Extruded Cushioning Insole
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
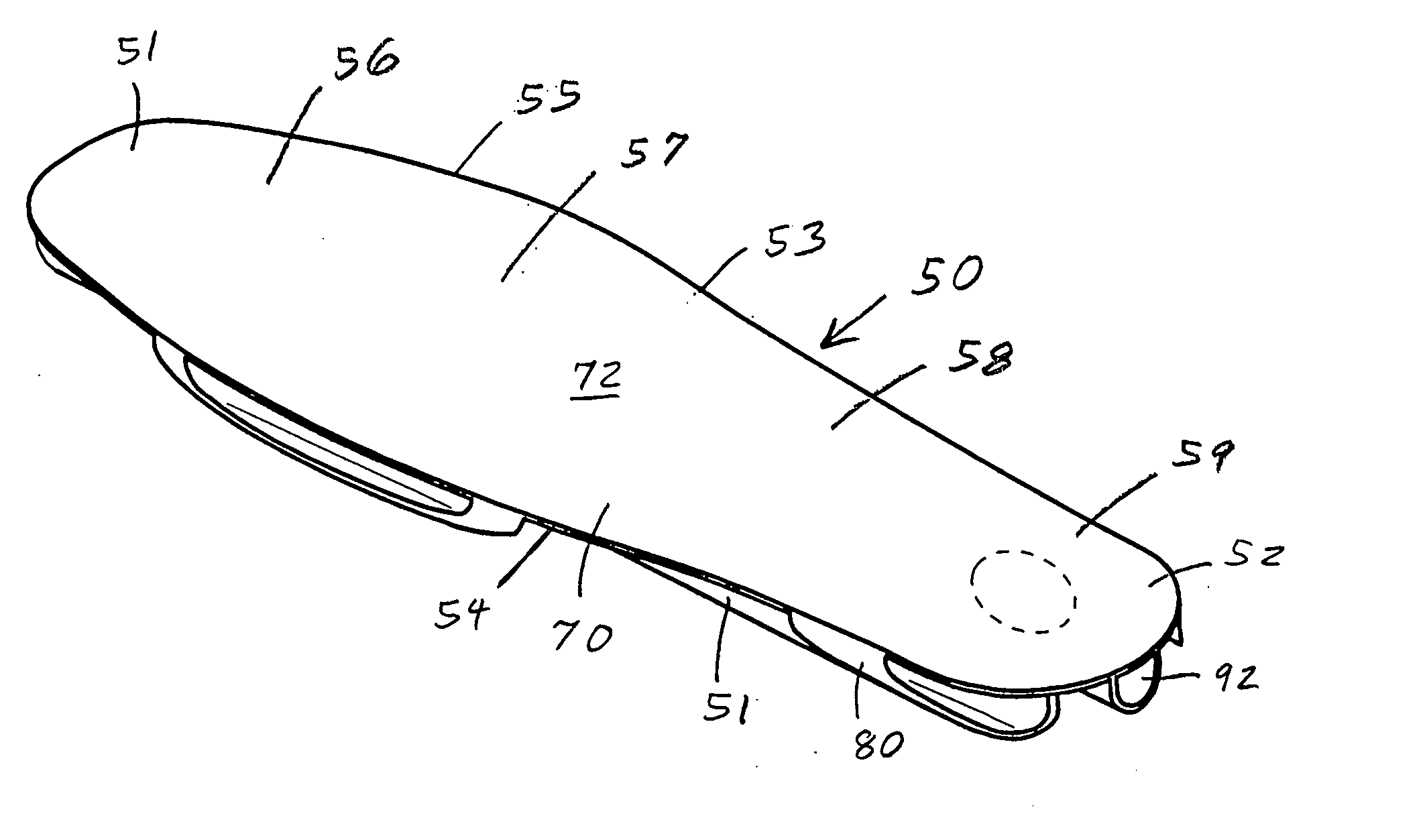
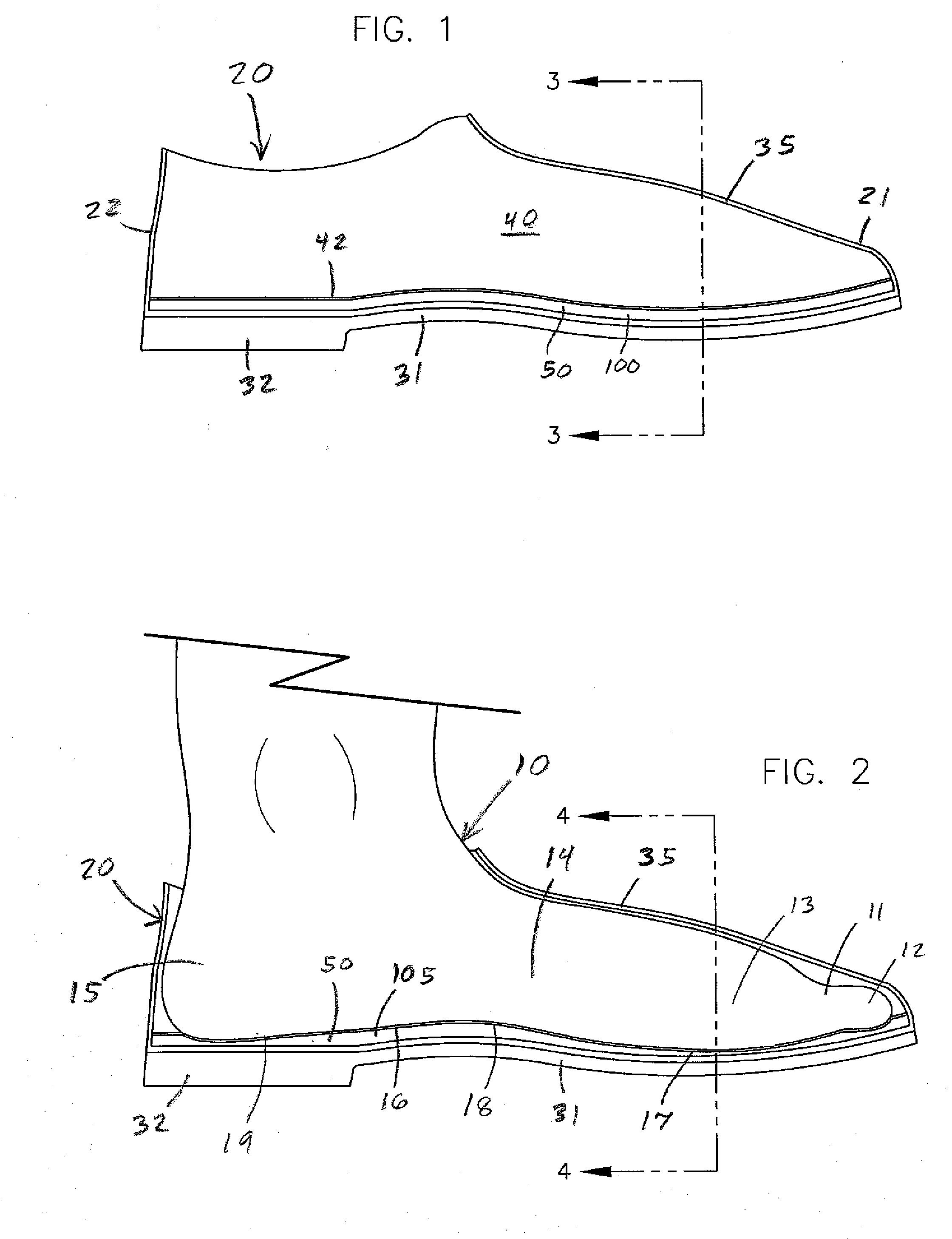
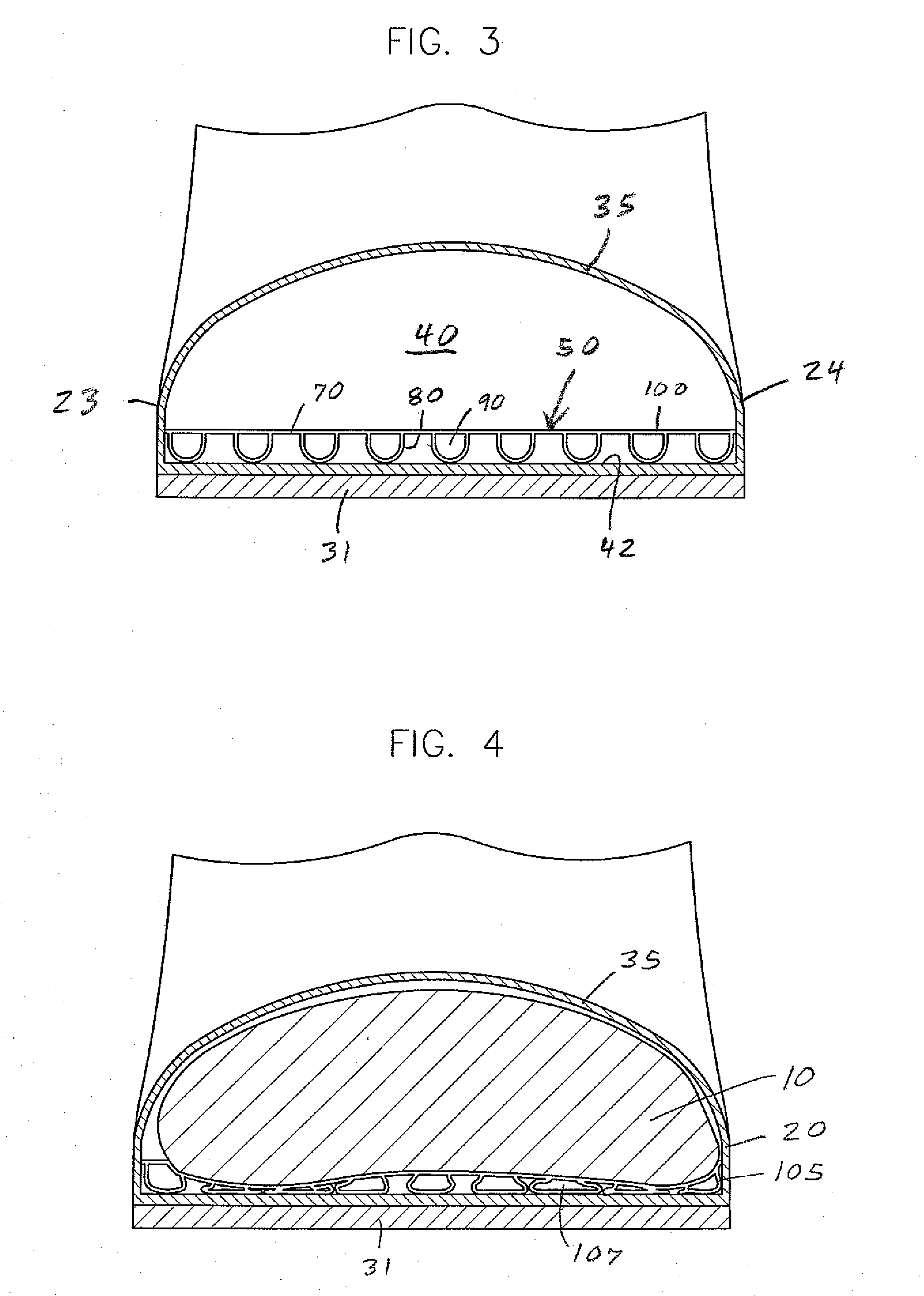
[0056]the insole or insert 50 is shown in FIGS. 3, 4, 6 and 7. This insert 50 has a continuous upper layer 70 and a plurality of hollow, lower tubes 80. The upper layer or flexible pad 70 has a solid body with generally flat, parallel upper and lower surfaces 72 and 74. The layer 70 has a uniform thickness of about 0.06 inch. The upper surface 72 can have a number of upwardly extending, uniformly spaced, gripping ridges, about 10 per inch (not shown) to allow the bottom surface 16 of the foot 10 or a sock to better grip the insert 50. Each ridge has a height of about 0.007 inch. The upper layer 70 is preferably continuous from one end of the insert to the other, and from one side of the insert to the other. The insole 50 can include one or more cutout areas 78 to relieve or avoid pressure from the bottom 16 of the foot 10 in those areas as in FIGS. 6 and 12.
