Method and Apparatus for Operatively Controlling a Virtual Reality Scenario with an Isometric Exercise System
a virtual reality and exercise system technology, applied in the field of interfaces, can solve the problems of difficult interfacing with the human body, high technology and cost, and the inclusion of physical interfaces in dismounted soldier simulations, and achieve the effects of simple, rugged and inexpensive, high cost and mechanical complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
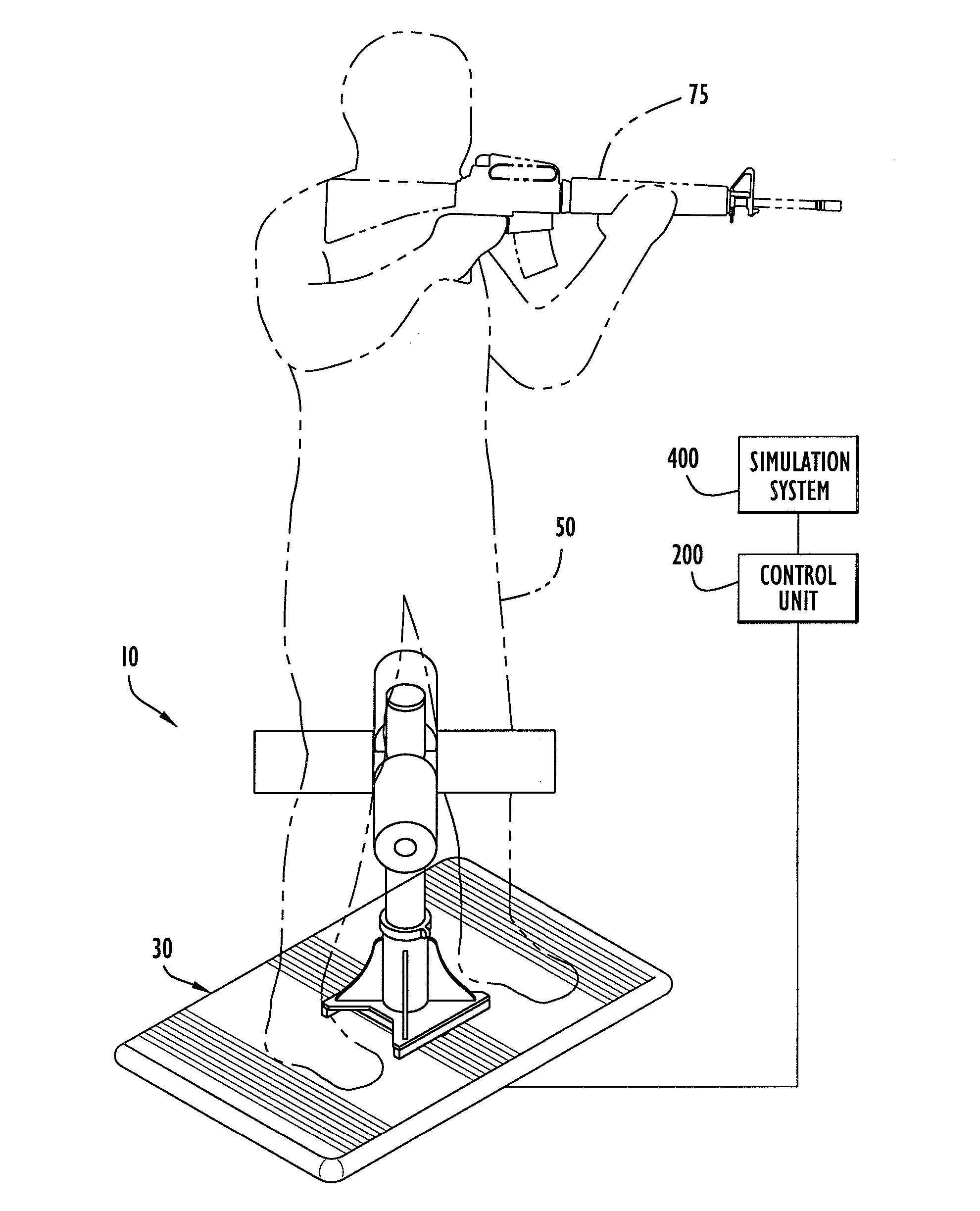
