Camera lens
A camera lens and lens technology, which is applied in the field of camera lenses, can solve problems such as poor compensation of dispersion and chromatic aberration, short optical system, and full-length constraints, so as to improve resolution and image quality, and improve resolution and image quality , the effect of compensating dispersion and distortion chromatic aberration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
[0071] Below, refer to Figure 2 to Figure 13 Examples of the present invention will be described.
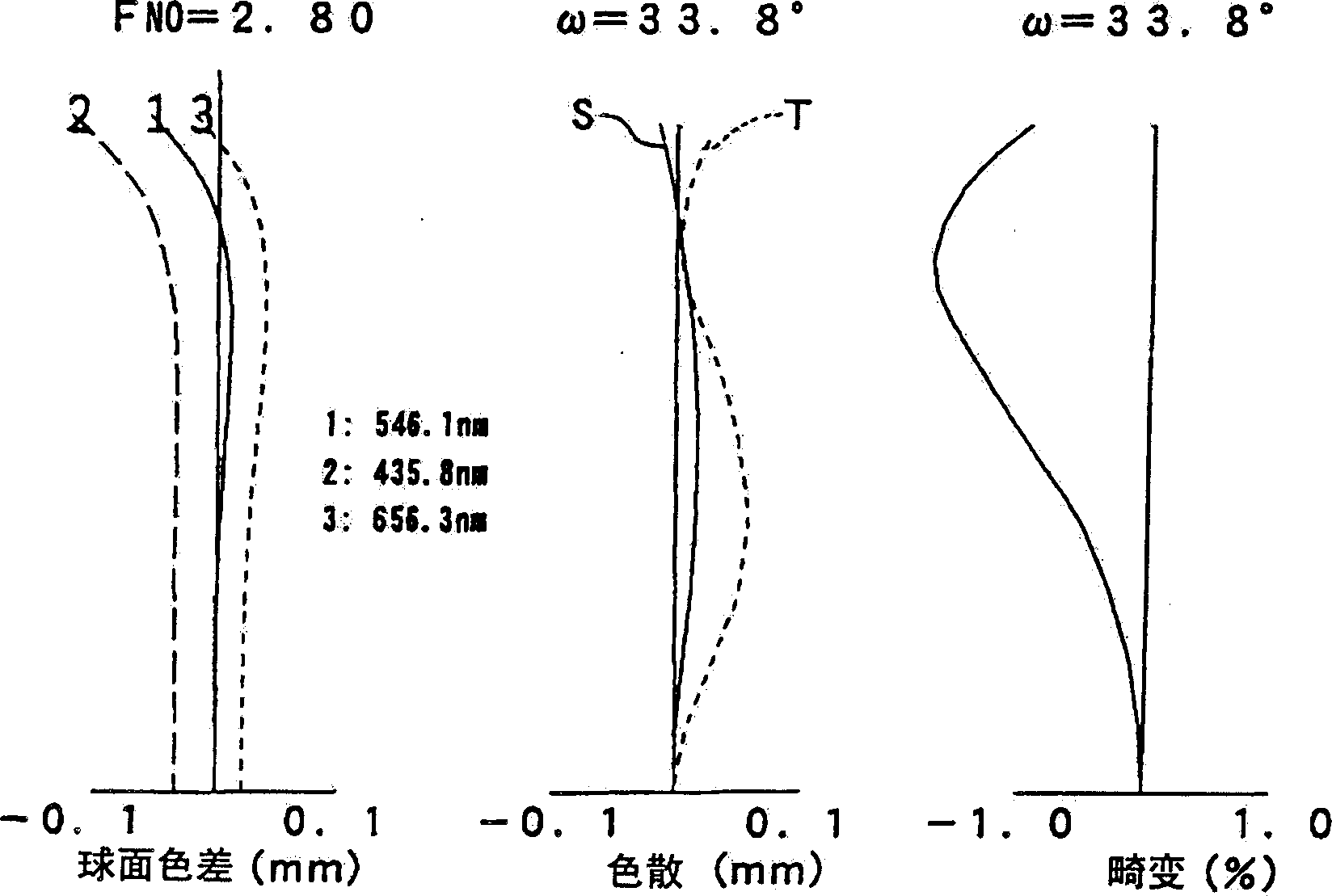
[0072] Here, in this embodiment, f is the focal length of the entire lens, and f 1 is the focal length of the first lens 3, f 2 is the focal length of the second lens 4, and FNO represents the F number. In addition, ω is the half angle of view, its double 2ω is the full angle of view (diagonal angle of view), r is the radius of curvature of the optical system (in the case of a lens, it is the central radius of curvature), and d is the radius of curvature of the optical system. Thickness or air gap, ne is the refractive index of each optical system when irradiated with e-line (green), and νd is the Abbe number of each optical system when irradiated with d-line (yellow).
