Patents
Literature
153 results about "Disk sector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
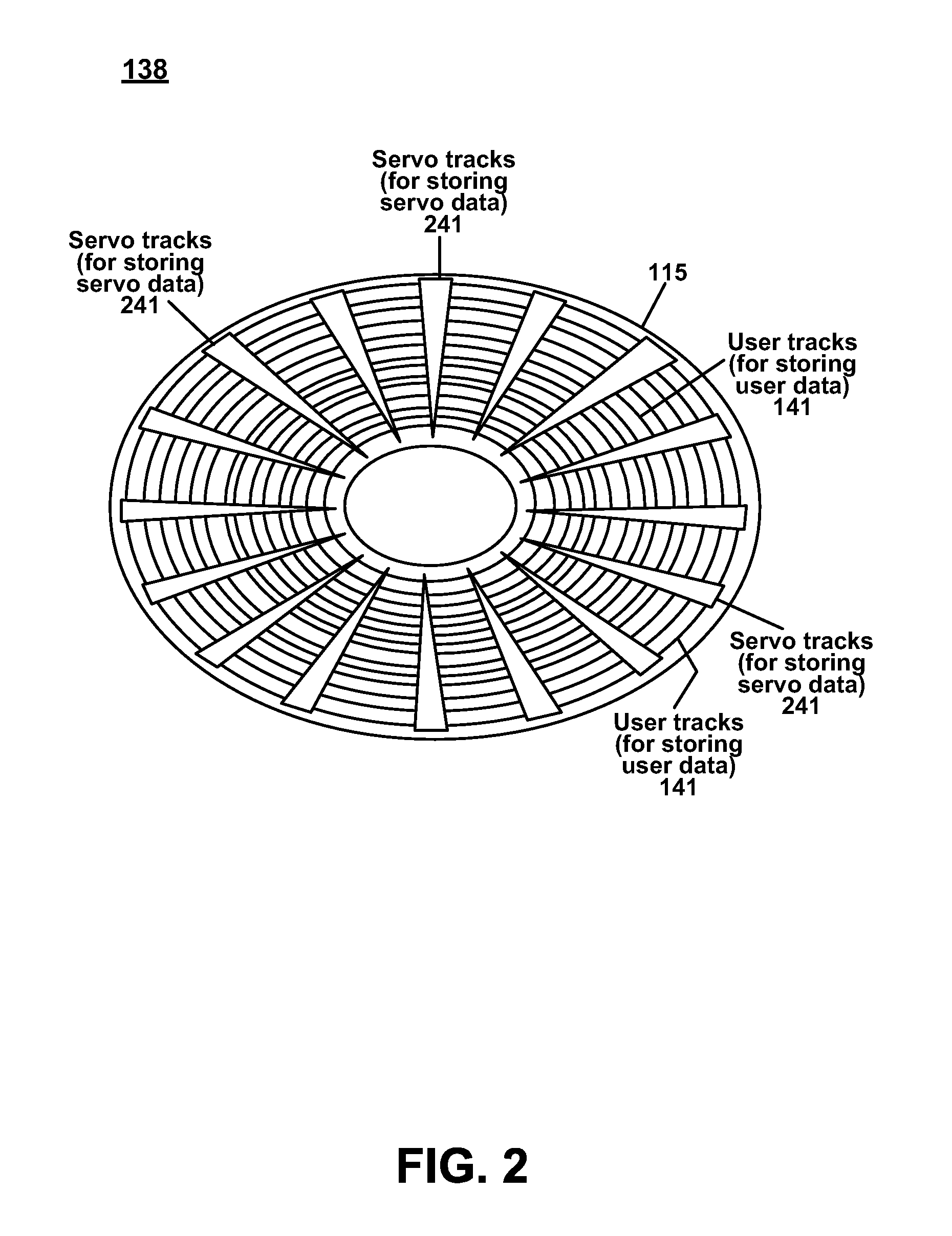
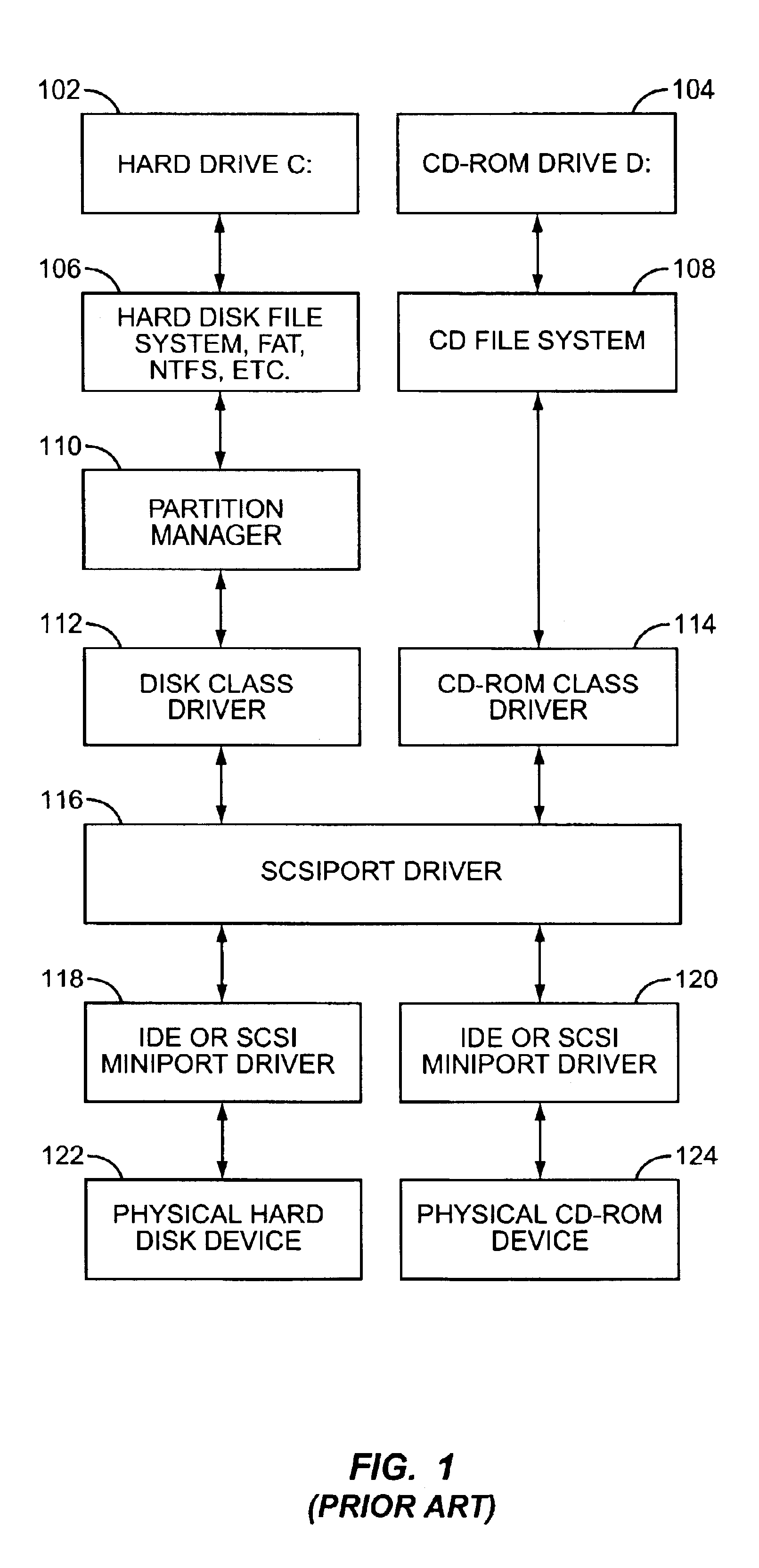
In computer disk storage, a sector is a subdivision of a track on a magnetic disk or optical disc. Each sector stores a fixed amount of user-accessible data, traditionally 512 bytes for hard disk drives (HDDs) and 2048 bytes for CD-ROMs and DVD-ROMs. Newer HDDs use 4096-byte (4 KiB) sectors, which are known as the Advanced Format (AF).
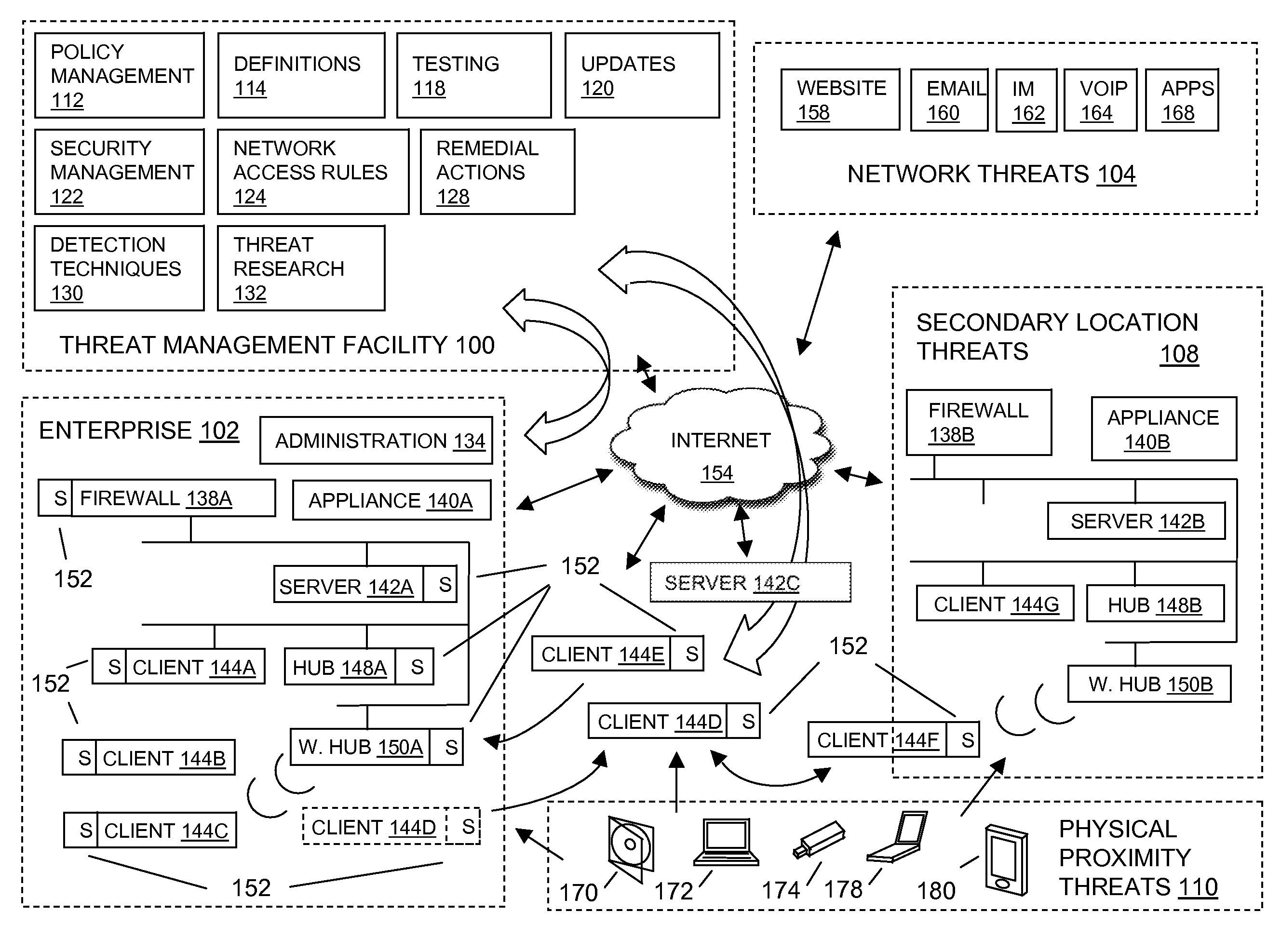
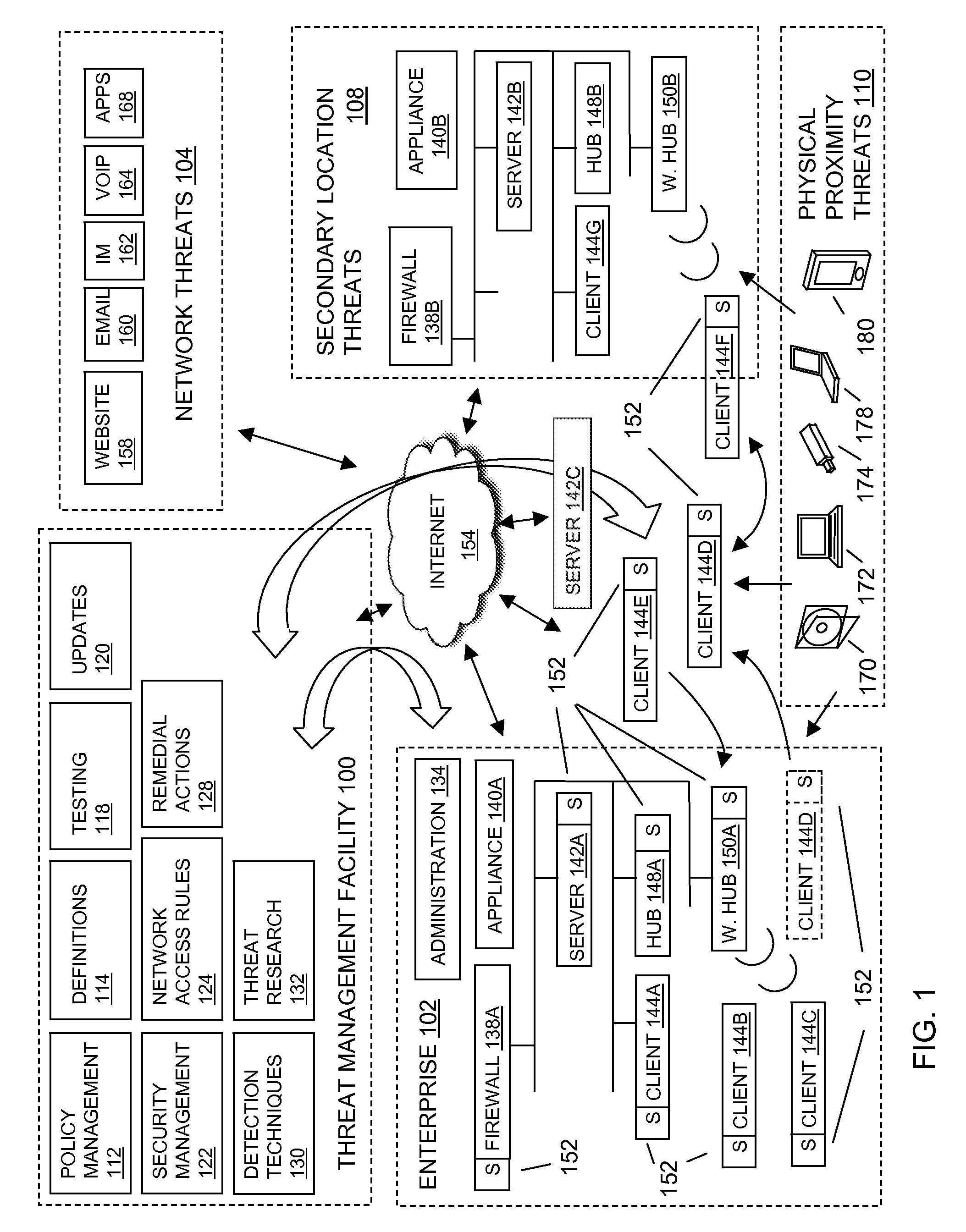
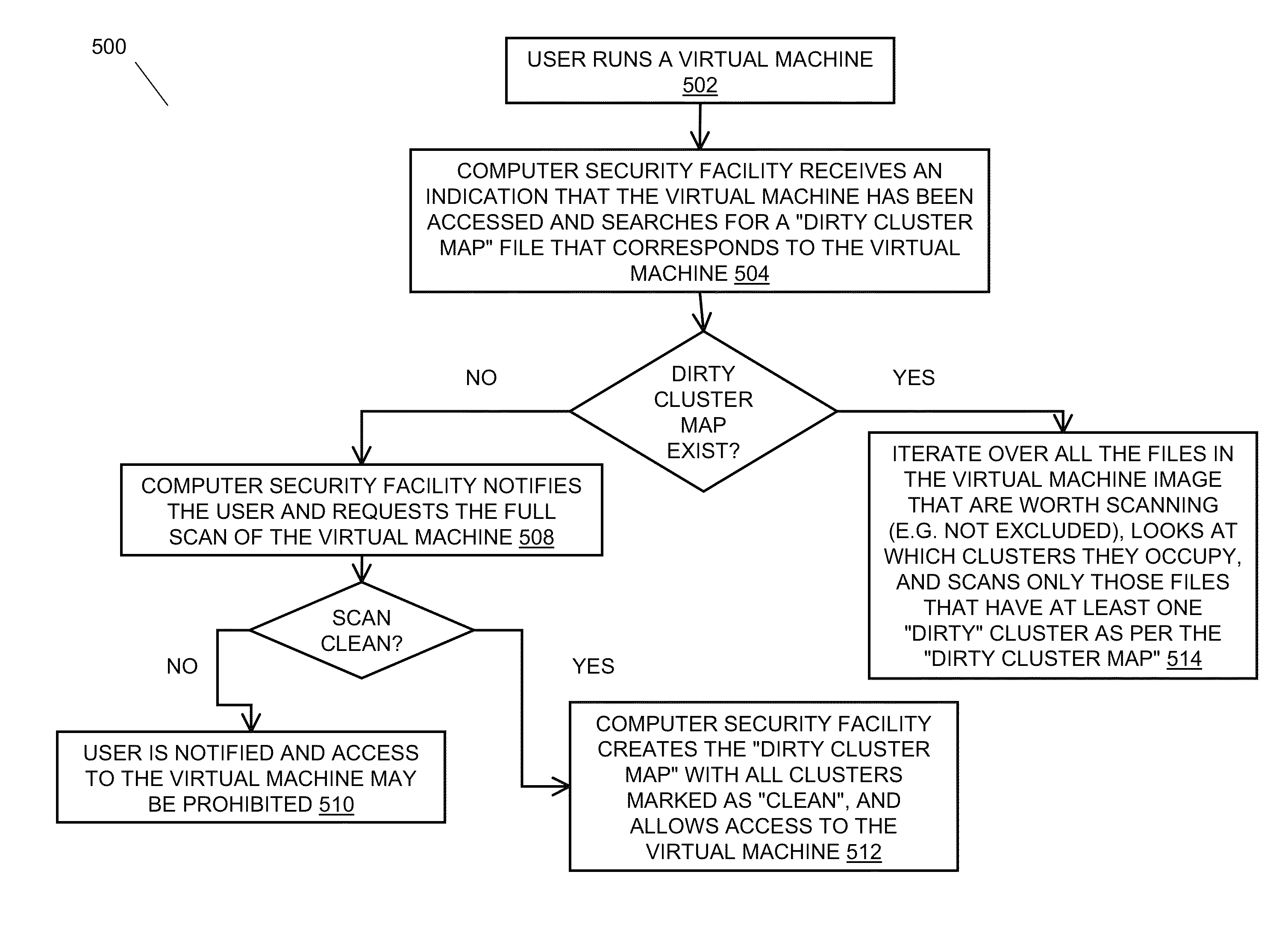
Modified file tracking on virtual machines
ActiveUS20100251363A1Access control be minimizedReduce controlMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionDisk sectorVirtual machine
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for tracking modified files on a virtual machine including the steps of identifying an altered disk sector, associating the altered disk sector with code that is operated in a virtual machine, and causing a malicious code scan to be performed on the code.
Owner:SOPHOS
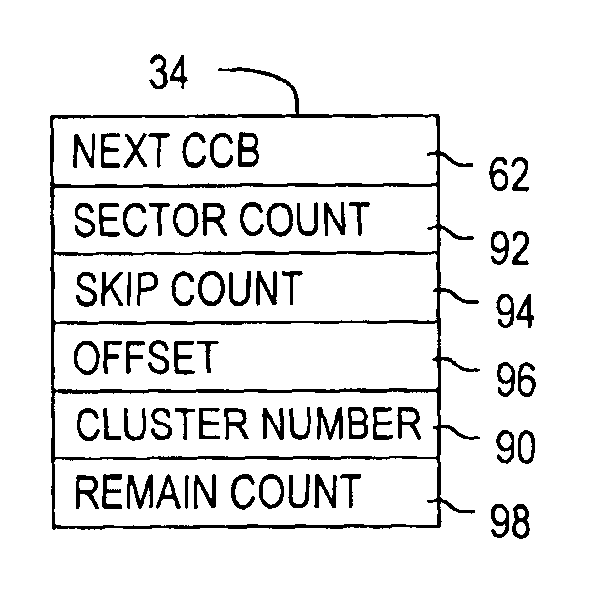
Cluster-based cache memory allocation
InactiveUS6996669B1Uniform sizeIncrease the lengthMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogical block addressingControl system
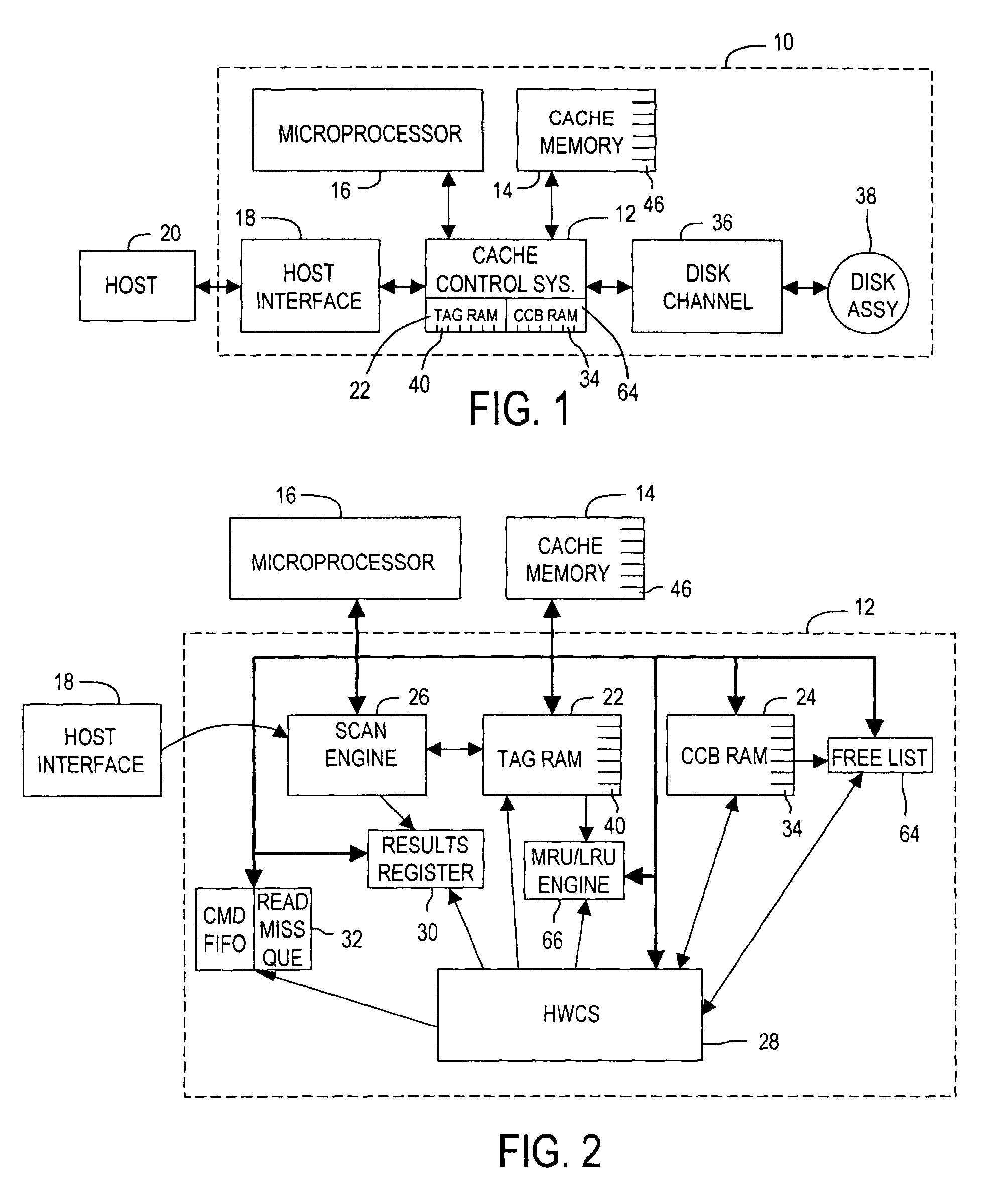
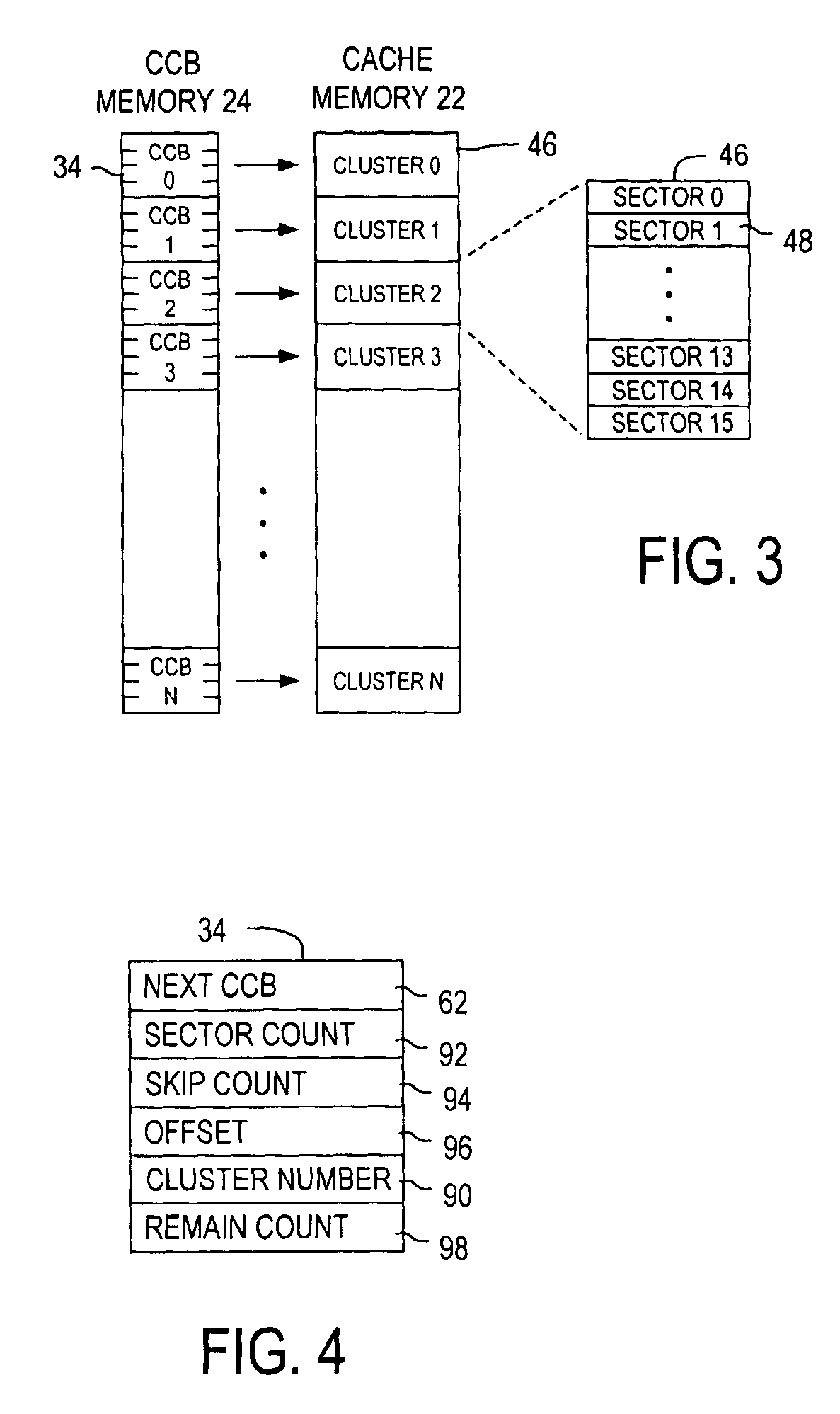
The present invention relates to a disk drive including a cache memory having a plurality of sequentially-ordered memory clusters for caching disk data stored in sectors (not shown) on disks of a disk assembly. The disk sectors are identified by logical block addresses (LBAs). A cache control system of the disk drive comprises a cluster control block memory, having a plurality of cluster control blocks (CCB), and a tag memory 22, having a plurality of tag records, that are embedded within the cache control system. Each CCB includes a cluster segment record with an entry for associating the CCB with a particular memory cluster and for forming variable length segments of the memory clusters without regard to the sequential order of the memory clusters. Each tag record assigns a segment to a continuous range of LBAs and defines the CCBs forming the segment. Each segment of the memory clusters is for caching data from a contiguous range of the logical block addresses. The cache control system efficiently exploits available memory clusters for responding to host commands.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
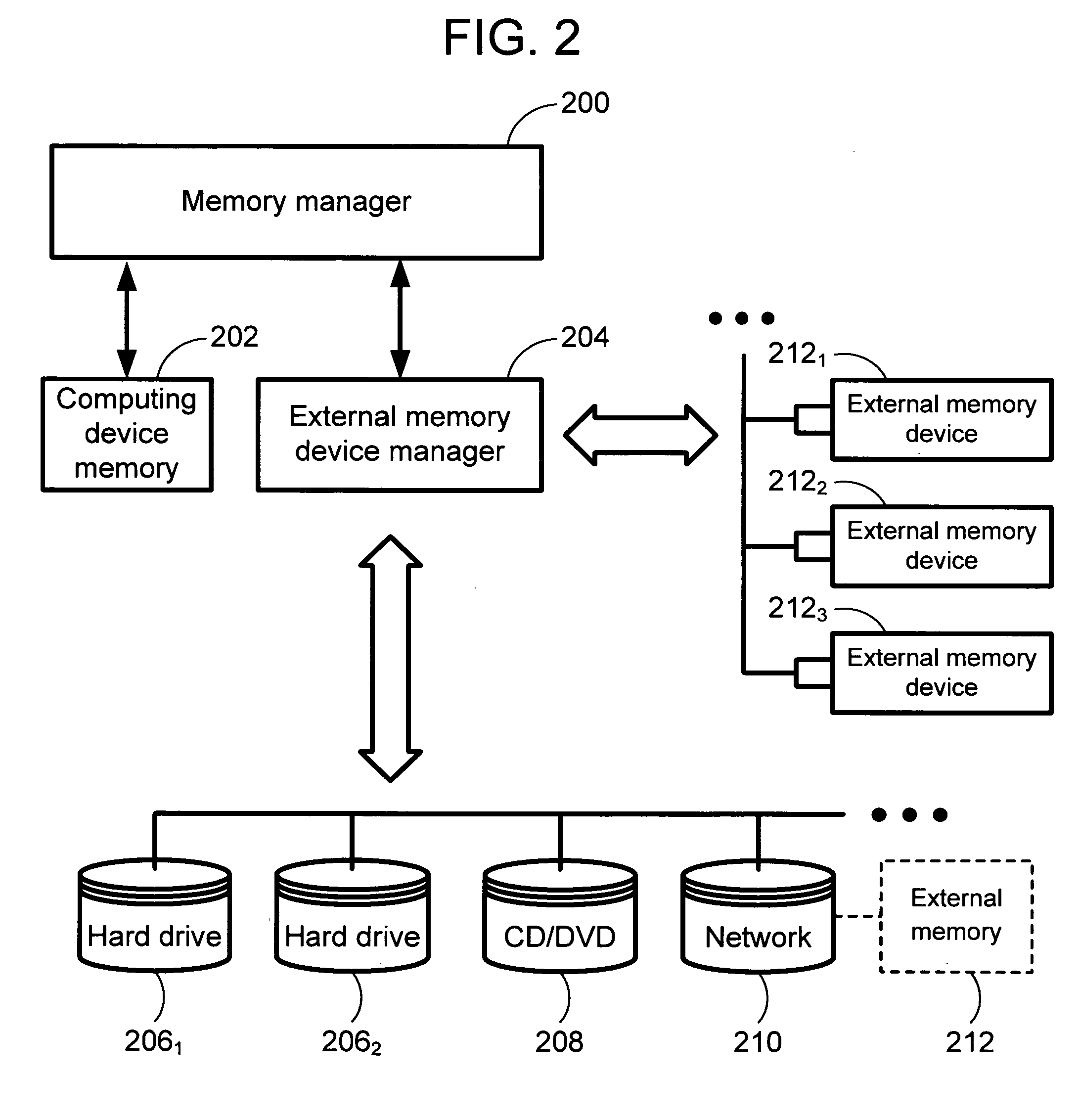
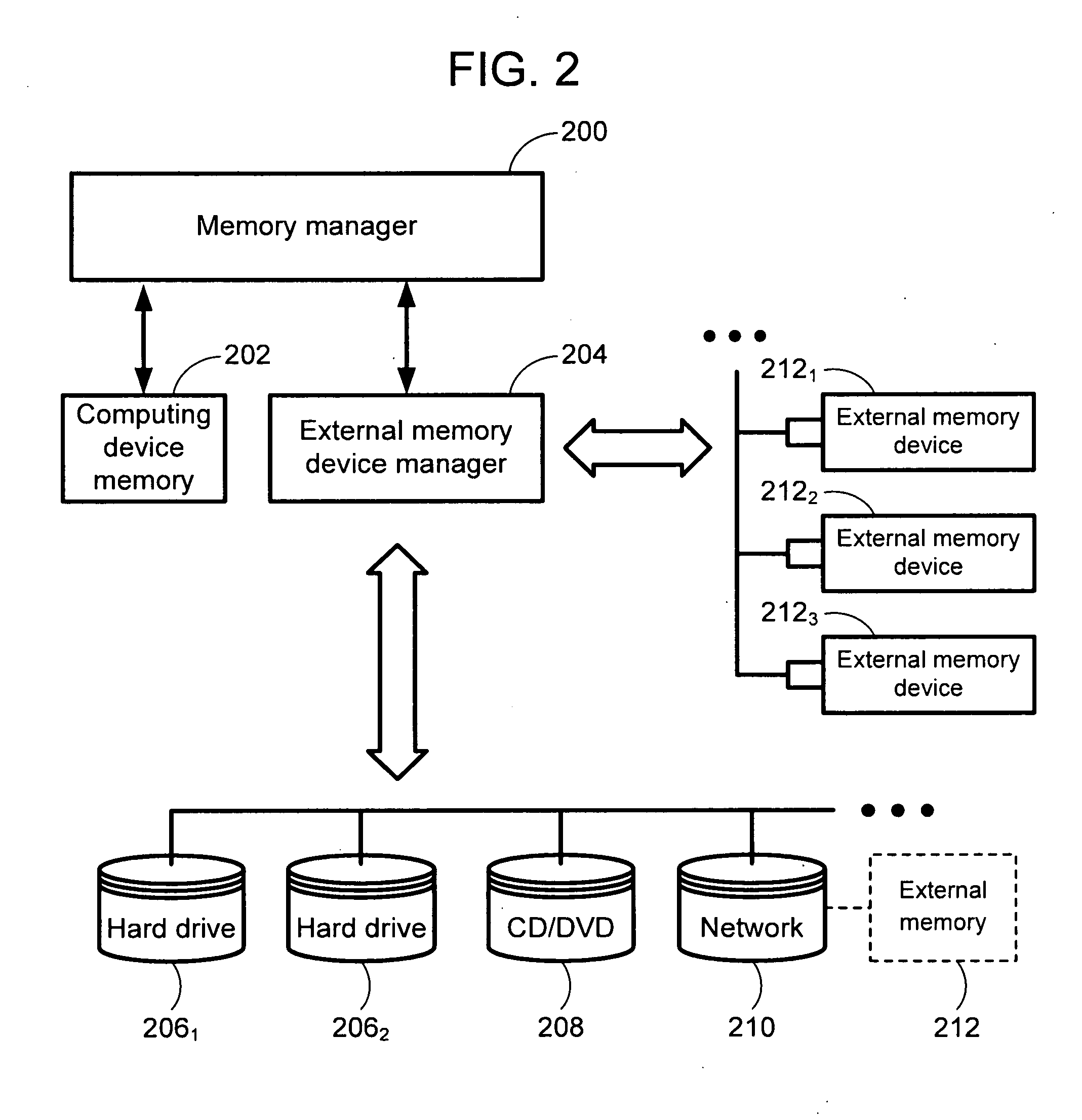
Using external memory devices to improve system performance
ActiveUS20060090031A1Improve performanceIncrease productivityInput/output to record carriersComponent plug-in assemblagesHard disc driveTerm memory
