Active matrix display devices
An active matrix, display device technology, applied in static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of not prolonging the life of the display
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052] It should be understood that the drawings described above are schematic and not shown to scale. For clarity and convenience of the drawings, relative sizes and proportions of parts of the above-mentioned drawings have been exaggerated or reduced.
[0053] A pixel circuit that has been proposed by the applicant (but not published before the filing date of this application) will be described first. In the pixel circuit described above, a constant gate voltage is used during the specified frame period and the time period during which the display element emits light (at constant brightness) taking into account aging effects caused by both the LED material and the drive transistor, and the desired brightness output. drive the drive transistor.
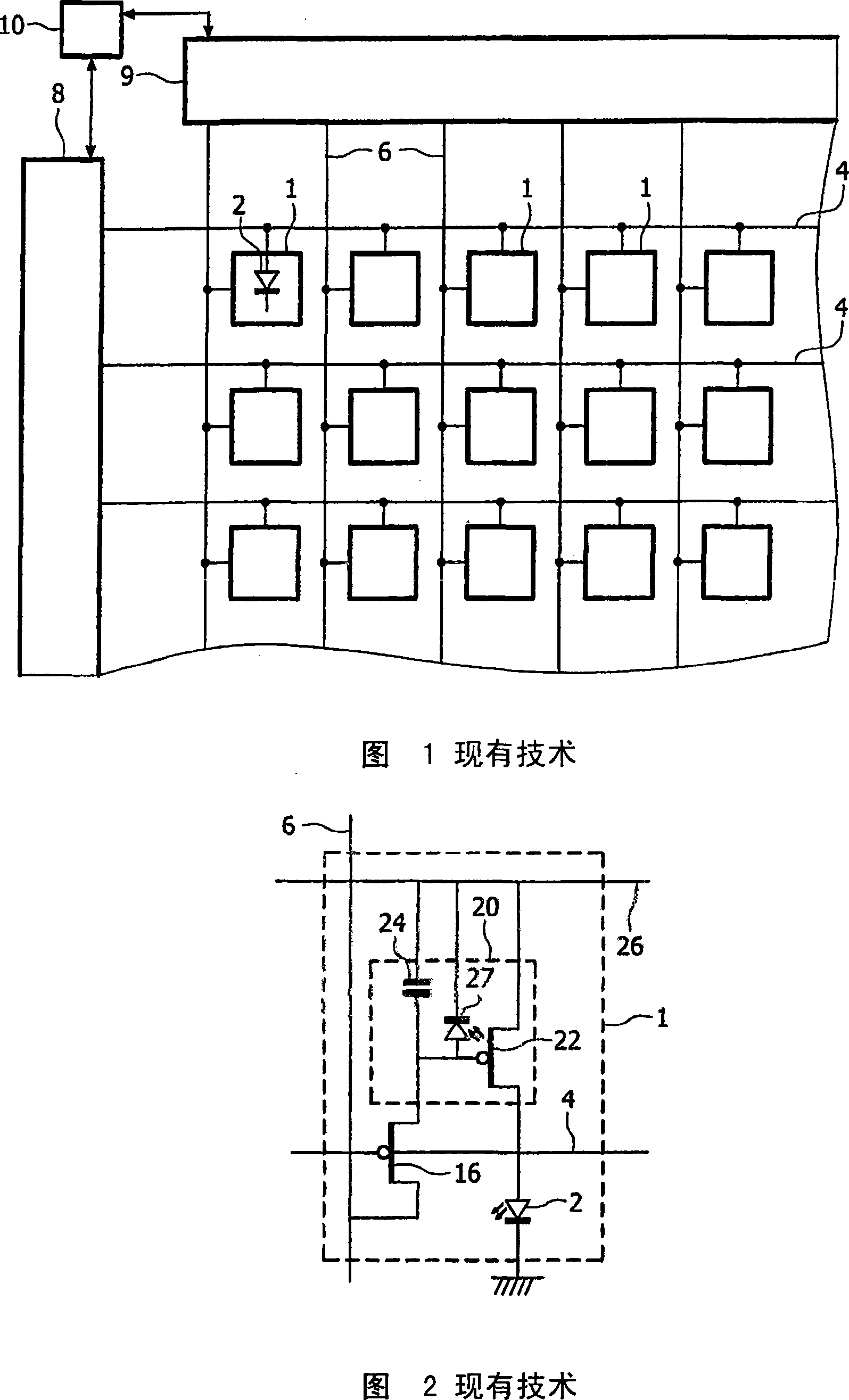
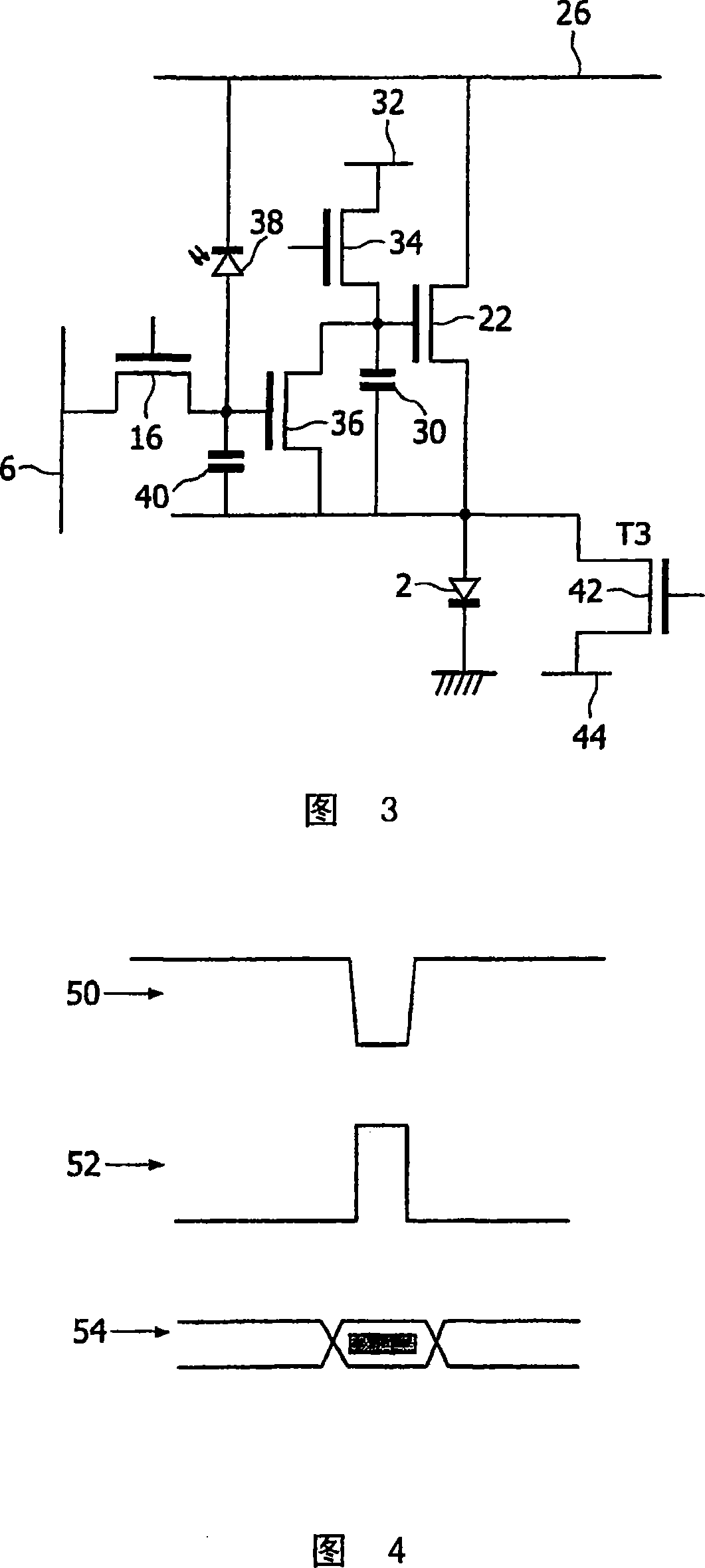
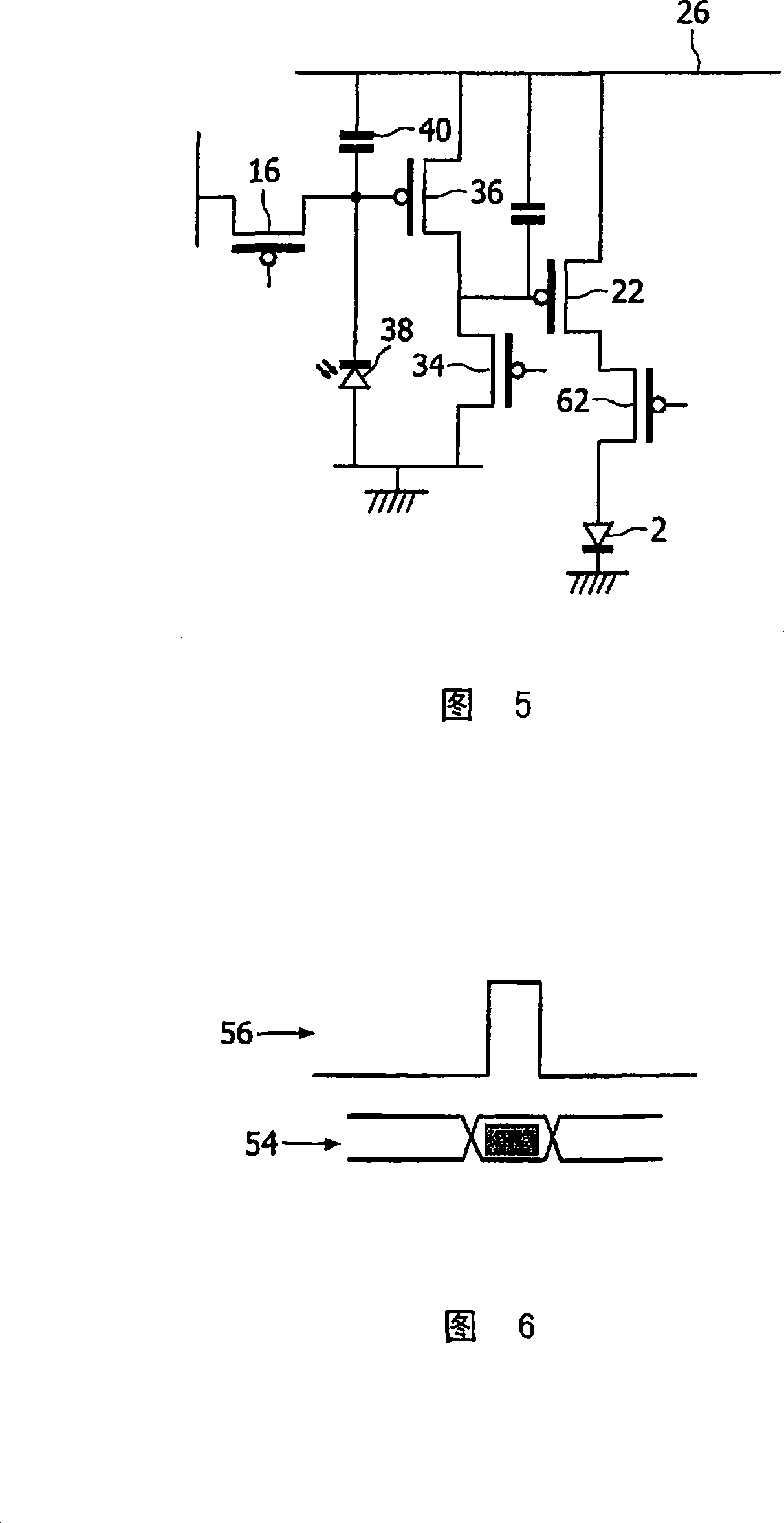
[0054] Figure 3 shows an example of the proposed pixel structure. Pixel circuits are used in displays such as that shown in FIG. 1 . The circuit of Figure 3 is suitable for implementation using amorphous silicon n-type transistors...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com