Protective device
A technology for protecting components and substrates, applied in electrical components, emergency protection devices, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as thinning of difficult-to-protect components, discrete thickness of protective components, and inability to guarantee the thickness of protective components, so as to achieve the effect of ensuring dimensional stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
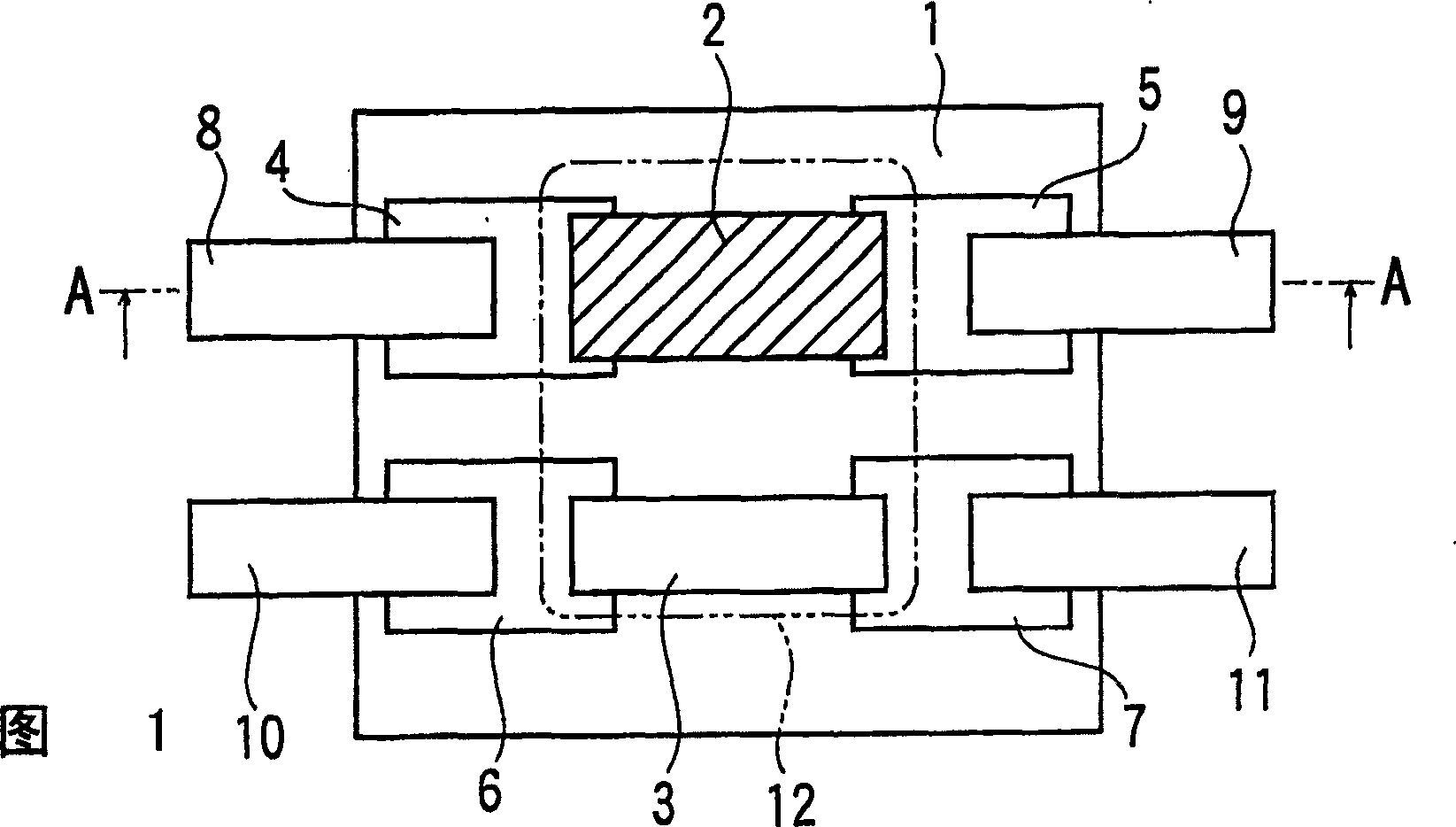
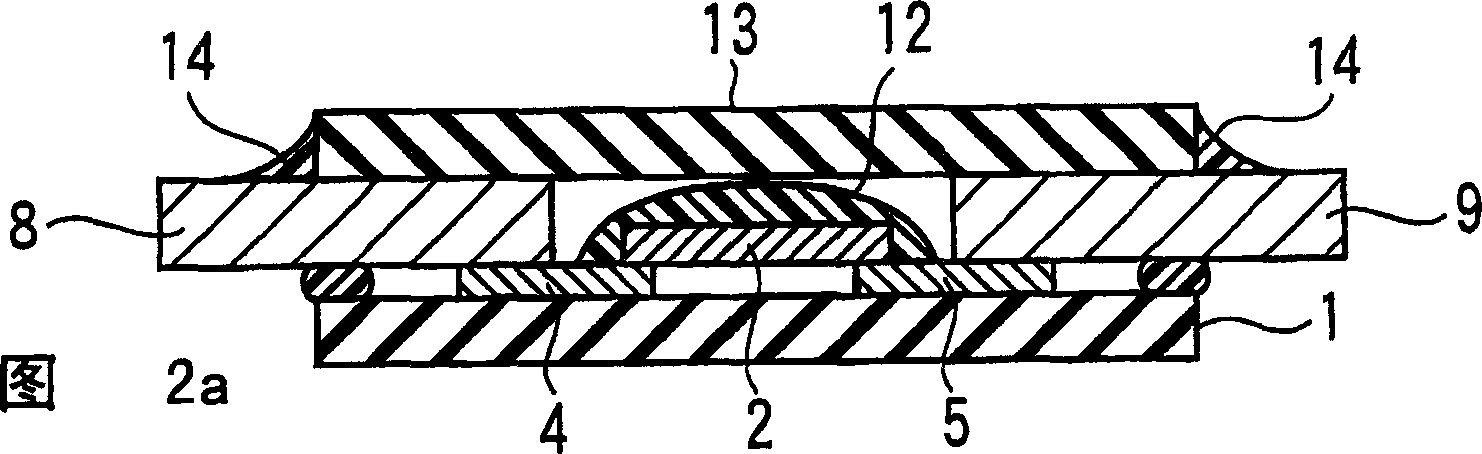
[0054] This example is in Image 6 Shown is an example of application of a self-fusing type protective element. Such as Image 6 As shown, the structure of the manufactured protection element is that a pair of electrodes 22, 23 are arranged on the base substrate 21, these electrodes are connected by a low-melting point metal body 24, and at the same time, wires 25, 26 are connected to the electrodes 22, 23 made.
