System and method for producing a tangible object
a tangible object and system technology, applied in the field of tangible three-dimensional objects, can solve the problems of long relatively time-consuming, and the inability to form a new resin layer in a relatively long time, so as to achieve faster production, reduce the period of time required to produce objects, and achieve the effect of fast construction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
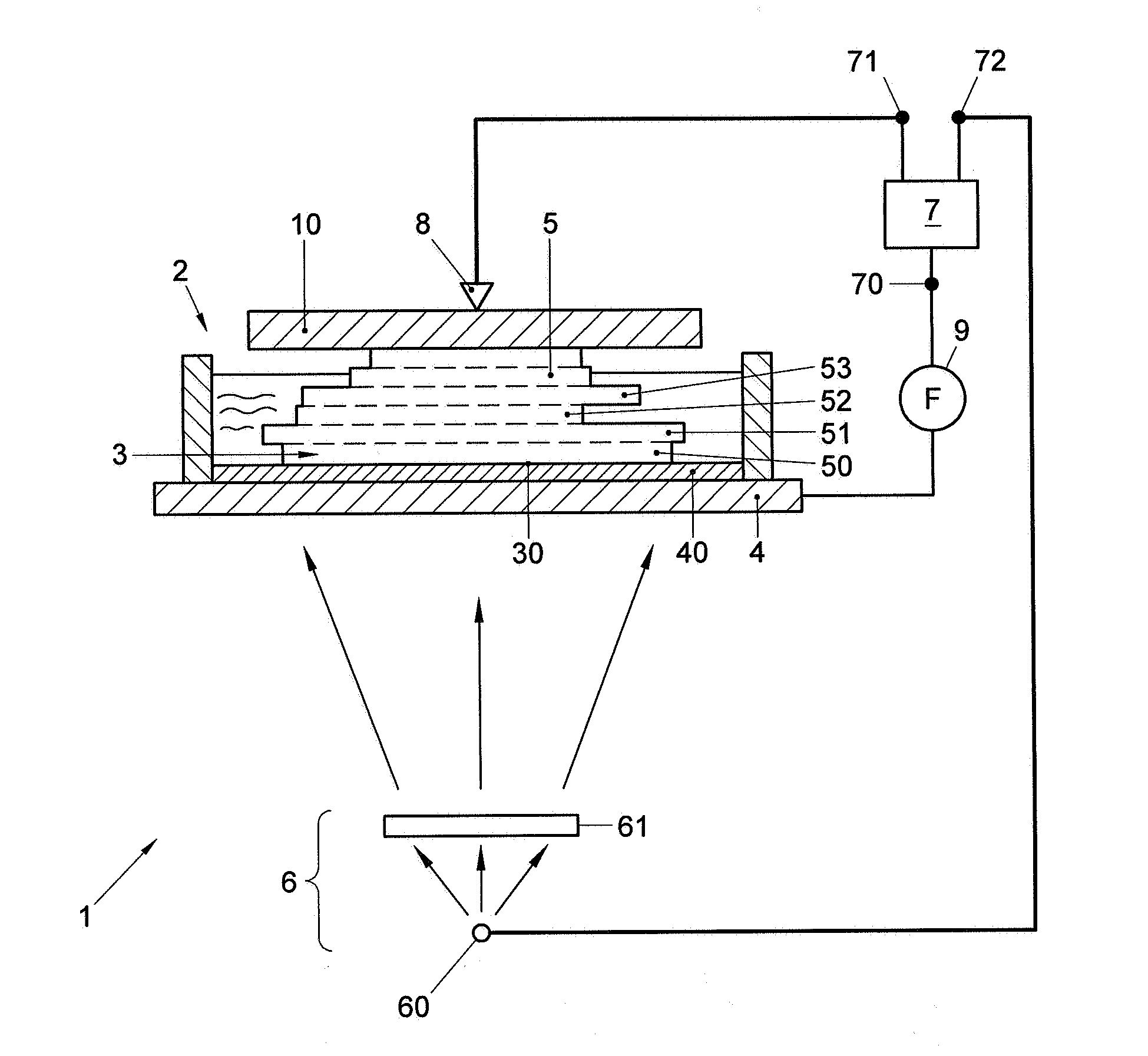
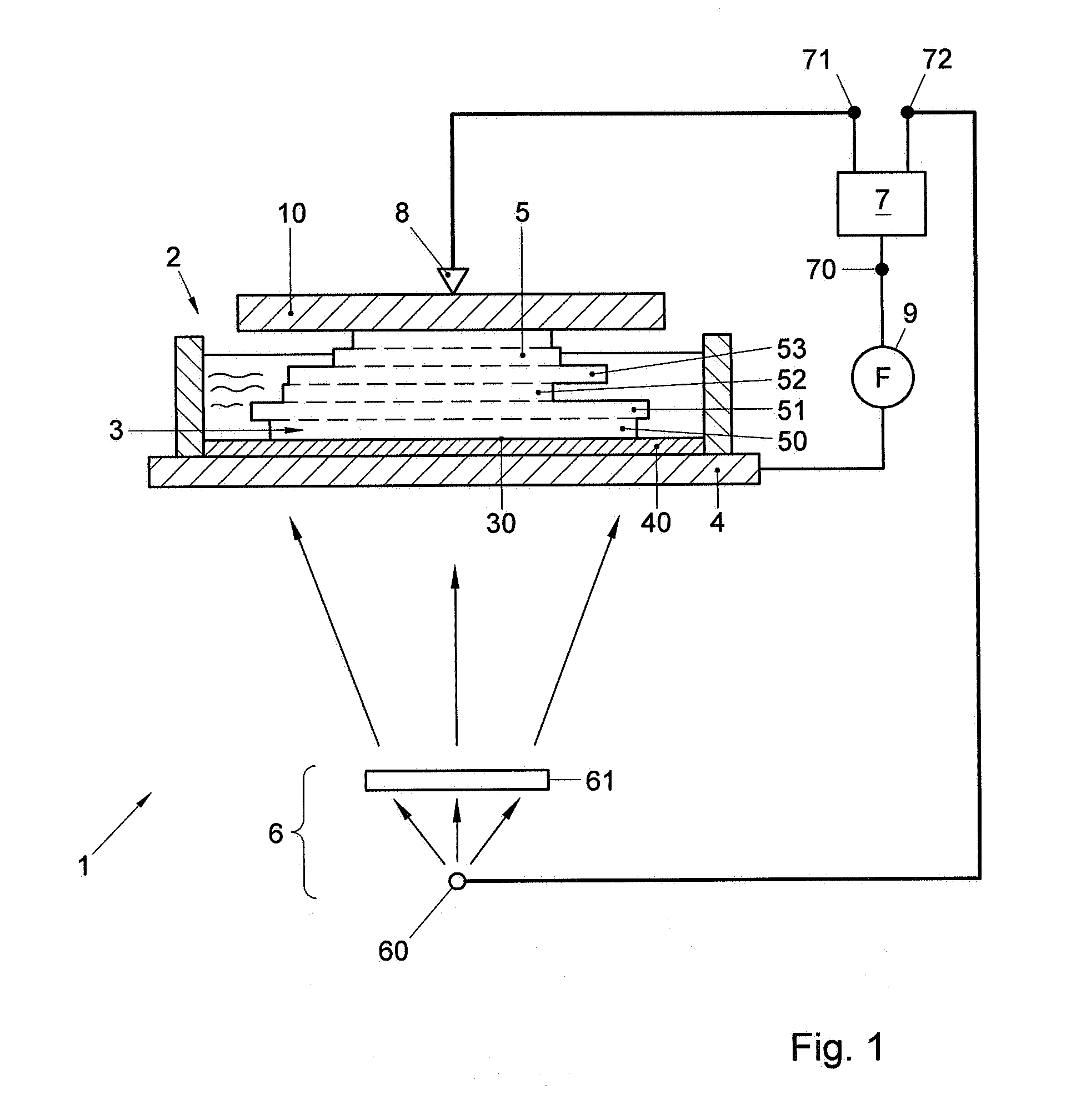
[0016]FIG. 1 shows an example of a system 1, for producing a tangible object. In this figure, the object 5 is shown while being produced. The tangible object 5 may for example be a prototype or model of an article of manufacture or other suitable type of object. The system 1 may, as shown in FIG. 1, include a basin 2 in which a liquid can be provided. In the example of FIG. 1, the basin 2 includes a space 3 which can be filled with the liquid, to form a layer of fluid which can be transformed into a solid layer. At least one side 30 of the space 3 is at least partially defined by a reference platform 4. In this example the reference platform 4 defines the bottom side of the space 3.
