Buckling restrained braces and damping steel structures
a technology of damping steel structure and restraint braces, which is applied in the direction of construction, building types, building components, etc., can solve the problems of inability to constrain the local buckling the adhesion-preventing film has still other problems, and the inability to absorb the expansion in the plate thickness direction of the steel-made center axial member
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
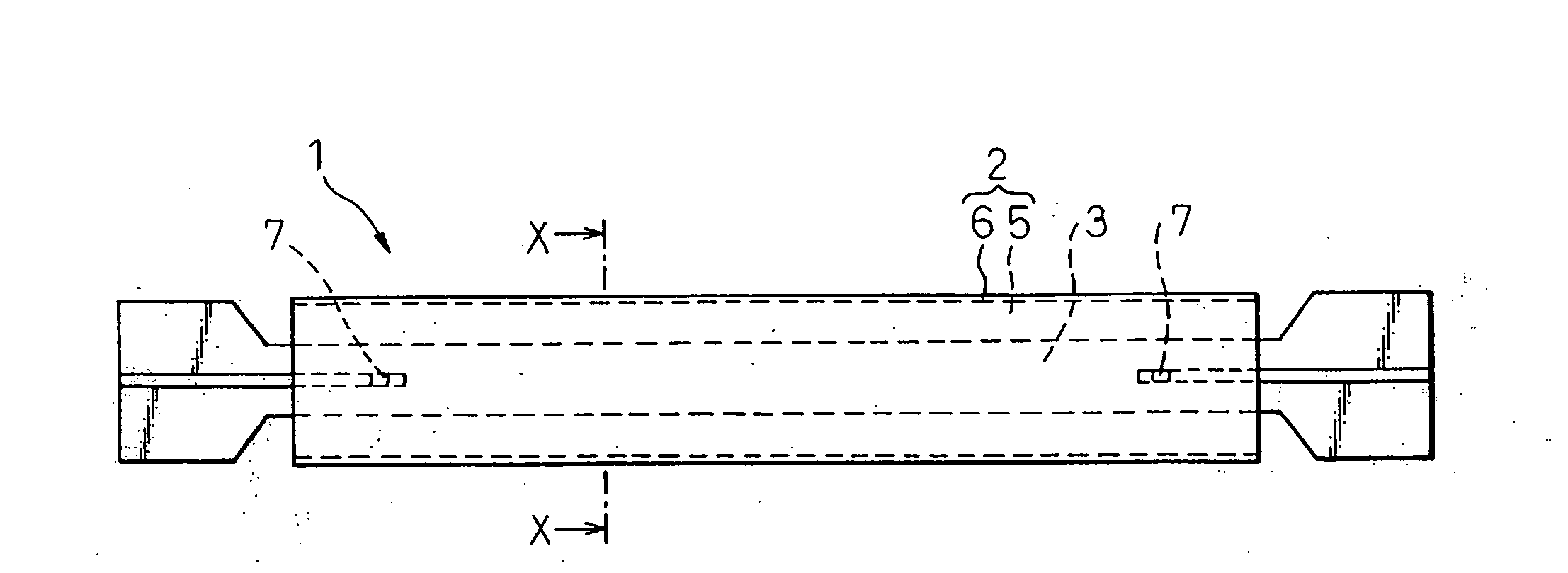
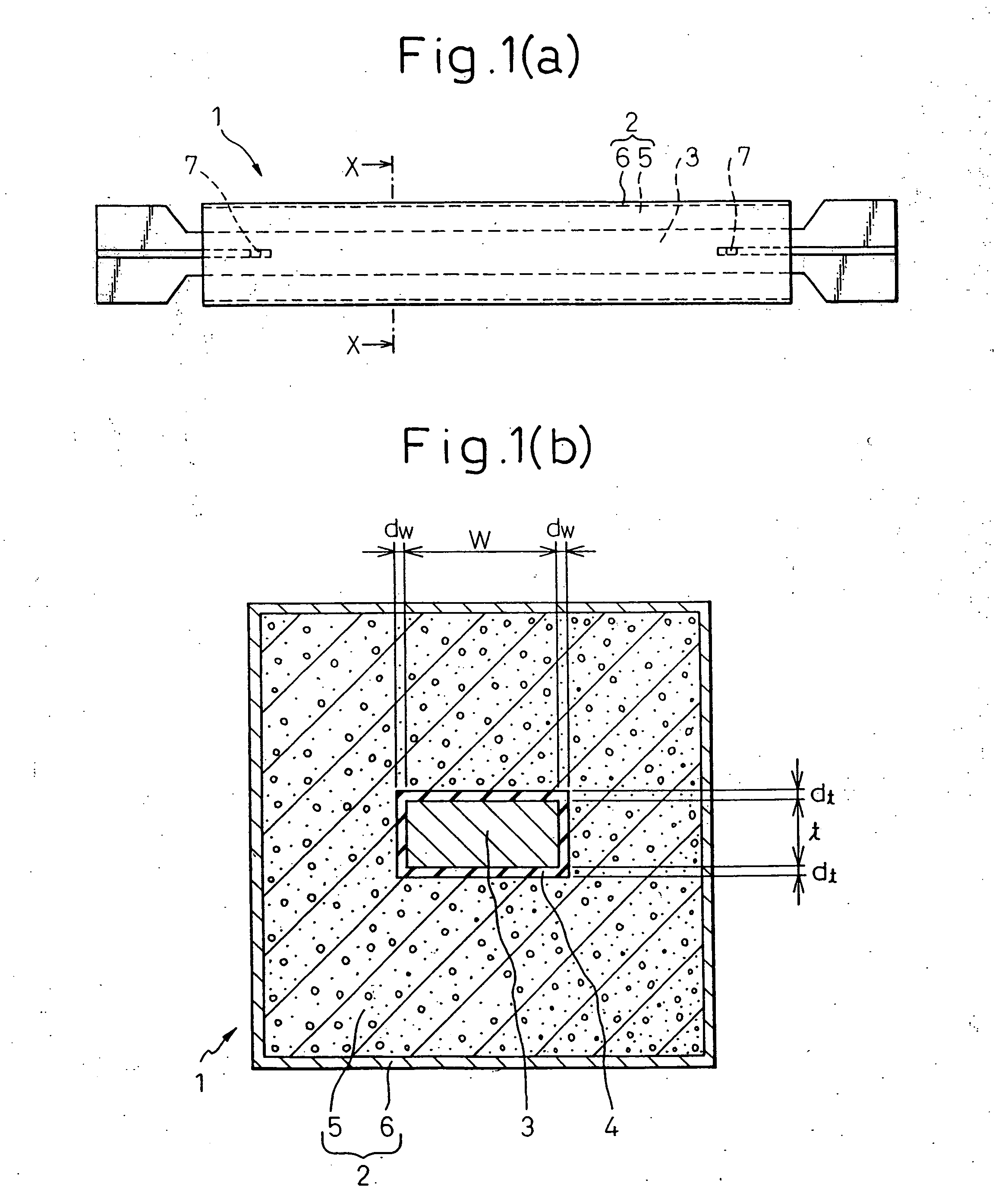
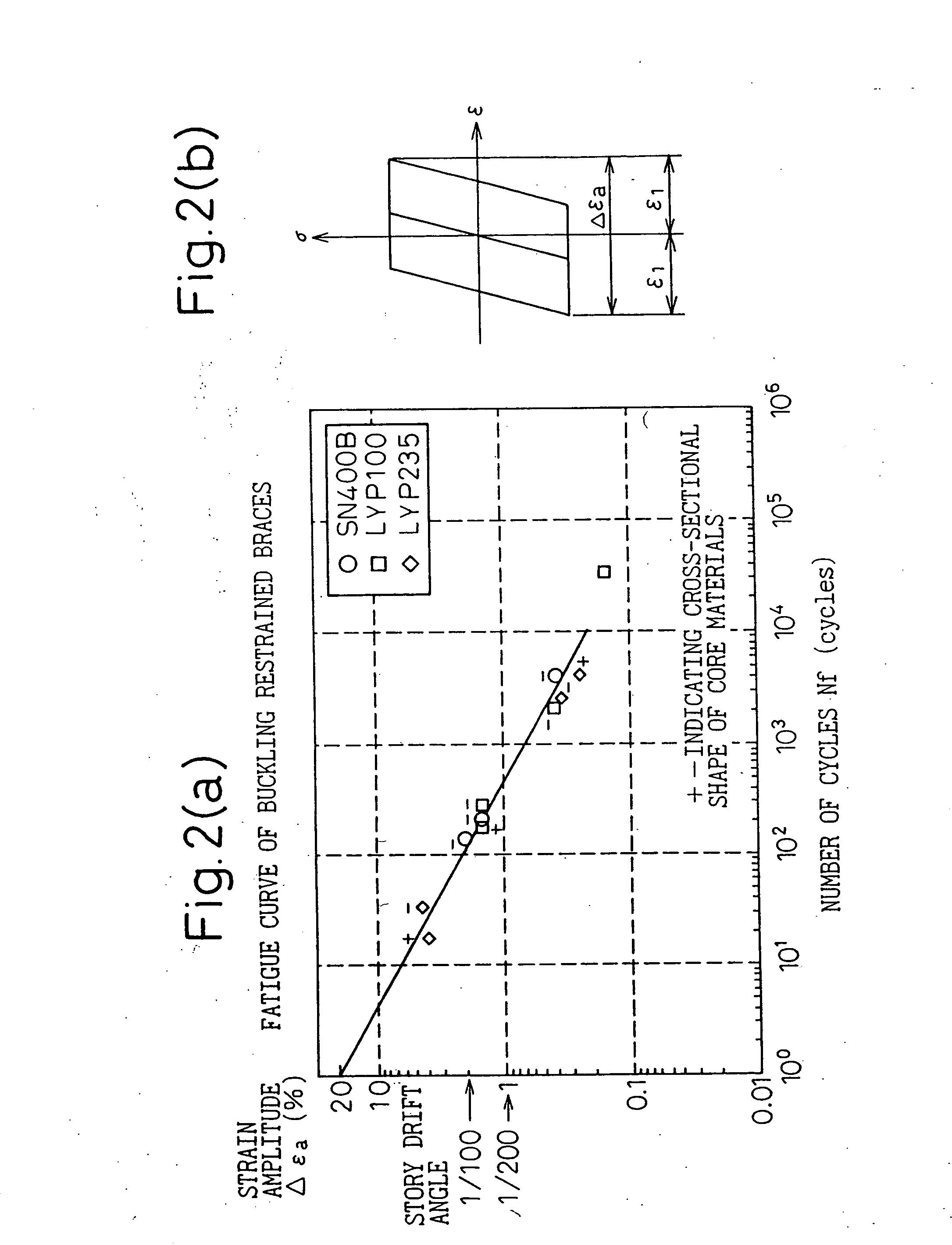
[0102] An adhesion-preventive film having a ratio (adhesion-preventive film ratio) of the film thickness to the plate thickness of a steel-made center axial member of at least 0.5 to 10% was provided between a buckling-constraining concrete member and the steel-made center