NF-kappaB oligonucleotide decoy molecules
a technology of oligonucleotide decoy and kappab, which is applied in the direction of sugar derivatives, antibacterial agents, organic active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of prolonging the survival of allografts and reducing the coronary artery disease of grafts, and achieves the effect of potent inhibitors of nf-b activity and negative gene transcription regulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0179] Design and Testing of NF-κB Decoy Molecules
[0180] Design
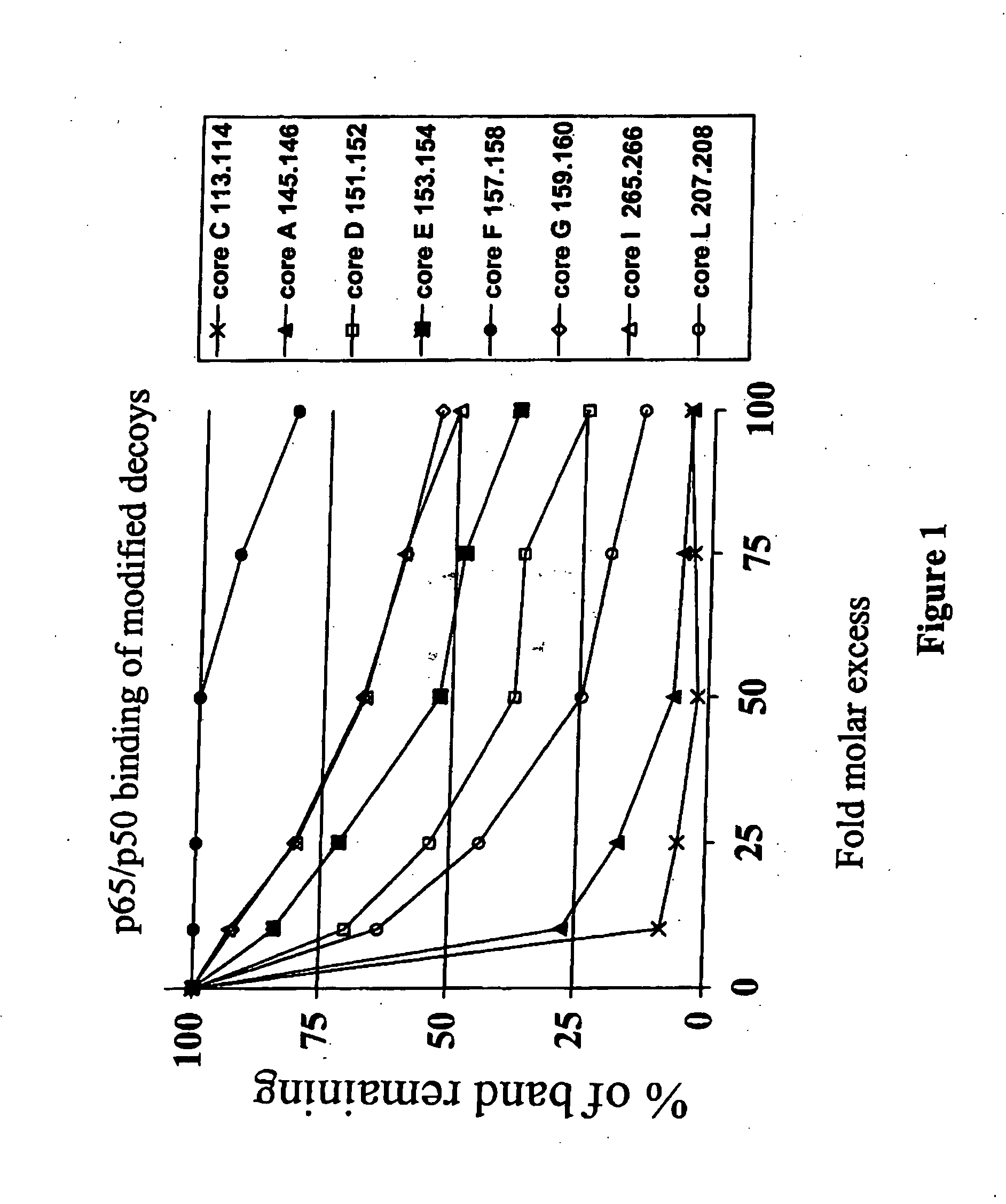
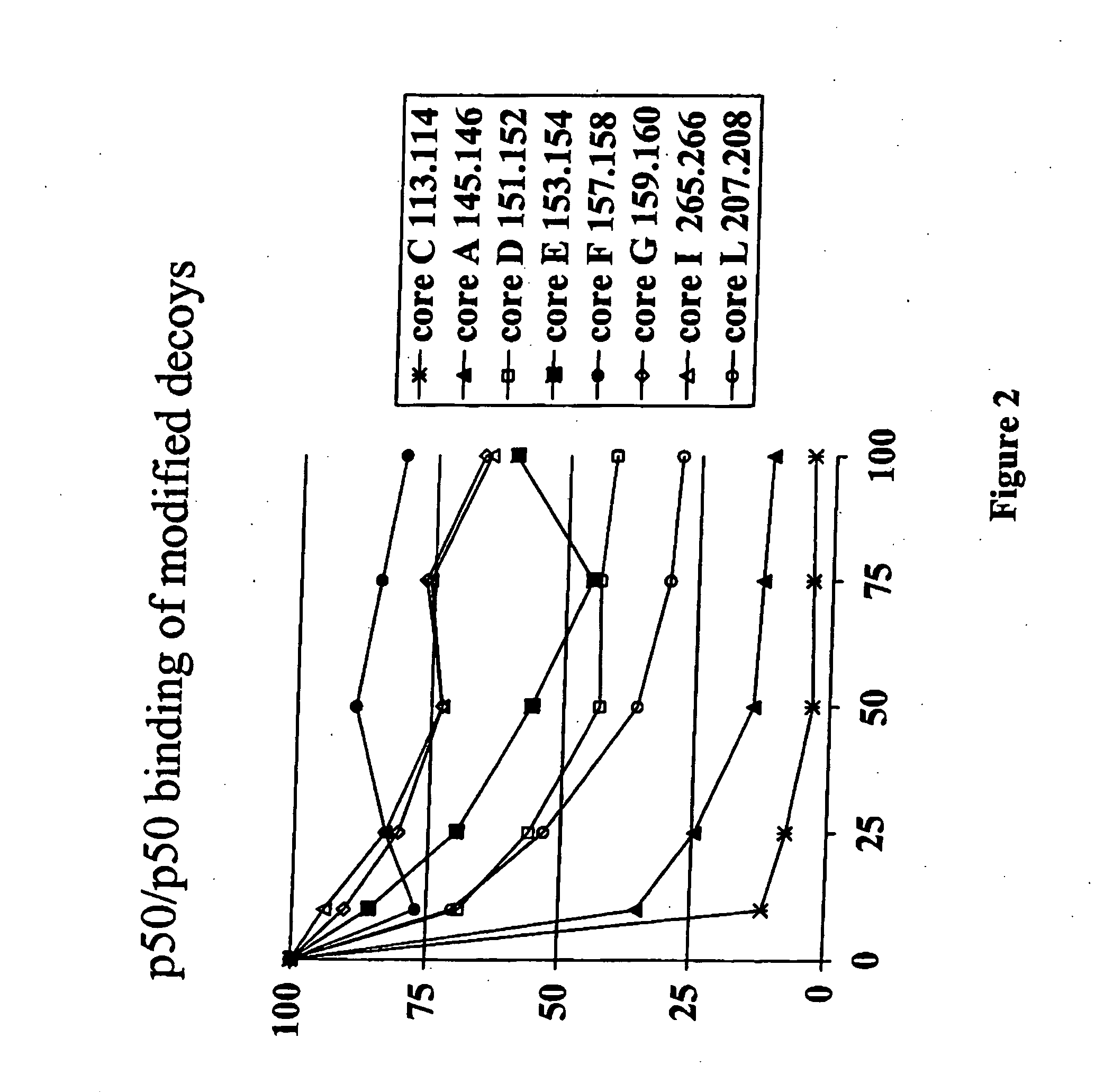
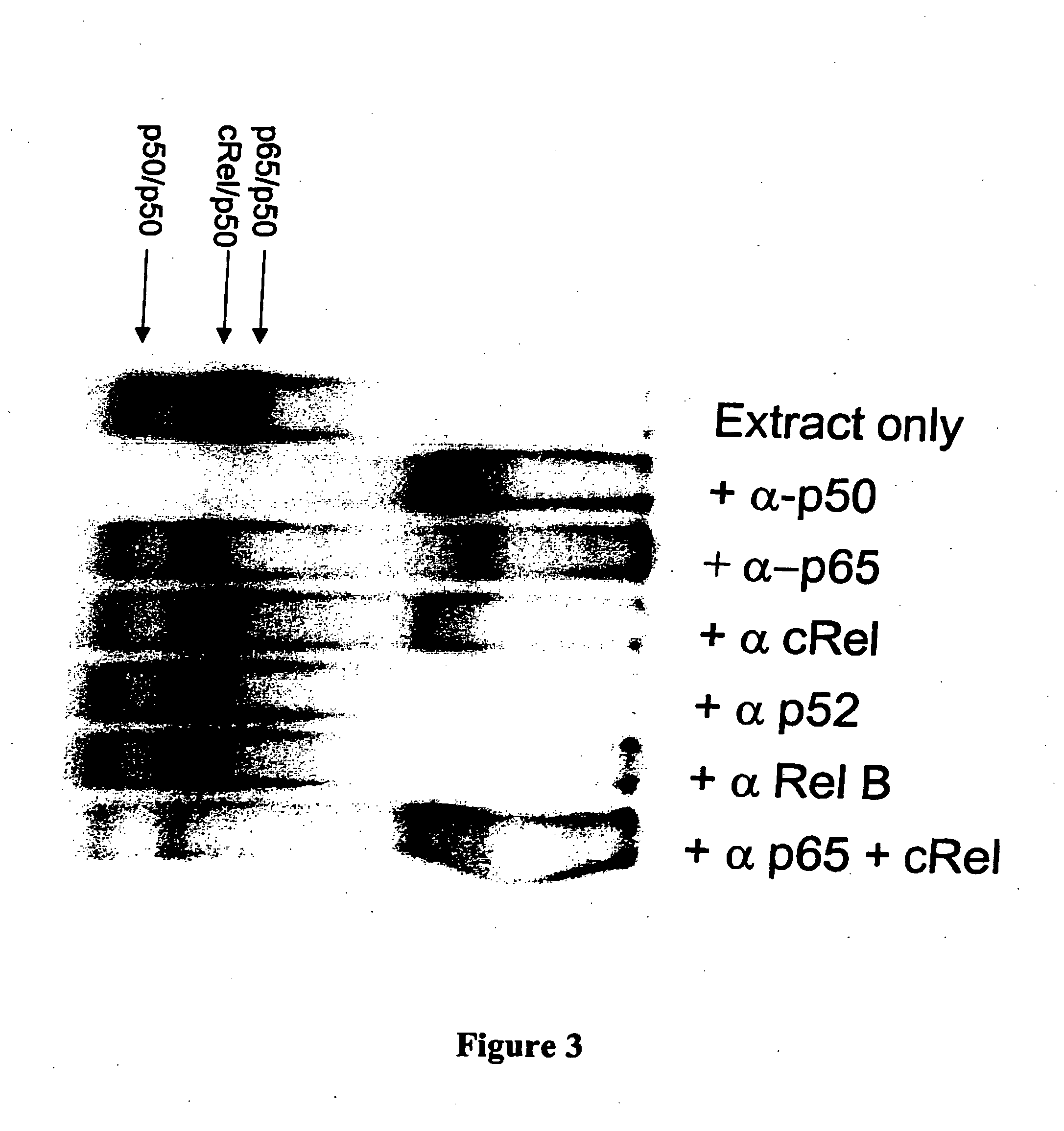
[0181] NF-κB dsODN decoy molecules were designed and tested for their ability to bind and / or compete for binding of NF-κB. In a particular aspect, the goal of the invention was to design NF-κB decoy molecules that preferentially bind p65 / p50 and / or cRel / p50 heterodimers over p50 / p50 homodimers. As a result of not blocking p50 / p50 homodimers, the selective decoy molecules of the invention allow these homodimers to block the promoters of NF-κB regulated genes, which provides an additional level of negative regulation of gene transcription.
