Method and system for global coverage analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
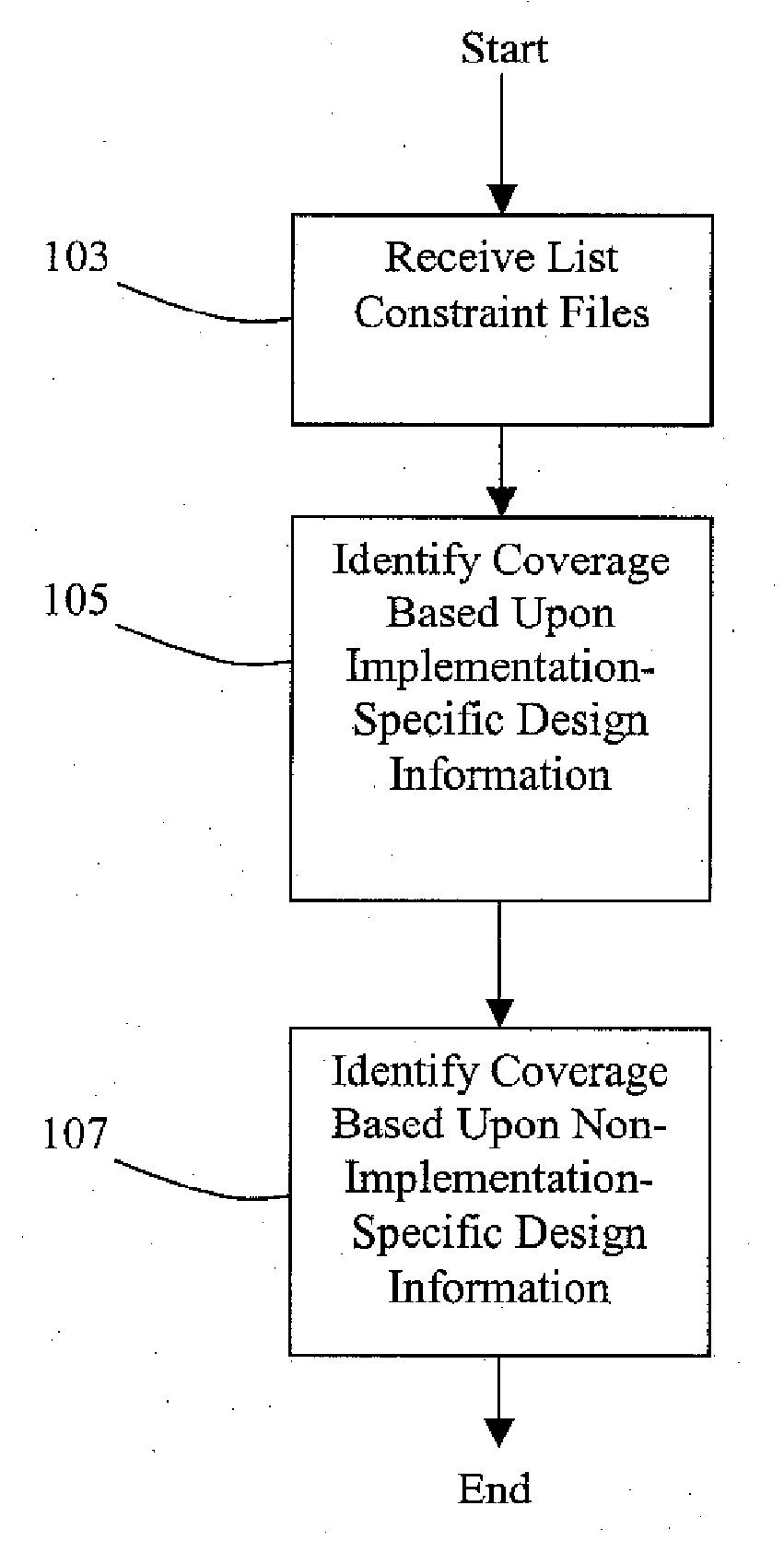
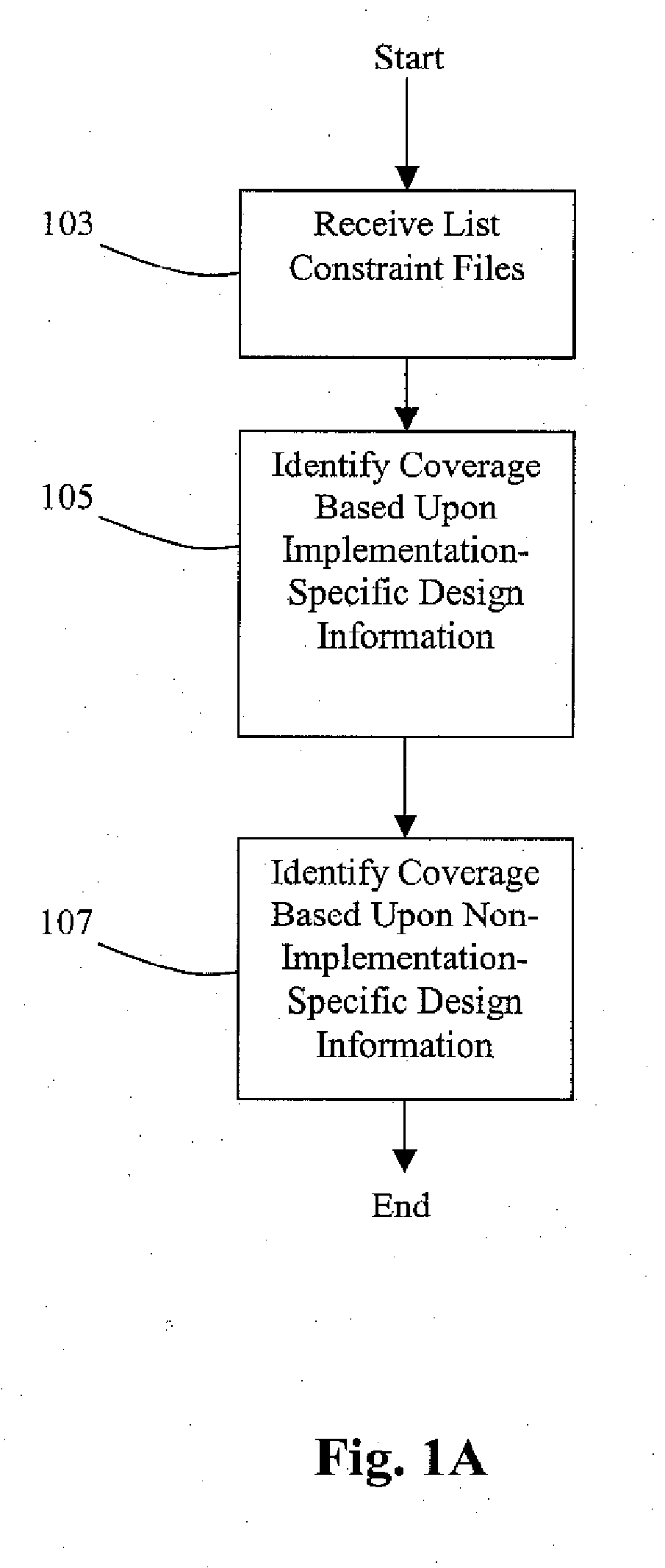
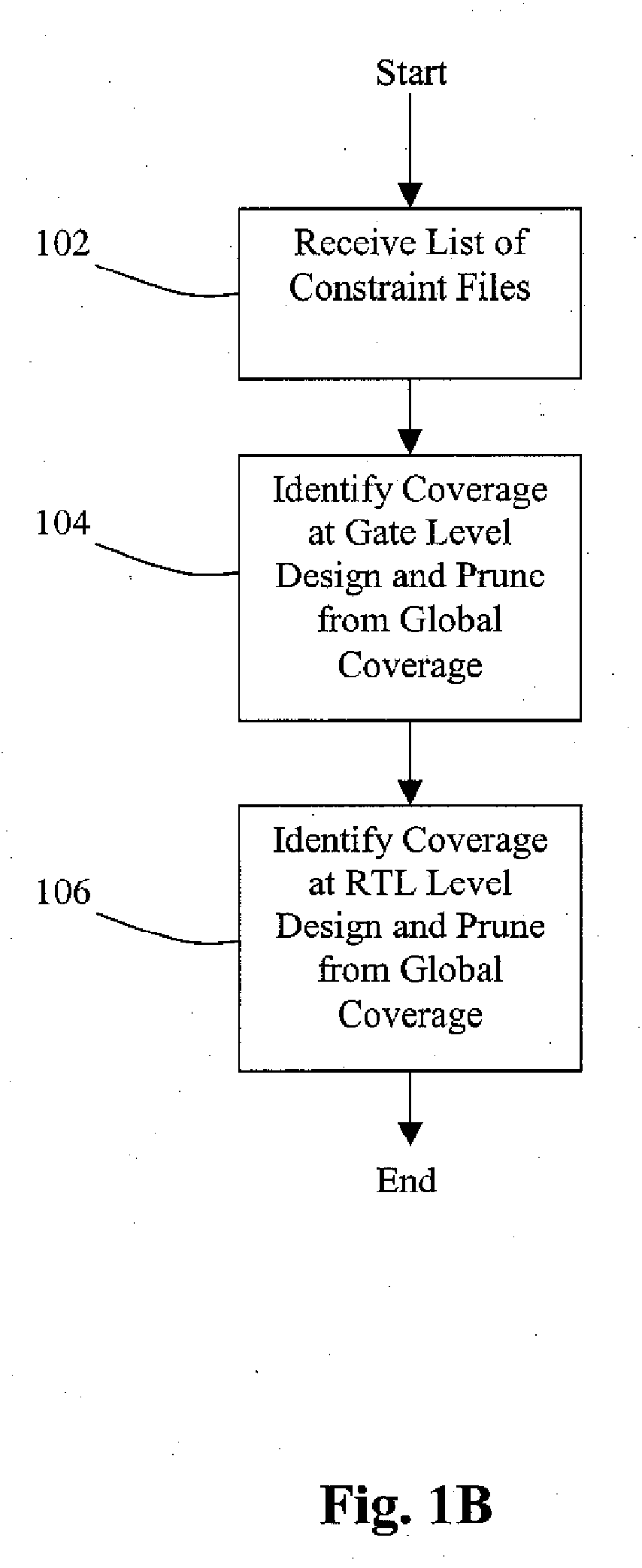
[0021]Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and system for performing automatic STA coverage analysis while existing constraints can be automatically verified and / or automatically regenerated to ensure complete STA coverage.
[0022]In one embodiment, several sets of constraints for independent STA rims are analyzed. Embodiments of the invention provide automatic methods and systems for coverage analysis of RTL or gate-level static timing analysis runs, identification of hidden logic, and constraint generation using architectural information. Accurate gate level timing data in conjunction with the architectural design date and formal methods can be used to identify false paths. The combination of formal techniques with static timing analysis to identify coverage using information from multiple STA runs as well as architectural information yields improved results in identifying global coverage. Some embodiments can use non-formal techniques such as simulation.
[0023]In so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com