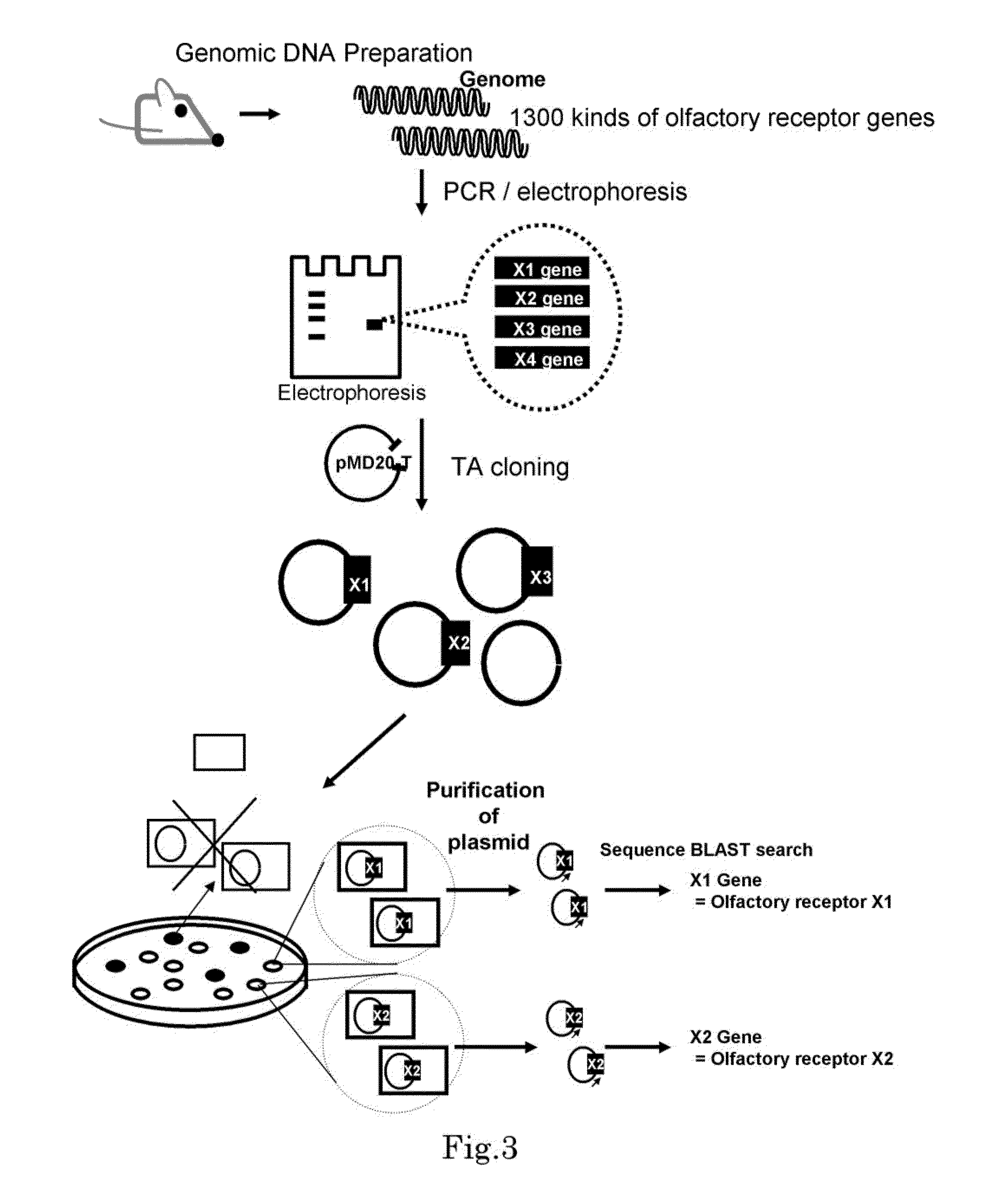
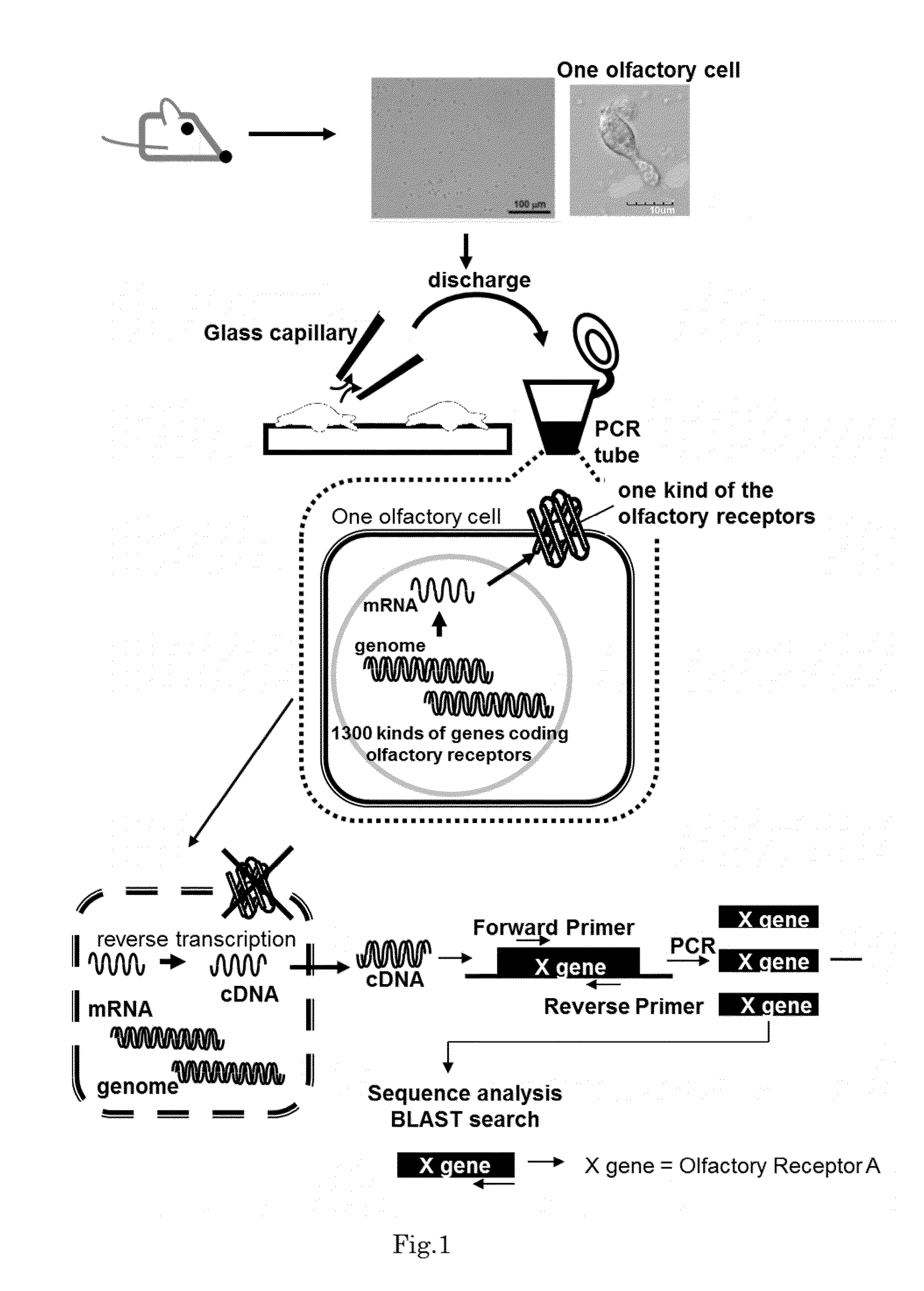
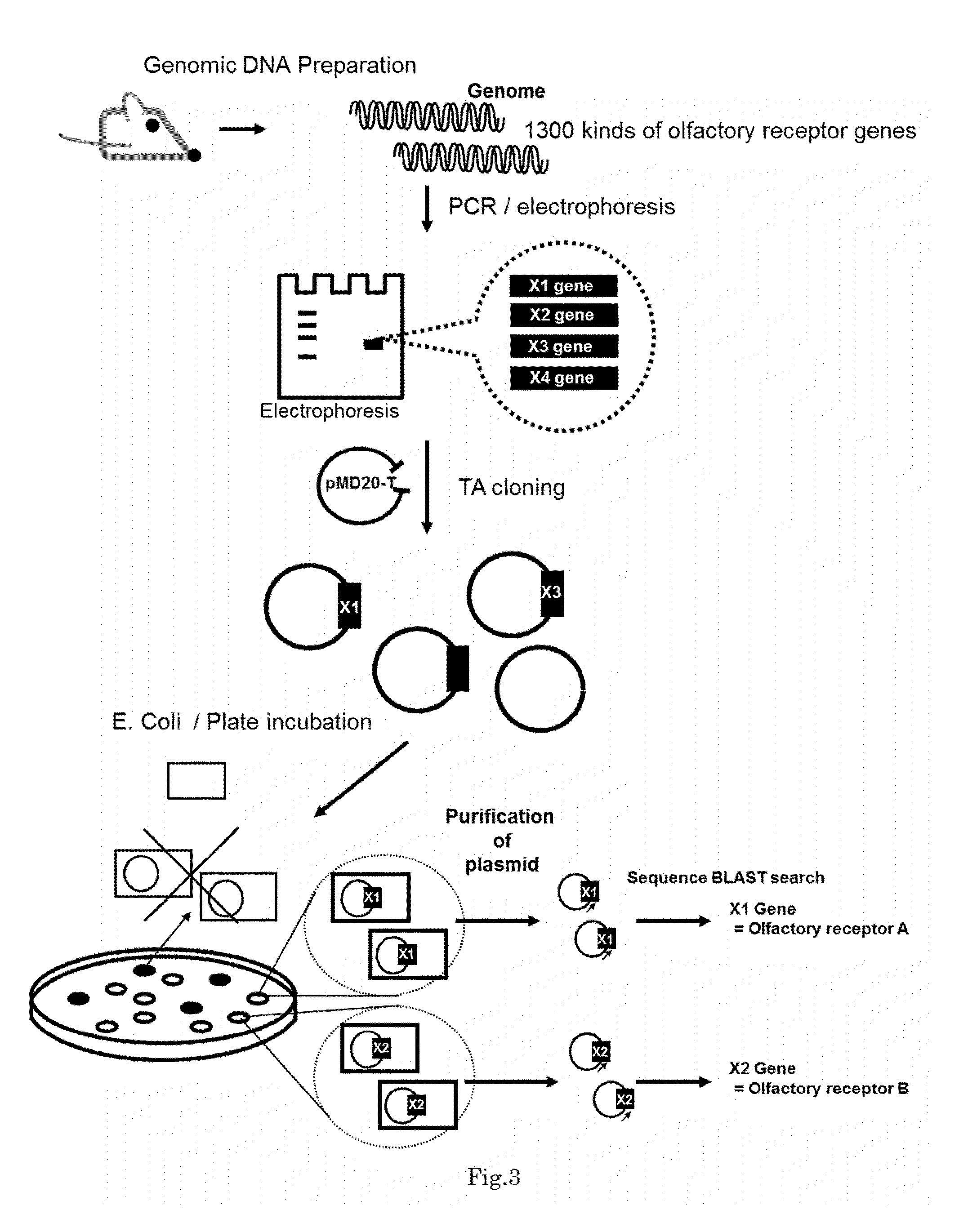
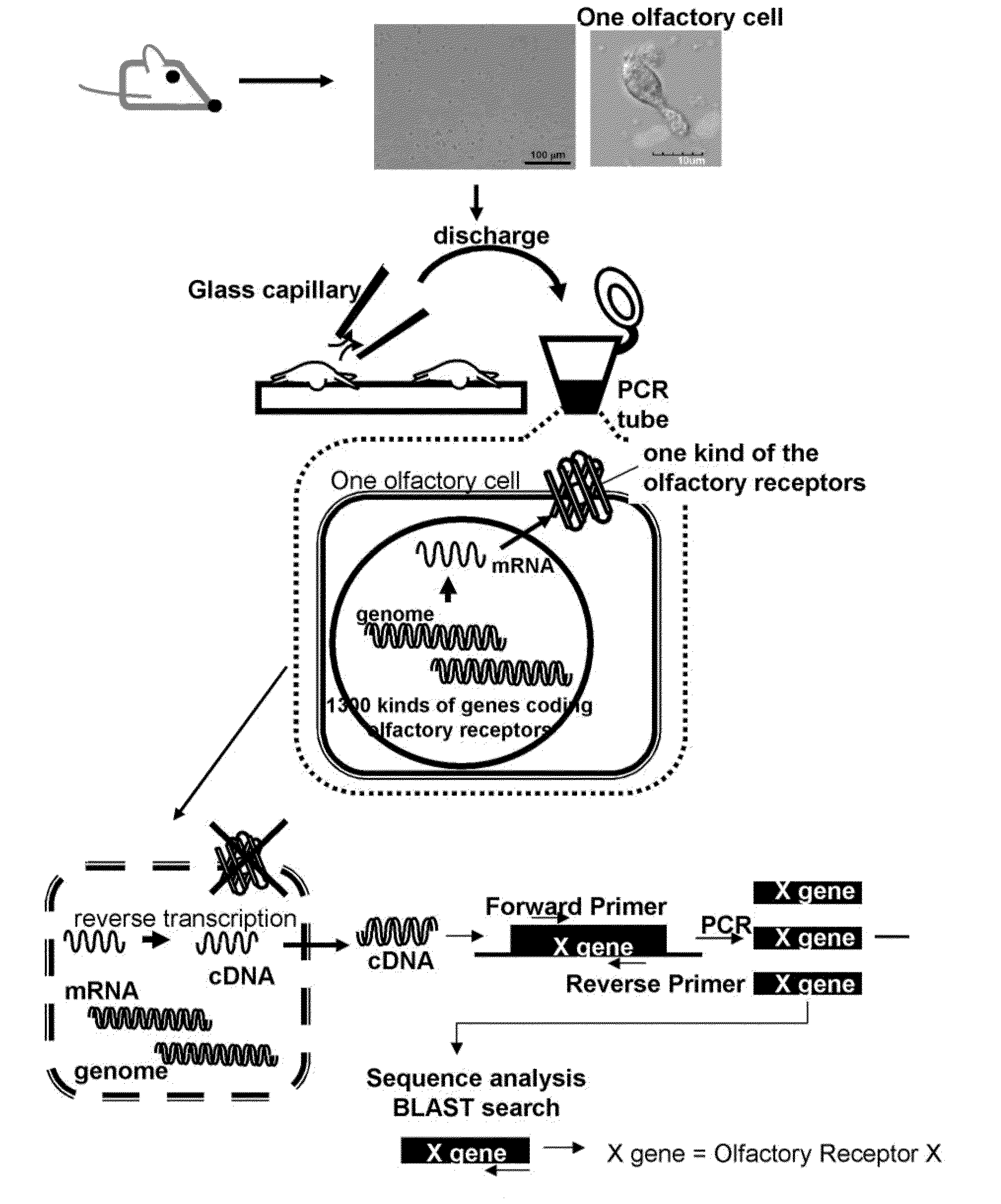
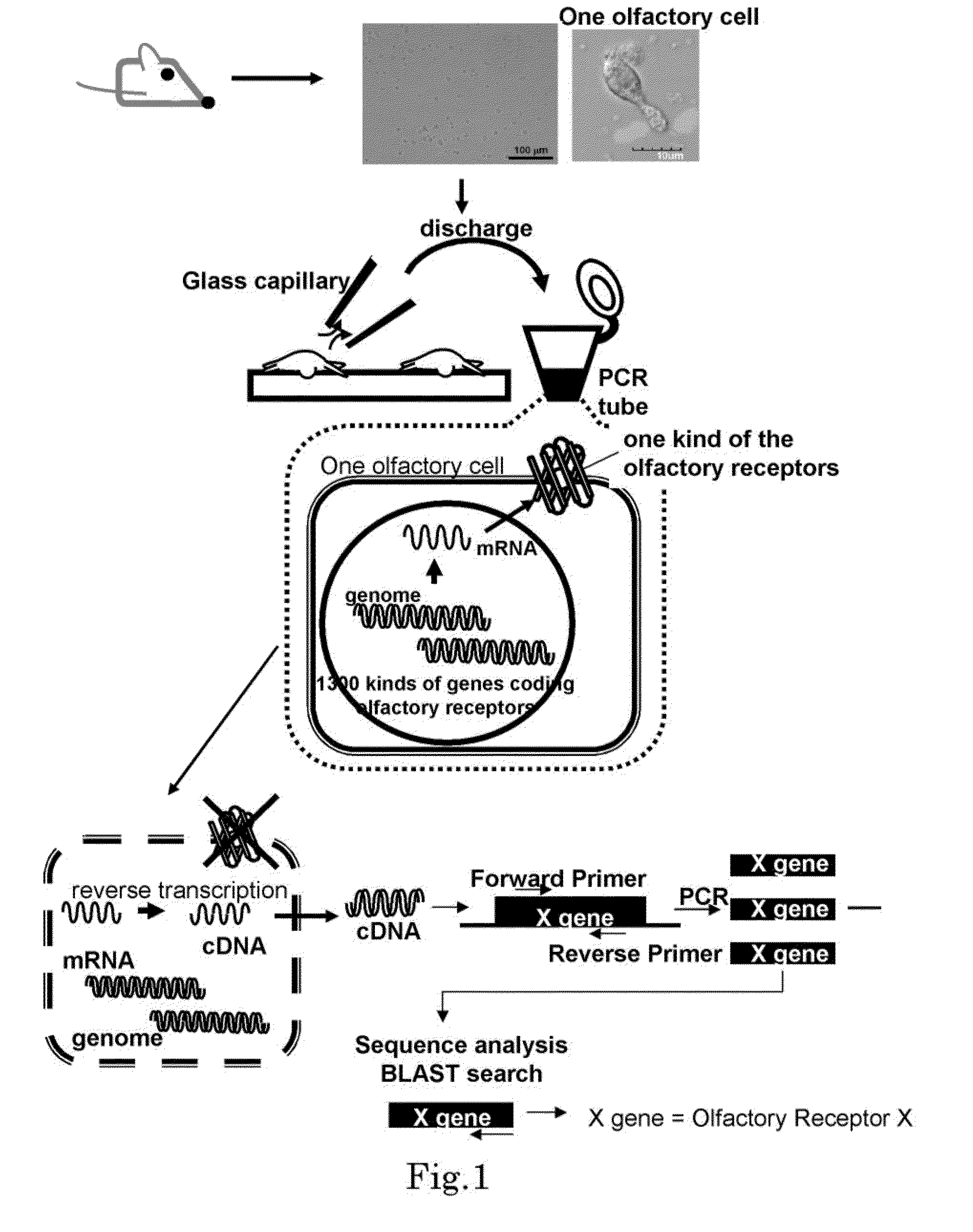
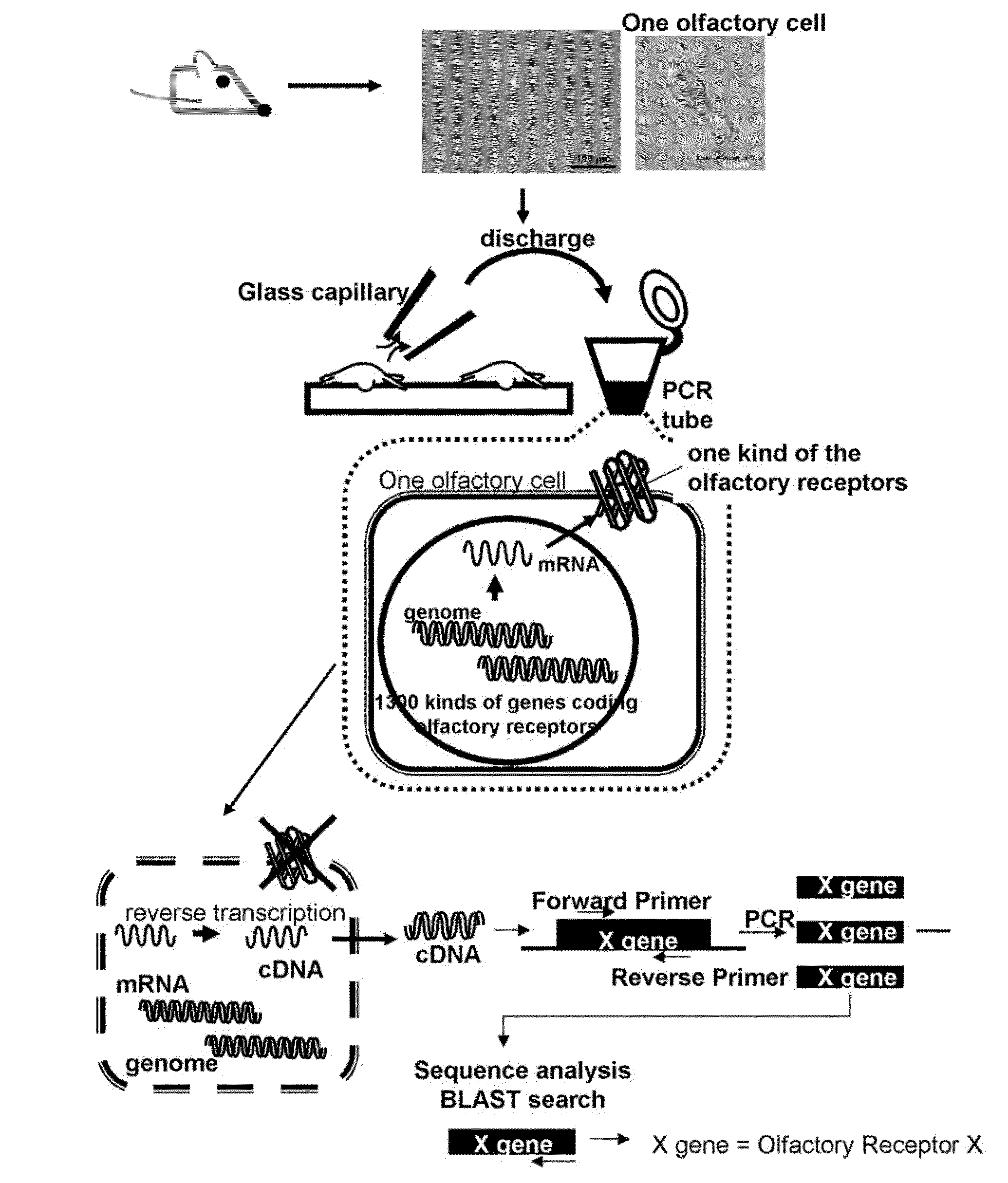
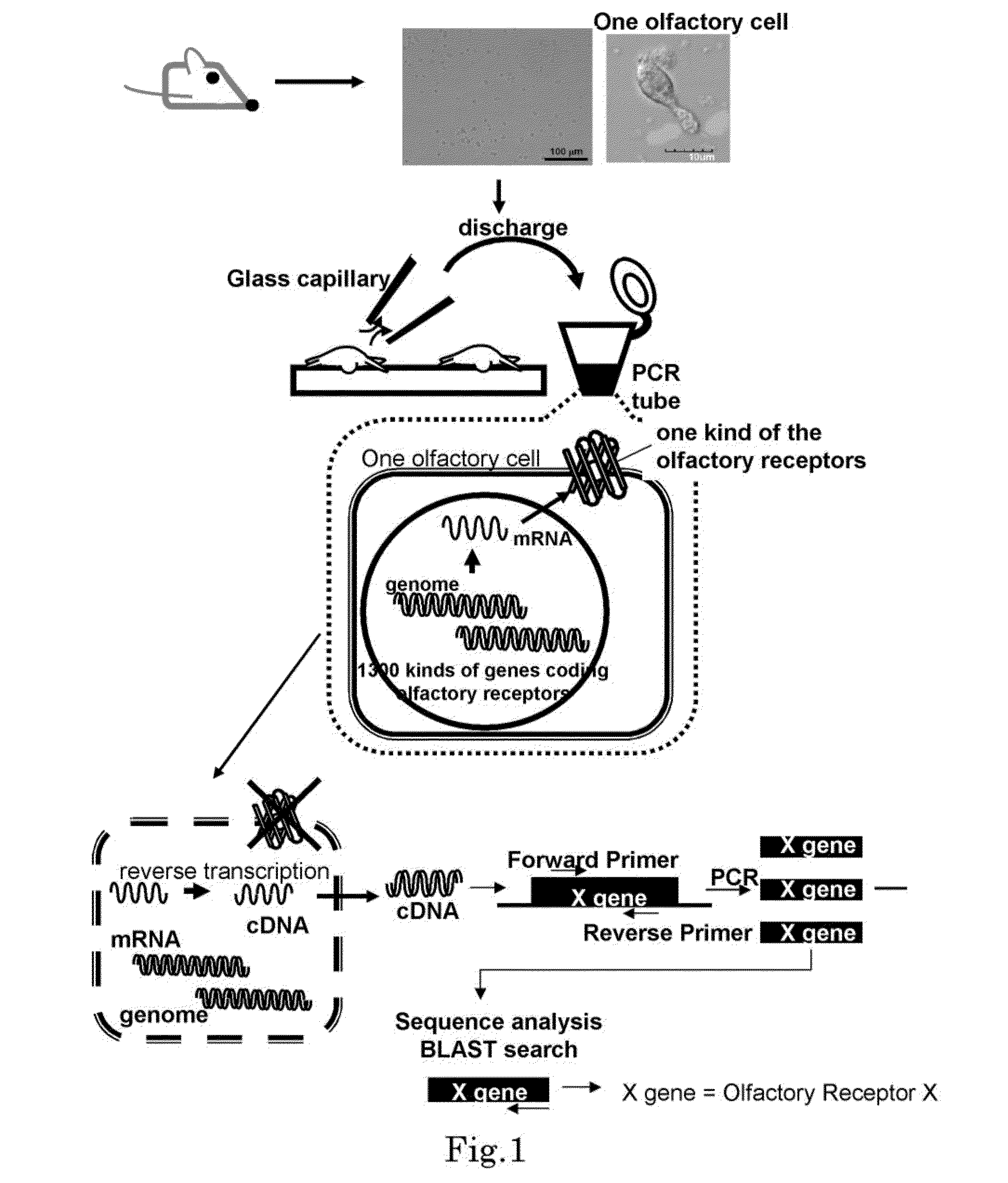
Method for identifying olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell
The present invention provides a novel method for identifying an olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell. In