Heat exchanger and tube for heat exchanger
a technology of heat exchanger and tube, which is applied in the direction of tubular elements, lighting and heating apparatus, and stationary conduit assemblies, etc. it can solve the problems of unsatisfactory core width with respect to mounting space of heat exchanger, and the width of tubes to be inserted into the tanks must be extremely small with respect to the outer diameter of the tanks, so as to achieve efficient assembly and small tank volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
[0093] Then, the invention will be described with reference to FIG. 7. As shown in FIG. 7, the radiator 300 of this embodiment is configured by overlaying a first core 300a and a second core 300b in an airflow direction. The tank 310 is disposed on both ends of the first core 300a and the second core 300b. And, on one side of the first core 300a and of the second core 300b, the inlet 320 for the refrigerant is disposed on the tank 310 into which the ends 301a of the tubes 301 of the first core 300a are inserted, and the outlet 330 for the refrigerant is disposed on the tank 310 into which the ends 301a of the tubes 301 of the second core 300b are inserted. On the other side of the first core 300a and of the second core 300b, the tank 310 into which the ends 301a of the tubes 301 of the first core 300a are inserted and the tank 310 into which the ends 301a of the tubes 301 of the second core 300b are inserted are communicated. The refrigerant successively passes through the first cor...
third embodiment
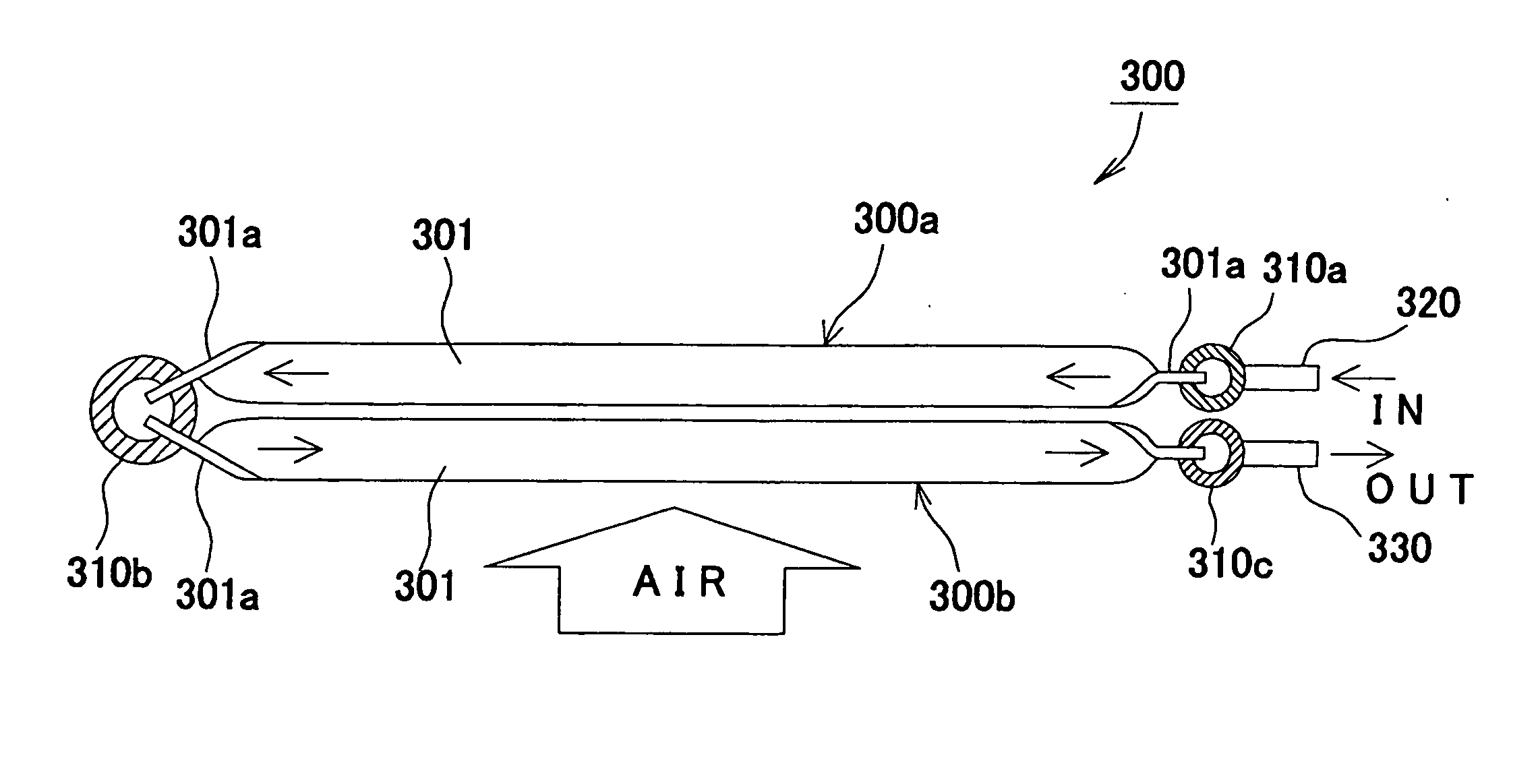
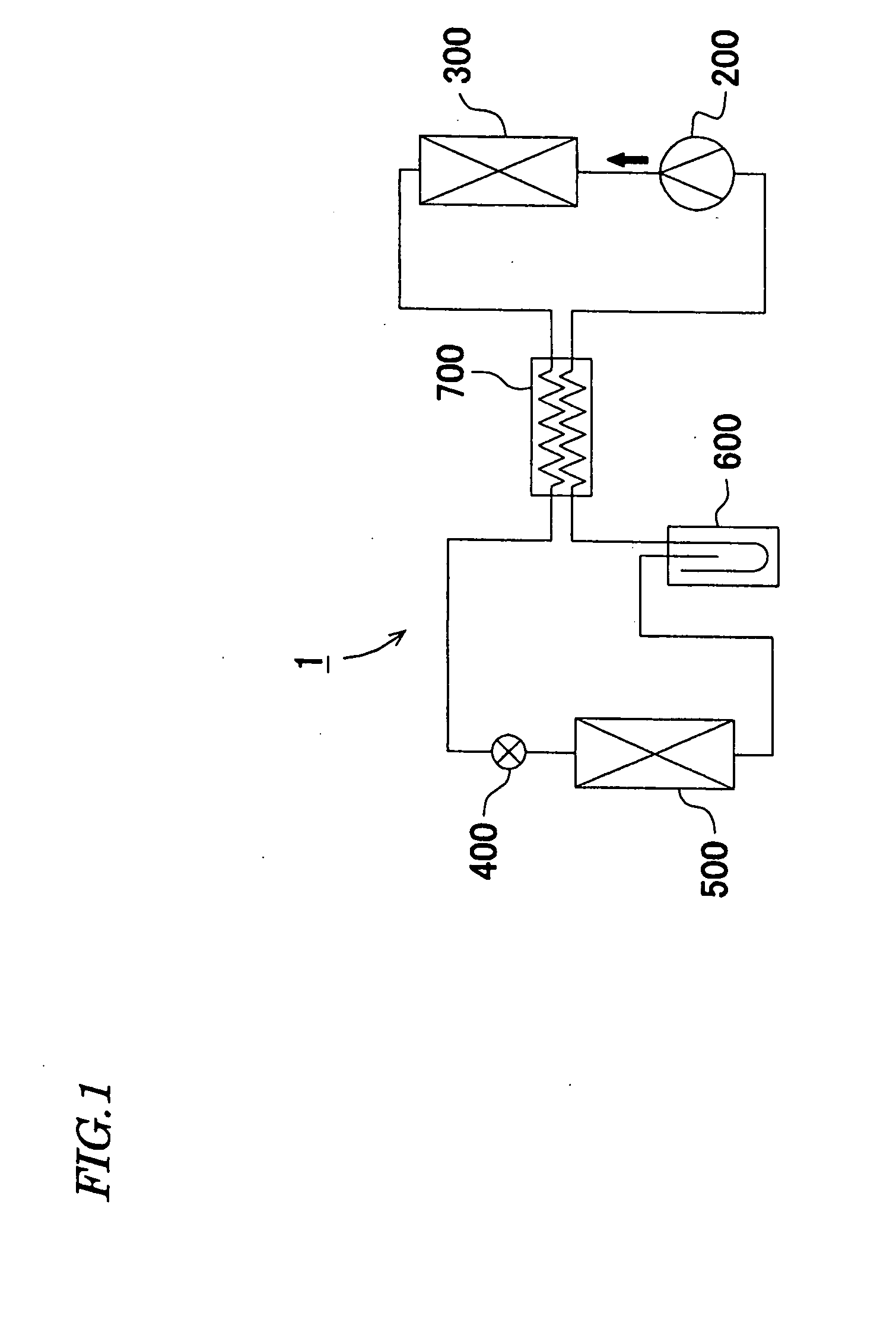
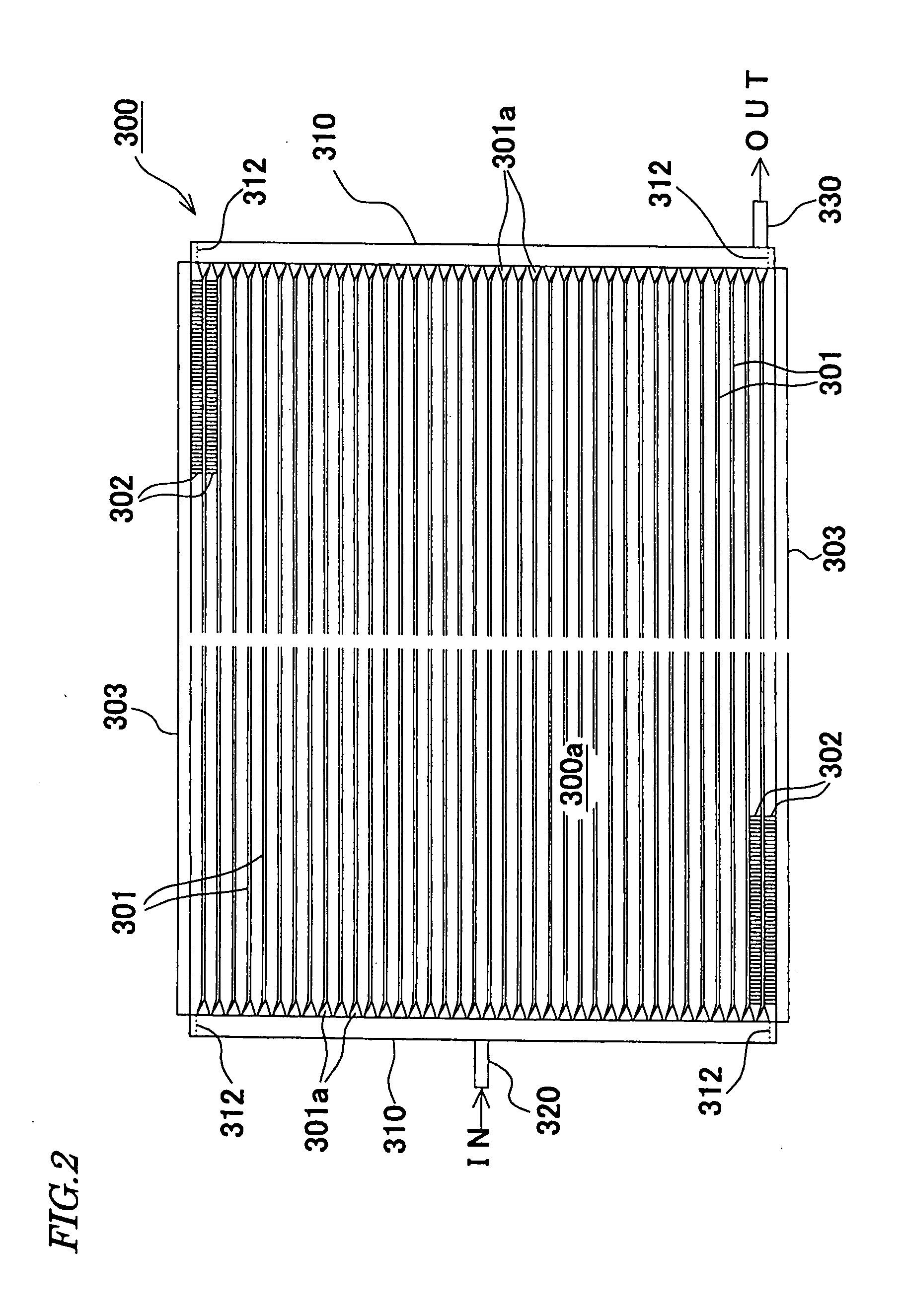
[0095] Next, the invention will be described. As shown in FIG. 8 to FIG. 10, the radiator 300 as the heat exchanger of this embodiment is provided with the first core 300a and the second core 300b which are comprised of lamination of the flat tubes 301 for flowing the refrigerant and the corrugated fins 302, a first tank 310a, a second tank 310b and a third tank 310c each having a pipe shape into which the ends 301a of the tubes 301 are inserted, the inlet 320 which is disposed on the first tank 310a and has a pipe shape for the refrigerant and the outlet 330 which is disposed on the third tank 310c and has a pipe shape for the refrigerant. The refrigerant sent from the compressor 200 enters the inlet 320, and the refrigerant discharged from the outlet 330 is sent to the expansion valve 400. In FIG. 8 to FIG. 10, arrows indicate the flowing directions of the refrigerant in the radiator 300, and the outline arrows indicate the airflow direction to the first core 300a and the second c...
fourth embodiment
[0104] Next, the invention will be described with reference to FIG. 17 and FIG. 18. As shown in FIG. 17, the radiator 300 of this embodiment is disposed on the windward of a radiator 800 of a vehicle, the positions of the first tank 310a and the third tank 310c are displaced in a direction orthogonal to the airflow direction on one side of the first core 300a and of the second core 300b, and the inlet 320 and the outlet 330 are directed toward the downwind side of the airflow direction. The tubes 301 of the first core 300a are determined to be somewhat shorter than the tubes 301 of the second core 300b. The other structure is the same as the previous embodiment.
[0105] According to this embodiment, the radiator 300 can be configured more rationally, and the piping structure in the layout of the refrigeration cycle 1 of a vehicle can be simplified. Especially, the inlet 320 and the outlet 330 in the pipe form for flowing a high-pressure refrigerant and piping to be connected to the in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com