Assay for detecting and quantifying HIV-1
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
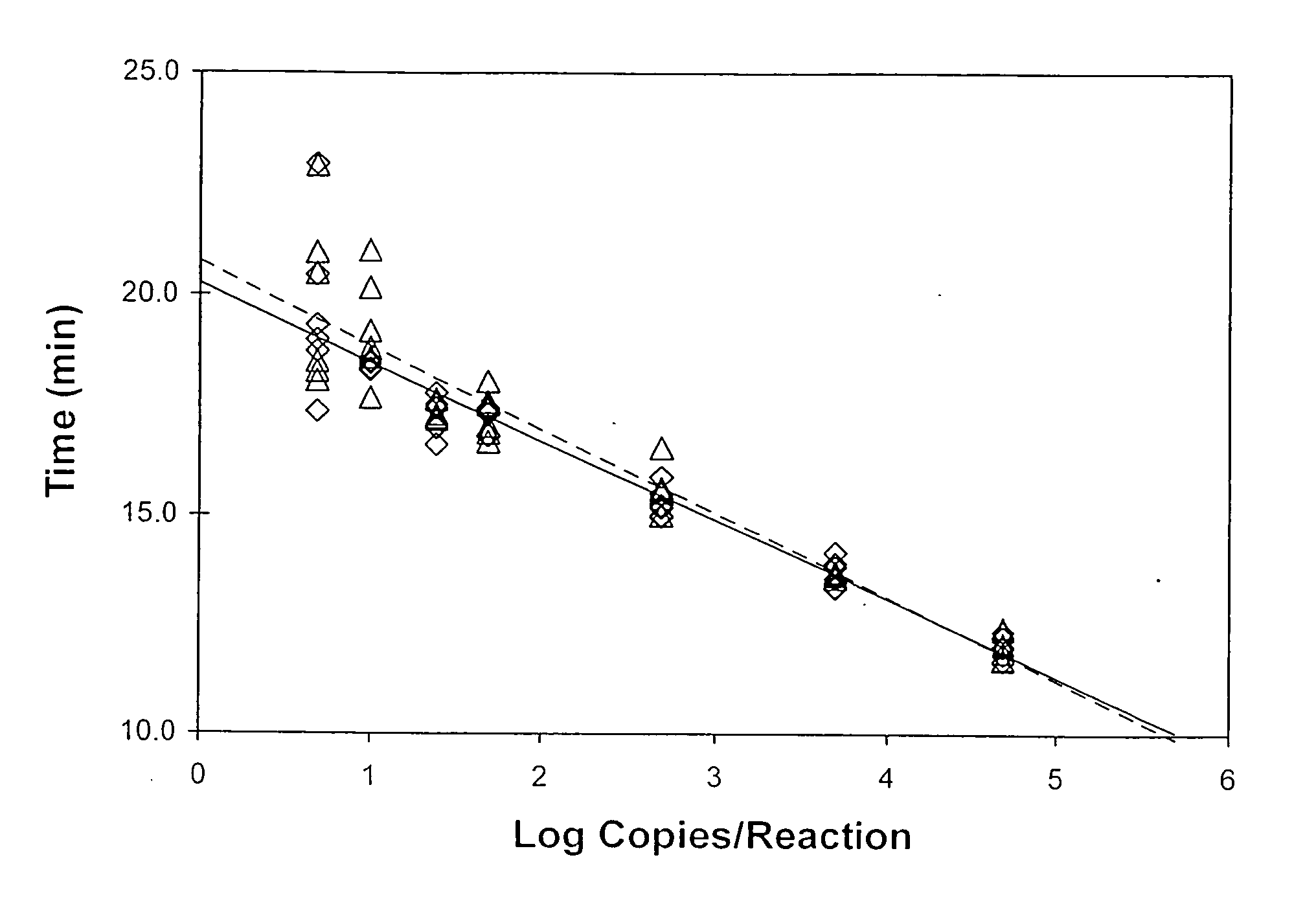
Time-Dependent Monitoring of HIV-1 M Group, Subtype B Amplicon Production
[0108] An in vitro synthesized transcript of known concentration included the sequence
(SEQ ID NO:29)GGTACCAGCACACAAAGGAATTGGAGGAAATGAACAAGTAGATAAATTAGTCAGTGCTGGAATCAGGAAAGTACTATTTTTAGATGGAATAGATAAGGCCCAAGATGAACATGAGAAATATCACAGTAATTGGAGAGCAATGGCTAGTGATTTTAACCTGCCACCTGTAGTAGCAAAAGAAATAGTAGCCAGCTGTGATAAATGTCAGCTAAAAGGAGAAGCCATGCATGGACAAGTAGACTGTAGTCCAGGAATATGGCAACTAGATTGTACACATTTAGAAGGAAAAGTTATCCTGGTAGCAGTTCATGTAGCCAGTGGATATATAGAAGCAGAAGTTATTCCAGCAGAAACAGGGCAGGAAACAGCATATTTTCTTTTAAAATTAGCAGGAAGATGGCCAGTAAAAACAATACATACTGACAATGGCAGCAATTTCACCGGTGCTACGGTTAGGGCCGCCTGTTGGTGGGCGGGAATCAAGCAGGAATTTGGAATTCCCTACAATCCCCAAAGTCAAGGAGTAGTAGAATCTATGAATAAAGAATTAAAGAAAATTATAGGACAGGTAAGAGATCAGGCTGAACATCTTAAGACAGCAGTACAAATGGCAGTATTCATCCACAATTTTAAAAGAAAAGGGGGGATTGGGGGGTACAGTGCAGGGGAAAGAATAGTAGACATAATAGCAACAGACATACAAACTAAAGAATTACAAAAACAAATTACAAAAATTCAAAATTTTCGGGTTTATTACAGGGACAGCAGAAATCCACTTTGGAAAGGACCAGCAAAGCTCCTCTGGAAAGGTGAAGGGGCAG...
