Patents
Literature
208results about How to "Reduce noise transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
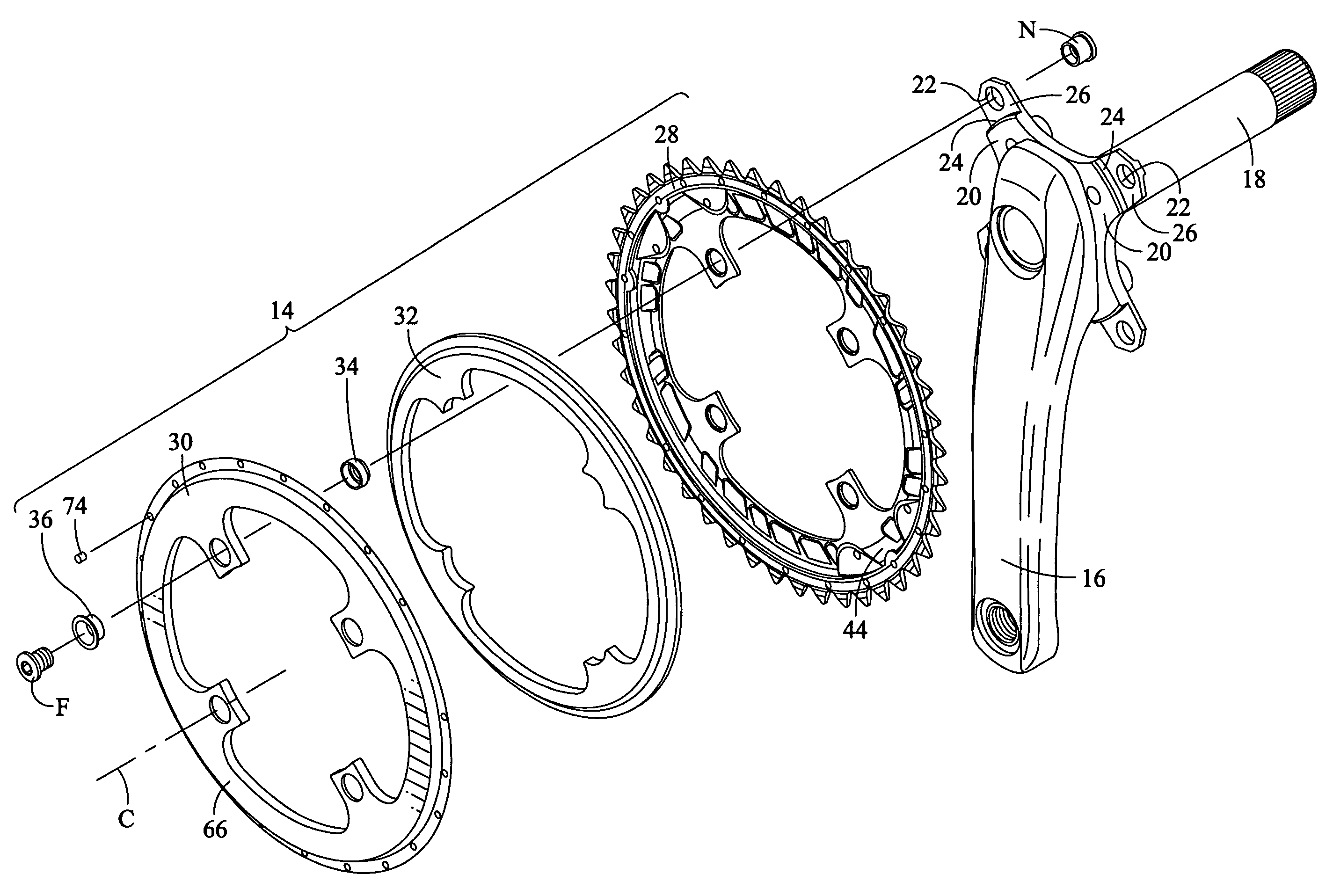
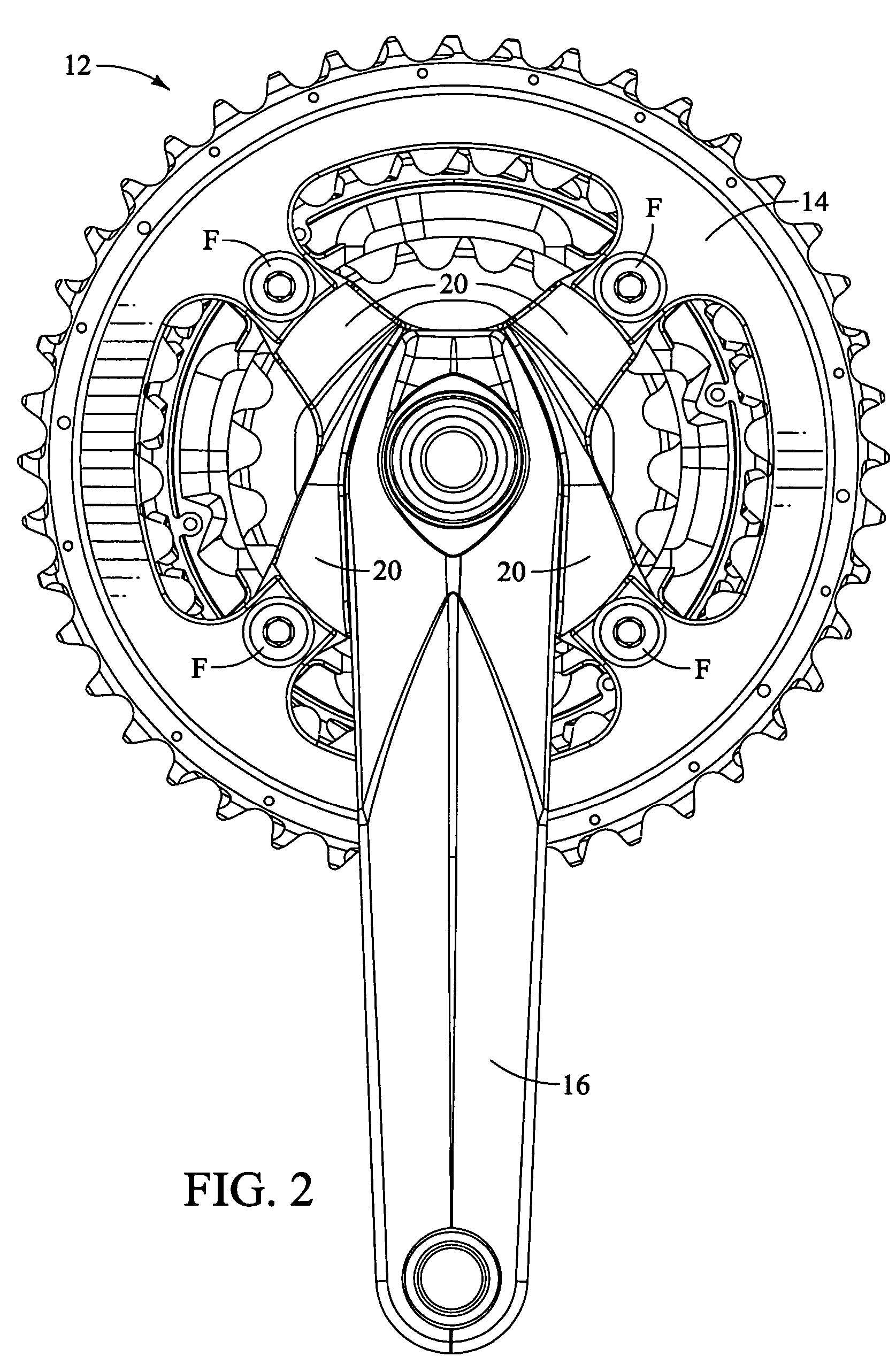
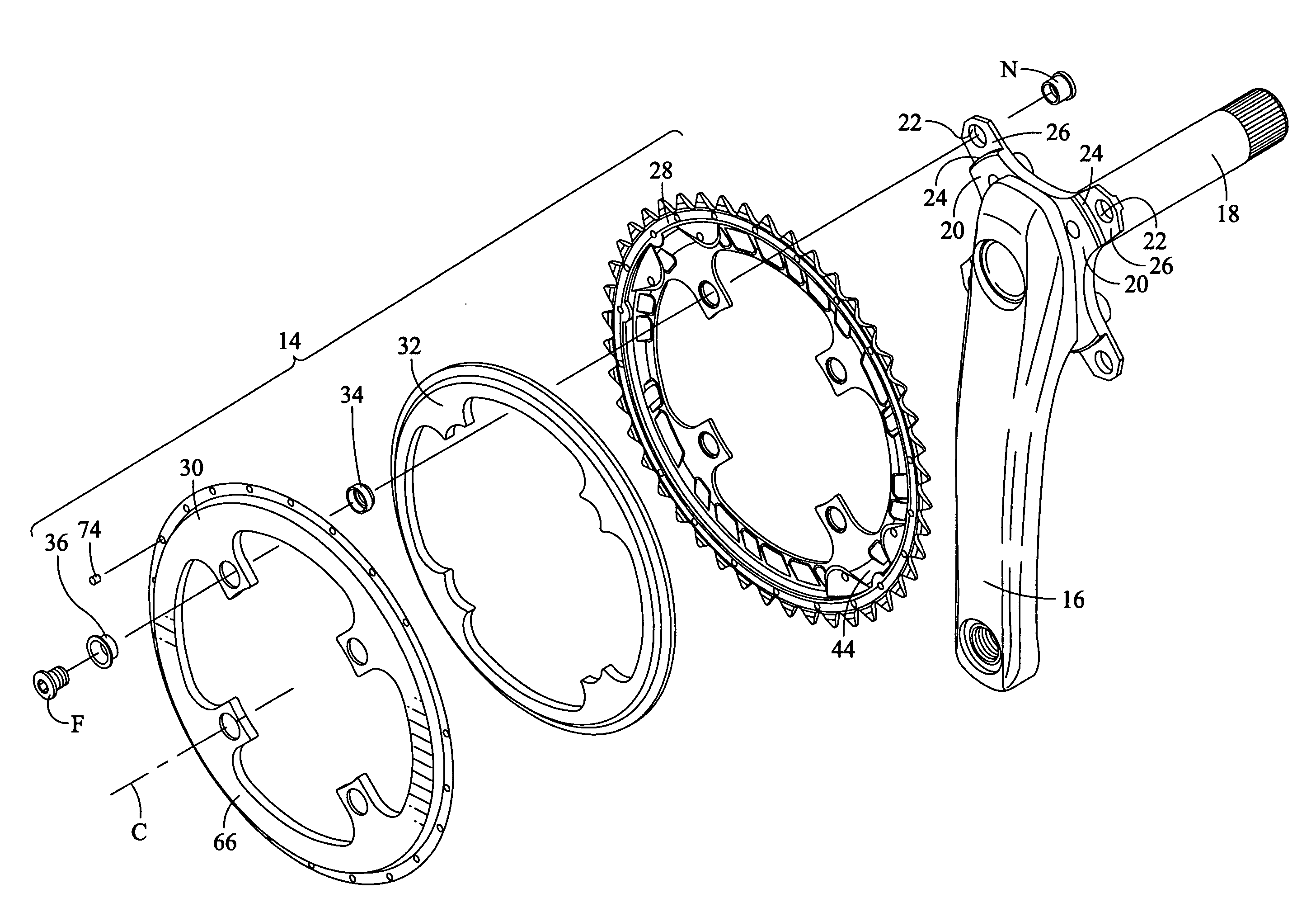
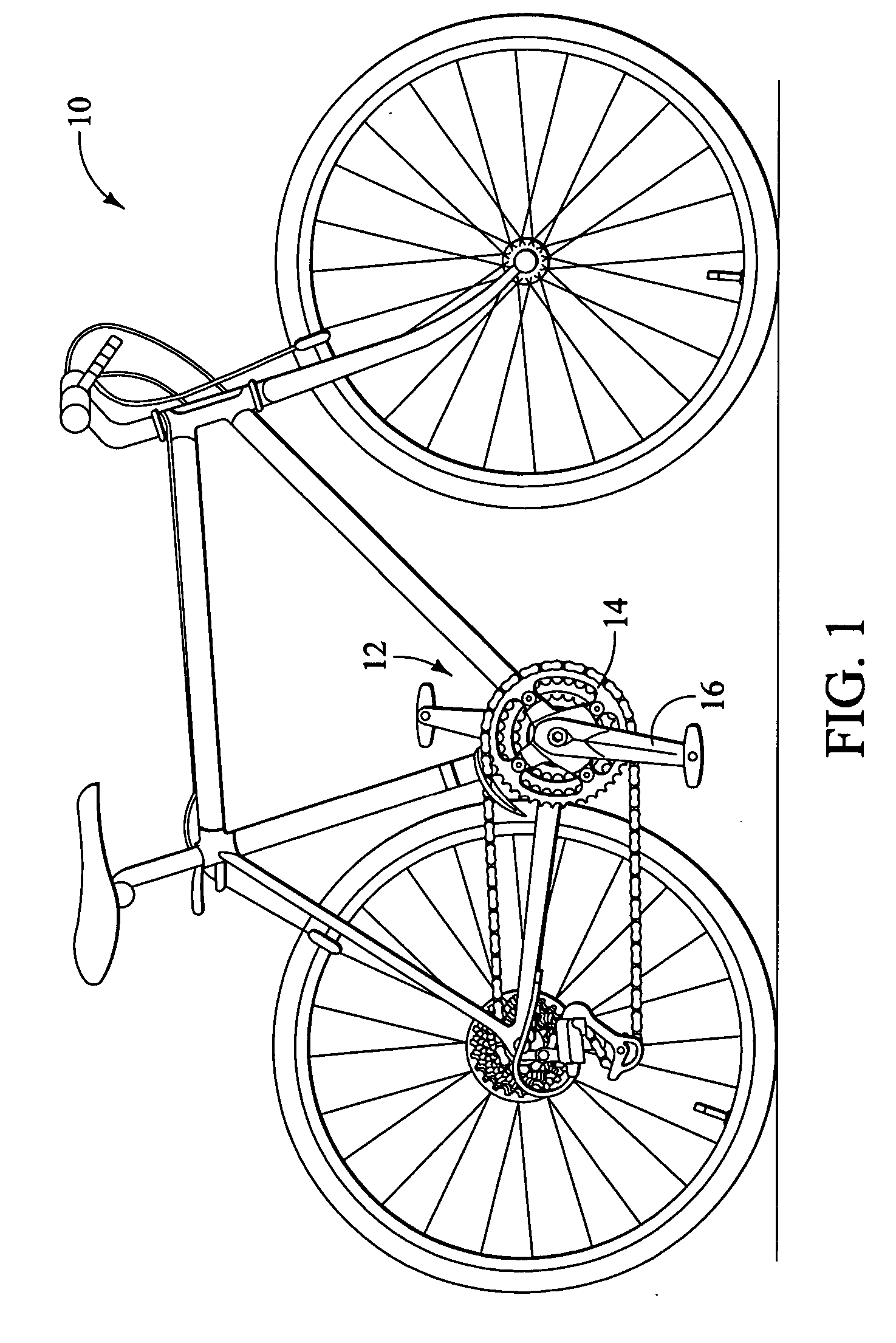
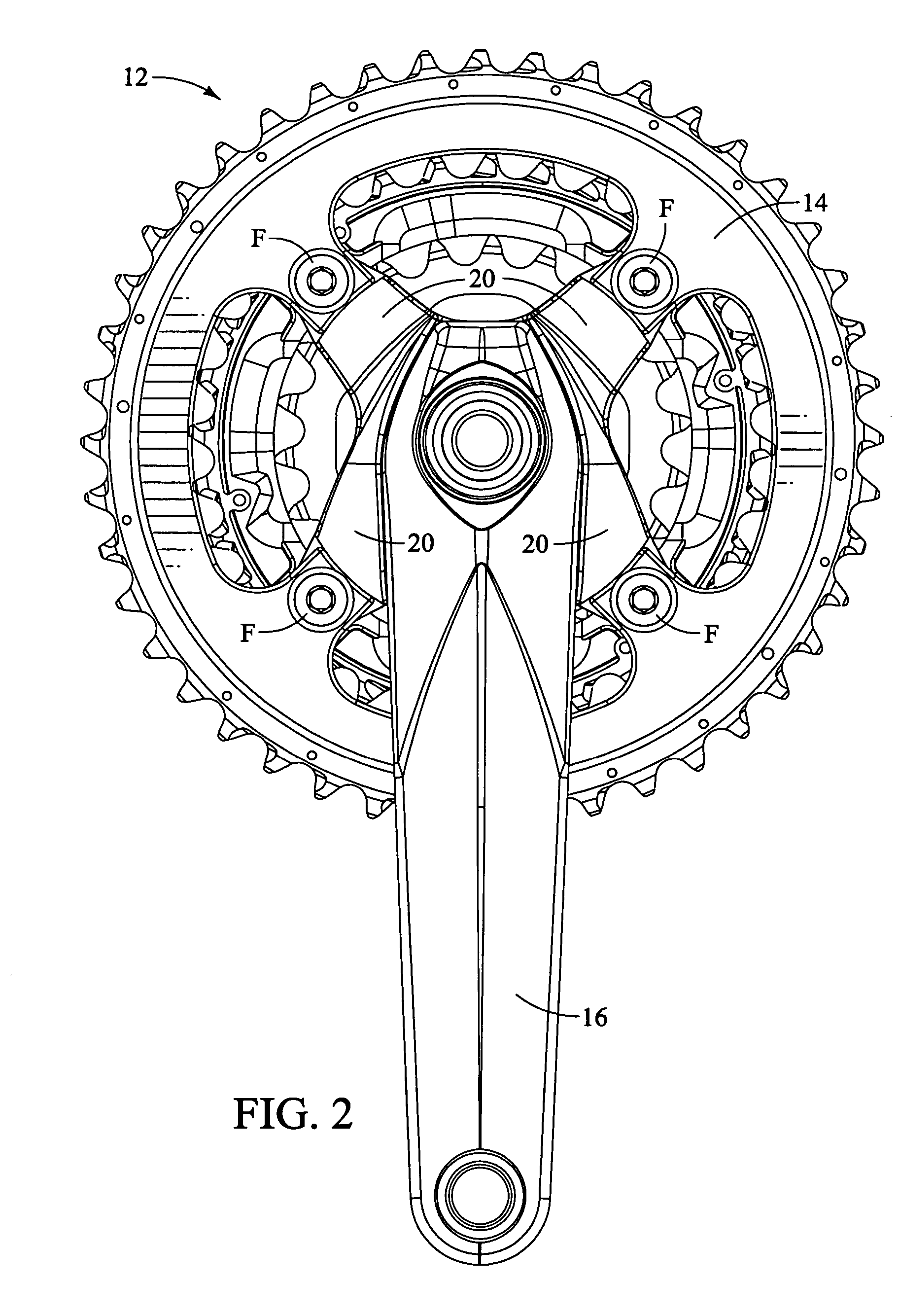
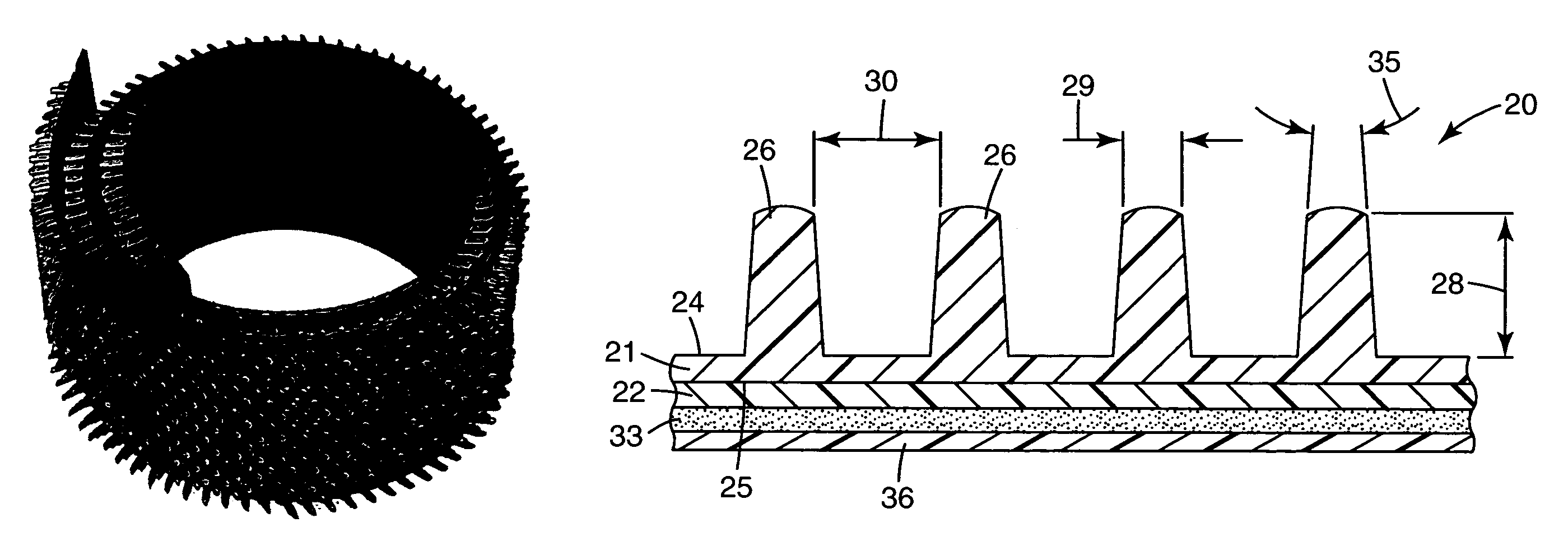
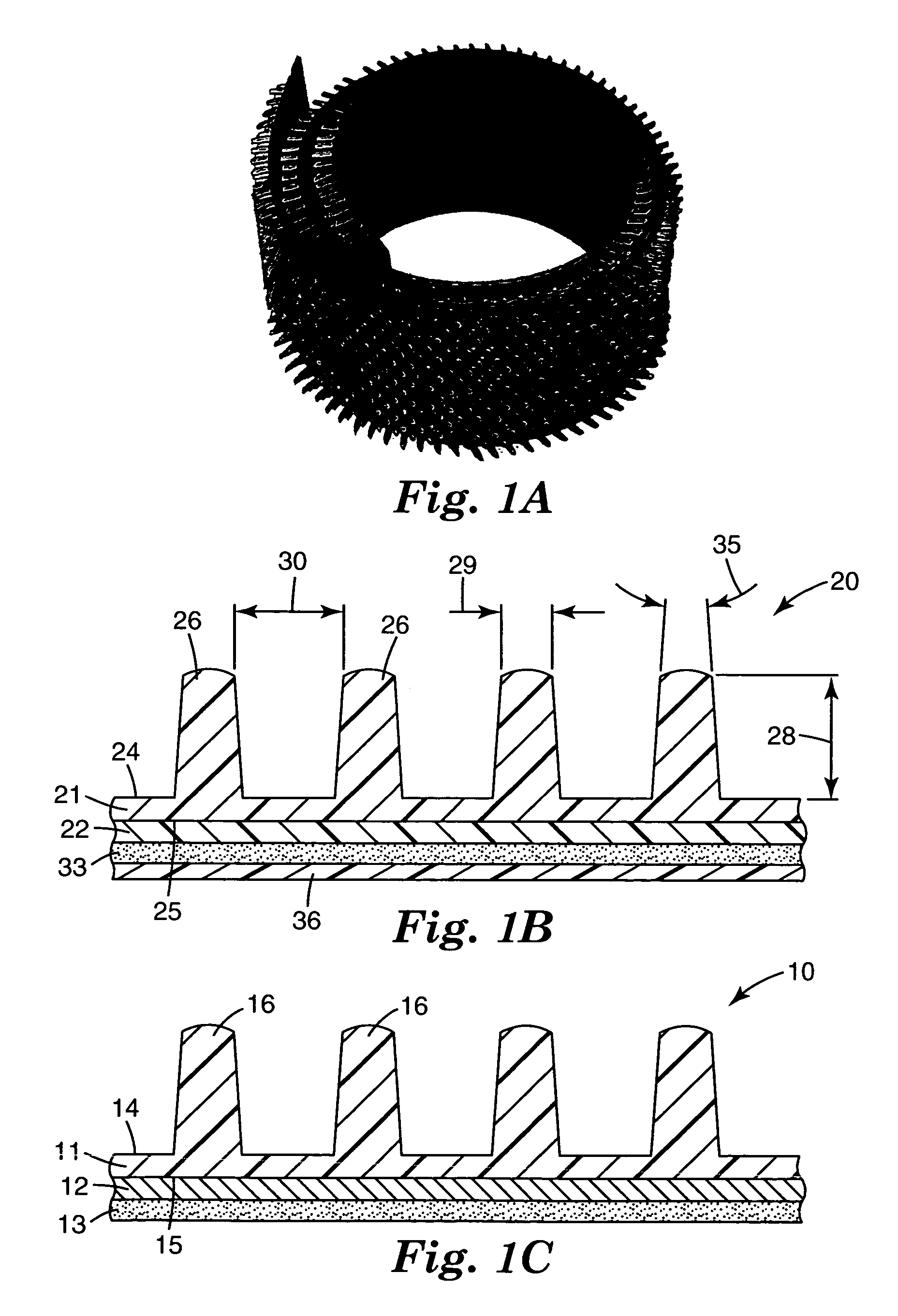
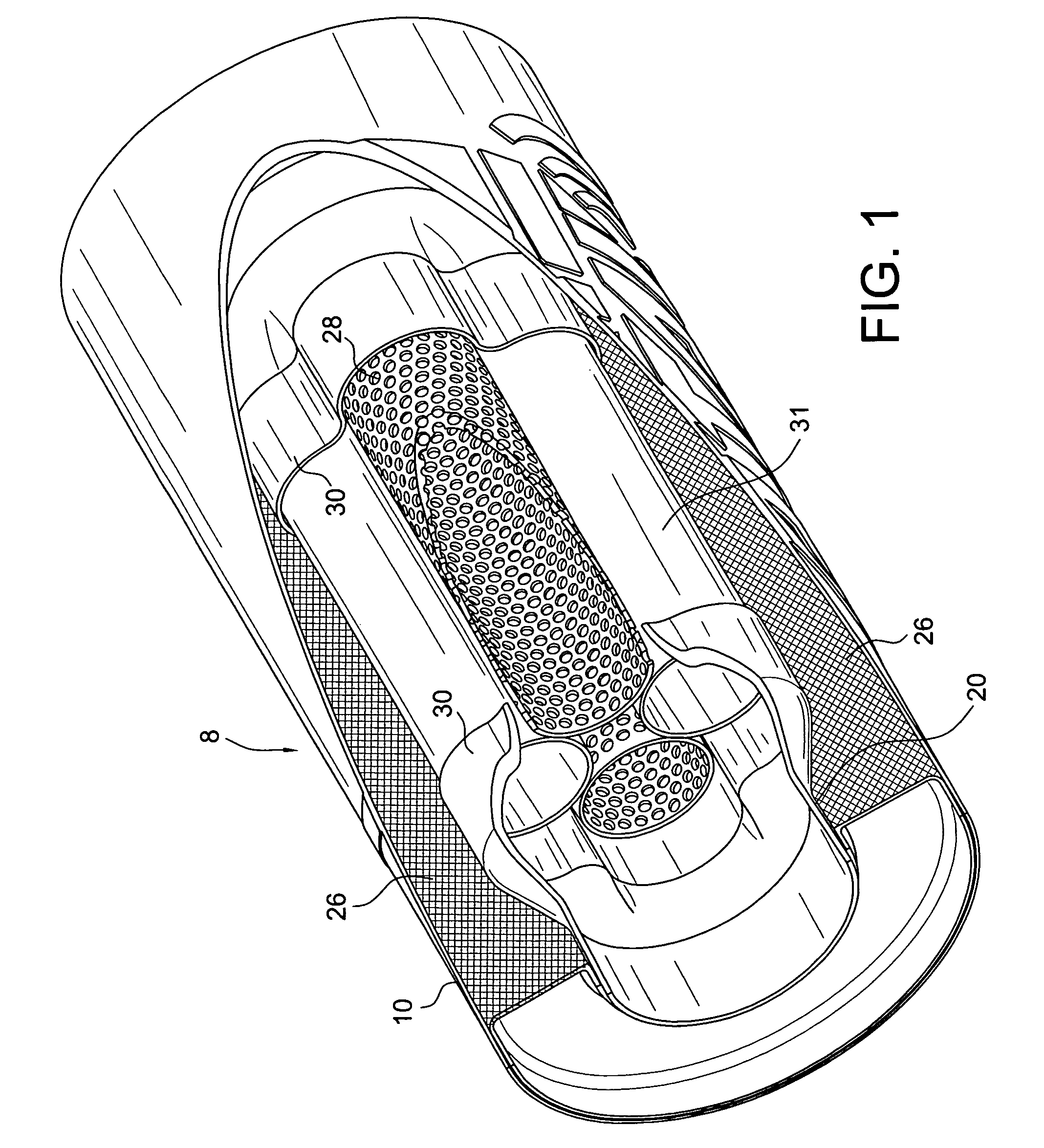
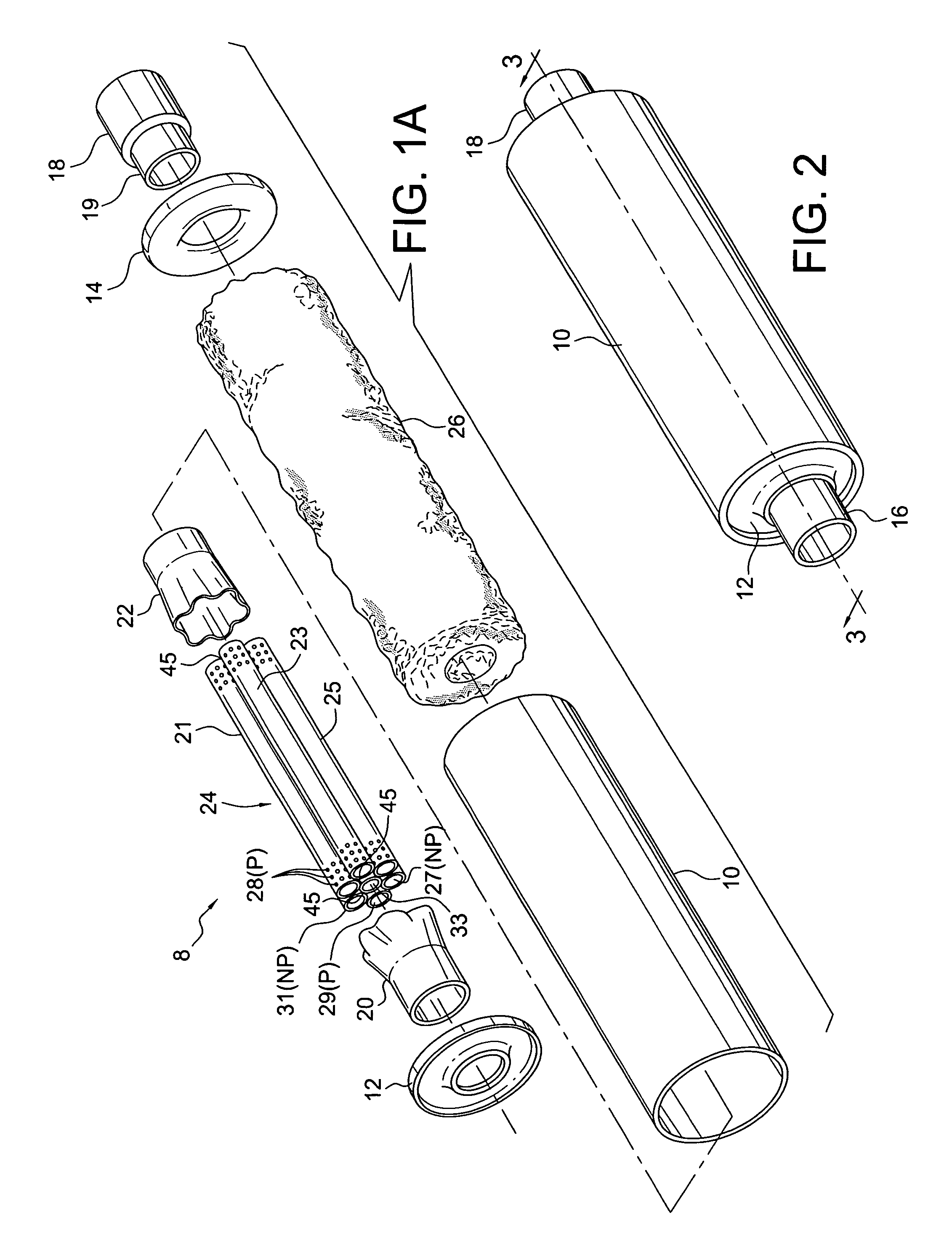
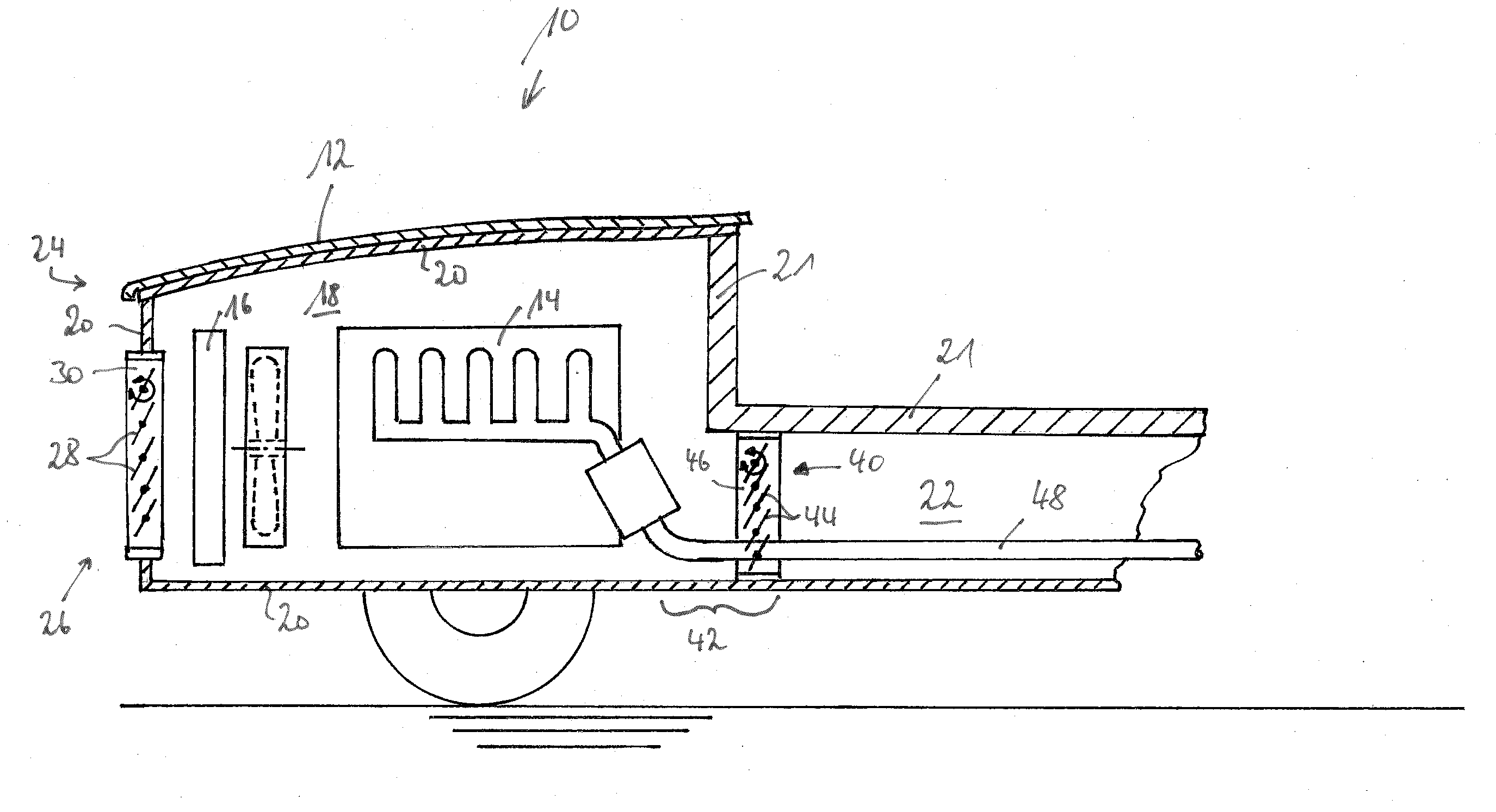
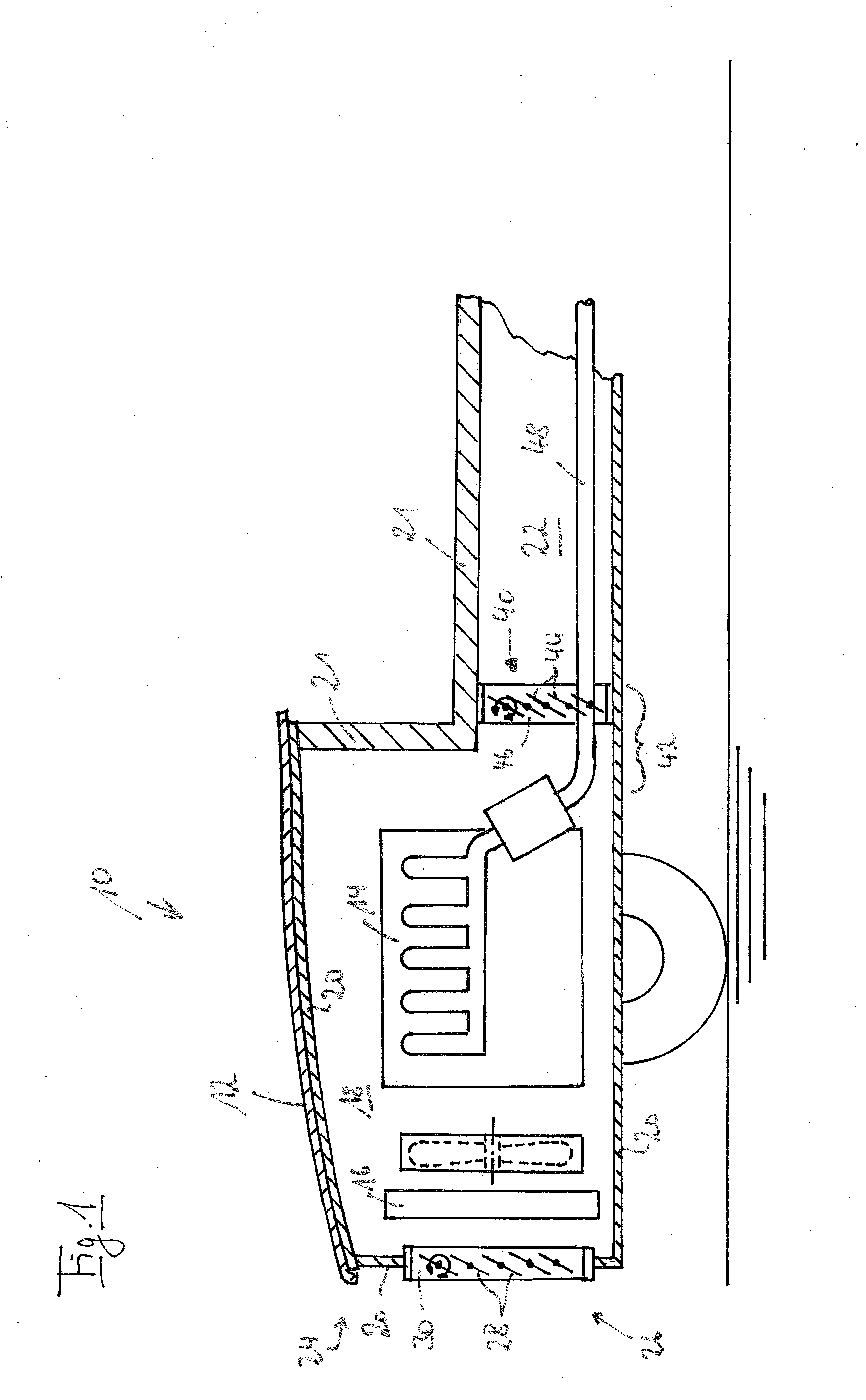
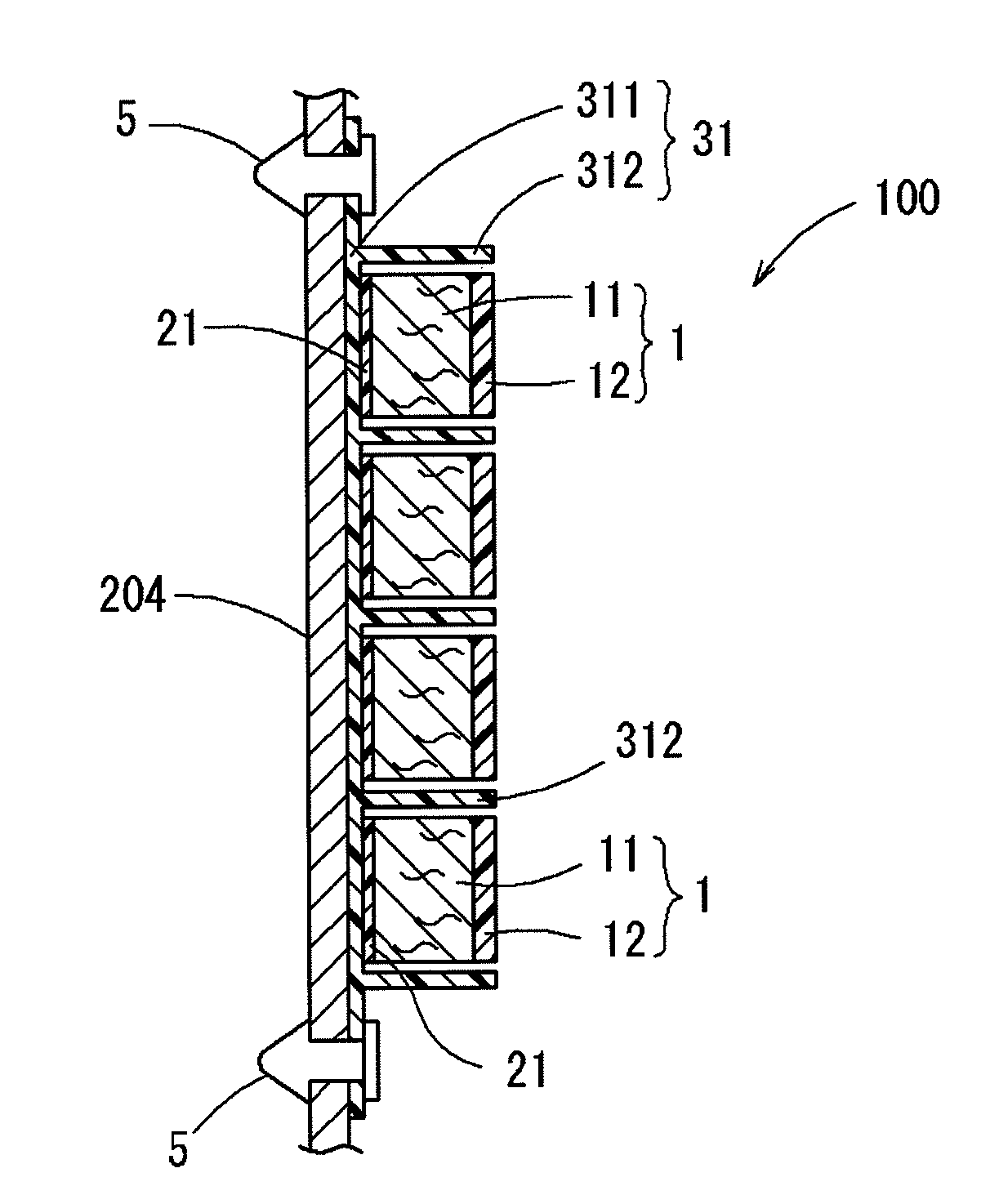
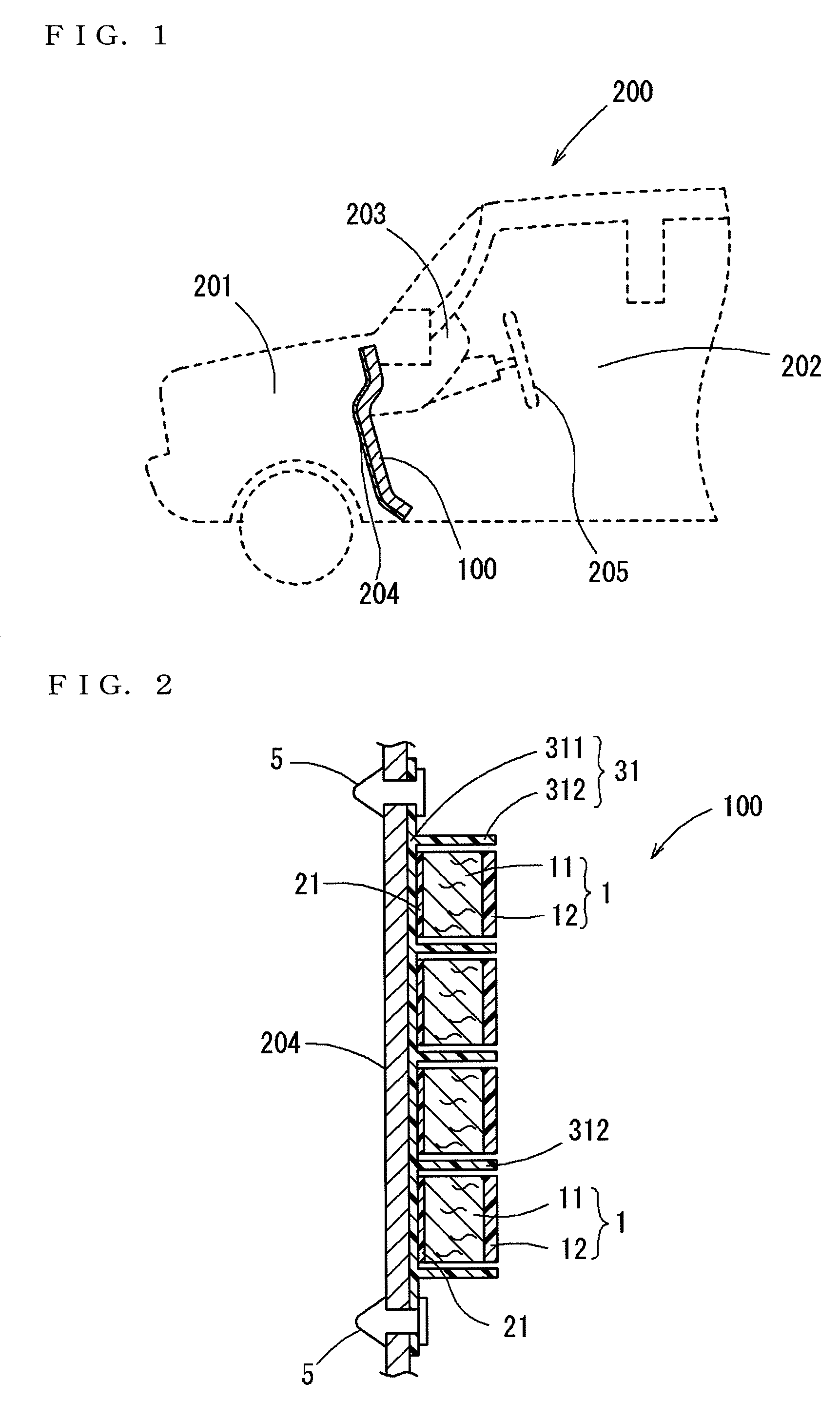