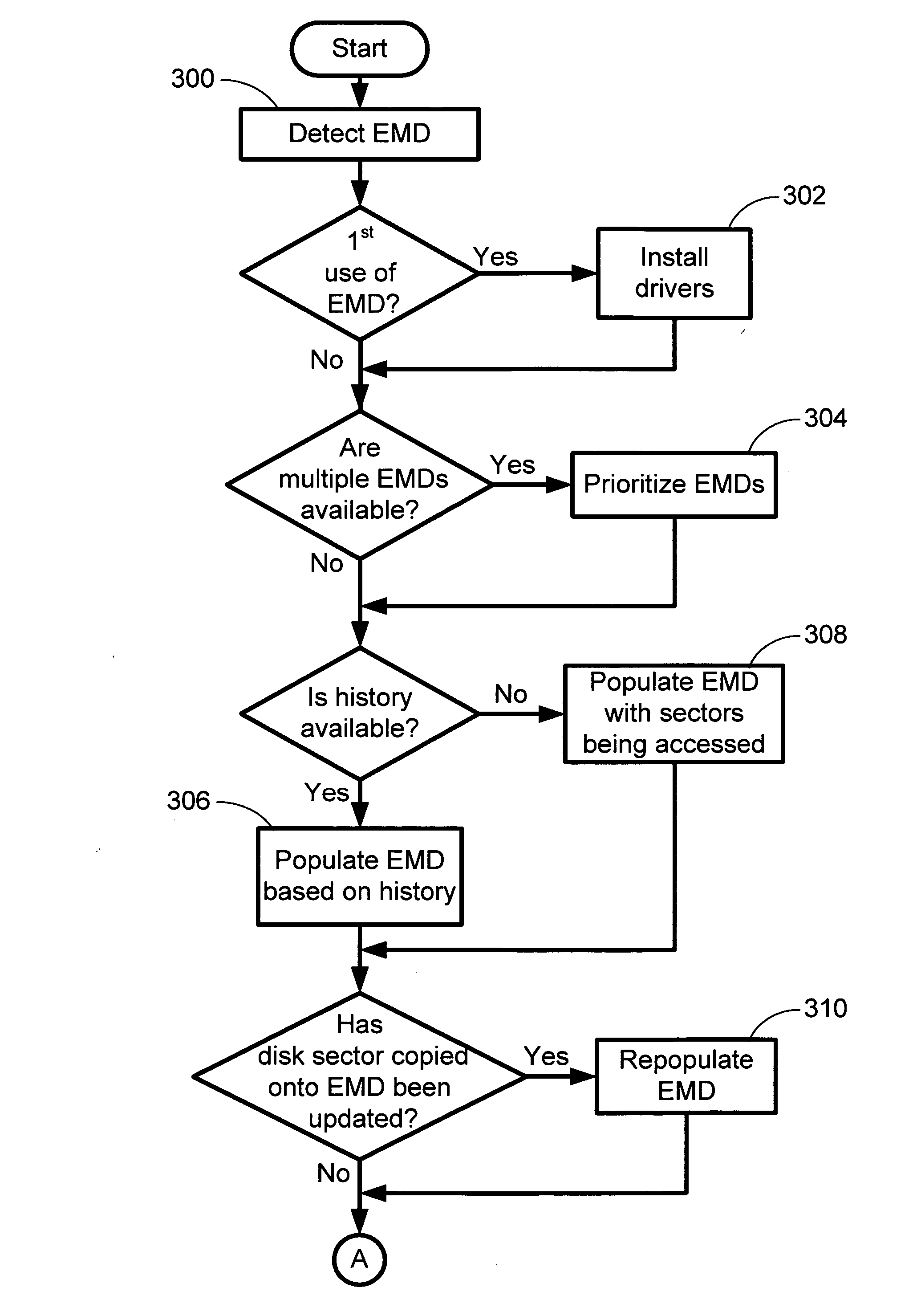
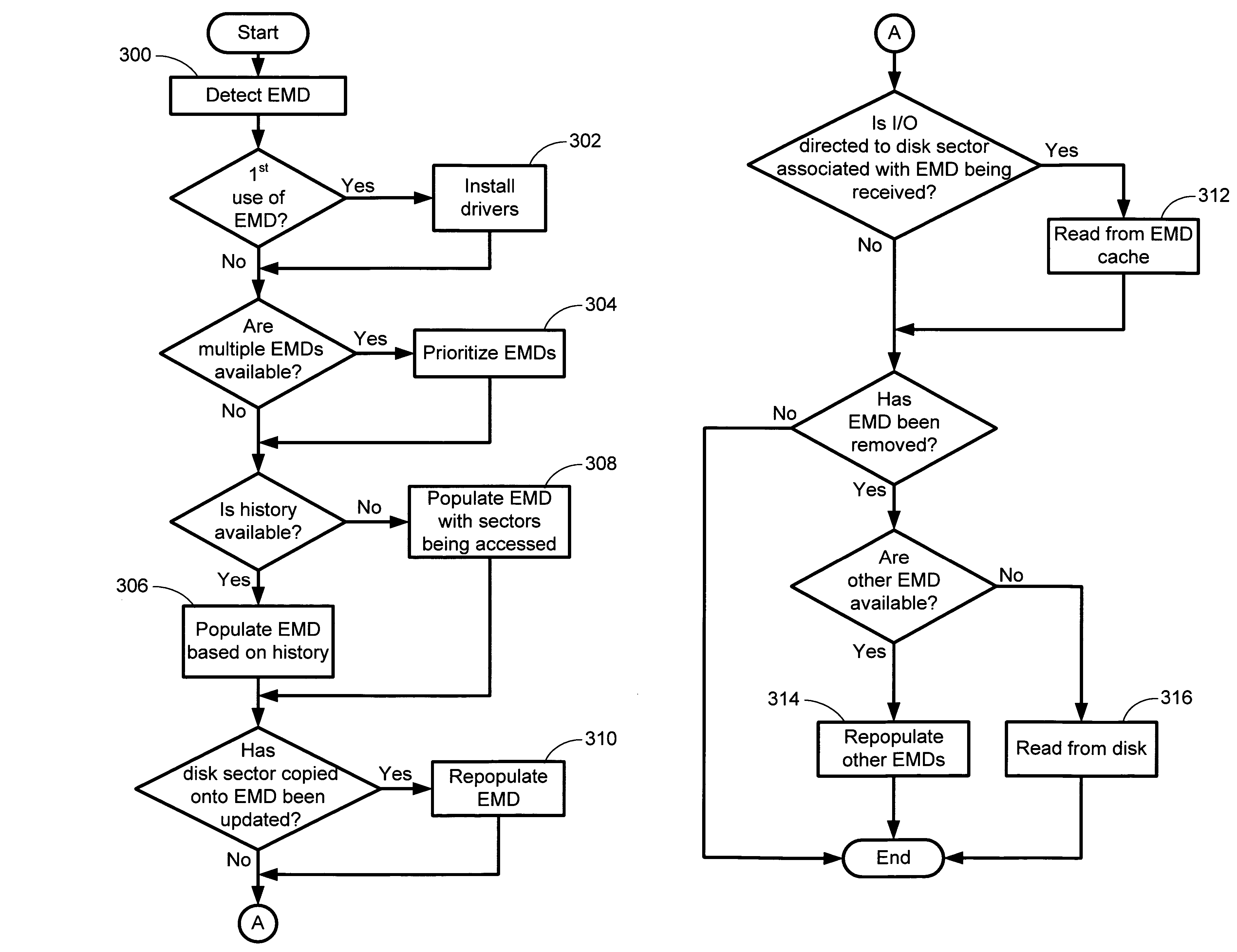
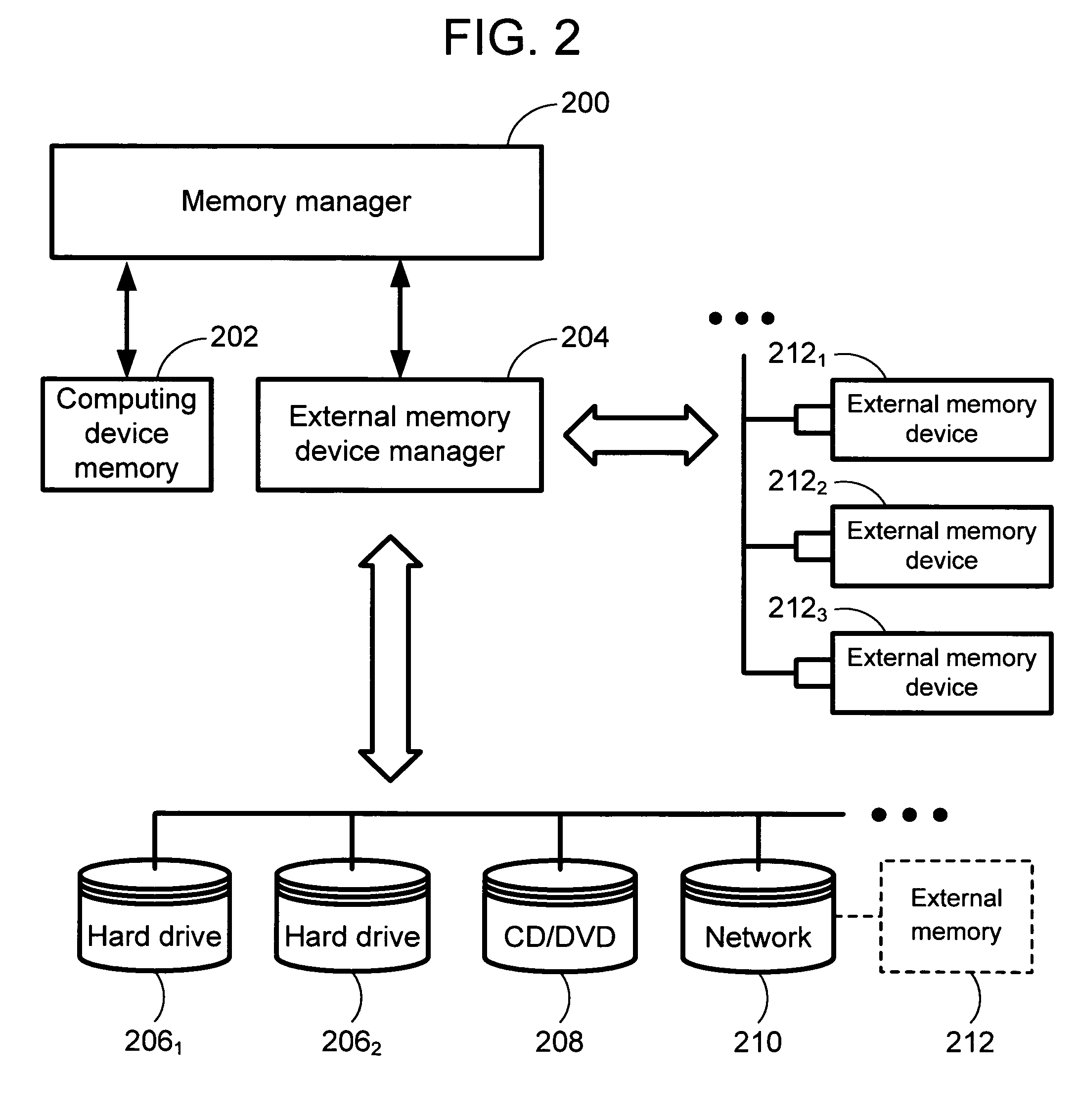
The invention is directed towards a system and method that utilizes external memory devices to cache sectors from a rotating storage device (e.g., a hard drive) to improve system performance. When an external memory device (EMD) is plugged into the computing device or onto a network in which the computing device is connected, the system recognizes the EMD and populates the EMD with disk sectors. The system routes I / O read requests directed to the disk sector to the EMD cache instead of the actual disk sector. The use of EMDs increases performance and productivity on the computing device systems for a fraction of the cost of adding memory to the computing device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
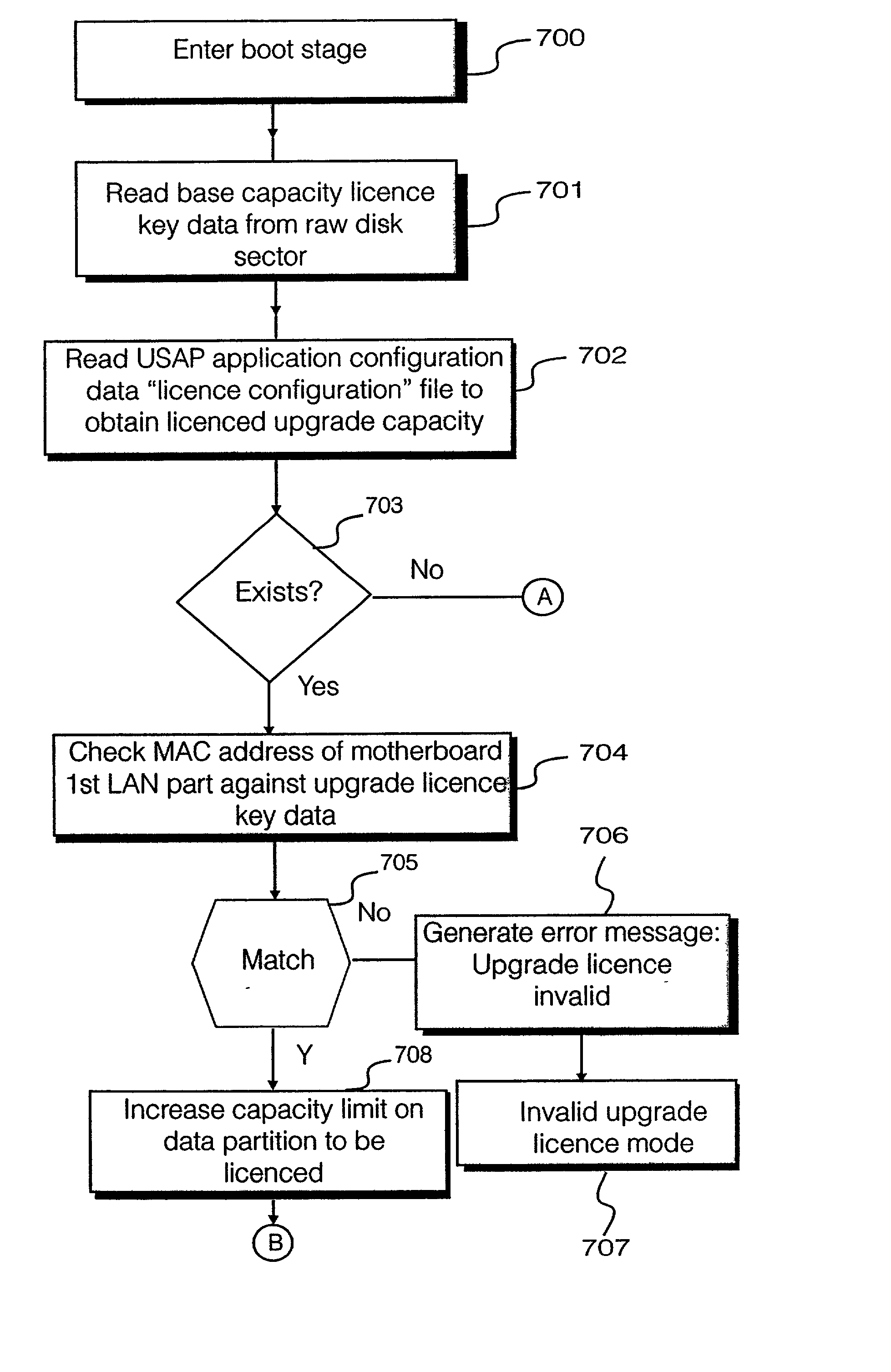
Upgrade of licensed capacity on computer entity
InactiveUS20020188704A1Need to replace data storage hardware is reduced or eliminatedEasy to upgradeDigital computer detailsData resettingData storingDisk sector
A headless computer entity is provided with a base license key data stored on a raw disk sector separate from a system disk and a data disk. The license key data is used to control the available data storage capacity within the headless computer entity, and protect the computer entity from unauthorized upgrade to a higher product specification. Upgrades in capacity of the computer entity can be achieved without replacement of data disk, by altering an upgrade license key data to allow use of spare data storage capacity on the data disk.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
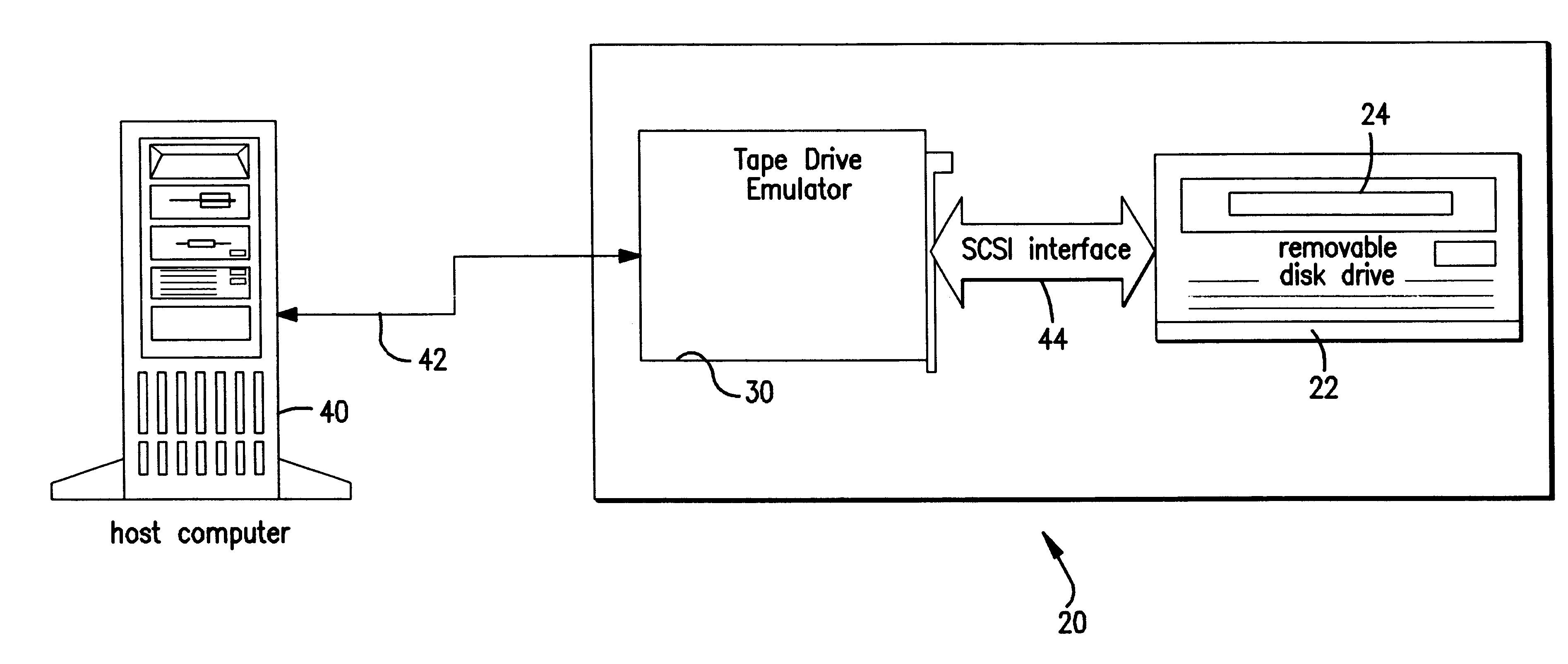
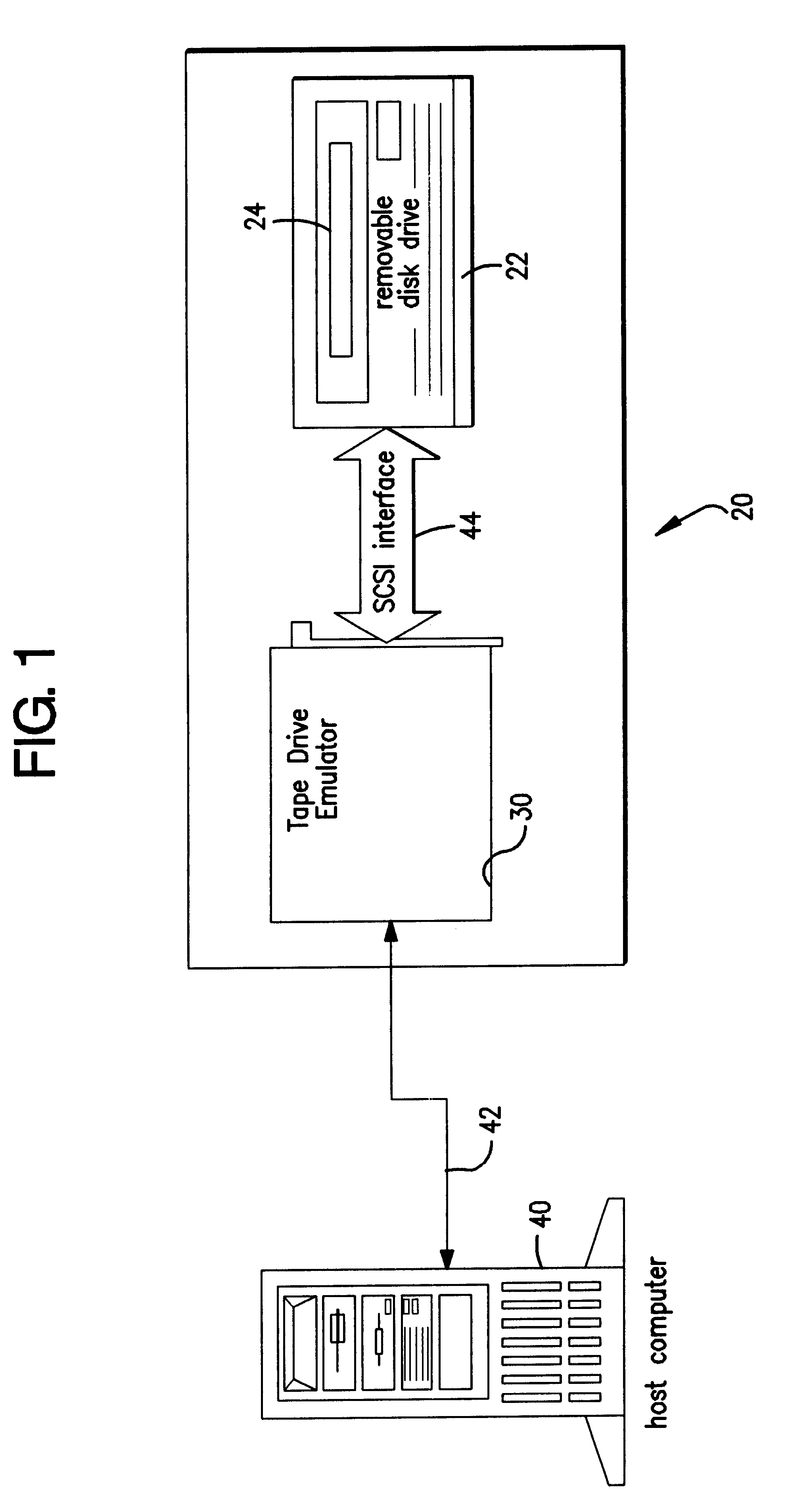
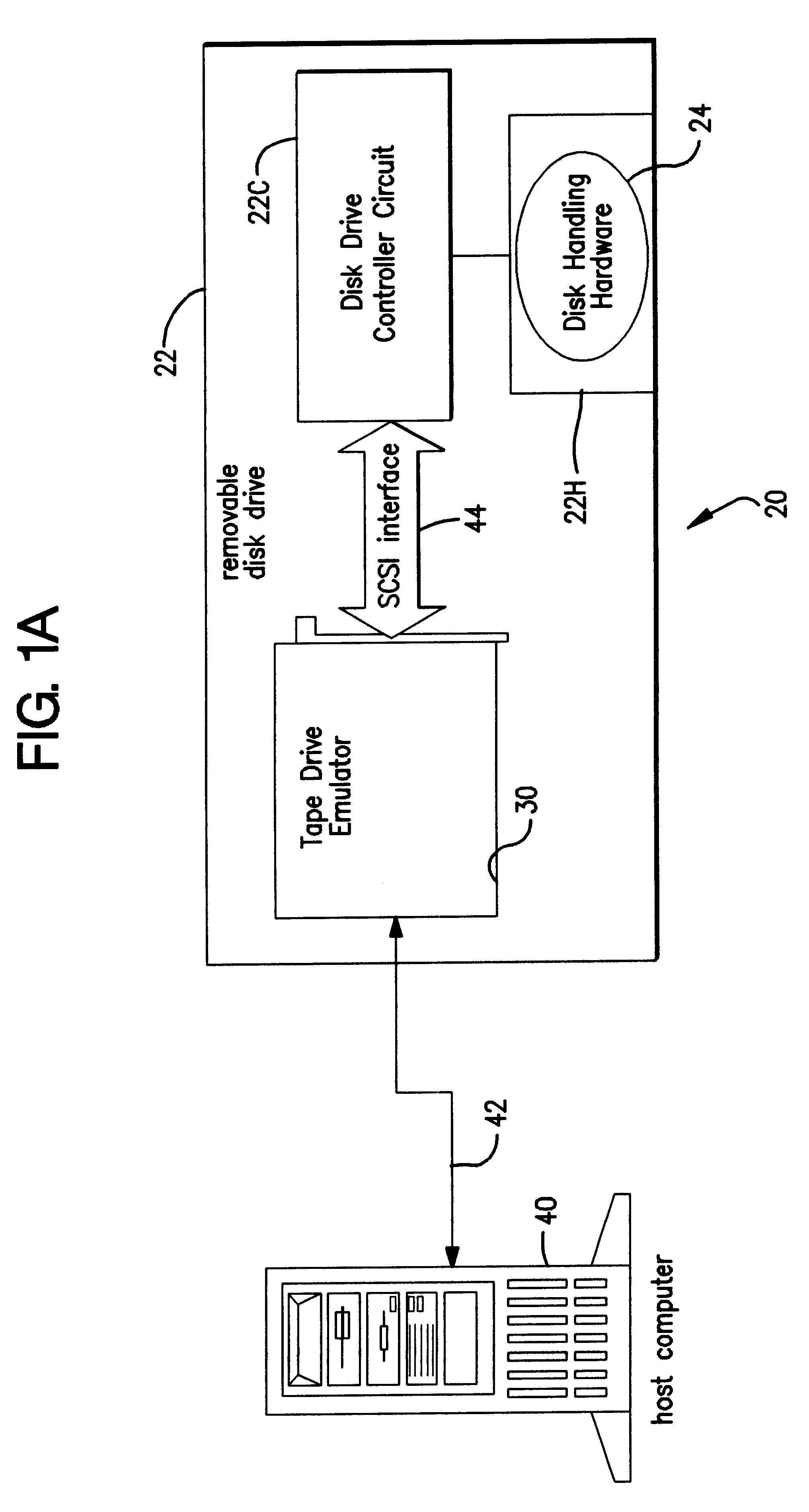
Tape drive emulation by removable disk drive and media formatted therefor
InactiveUS6389503B1Input/output to record carriersRecord information storageData integrityFrame based
A disk drive detects whether a disk inserted therein has a frame-based enhanced formatting. Disks having the frame-based enhanced formatting are readable by enhanced drives, e.g., those with the tape drive emulators. The frame-based enhanced formatting imposes on the data (1) an data organization, imperceptible to disk drive 22, for rendering the data expressible and locatable in a tape drive format, and (2) an additional degree of error correction that provides enhanced data integrity necessary for data backup / restore operations. The detection stems from a secondary formatting operation of the invention in which a format type identification is recorded on the disk. Preferably, the format type identification is recorded as one disk sector at a beginning logical block address of the disk, and forms part of a volume header frame. The volume header frame is followed by a directory comprising one or more directory frames.