example 2
Different Kinetic Profiles Characterize Amplification of HIV-1 Variants
[0114] Amplification reactions were performed essentially as described under Example 1 with the following modifications. Parallel reactions were conducted using a first-strand promoter-primer having the target-hybridizing sequence of SEQ ID NO:13, a second-strand primer having the target-complementary sequence of SEQ ID NO:2, and variable amounts of either the subtype B template described in Example 1, or an O group template that included the sequence
(SEQ ID NO:32)AGTGGGTTCATAGAAGCAGAAGTGATACCAGCAGAAACAGGACAAGAAACTGCCTACTTCCTGTTAAAACTGGCTGCAAGATGGCCTGTTAAAGTAATACATACAGACAACGGGCCTAATTTTACAAGTACAACTATGAAGGCTGCATGTTGGTGGGCCAACATACAACATGAGTTTGGAATACCATATAATCCACAAAGTCAAGGAGTAGTAGAAGCCATGAATAAGGAATTAAAATCAATTATACAGCAGGTGAGGGACCAAGCAGAACACTTAAGAACAGCAGTACAAATGGCAGTATTTGTTCACAATTTTAAAAGAAAAGGGGGGATTGGGGGGTACACTGCAGGAGAAAGGATAATAGACATATTAGCATCACAAATACAAACAACAGAATTACAAAAACAAATTTTAAAANTTCACAAATTTCGGGTCTATTACAGAGACAGCAGAG...
