Method, system and program products for a dynamic, hierarchical reporting framework in a network job scheduler
a job scheduler and hierarchical reporting technology, applied in the field of job scheduling systems, can solve the problems of scheduling agents that are easily damaged by heavy communication load, so as to improve the scalability and performance of scheduling agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
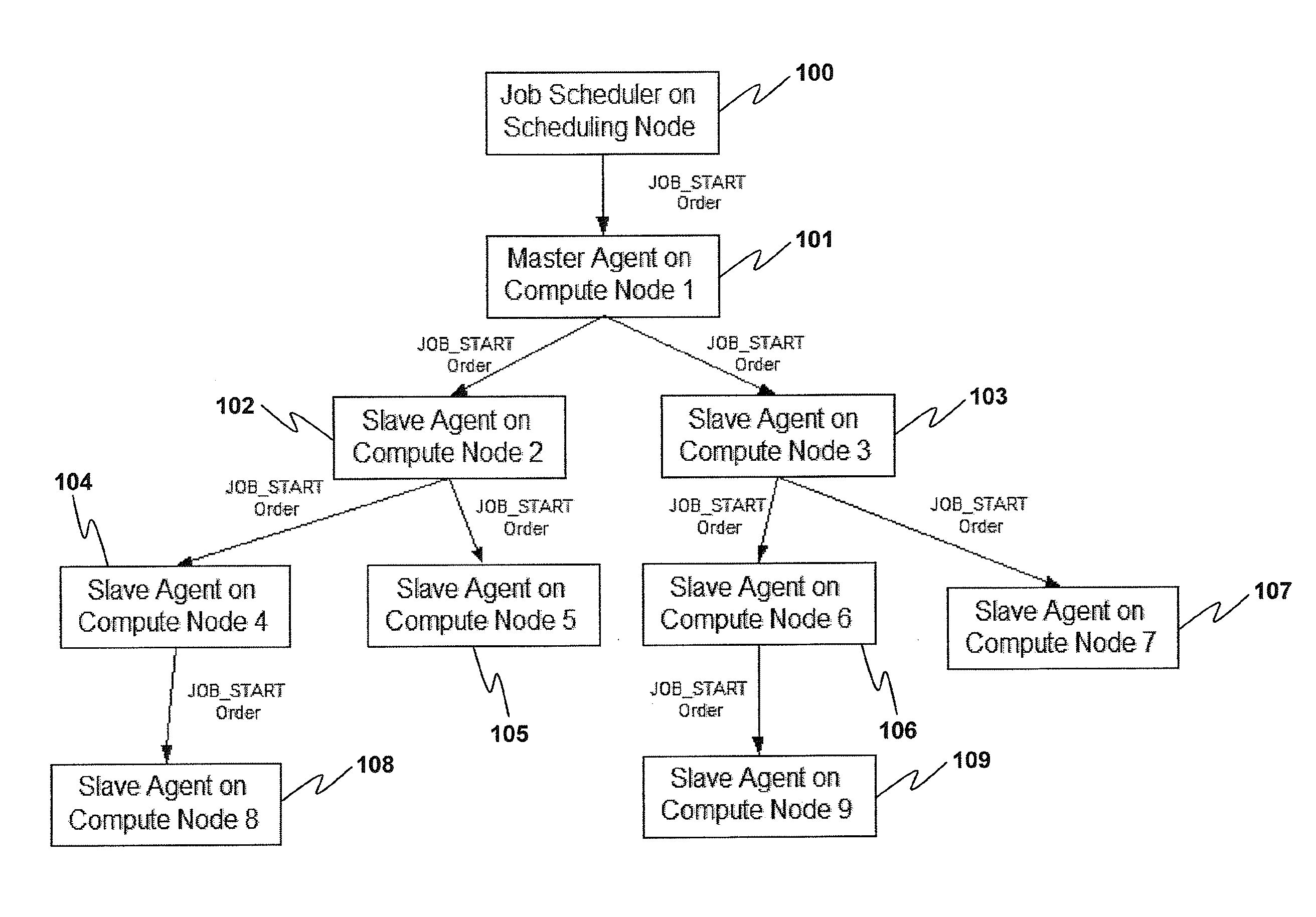
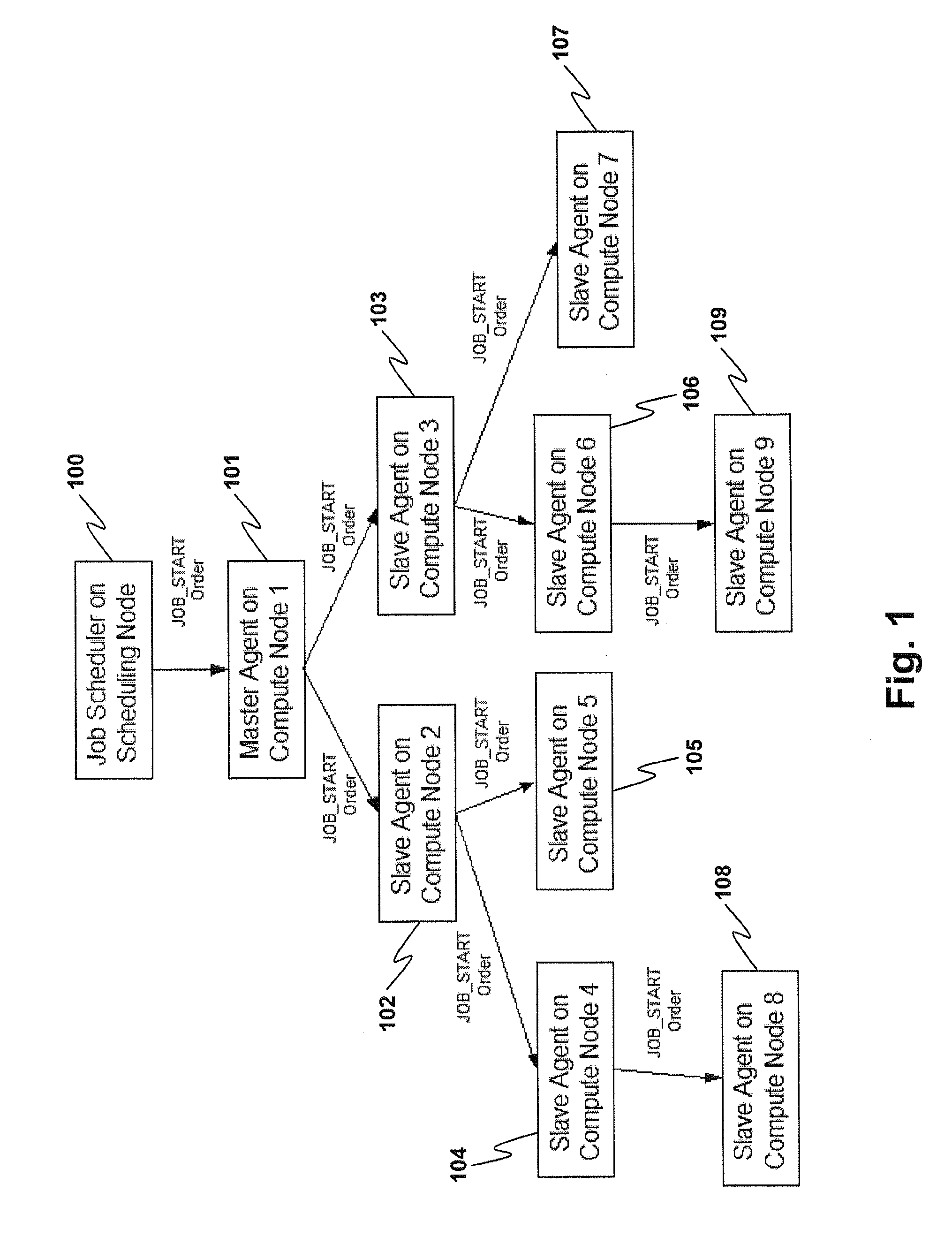
[0013]When a job is submitted for execution to the, scheduling agent determines a set of nodes on which this job can run based on the requirements of the job as well as the availability of necessary resources on these compute nodes. Each compute node runs an agent that is capable of reporting the status of jobs dispatched to them for execution.