[0055] Specifically, a ceramic substrate having a size of 6 mm×6 mm and a thickness of 0.5 mm was used as the base substrate 21 , and the electrodes 22 and 23 were formed on the base substrate 21 . Electrodes made of Ag—Pd were formed by printing as the respective electrodes 22 and 23 .
[0056] Furthermore, a low-melting-point metal body (width 1 mm, thickness 0.1 mm) was welded and connected between these electrodes 22 and 23, and it sealed with rosin-based flux (not shown). In addition, on the electrodes 22 and 23 , Ni-plated Cu wires (1 mm in width and 0.5 mm i...
Embodiment 2
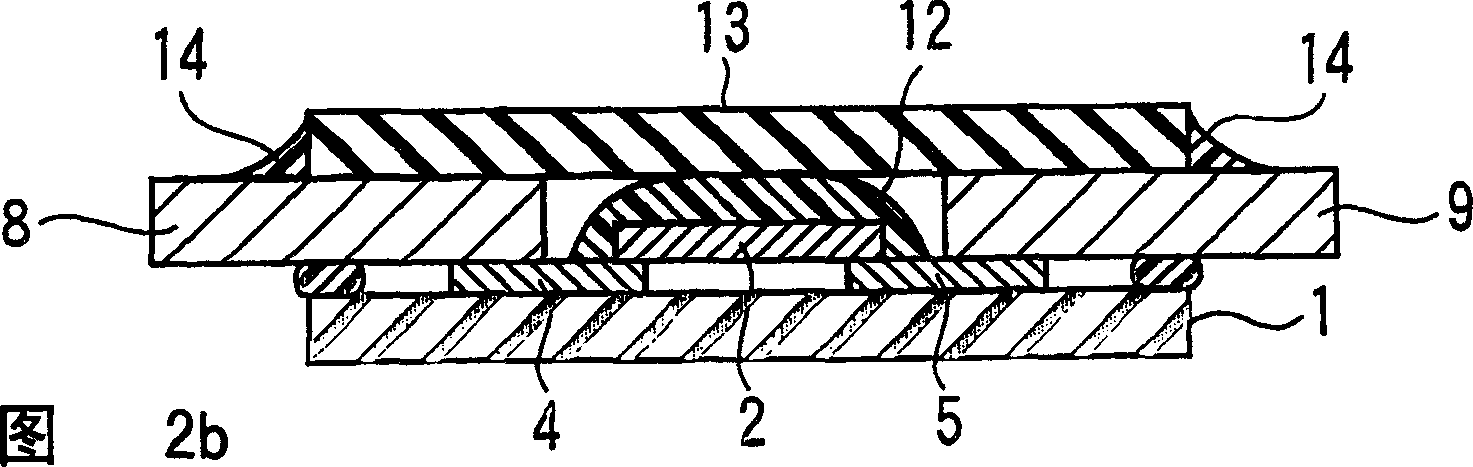
[0059] The structure of the basic protection element is the same as that of the previous embodiment. In this example, when the two-component epoxy resin is curing, a weight is placed on the insulating cover to suppress flow during curing.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com