Suppression of undesirable signal propagation mode(s) downstream of a mode converter
A mode converter and propagation mode technology, applied in the field of optical transmission, can solve problems such as difficult production of optical fibers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The invention relates to suppression of unwanted guided modes downstream of a mode converter.
[0028] For this purpose, an optical device for transforming the propagation mode of an optical signal is proposed, which device may for example be embedded in (or constitute) a dispersion compensation module embedded in an optical fiber transmission line.
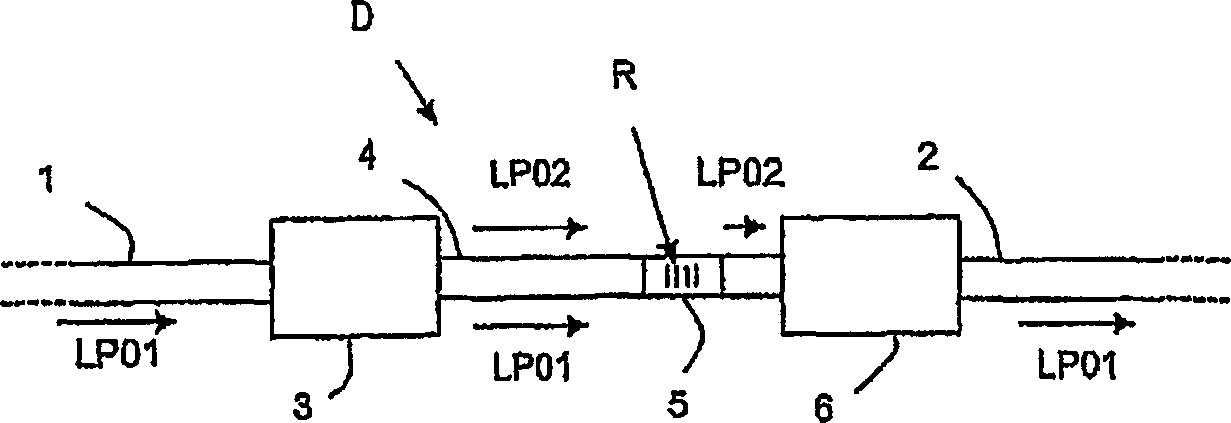
[0029] figure 1 The illustrated transmission line comprises an upstream optical fiber 1 connected to a downstream optical fiber 2 by means of a transmission device D according to the invention.
[0030] Similar to the downstream fiber 2, the upstream fiber 1 is for example a single mode fiber (SMF) in which a signal in a first guided mode, for example a fundamental LP01 mode, is propagated.
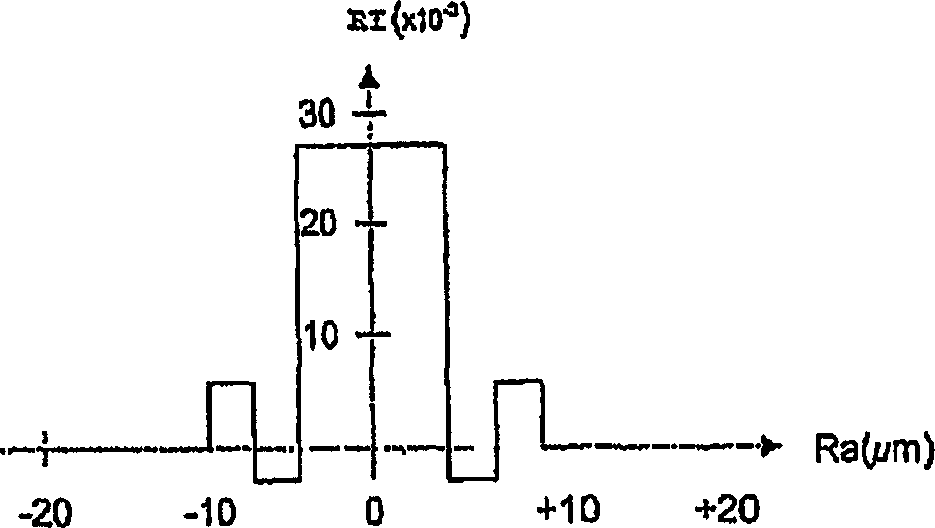
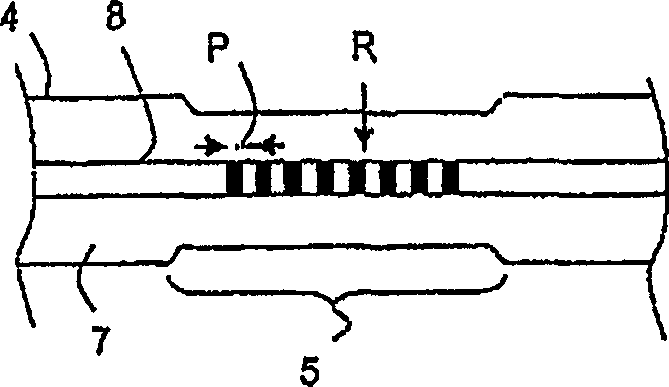
[0031] The illustrated conversion device D comprises a first mode converter 3 coupled to a multimode or multimode optical fiber (or also a HOM optical fiber) 4, wherein the optical fiber 4 is provided with a passive mode filter 5 and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com