[0017]However, it is also possible that the reference platform 4 defines the top side of the space 3. In this example, the reference platform 4 includes an anti-stick layer 40, such as a rubber-like layer or a silicon layer, which forms a wall of the space and reduces the sticking of the layer 50 to the r...
PUM
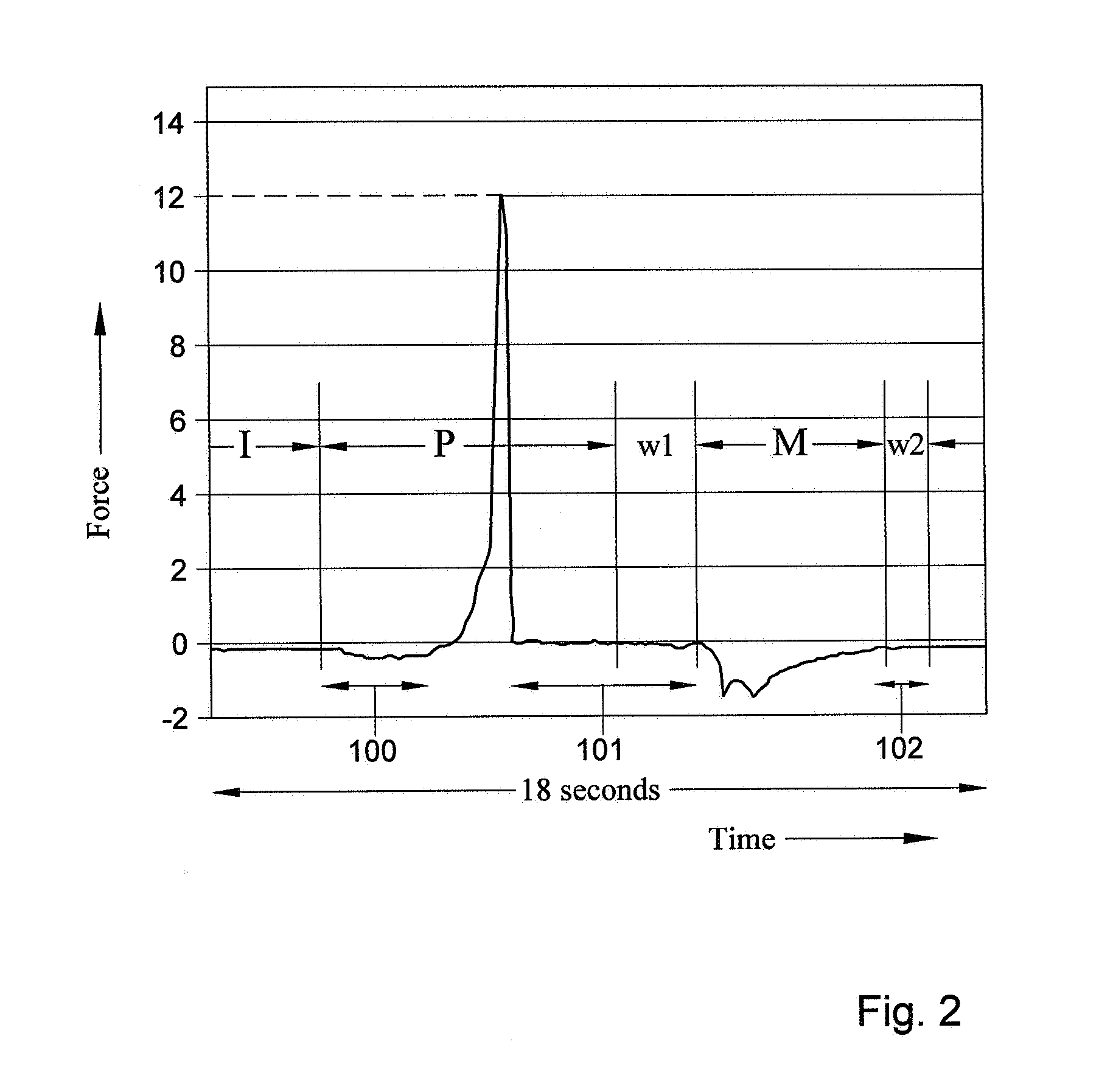
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com