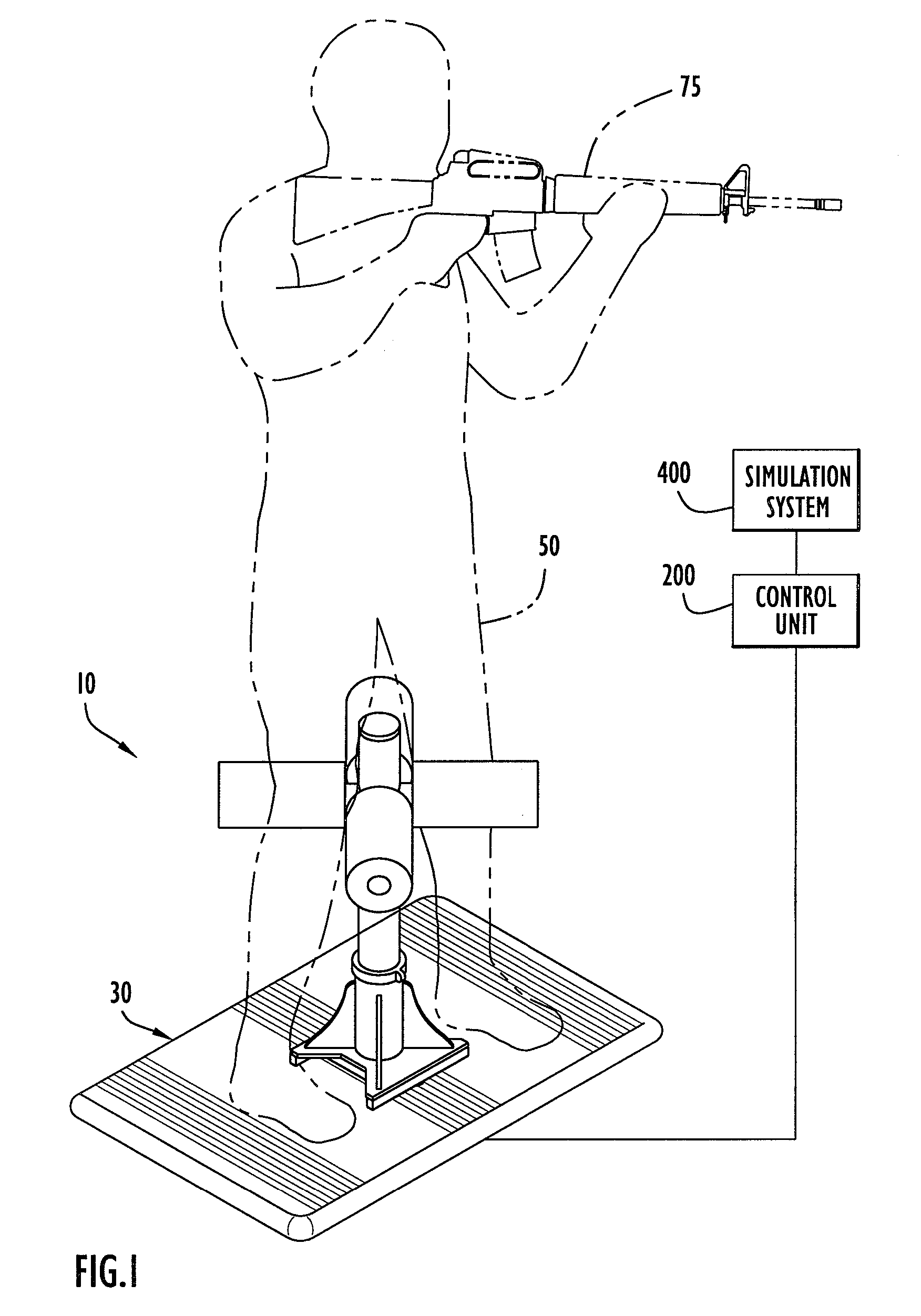
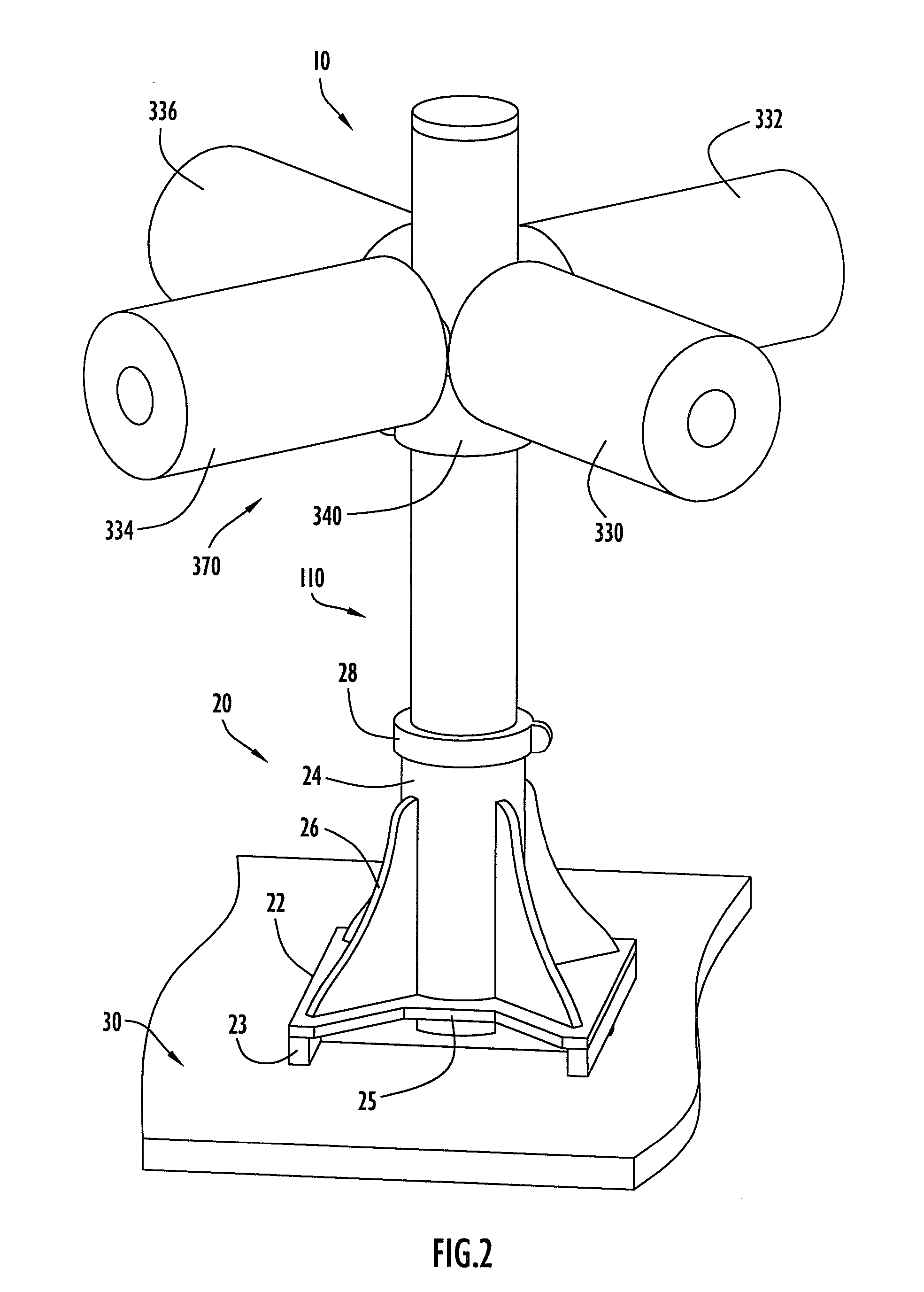
[0038] An interface device according to the present invention and coupled to a simulation system is illustrated in FIG. 1. Initially, an interface device 10 according to the present invention is preferably coupled to a device control unit 200 that processes information from the interface device. The control unit is further coupled to a simulation system 400 that provides and updates a simulation or a virtual environment in accordance with manipulation of the interface device by a lower body portion (e.g., legs, etc.) of a user 50. The simulation system typically includes a simulation processor 414 (FIG. 5) and a monitor or other display device 416. For example, user 50 may employ a head set as display device 416 to provide the virtual environment. The simulation processor basically includes a processing device to execute simulation software to provide a virtual reality environment on the display device. The simulation system may be implemented by a Silicon Graphics or Evans and Suth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com