[0073] k, A, B, and C represent coefficients in the following formula (7). That is, the aspheric shape of the lens is the Z axis in the direction of the optical axis, the Y axis is the direction perpendicul...
no. 1 Embodiment
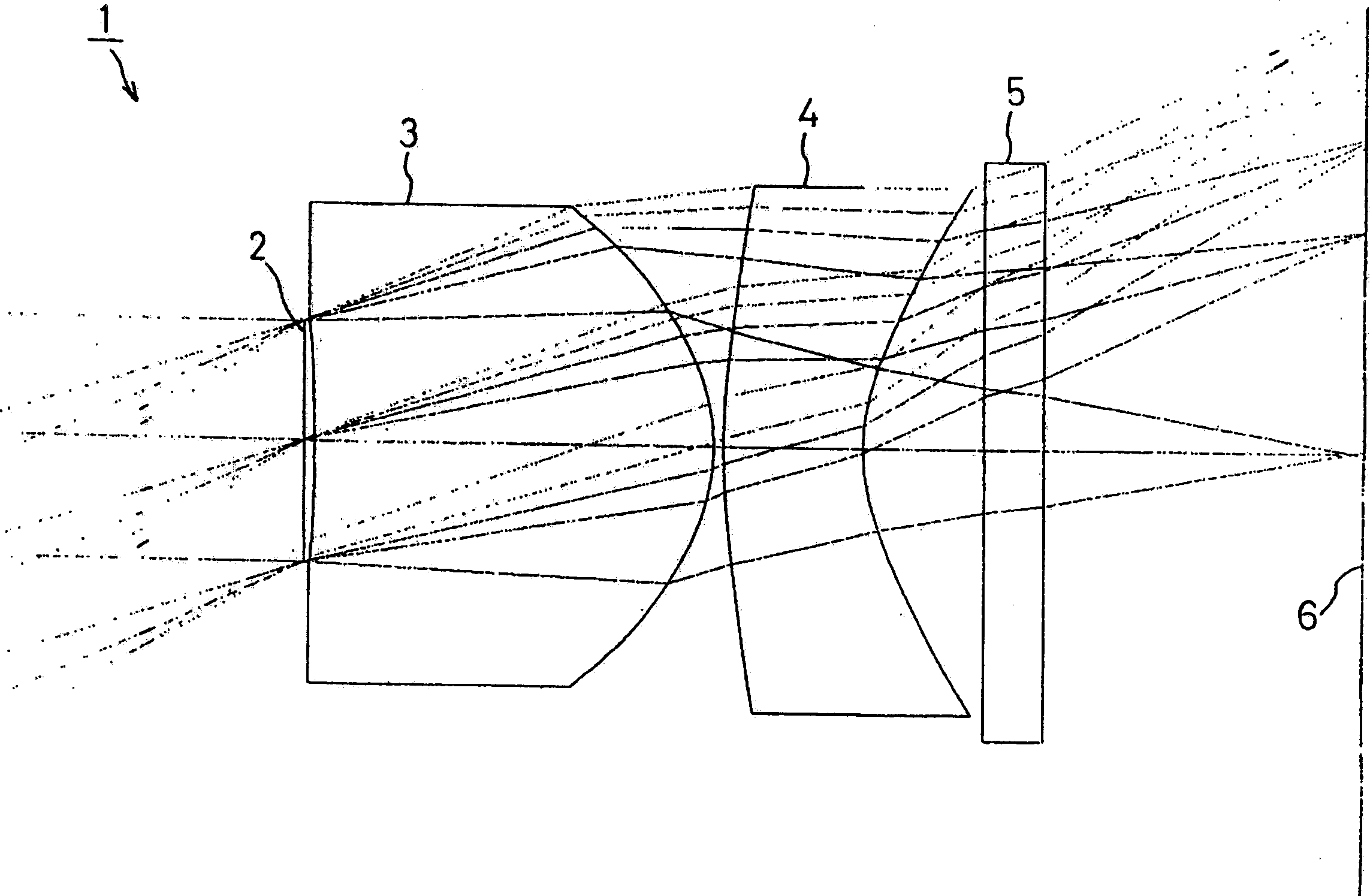
[0077] figure 2 Shown is the first embodiment of the present invention, in this embodiment, with figure 1 The imaging lens 1 with the structure shown is similarly provided with a diaphragm 2 on the object side of the first lens 3 and a cover glass 5 on the imaging surface 6 side of the second lens 4 .
[0078] The following conditions are set for the imaging lens 1 of the first embodiment.
[0079] f=3.40mm, FNO=2.8, 2ω=67.5°, f 1 =1.81mm, f 2 =-2.48mm
[0080] Surface Radius of curvature r Distance between surfaces d Refractive index ne Abbe number νd
[0081] (object point) ∞
[0082] (stop) 0.05
[0083] 1 (1st lens surface 1) -14.728 2.00 1.52692 56.2
[0084] 2 (1st lens 2nd surface) -0.936 0.05
[0085] 3 (2nd lens 1st surface) 3.417 0.70 1.58961 30.0
[0086] 4 (second lens surface 2) 0.945 0.60
[0087] 5 (1st side of cover glass) 0 0.30 1.51825 64.2
[0088] 6 (2nd side of cover glass) 0 1.575
[0089] (imaging surface)
[0090] Face k A B C
[0091] 1 ...
