Preparation method of visible rhinopharyngocele cancer model
A technology for nasopharyngeal carcinoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma, applied in the field of medical models, can solve problems such as difficulty in detecting early primary microtumors, and achieve the effect of improving sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] 1. Preparation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma model by orthotopic inoculation of EGFP transfected CNE2 nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in nude mice.
[0039] The first step: prepare EGFP transfection nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
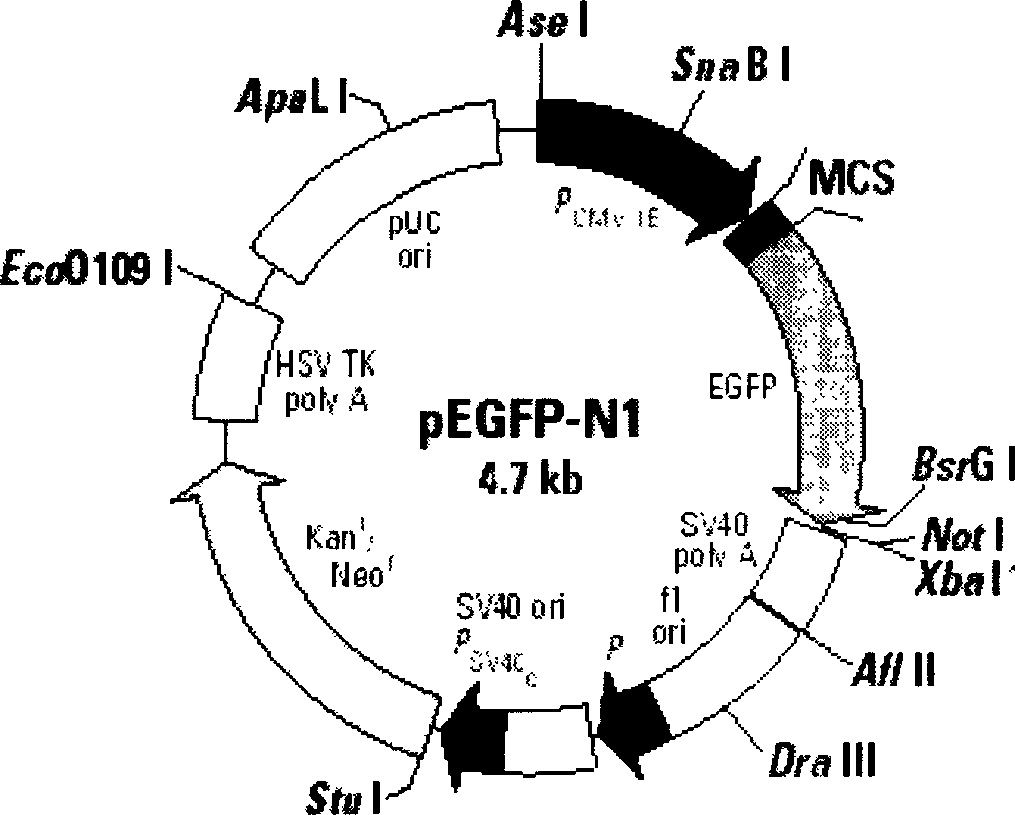
[0040] 24 hours before transfection, the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE2 was divided into 2 × 10 5 Inoculate in 24-well plates, culture in 1640 medium containing 15% calf serum and no antibiotics, discard the medium when the cells grow to about 80% confluence, wash the cells twice with 1640 medium without serum, and then Add 1ml of serum-free 1640 to continue culturing, and perform cell transfection when the cells grow to a confluence of about 90%. Prepare solutions A, B in microcentrifuge tubes. Solution A: 50 μl OPTI-MEM+5 μllipofectamine2000; Solution B: 50 μl OPTI-MEM+3 μg plasmid pEGFP-N1. Mix A and B liquids and place at room temperature for half an hour, then evenly drop the mixture on the surface of the transfected cells, mix...
Embodiment 2
[0049] 1. Preparation of EGFP-transfected 6-10B nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell model orthotopic inoculation in nude mice.
[0050] The first step: prepare EGFP transfection nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.
[0051] The transfection method was the same as that in Example 1, and 6-10B cells were transfected with EGFP by cationic liposome method. 6-10B nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells stably transfected with EGFP gene were obtained which were independent of G418.
[0052] The second step: transfection and inoculation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in the nasopharynx of nude mice to establish a nasopharyngeal carcinoma model in situ.
[0053] The method of transfecting 6-10B nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells with EGFP and inoculating them in mice was the same as that in Example 1. EGFP-transfected 6-10B nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells were inoculated into 25 nude mice.
[0054] 2. Observation results of nasopharyngeal carcinoma model.
[0055] Carefully observe the diet and activit...
Embodiment 3
[0059] 1. EGFP transfection of 5-8F nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells orthotopic inoculation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma models in nude mice.
[0060] Step 1: Preparation of EGFP-transfected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
[0061] The transfection method is the same as that in Example 1, and 5-8F cells are transfected with EGFP by cationic liposome method. Obtain 5-8F nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells that are not dependent on G418 and stably transfected with EGFP gene.
[0062] The second step: transfection and inoculation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in the nasopharynx of nude mice to establish a nasopharyngeal carcinoma model in situ.
[0063] The method of transfecting 5-8F nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells with EGFP and inoculating them in mice is the same as that in Example 1. EGFP-transfected 5-8F nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells were orthotopically inoculated into 23 nude mice.
[0064] 2. Observation results of nasopharyngeal carcinoma model.
[0065] Carefully observe ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com