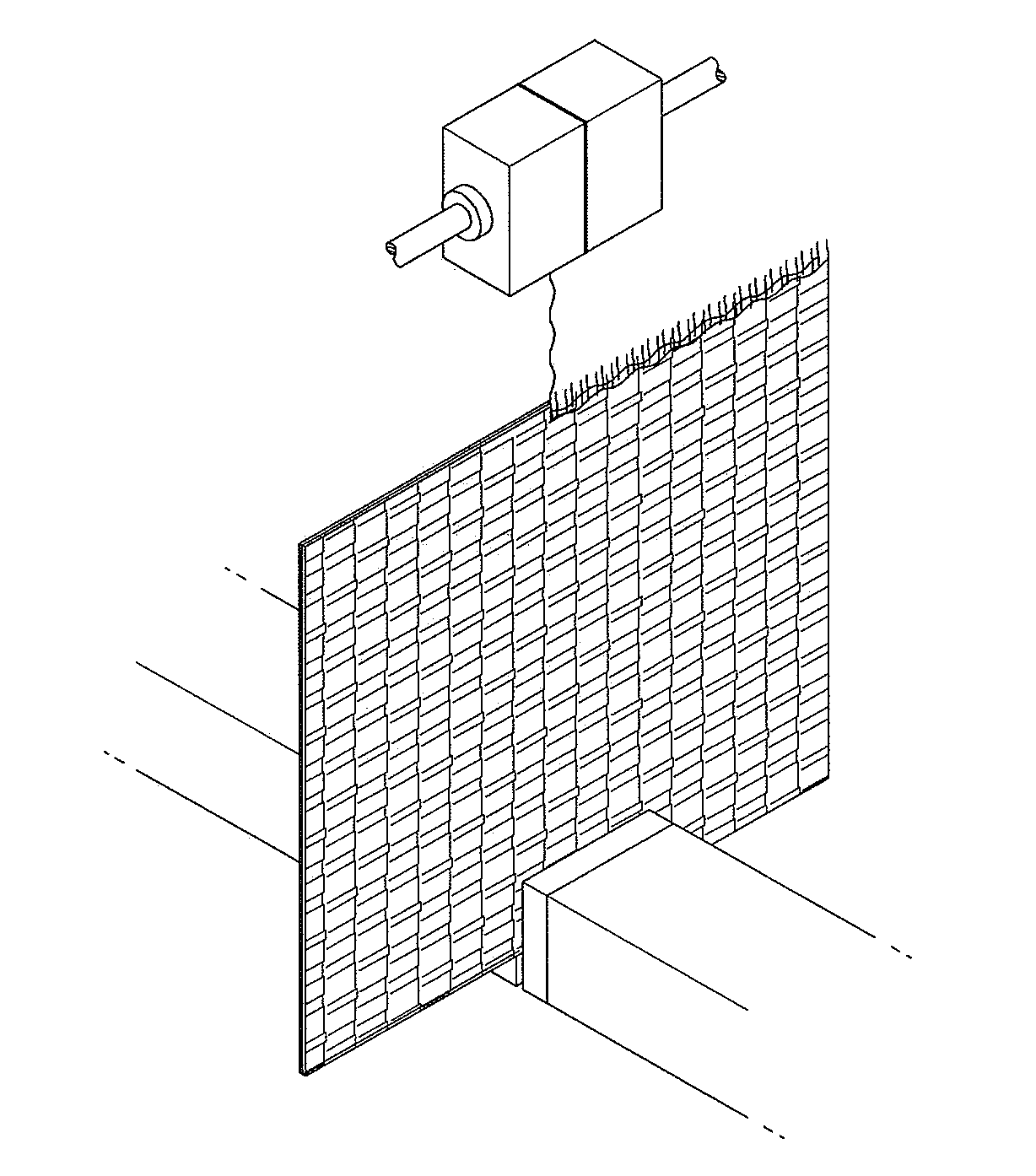
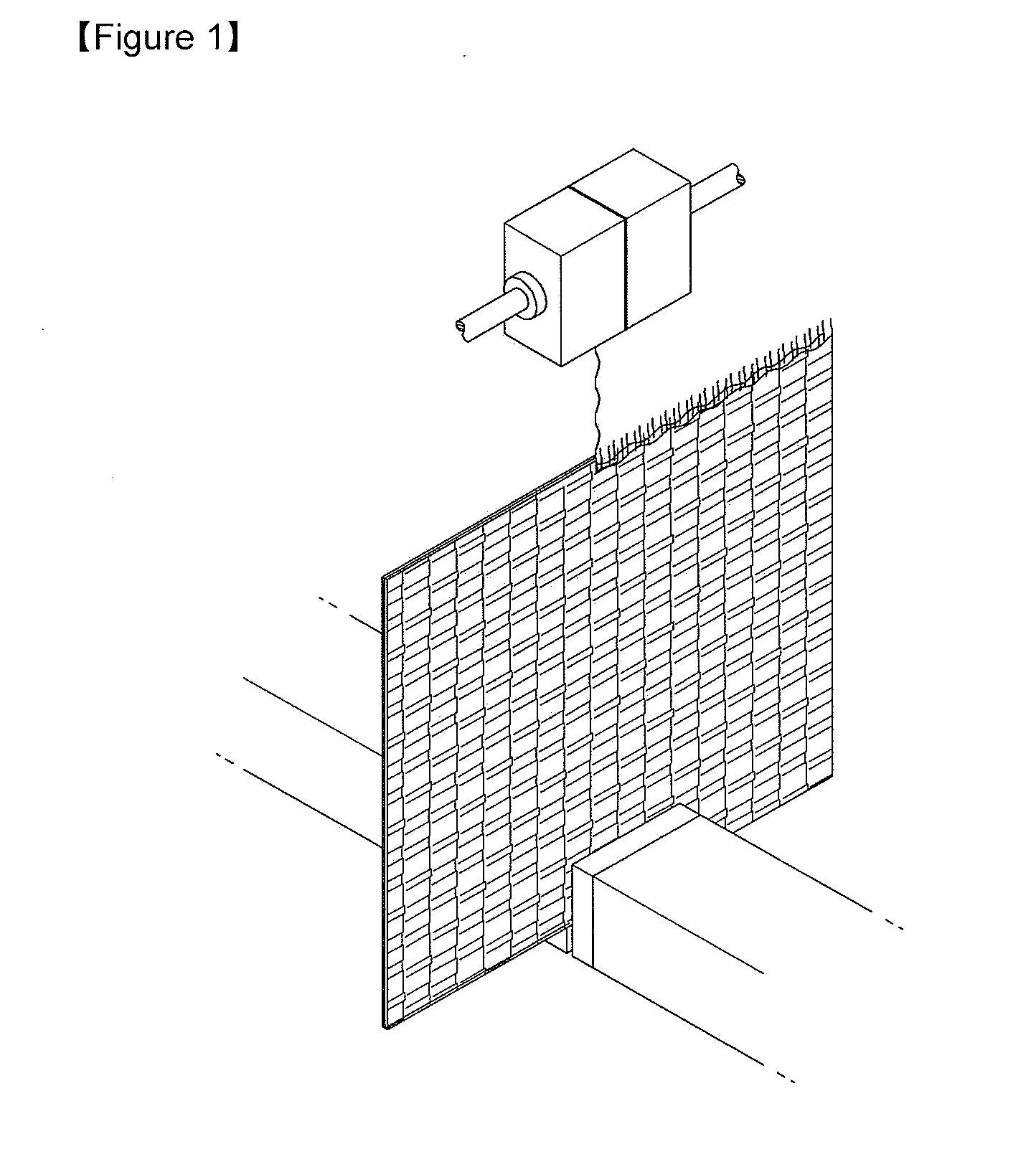
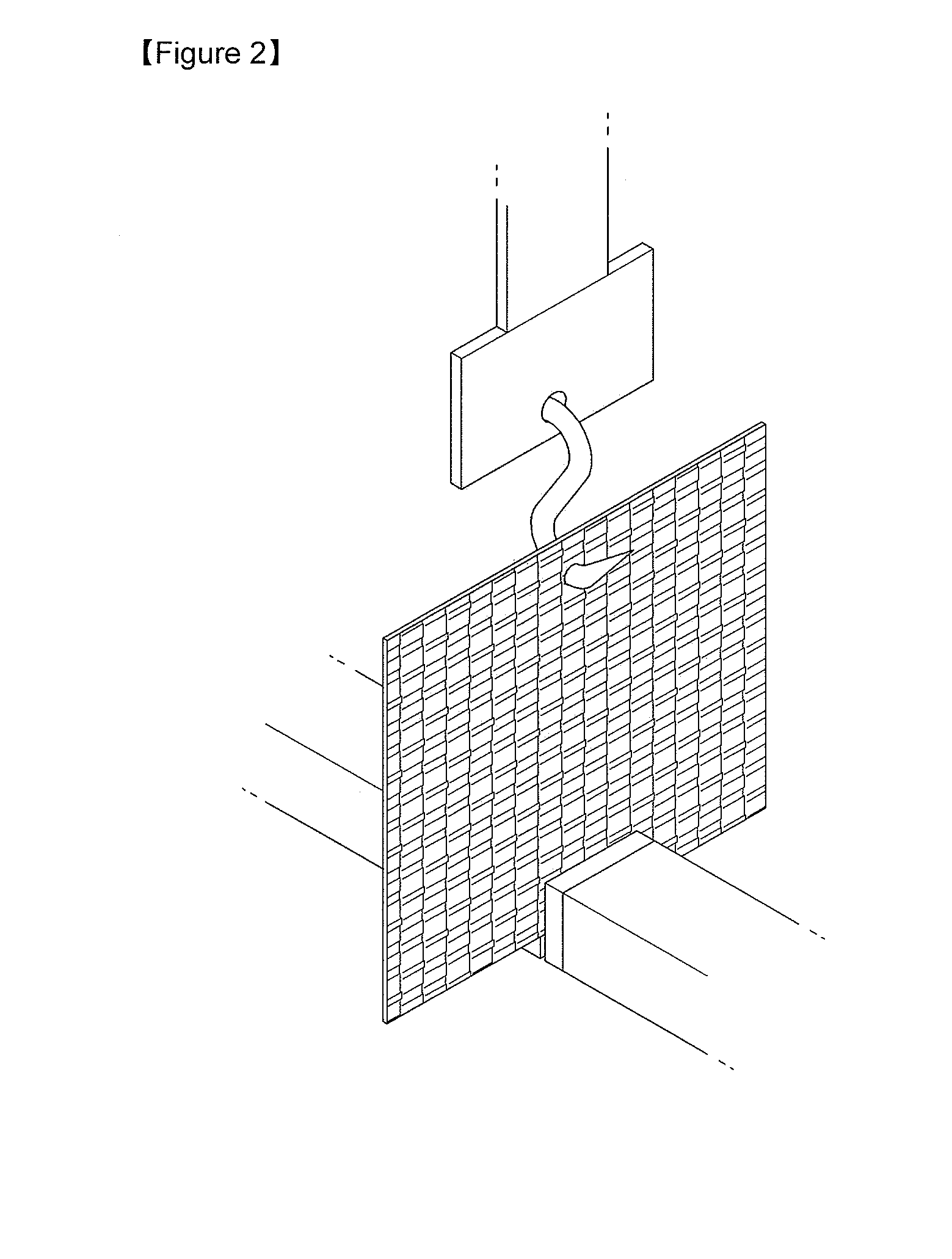
Fabric including low-melting fiber
a technology of low-melting fiber and fabric, which is applied in the manufacture of flame-proof filaments, textiles and paper, weaving, etc., can solve the problems of poor adhesion of fabrics, rough feeling after use, and indoor environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0047]A regular polyester fiber as warp was woven with a sheath / core type conjugate fiber as weft by plain weaving to produce a fabric. The conjugate fiber was composed of a plied fiber of a low-melting polyester (30 wt %) as the sheath and a regular polyester (70 wt %) as the core. The fabric had a warp density of 100 yarns / inch and a weft density of 100 yarns / inch. The woven fabric was processed to adjust the fusion rate of the low-melting polyester to 30%.
examples 2-5
[0048]Fabrics were produced in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the fusion rates were adjusted to 50%, 70%, 90% and 100%.
examples 6-10
[0049]Fabrics were produced in the same manner as in Examples 1-5, except that the amount of the low-melting polyester was adjusted to 40 wt %.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| yarn slip length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| bending length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com