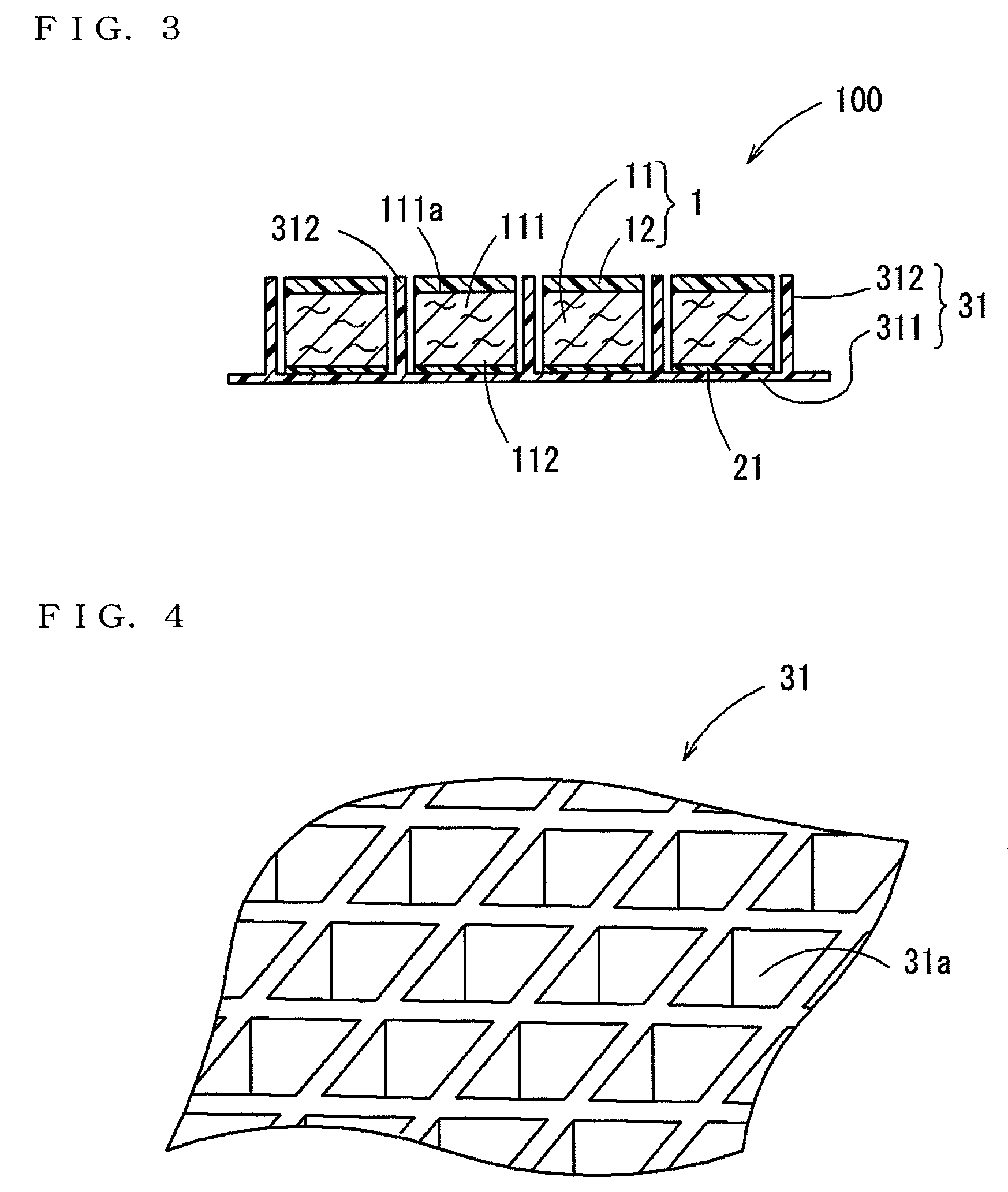
Bicycle chainring
InactiveUS7686721B2Reduce weightGood lookingChain/belt transmissionGearingRotational axisEngineering
A bicycle chainring is formed from a first member and an second member. The first member includes a center rotational axis, a crank attachment portion with a plurality of chainring attachment openings and an annular tooth portion with a plurality of chain engaging gear teeth. The second member disposed around the center rotational axis and is fixedly attached to overlie at least one of the crank attachment portion and the annular tooth portion to reinforce the first member without obstructing access to the chainring attachment openings.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