Owner:TANDBERG DATA
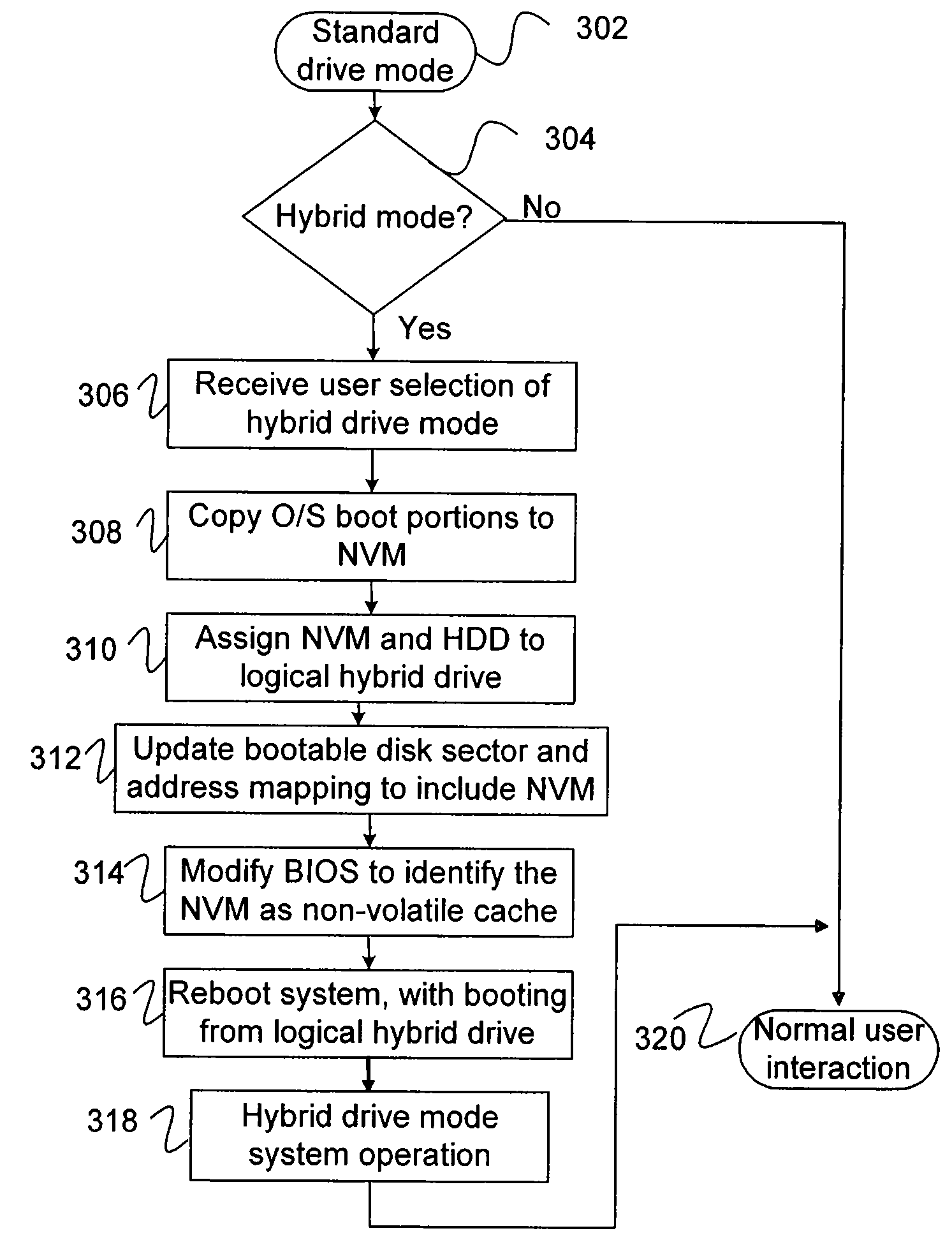
Method of configuring non-volatile memory for a hybrid disk drive
InactiveUS20080005462A1Increase flexibilityGreat backward-compatibilityMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTHard disc driveOperational system
A method is provided to operate a non-volatile memory (NVM) in a hybrid drive mode in response to a user selection. To operate in hybrid drive mode, a computer operating system and a basic input / output system are preferably updated to identify the NVM as part of the same logical bootable disk, or logical hybrid drive, as a hard disk drive. Bootable disk sector and address mapping can be modified to reflect the addition or removal of the NVM. The NVM is preferably user-replaceable and upgradeable without opening the computer's casing. When the NVM includes more than one NVM module, a first NVM module can operate in hybrid disk mode while a second NVM module operates in a normal storage mode. Since no internal hardware modification is required, this approach can provide hybrid disk performance using conventional hardware, or to enhance performance of an existing hybrid drive.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
Rapid regeneration of failed disk sector in a distributed database system
ActiveUS7281160B2Avoid the needPromote recoveryRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsRecord information storageFailoverRAID
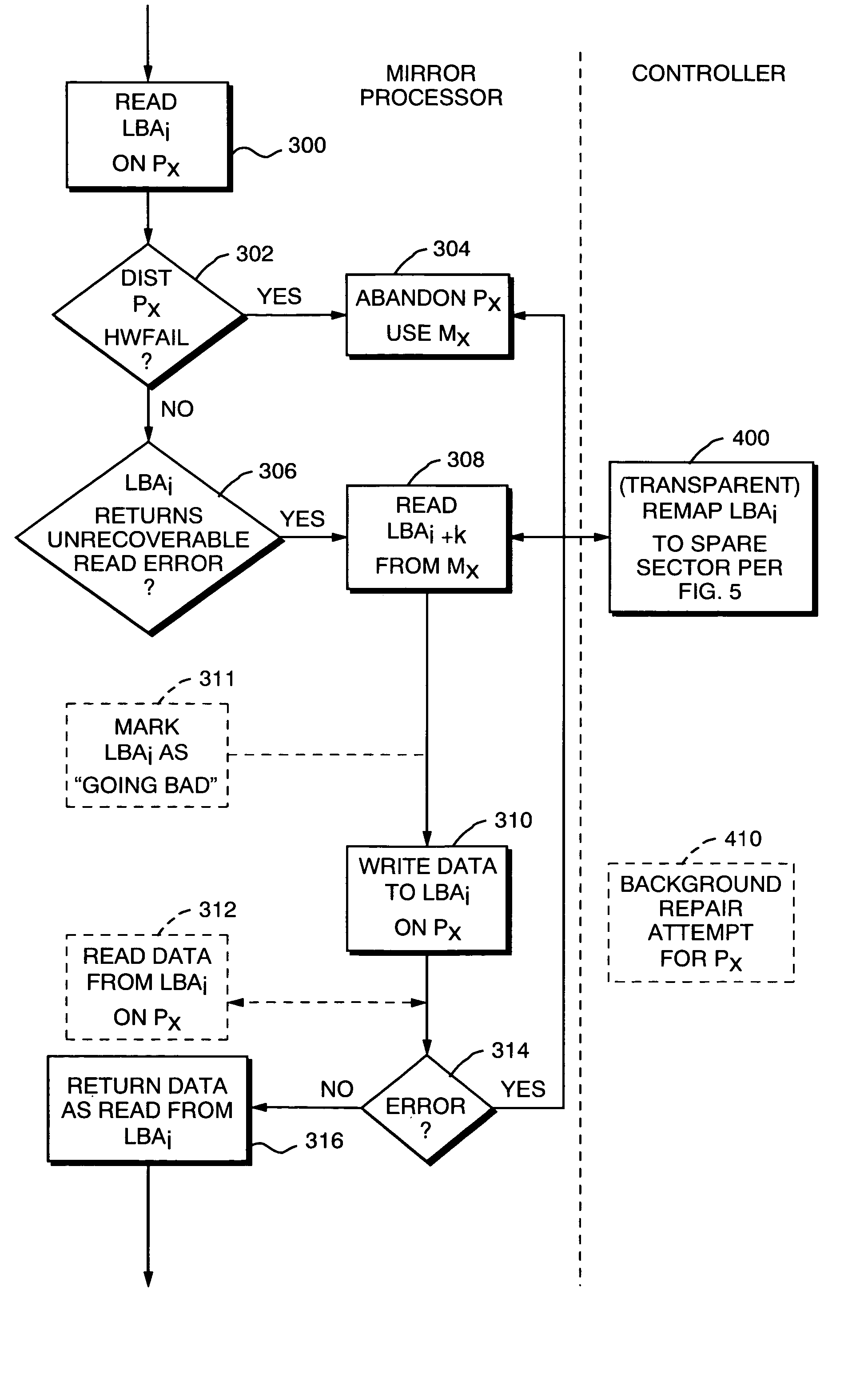
A technique for read error failover processing in a mirrored disk system such as a Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) system, where individual disk units perform Logical Block Address (LBA) remapping. A read error causes a disk controller to report an “unrecoverable” read error to a RAID controller. After receiving this report of an unrecoverable read error, rather than simply switching over to a mirror, the RAID controller first checks to see whether the disk that caused the error can successfully reassign an LBA. In particular, the RAID controller can retrieve the data that was associated with the failed LBA from the mirror, and then write that data to the offending disk. The disk controller for that disk will then perform its standard LBA remapping, and write the data to a new, good sector. Only if this process does not succeed is the offending disk then treated by the RAID controller as having failed sufficiently to require failover to the mirror.
Owner:IMB INT GRP BV
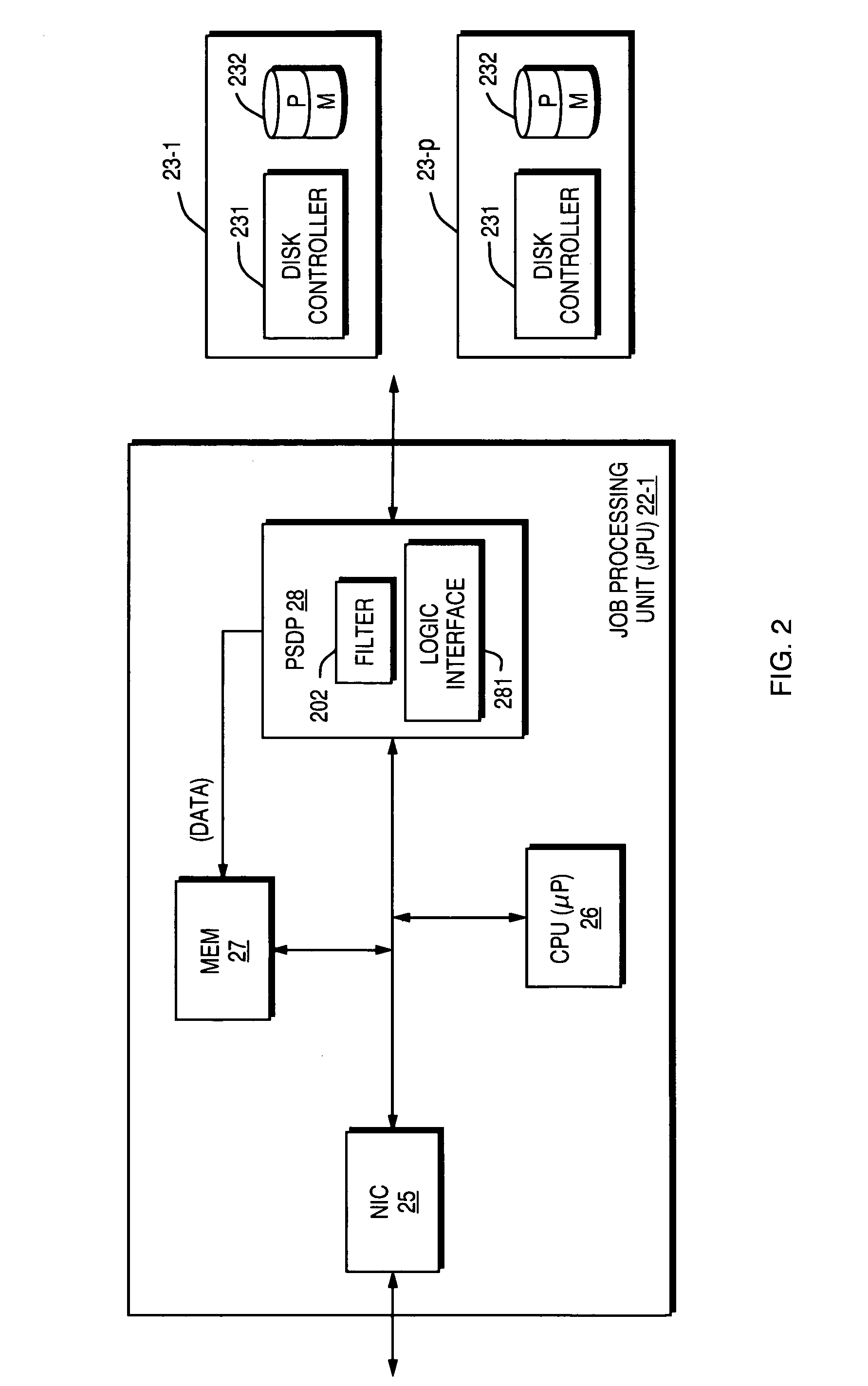
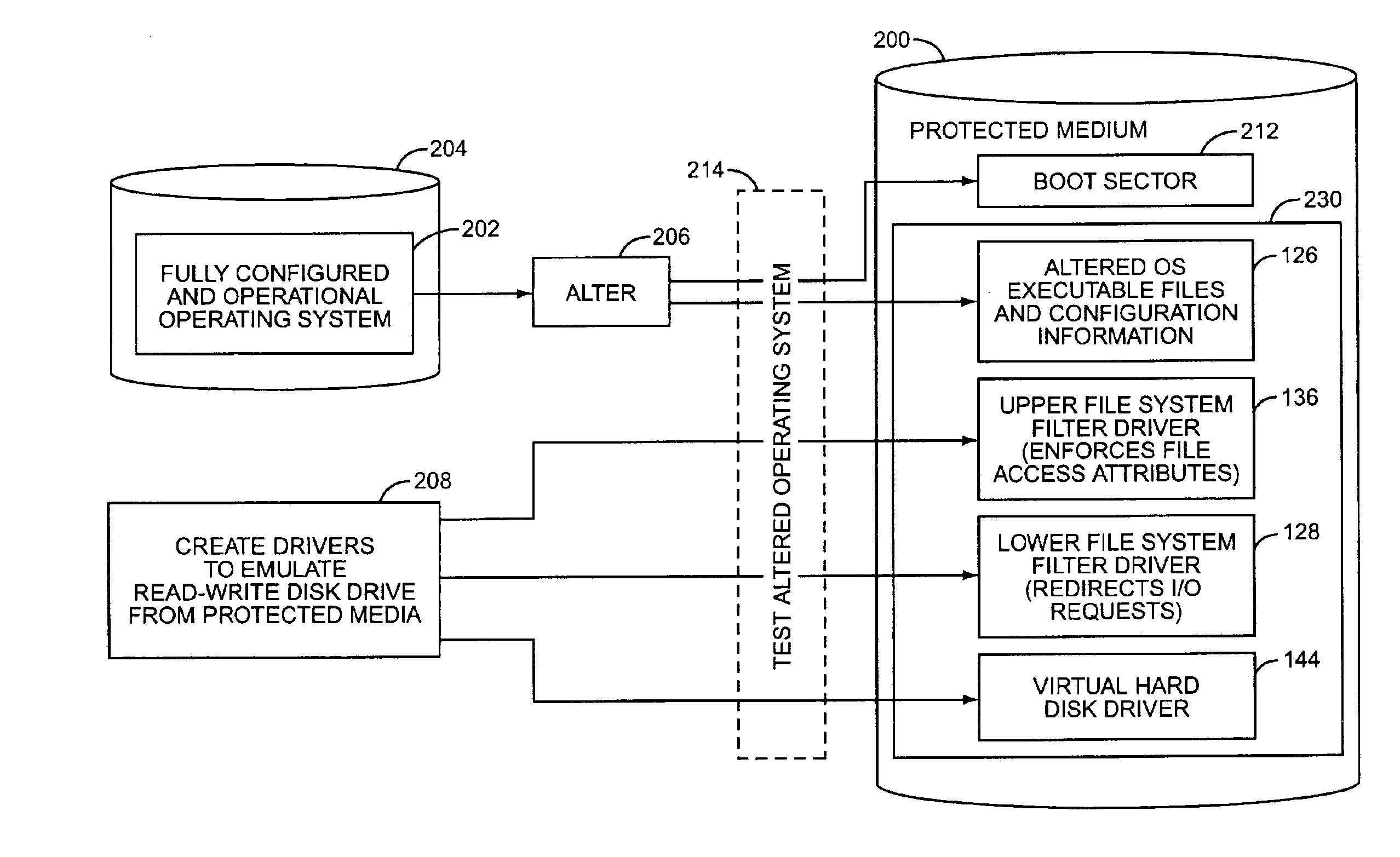
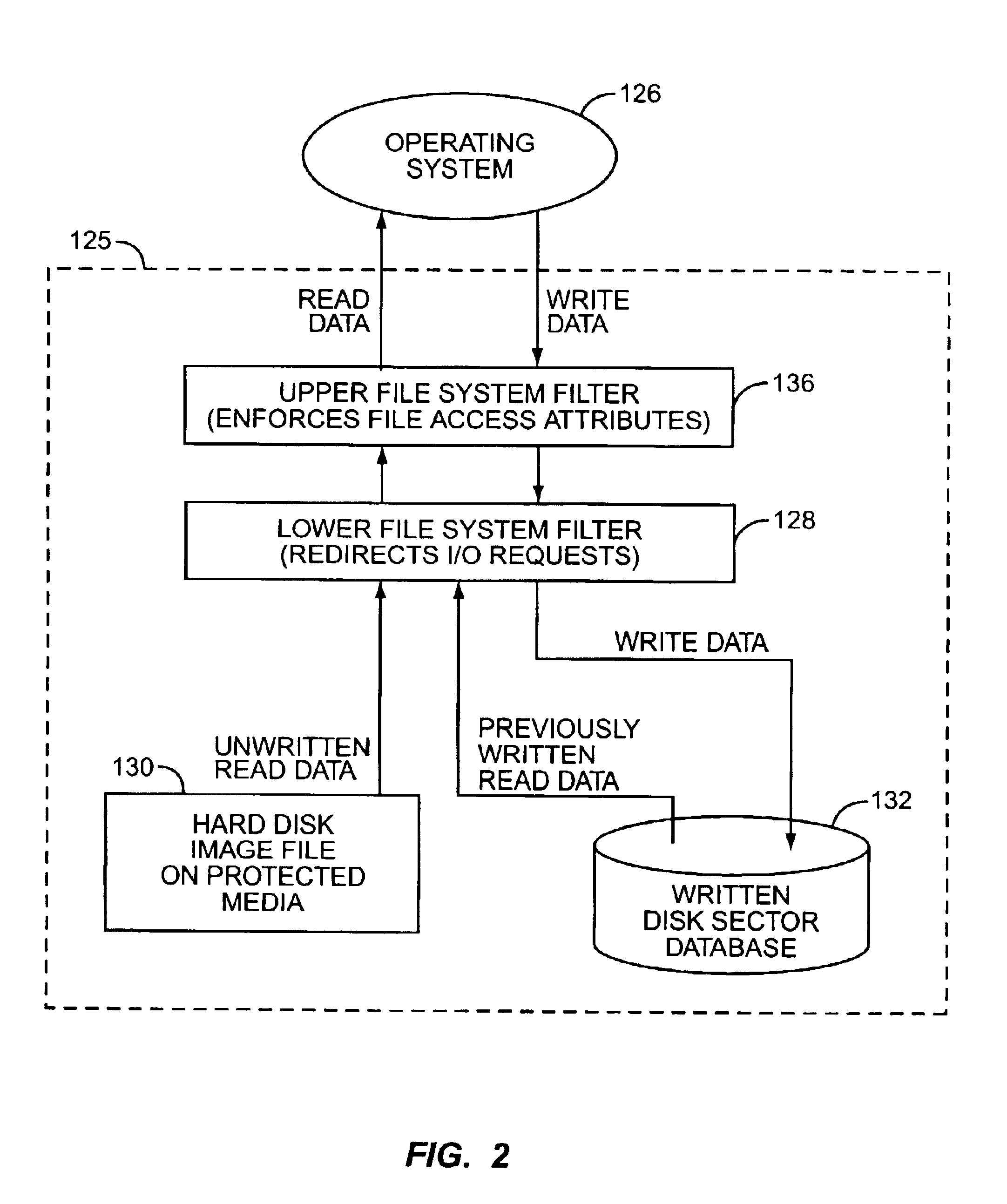
Method of altering a computer operating system to boot and run from protected media
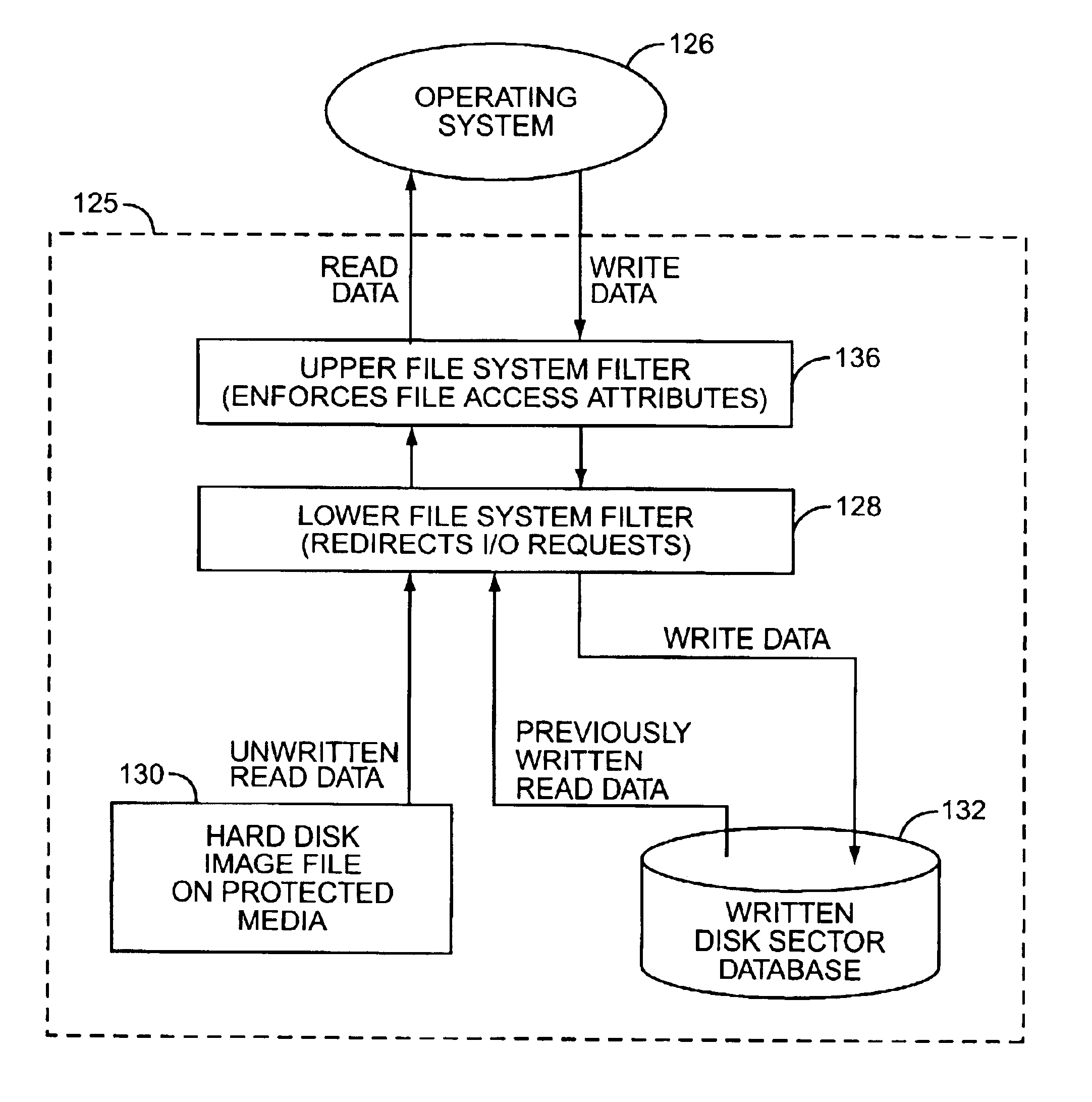
A modern computer operating system is altered to boot and run from a protected medium such as a CD-ROM. Files and configuration information are copied from a fully configured and operational OS to a hard drive image file. File system filters and device drivers are added that implement an emulated read-write hard disk drive by servicing initial read requests from the image file, and write requests and read requests to previously written data, from a written disk sector database. The OS is altered to load the filters and drivers during boot, and to subsequently run from the emulated read-write hard disk drive. The hard drive image file is then placed on a bootable protected medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Using external memory devices to improve system performance
ActiveUS7490197B2Improve productivity and performanceImprove system performanceInput/output to record carriersComponent plug-in assemblagesProduction rateHard disc drive
The invention is directed towards a system and method that utilizes external memory devices to cache sectors from a rotating storage device (e.g., a hard drive) to improve system performance. When an external memory device (EMD) is plugged into the computing device or onto a network in which the computing device is connected, the system recognizes the EMD and populates the EMD with disk sectors. The system routes I / O read requests directed to the disk sector to the EMD cache instead of the actual disk sector. The use of EMDs increases performance and productivity on the computing device systems for a fraction of the cost of adding memory to the computing device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for increasing booting speed of computer
ActiveCN101814038AFast startupSolve the problem of slow speed in the startup phaseInput/output to record carriersProgram loading/initiatingData needsDisk sector
