Wave-division multiplexing passive optical fiber network system
A technology of passive optical fiber network and wavelength division multiplexing, which is applied in the field of passive optical fiber network system of wavelength division multiplexing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
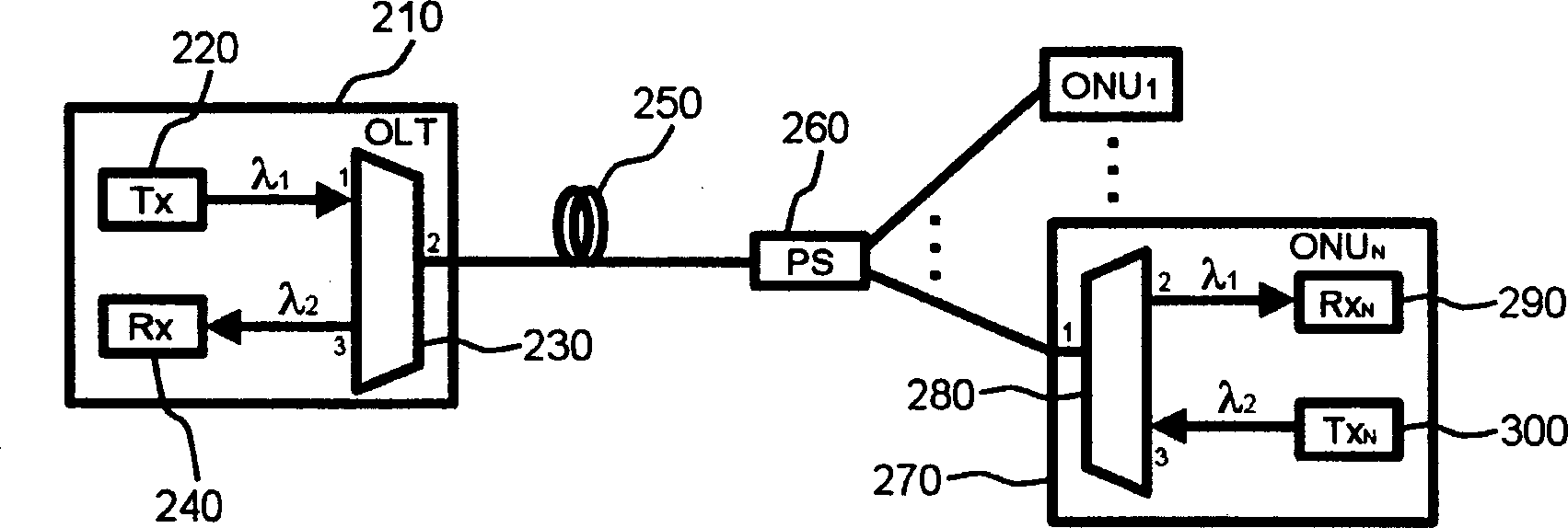
[0033] Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings. In the drawings, well-known functions, elements, devices or structures are not described in detail since they would obscure the invention in unnecessary detail.
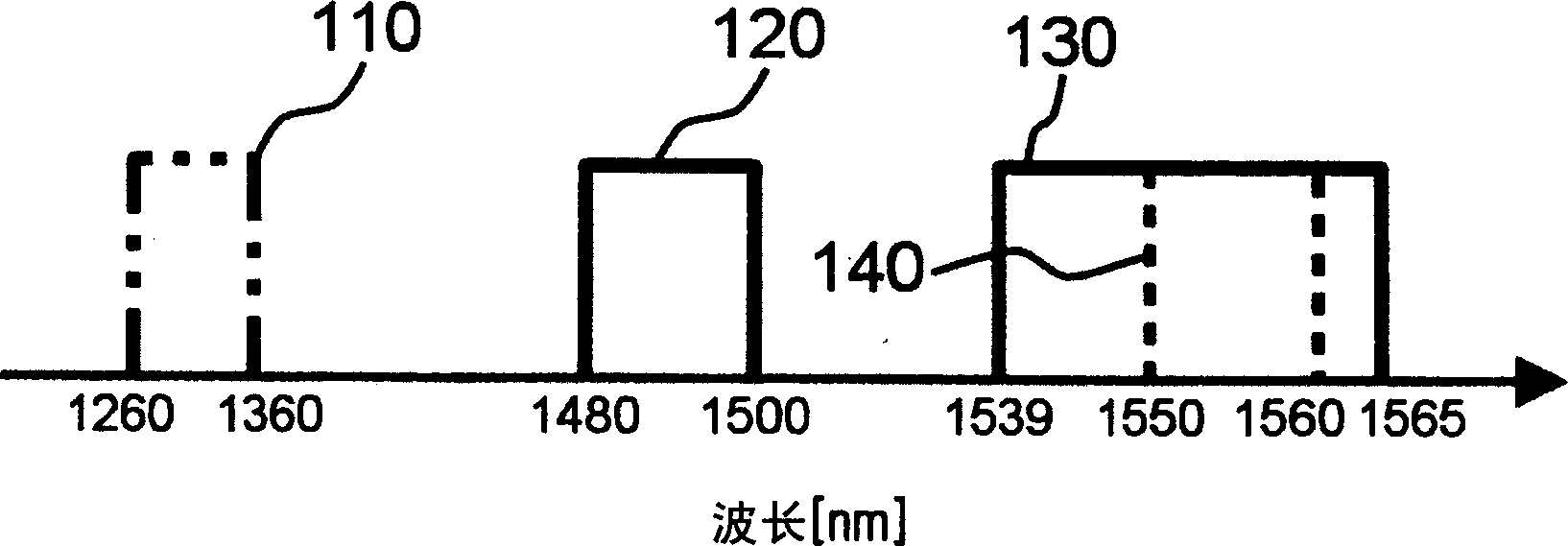
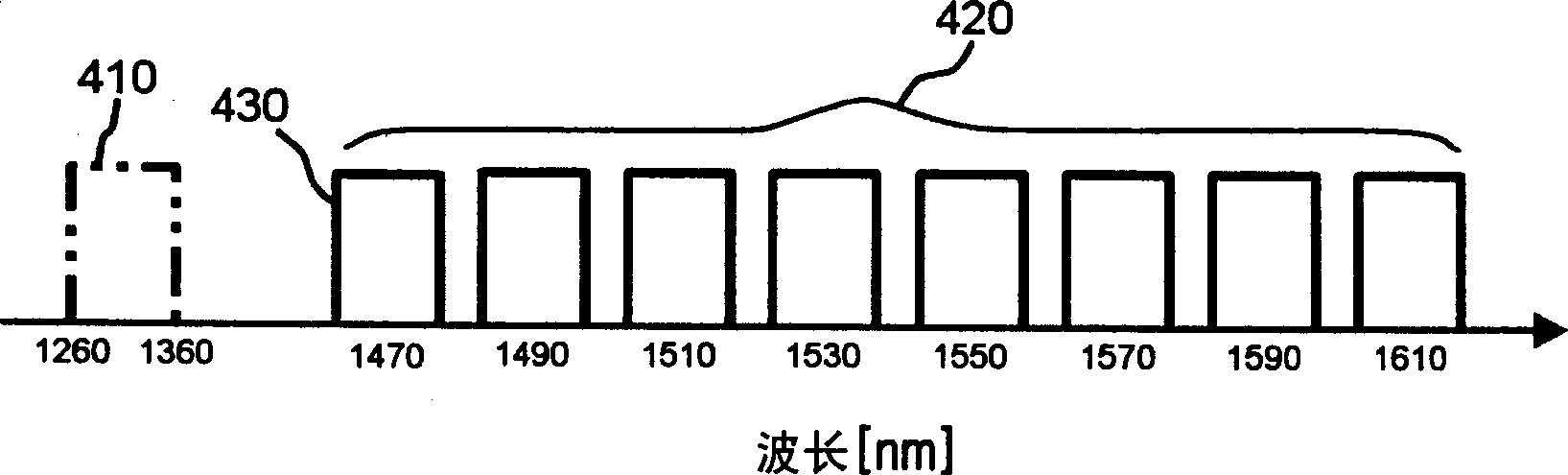
[0034] image 3 is a graph showing the wavelength allocation of a passive optical network system according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention. image 3 An upstream wavelength band 410 is depicted, and a downstream wavelength band of 1550 nm (or 1490 nm) with an additional bidirectional wavelength band 420 is depicted.
[0035] The wavelength allocated to the upstream wavelength band 410 falls within the range of 1260-1360 nm, and it is used as the wavelength band used by optical signals going from the fiber optic network elements to the fiber optic transmission terminals.
[0036] A wavelength band in the range of 1470-1610 nm is allocated to an additional bidirectional waveleng...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com