Centrifugal pellet dryer with plastic wall panels
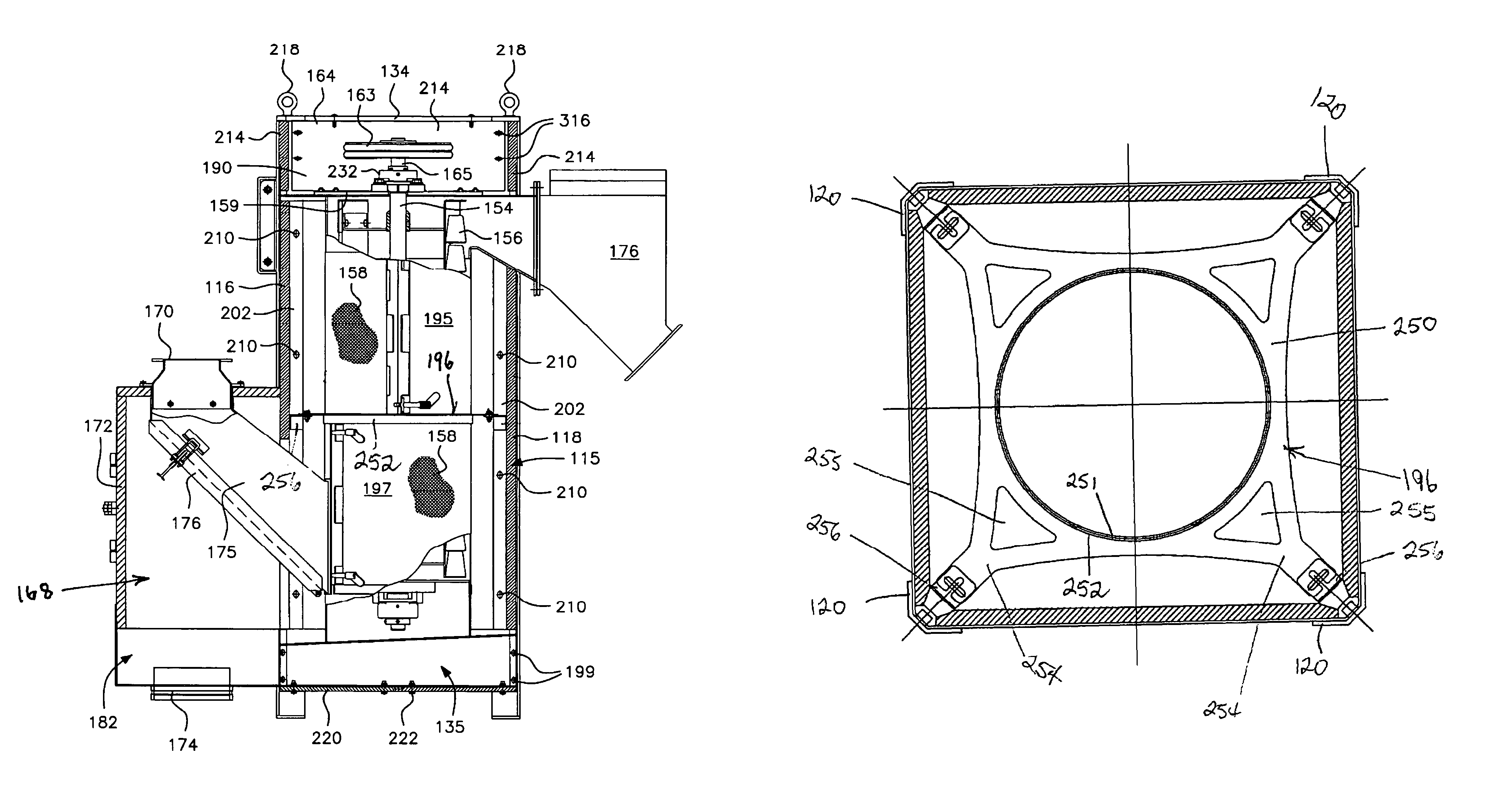
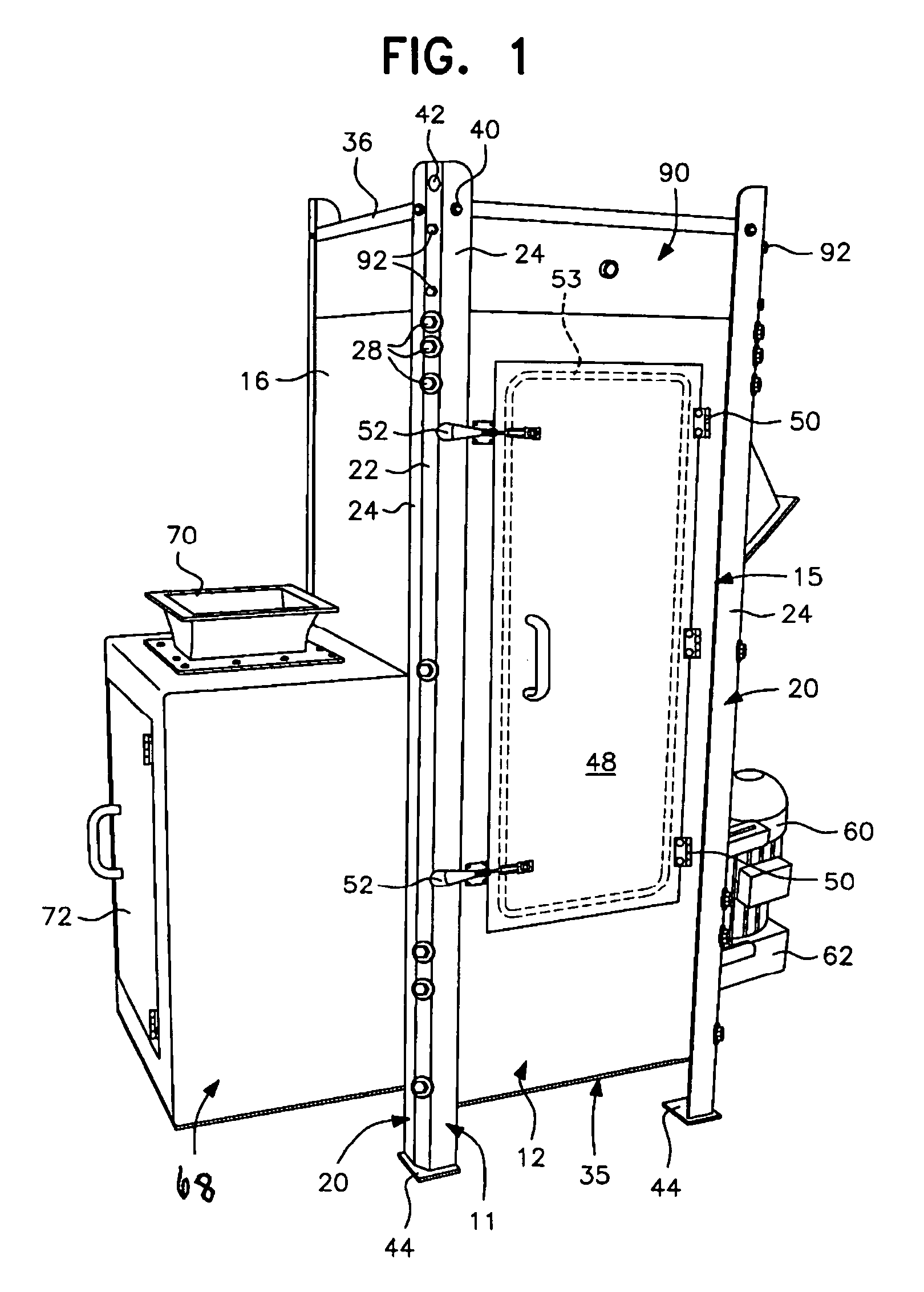
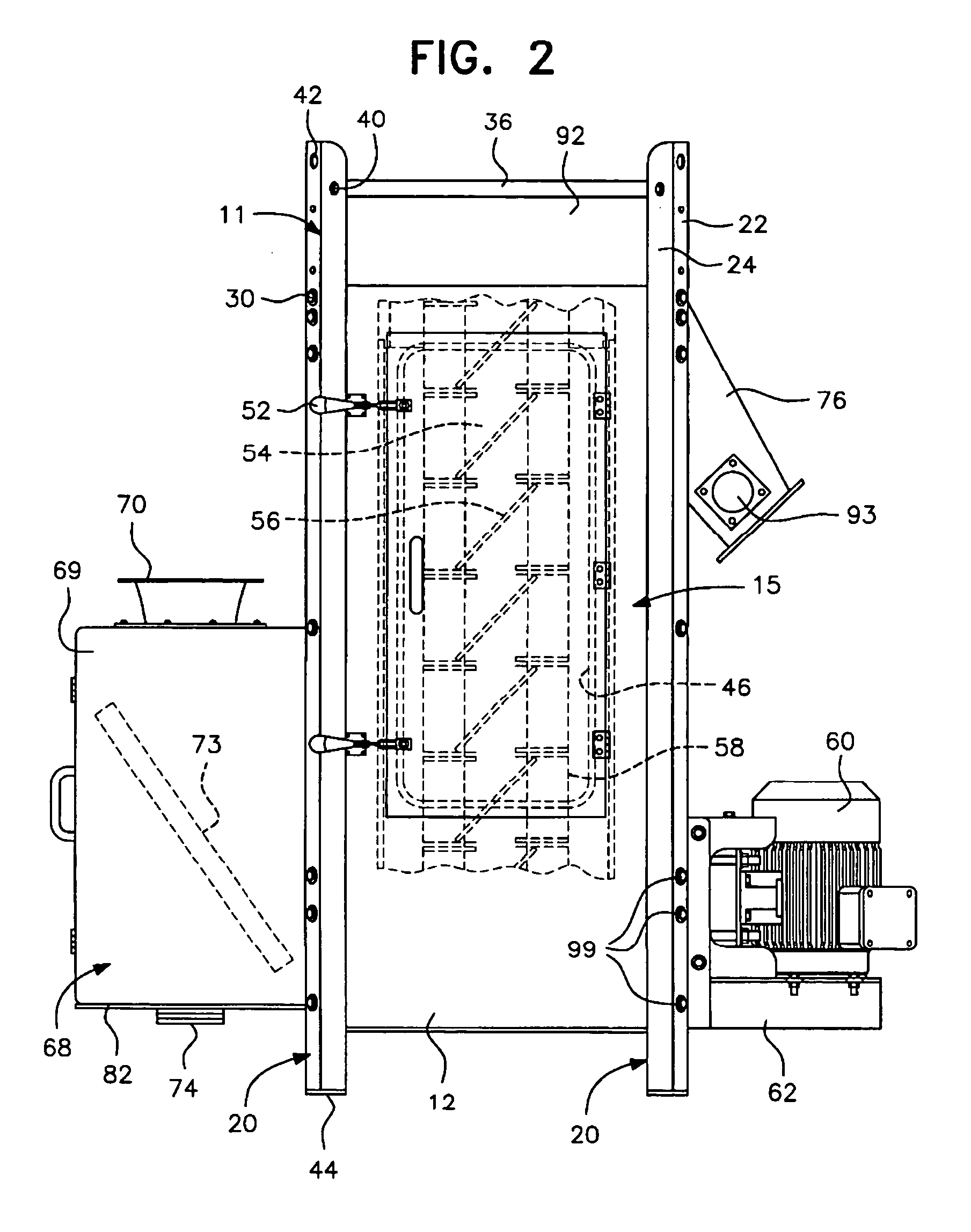
InactiveUS7024794B1Reduce noise transmissionEasy constructionWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationDrying solid materials without heatMetal frameworkEngineering
A centrifugal pellet dryer including a stationary cylindrical screen, a driven elevating rotor in said screen elevating wet pellets inside the screen and imparting radial forces to the wet pellets to impact them against the interior of the screen to enable moisture on the pellets to be separated and discharged through the screen, a housing enclosing the screen and rotor and including an inlet for a slurry of pellets, an outlet for dried pellets and an outlet for water removed from the pellets. The side walls of the housing are constructed of a plurality of relatively large, flat panels made of plastic sheet material are supported in a metal framework to attenuate noise of the dryer produced by rotation of the drier rotor and impact of the wet pellets against the screen. A dewaterer in advance of the dryer also has walls made of plastic sheet material.