the present invention, amplified is the cDNA derived from the mRNA of the one olfactory cell by a PCR method using a forward primer represented by SEQ ID: 01 and a reverse primer represented by SEQ ID: 02. Subsequently, determined is whether or not a gene sequence of the amplified cDNA is identical to one gene sequence included in gene sequences coding for olfactory receptors included in the mouse olfactory receptor group A. Finally, determined is that the olfactory receptor included in the one olfactory cell is the olfactory receptor corresponding to the one gene sequence which is identical to the gene sequence of the cDNA in the previous step, if the gene sequence of the cDNA is identical to the one gene sequence in the previous step.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Signalling system
ActiveUS11466070B2Adverse toxic effectPrevents co-localisationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorsAntigen binding
The present invention provides a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) system comprising; (i) a receptor component comprising a antigen binding domain and a first binding domain; and (ii) a signalling component comprising a signalling domain and a second binding domain which binds the single domain binder of the first binding domain of the receptor component wherein either the first or second binding domains comprise a single domain binder, and wherein, binding of the first and second binding domains is disrupted by the presence of an agent, such that in the absence of the agent, the receptor component and the signalling component heterodimerize and binding of the antigen binding domain to antigen results in signalling through the signalling domain; whereas in the presence of the agent, the receptor component and the signalling component do not heterodimerize and binding of the antigen binding domain to antigen does not result in signalling through the signalling domain.