The invention discloses a method for increasing a booting speed of a computer. The method comprises the following steps of: setting data needing to be pre-read for booting of the computer and creating a list file of the data to be pre-read; according to the list file, reading designated pre-read contents from a magnetic disk by a private interface, buffering the designated pre-read contents in a reserved space(memory), intercepting magnetic disk reading / writing operation, if the related magnetic disk sectors of the reading / writing operation have intersection sets with the magnetic disk sectors in which the pre-read contents A are located, according to a relationship recorded in the first space, finding out positions corresponding to the sectors of the intersection set from the reserved space, and directly operating the contents related to the sectors of the intersection set and needing the reading / writing operation according to the corresponding positions in the reserved space. In the method, the actual magnetic disk reading / writing operation is unnecessary, but the reserved space reading / writing operation is just performed, so that the reading / writing operation of the magnetic disk is reduced, and the booting speed of the system is increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU SHUNWANG TECH
Method for storing embedded real-time video files
InactiveCN102136290AReduced service lifeExtended service lifeCarrier indexing/addressing/timing/synchronisingVideo storageChronological time
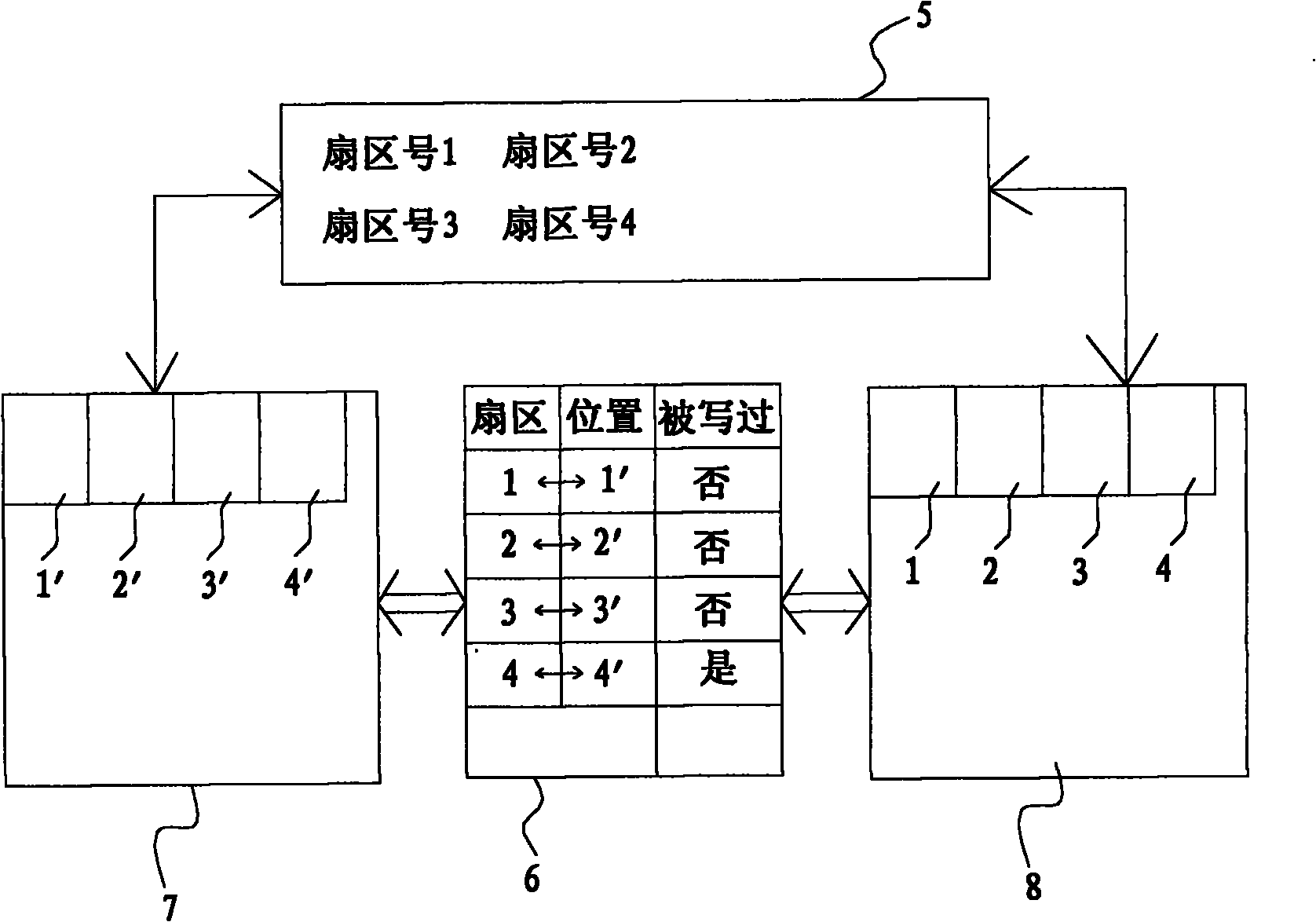
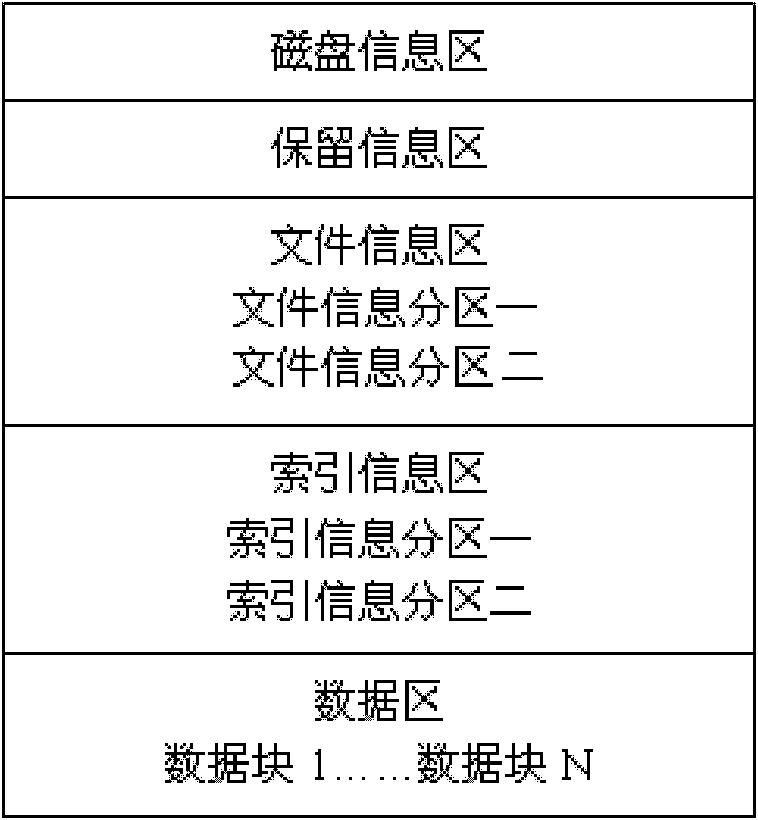
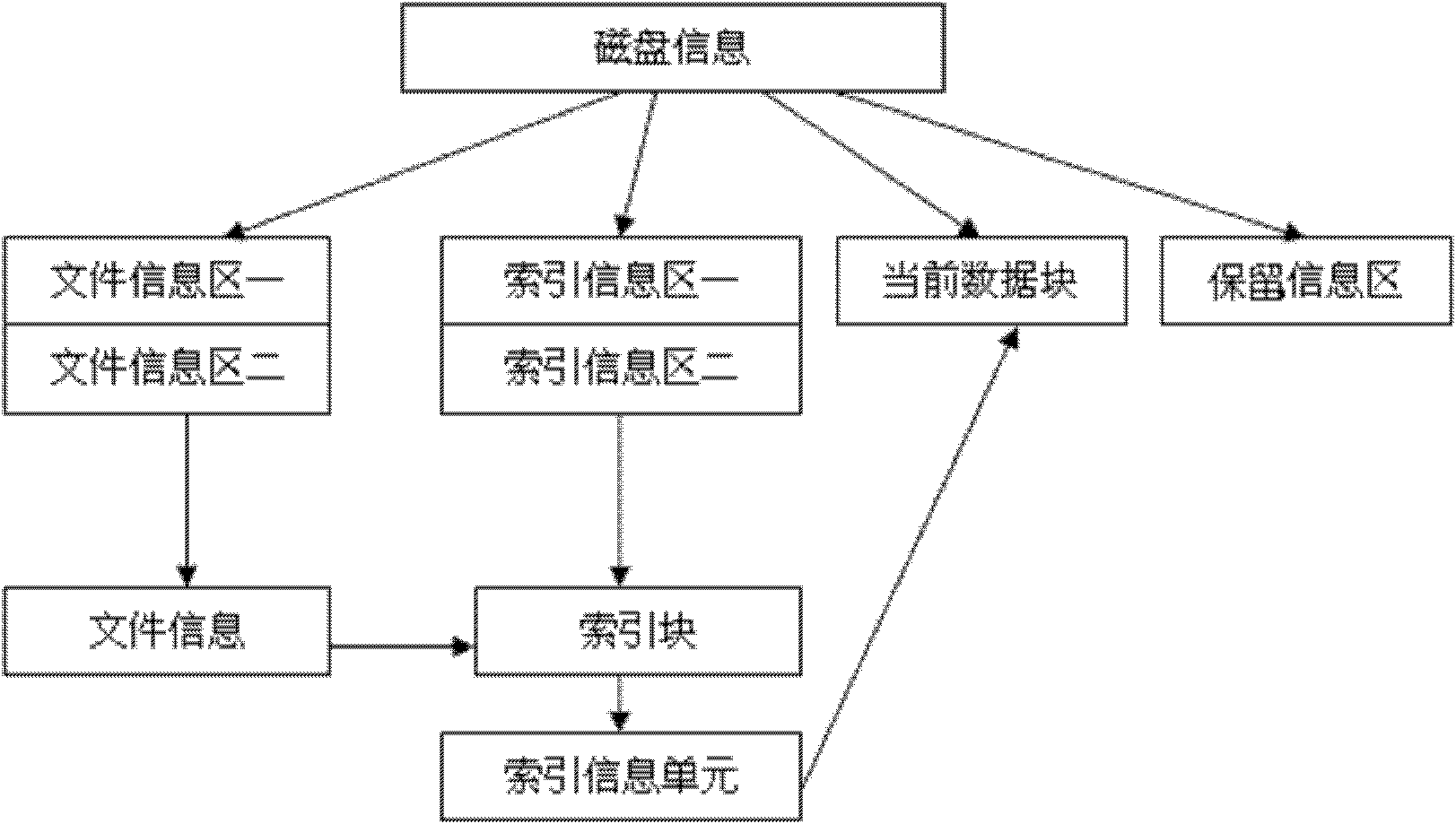
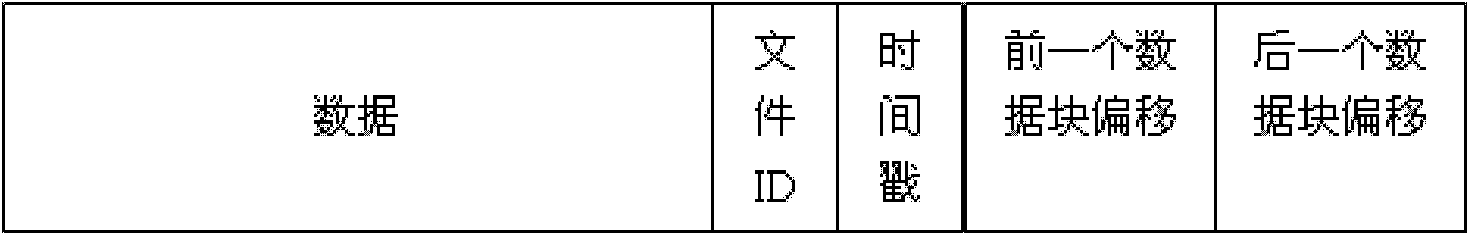
The invention relates to a method for storing embedded real-time video files, comprising the following steps: (1) dividing a hard disk sector into five zones, i.e. a disc disk information zone, a retained information zone, a file information zone, an index information zone and a data zone according to the characteristic that videos are stored in the time sequence; (2) positioning the file information, the index information, the retained information and the data zone by the hard disk information, and positioning the index information by the file information; (3) after video file index information in the index information zone is updated and processed by a partition 1 and a partition 2 in the index information zone, obtaining the video file index information; and (4) finding corresponding index information for the video file information in the file information zone by the partition 1 and the partition 2 in the index information zone, finding a corresponding data block by the index information to store data, and storing the video data into the disc disk in the mode of data blocks. The method can be used for improving the safety of data and prolonging the service life of the hard disk. The invention can be widely applied to various fields of data storage.
Owner:BEIJING UNION UNIVERSITY
Computer apparatus, method and memory including license key
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Devices and Methods for Optimizing Data-Parallel Processing in Multi-Core Computing Systems
InactiveUS20120131584A1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsMulti core computingMulti processor
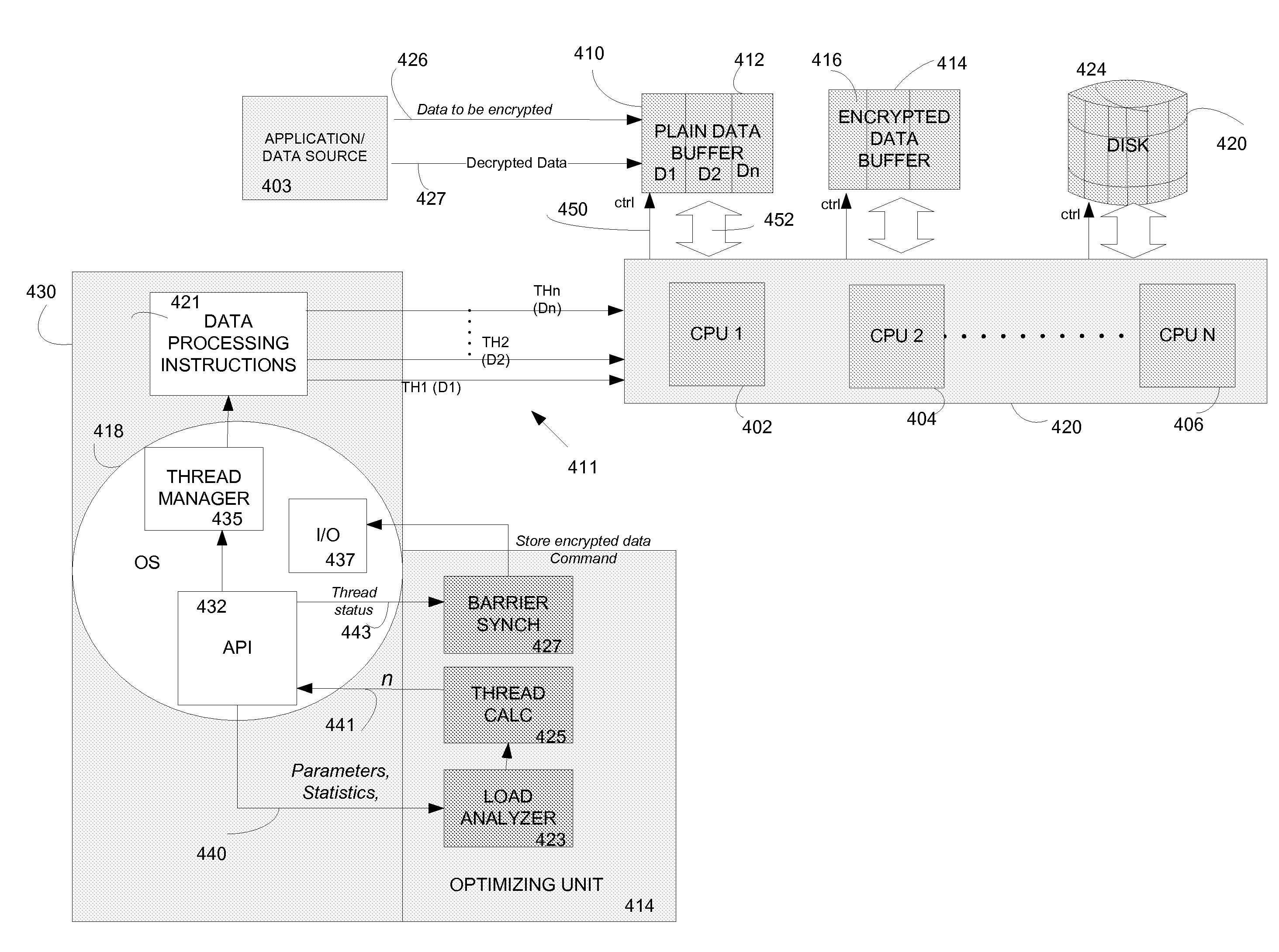
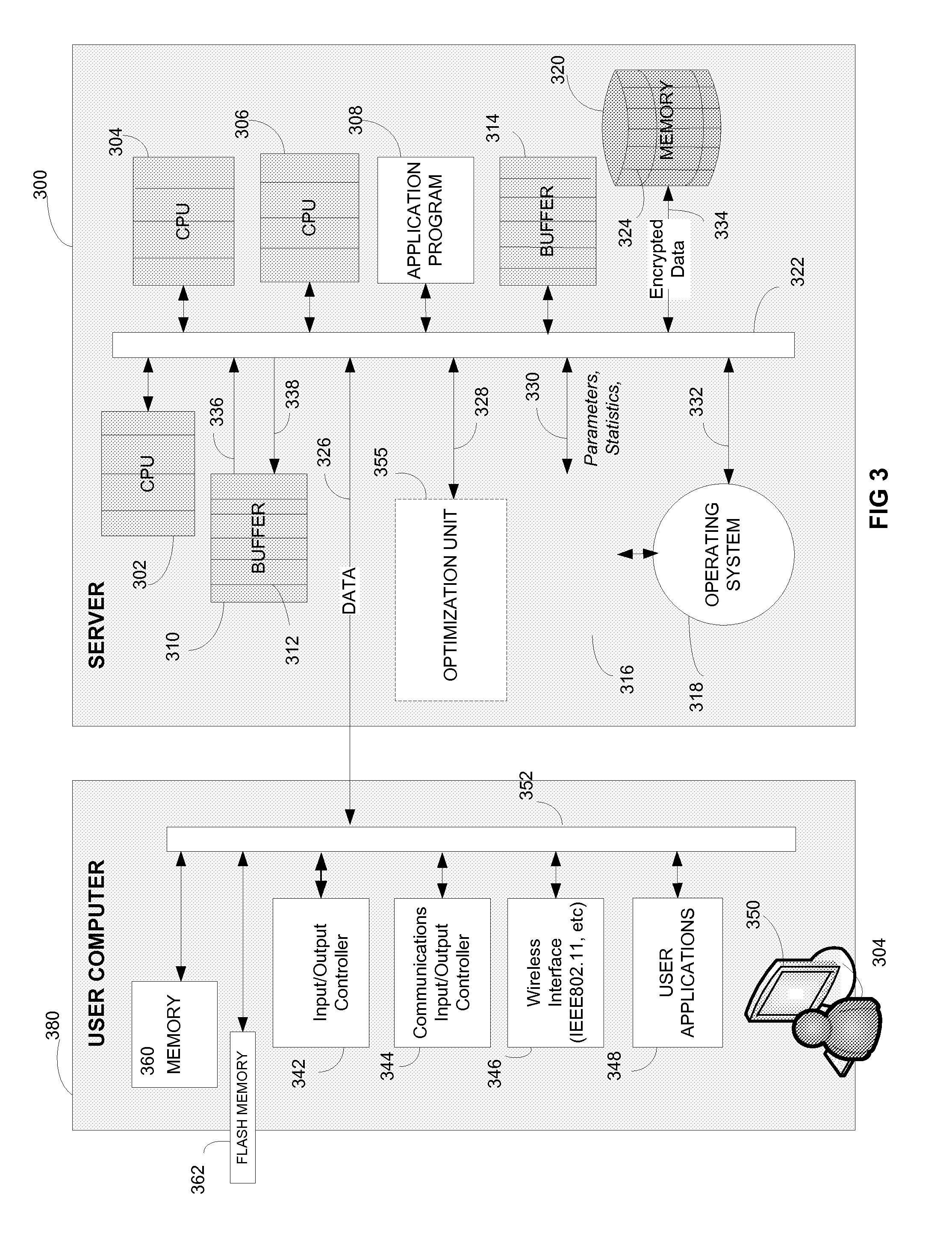
According to an embodiment of a method of the invention, at least a portion of data to be processed is loaded to a buffer memory of capacity (B). The buffer memory is accessible to N processing units of a computing system. The processing task is divided into processing threads. An optimal number (n) of processing threads is determined by an optimizing unit of the computing system. The n processing threads are allocated to the processing task and executed by at least one of the N processing units. After processing by at least one of N processing units, the processed data is stored on a disk defined by disk sectors, each disk sector having storage capacity (S). The storage capacity (B) of the buffer memory is optimized to be a multiple X of sector storage capacity (S). The optimal number (n) is determined based, at least in part on N, B and S. The system and method are implementable in a multithreaded, multi-processor computing system. The stored encrypted data may be later recalled and decrypting using the same system and method.
Owner:RAEVSKY ALEXEY
Rapid regeneration of failed disk sector in a distributed database system
InactiveUS20070300101A1Avoid the needPromote recoveryRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsRecord information storageRAIDFailover
A technique for read error failover processing in a mirrored disk system such as a Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) system, where individual disk units perform Logical Block Address (LBA) remapping. A read error causes a disk controller to report an “unrecoverable” read error to a RAID controller. After receiving this report of an unrecoverable read error, rather than simply switching over to a mirror, the RAID controller first checks to see whether the disk that caused the error can successfully reassign an LBA. In particular, the RAID controller can retrieve the data that was associated with the failed LBA from the mirror, and then write that data to the offending disk. Only if this process does not succeed is the offending disk then treated by the RAID controller as having failed sufficiently to require failover to the mirror.