Owner:GALA INDUSTRIES INC
Isolated fuel delivery system
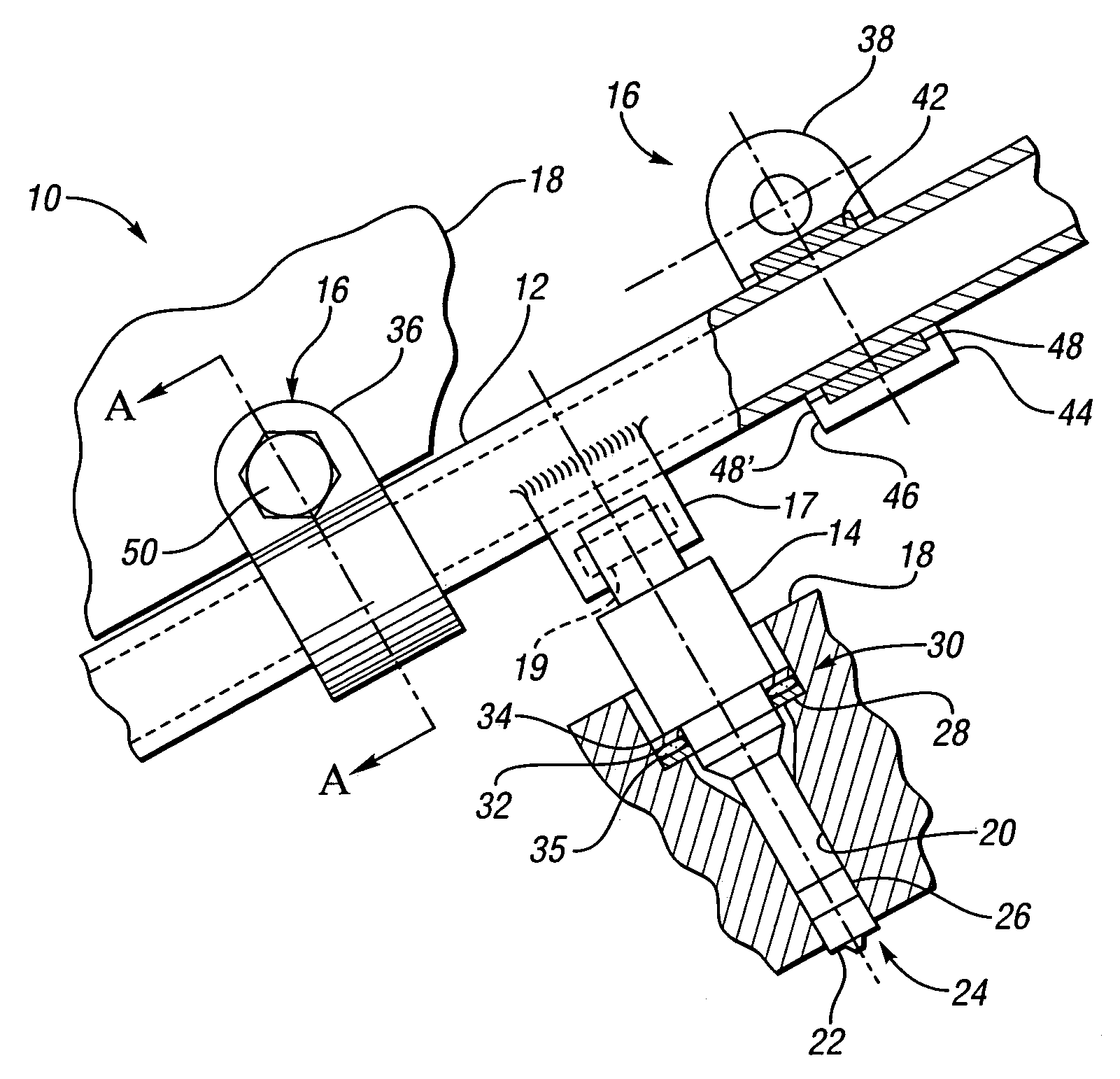
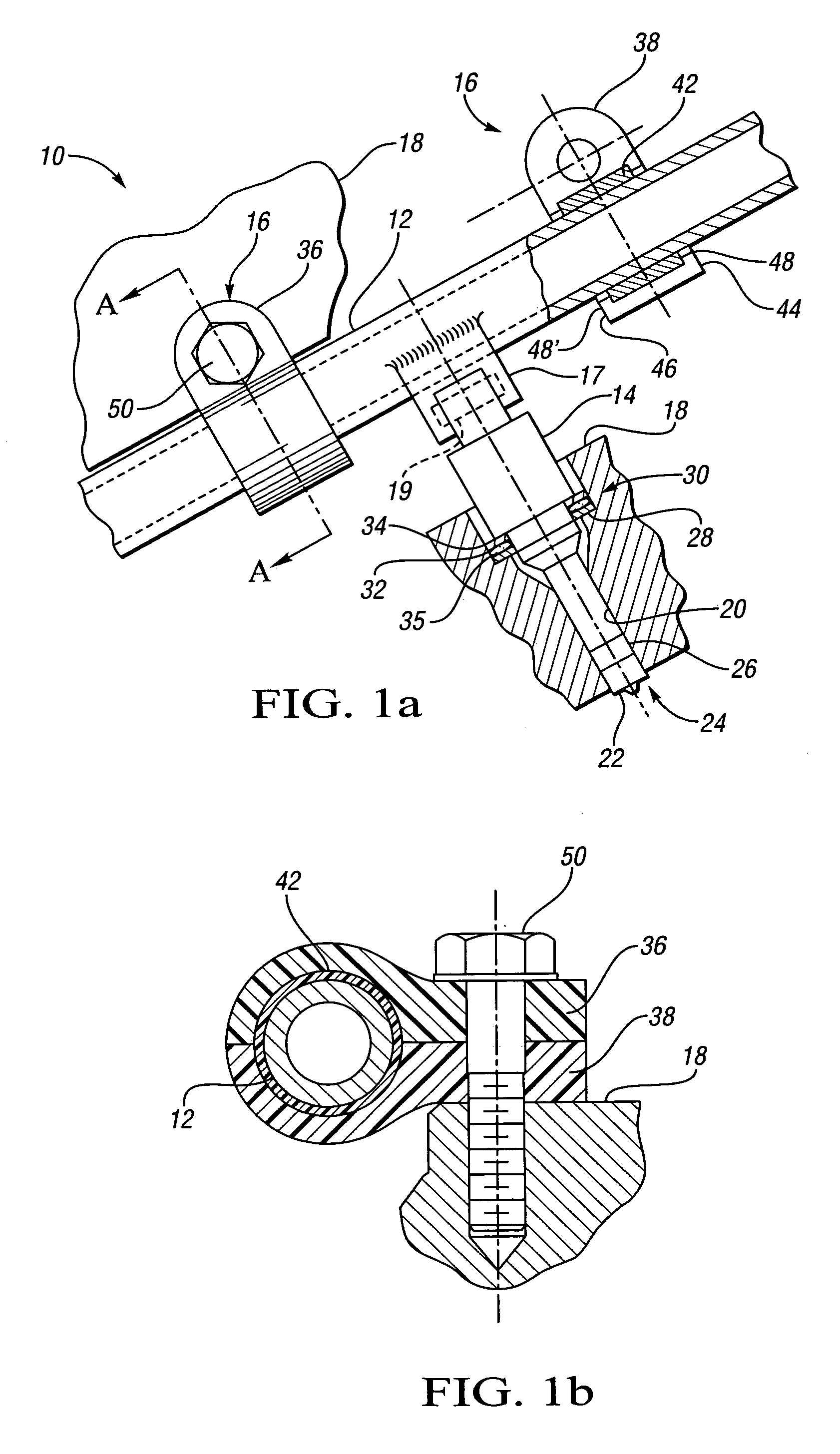
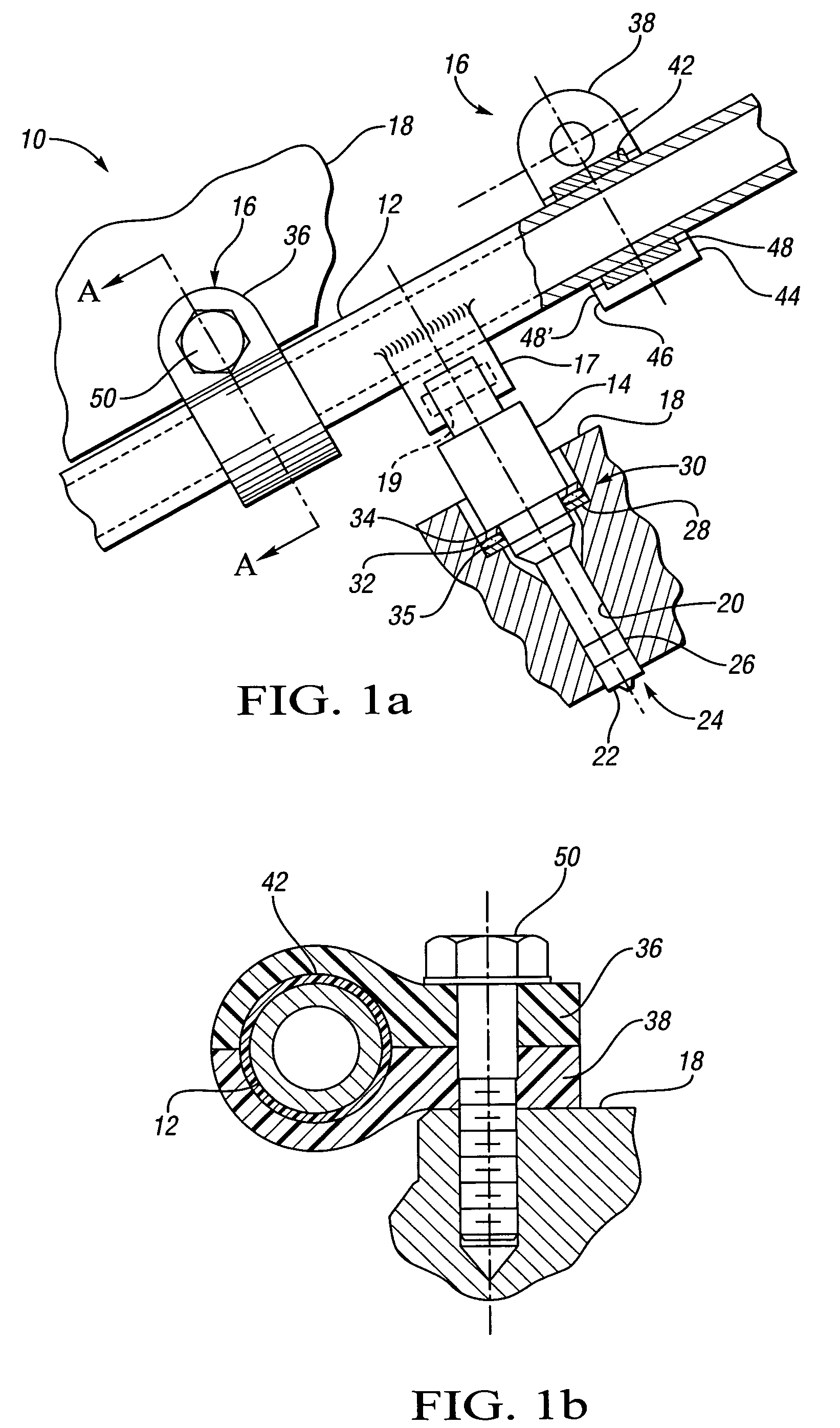
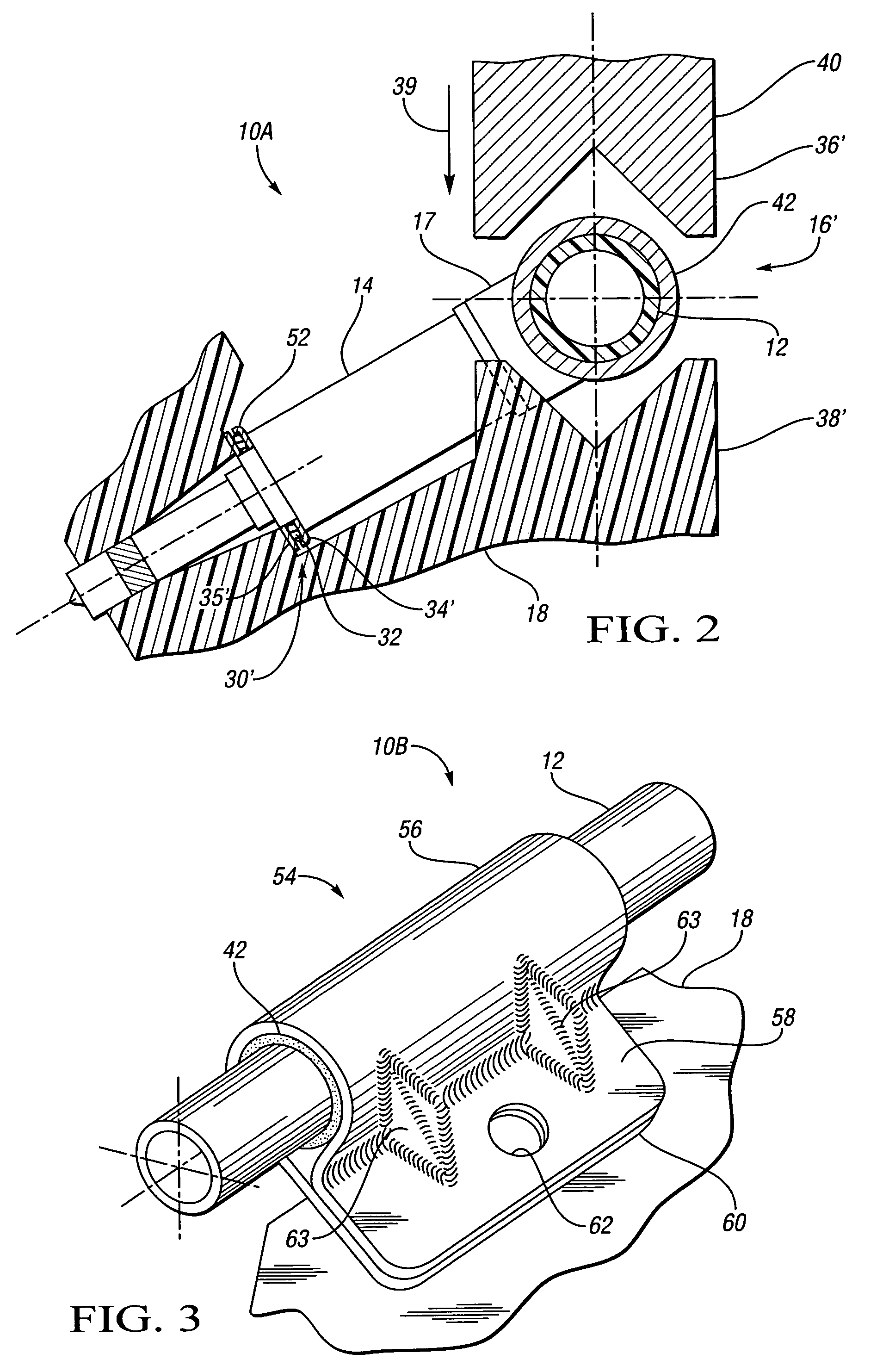
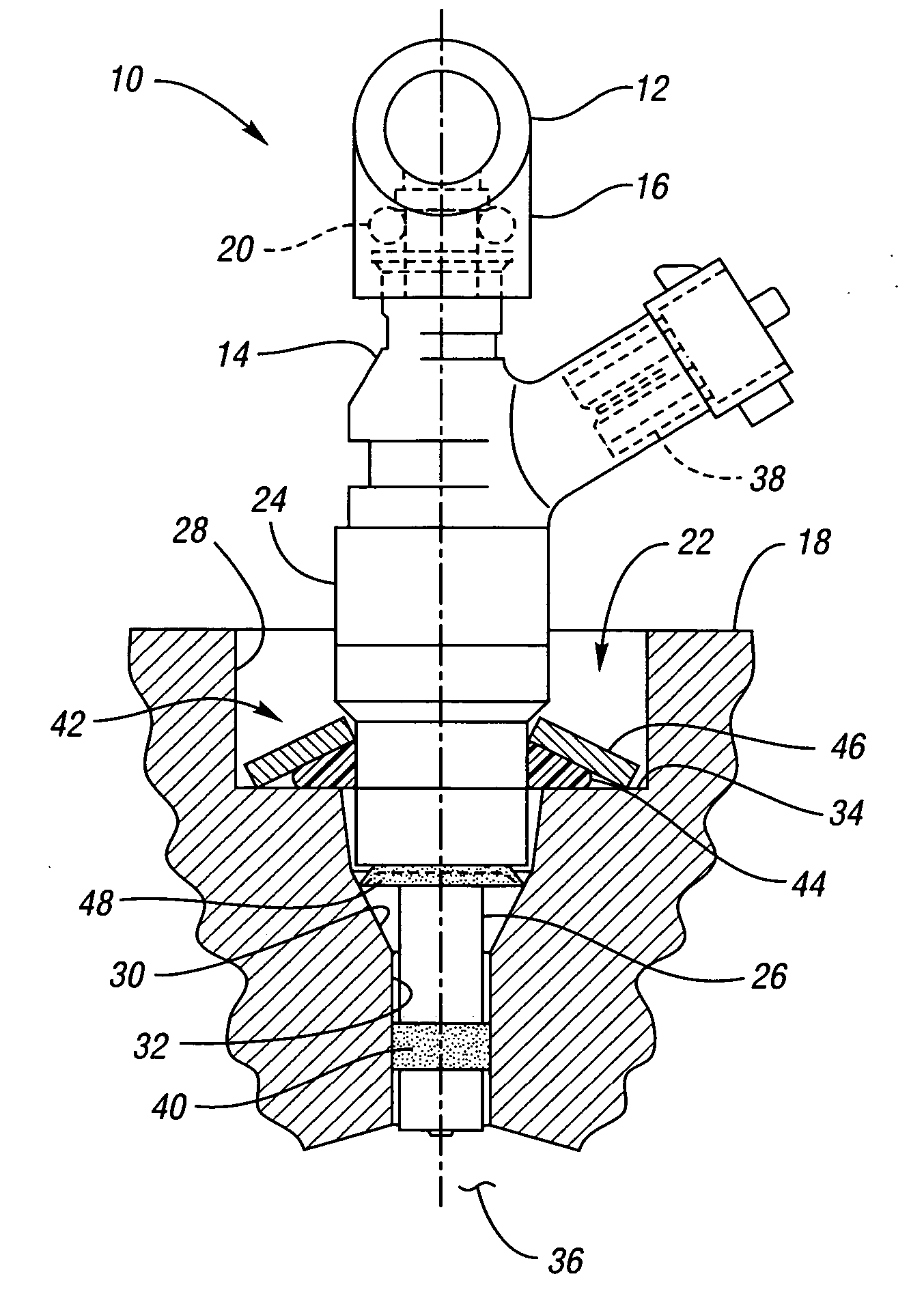
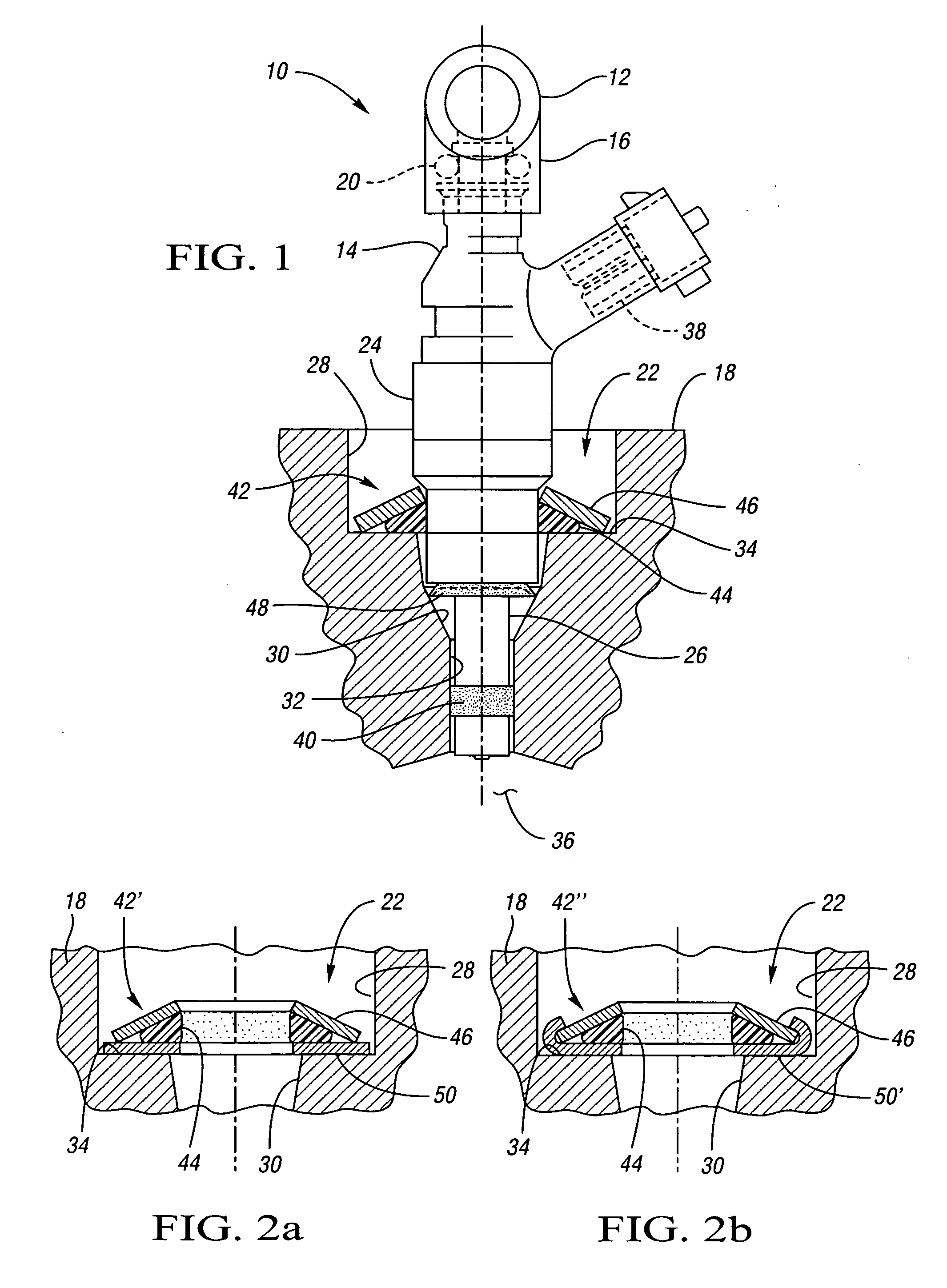
InactiveUS20070163545A1Reduce noise transmissionHigh-frequency vibrationNutsLow pressure fuel injectionCylinder headEngineering
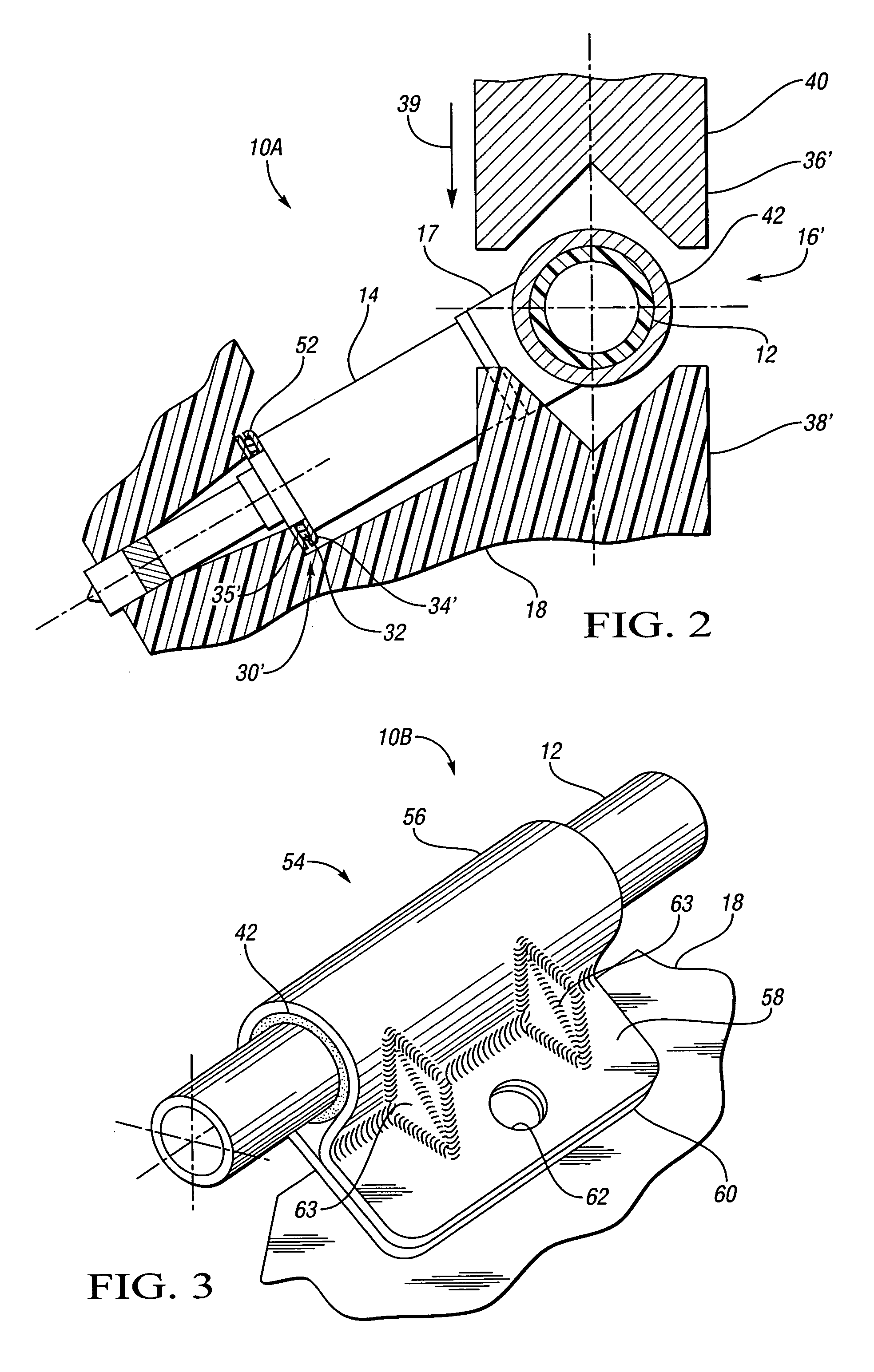
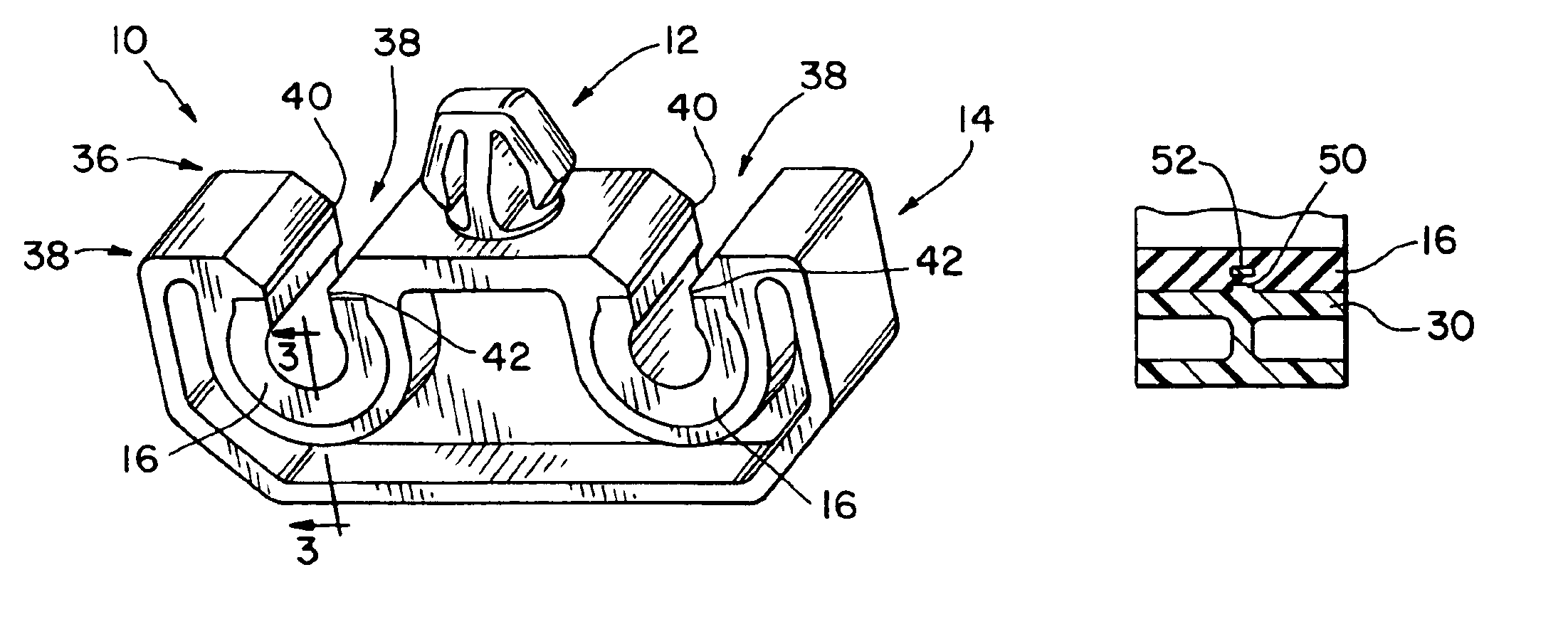
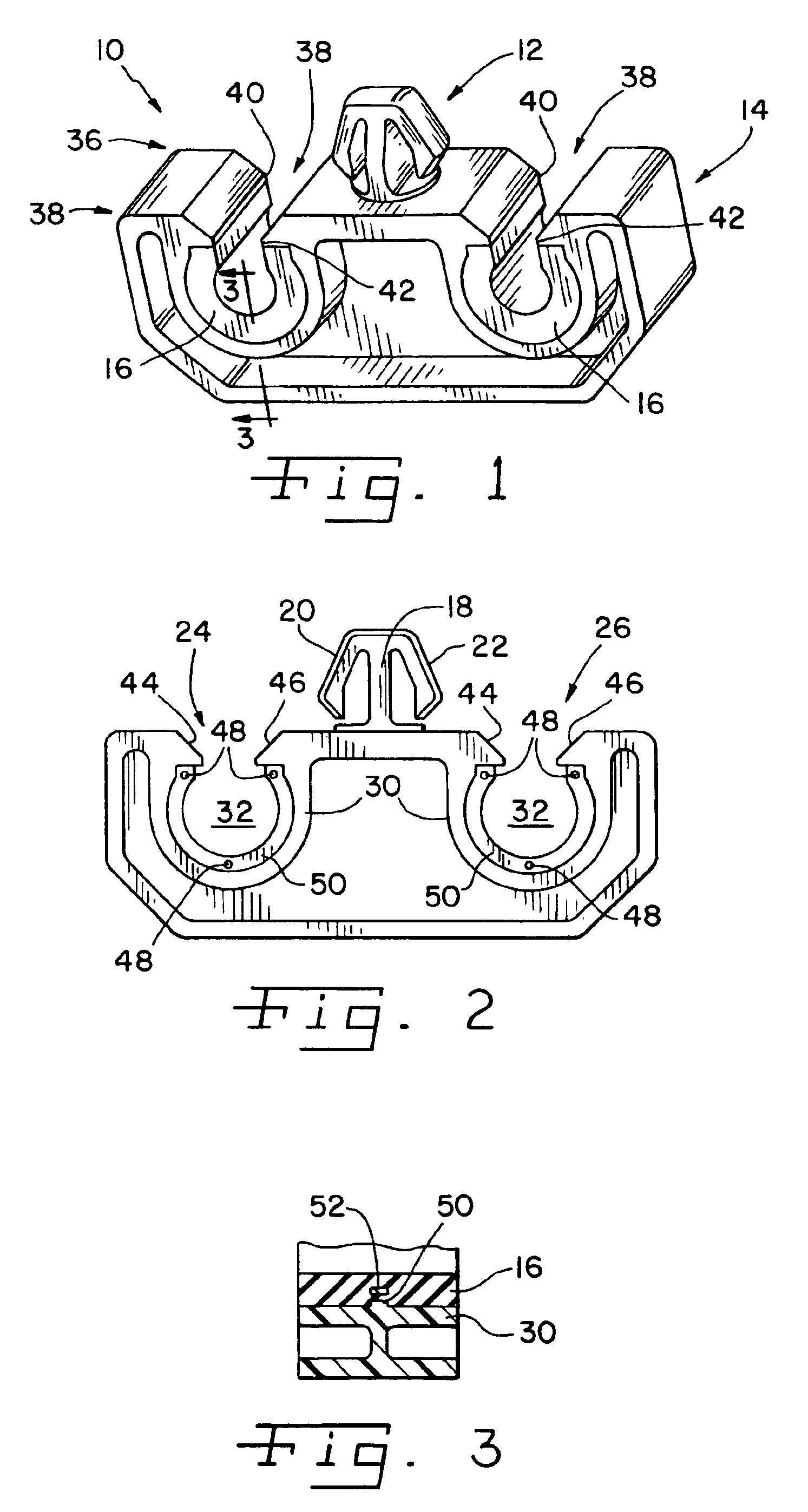
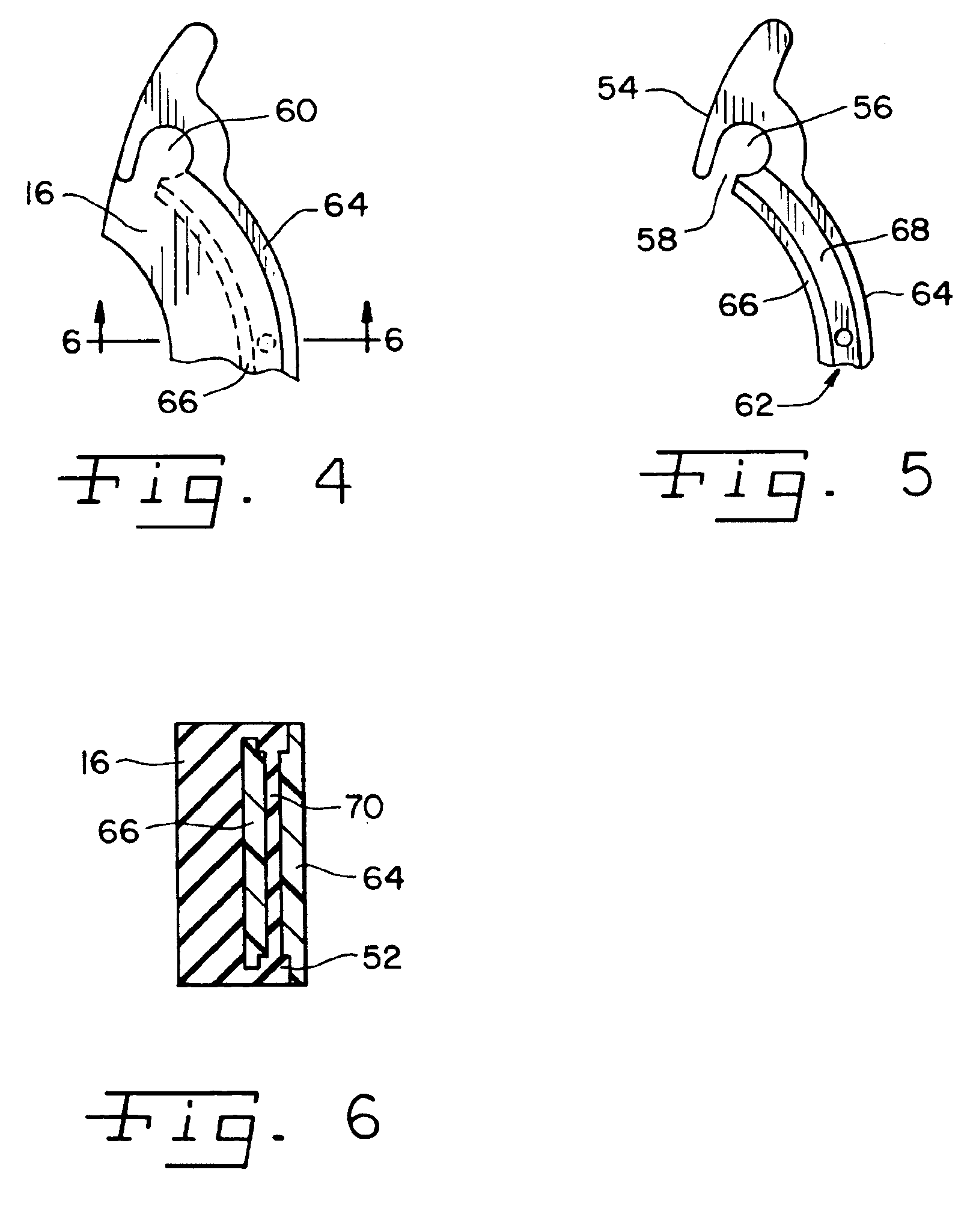
An isolated fuel delivery system for an internal combustion engine includes a fuel rail with a clamping method operable to retain an isolating member with respect to the fuel rail. The isolating member operates to isolate the vibratory motion of the fuel delivery