Owner:AUTOLUS LIMIED
Signalling System
ActiveUS20190330299A1Reduce adverse toxic effectAdverse toxic effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyBinding domainAntigen binding
The present invention provides a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) system comprising; (i) a receptor component comprising a antigen binding domain and a first binding domain; and (ii) a signalling component comprising a signalling domain and a second binding domain which binds the single domain binder of the first binding domain of the receptor component wherein either the first or second binding domains comprise a single domain binder, and wherein, binding of the first and second binding domains is disrupted by the presence of an agent, such that in the absence of the agent, the receptor component and the signalling component heterodimerize and binding of the antigen binding domain to antigen results in signalling through the signalling domain; whereas in the presence of the agent, the receptor component and the signalling component do not heterodimerize and binding of the antigen binding domain to antigen does not result in signalling through the signalling domain.
Owner:AUTOLUS LIMIED
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) signalling system
ActiveUS10588967B2Avoid toxicityLimited potencyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsIntracellular signallingAntigen receptor
Owner:AUTOLUS LIMIED
Adjuvant compositions
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the stimulation of immune responses. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions for enhancing an immune response to one or more antigens. Compositions and methods of the invention are useful for the treatment and / or prevention of microbial infections, such as infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, as well as the treatment and / or prevention of cancer and malignant diseases. Compositions and methods of the invention include one or more antigens / immunogens together with an adjuvant formulation comprising an emulsion delivery system in combination with one or more immunostimulatory compounds (e.g., a compound that stimulates the innate immune system (e.g., a toll-like receptor antagonist (e.g., synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides (ODN)))) that enhance immune responses to the one or more antigens / immunogens when administered to a subject. Compositions and methods of the invention find use in, among other things, clinical (e.g. therapeutic and preventative medicine (e.g., vaccination)) and research applications.
Owner:NANOBIO CORP +1
Gastrin releasing peptide compounds
InactiveUS20130136691A1Improve targetingAffect activityBiological material analysisRadioactive preparation carriersPeptideNuclear medicine
Methods and compositions for diagnosing, staging disease, monitoring therapeutic effect of drugs and imaging a patient are provided, including radiopharmaceutical formulations. Compositions comprising Ga-AMBA complexed with a radioactive isotope are provided; as are methods of imaging Gastrin Releasing Peptide receptor (GRP-R) bearing tissue and methods of diagnosing or staging disease in patients suspected of having disease associated with aberrant GRP-R function. Further, methods of monitoring therapeutic effect of a drug targeted to a receptor that crosstalks with GRP-R are provided; as are methods of pre-dosing / co-dosing non-target tissues containing GRP-R. Particularly, methods of monitoring activity of receptors and receptor pathways in vivo / in vitro by using a ligand that binds to the GRP-R are provided; as are methods of measuring the activity of a receptor or group of receptors and their associated pathways that exhibit crosstalk with the GRP-R by using such a ligand which is also detectable by external means.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Method for identifying olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell
The present invention provides a novel method for identifying an olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell. In the present invention, amplified is the cDNA derived from the mRNA of the one olfactory cell by a PCR method using a forward primer represented by SEQ ID: 01 and a reverse primer represented by SEQ ID: 02. Subsequently, determined is whether or not a gene sequence of the amplified cDNA is identical to one gene sequence included in gene sequences coding for olfactory receptors included in the mouse olfactory receptor group A. Finally, determined is that the olfactory receptor included in the one olfactory cell is the olfactory receptor corresponding to the one gene sequence which is identical to the gene sequence of the cDNA in the previous step, if the gene sequence of the cDNA is identical to the one gene sequence in the previous step.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Programmable immunocyte receptor complex system
PendingUS20200299352A1Immunoglobulin superfamilyGenetically modified cellsReceptor subunitReceptorome
A programmable receptor complex expressed by an immunocyte, wherein the programmable receptor complex includes a plurality of native or endogenously expressed receptor subunits, wherein the native or endogenously expressed receptor subunits have been engineered or modified to include FcγRI receptor components, biotin-binding components, or both, and wherein the FcγRI receptor components and biotin-binding components are operative to bind to target detector molecules that bind to or otherwise interact with predetermined targets.