example 3
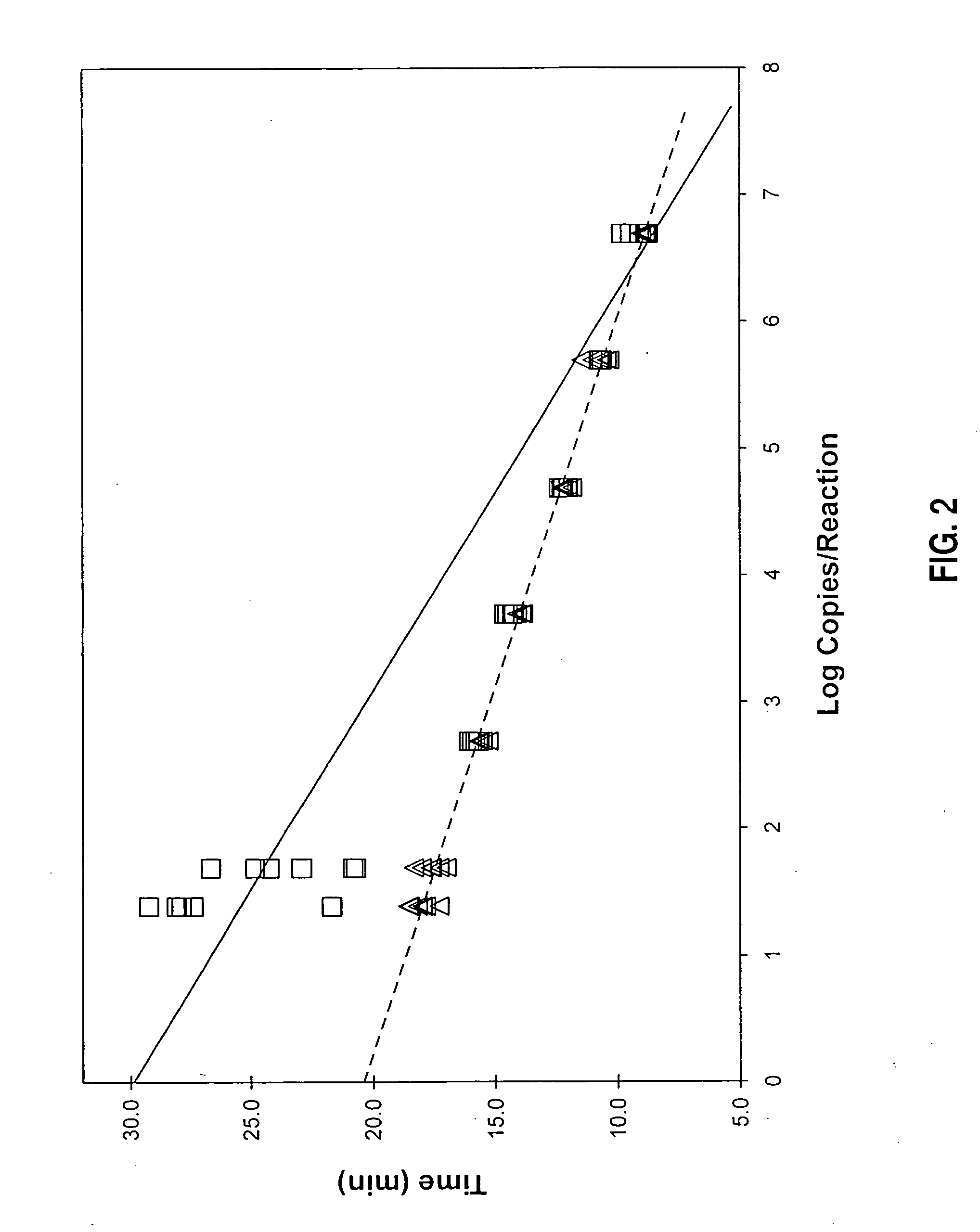
Enhancement of Amplification Kinetics of HIV-1 O Group Templates
[0120] Parallel sets of amplification reactions were prepared to compare the effects of two different primer combinations on the kinetics of amplification of HIV-1 subtype B and HIV-1 O group templates. In each instance, a first-strand promoter-primer having the target-hybridizing sequence of SEQ ID NO:13 or SEQ ID NO:15 was used in combination with a second-strand primer having the target-complementary sequence of SEQ ID NO:2. Notably, the sequence of SEQ ID NO:15 differed from the sequence of SEQ ID NO:13 by the substitution of adenine for thymidine at position 15 in the target-hybridizing portion of the primer. This substitution corresponds to position 41 of the promoter-primers identified by SEQ ID NO:19 and SEQ ID NO:17. Amounts of HIV-1 templates used in the reactions ranged from 5 to 5×104 copies / reaction. Amplification reactions were prepared and monitored using materials and procedures essentially as described...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com