Superconducting cable line
A technology of superconducting cables and lines, applied in superconducting devices, circuits, superconducting/high-conducting conductors, etc., which can solve problems such as differences and large heat
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
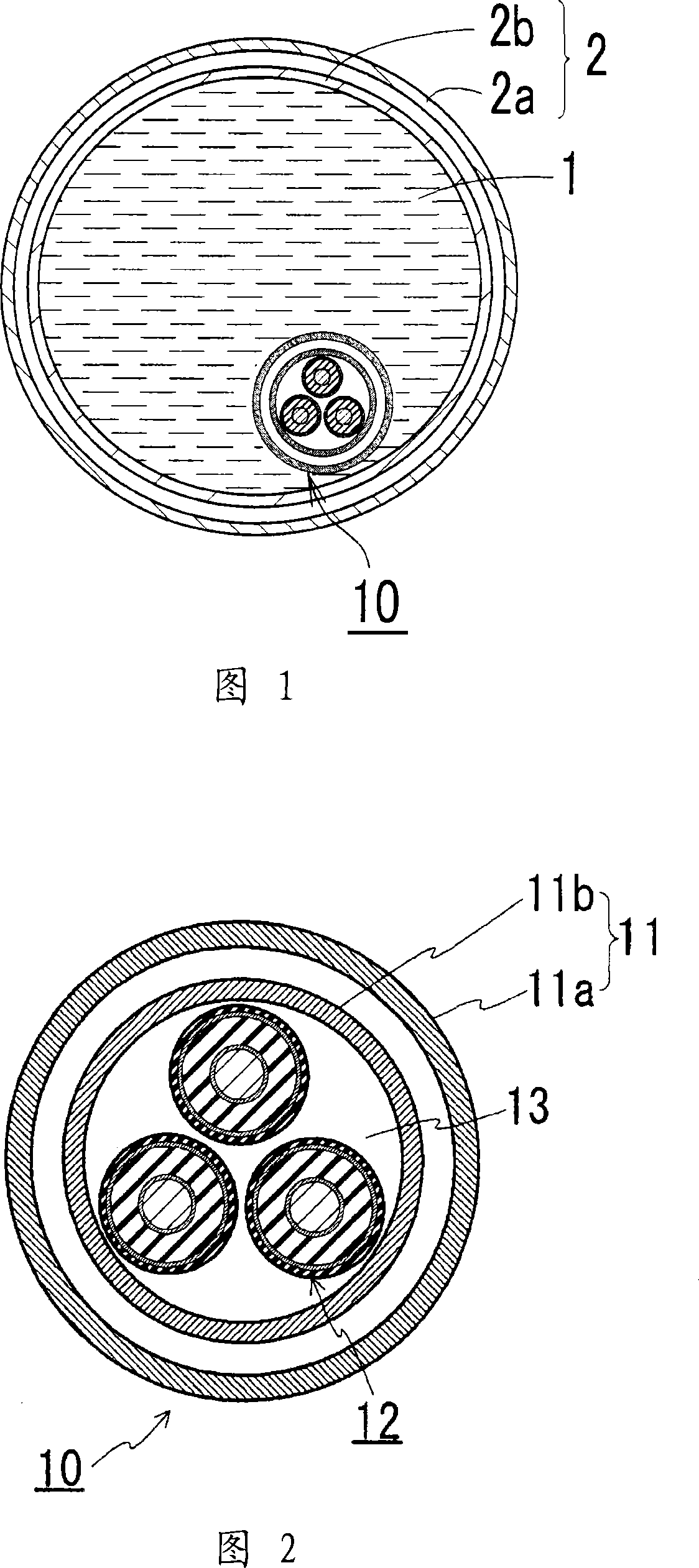
[0051] Fig. 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view of the structure of a superconducting cable line of the present invention. Fig. 2 is a schematic cross-sectional view of the structure of a portion near the superconducting cable in the superconducting cable of the present invention. Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of a structure in which the conductive cabling of the present invention is constructed. The same characters in the drawings indicate the same parts. The superconducting cable of the present invention includes a heat insulating pipe 2 for fluid used to transport liquid hydrogen 1, a superconducting cable 10 housed in the heat insulating pipe 2 for fluid, and a cable for regulating the temperature of liquid hydrogen 1 The temperature of the coolant in the heat exchange device 30.