no. 2 Embodiment
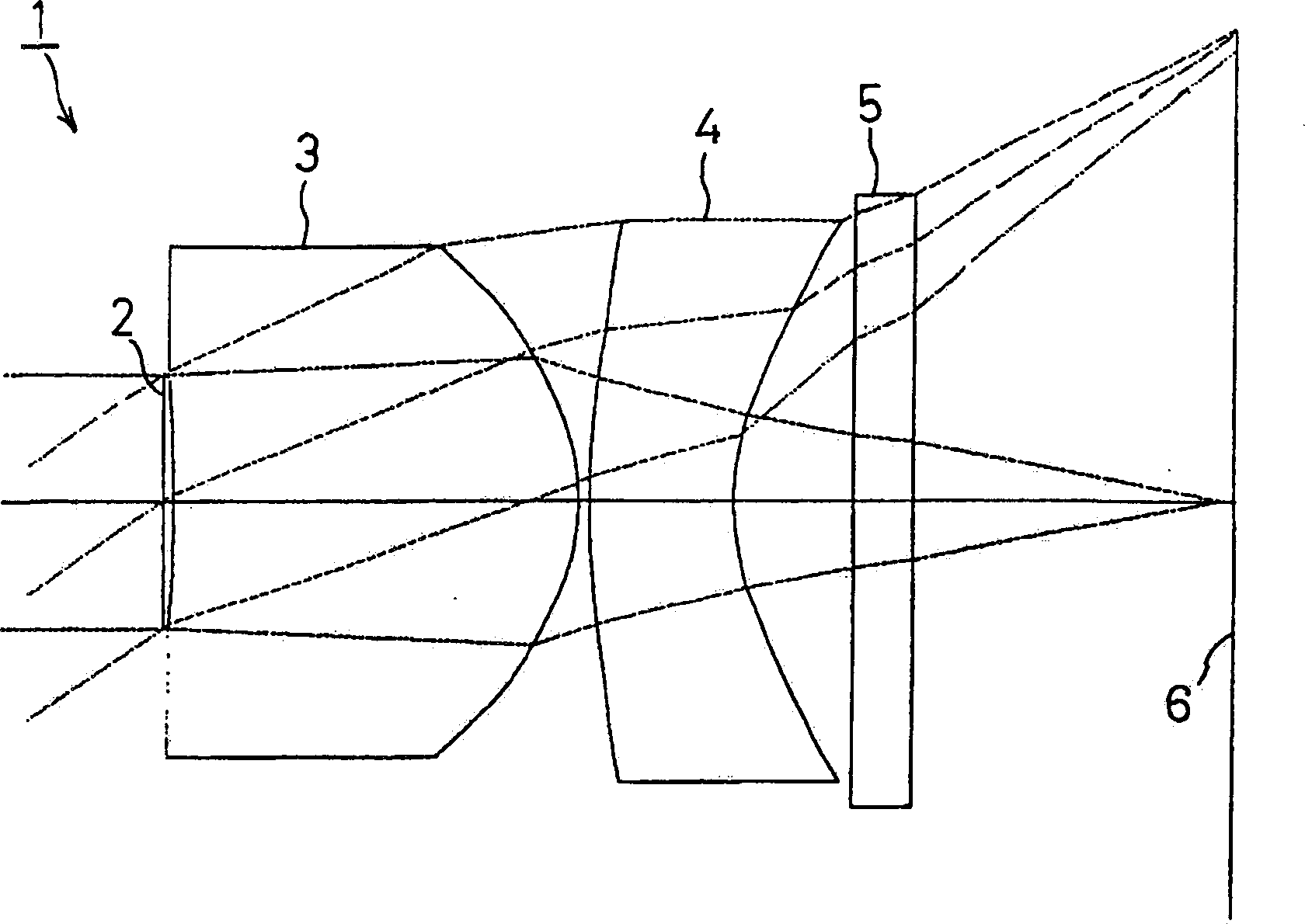
[0101] Figure 5 Shown is the second embodiment of the present invention, in this embodiment, with figure 1The imaging lens 1 with the structure shown is similarly provided with a diaphragm 2 on the object side of the first lens 3 and a cover glass 5 on the imaging surface 6 side of the second lens 4 .
[0102] The following conditions are set for the imaging lens 1 in the second embodiment.
[0103] f=3.40mm, FNO=2.8, 2ω=66.2°, f 1 =1.84mm, f 2 =-2.46mm
[0104] Surface Radius of curvature r Distance between surfaces d Color refractive index ne Abbe number νd
[0105] (object point) ∞
[0106] (stop) 0.05
[0107] 1 (1st lens surface 1) -25.266 2.00 1.49405 57.0
[0108] 2 (1st lens 2nd surface) -0.899 0.05
[0109] 3 (2nd lens 1st surface) 3.105 0.70 1.58961 30.0
[0110] 4 (second lens surface 2) 0.905 0.60
[0111] 5 (1st side of cover glass) 0 0.30 1.51825 64.2
[0112] 6 (2nd side of cover glass) 0 1.499
[0113] (imaging surface)
[0114] Face k A B C
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com