Owner:FUNDAMENTAL SOLUTIONS
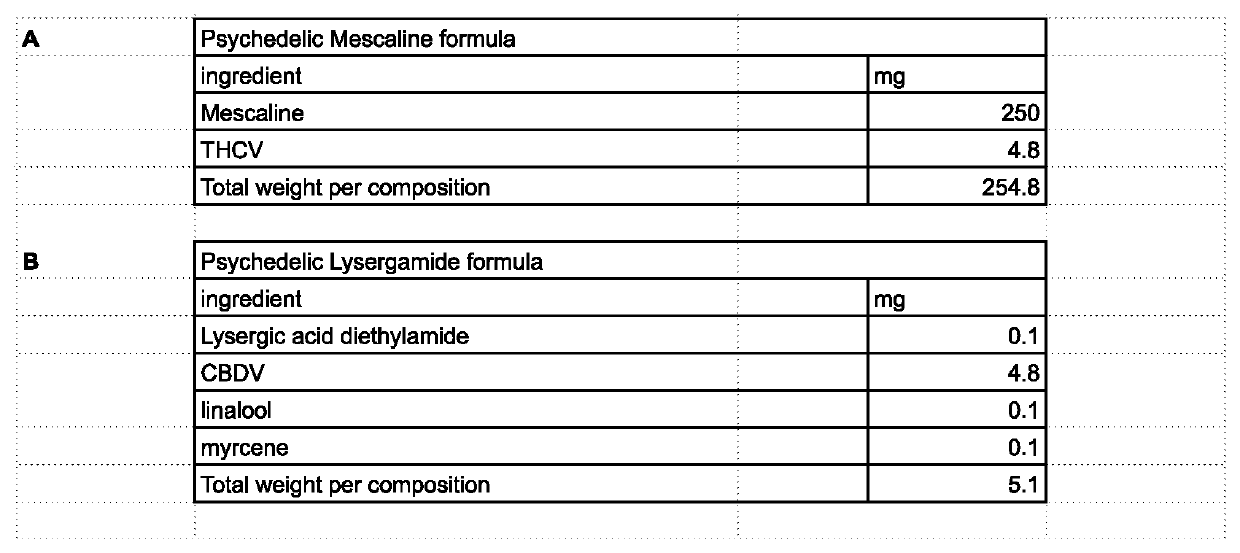
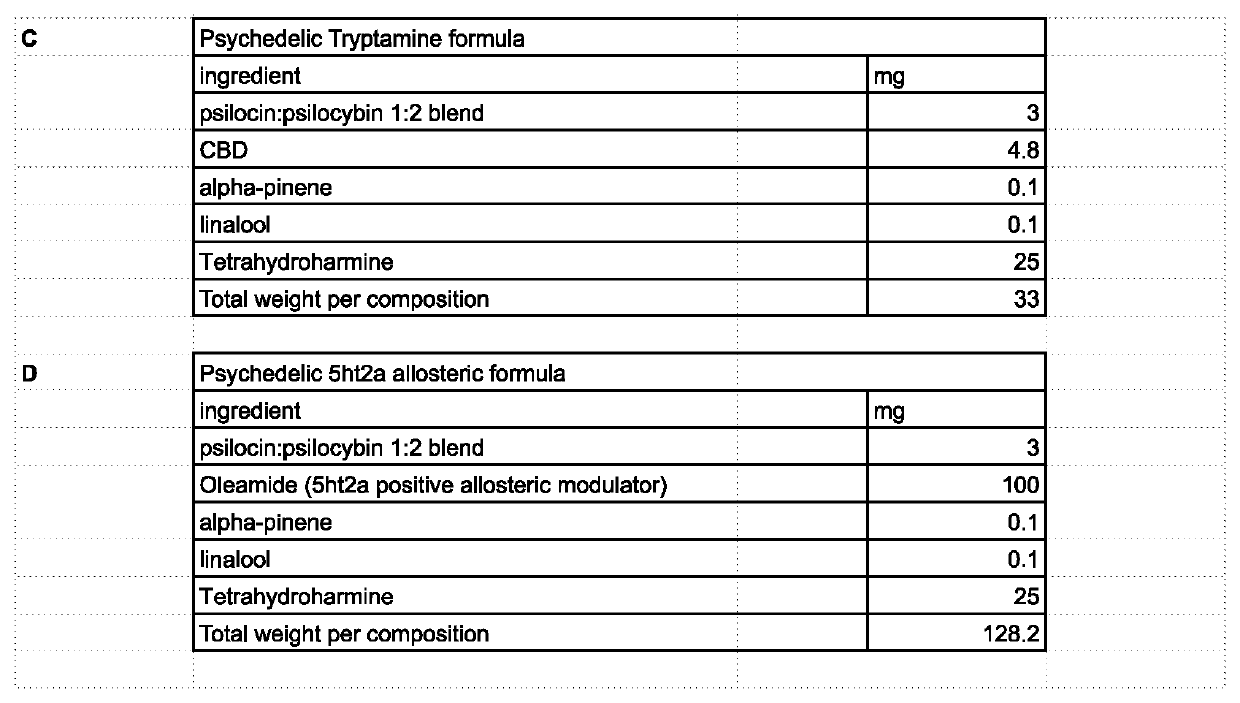
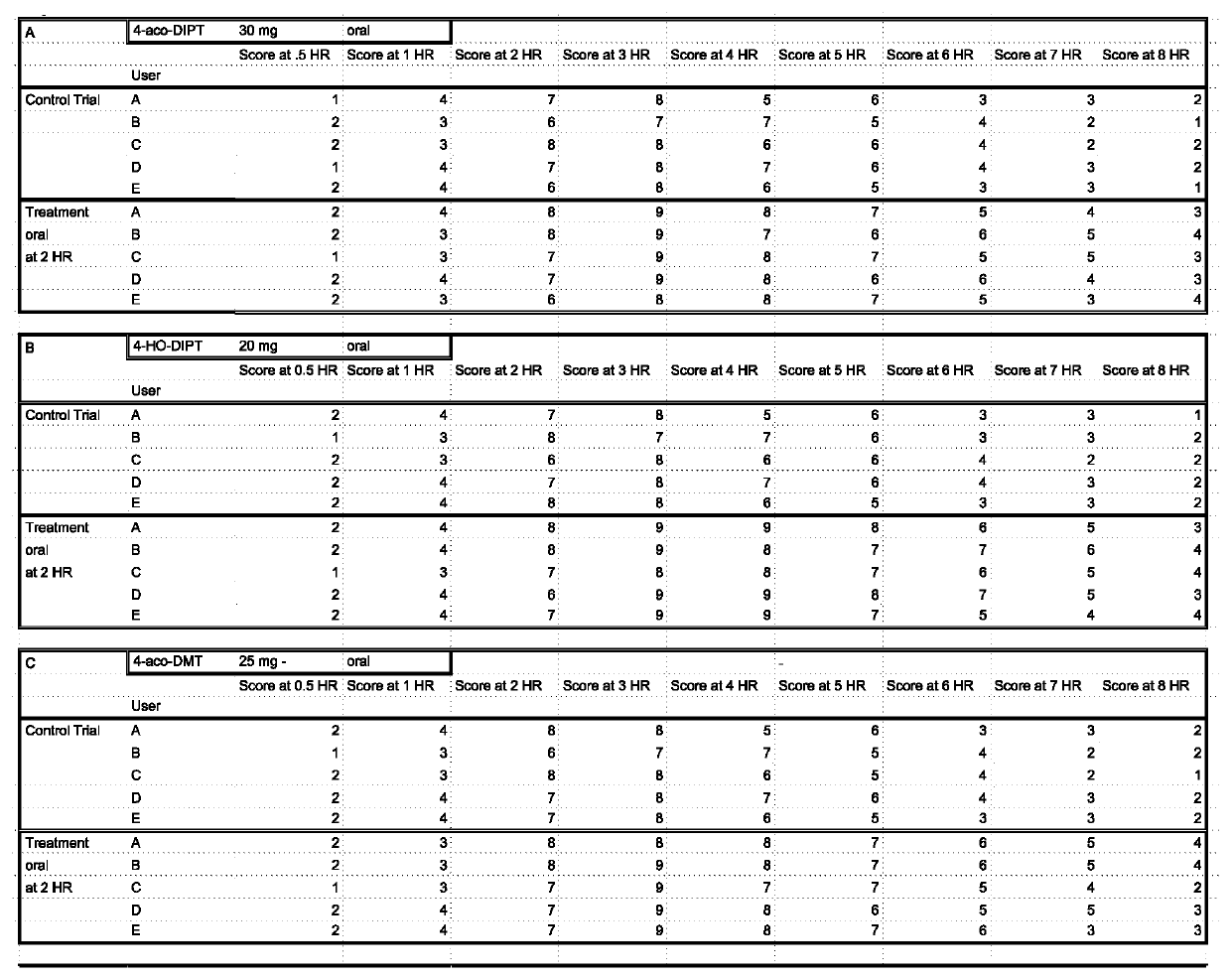
Methods of use and formulations of allosteric modulators of the serotonin, dopamine and other receptor systems for medical, recreational, religious, research and other uses.
PendingUS20220265601A1Lower Level RequirementsHydroxy compound active ingredientsAmide active ingredientsIonic ChannelsMuscarinics
The invention involves the use of formulations of positive, negative, inverse agonist, or neutral allosteric modulators of receptors such as, but not limited to: 5ht1a / b / c / d, 5ht2a / b / c, 5ht3, 5ht4, 5ht5, 5ht6, 5ht7, dopamine receptors (D1, D2, D3, D4, D5), adrenergic receptors (α1A, α1B, α2A, α2B, α2C, β1, β2), serotonin transporter (SERT), DA transporter (DAT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), imidazoline1 receptor (I1), Sigma receptors (σ1, σ2), delta opioid receptor (DOR), kappa opioid receptor (KOR), mu opioid receptor (MOR), muscarinic receptors (M1, M2, M3, M4, M5), histamine receptors (H1, H2), calcium ion channel (Ca+) and N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor; alone or in combination with items such as, but not limited to: cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids, minerals, psychedelic and psychoactive compounds such as, but not limited to 5ht2a receptor agonists or other compounds; for medical, recreational, religious, research and other uses.
Owner:HELDRETH JR DAVID ALAN
Method for identifying olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Method for identifying olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell
The present invention provides a novel method for identifying an olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell. In the present invention, amplified is the cDNA derived from the mRNA of the one olfactory cell by a PCR method using a forward primer represented by SEQ ID: 01 and a reverse primer represented by SEQ ID: 02. Subsequently, determined is whether or not a gene sequence of the amplified cDNA is identical to one gene sequence included in gene sequences coding for olfactory receptors included in the mouse olfactory receptor group A. Finally, determined is that, if the gene sequence of the cDNA is identical to the one gene sequence in the previous step, the olfactory receptor included in the one olfactory cell is the olfactory receptor corresponding to the one gene sequence which is identical to the gene sequence of the cDNA in the previous step.