[0057]The tubes 80 project down from and are uniformly spaced across the lower surface 74 of the upper layer 70. Each tube 80 i...
second embodiment
[0061]the insole or insert 150 is shown in FIG. 8. This insert 150 also has a continuous, flexible pad 70 with a uniform thickness of about 0.06 inch, and several evenly spaced conjoined tubes 80. Each tube 80 is formed by a wall 82 having opposed side portions 83 and an arced bottom portion 84. The wall 82 has a uniform thickness of about 0.03 to 0.04 inch. Each tube 80 has a height of about 0.18 inch and a width of about 0.25 inch. The insert 150 has a total relaxed or uncompressed height of about 0.24 inch. Adjacent tubes 80 share a common side portion 83 so there are about 16 longitudinal tubes in a 4 inch wide insole 150. When in a relaxed or extended position 100, each tube 80 has a half circle or hemisphere shape. When in a compressed position, the deformable side walls 83 bend and the bottom wall 84 flattens and buckles.
third embodiment
[0062]the insole 170 is shown in FIG. 9. This insert 170 has a continuous, flexible pad 70 with a uniform thickness of about 0.06 inch, and several evenly spaced tubes 80. The tubes 80 are similar to those of insole 150. Each tube 80 is formed by a wall 82 having opposed side portions 83 and an arcuate bottom portion 84. The wall 82 has a uniform thickness of about 0.03 to 0.04 inch. Each tube 80 has a height of about 0.18 inch and a width of about 0.36 inch. The insert 170 has a total uncompressed height of about 0.24 inch. Adjacent tubes 80 are relatively close together, but do not share a common side portion 83. There are about 11 longitudinal tubes in a 4 inch wide insole 170. When in a relaxed or extended position 100, each tube 80 has a half circle or hemisphere shape. When in a compressed position, the deformable side walls 83 bend outwardly and the bottom wall 84 flattens and buckles.
[0063]Insoles 150 and 170 are preferably made of FPVC plastic having a specific gravity of a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com