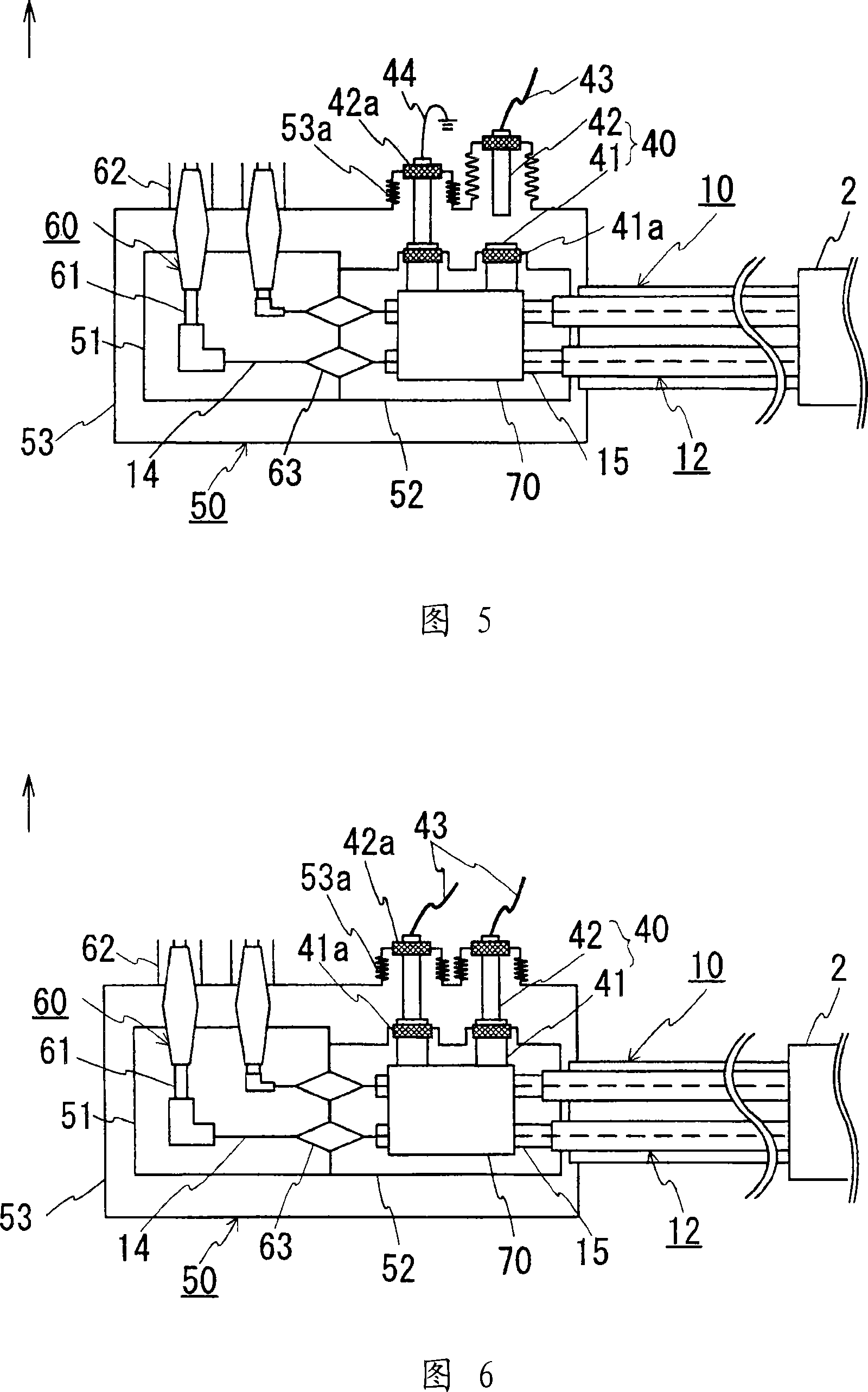
[0052] The superconducting cable 10 used in this example has a structure in which three cable cores 12 are twisted and housed in a heat insulating tube 11 for the cable, and its structure is...
