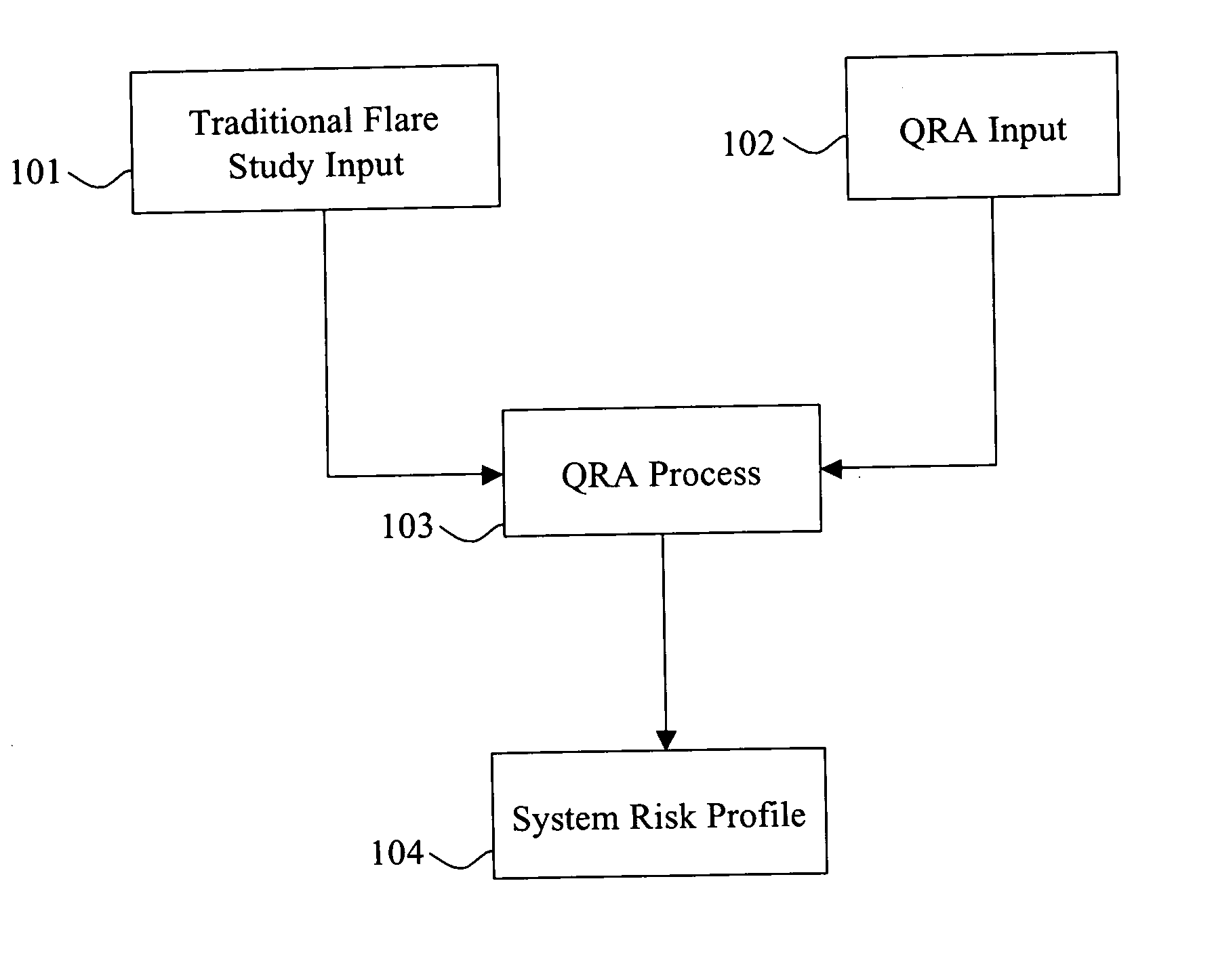
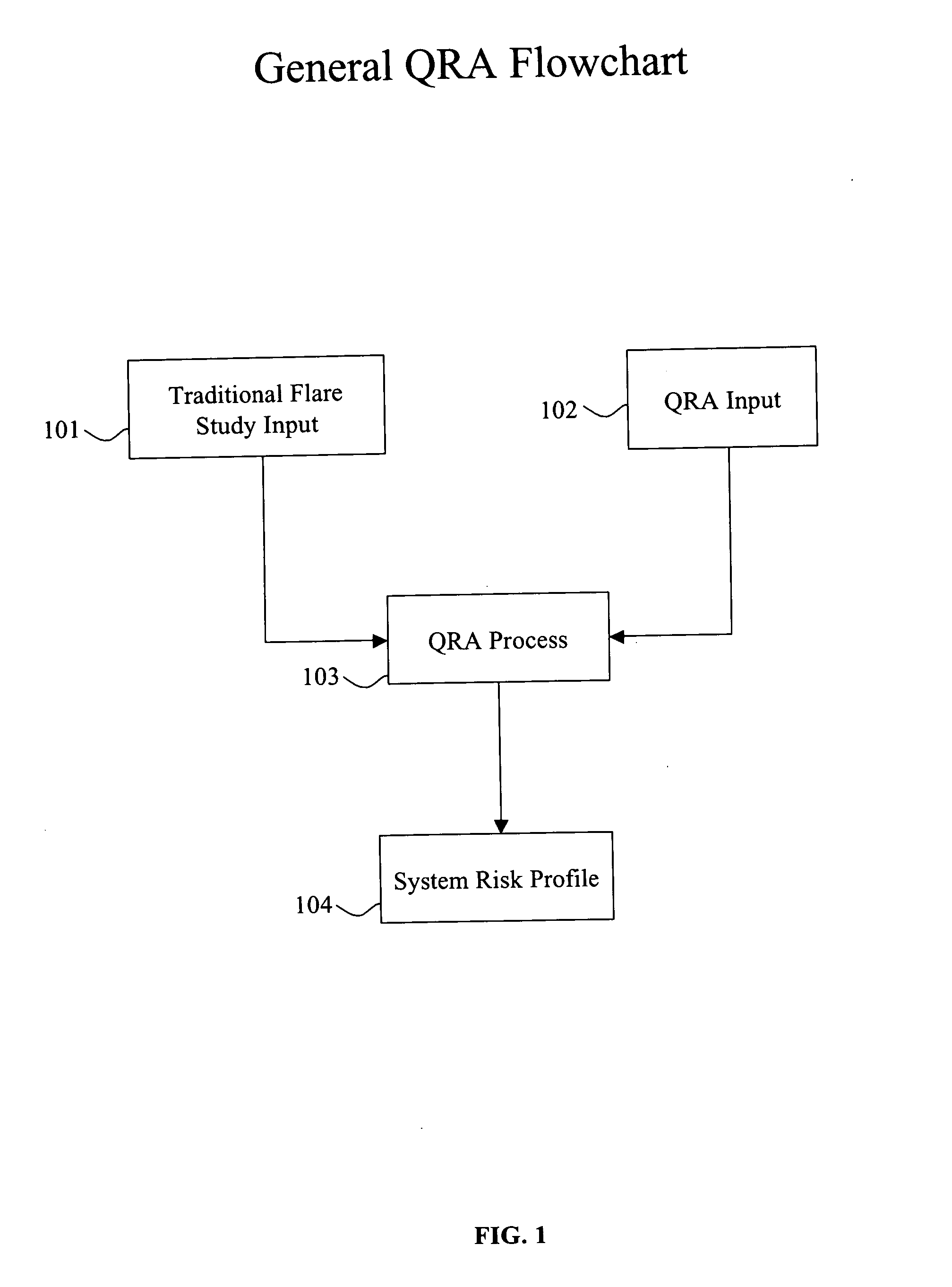
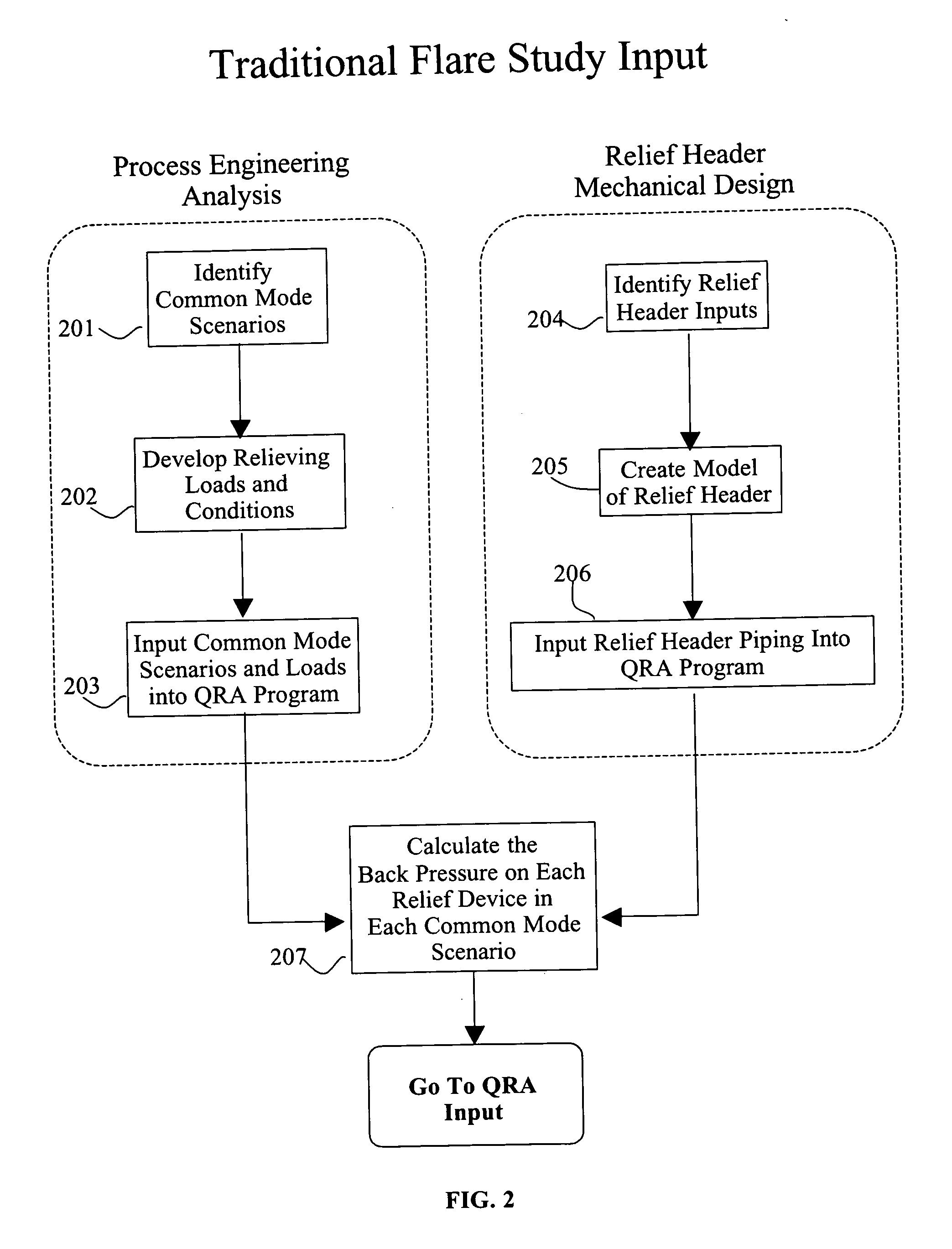
[0013] The present invention provides a probability or risk assessment of the impact of safeguards on a relief pressure system. The risk assessment system provides an analysis of the operation of the safeguards, the pressure relief valves, the header performance for multiple scenarios, given the risk of individual safeguards or subsystem safeguards, and their impact upon the overall system or subsystem of a facility. Such analysis can provide an overall risk assessment and a determination of header performance. Such information can be used by a facility to determine within a given acceptable probability whether a larger header is actually needed compared to simply conservatively estimated values.
[0014] Further, such risk can be determined based upon historical data, engineering judgment, or industry-wide performance capabilities. Thus, a facility may save millions of dollars by undertaking such a risk assessment in some instances. In general, the risk assessment system can estimate an event frequency of failures for given time periods, establish an assessment of the failure probability of safeguards and assess given safeguards for individual containers and / or locations, establish risk target goals for equipment and the overall system, iteratively calculate the frequency of overpressure events with a statistical analysis, and then input such data into additional software, either internal or external to the risk assessment system, that calculates individual and global system performance for all the given scenarios, then analyze the data based upon such risk assessment