system form the attachment point or points. The attachment point is typically a cylinder head of the internal combustion engine. Additionally, an isolating ring assembly is provided having a first and second stiffening member with an isolating ring member disposed therebetween. The isolating ring assembly is disposed between a fuel injector of the isolated fuel delivery system and the cylinder head. The isolating ring member operates to isolate the vibratory motion of the fuel injector from the internal combustion engine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Vibration damping clip
InactiveUS6926237B2Easy to manufactureReduce noise transmissionPipe supportsRod connectionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
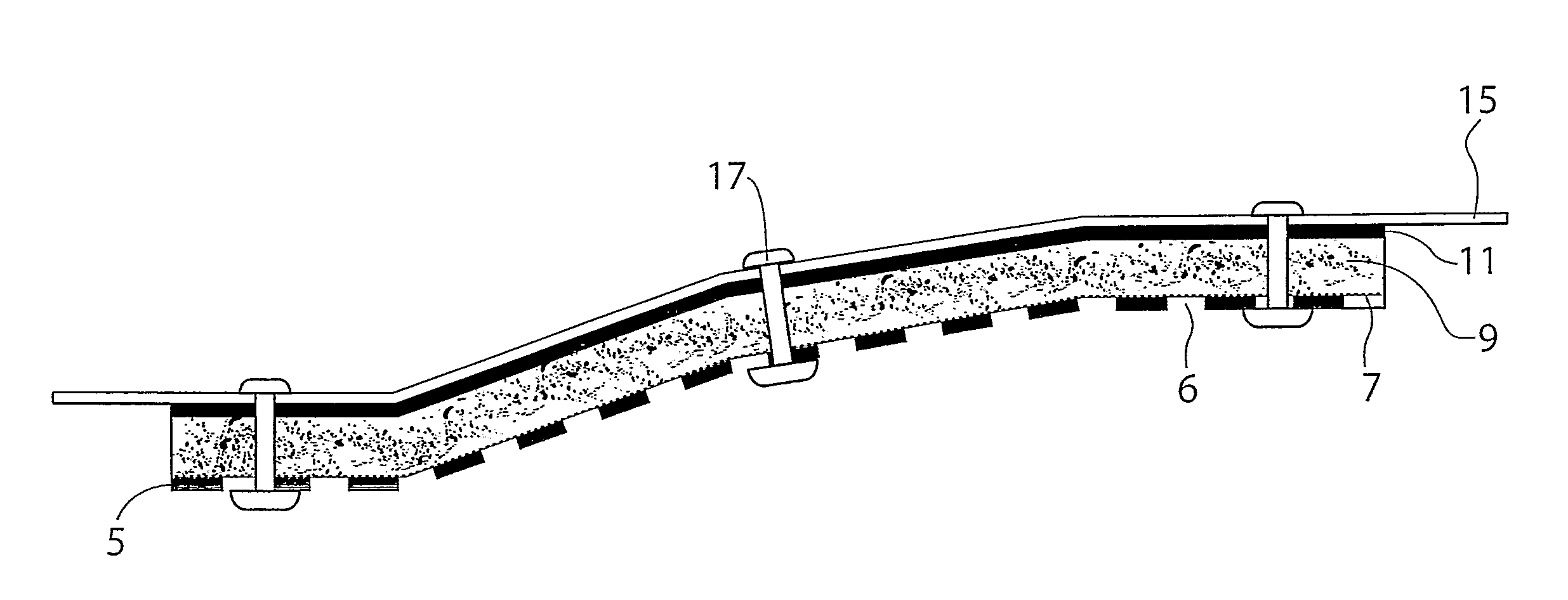
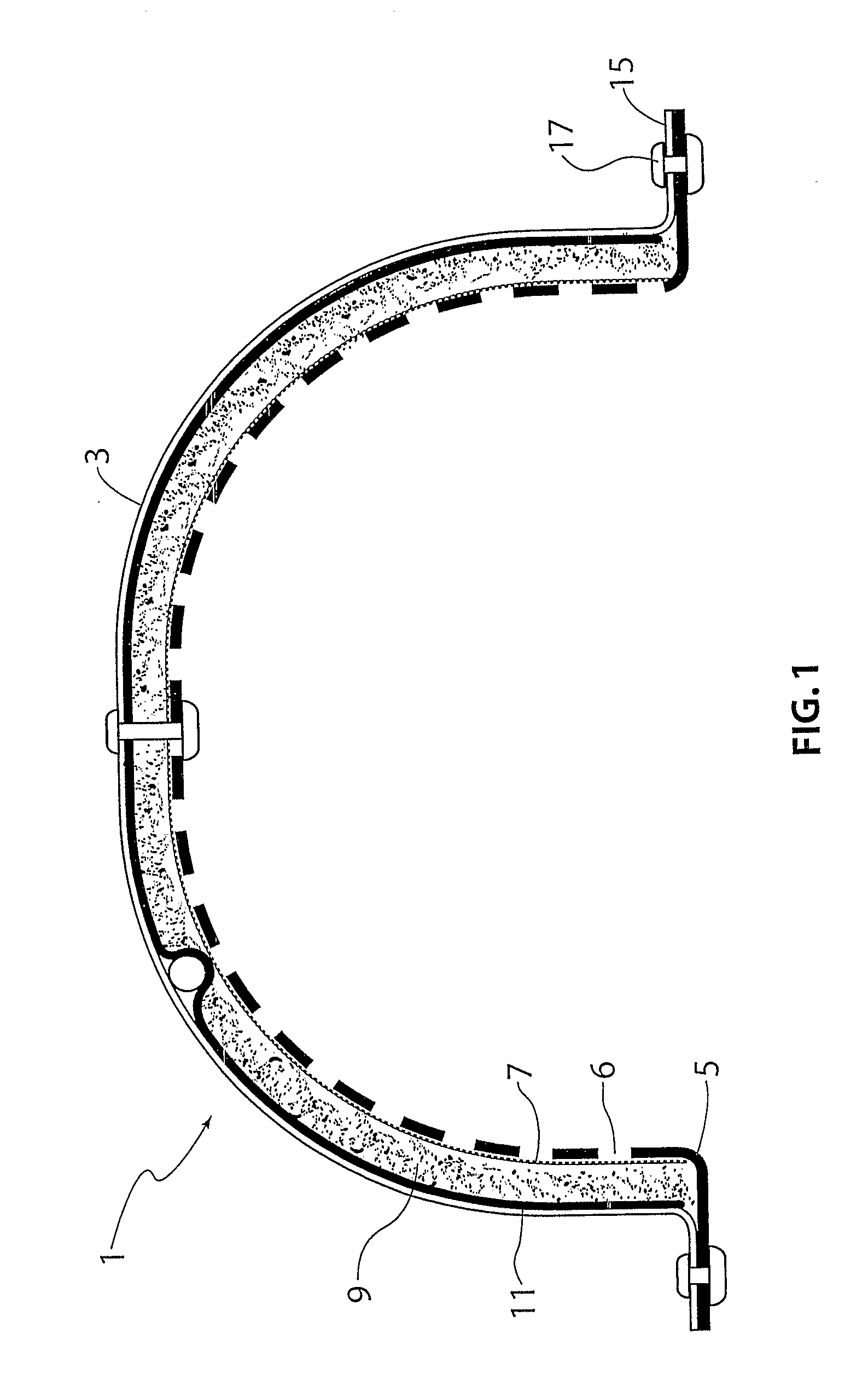
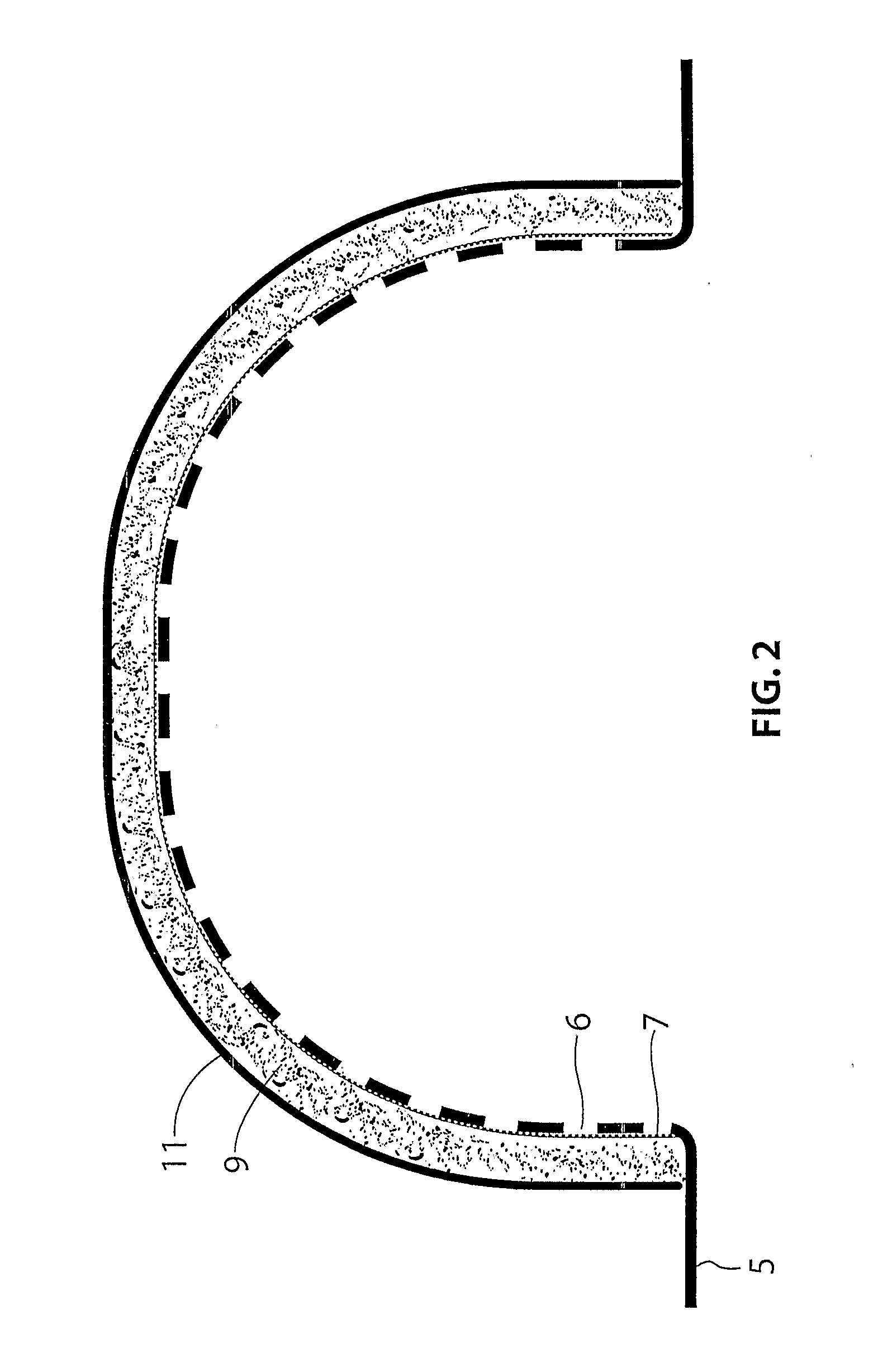