[0182] In designing the oligonucleotide decoys, information available from crystal structure studies and computational analysis of the known NF-κB binding sites were utilized.
[0183] As discussed above, based on study of the crystal structure of the p50 / p65 heterodimer bound to the immunoglobulin light-chain gene, which contains the consensus sequence of 5′-GGGACTTTCC-3′ (SEQ ID NO: 2)...
example 2
[0218] NF-κB Decoy Molecules Comprising a Nuclear Localization Signal
[0219] In order to determine the ability of a nuclear localization signal (NLS) containing peptide to improve the entry of an oligonucleotide decoy into the nucleus, a peptide with the NLS sequence based on the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen (PKKKRKVEDPYC) (SEQ ID NO: 93) was synthesized by Sigma Genosys and conjugated to the NF-κB 153 H3 oligonucleotide as follows. Briefly, 6.5 nmols of oligonucleotide was first incubated with 40-fold molar excess of the linker Sulfo-SMCC (Pierce) at room temperature for 2 hours. After removal of excess linker from the reaction by a NAP-10 column (Pharmacia Biotech), the activated oligonucleotide was incubated with 5-fold molar excess of the NLS peptide at room temperature overnight. To assess the percentage of oligonucleotide successfully conjugated to the NLS peptide, the reaction was analyzed by loading 1 μl onto a 20% PAGE gel (non-denaturing). The gel was stained with S...
example 3
[0221] NF-κB Decoy Reduces Ear Swelling in Murine Atopic Dermatitis
[0222] To determine the efficacy and effective dose range of NF-kB decoy in Dustmite Ag (Dp) induced contact dermatitis in NC / Nga mice.
[0223] Method
[0224] Dp Ag induced dermatitis was induced as previously described (Sasakawa, T et al., Int Arch Allergy Immunol 126:239-47 (2001); Sasakawa et al., Int Arch Allergy Immunol 133:55-63 (2004)). Briefly, Six week old male NC / Nga mice were injected intradermally with 5 μg of Dp extract (Greer Laboratories, Lenoir, N.C.) dissolved in saline on the ventral side of their right ears on days 0, 2, 4, 7, 9, and 11. Starting on day 11, the DP injected ear was topically treated 2 times a day for 10-12 days with 20 μl of vehicle, vehicle containing 0.25% or 0.1 % NF-κB decoy or betamethasone as a control. The ear thickness was measured with an ear thickness gauge (Oditest, Dyer, Inc., Lancaster, Pa.) 24 hr after each intradermal injection or treatment.
[0225] Results
[0226] To ex...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com