Display device, method of laying out light emitting elements, and electronic device
a technology of light emitting elements and display devices, applied in semiconductor devices, instruments, computing, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the period of an electrooptic element, reducing the power consumption of the display device, and reducing the difficulty of realizing a large and high-definition display device, so as to achieve excellent display quality and reduce the effect of changing the characteristics of the pixel transistor from color to color due to the effect of leakage light from an adjacent pixel
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
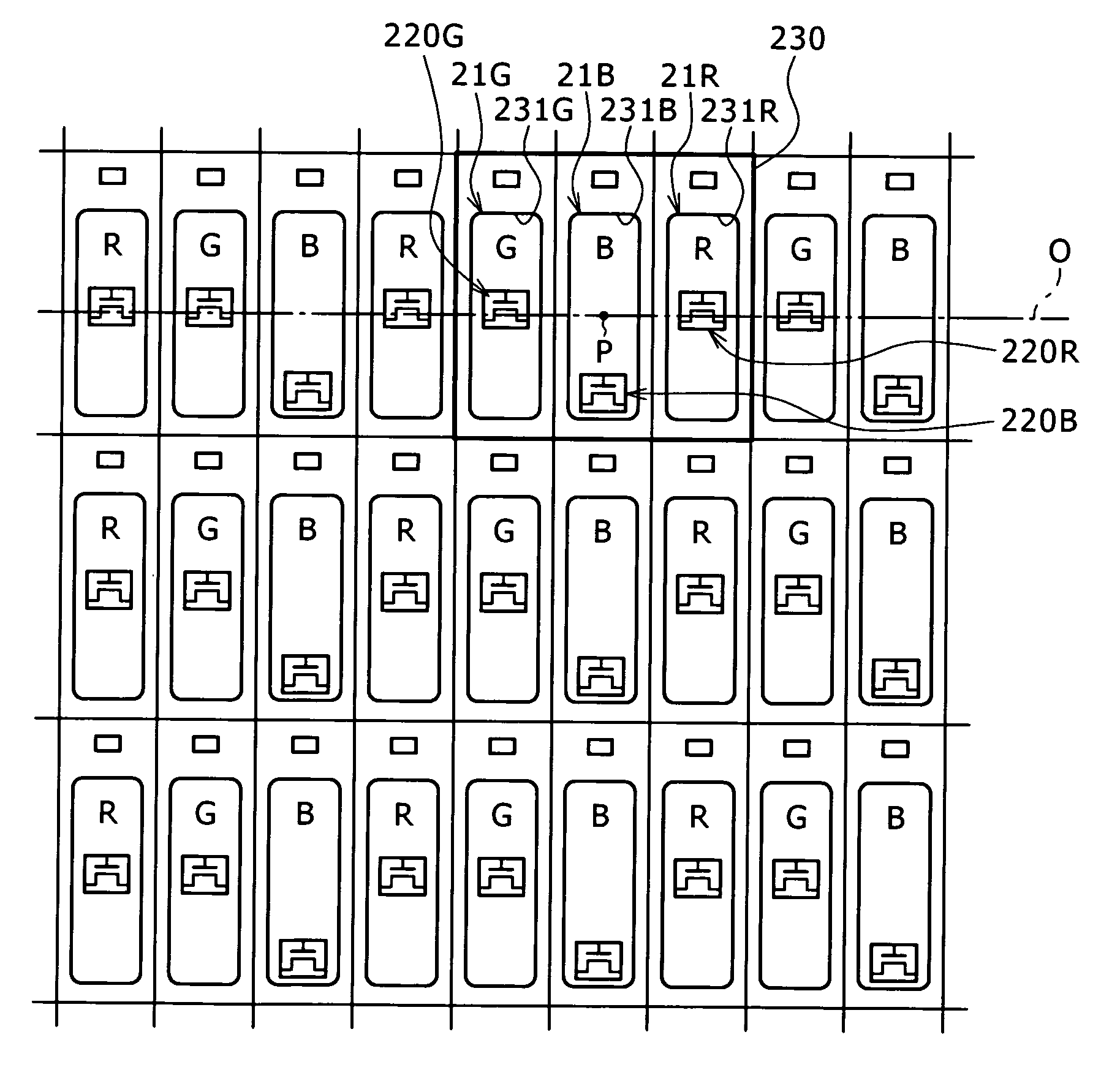
[0136]FIG. 11 is a plan view conceptually showing a layout structure according to a first embodiment. As shown in FIG. 11, the organic EL elements 21R, 21G, and 21B of RGB are arranged so as to be adjacent to each other within a pixel forming region 230 of a square shape, for example, as a region for forming one pixel.
[0137]Specifically, the respective windows (light emitting sections) 231R and 231G of the organic EL elements 21R and 21G of RG are formed side by side in a shape close to a square on one side (lower side in the present example) in a column direction (direction of arrangement of pixels of a pixel row) of the pixel forming region 230. In addition, the window 231B of the organic EL element 21B of B is formed in a rectangular shape over the widths of the windows 231R and 231G on another side (upper side in the present example) in the column direction of the pixel forming region 230.