Owner:IMB INT GRP BV +1
Method and system to perform caching based on file-level heuristics
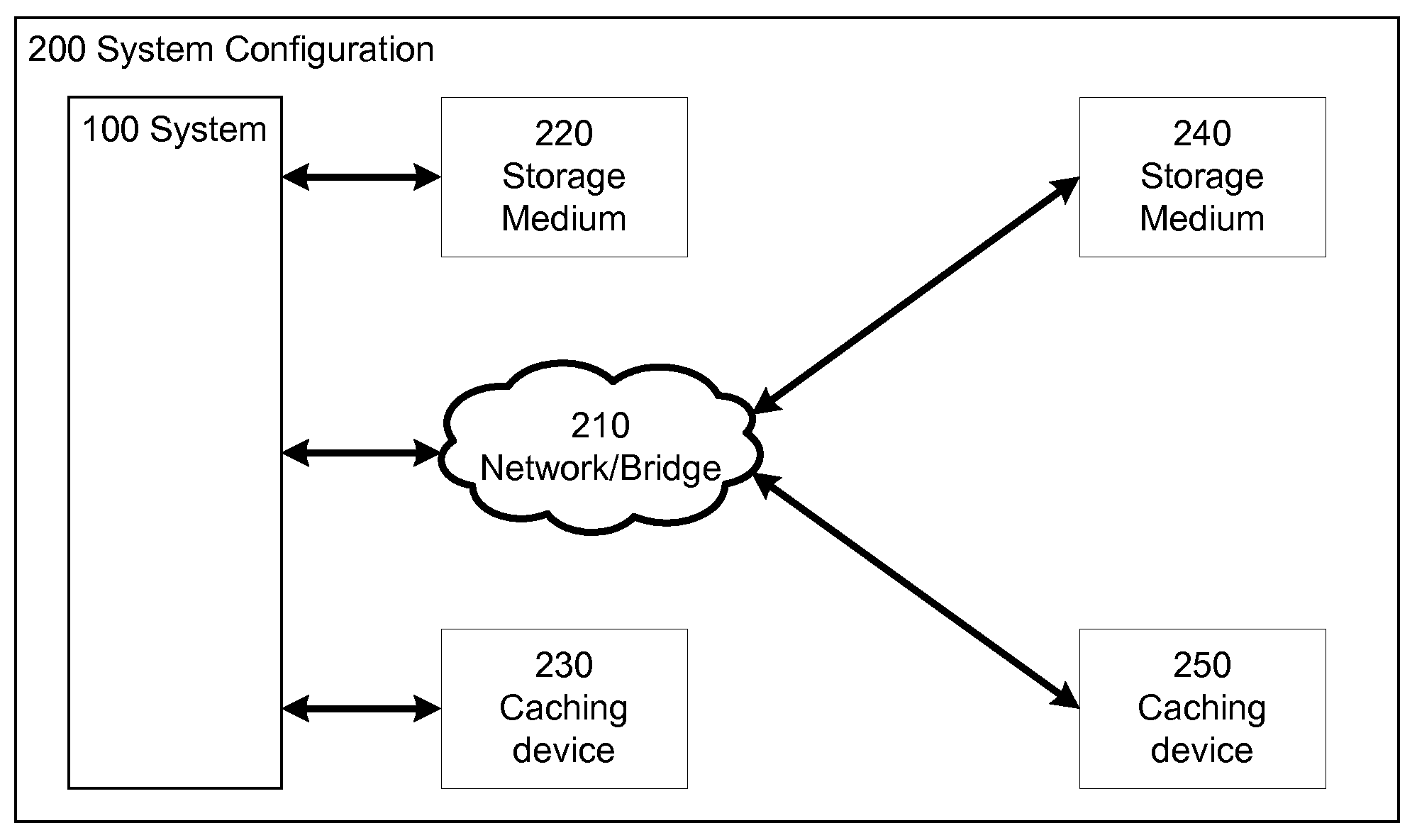
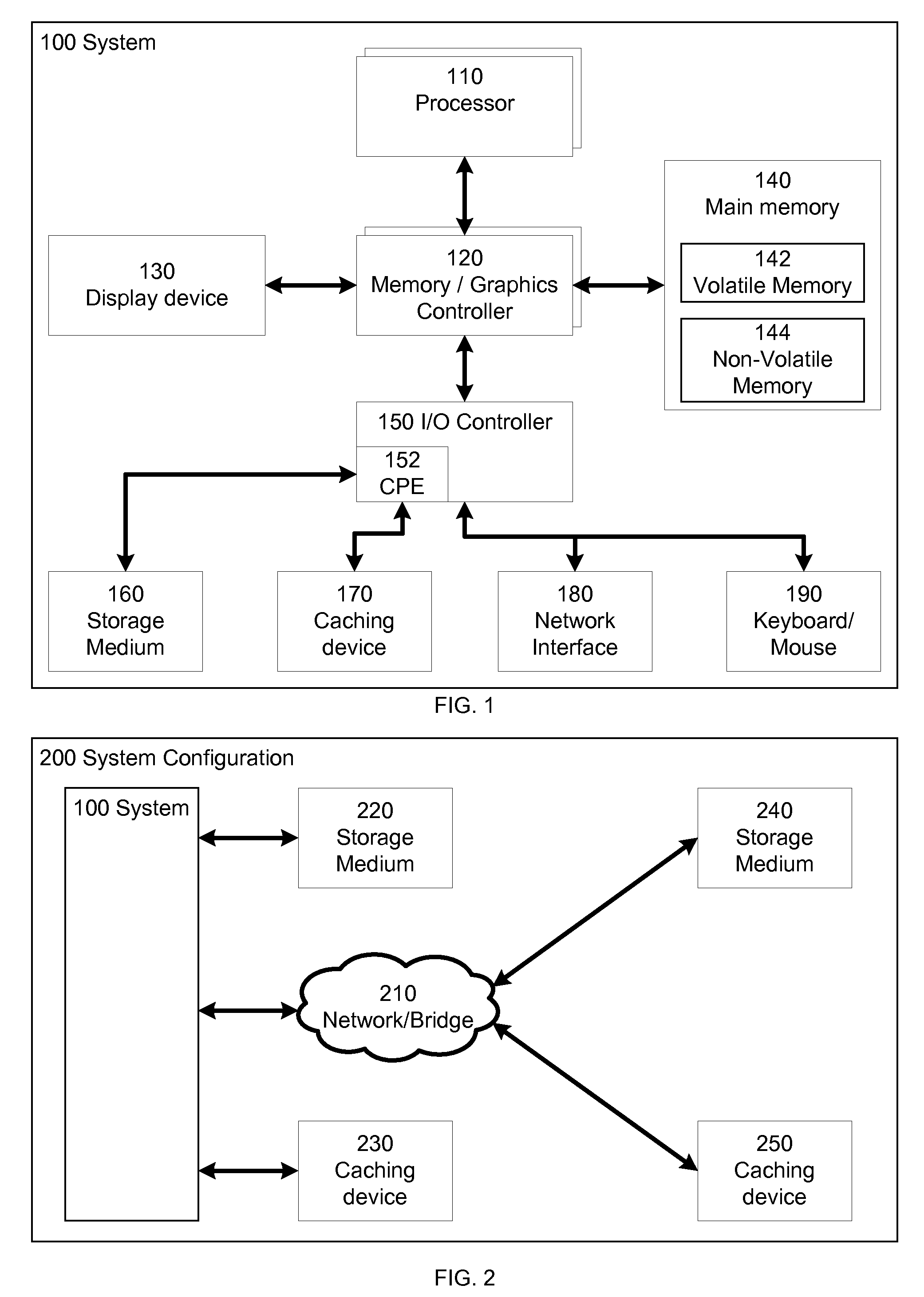
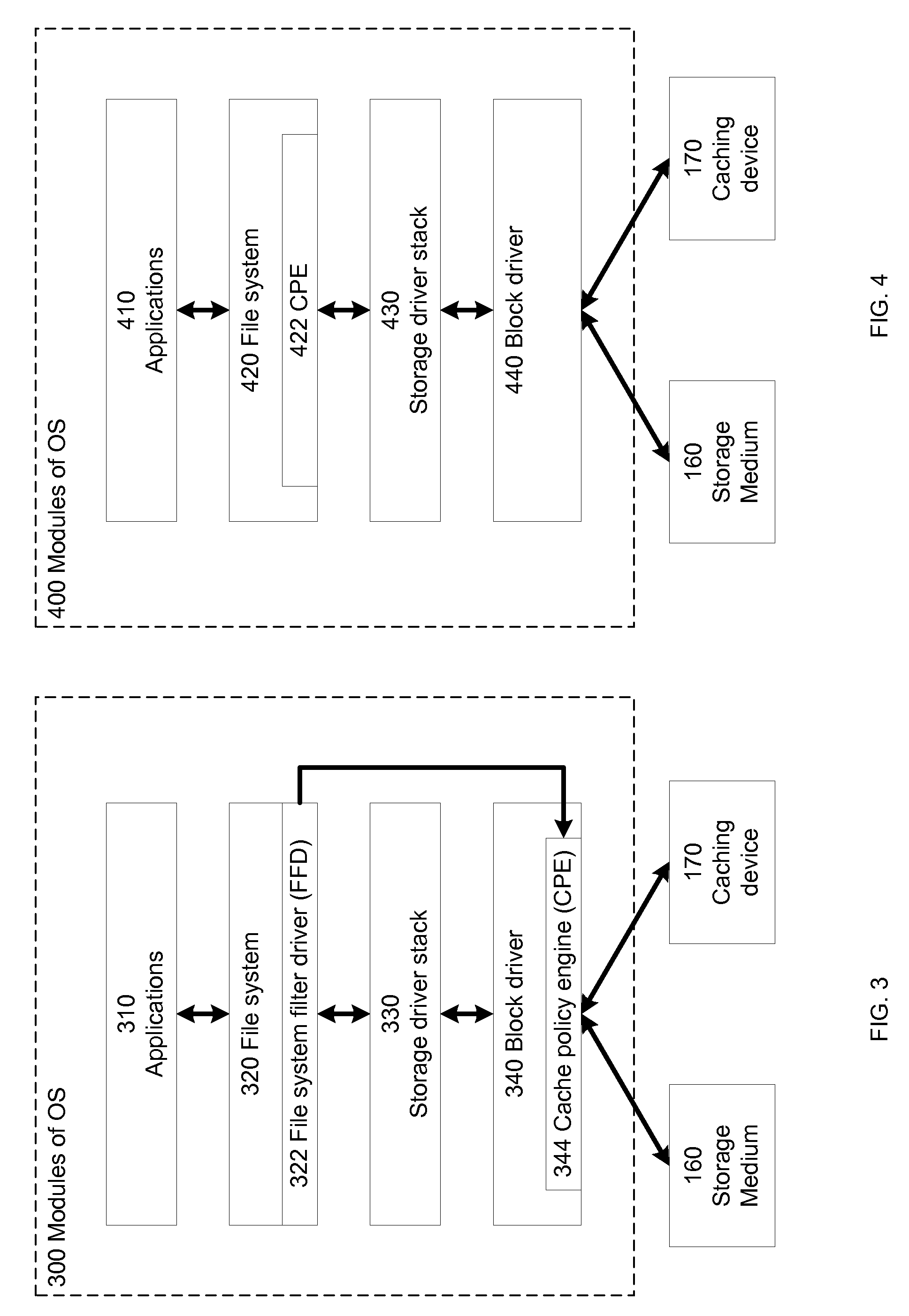
ActiveUS20100250834A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogical block addressingData selection
A method and system to perform caching based at least on one or more file-level heuristics. The caching of a storage medium in a caching device is performed by a cache policy engine. The cache policy engine receives file-level information of input / output access of data of the storage medium and caches or evicts the data of the storage medium in the caching device based on the received file-level information. By utilizing information about the files and file operations associated with the disk sectors or logical block addresses of the storage medium, the cache policy engine can make a better decision on the data selection of the storage medium to be cached in or evicted from the caching device in one embodiment of the invention. Higher cache hit rates can be achieved and the performance of the system utilizing the cache policy engine is improved.
Owner:SK HYNIX NAND PROD SOLUTIONS CORP
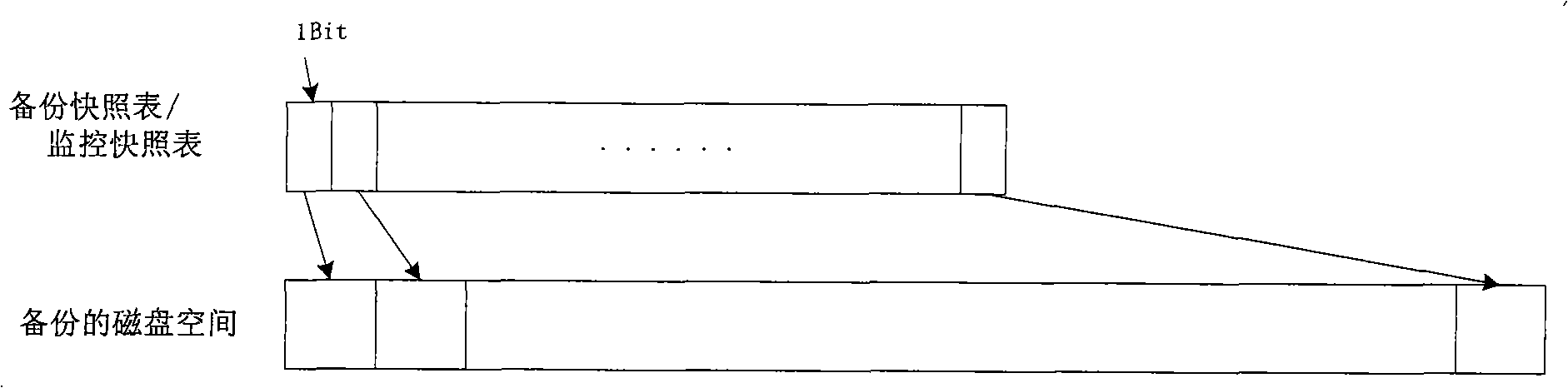
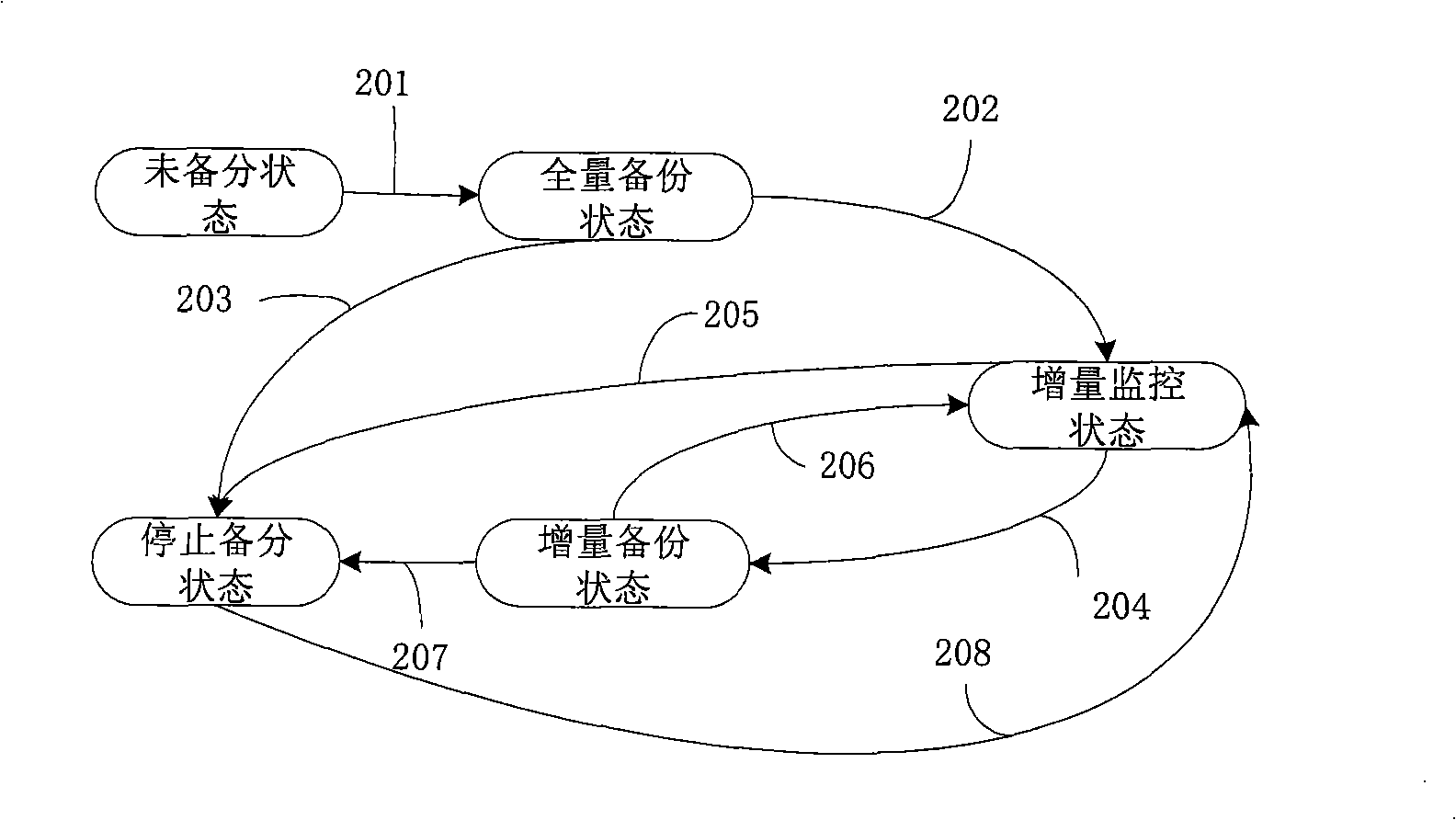
Magnetic disk data backup system and method
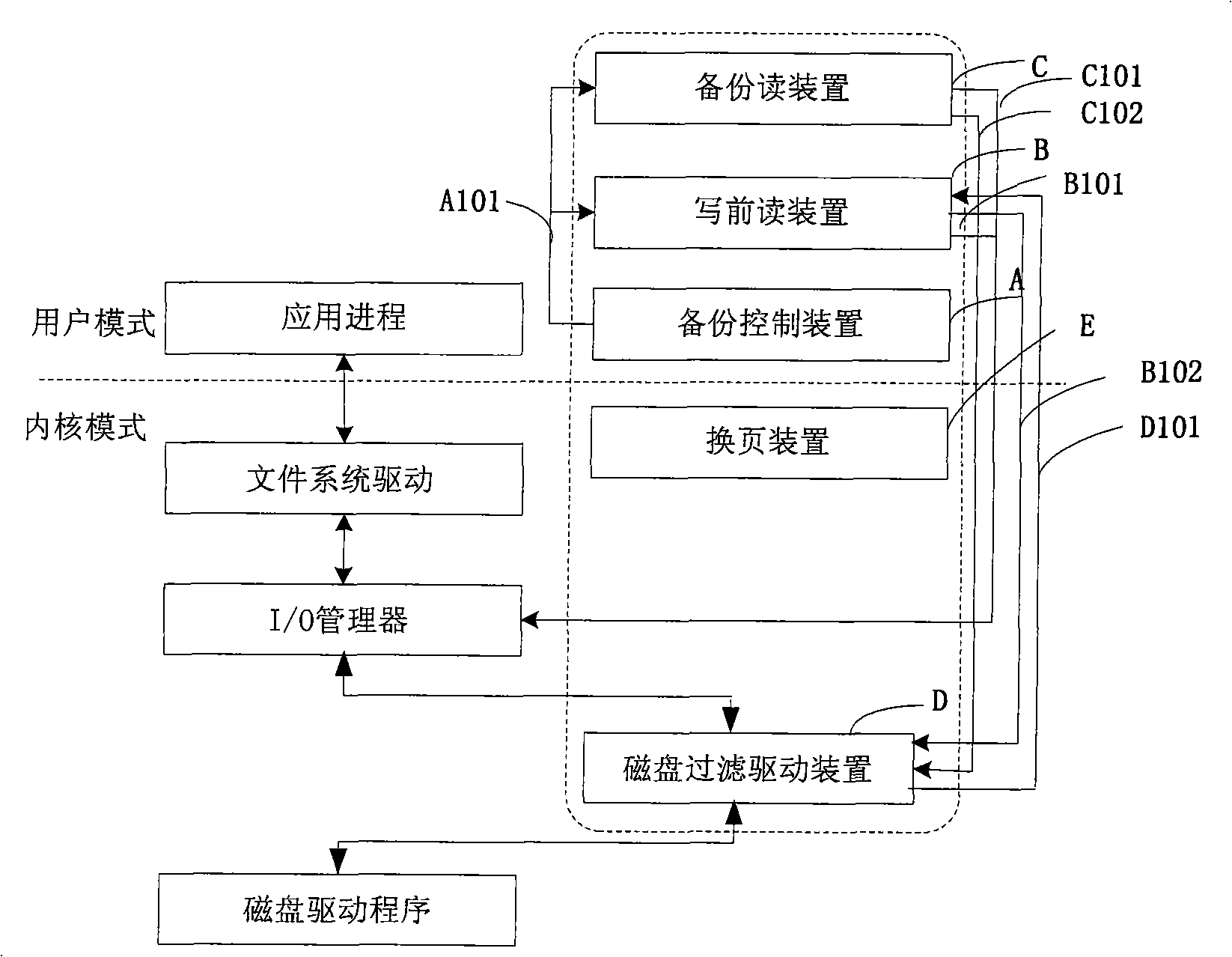
InactiveCN101295276AEnsure consistencyAvoid deadlockInput/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionDisk sectorDeadlock
The invention provides a magnetic disk data backup system and a running method thereof. The system comprises a backup control device, a device for reading before writing, a backup reading device, a magnetic disk filter driving device, a page-change device, a backup snapshot table, a memory buffering queue and a hard disk buffering file. The system preferably gains the backup snapshot table which is used for recording whether the magnetic disk sector data requires backup or not; the magnetic disk sector data required for backup are sequentially read in the magnetic disk according to the gained backup snapshot table so as to carry out the backup, meanwhile, the operation of the magnetic disk started to be monitored; the write operation of the magnetic disk is monitored and intercepted; if the write operation signal is intercepted during the backup process, the data is read in the written magnetic disk and memorized to the memory buffering queue, and when the data of the memory buffering queue exceeds the pre-arranged length, the data is moved out to the hard disk buffering file, and a write operation allowance signal is sent so as to complete the operation of reading before writing. The system and the method of the invention can ensure the consistent time of the backup data, avoid the headlock under the situation that the upper-layer service is not interrupted, and has high service application independence.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
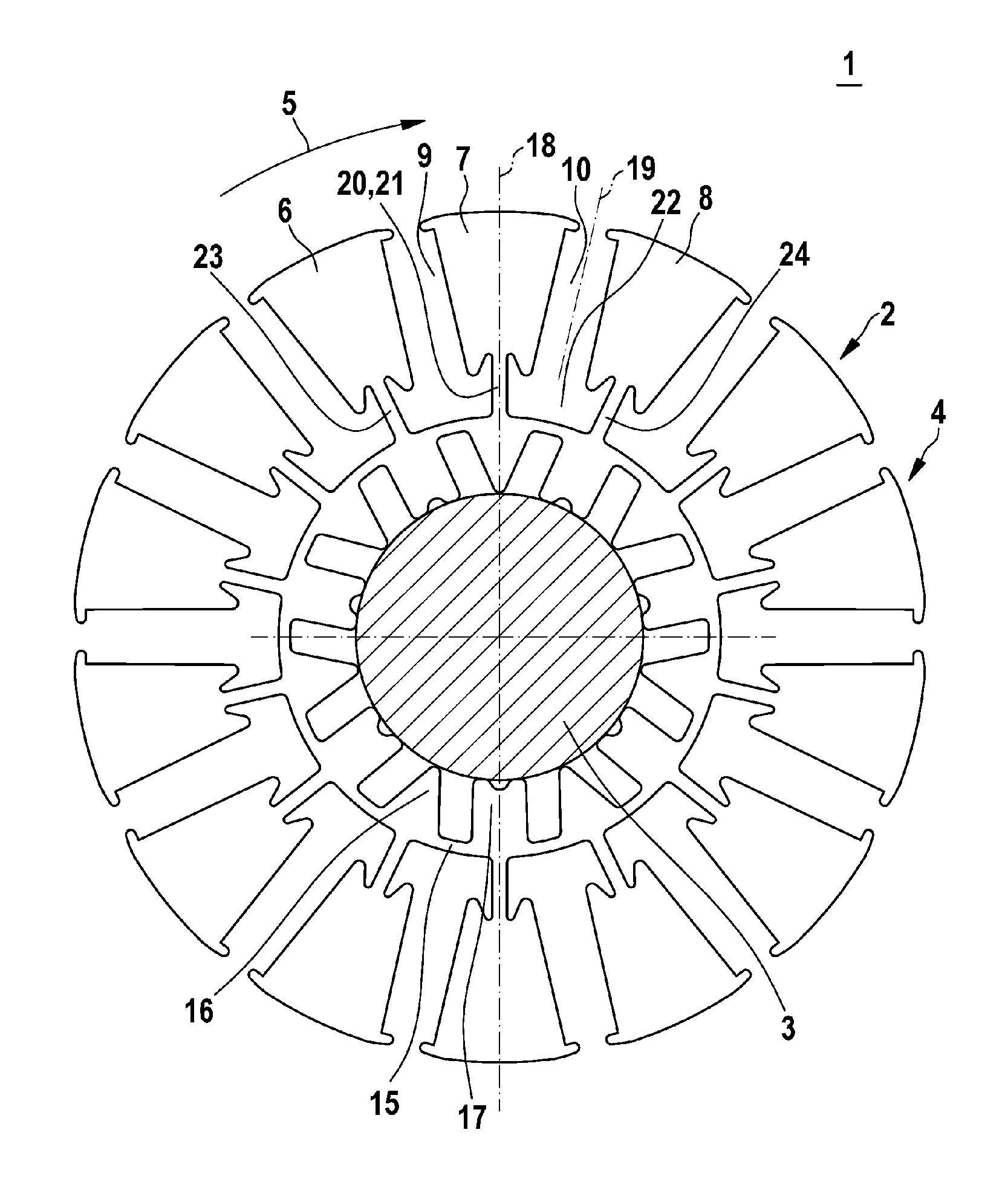
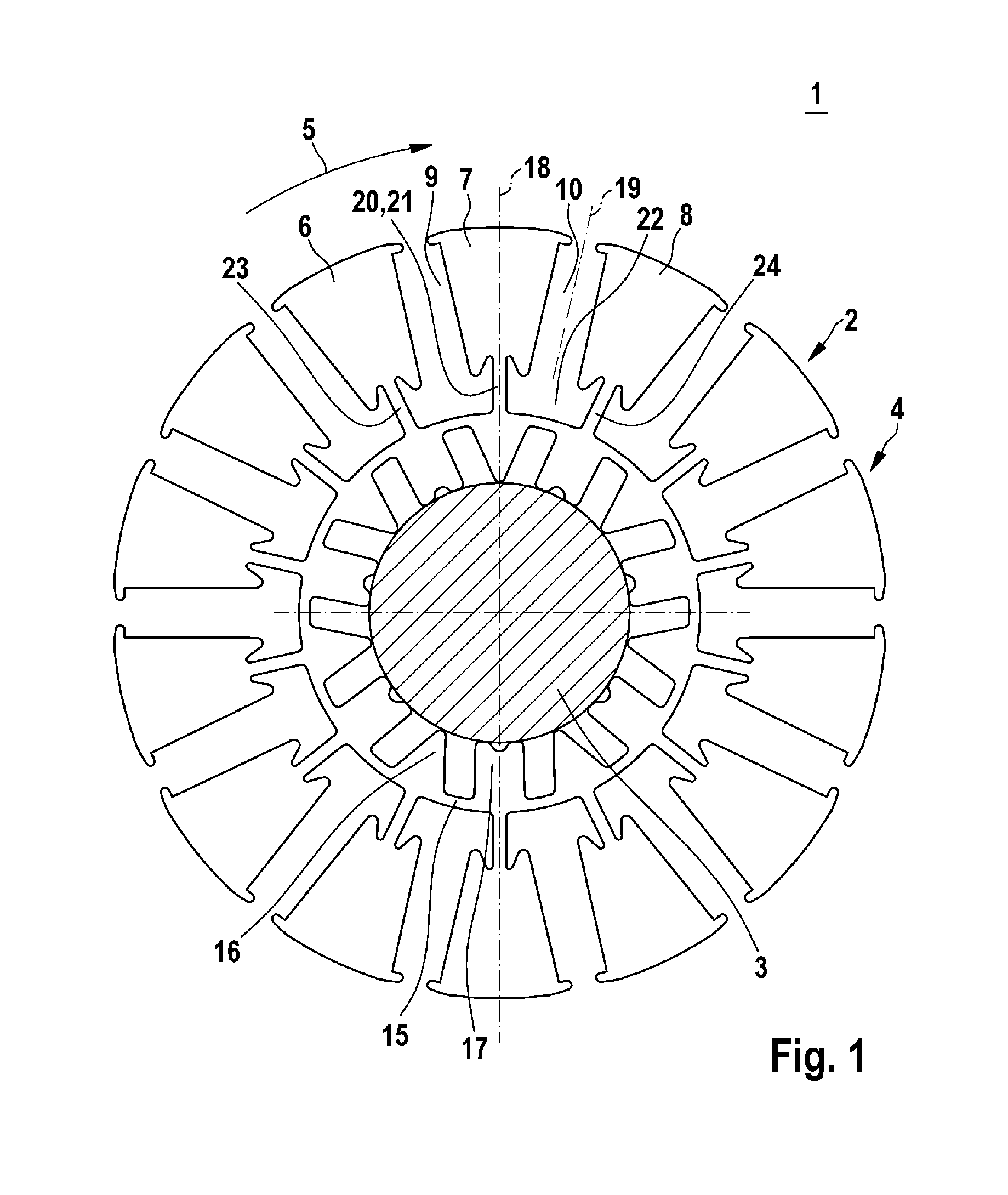
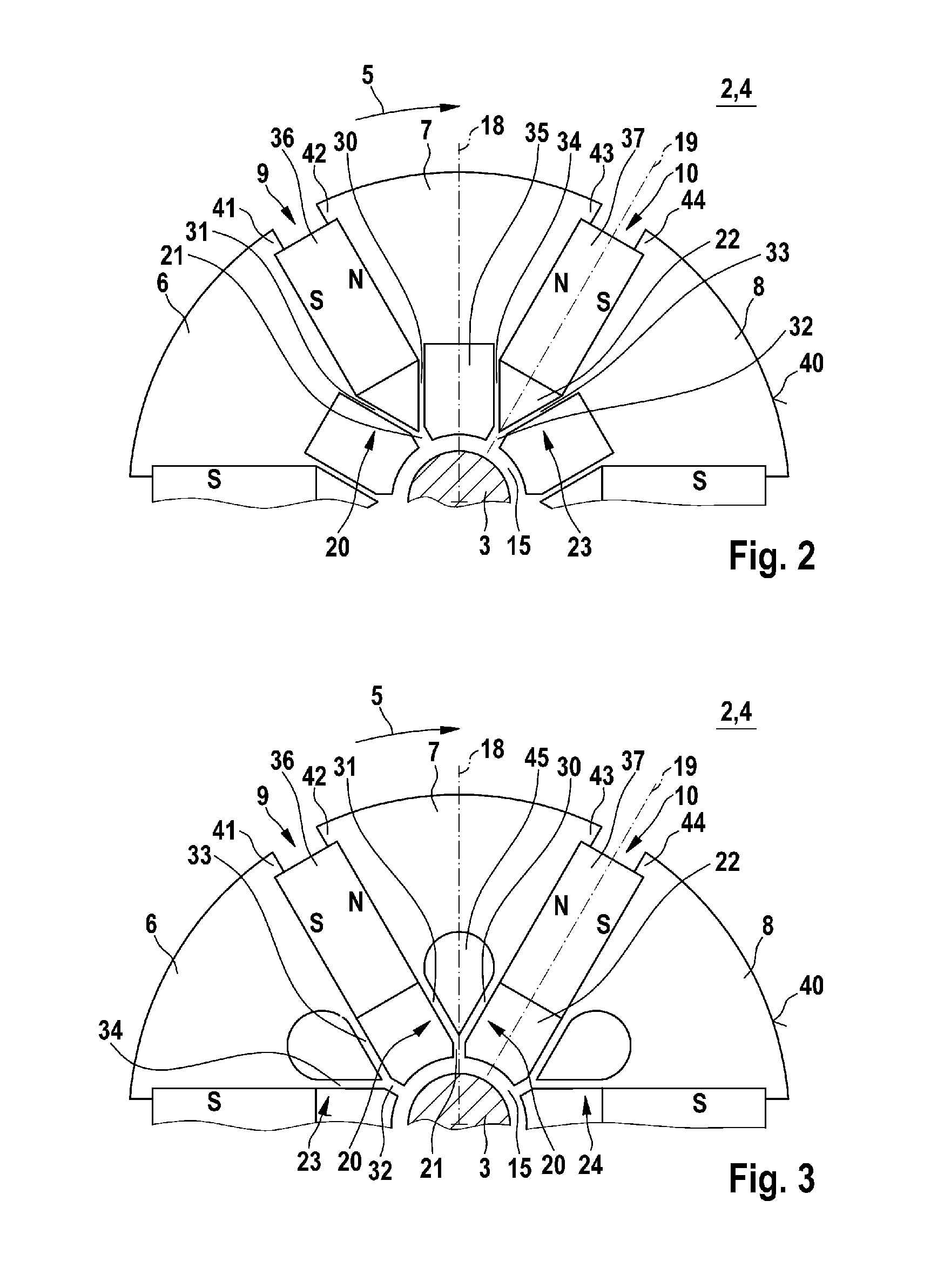
Electric machine
InactiveUS20120112591A1Minimizing flux lossMagnetic flux losses for a predetermined mechanical load capacity can be reducedMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic currentElectric machine
An electric machine (1), particularly used as an electric motor, has a rotor (2) comprising a plurality of disks (4). A disk (4) of the rotor (2) is divided in a circumferential direction (5) into a plurality of disk sectors (6, 7, 8) between which magnetic pockets (9, 10) are designed. Furthermore, the disk (4) has an inner fastening collar (15) and connecting members (20, 23, 24) connecting the disk sectors (6, 7, 8) to the fastening collar (15). Such a connecting member (20) comprises a main web (21), a side arm (30) branching off the main rib (21) in the circumferential direction (5), and a side arm (31) branching off the main web (21) opposite to the circumferential direction (5). High mechanical stability of the disk (4) can thus be ensured, wherein magnetic flow losses are reduced.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
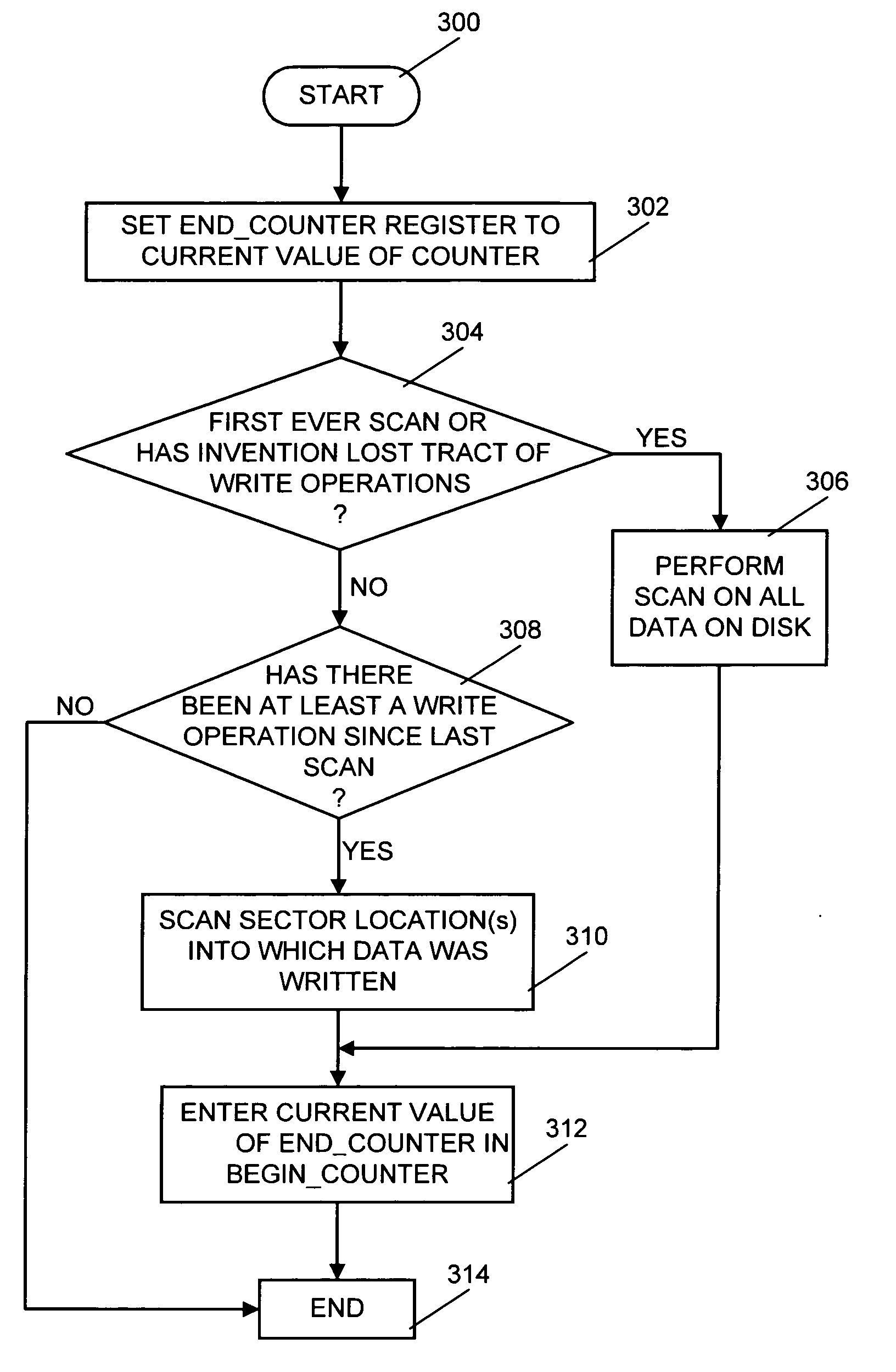
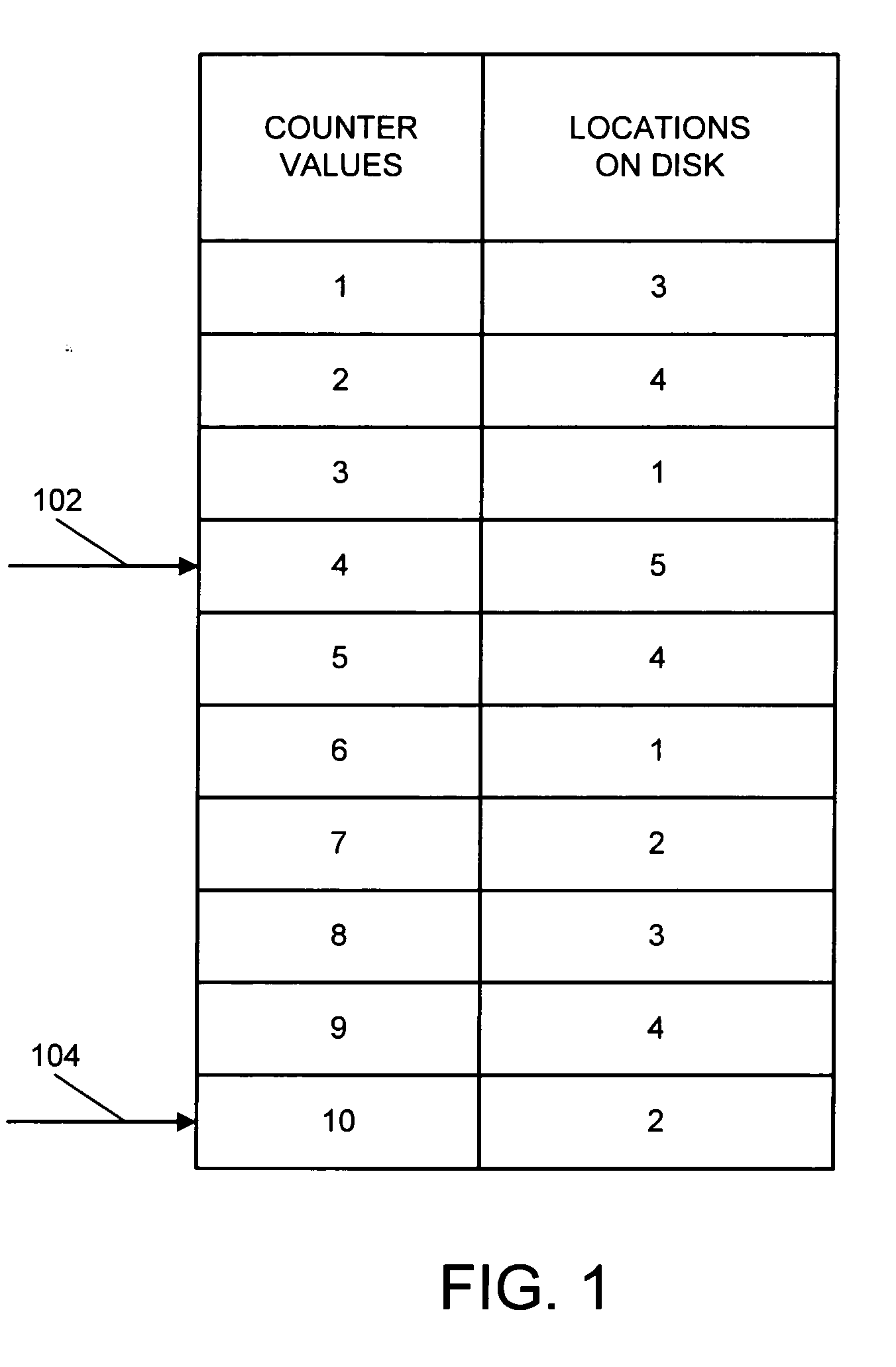
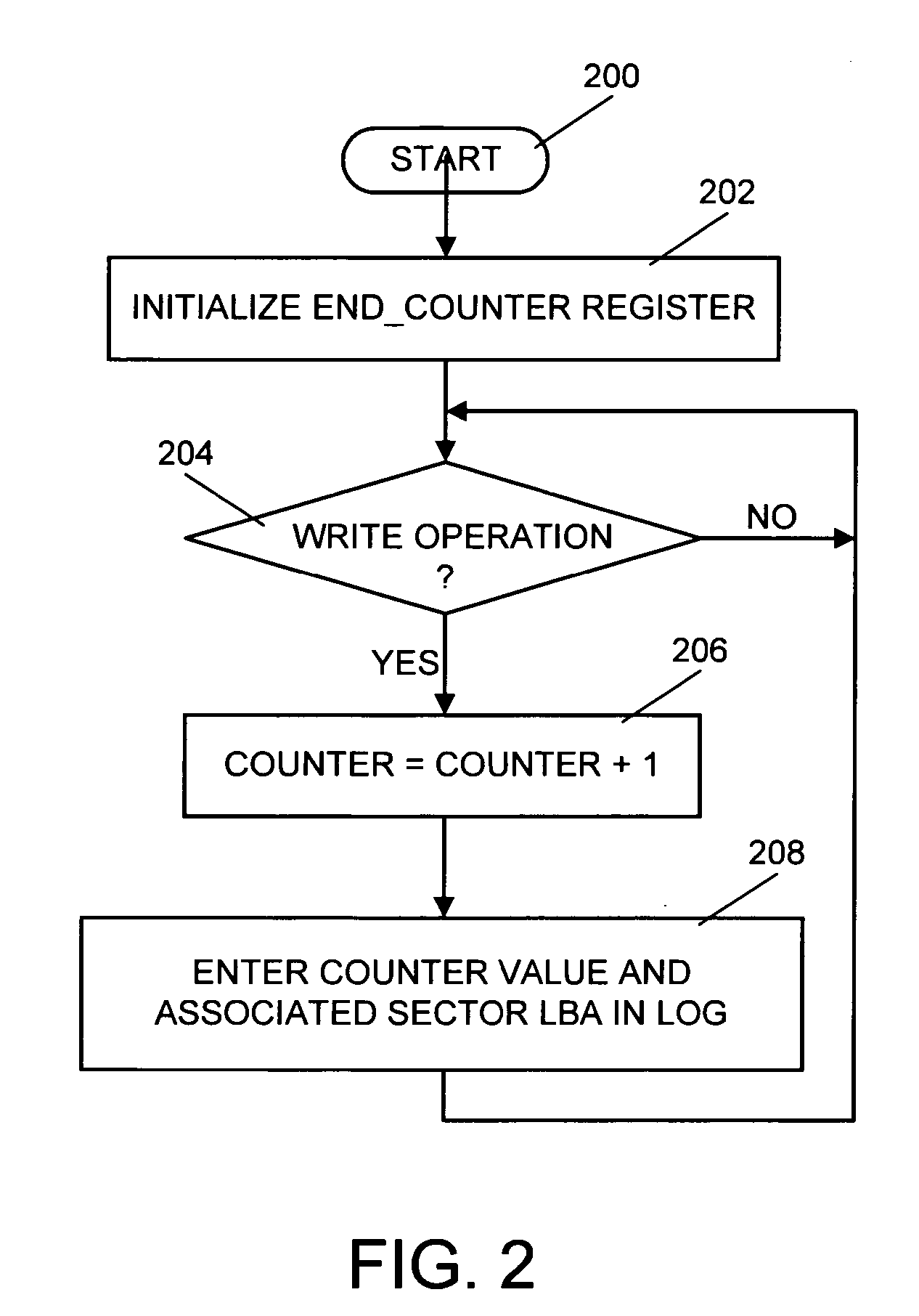
System, computer program product and method of selecting sectors of a hard disk on which to perform a virus scan
