Gadoxetate disodium enhanced MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)-based radiomics characteristic acquisition method for predicting histological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma
A technology of hepatocellular carcinoma and disodium gadoxetate, which is applied in the fields of medical informatics, informatics, image analysis, etc., can solve problems such as lack, achieve accurate feature selection, and improve the reproducibility of functional clustering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
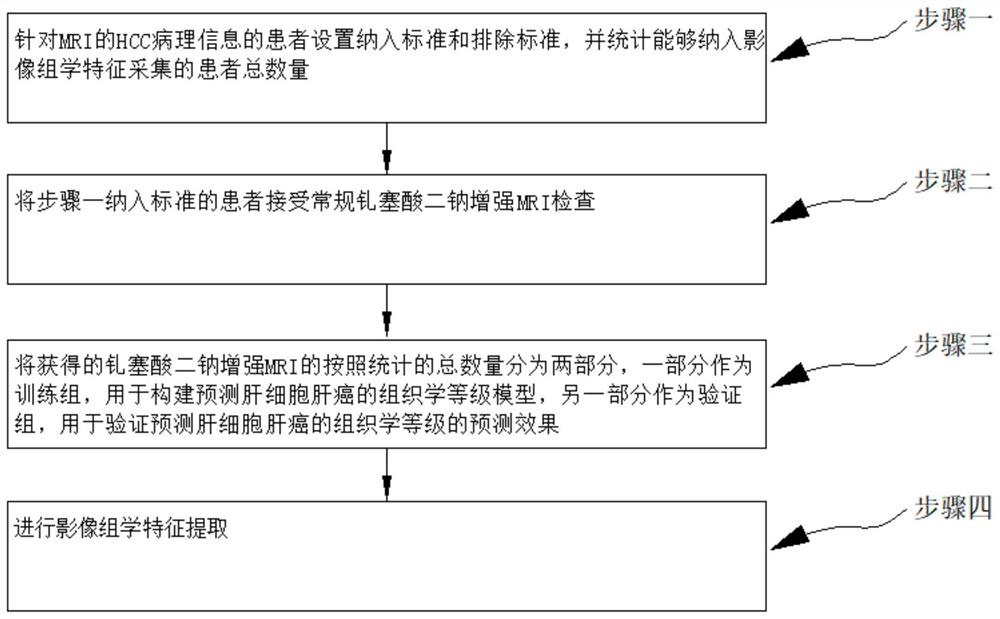
[0069] The radiomics feature acquisition method based on gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI for predicting the histological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma in this embodiment, such as figure 1 As shown, the method is realized by the following steps:
[0070] Step 1. Set inclusion and exclusion criteria for patients with HCC pathological information from MRI, and count the total number of patients who can be included in the collection of radiomics features.
[0071] The inclusion criteria are:
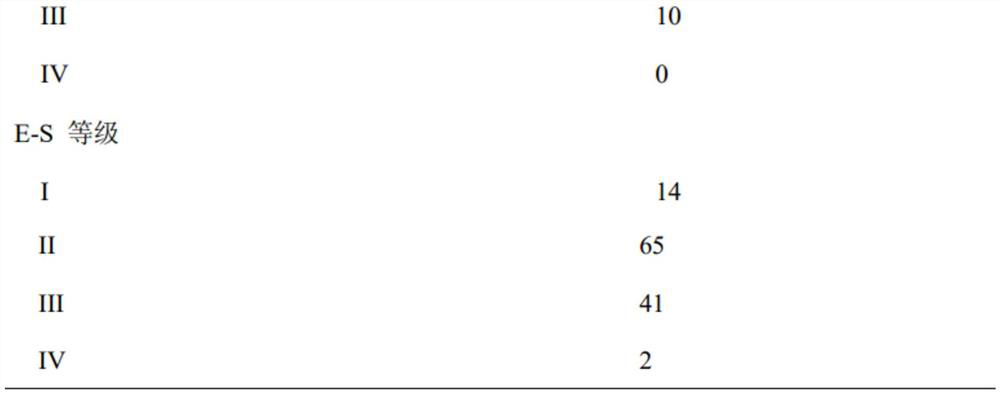
[0072] (1) Edmondson-Steiner (E-S) grade confirmed by postoperative pathology; Edmondson-Steiner grade is the commonly used pathological grade of liver cancer in the world;
[0073] (2) Have a complete gadoxetate disodium-enhanced Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI image within 3 weeks before surgery;
[0074] The exclusion criteria are:
[0075] (1) Receive any systemic or local anti-tumor therapy before surgery, such as radiofrequency or microwave ablation, TACE or molecular targeted therapy...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0088] Different from Embodiment 1, the radiomics feature acquisition method based on gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI for predicting the histological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma in this embodiment,
[0089] The pathological information described in step 1 is obtained from the electronic pathology system, and the pathological information includes: gender, age, serum AFP level (>10ng / mL or ≤10ng / mL), serum carcinoembryonicantigen (CEA) level (>5ng / mL or ≤5ng / mL), serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (carbohydrateantigen19-9, CA19-9) level (>39U / mL or ≤39U / mL), ALT (U / L), AST (U / L) ), TNM stage, E-S grade.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0090] Different from the second embodiment, the gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI-based radiomics feature acquisition method for predicting the histological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma in this embodiment,
[0091] The process of performing radiomic feature extraction described in step 4 is as follows:
[0092] Step 41. Obtain the MRI imaging features of gadoxetate disodium-enhanced;
[0093] Acquire Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI images of gadoxetate disodium. Arterial phase (stage 2) and hepatobiliary images of all HCC patients with 2.5 mm slice thickness were obtained from the Image Archiving and Communication System (PACS) in accordance with the Digital Imaging and Imaging and Comminications in Medicine (DICOM) protocol.
[0094]ROIs were manually delineated layer by layer along the tumor margin on the arterial and hepatobiliary MRI images, respectively, including necrotic or cystic areas within the tumor, avoiding the surrounding liver parenchyma, blood vessels, and adjac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com