Radio resource management method in cellular telephone networks
A technology of radio resources and management methods, applied in the field of radio resource management, can solve problems such as incompletely orthogonal coding sequences and CDMA channels being easily affected by adjacent channels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] In the following description, it is considered that the basic unit of a communication network for constructing a communication network is a cell, which is usually modeled with a hexagon, but a cell of any shape is also possible. For the purposes of this invention, the primary question is the location of the BTS within the hexagon, two situations arise:
[0029] 1. BTS is in the center of the hexagon;
[0030] 2. BTS is on the edge.
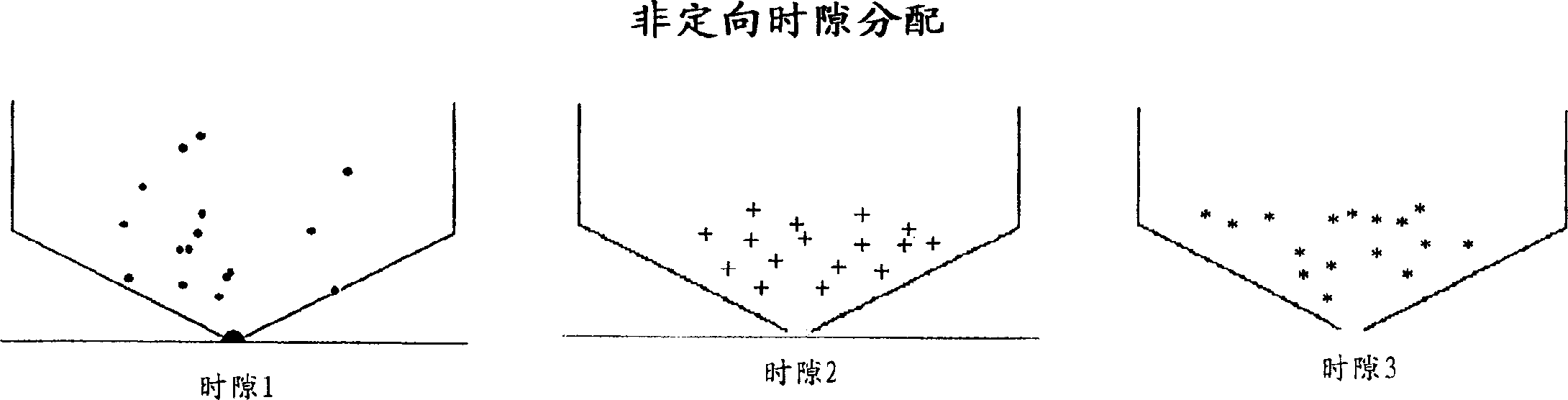
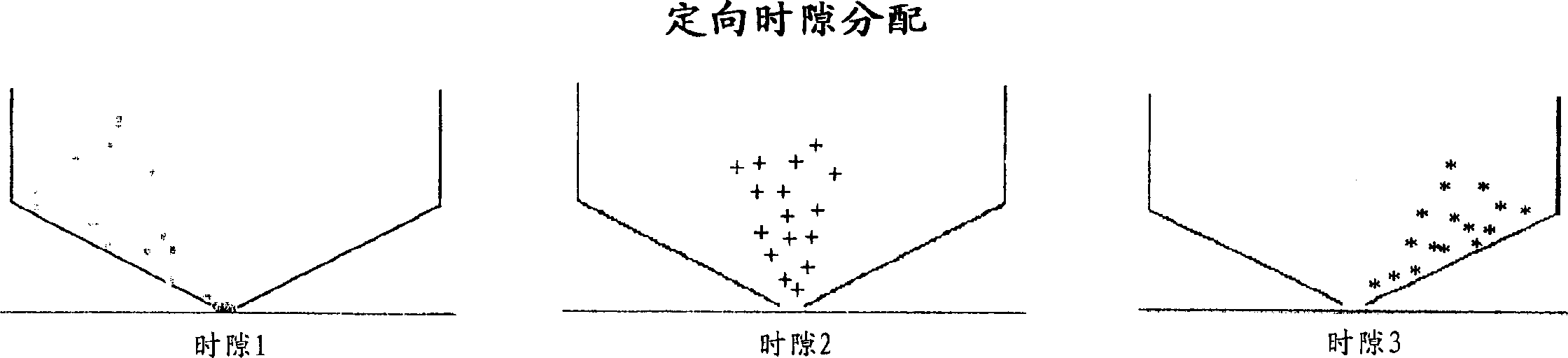
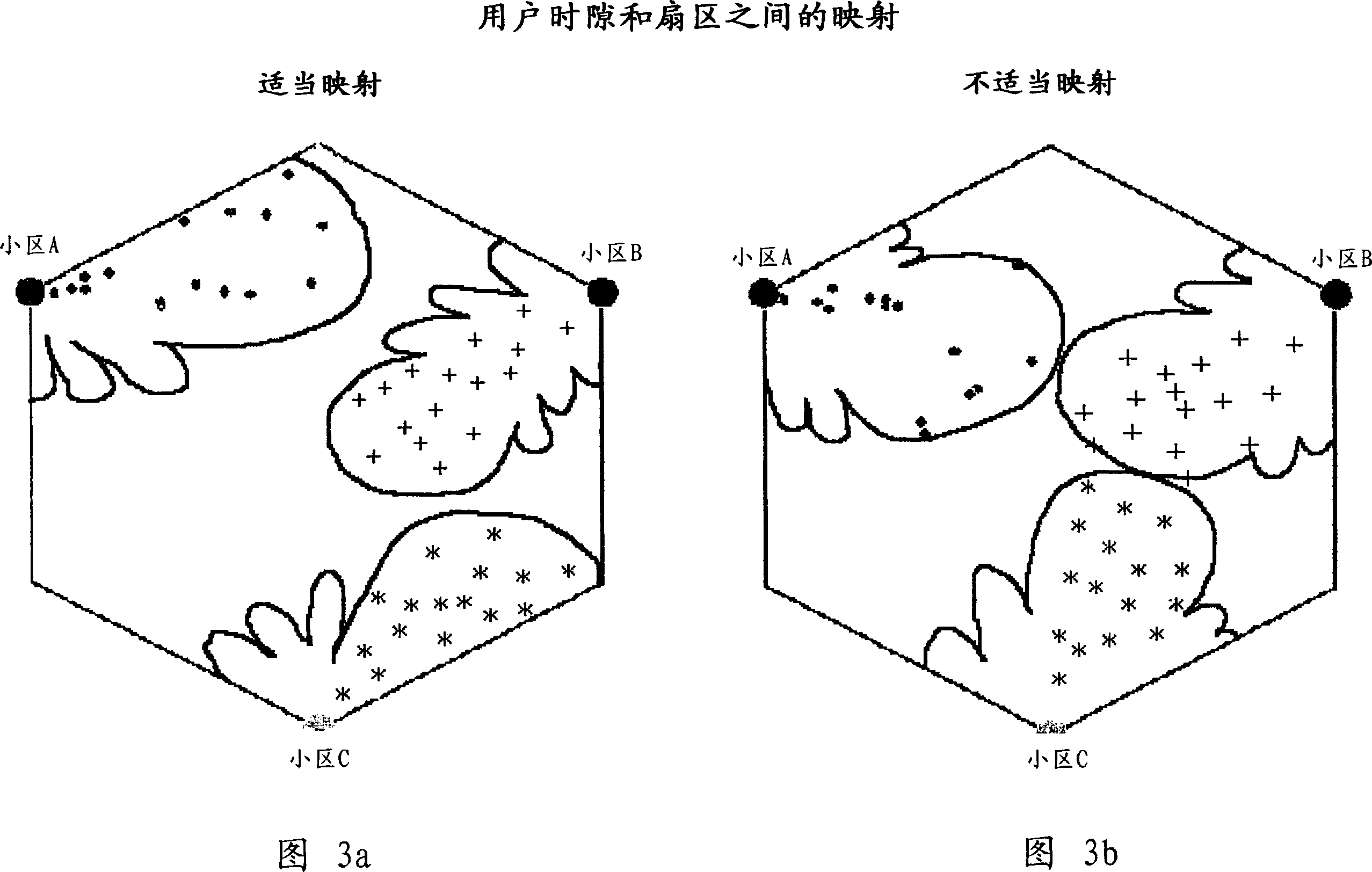
[0031] 8a to 8e, the first step in the direction of the present invention is to subdivide the hexagon into K areas, where K is the number of BTSs included therein, and one BTS corresponds to one cell. That is, K is the number of cells supported by each hexagon. For K≠1, the shape of the cells differs from that of a hexagon. The number K depends on the business problem and, therefore, on the trade-off between cost (number of BTSs) and capacity. The second step consists in subdividing each cell into N sectors with a common apex at the BTS...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com