A system, computer program product and method of selecting sectors of a disk on which to perform a virus scan are provided. Initially, all data in all sectors of a disk is scanned for viruses. After the initial scan each sector into which new or modified data is written is recorded. This allows only new or modified data that has been added to the disk since a preceding scan to be scanned for viruses at a succeeding scan.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Distributed track identifier on a hard disk drive
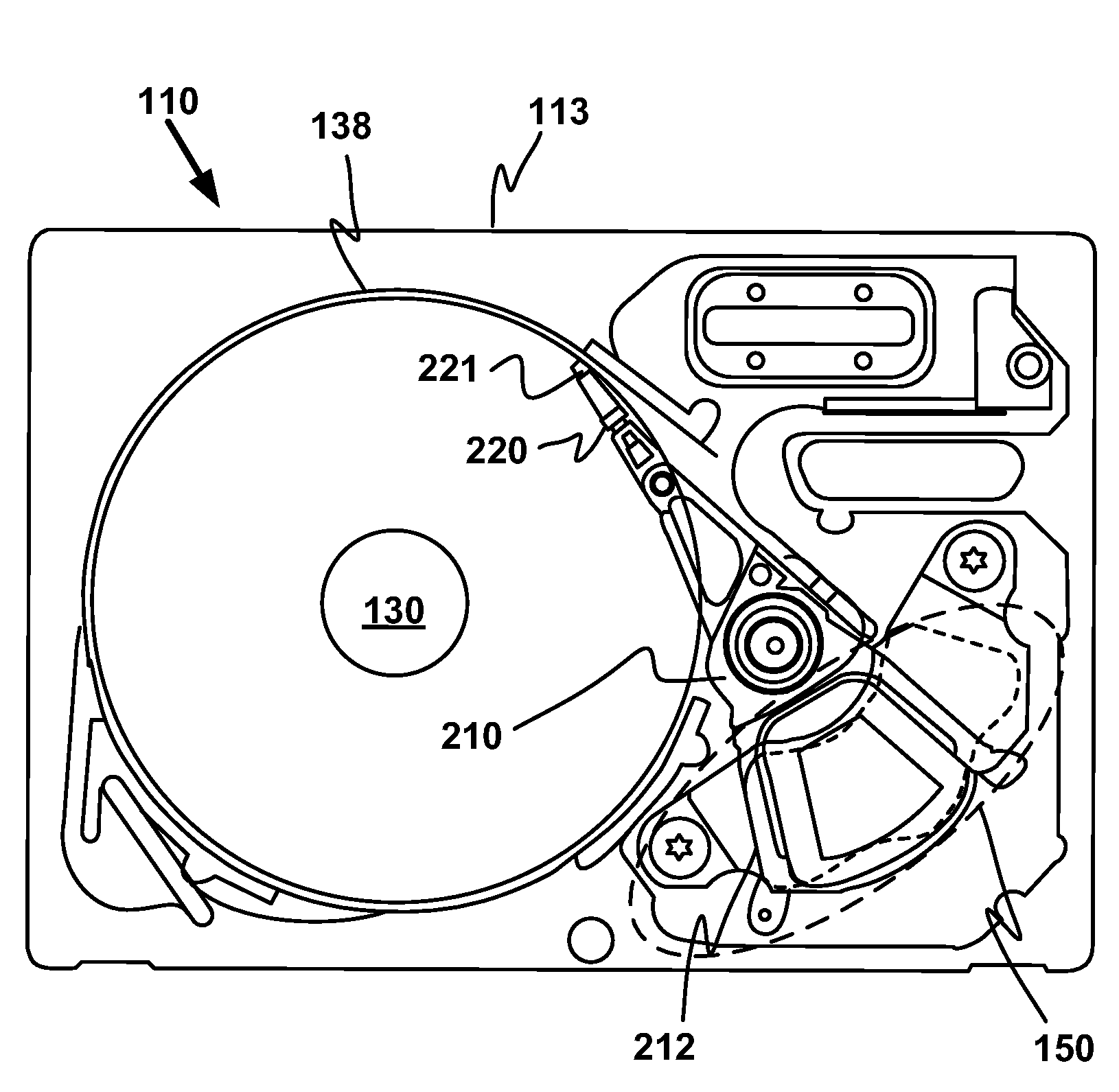
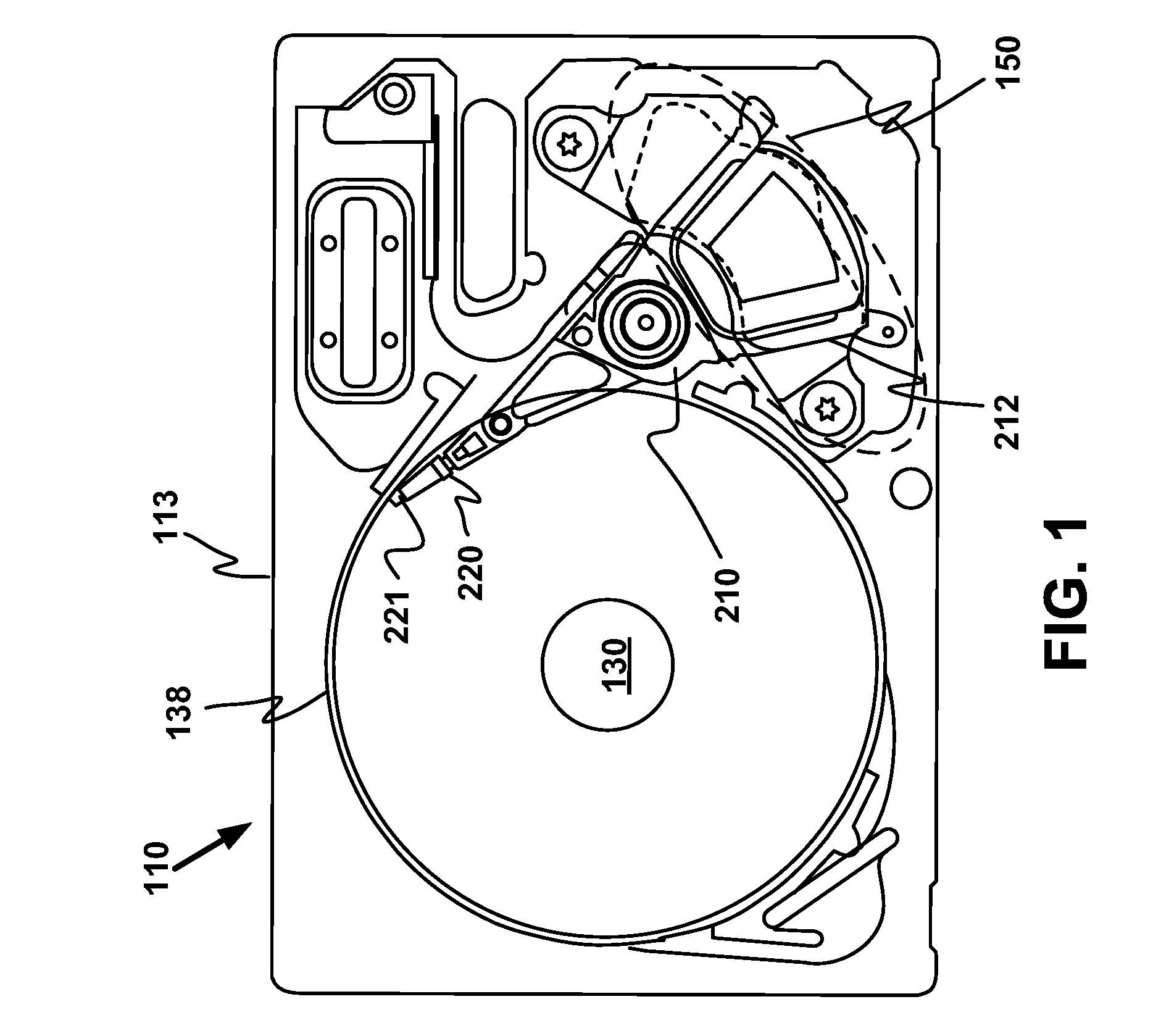
InactiveUS20090168227A1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksHard disc driveDisk sector
A magnetic disk for a hard disk drive comprising a distributed track identifier is described. The disk includes a first portion of a track identifier physically located at a first location on a disk sector and a second portion of the track identifier physically located at a second location on the disk sector wherein the first portion and the second portion of the track identifier are discontinuous on the sector.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
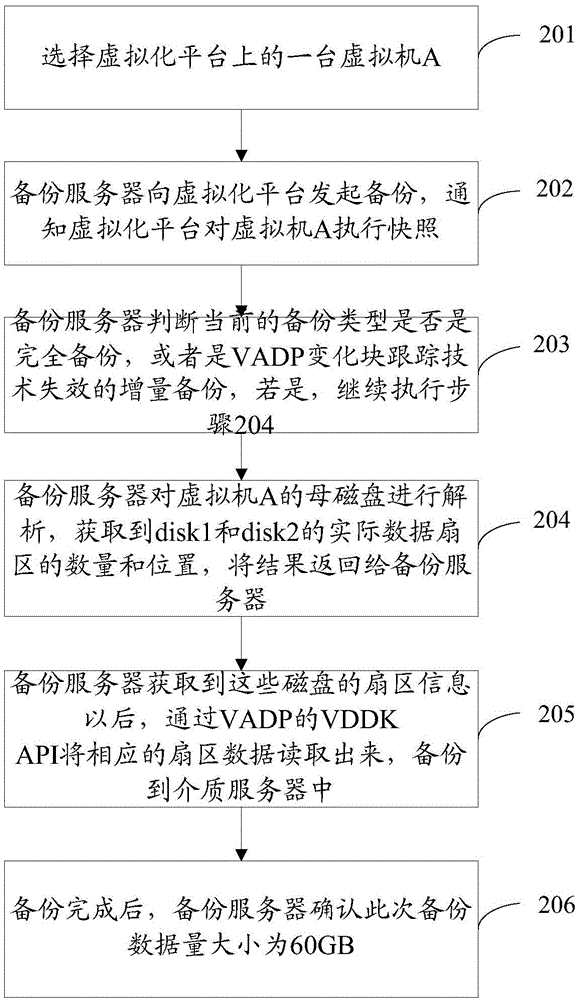
Disk backup method of virtue machine
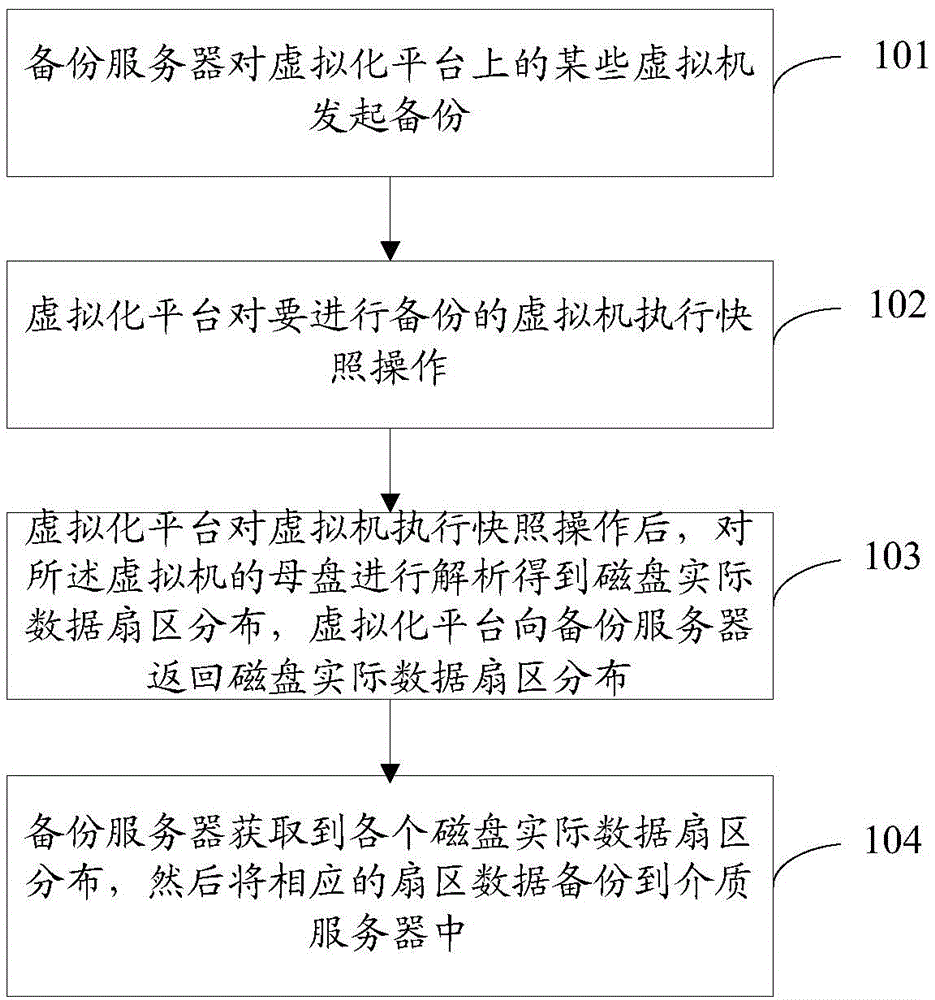
ActiveCN103605588AShorten the durationReduce resource usageInput/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionVirtualizationMedia server
The invention discloses a disk backup method of a virtue machine. The disk backup method includes that A, a backup server initiates backups to the virtue machine on a virtualization platform; B, the backup server communicates with the virtualization platform to inform the virtualization platform to perform snapshot operation upon the virtual machine; C), after the virtualization platform performs the snapshot operation upon the virtual machine, a motherboard of the virtual machine is parsed to obtain actual data disk sector distribution, and the virtualization platform returns the actual data disk sector distribution to the backup server; D), the backup server obtains all the actual data disk sector distribution and then backups corresponding sector data to a media server. By the disk backup method, time spent on backuping and recovering a window is enabled to be shortened, resource occupation of the virtualization platform is reduced, and more storage space is saved for customers.
Owner:EISOO SOFTWARE
Integrated-circuit implementation of a storage-shelf router and a path controller card for combined use in high-availability mass-storage-device shelves and that support virtual disk formatting
InactiveUS20100064104A1Input/output to record carriersError detection/correctionMass storageHigh bandwidth
An integrated circuit implementing a storage-shelf router used alone, or in combination with other storage-shelf routers, and in combination with path controller cards, to interconnect the disks within a storage shelf or disk array to a high-bandwidth communications medium through which data is exchanged between the individual disk drives of the storage shelf and a disk-array controller. In various embodiments, the present invention provides virtual disk formatting by a storage shelf router and the storage shelf in which the storage-shelf is included, to external computing entities, such as disk-array controllers and host computers. By providing virtual disk formatting, a storage-shelf router can provide to a disk-array controller, and other external computing entities, the disk-formatting convention expected by the disk-array controller, even though disk drives and other storage systems that do not conform to the expected formatting conventions may be included in the storage shelf and interconnected to a disk-array controller and other external processing entities via an interface provided by a storage-shelf router. Virtual disk formatting, in addition, allows a storage-shelf router to format a disk drive differently from the disk formatting expected by external computing entities, so that the storage-shelf router can transparently include additional information into disk sectors, such as additional error detection and error-correction information.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Modified file tracking on virtual machines
ActiveUS9177145B2Ensure facility securityClient firewall may be minimizedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionDisk sectorVirtual machine
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for tracking modified files on a virtual machine including the steps of identifying an altered disk sector, associating the altered disk sector with code that is operated in a virtual machine, and causing a malicious code scan to be performed on the code.
