Diesel Exhaust Soot Sensor System and Method
a technology of exhaust soot sensor and diesel engine, which is applied in the direction of exhaust treatment, machines/engines, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of engine thermal efficiency decline, exhaust gases experience a significant pressure drop passing through the increasingly restrictive filter, and problems such as problems such as the effect of affecting the operation of the engin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
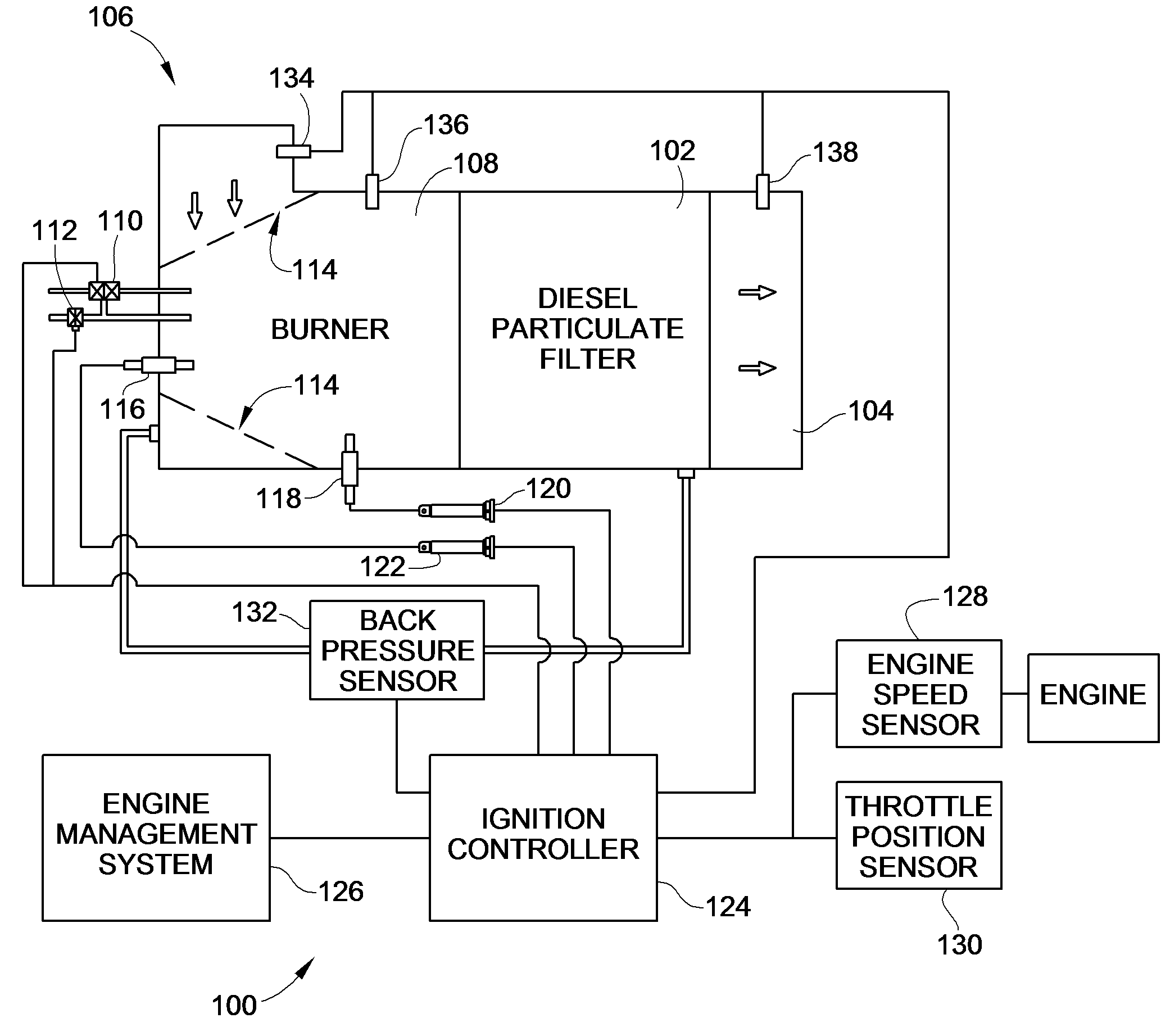