by accumulated data on whether the risk target goals are met. Such data can be used to determine whether the individual units are global system needs, engineering needs and / or modifications to meet the risk target goals. If the system is modified, additional risk assessment analysis can be performed in like manner until the system meets the risk target goals.
[0015] The invention provides a method of assessing risks to pressure equipment associated with at least one pressure relief system having a relief header, comprising identifying one or more relief header inputs associated with the equipment, identifying one or more common mode failure scenarios for the relief header inputs, calculating a first hydraulic model for the one or more common mode failure scenarios, defining a risk acceptance criteria for an accumulation in one or more members of the equipment associated with the relief header inputs, defining initiating events frequency of occurrence for one or more common mode failure scenarios, determining at least one of the risk acceptance criteria is not met by the first hydraulic model, defining a probability of failure for one or more protection systems associated with the equipment; and calculating an output by correlating an accumulation of the one or more members of the equipment with the frequency of occurrence.
[0016] The invention further provides a method of assessing risks to pressure equipment associated with at least one pressure relief system having a relief header, comprising identifying one or more relief header inputs associated with the equipment, identifying at least one common mode failure scenario for the relief header inputs, calculating a first hydraulic model for the at least one common mode failure scenario, defining a risk acceptance criteria for an accumulation in the equipment associated with the relief header inputs, defining initiating events frequency of occurrence for the at least one common mode scenario, determining whether the risk acceptance criteria are met by the first hydraulic model.
[0017] The invention also provides a system for assessing risks to pressure equipment associated with at least one pressure relief system having a relief header, comprising an electronic processor, a memory coupled to the electronic processor, the memory containing one or more programs to be processed by the electronic processor, the one or more programs being adapted to use input data for identified relief header inputs, identified common mode failure scenarios for the relief header inputs, defined risk acceptance criteria for an accumulation in the equipment associated with the relief header inputs; and defined initiating events frequency of occurrences for the common mode scenarios, defined probability of failure for one or more protection systems coupled to one or more of the relief header inputs, calculate a first hydraulic model for at least one of the common mode failure scenarios, automatically calculate probability of failures for combinations of protection systems associated with the relief header inputs; and automatically correlate an accumulation of one or more members of the equipment with the frequency of occurrences; and an output element coupled to the memory for producing an output of the correlation of the accumulation of one or more members of the equipment with the frequency of occurrences.
 Login to View More
Login to View More