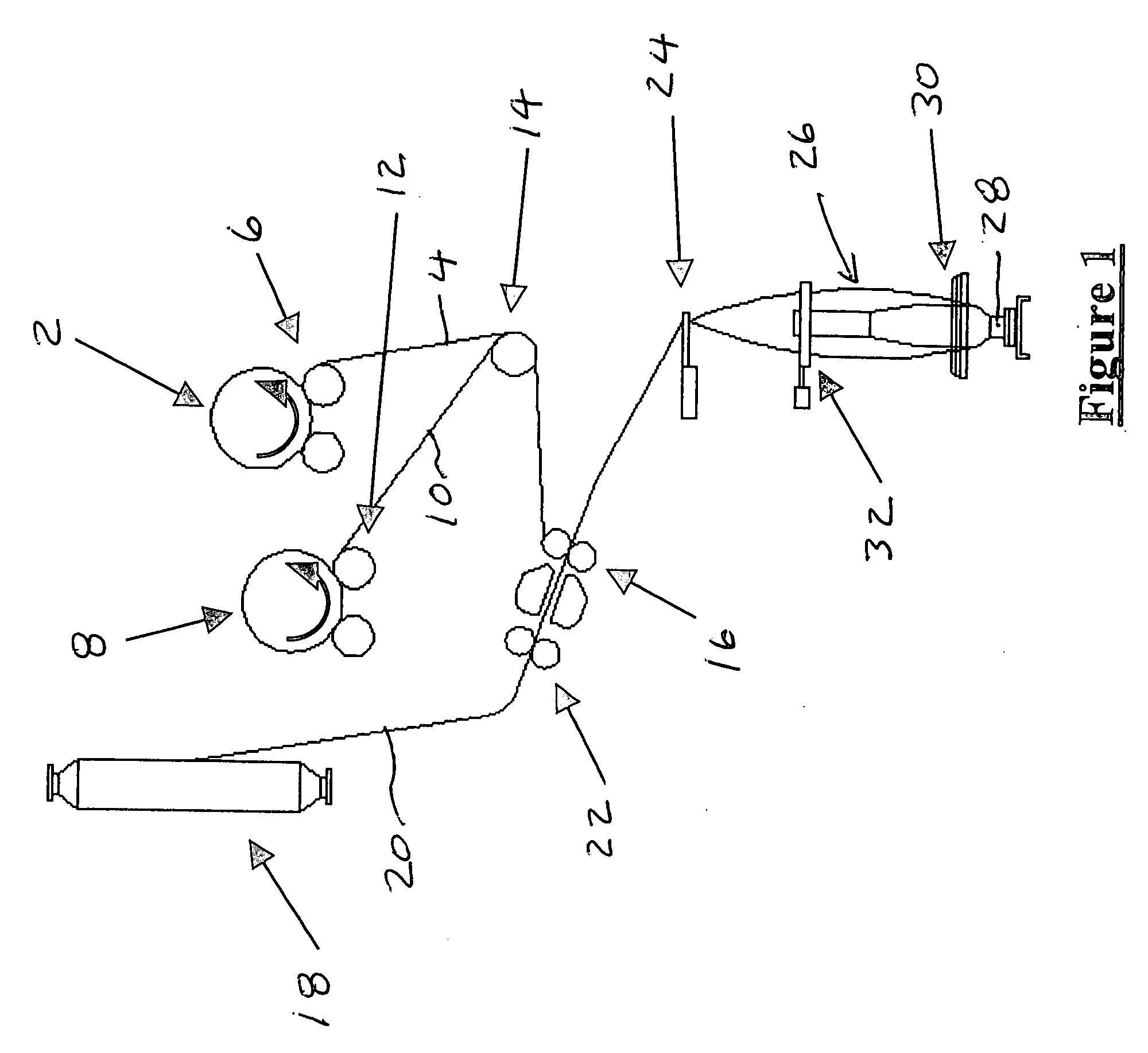
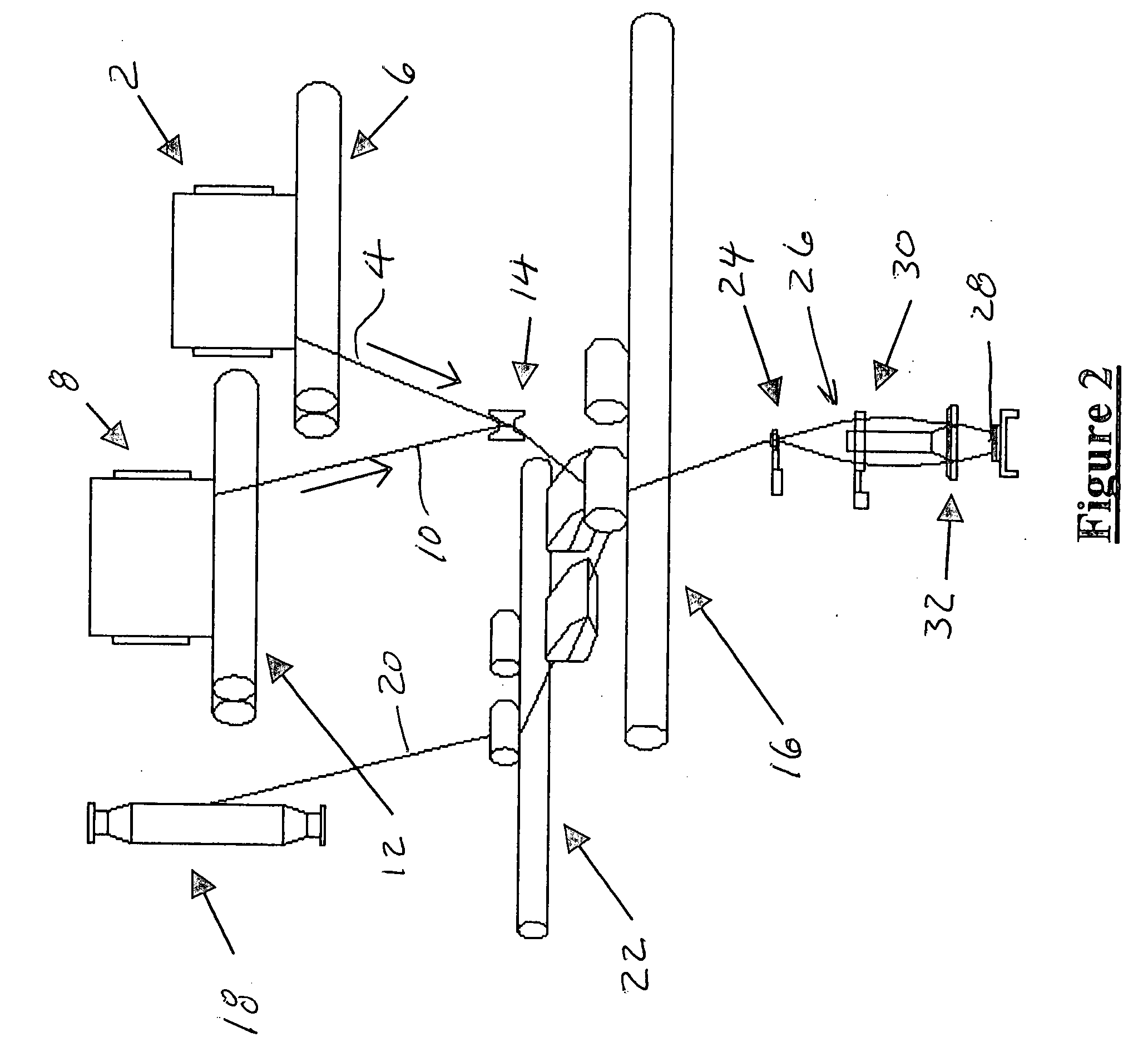
Core spun yarn and woven stretch fabric
a stretch fabric and core spun technology, applied in the field of core spun yarns, can solve the problems of poor appearance after finishing operation or in-house washing, high shrinkage, and excessive stretch power of conventional stretch fabrics made by using core spun spandex yarns, and achieve the effect of high dra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
t Stretch Fabric
[0035]This example shows the weft stretch denim fabric as shown in Table 1 below. Fabric no. 1 is in accordance with the present disclosure and uses a core bi-component polyester and spandex spun yarn in the weft, whereas fabric no. 2 and fabric no. 3 are previously known stretch fabrics made by using core bi-component polyester filament and a bare bi-component polyester filament respectively. As will be noted, fabric no. 1, in accordance with the present invention, obtains a better elongation as compared to fabrics no. 2 and fabric no. 3, and has a 100% cotton feel. Without any heat set process, fabric no. 1 achieves a good dimensional stability (−6.2%), good elongation (20%) and growth (2.5%). Other characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
TABLE 1Denim Woven Stretch Fabric - Weft StretchFabric Sample No.Fabric No. 1Fabric No. 2Fabric No. 3YarnWarp YarnNe7 SlubNe7 SlubNe7 SlubWeft YarnNe10 CSY 75D bi-Ne10 CSY 150D bi-Bare 600D bi-componentcomponent polyestercompone...
example 2
DYED WEFT STRETCH FABRIC
[0036]This example demonstrates a weft stretch fabric which has been dyed with a single step process. As shown in Table 2, fabric no. 4 is a fabric which uses a weft yarn in accordance with the present disclosure, which is a core bi-component polyester filament and spandex. Fabric