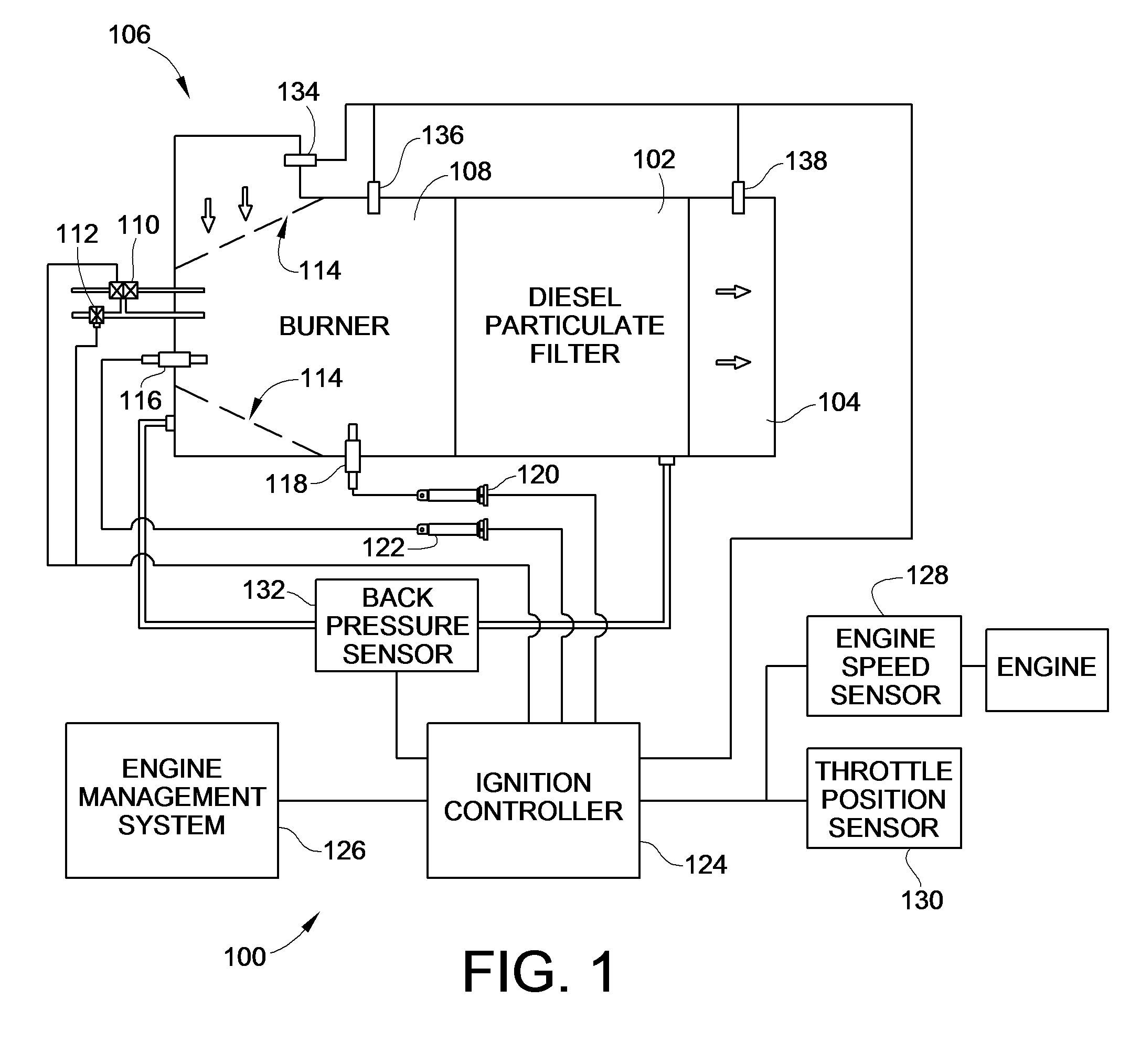
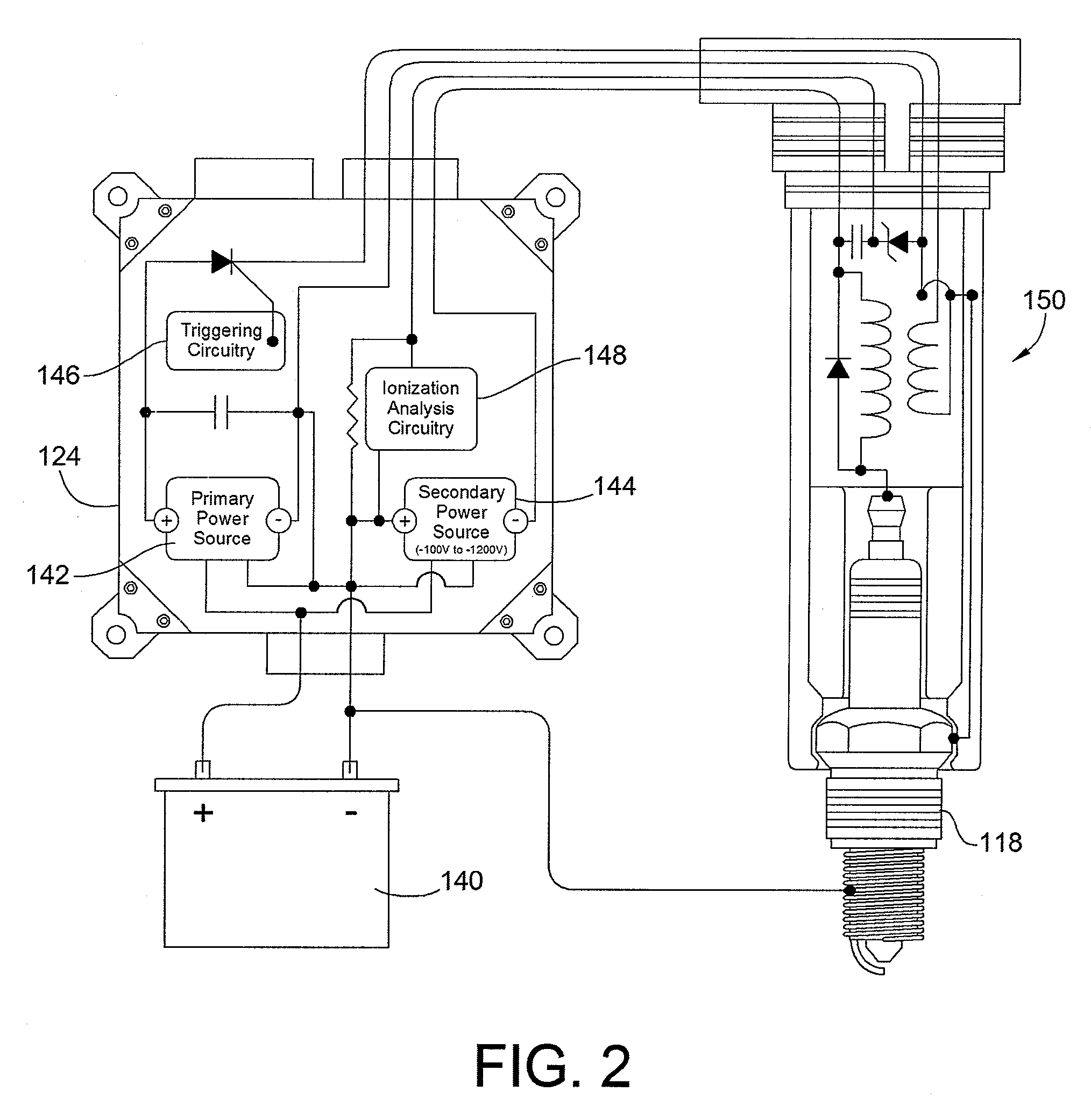
[0025]Turning now to the drawings, there is illustrated in FIG. 1 an embodiment of a system 100 constructed in accordance with the teachings of the present invention that is capable of determining an appropriate time to initiate regeneration of a diesel particulate filter (DPF) 102. As discussed above, the DPF 102 is installed before or upstream of an exhaust outlet 104 to filter out particulates from the diesel engine exhaust. In order to clean the collected particulates, e.g. soot, off of the DPF 102, a burner 108 may be used upstream of the DPF 102 but downstream from the exhaust inlet 106 from the engine. Such a burner 108 may be any source of auxiliary heat, such as a fuel fired burner, and electrical burner, RF burner, DOC, or via modified engine operation. The engine exhaust gases flow through openings 114 of the burner 102 and through the DPF 102 before exiting into the environment via the exhaust outlet 104.
[0026]In a fuel fired burner 108 fuel and air are supplied via a fu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com