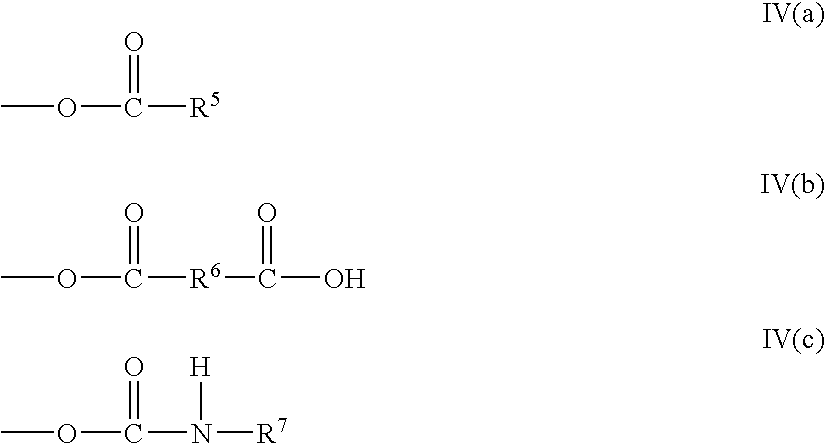
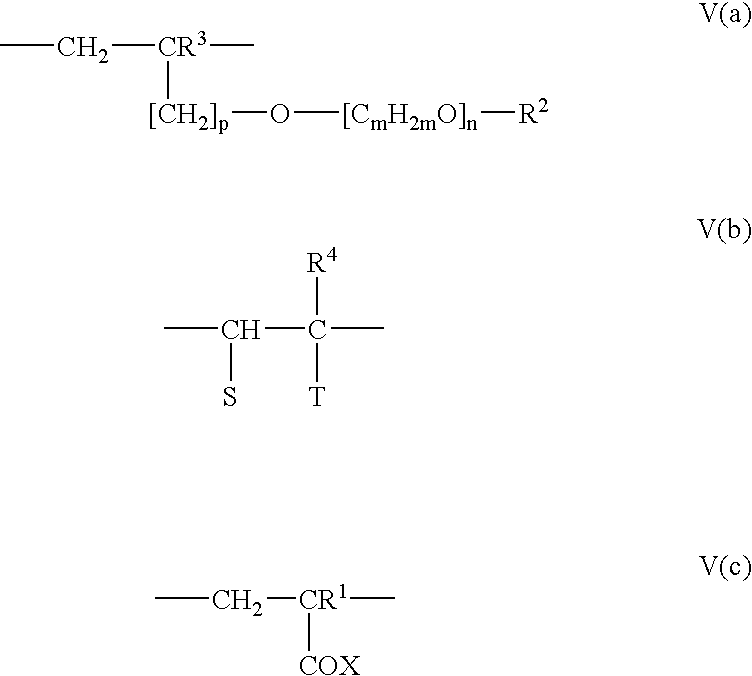Method of making a gypsum slurry with modifiers and dispersants
a technology of gypsum and dispersant, which is applied in the field of making gypsum products using gypsum slurry and gypsum panels, can solve the problems of less product lost that does not meet specifications, less effective modifiers, etc., and achieves the effects of reducing dispersant cost, reducing dosage, and sufficient fluidity to pour easily
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
[0060] This example demonstrates the importance of the order of addition of the modifier and the dispersant. Four hundred grams of stucco from Southard, Okla., 220 g of water, 0.7 g of HRA set accelerator and 0.89 g of MELFLUX 2500L dispersant that includes 45% solids were used in each of the following tests. Additionally, 0.6 g soda ash was added to two of the samples as described below. The water and dispersant were added to the water prior to the addition of the stucco and modifier (if present) in all cases. After addition of the stucco, the mixture was allowed to soak for 15 seconds, then mixed for 30 seconds to form a slurry. The modifier was added as described below.
[0061] Condition 1 was the control sample, to which no soda ash modifier was added. In Condition 2, soda ash was added to the mixing water prior to stucco addition to the water. The soda ash was added after the stucco was added to the mixing water in Condition 3, just prior to turning on the mixer after the soak t...
example 2
[0064] In this comparative example, lime was added to a gypsum slurry used to make gypsum panels and resulted in little improvement in fluidity. All component amounts are expressed as pounds per 1000 square feet (104 m2) of gypsum panel (“lbs / MSF”). Twelve hundred eighty five pounds of stucco was combined with other dry components, including three pounds of starch, three pounds of cerelose, and 0.32 pounds (145 g) of retarder. Ivory lime was premixed with water and added directly to the mixer through one of several water injection orifices adjacent to the stucco inlet. The dispersant, Melflux 2500L, was added directly to the gauge water and blended until homogenous, and the mixture then was added to the mixer through the remaining water injection orifices adjacent to the stucco inlet. The dry components were blended with the stucco, which was then added to the mixer through the stucco downspout.
TABLE IISampleWith 0.18% LimeNo LimeHRA Accelerator32 lbs / MSF38.8 lbs / MSFWater831855WSR...
example 3
[0066] A plant trial was held whereby the dispersant and the modifier were both dissolved in the gauging water. The modifier, soda ash, was dissolved in water to make a 10% solution by weight. 3.9 lbs / msf of Melflux 2500L, diluted to 32% solids, was added to the gauging water, then 11.3 lb / msf of the soda ash slurry was added to the gauging water, and all components were mixed to form a homogeneous solution. Twelve hundred fifty-seven pounds of stucco was added to the mixer to form the gypsum slurry.
TABLE IIISampleWith 0.1% Soda AshNo Soda AshHRA Accelerator35 lbs / MSF29 lbs / MSFPotassium Sulfate 0 lbs / MSF 4 lbs / MSFWater861965WSR0.690.77
[0067] As shown in Table III, the use of 0.1% soda ash in this process allowed a signficant reduction in water.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com