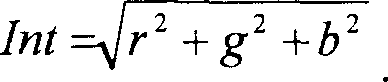Novel subtilases
A technology of subtilase and subtilisin, which is applied in the directions of hydrolase, detergent compounding agent, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate results and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0395] Construction of Savinase variant library
[0396] Libraries based on subtilase positions V28, I35, T71, I72, A73, M175 and T224 (BPN' numbering) have been synthesized. The library specifically contains the changes suggested by TY145 and covers the mutations introduced in the oligopeptides V28I, A, L; I35V, A, L; T71S; I72A, G, v; A73L, G; M175V, A; T224S, A, where Some mutations for doping. The nucleotide base doping required for doping from individual amino acid residues used in the following examples can be calculated as described on page 18 herein.
[0397] In the accompanying sequence listing, the following doped nucleotides are given the nucleotide designations recommended by WIPO standard ST25.
[0398] The list of constructed oligopeptide primers is as follows. Primers are named by where the modification occurs, so 28-35-CN could have changes at positions 28 and 35, 71-72-73-NC could have changes at positions 71, 72 and 73, etc.
[0399] 28-35-CN, SEQ ID NO: ...
Embodiment 2
[0435] Transfer of a region from TY145 to BPN' subtilase
[0436] It has been chosen to transfer the hyperactive regions in TY145 mentioned below from TY145 to Savinase. The TY145 region (SEQ ID NO: 1) was inserted after deletion of the Savinase region (BPN' numbering) instead. Alternatively, regions can be selected for transfer between psychrophilic TA41 / TA39 and BPN'-type protease-like Savinases, or from TA39 / TA41 to TY145-type non-psychrophilic subtilases.
[0437] Fragment I
[0438] TY145 SAKDSLIASAVD, position 144-155 (SEQ ID NO: 22)
[0439] Savinase PSPSATLEQAVN, position 129-140 (SEQ ID NO: 23)
[0440] Fragment II
[0441] TY145 AGNSGSGSNTIGFPGGLV, position 168-185 (SEQ ID NO: 24)
[0442] Savinase SGNSGAGSISYPARYA, position 153-172 (SEQ ID NO: 25)
[0443] Fragment IV
[0444] TY145 ASVESTWYTGGYNTIS, position 233-248 (SEQ ID NO: 26)
[0445] Savinase VNVQSTYPGSTYASLN, position 203-218 (SEQ ID NO: 27)
[0446] Savinase modified to receive TY145 fragment II (...
Embodiment 3
[0448] Transfer of regions from S39 and S41 to BPN' subtilases
[0449] The high activity regions in the TA39 subtilase S39 and TA41 subtilase S41 mentioned below have been selected for transfer to Savinase, the high activity regions of which were identified by the homology building procedure described above. Delete the Savinase region (BPN' number) and insert the S39 region or S41 region instead. Hereinafter the areas S39 and S41 are numbered according to FIG. 1 . Alternatively selectable regions can be transferred between the psychrophilic TA41 / TA39 and TA145 non-psychrophilic subtilases. Savinase variant V194S was used as acceptor for S39 fragment II.
[0450] Fragment I
[0451] S39 MSLGSSG, position 137-143 (SEQ ID NO: 28)
[0452] Savinase2 LSLGSPS, position 124-130 (SEQ ID NO: 29)
[0453] Fragment II
[0454] S39 MSLGSSGESSLI, position 137-148 (SEQ ID NO: 30)
[0455] Savinase variant V104S LSLGSPSPSATL, position 124-135 (SEQ ID NO: 31)
[0456] Fragment III
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com