no. 5 is a common stretch fabric with the weft yarn being a core bi-component polyester filament only. Both weft yarns had a cotton sheath, and were subjected to a one step dyeing process. As will be noted, fabric no. 4, in accordance with the present disclosure, achieved weft elongation of 21.6% and had growth of 1.9% and good stability of 3.5%. One significant advantage as compared to the use of the bare bi-component polyester filament or core bi-component polyester filament spun yarn is that the exposure of the bare polyester filament is improved. As shown in FIG. 7a, no bare polyester can be seen on fabric no. 4. On the other hand, FIG. 7b shows exposure of the bare polyester fi...
example 3
H DENIM FABRIC
[0037]This example shows the advantage of the use of yarns in accordance with the present disclosure in bi-stretch denim fabric as shown in Table 3. Fabric no. 6 uses yarns in accordance with the present disclosure and comprises a core bi-component polyester filament and spandex spun yarn both in the warp and weft direction. Fabric no. 7 comprises only a core bi-component polyester filament in the warp and weft as in previously known stretch fabrics. As shown in the table, fabric no. 6, has a higher stretch power (29%) in the weft direction. Further, the concern of exposure of the bare polyester in the warp of the previously known core bi-component polyester filament spun yarn is not a problem with the fabric no. 6 as the percentage of the polyester is much less. In this example, the exposure of the bare polyester was not seen on the finished fabric using the yarns in the present disclosure. The fabric's characteristic is summarized in Table 3.
TABLE 3Denim Woven Stretc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| warp elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com