Event structured file system (ESFS)
a file system and event technology, applied in the field of computer and file system, can solve the problems of inefficiency, non-portability of the file system across different operating systems and media, etc., and achieve the effect of efficient and consistent implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
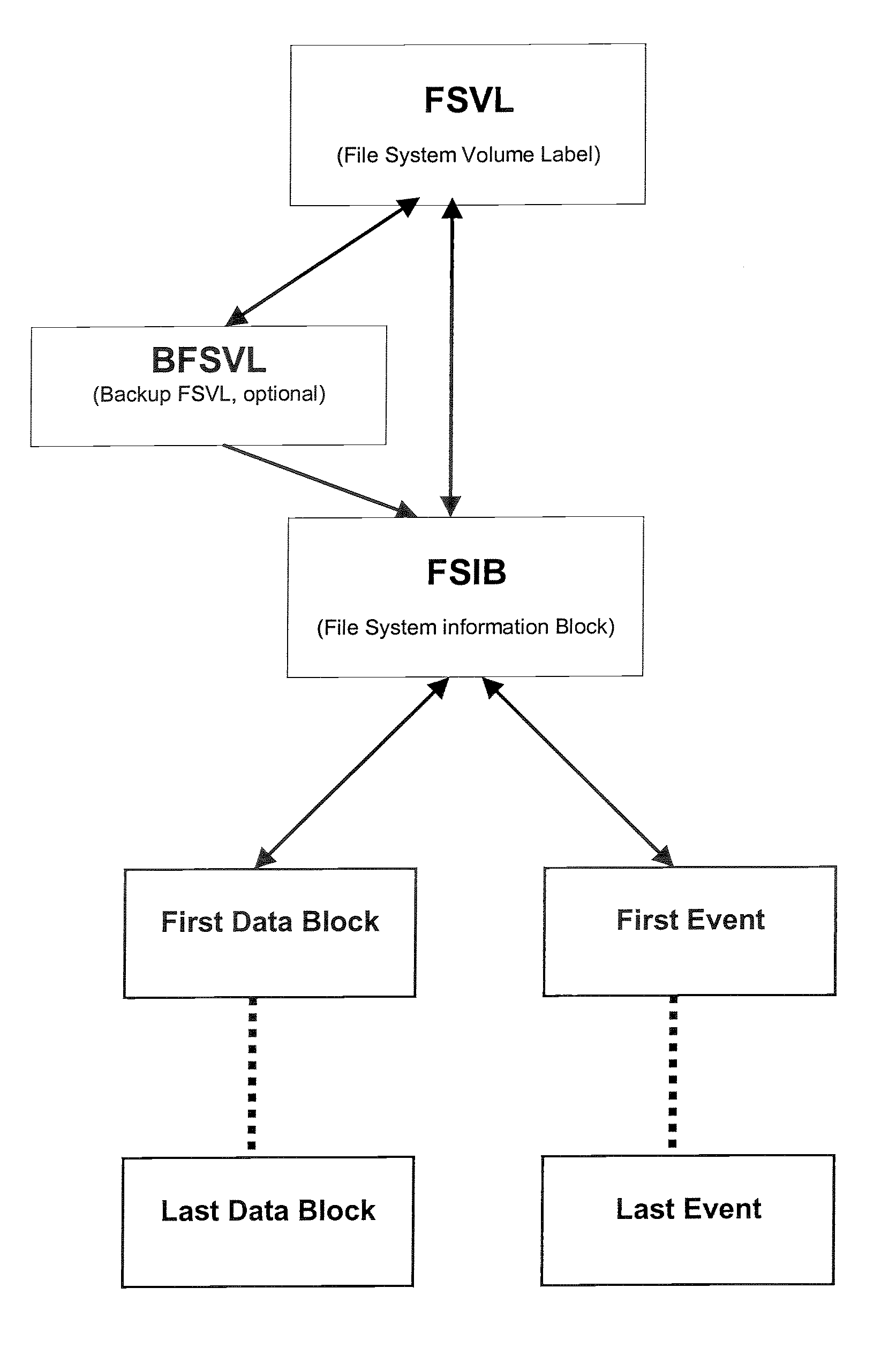
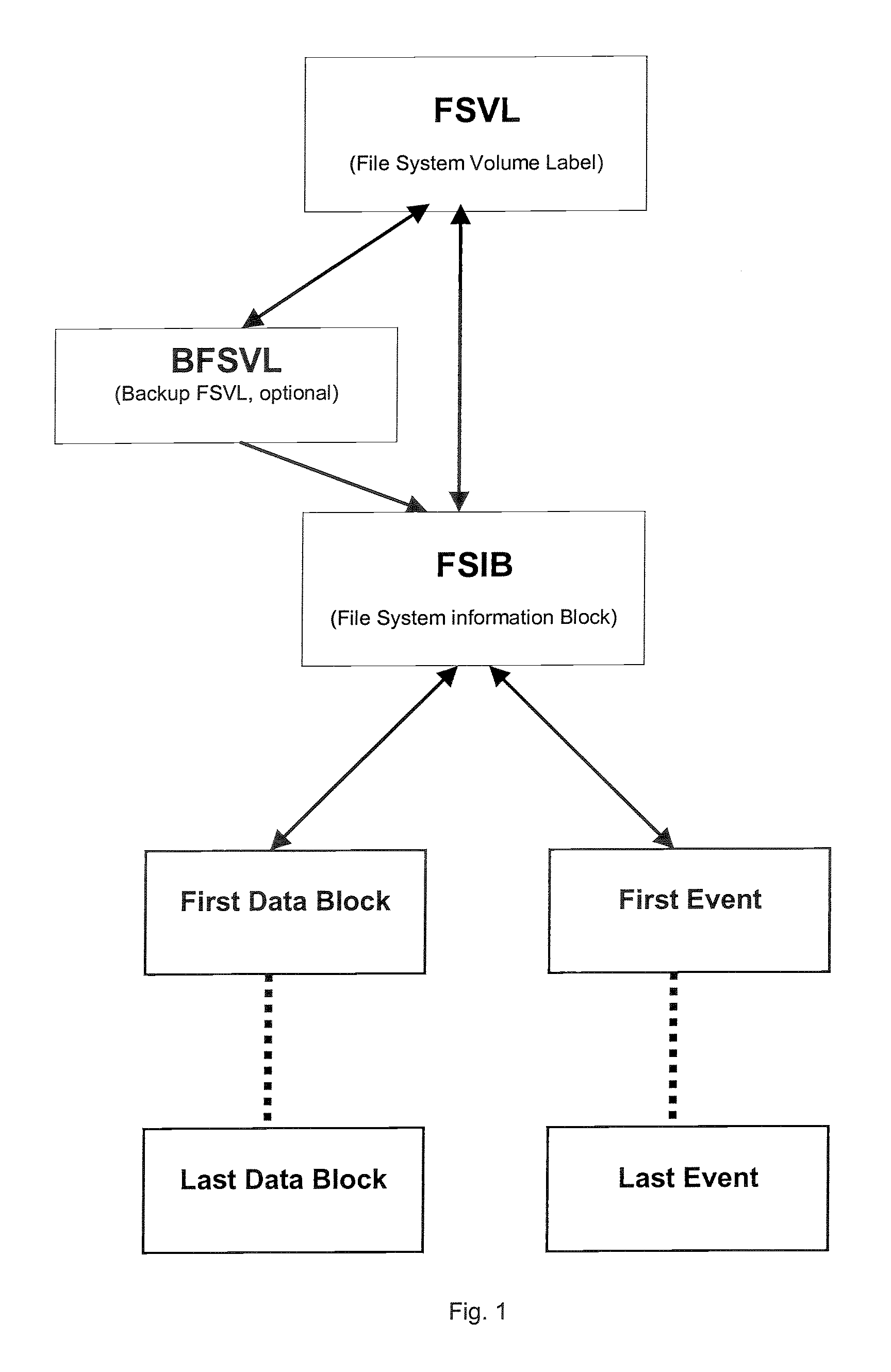
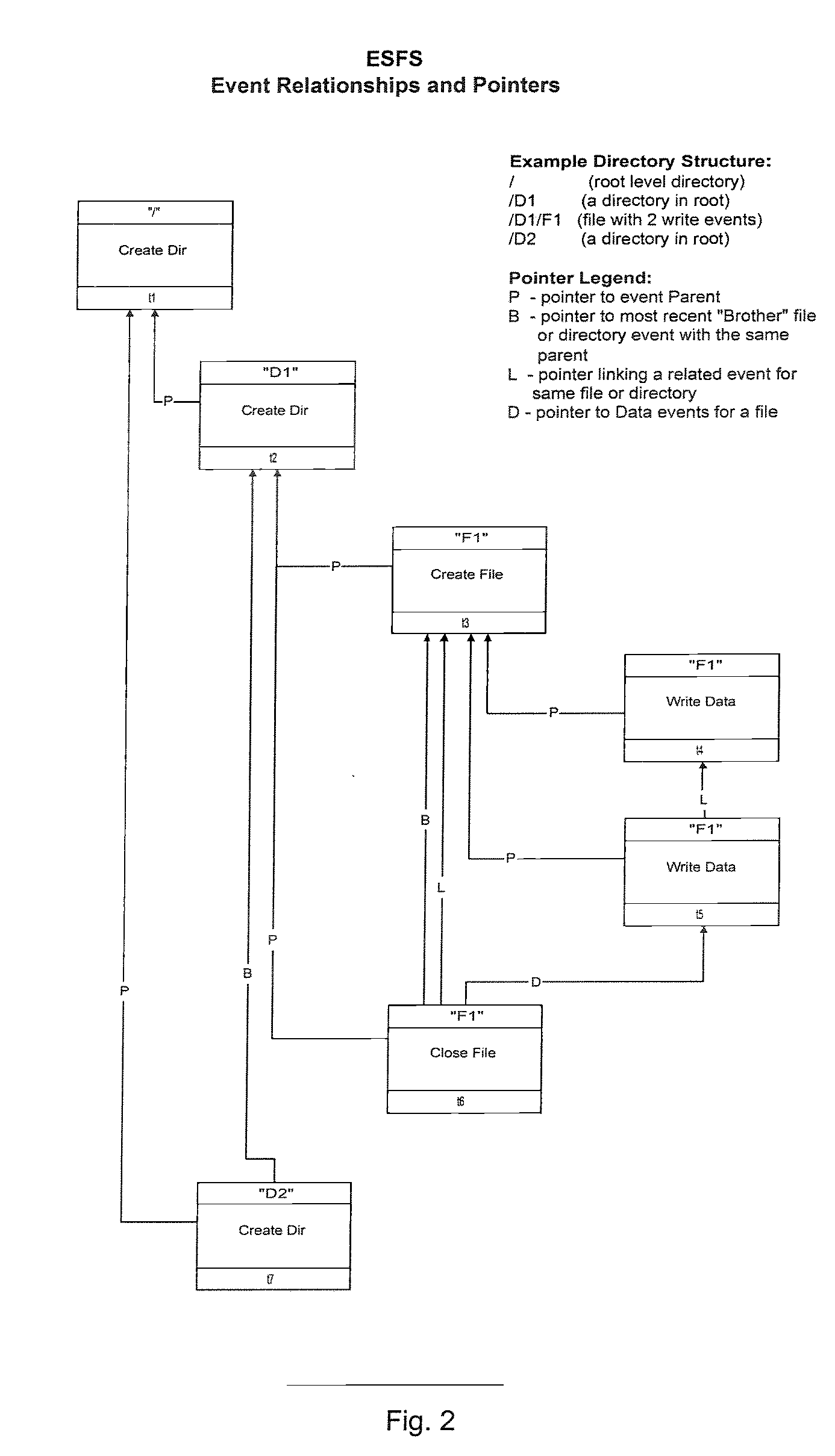
[0070] Generally, the present invention provides a File System comprising an ordered list of Events associated with Data, that may be implemented identically on all common digital storage media types, including, write-once, erasable, and rewritable media, whether in sequential or random-access mode, (or otherwise).
[0071] The system uses the sequence and type of Event with its associated Data without reference to any external table or journal entry to operate and be verifiable.
[0072] The system's list of Events is accessible in a predefined sequence, normally, but not limited to, reverse chronological order.
[0073] ESFS includes an ordered list of Events associated with Data made verifiable in whole or in part by provision of checksums and security information within the Events and data verification means.
[0074] ESFS may be efficiently implemented using a “Write Once Read Many” (WORM) model, irrespective of the underlying media type. Previously written areas of the media may be re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com