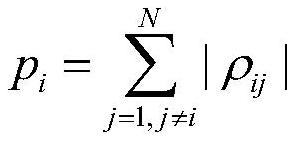Multi-level dimension reduction method for high-dimensional database
A database and multi-level technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve problems such as complex operating costs of machine learning algorithms, and achieve the effects of dynamic dimensionality reduction, overcoming dependencies, and high operating efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
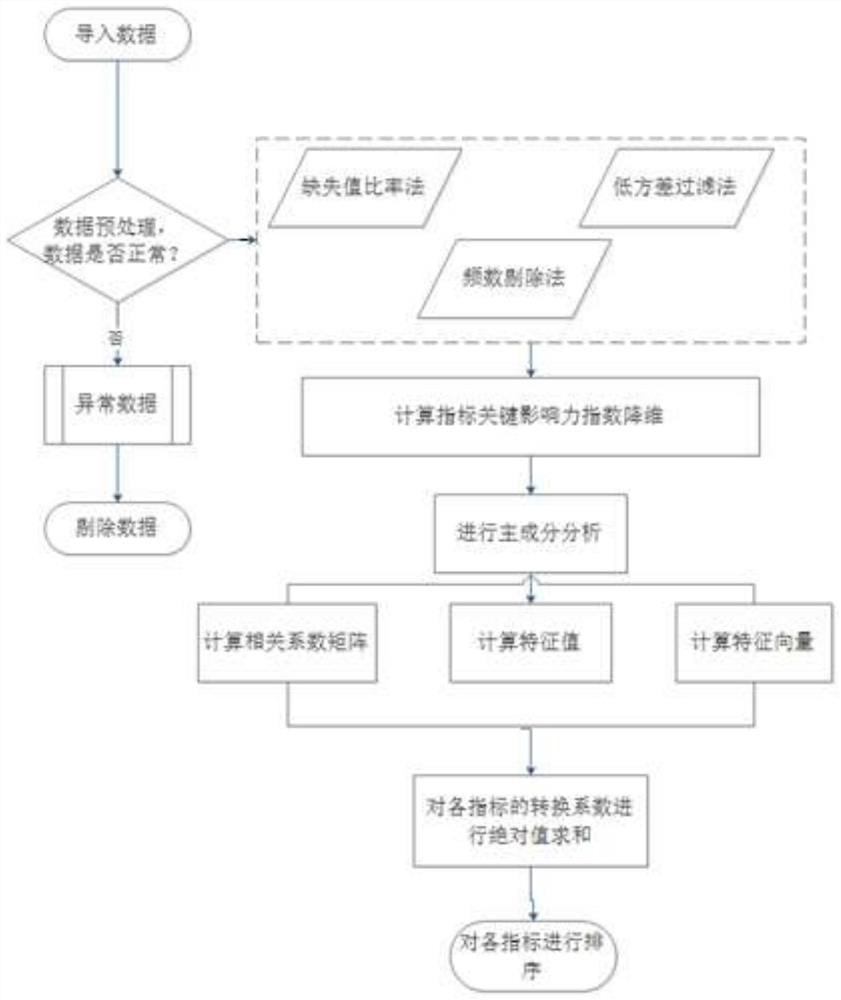
[0046] like figure 1 As shown in the figure, a multi-level dimensionality reduction method for a high-dimensional database is characterized in that, it includes the following steps:
[0047] Step 1: Obtain a sample data set containing multi-dimensional indicators, and preprocess the sample data set;
[0048] Step 2: Standardize the preprocessed sample data set to make the data of each indicator dimensionless;
[0049] Step 3: Perform the first dimension reduction on the sample data set, delete the data set containing insufficient information, reduce the calculation amount of subsequent operations, and improve the calculation speed;
[0050] Step 4: Use the key influence index sorting method to perform a second dimension reduction on the sample data set after one dimension reduction to reduce the collinearity problem in the subsequent steps;
[0051] Step 5: Perform a third dimension reduction on the sample data set after the second dimension reduction based on the improved p...
Embodiment 2
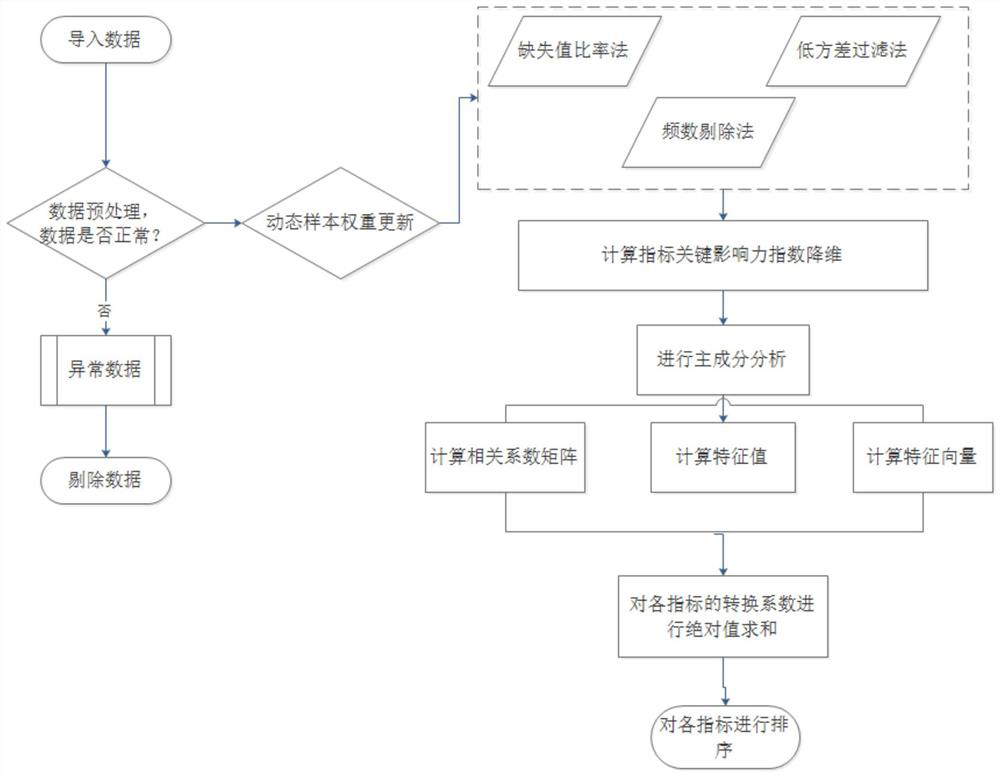
[0070] The difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that the dynamic time dimension of the indicator data set is increased.
[0071] Specifically, as figure 2 As shown, the core steps of the invention are as follows:
[0072] 1. Import the database, and preprocess the database to check whether the data indicators are abnormal (such as garbled characters). If there are abnormalities, it is necessary to eliminate abnormal data or abnormal indicators.
[0073] 2. After confirming that there is no abnormality in the data, standardize all index data to make the data dimensionless: standardize the index data by the traditional method of subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation.
[0074] 3. Sample weight update. A time penalty factor is introduced to update the sample weights at different time points.
[0075] with indicator dataset For example, the indicator dataset contains m indicators. In a time unit, n sample data are newly generated, and at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com