Acoustic shield
InactiveUS20110139542A1Reduce noise transmissionGreat degreeWallsSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical and Electronics engineering
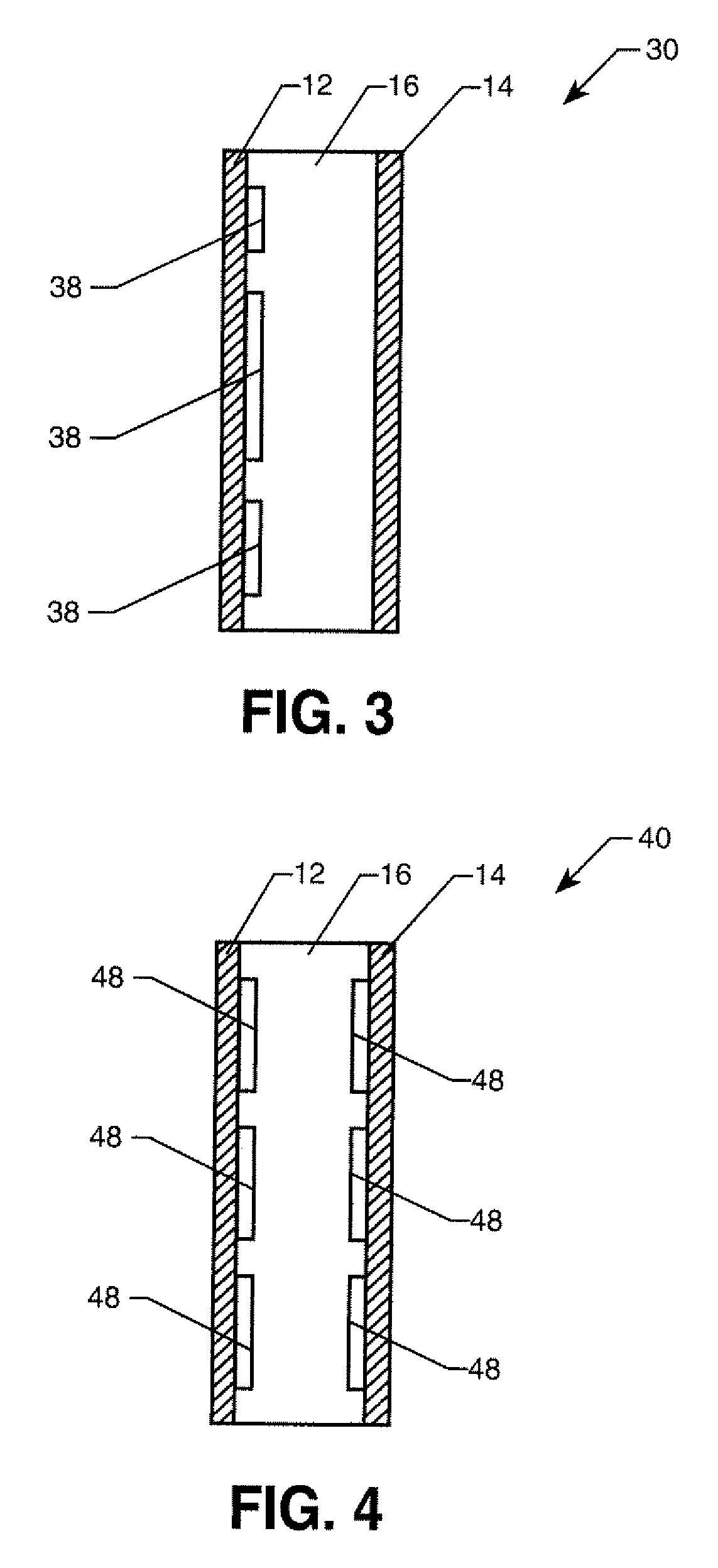
A multilayered acoustic shield (1) for mounting to a panel of a vehicle, the shield (1) including an outer portion and an inner portion, the outer portion including a support layer (5) having apertures (6) therein, the inner portion including a sound-absorbing layer (9) and a vibration-dampening layer (11), wherein the shield (1) is fastenable to the panel of the vehicle such that at least a portion of the dampening layer (11) engages the panel with the sound-absorbing layer (9) being compressed between the outer portion and the dampening layer (11), to thereby reduce the transmission of noise into a cabin of the vehicle.
