Reverser mechanism for uni-directional rotational driving of a wheel set
a technology of uni-directional rotation and reversing mechanism, which is applied in the direction of electromechanical clocks, timers, time indications, etc., can solve the problems of high friction force at high speeds, large assembly number of parts, and relative cumbersomeness, and achieves the effect of low cost and higher or equal performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
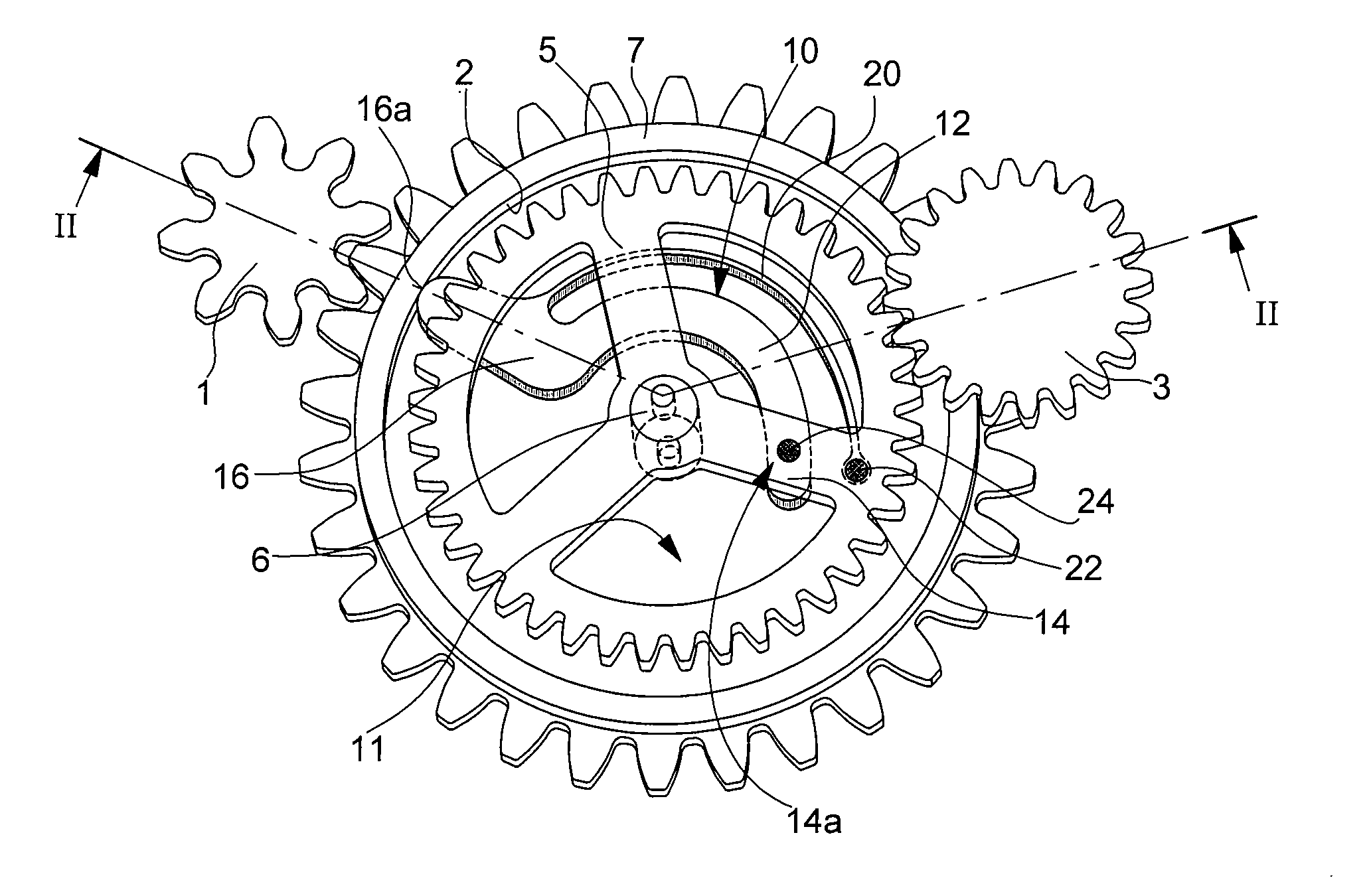
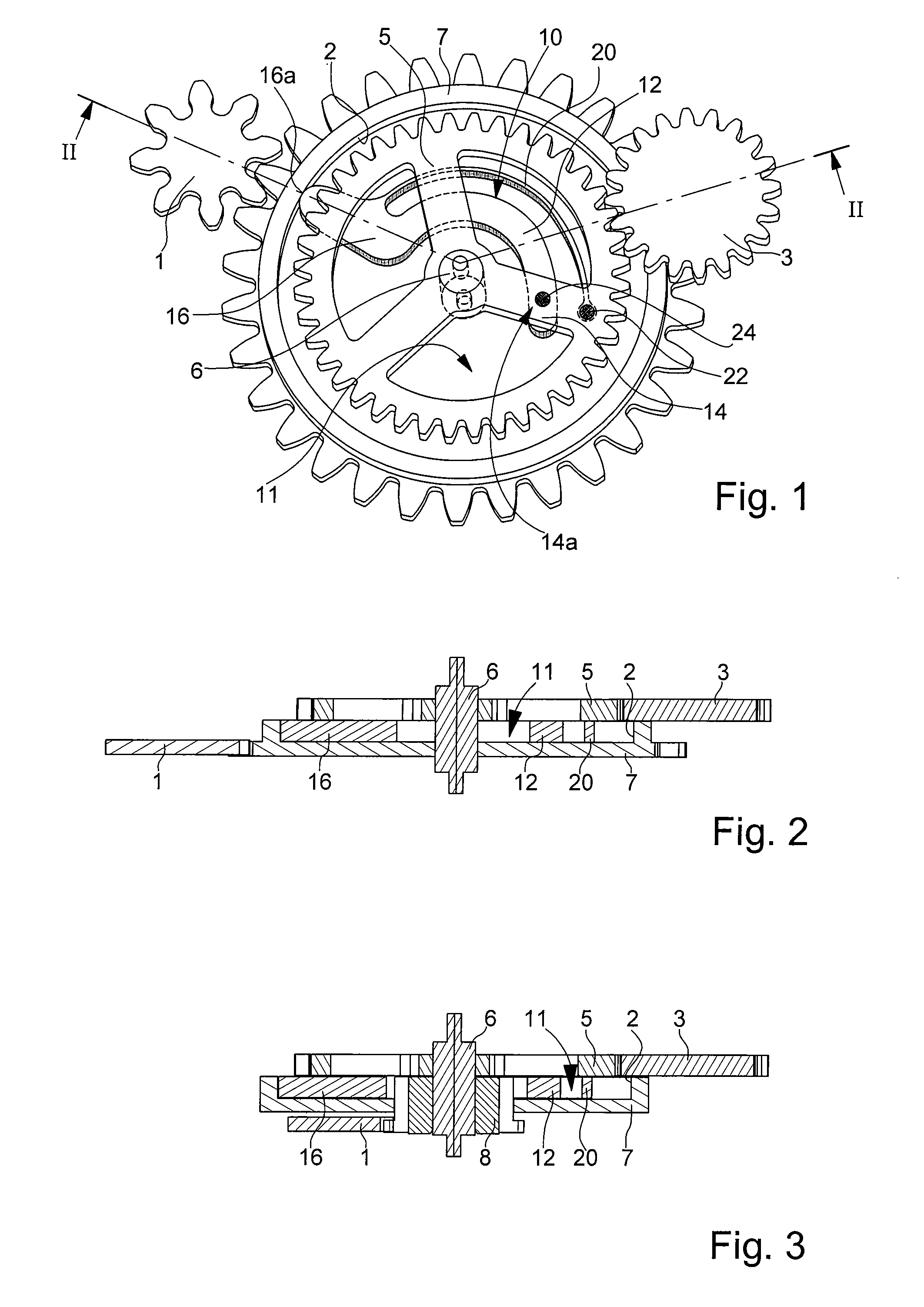
[0026]Referring first of all to FIGS. 1 and 2, we will describe below a reverser mechanism according to the invention, which will be illustrated by way of example by an automatic winding mechanism for a mechanical watch via an oscillating weight whose drive pinion 3 acts in a single direction to drive the first wheel set 1 of a kinematic reduction chain (not shown), the last wheel set of which is meshed with the barrel ratchet.
[0027]Drive pinion 3 of the oscillating weight meshes with a first toothed driving wheel 5 freely mounted on an arbour 6 pivoting between a plate and a bridge (not shown), or between any other armature for positioning the parts of a timepiece mechanism in relation to each other.
[0028]A second driven wheel 7 is positioned below drive wheel 5 and is also freely mounted on arbour 6 about which it rotates. It also comprises a toothing meshed with the first wheel set 1 of the kinematic chain.
