Compositions and methods for binding antibodies and inhibiting neutralizing antibodies
An antibody, binding site technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the moderate increase in antibody escape, insufficient resistance to polyclonal anti-AAV serum, low efficacy, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0362] Example 1: Method
[0363] AAV virus production: AAV vectors were produced in HEK293 cells by the standard method of three-plasmid transfection. Briefly, the AAV transgenic plasmid pTR CBA-Luc was co-transfected with the AAV Rep / Cap helper plasmid (pXR2 or pXR8) and the adenovirus helper plasmid pXX6-80. After 72 hours, cell cultures were harvested and lysed by freeze-thawing and sonication. Clarified cell lysates were DNase-treated and ultracentrifuged with a 15% / 25% / 40% / 60% iodixanol gradient and purified by anion exchange Q-columns. Purified AAV vectors were titrated by qPCR with primers used to amplify the packaged AAV transgene segment.
[0364] Protein production: Rajesh widely provided the plasmid pET-28b(+), which encodes protein M, a truncated M. genitalium protein MG281, lacking the transmembrane domain (amino acids 74 to 479) and carrying an N-terminal His-tag and Thrombin cleavage site. Plasmids were propagated in electrocompetent DH10B cells and purifie...
Embodiment 2
[0371] Example 2: Protein M abolishes the inhibitory activity of IVIG on AAV transduction
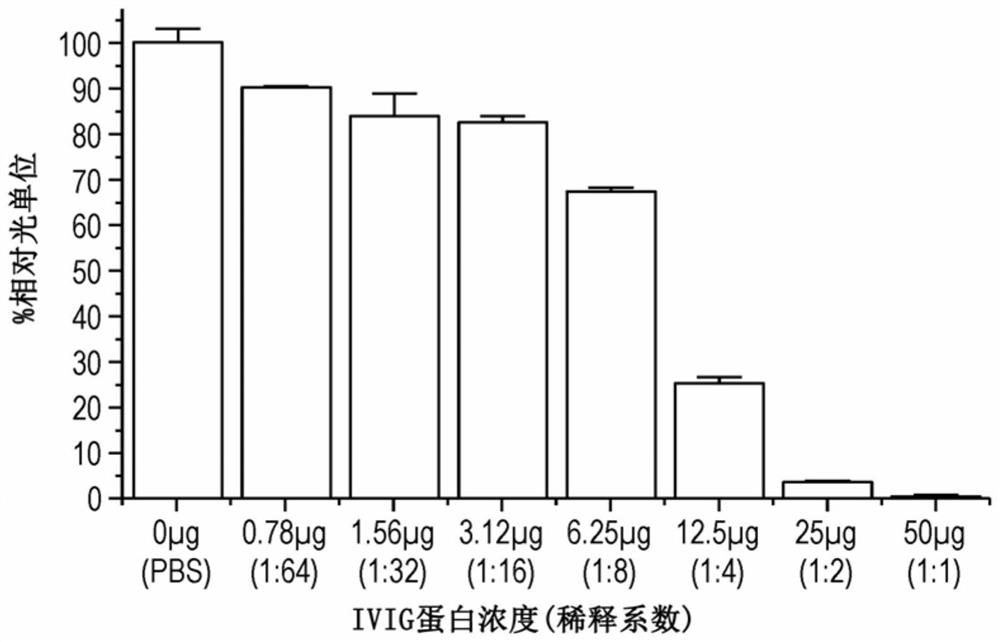
[0372] To investigate the antibody-blocking function of protein M, a human intravenous immunoglobulin gamma (IVIG) in vitro AAV neutralization assay was established. AAV neutralization assays were performed using serial dilutions of IVIG to determine the amount of IVIG that would neutralize a given amount of AAV2. Luciferase activity resulting from transduction of cells with AAV luciferase vector serves as a functional readout of gene expression. The neutralization was determined as a percentage of luciferase activity normalized to the no IVIG control. 12.5 μg of IVIG was found to neutralize 75% (+ / - 5%) of AAV2 ( figure 1 ), select this amount of IVIG for experimental design to test that protein M blocks IVIG from neutralizing AAV. Next, a dose dilution series was performed on protein M (SEQ ID NO:2), collected by thrombin cleavage to remove the His-tag, and its ability to block 12....
Embodiment 3
[0373] Example 3: Interaction of protein M with AAV vector virions enhances AAV transduction
[0374] Previous studies by the inventors have shown that the interaction of serum proteins with AAV virions enhances AAV transduction. To further characterize the enhancing function of protein M on AAV transduction, a dose-response assay was performed without the use of IVIG, in which protein M was incubated with AAV at serial 2-fold dilutions for 1 h prior to cell culture transduction. exist Figure 4 found that in the absence of IVIG, an 8:1 ratio of protein M (33 μg of protein M) in previous experiments was able to dose-dependently enhance AAV transduction, and for 2x10 8 virus particles, loss of enhancement at dilutions below 2 μg of protein M. The equivalent molar ratio of protein M molecules that lost the enhancement effect to AAV particles was lower than 40000:1. Next, it was demonstrated that the enhanced transduction of protein M was dependent on the incubation of protein...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com