example 2
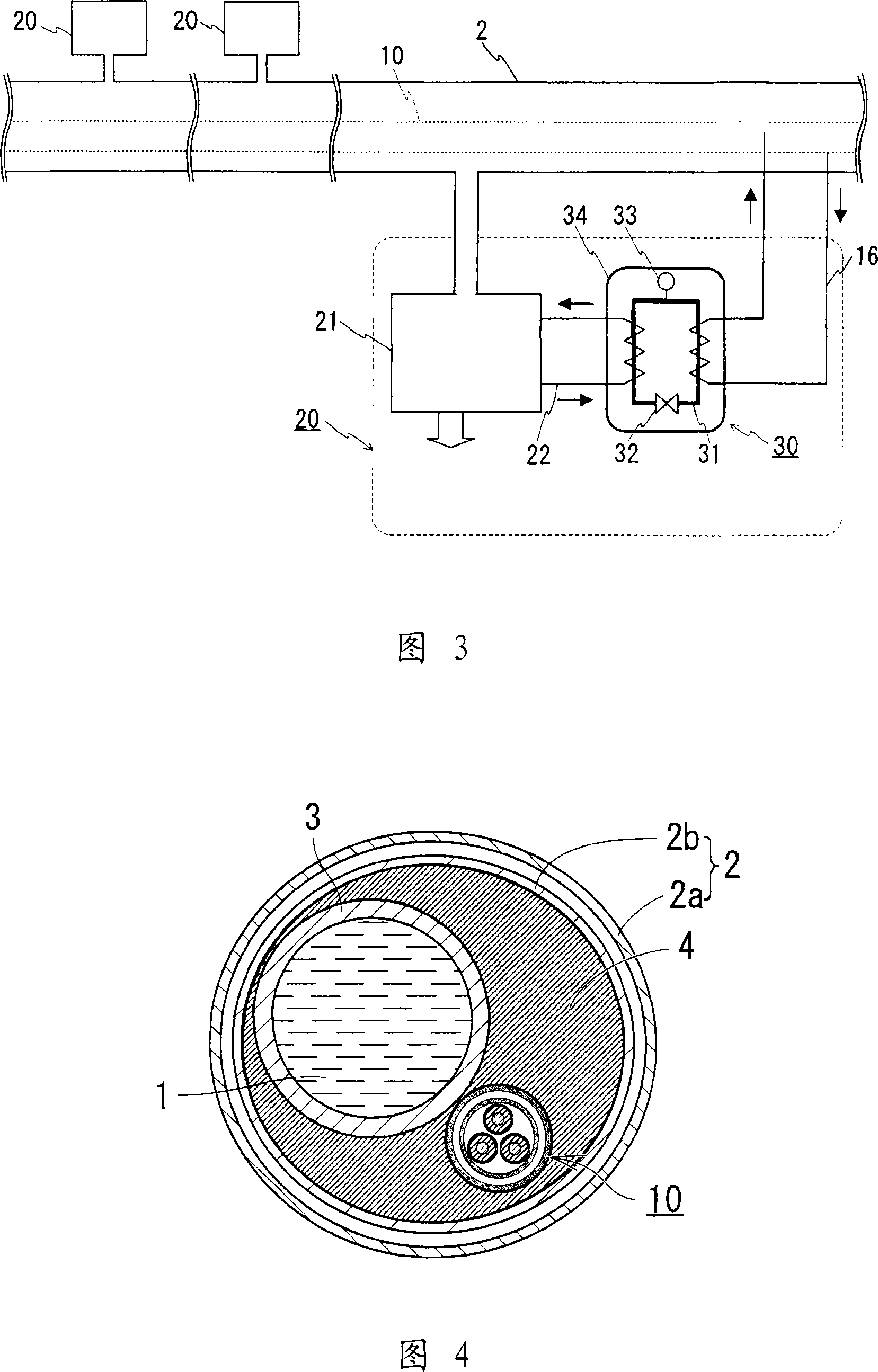
[0059] Although the superconducting cable is immersed in liquid hydrogen in the above-mentioned Example 1, the superconducting cable may be housed in a heat insulating pipe for fluid without being immersed in liquid hydrogen. As an example, a delivery channel for liquid hydrogen may be provided separately in a thermally insulating tube for fluid. Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the superconducting cable of the present invention, which includes a delivery tube for liquid hydrogen and a heat exchanger partition inside the thermal insulation tube for fluid, which is a schematic horizontal view of the structure near the cable Sectional view. The superconducting cable has a structure including a separate delivery tube 3 for delivery of liquid hydrogen in the inner tube 2b of the heat insulating tube 2 for fluid. The heat exchanger partition plate 4 having high thermal conductivity is provided in a space surrounded by the inner periphery of the inner pipe 2b, the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dielectric constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com