Turbocharger with variable nozzle mechanism
a variable nozzle and turbocharger technology, applied in the field of turbochargers, can solve the problems of water freezing, affecting the operation of the nozzle vanes, and the deformation of the variable nozzle mechanism,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0015]the present invention will now be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 5.
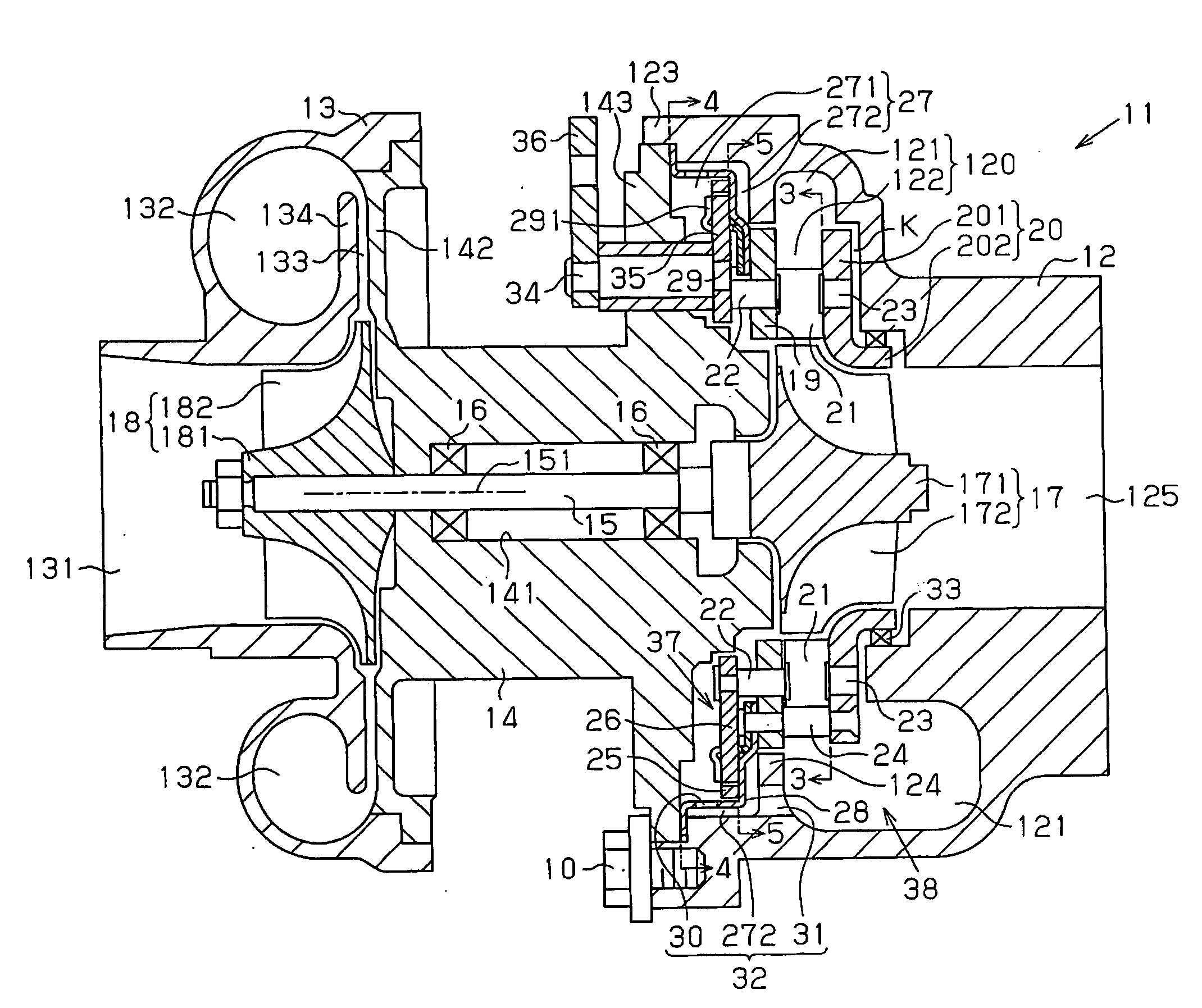
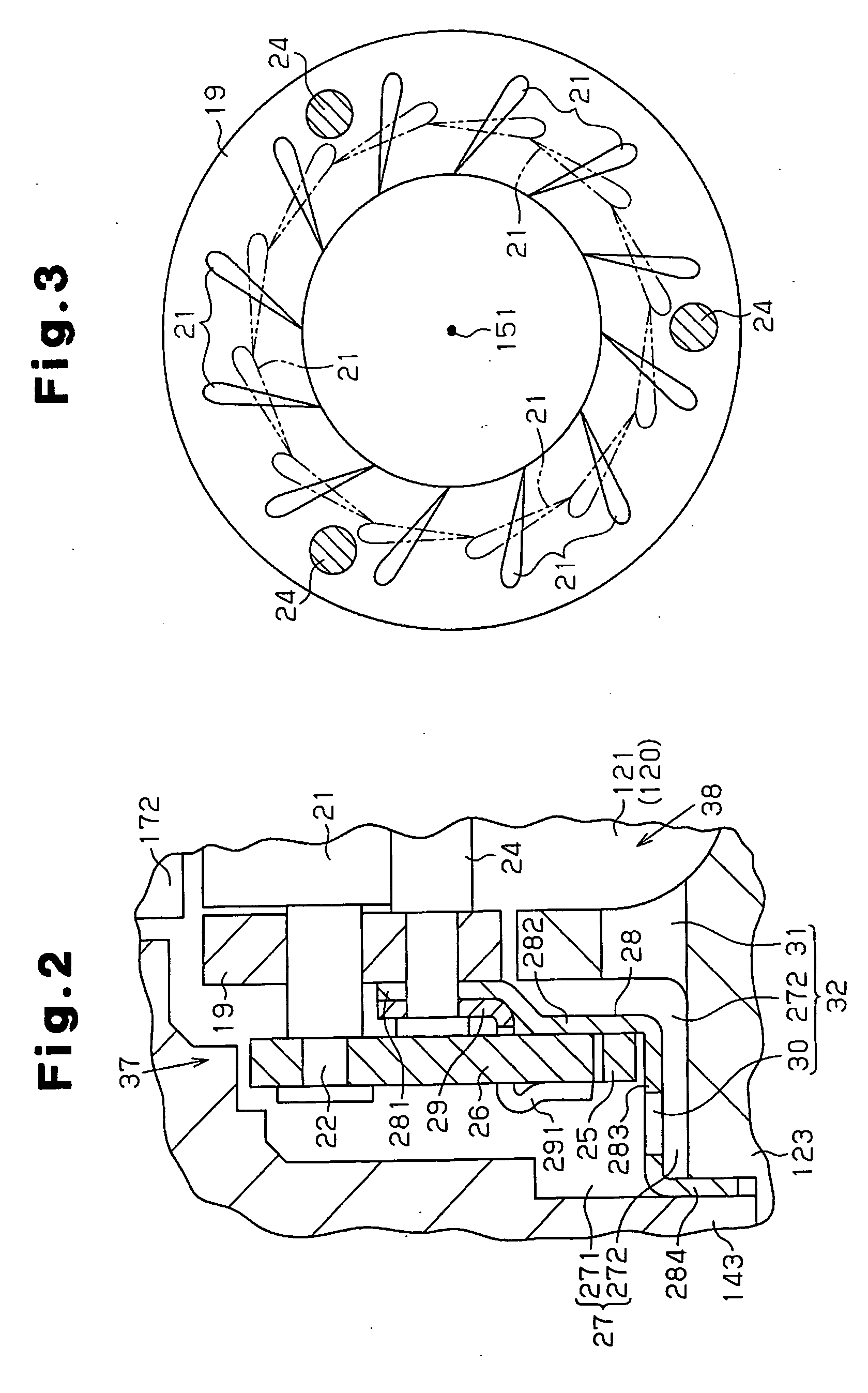
[0016]As shown in FIG. 1, a turbocharger 11 includes a turbine housing 12, a compressor housing 13, and a center housing 14. The turbine housing 12 is arranged in an exhaust passage (not shown) of an internal combustion engine (not shown). The compressor housing 13 is arranged in an intake passage (not shown) of the engine. The center housing 14 connects the turbine housing 12 to the compressor housing 13. A connecting cylindrical portion 123 is formed integrally with the turbine housing 12, and a flange wall 143 is formed integrally with the center housing 14. The flange wall 143 is engaged with the connecting cylindrical portion 123. Specifically, the flange wall 143 is connected to the connecting cylindrical portion 123 through a screw 10 threaded into the connecting cylindrical portion 123 so that the flange wall 143 does not separate from the connecting cylindrical portion 123. This arrangement con...