Owner:SOPHOS
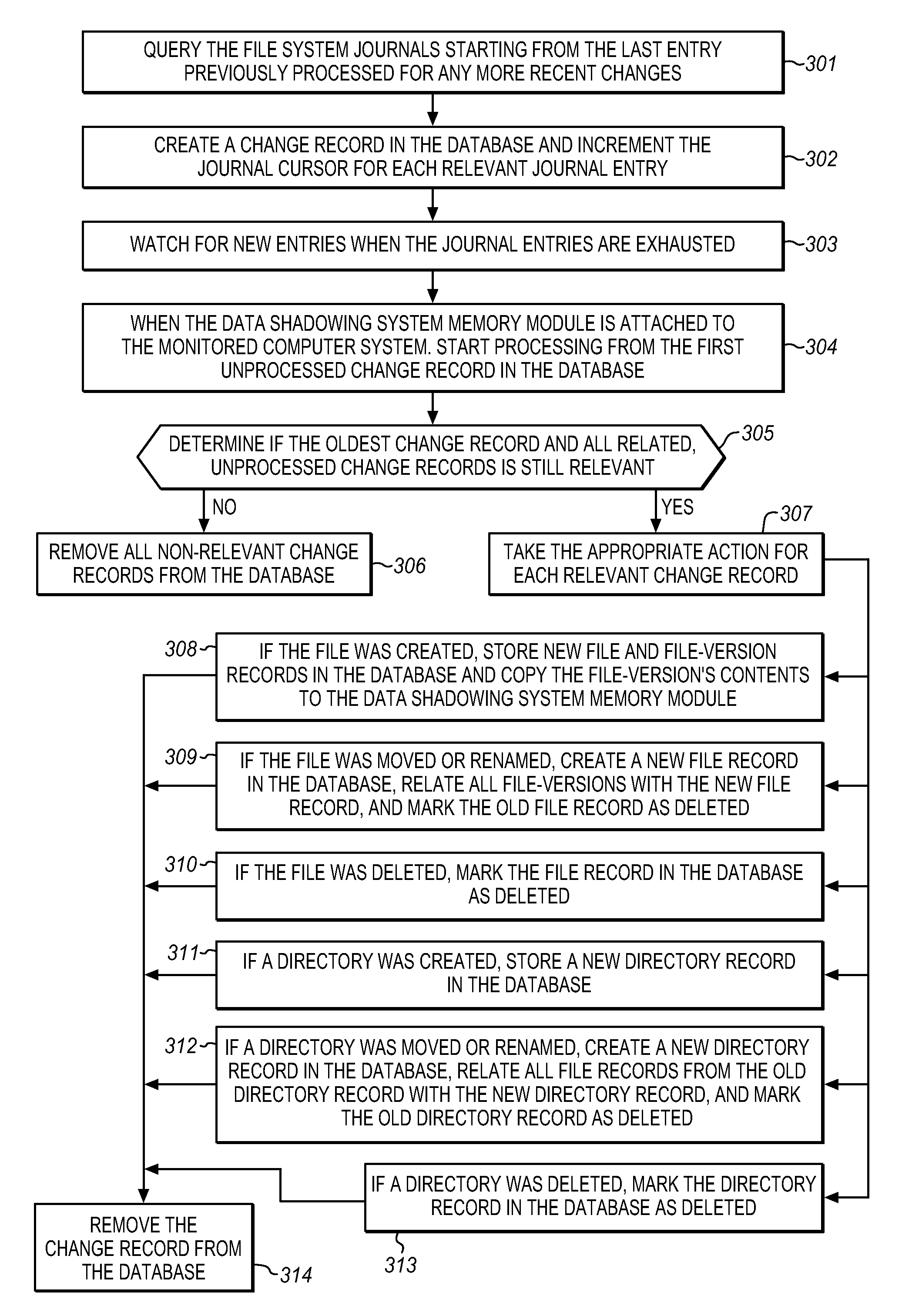
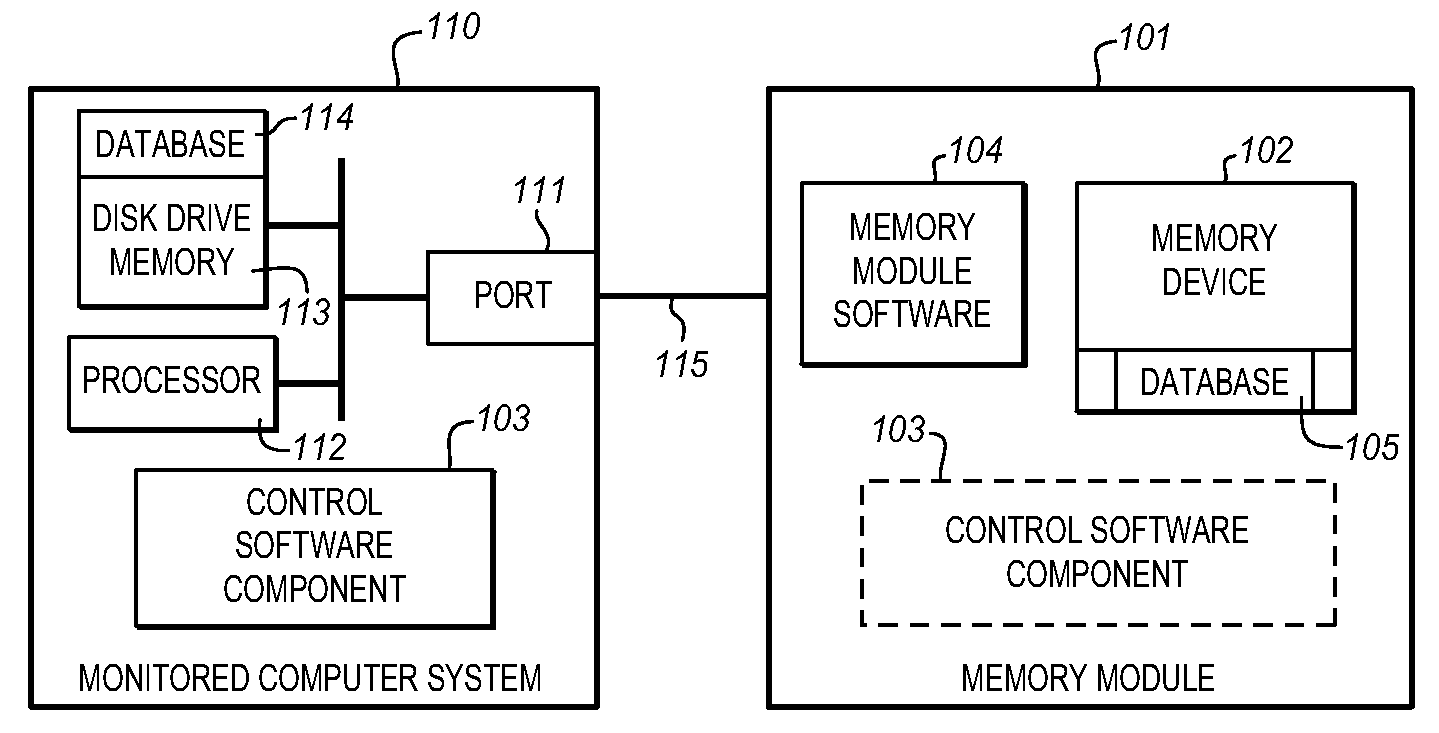
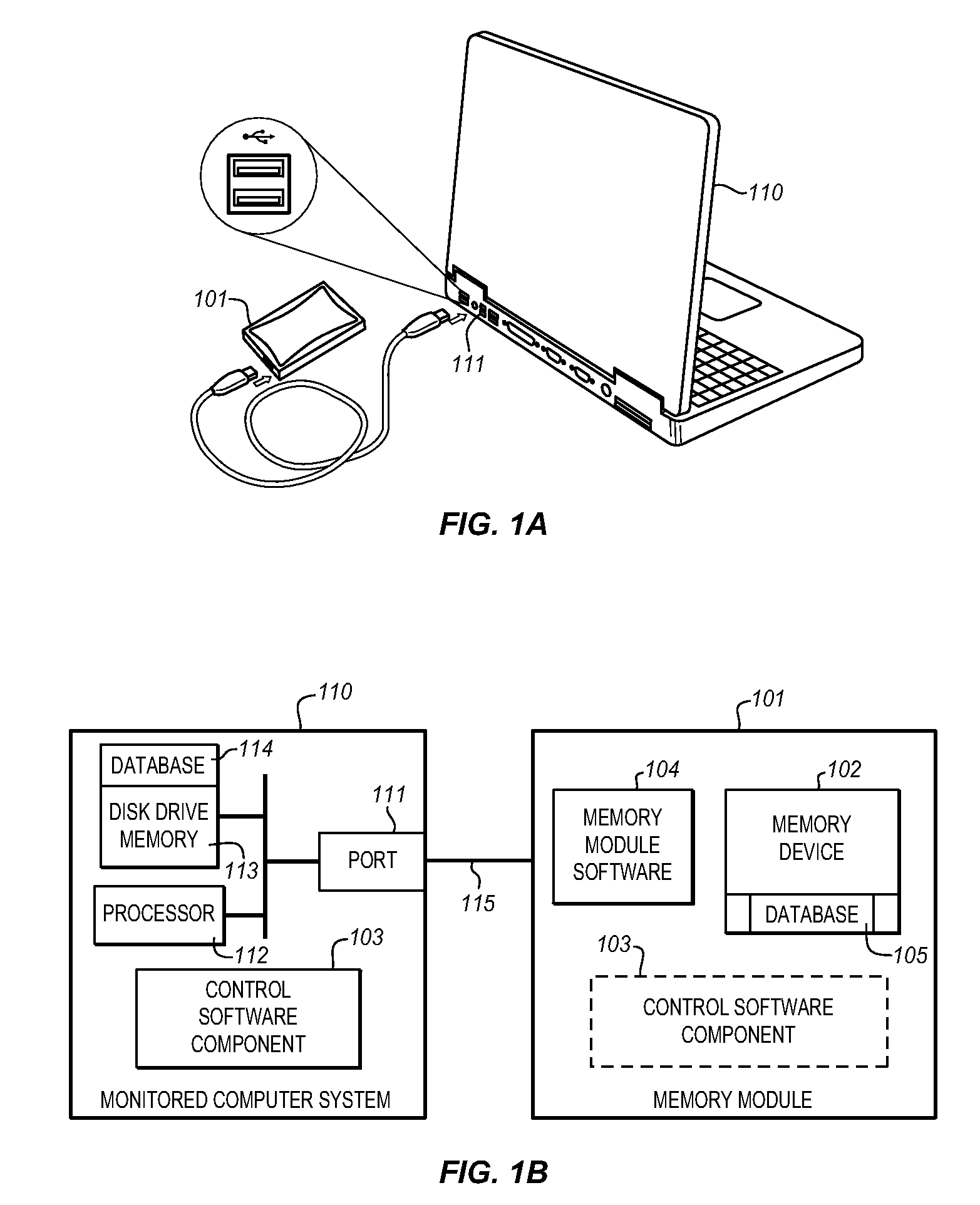
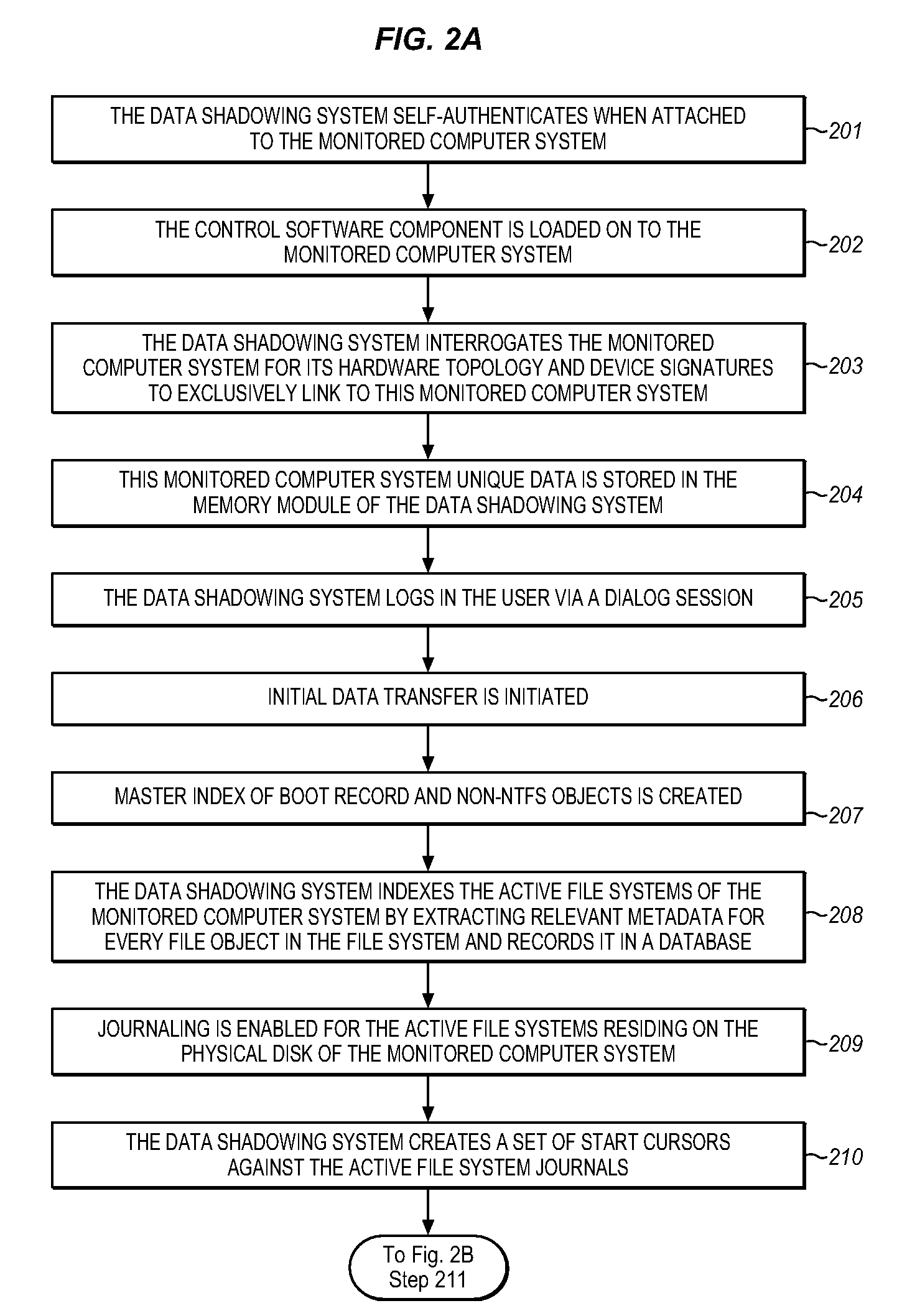
System for automatically shadowing data and file directory structures that are recorded on a computer memory
ActiveUS20080104147A1Efficiently track and storeData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalFile systemComputerized system
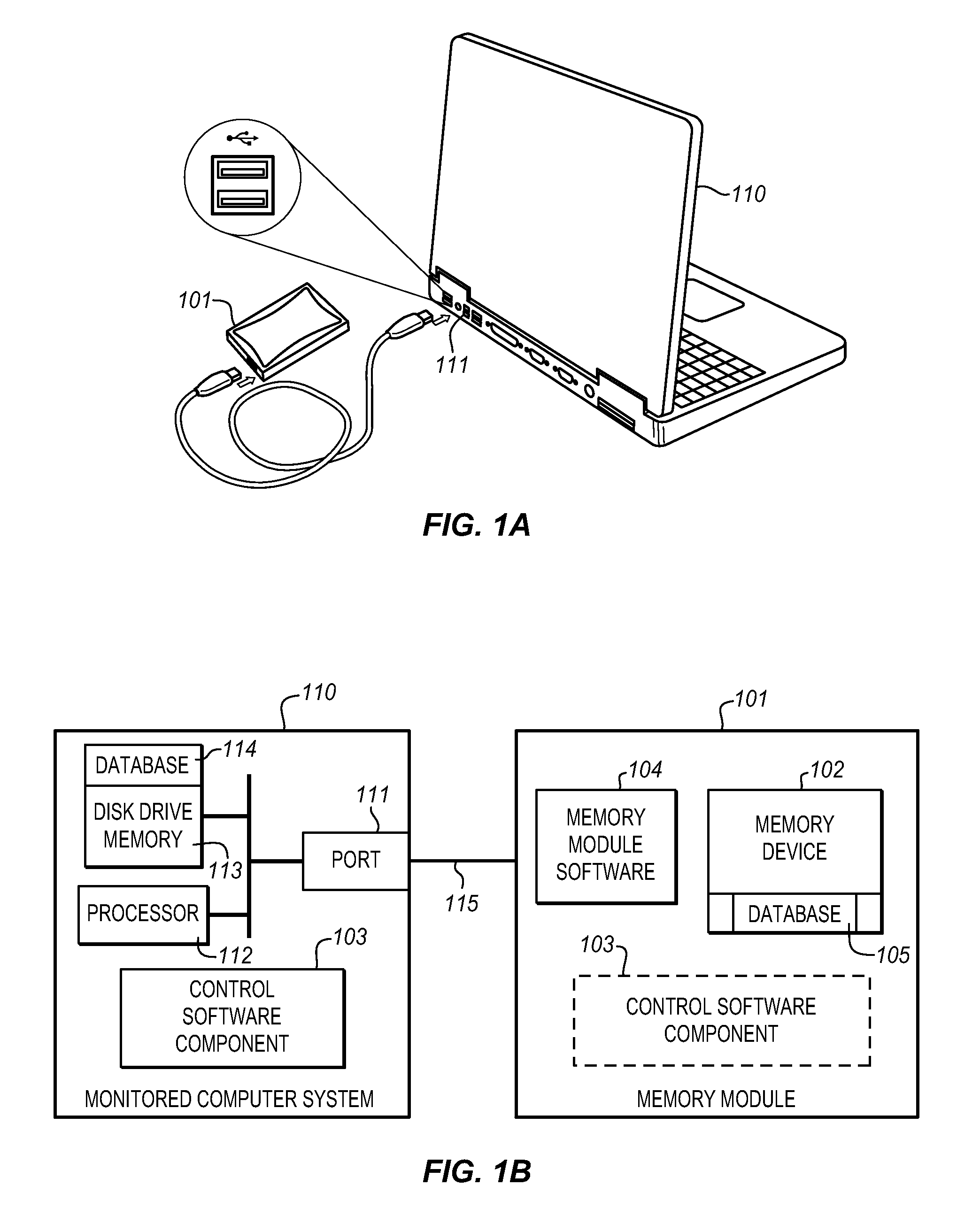
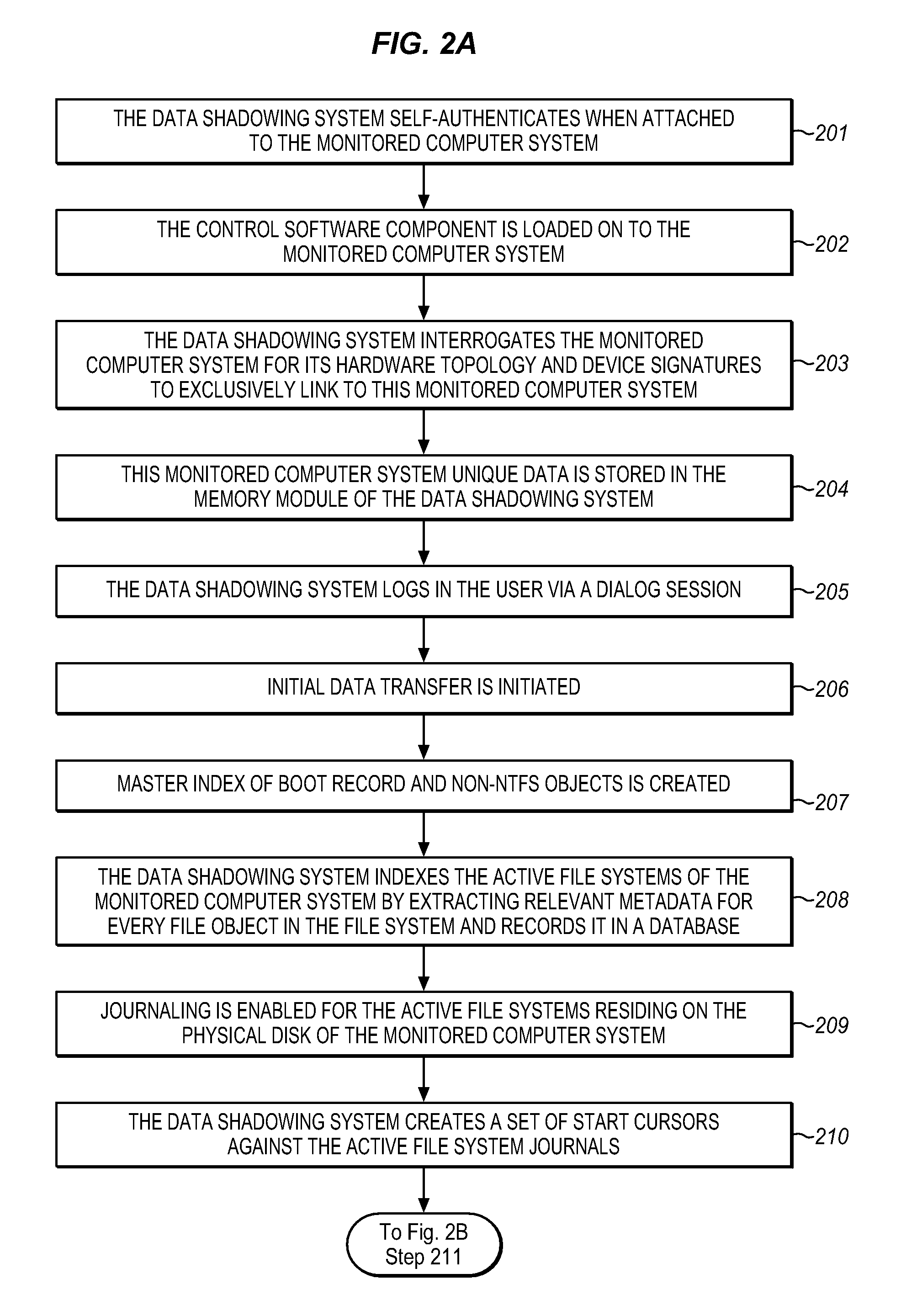
The Data Shadowing System comprises a memory module that is connected to the monitored computer system via an existing input / output port to store the shadowed data. The memory module includes a memory device for data storage as well as software, including a control software component that is automatically installed on the monitored computer system when the memory module is first connected to the monitored computer system, as well as associated module software for maintaining a record of the data stored on the memory device. The Data Shadowing System automatically stores the data on the memory module in a single format, while representing it in a data management database in two formats: disk sectors and files. The Data Shadowing System thereby efficiently tracks and stores the state of multiple file systems over time, while allowing for correct disk-level and file-level restoration to a point-in-time without storing redundant data.
Owner:CARBONITE CORP
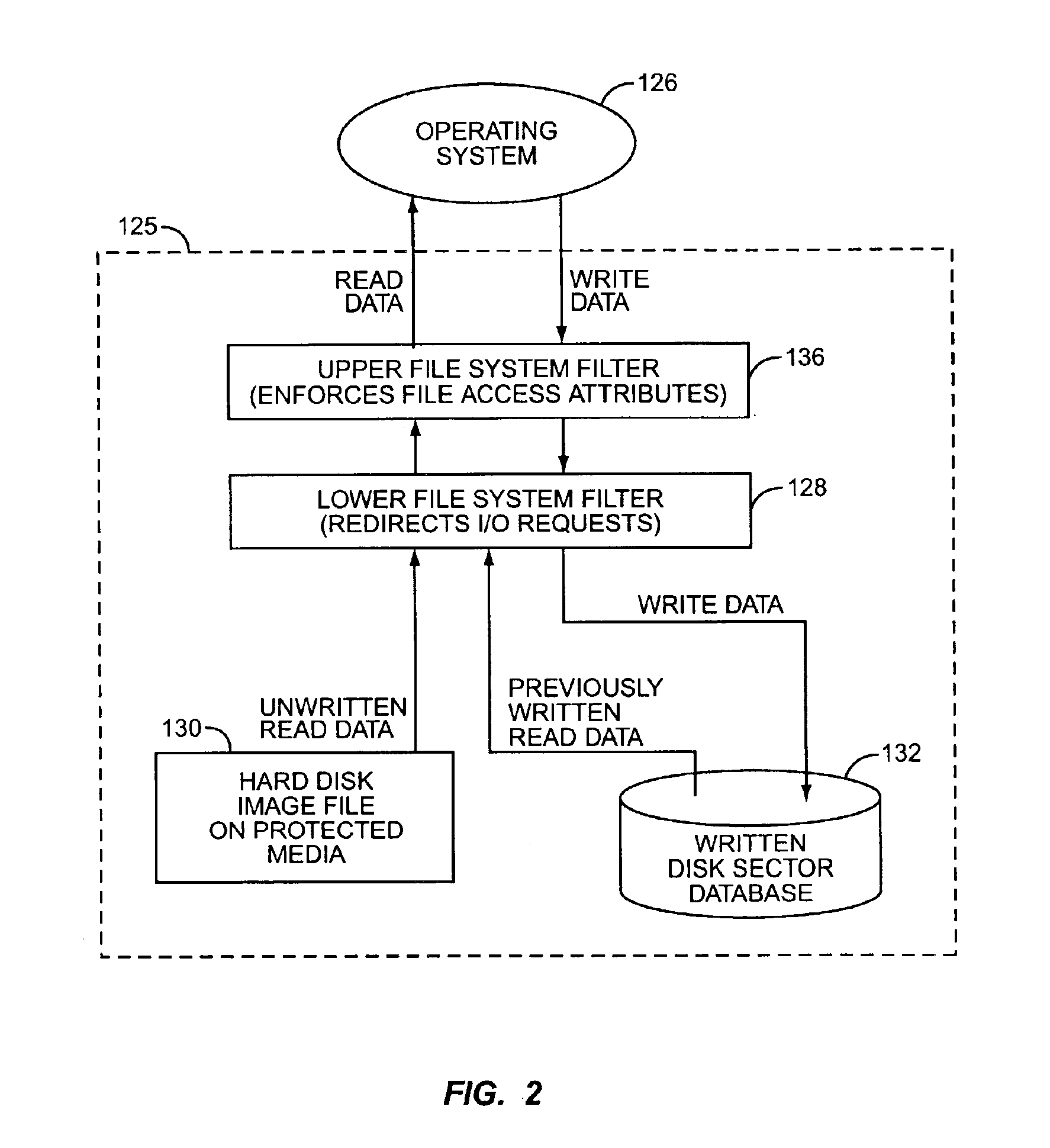
Emulated read-write disk drive using a protected medium
ActiveUS6999913B2Input/output to record carriersRecord information storageHard disc driveOperational system
A read-write hard disk drive is emulated using a hard disk drive image file on a protected medium such as a CD-ROM, a written disk sector database, and file system filters. A file system filter intercepts file I / O requests from the operating system. Initial read requests are serviced from the hard disk drive image file. Write operations are directed to a database, such as in RAM. Subsequent read requests for previously written data are serviced from the database. Another file system filter monitors attempts to alter the file access attributes, and prevents pre-existing read-only files on the emulated drive from being written or deleted. The maximum size of the written disk sector database is the sum of sectors on the hard disk drive image file allocated to read-write files and free space. The emulated read-write hard disk drive allows for the execution of programs requiring a read-write native media.
Owner:III HLDG 1
System for automatically recovering a computer memory using shadowed data and file directory structures
ActiveUS20080104148A1Efficiently track and storeError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsFile systemTerm memory
The Data Shadowing System comprises a memory module that is connected to the monitored computer system via an existing input / output port to store the shadowed data. The memory module includes a memory device for data storage as well as software, including a control software component that is automatically installed on the monitored computer system when the memory module is first connected to the monitored computer system, as well as associated module software for maintaining a record of the data stored on the memory device. The Data Shadowing System automatically stores the data on the memory module in a single format, while representing it in a data management database in two formats: disk sectors and files. The Data Shadowing System thereby efficiently tracks and stores the state of multiple file systems over time, while allowing for correct disk-level and file-level restoration to a point-in-time without storing redundant data.
