Photoresist removal process and semiconductor manufacturing process
A photoresist and process technology, used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as substrate damage, and achieve the effect of improving manufacturing efficiency and product yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0031] like figure 1 As shown, the photoresist removal process provided by this embodiment includes:
[0032] Step S1: peel off the photoresist 2 on the substrate 1 and obtain the substrate 1 with the residual photoresist attached;
[0033] Step S2: Put the substrate 1 with the residual photoresist attached into the chamber, and adjust the ambient temperature in the chamber to be greater than or equal to the preset temperature, and then continue to introduce an inert gas into the chamber, while every first The hydrogen-containing gas is passed into the chamber for a long time to remove the residual photoresist 2 on the substrate 1 .
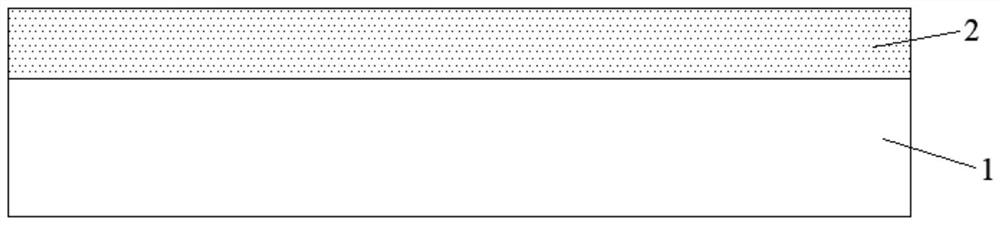
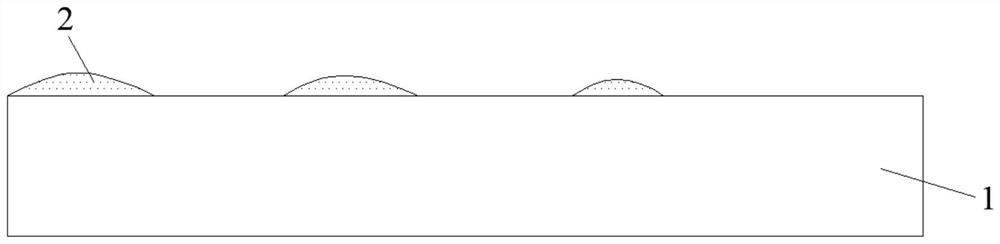
[0034] In the photoresist removal process provided in this embodiment, step S1 is first performed to peel off the photoresist 2 on the substrate 1 of the semiconductor. After step S1, as follows figure 2 and image 3 As shown, most of the photoresist 2 on the substrate 1 is peeled off, but there is still residual photoresist 2 . Wherein, in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com