second embodiment
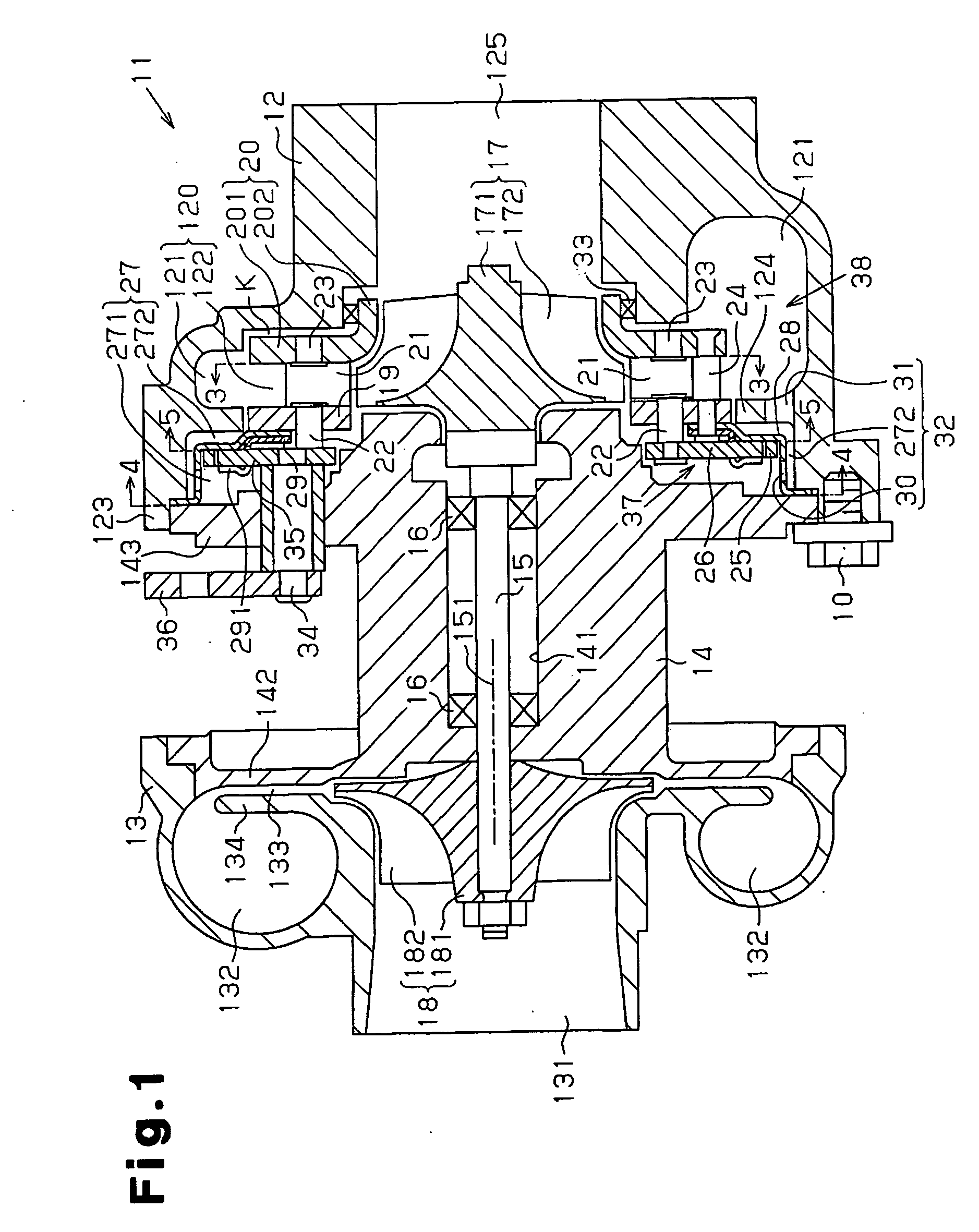
[0044]In the second embodiment, the outer circumferential surface of the cylindrical portion 233 of the support ring 28 contacts the inner circumferential surface of the connecting cylindrical portion 123 of the turbine housing 12 in a surface-contact manner. A groove 39, or a portion of a drain passage 32A connected to the gas passage 120, extends in the axial direction along the inner circumferential surface of the connecting cylindrical portion 123.
[0045]The second embodiment has advantages equivalent to those of the first embodiment.
[0046]The present invention may be embodied in the following forms.
[0047]In the first embodiment, a plurality of drain holes 30 may be provided.
[0048]In the first embodiment, a plurality of drain holes 31 may be arranged.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com