[0014]To start the job, the scheduling agent sets up a master compute node and sends the job object to it in a JOB_START transaction. This master compute node forwards this “job start order” to a predetermined number of slave nodes while initiating the hierarchical job launch tree. The master node informs each slave node who its child nodes are. Each slave node further forwards the job to its children until all the nodes on which the job runs have received the job start transaction (See FIG. 1).
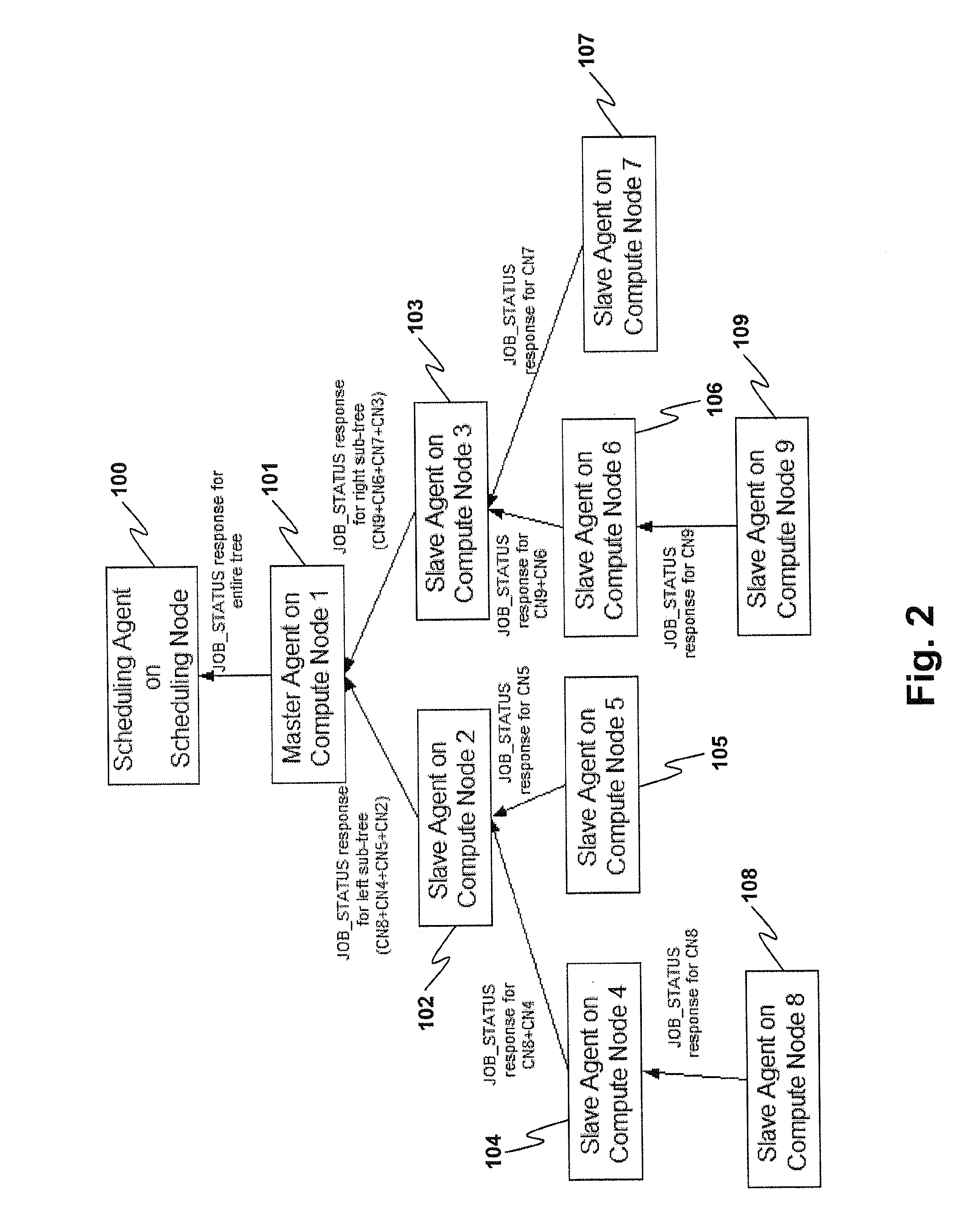
[0015]Every node in the tree now communicates that it is ready to receive the executable or task(s) to be run. In most existing schemes, all of the age...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com