Method for driving display
A driving method and display technology, applied in static indicators, instruments, semiconductor lamps, etc., can solve problems such as uneven brightness, critical voltage shift of thin film transistors, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] The "electroluminescence display and its driving method" of the present invention is described in detail with the drawings, and the preferred
[0043] Embodiment description is as follows:
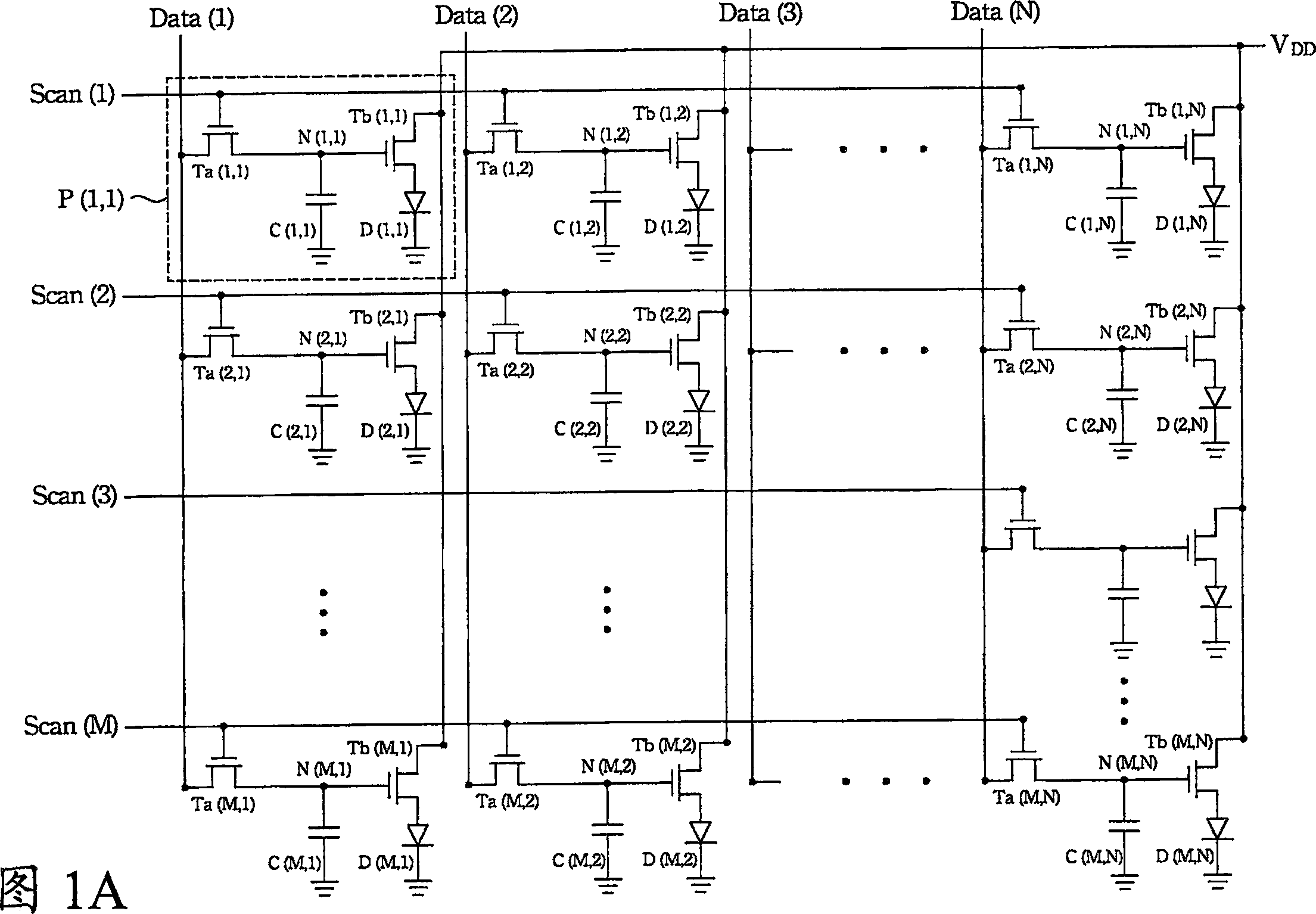
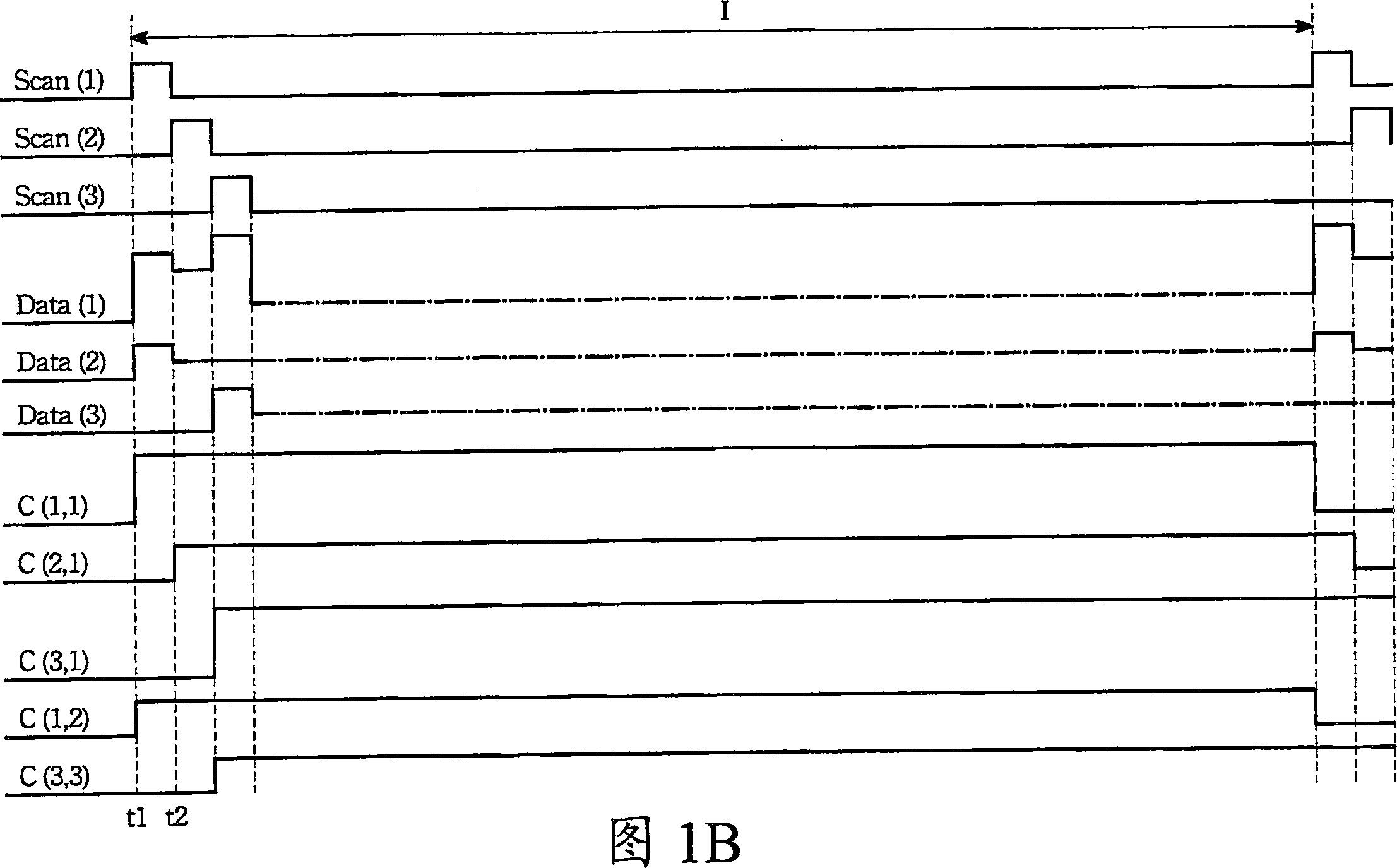
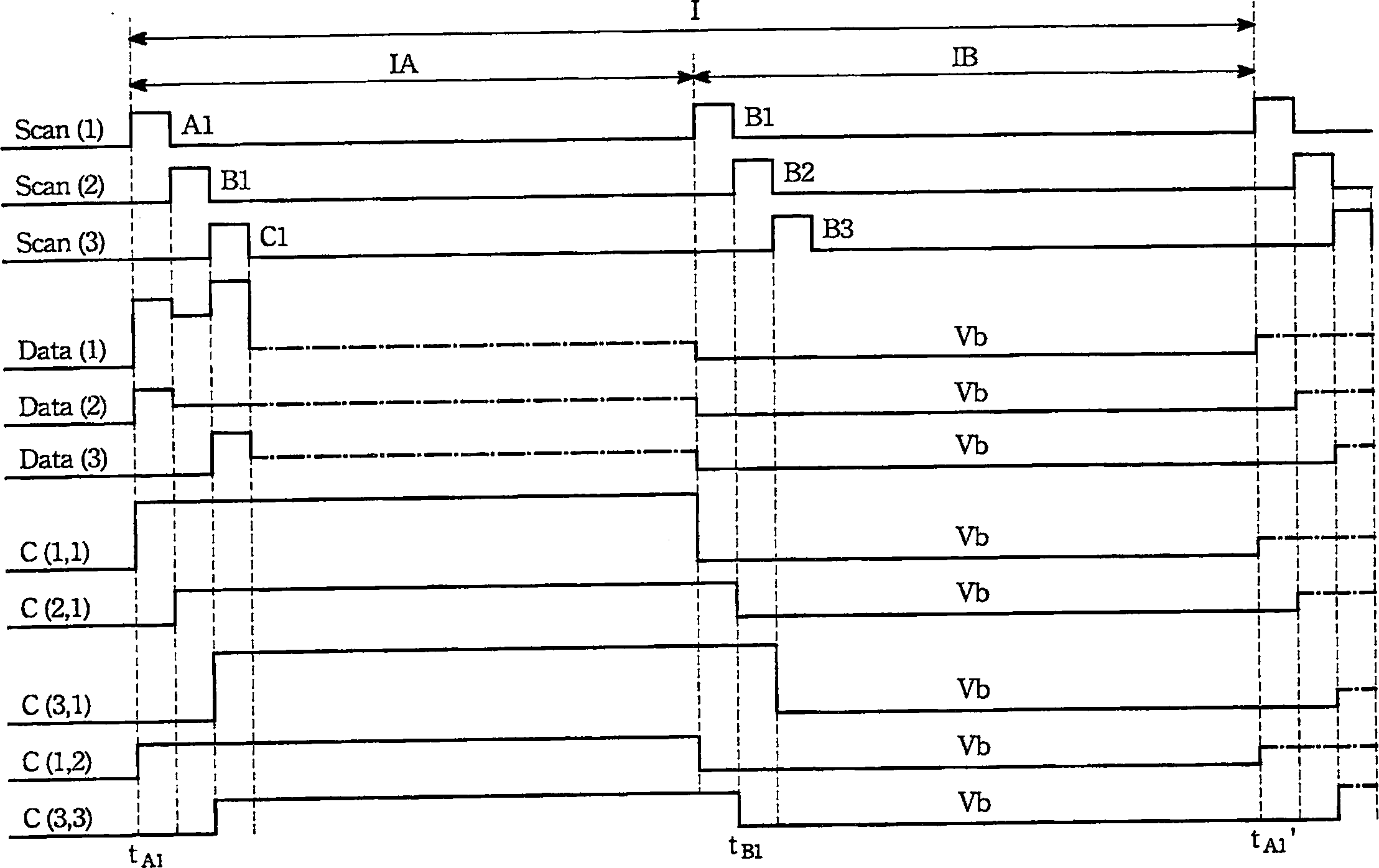
[0044] In the electroluminescence display of the present invention, the circuit diagram of the OLED pixel array and its pixel structure are shown in FIGS. 2A-2B . The electroluminescent display has M scanning lines Scan, N data lines Data and a pixel array of M columns and N rows. The pixel array has M×N pixels for displaying a frame in a display period. Each pixel P has a switching transistor Ta, a driving transistor Tb, a light emitting unit D and a capacitor C. As shown in FIG. The source S and the gate G of the switch transistor Ta are respectively connected to a data line Data and a scan line Scan. The drain and source S of the driving transistor Tb are respectively electrically connected to a display voltage source V DD And the light emitting unit D, the gate G of which is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com