axial member. When considering the pressure for placing concrete 5 in manufacturing a buckling-restraining brace 1, a lower limitation of a minimum thickness ratio dt(min) / t of the adhesion-preventive film 4 and a steel-made center axial member 3 is preferably about 1.2%. The adhesion-preventive film had a secant modulus in the thickness direction of at least 0.1 N / mm2 between a point having a compressive strain of 0% and a point having a compressive strain of 50%, and up to 21,000 N / mm2 between a point having a compressive strain of 50% and a point having a compressive strain of 75%. In the present example, a maximum axial strain amplitude Δεa of 4% was applied to a buckling restrained brace having an adhesive-pr...
example 2
[0104] Buckling restrained braces and a damping steel structure were clamping jointed with high tensile bolts. As shown in FIGS. 16 (a) and 16 (b) and FIGS. 17 (a) and 17 (b), steel-made connecting plates 27 having a surface hardness (Vickers hardness) and a surface roughness (ten point average roughness) 1.3 times larger than the surface hardness and surface roughness of both ends 22, 23 of the steel-made center axial members were used. Alternatively, in the friction jointing with high tension bolts mentioned above, both ends 22, 23 of the steel-made center axial member and the steel made-connecting plates 27 forming one friction jointing face were joined by the following procedure: the ratio of a hardness of the frictional surface layer portion of one of the two steel materials to a hardness of the frictional surface layer portion of the other steel material is at least 2.5; the depth of the surface layer portion having a higher hardness is at least 0.2 mm; a plurality of triangul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com