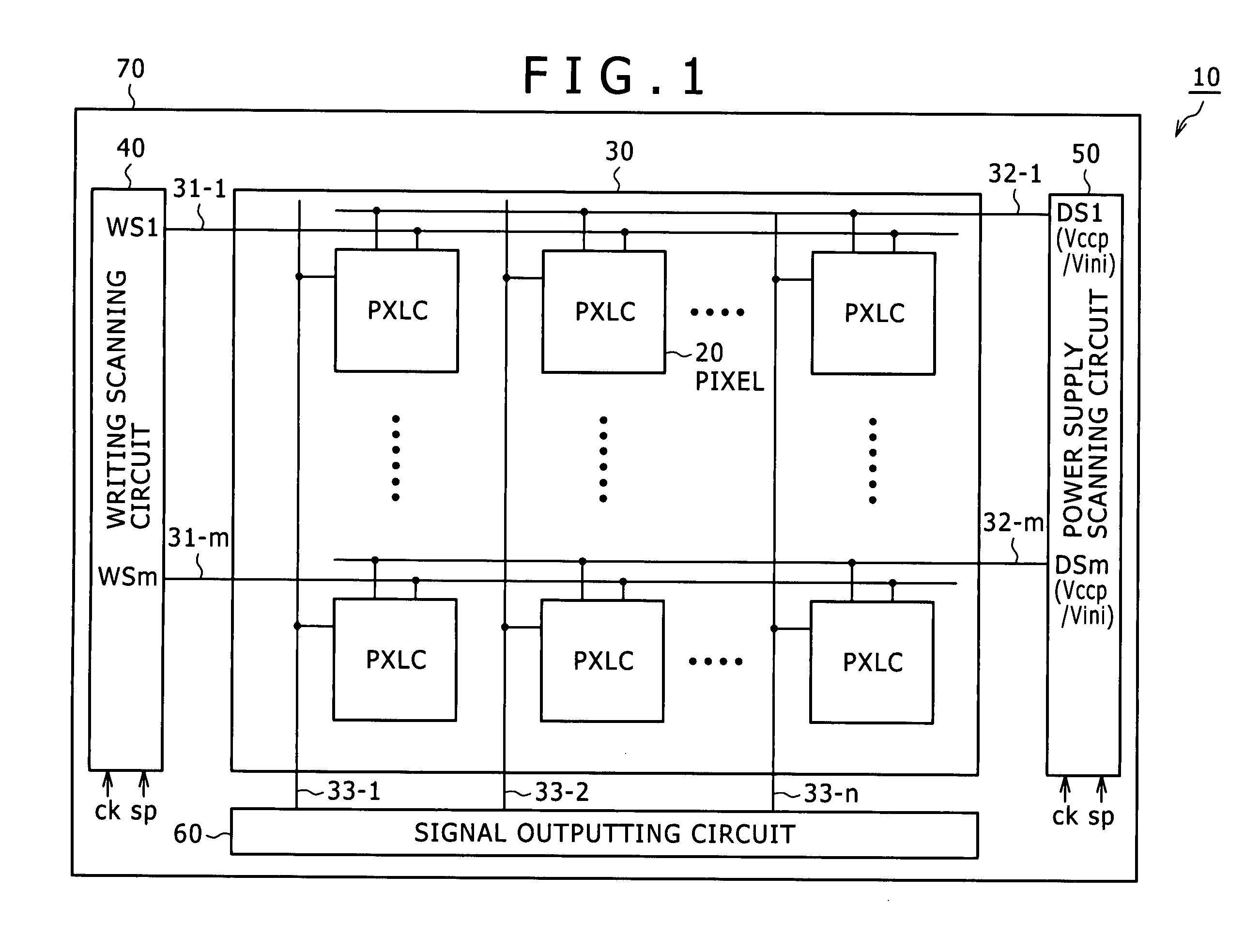
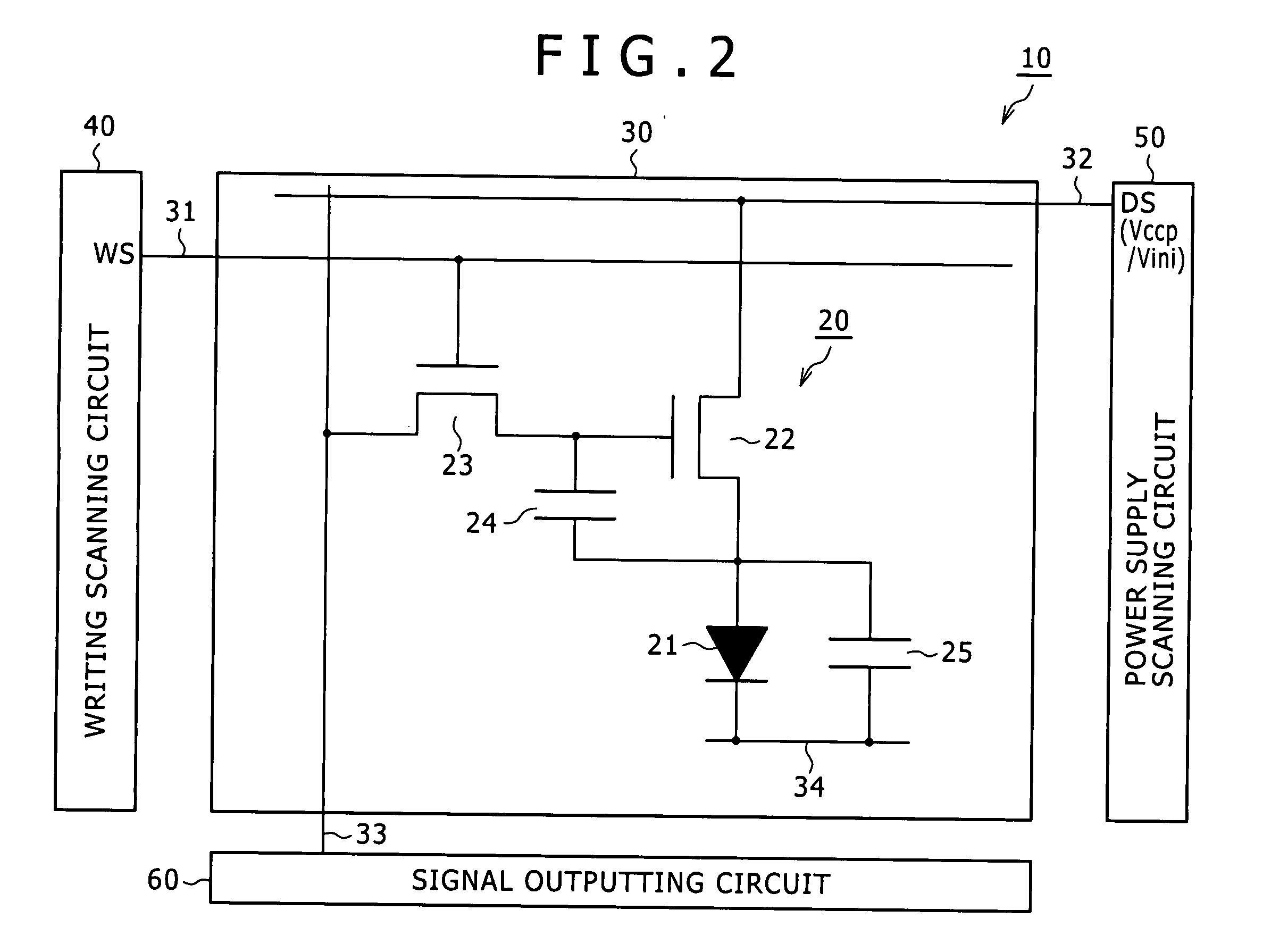
[0138]In addition, within the pixel forming region 230, the respective pixel transistors (f...
second embodiment
[0141]FIG. 12 is a plan view conceptually showing a layout structure according to a second embodiment. In FIG. 12, same parts as in FIG. 11 are identified by the same reference numerals. As is clear from FIG. 12, the shapes and arrangement relation of the respective windows (light emitting sections) 231R, 231G, and 231B of organic EL elements 21R, 21G, and 21B are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0142]On the other hand, whereas a surface light source is used as the organic EL element 21B emitting blue light in the first embodiment, a point light source is used as the organic EL element 21B in the present second embodiment. Because the organic EL element 21B is a point light source, the light emission point P of the organic EL element 21B can be considered to be the center of the window 231B of the organic EL element 21B.
[0143]When the light emission point P of the organic EL element 21B is the center of the window 231B, in the layout of the pixel transistors 220R, 220G, and 220B...
third embodiment
[0145]FIG. 13 is a plan view conceptually showing a layout structure according to a third embodiment. In FIG. 13, same parts as in FIG. 11 are identified by the same reference numerals.
[0146]In the present third embodiment, in a pixel arrangement of pixels (sub-pixels) 20R, 20G, and 20B of RGB repetitively arranged along a row direction (direction of arrangement of pixels of a pixel row), three pixels 20G, 20B, and 20R with the pixel 20B in the middle form a unit of one pixel. The organic EL element 21B may be a surface light source or a point light source.
[0147]Description in the following will be made of a case where a point light source is used as the organic EL element 21B. When the organic EL element 21B is a point light source, the light emission point P of the organic EL element 21B can be considered to be the center of the window 231B of the organic EL element 21B. Blue light emitted from the light emission point P of the organic EL element 21B can be considered to irradiate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com