[0029]Referring now to the cross-section of FIG. 2, it can be seen that dr...
second embodiment
[0032]As can be seen in the perspective diagram in FIG. 1, the angle formed by axis 6 with pivoting point 14a and point of abutment 16a is an obtuse angle, slightly less than 180°, meaning that the arm allows driving wheel 5 to rotate freely in one direction, without driving driven wheel 7, and conversely drives driven wheel 7 when driving wheel 5 is rotating in the other direction, as will be described in detail with reference to the
[0033]The cross-sectional diagram of FIG. 3 concerns a variant of the first embodiment regarding the position of the power take-off on driving wheel 5 and on driven wheel 7. As is clear, it is essential that driving wheel 5 and driven wheel 7 are free to rotate in relation to each other when coupling mechanism 10 is not active. In the example shown, driven wheel 7 no longer has a toothing but it is driven onto an additional pinion 8, which is itself secured to arbour 6, whereas driving wheel 5 remains freely mounted on said arbour 6. The first wheel set...
fourth embodiment
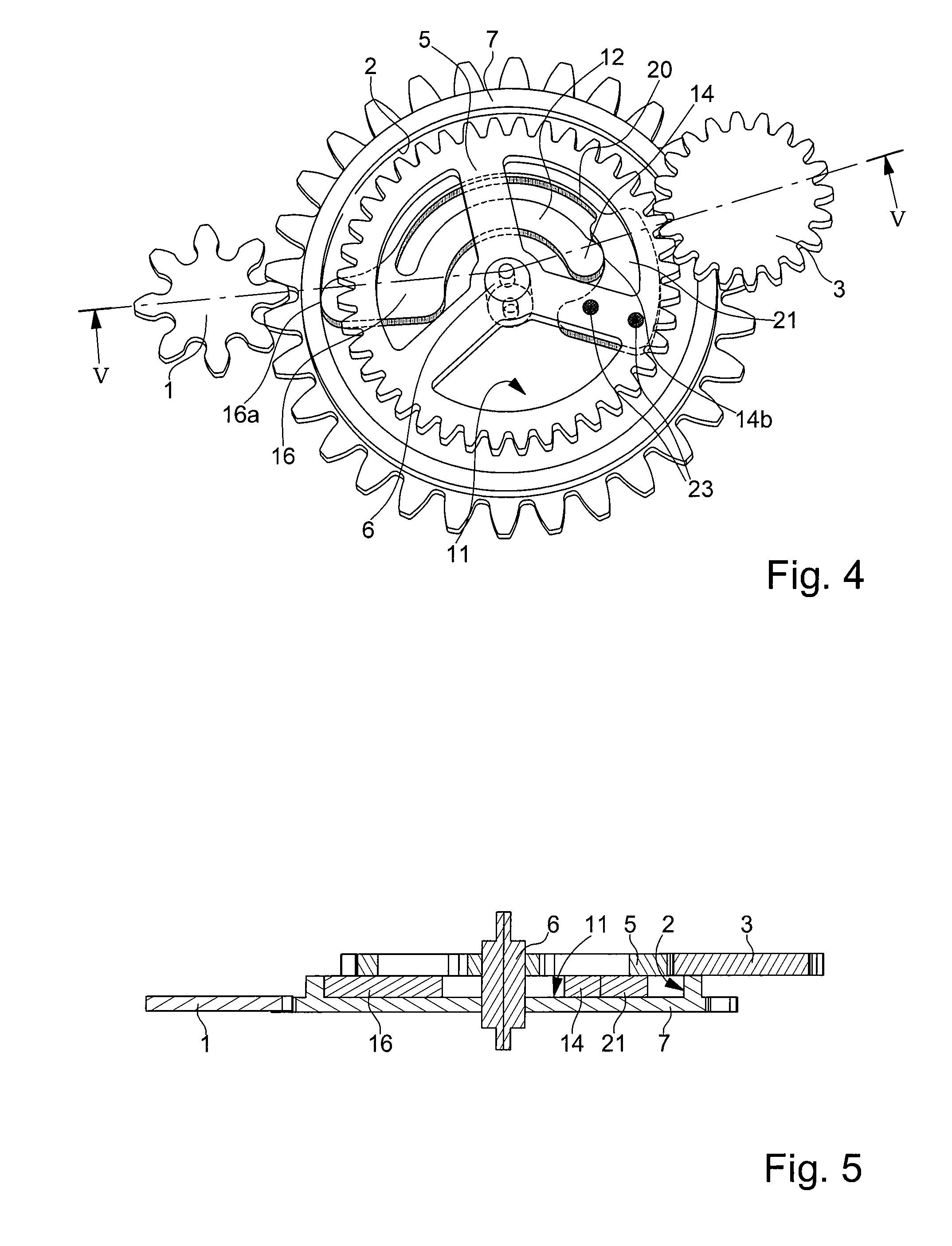
[0047]With reference now to FIGS. 13 to 16, a third and fourth embodiment will be described below concerning a “double direction” reverser mechanism, which basically consists in coupling a first single direction reverser mechanism, whose references will be followed by the letter “a”, and a second single direction reverser mechanism whose references will be followed by the letter “b”.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com