Owner:CARBONITE CORP
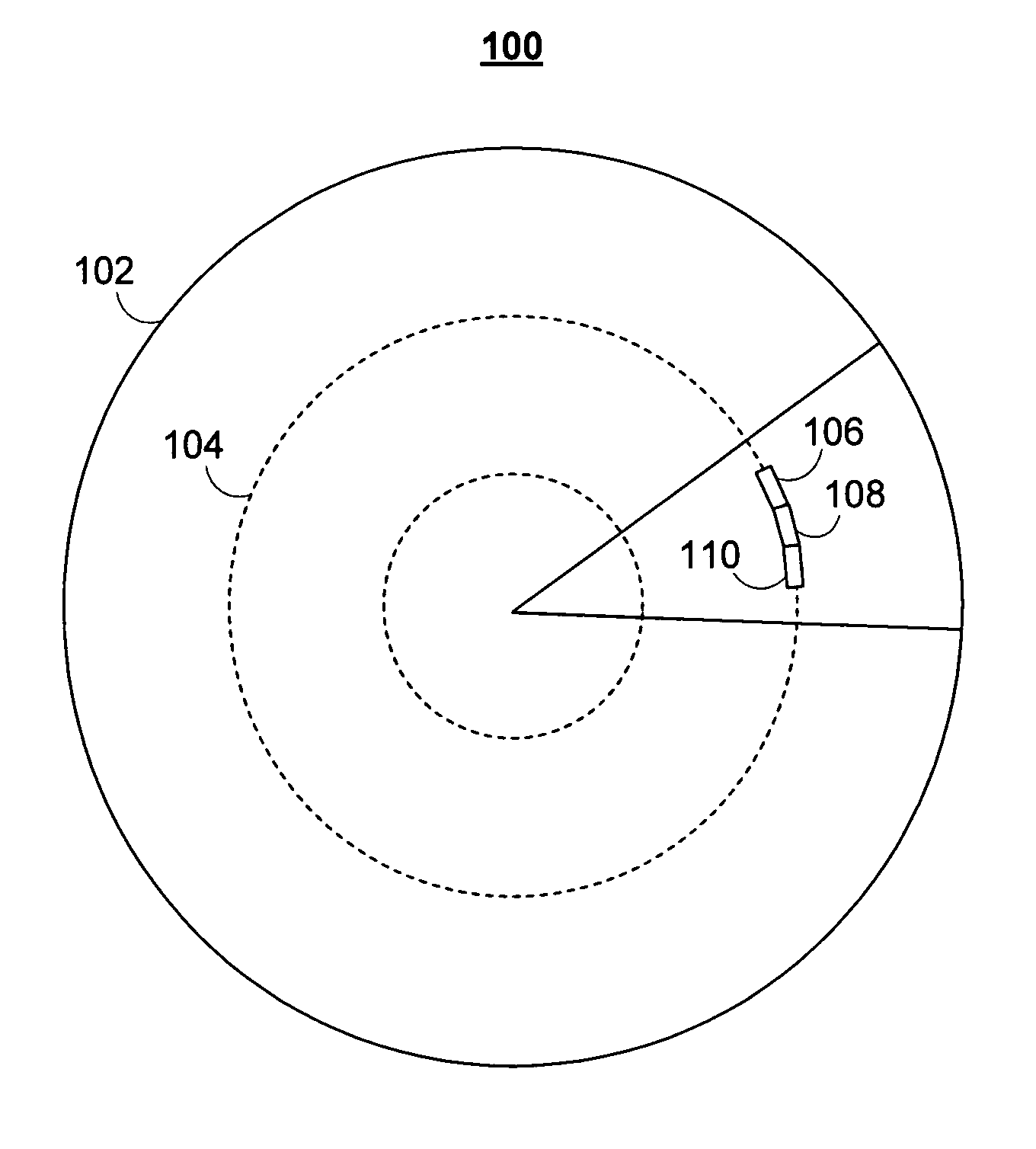
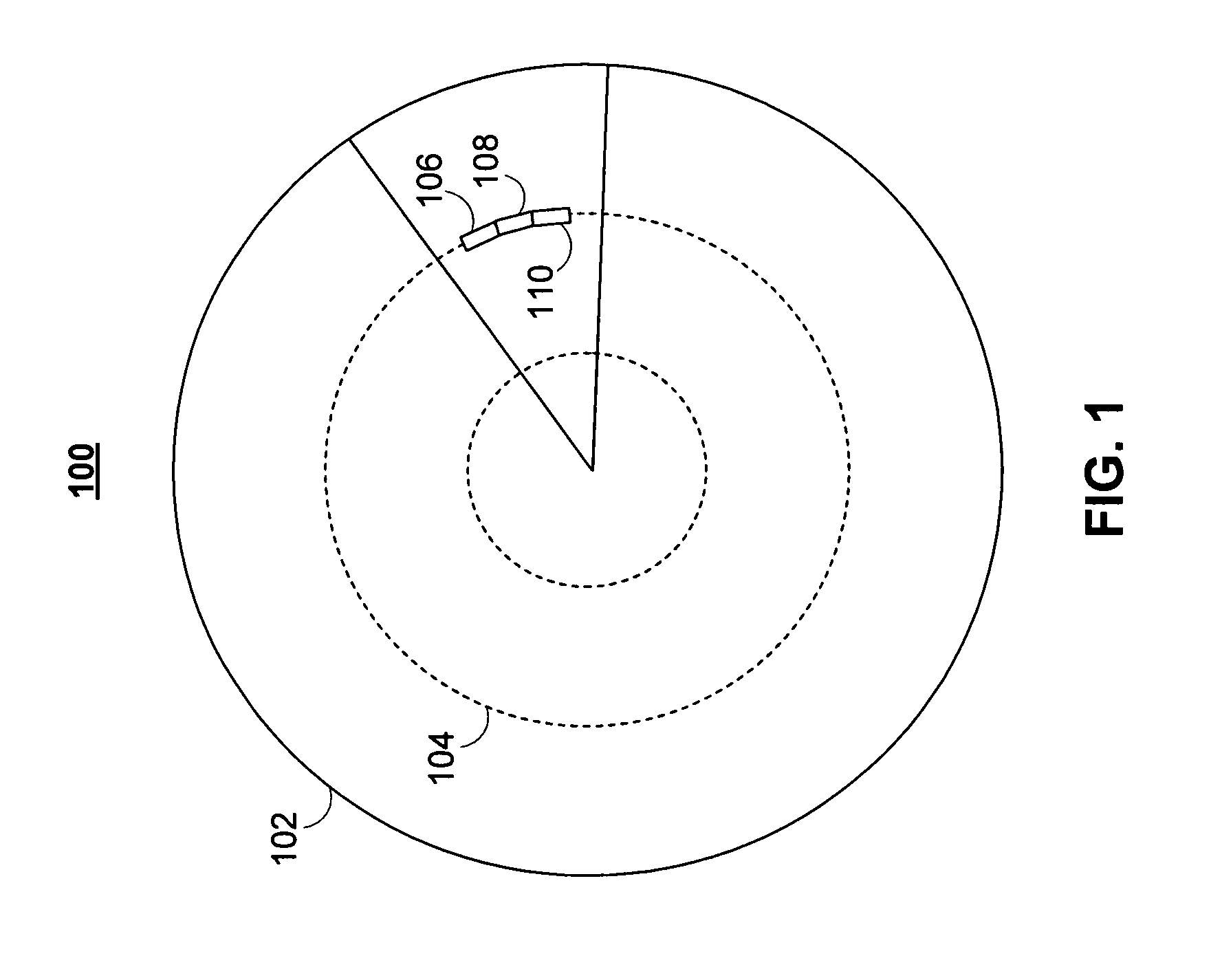
Sync mark detection with polarity uncertainty
InactiveUS7881164B1Small likelihoodModification of read/write signalsRecord information storageElectrical polarityDisk sector
Systems and methods for detecting a disk sync mark are provided. The systems and methods for detecting the disk sync mark rely on a detecting the disk sync mark on at least one timing interval. A window of data read bits from a particular disk sector are examined to determine whether they match the disk sync mark. The disk sync mark may be differentiated from expected versions of the disk sync mark using a calculated set of thresholds.
Owner:MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD
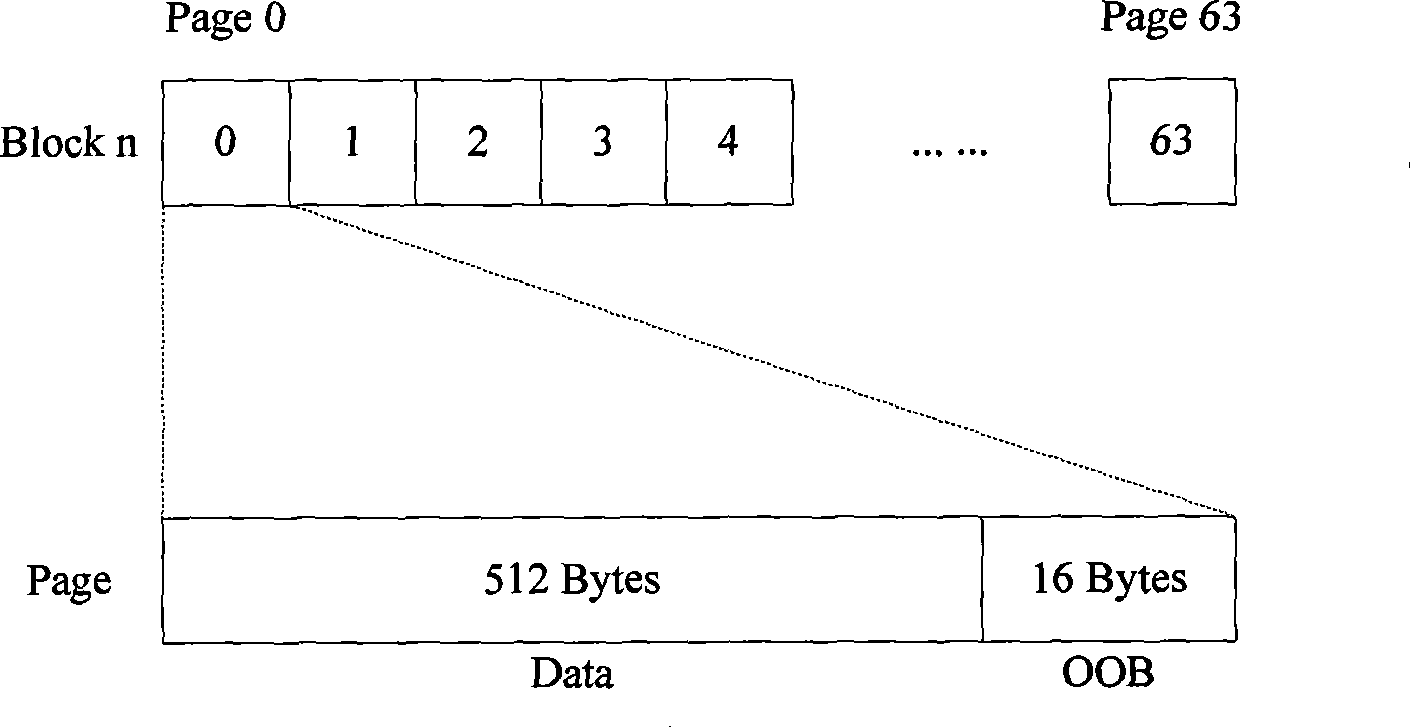
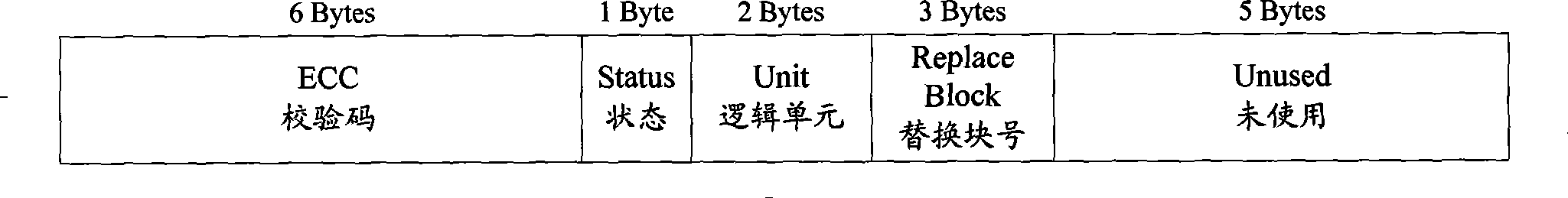
Method and device for simulating Nand flash of 2048 byte page into hard disk
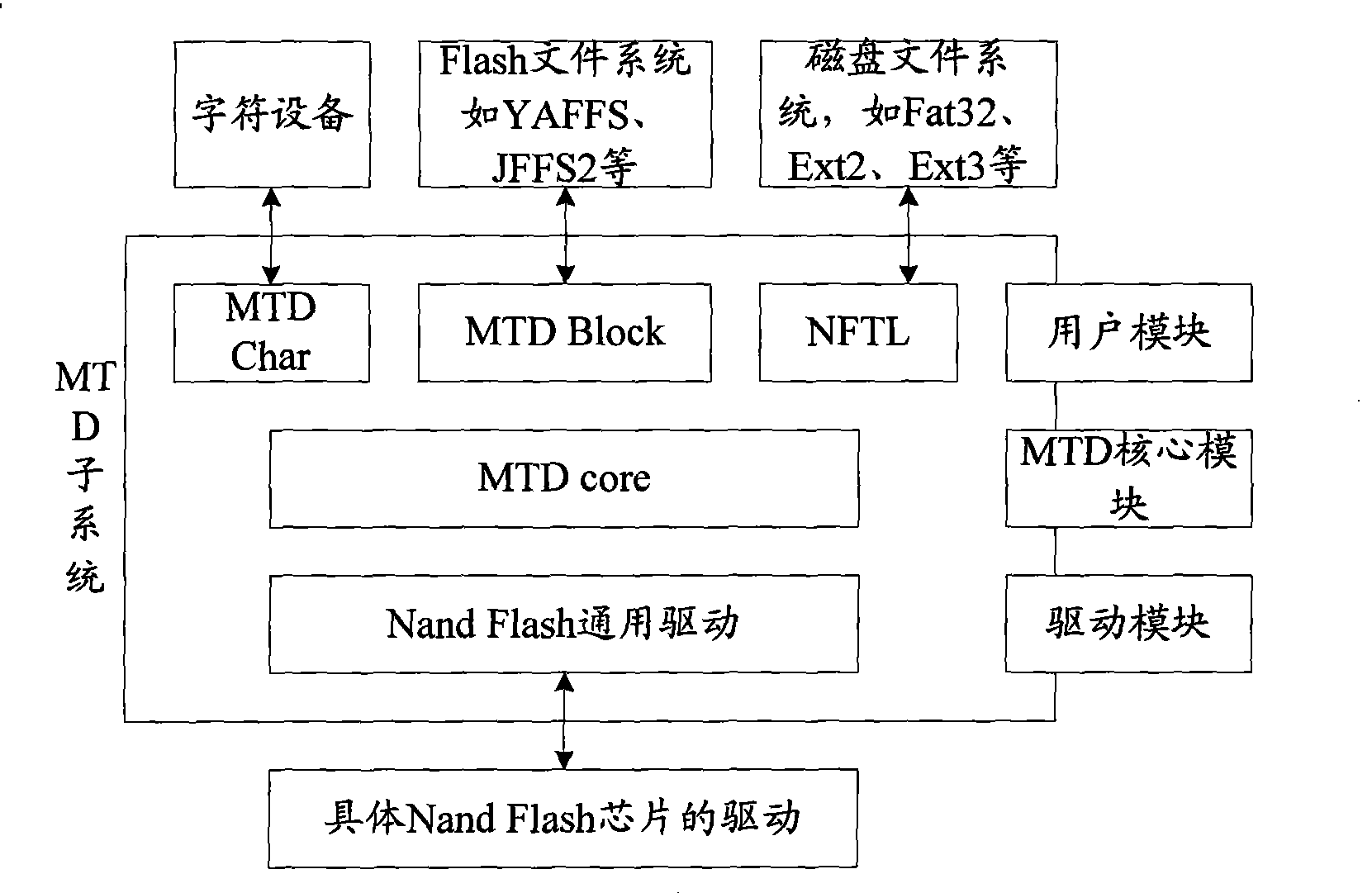
ActiveCN101364166AInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile systemByte
The invention discloses a method and a device for simulating a 2048 byte page Nand Flash into a hard disk. The method comprises the following steps: the read operation or the write operation of a disk file to a disk sector is received; a 512 byte page corresponding to the disk sector is acquired according to the OOB information of the 512 byte page in Nand Flash, and read operation or the sequential write operation in the page in a block is performed to the acquired 512 byte page, wherein, the 512 byte page is obtained by dividing each 2048 byte page in advance; the OOB information comprises the logic unit, the state, the logic sector corresponding to the 512 byte page and the replacing block of the block. The method divides each page of each block in the Nand Flash of the 2048 byte page into four 512 byte pages, and realizes the simulating of the 2048 byte page Nand Flash the a hard disk according to the OOB information of the 512 byte page in Nand Flash, thereby running the disk file system on the large page Nand Flash.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Using external memory devices to improve system performance
InactiveUS20090144495A1Improve productivity and performanceImprove system performanceInput/output to record carriersDigital computer detailsProduction rateHard disc drive
The invention is directed towards a system and method that utilizes external memory devices to cache sectors from a rotating storage device (e.g., a hard drive) to improve system performance. When an external memory device (EMD) is plugged into the computing device or onto a network in which the computing device is connected, the system recognizes the EMD and populates the EMD with disk sectors. The system routes I / O read requests directed to the disk sector to the EMD cache instead of the actual disk sector. The use of EMDs increases performance and productivity on the computing device systems for a fraction of the cost of adding memory to the computing device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
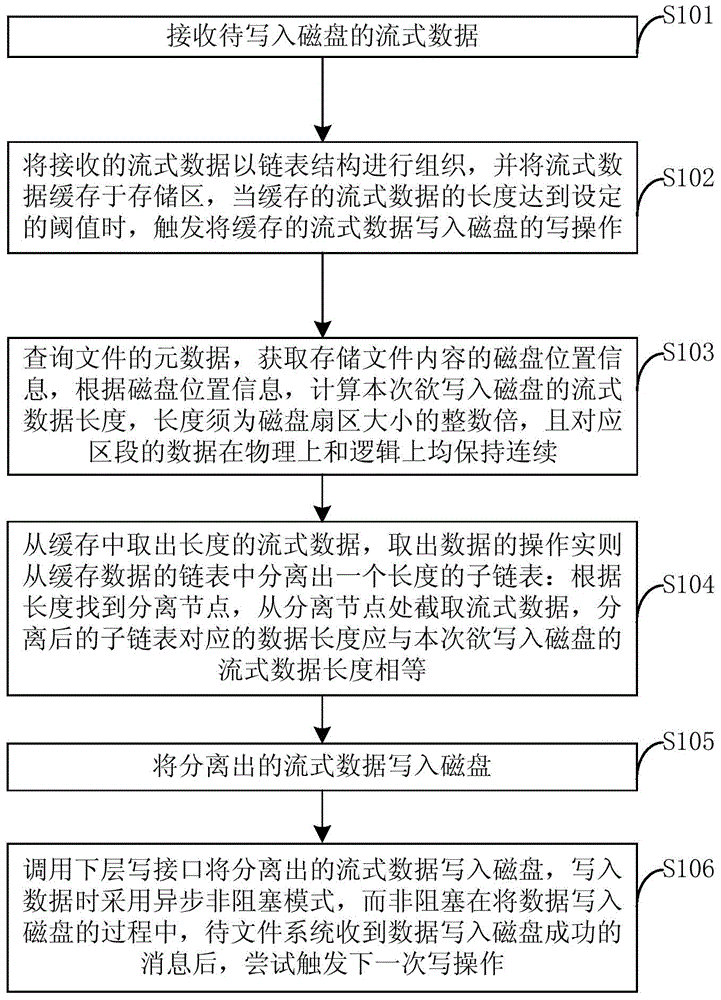
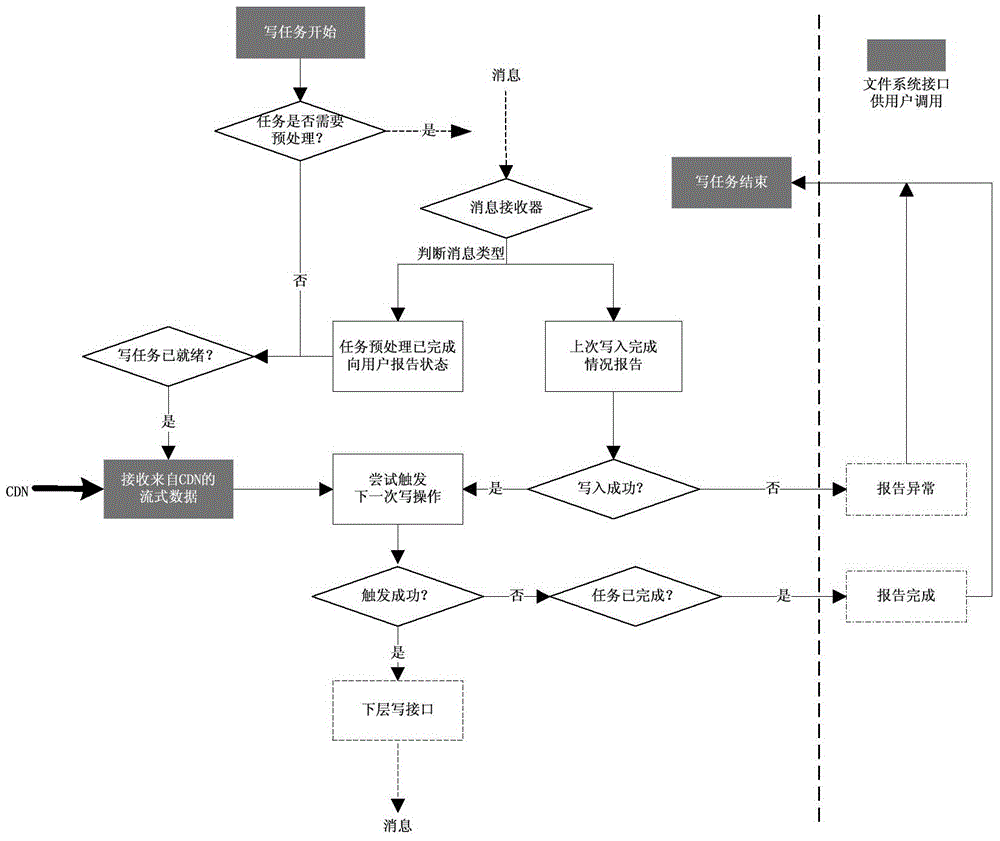
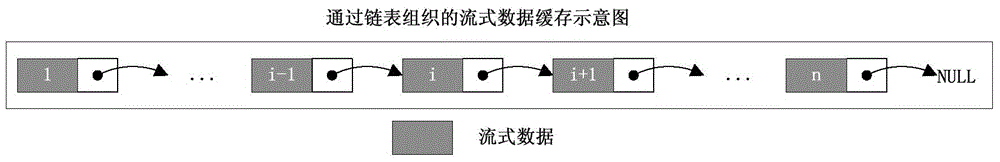
Streamed data write-in method based on embedded file system
ActiveCN104536699ATiming OKImprove writing efficiencyInput/output to record carriersSpecial data processing applicationsStreaming dataFile system
The invention relates to a streamed data write-in method based on an embedded file system. The method includes that streamed data of a to-be-written in disk are received; the received streamed data are organized and cached in a chain list structure, and when length of the cached data reaches a set threshold value, a write operation that writes the cached streamed data in the disk is triggered; the streamed data are separated from a cache, data length of the to-be-written in disk at the time is calculated, the length is required to be integer multiples of the size of a disk sector, data of corresponding sections are kept continuous physically and logically, and corresponding data length of subchain tables after separation is required to be equal to the data length of the to-be-written in disk at the time; the separated streamed data are written in the disk, a lower layer write interface is called to write the separated streamed data in the disk, an asynchronous non-blocking mode is applied when the data are written in, and the write operation of next time is tried to be triggered after the file system receives a message that the data are successfully written in the disk in the process of writing the data in the disk in the non-blocking mode.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU SEANET TECH CO LTD
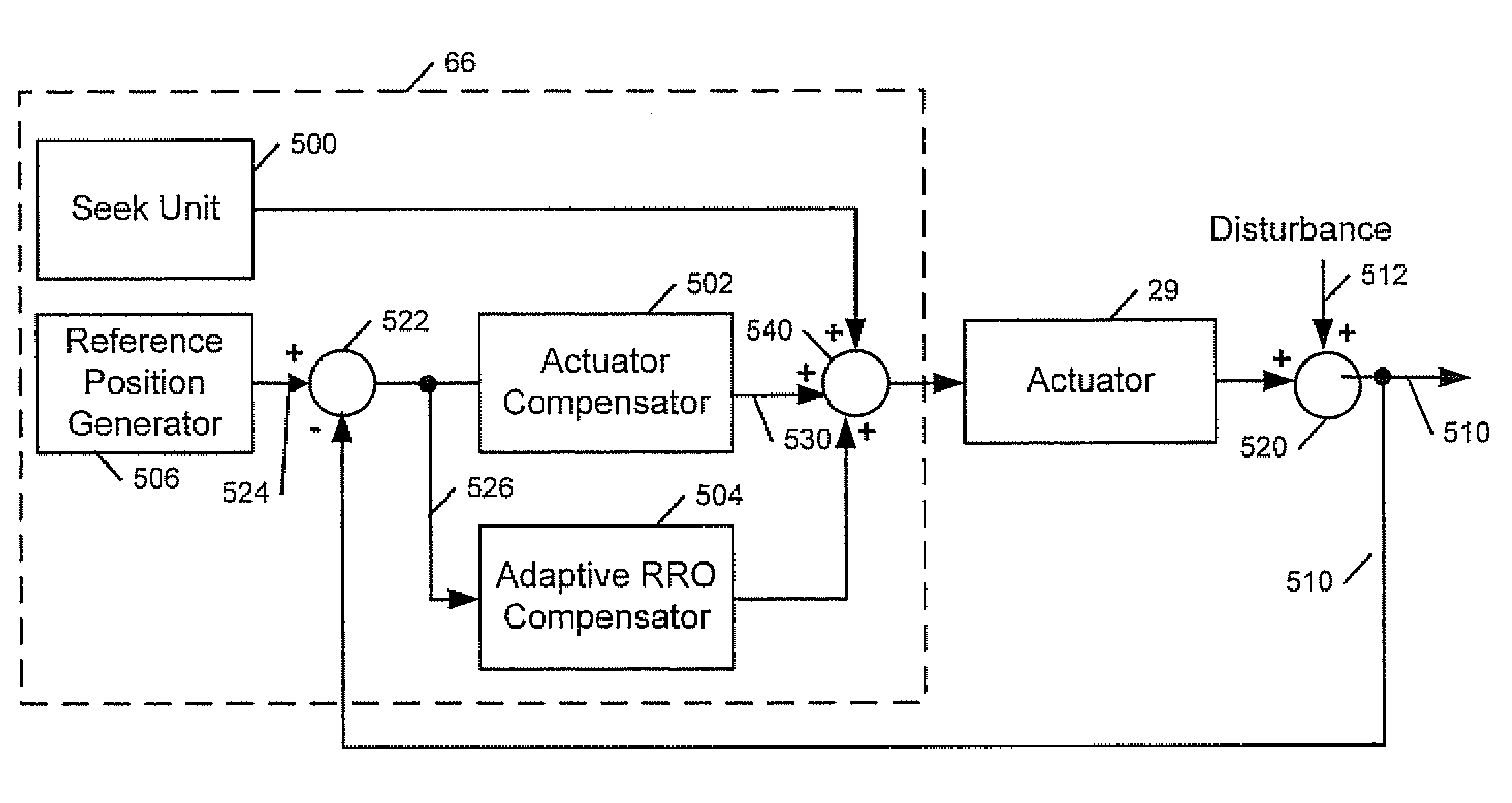
Adapting compensation for repeatable runout of sectors based on tracked sector adaptation status
InactiveUS7139149B1Driving/moving recording headsRecord information storageDisk sectorIndustrial engineering
Methods, servo controllers, disk drives, and computer program products are provided for adapting compensation for repeatable runout (RRO) of sectors of a disk in a disk drive. RRO of a plurality of sectors of the disk is compensated. A status of whether the RRO compensation has been adapted is tracked for at least some of the sectors of the disk, and corresponding records are formed based on the statuses. The RRO compensation of the tracked sectors is selectively adapted or not adapted based on the records.
Owner:MAXTOR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com