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Method for identifying olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell
The present invention provides a novel method for identifying an olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell. In the present invention, amplified is the cDNA derived from the mRNA of the one olfactory cell by a PCR method using a forward primer represented by SEQ ID: 01 and a reverse primer represented by SEQ ID: 02. Subsequently, determined is whether or not a gene sequence of the amplified cDNA corresponds with one gene sequence included in gene sequences coding for olfactory receptors included in the mouse olfactory receptor group A. Finally, determined is that the olfactory receptor included in the one olfactory cell is the olfactory receptor which corresponds to the one gene sequence which corresponds with the gene sequence of the cDNA in the previous step, if the gene sequence of the cDNA corresponds with the one gene sequence in the previous step.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for identifying olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell
The present invention provides a novel method for identifying an olfactory receptor included in one olfactory cell. In the present invention, amplified is the cDNA derived from the mRNA of the one olfactory cell by a PCR method using a forward primer represented by SEQ ID: 01 and a reverse primer represented by SEQ ID: 02. Subsequently, determined is whether or not a gene sequence of the amplified cDNA corresponds with one gene sequence included in gene sequences coding for olfactory receptors included in the mouse olfactory receptor group A. Finally, determined is that the olfactory receptor included in the one olfactory cell is the olfactory receptor which corresponds to the one gene sequence which corresponds with the gene sequence of the cDNA in the previous step, if the gene sequence of the cDNA corresponds with the one gene sequence in the previous step.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com