Owner:BELLMAX ACOUSTIC
Bicycle chainring
InactiveUS20060258498A1Reduce weightGood lookingChain/belt transmissionGearingRotational axisEngineering
A bicycle chainring is formed from a first member and an second member. The first member includes a center rotational axis, a crank attachment portion with a plurality of chainring attachment openings and an annular tooth portion with a plurality of chain engaging gear teeth. The second member disposed around the center rotational axis and is fixedly attached to overlie at least one of the crank attachment portion and the annular tooth portion to reinforce the first member without obstructing access to the chainring attachment openings.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
Vacuum cleaner
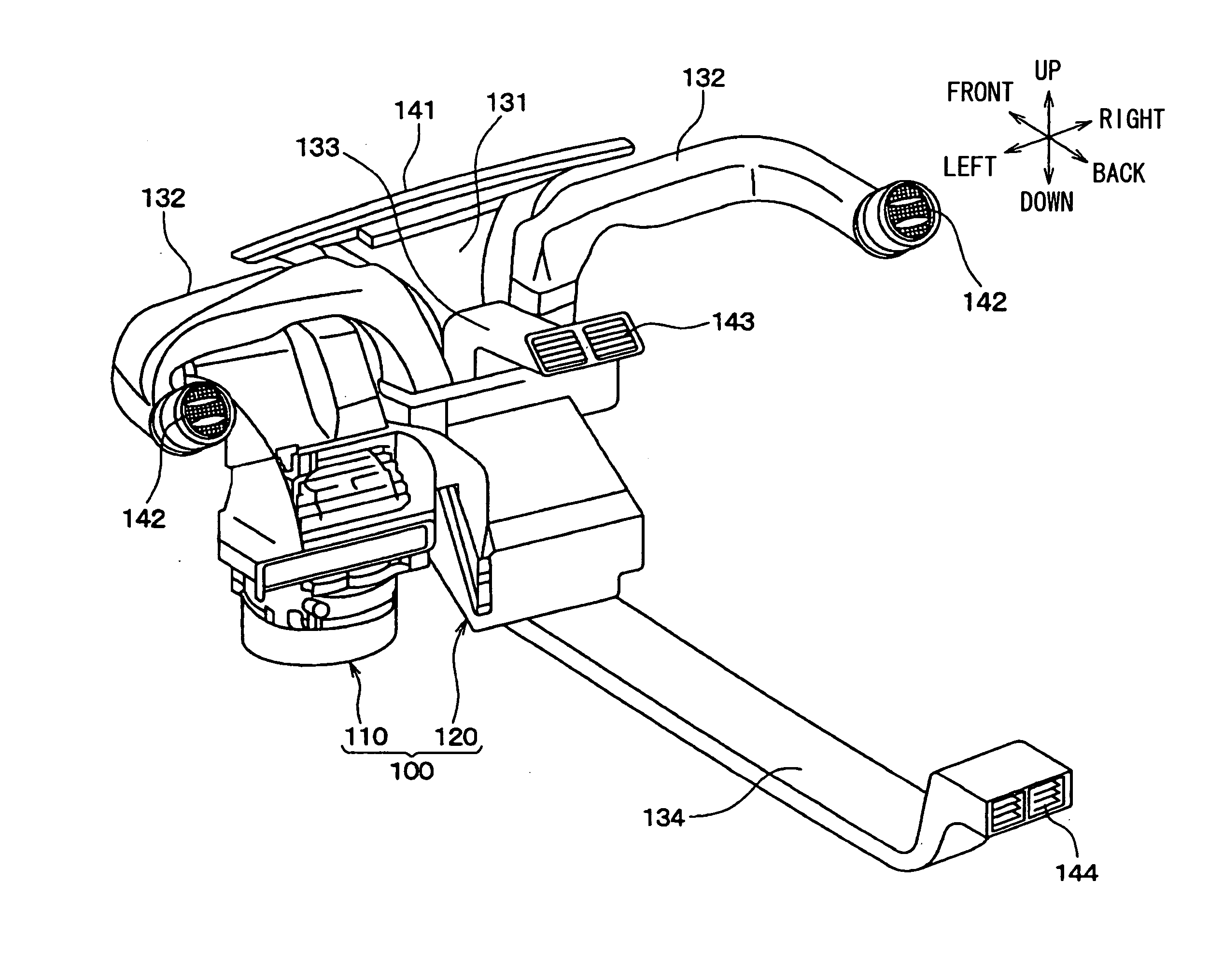
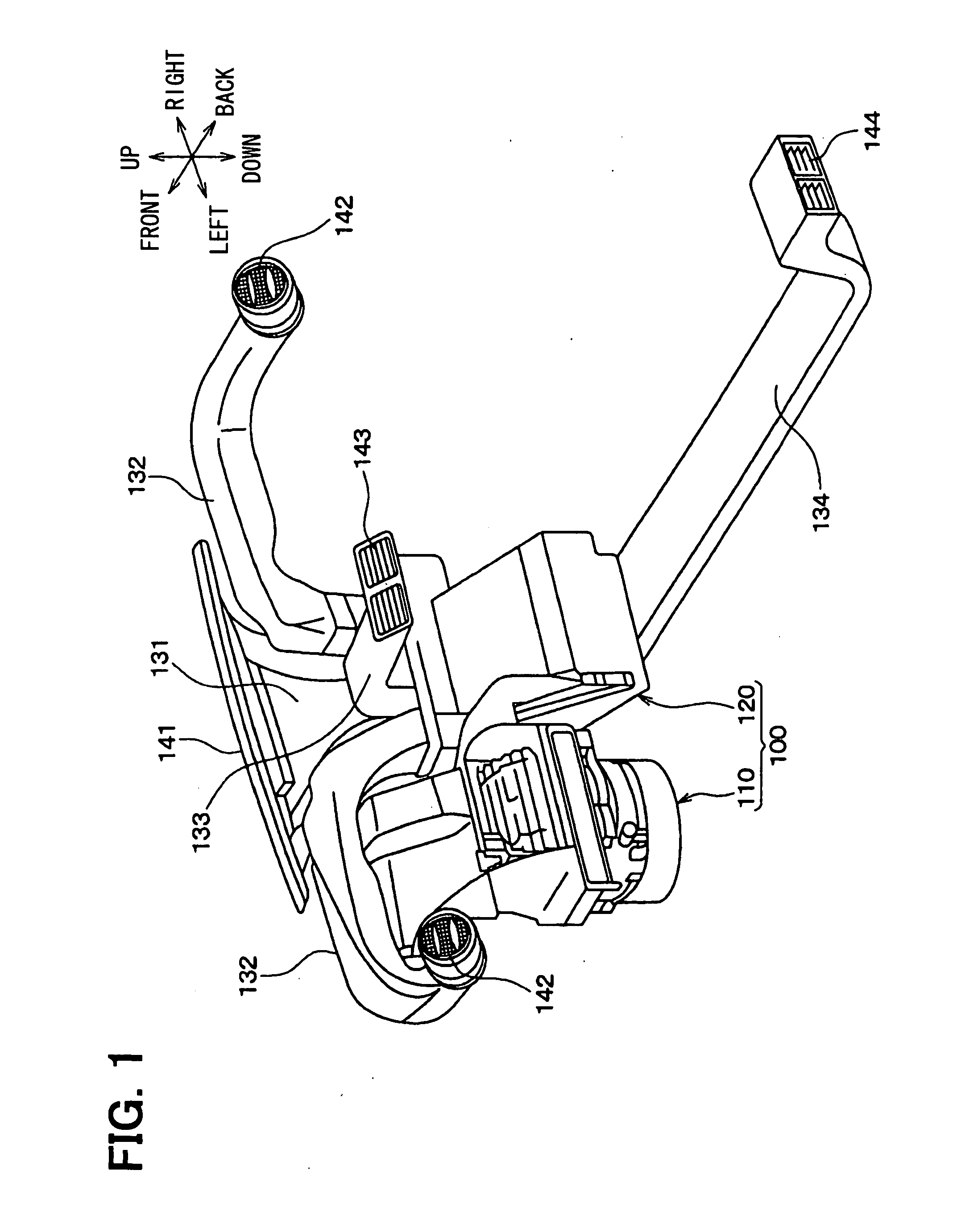
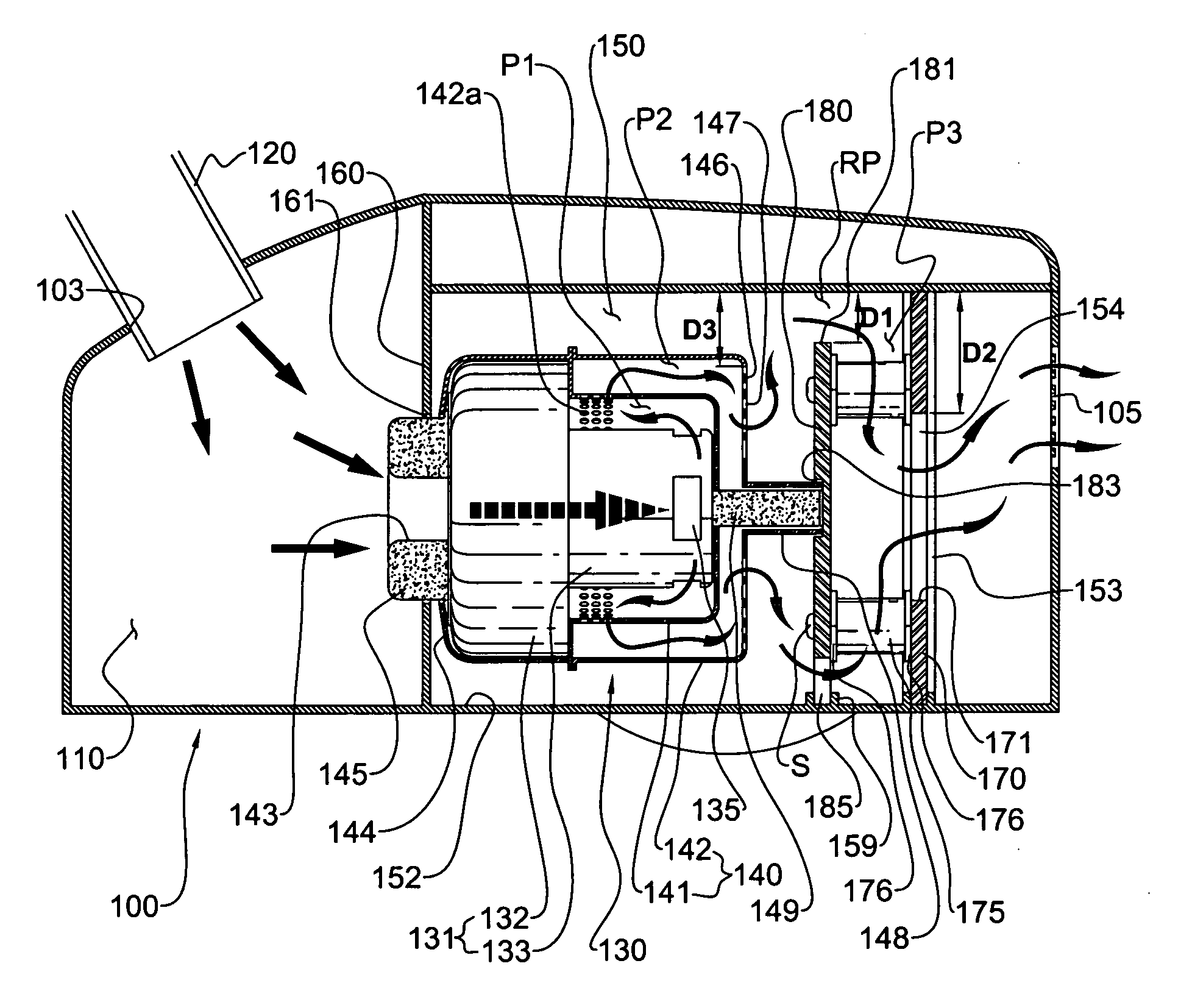
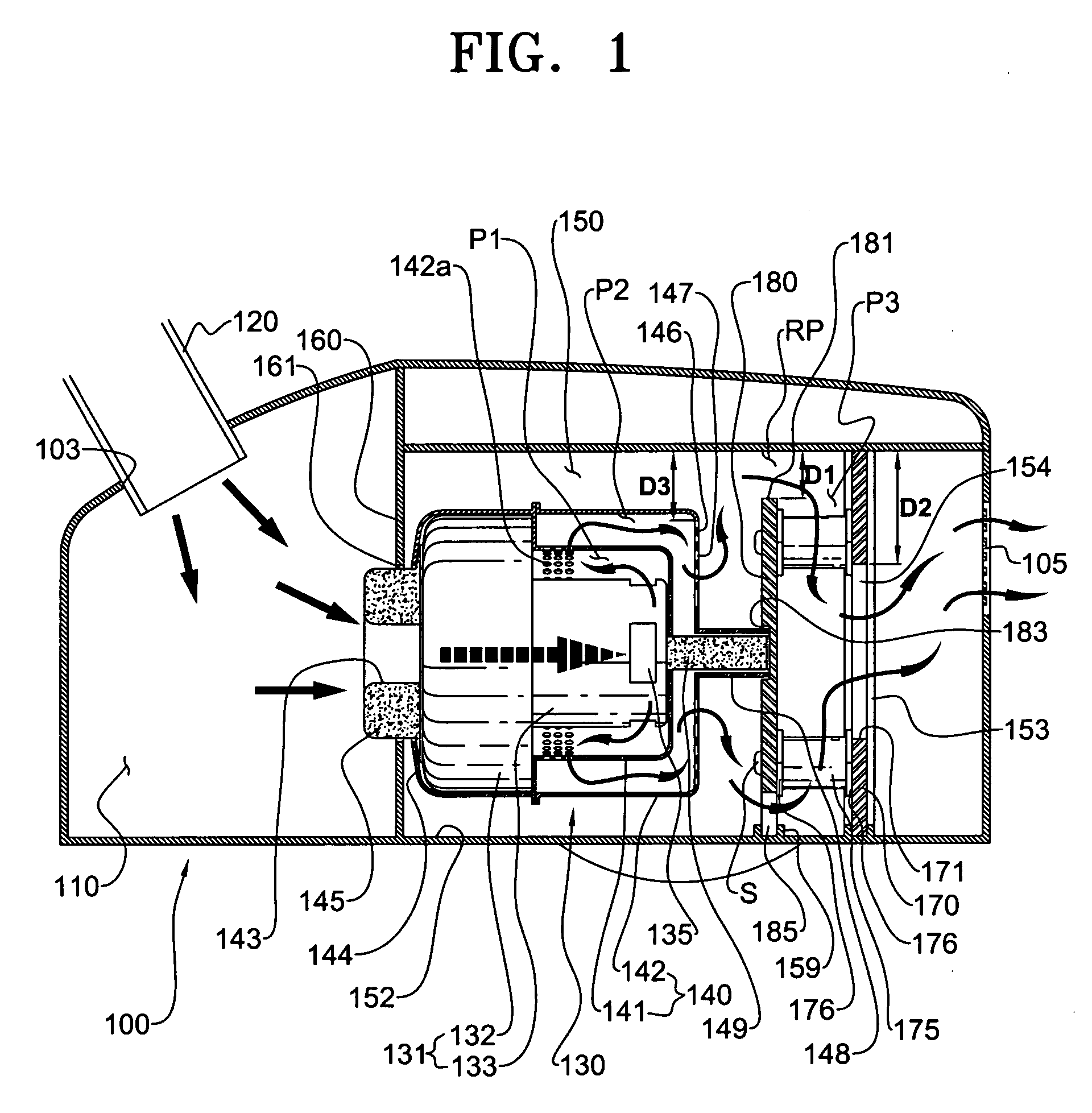
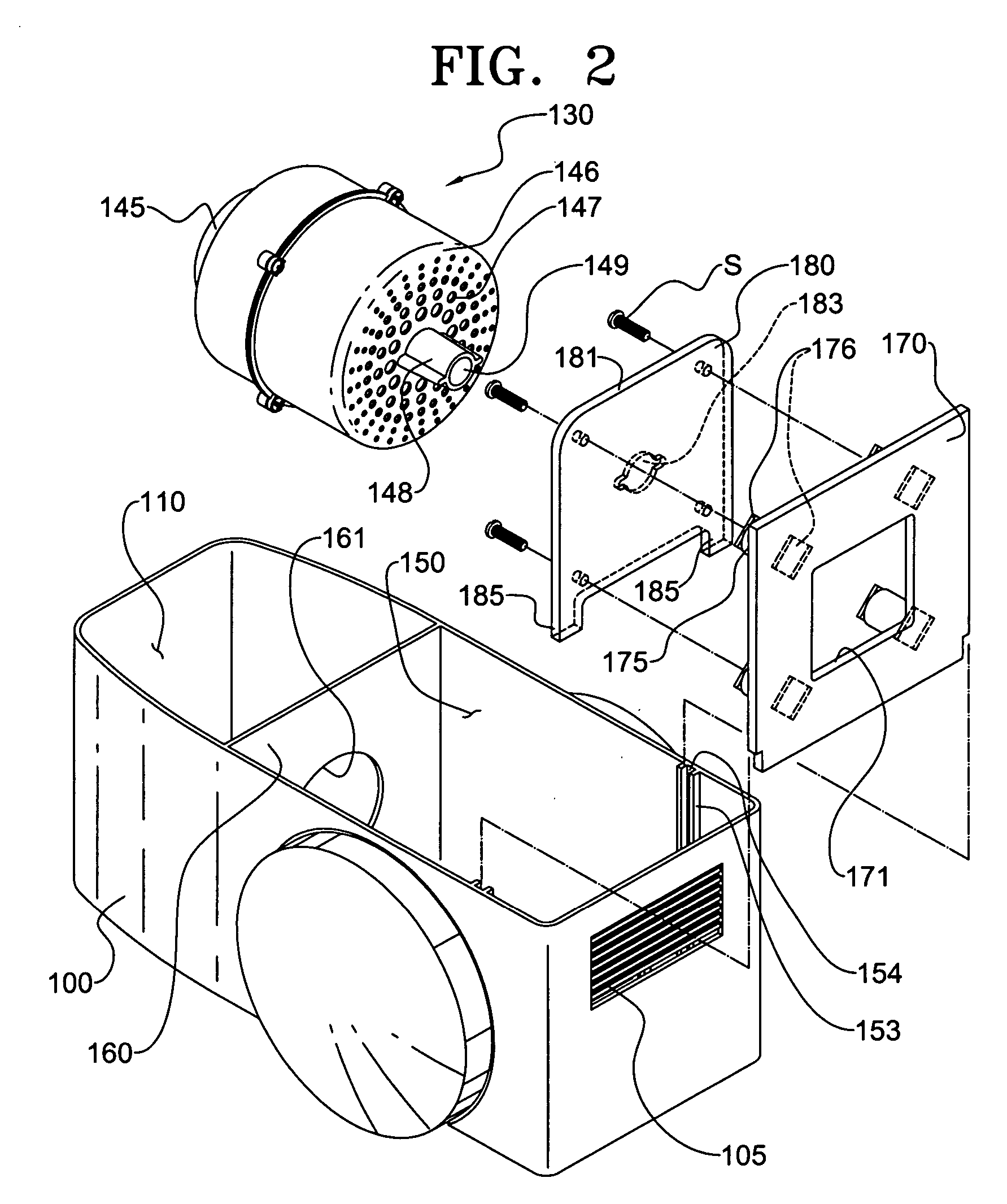
InactiveUS20060277711A1Avoid noiseReduce noise transmissionSuction filtersPump componentsForeign matterSuction force
A vacuum cleaner for reducing noise from being transmitted to the exterior. The vacuum cleaner includes a main body forming an outer appearance of the vacuum cleaner and including a blower unit for generating suction force and blowing force and a discharge hole through which purified air from which foreign matter has been filtered is discharged, a discharge passage for guiding air discharged from the blower unit to the discharge hole, and a spiral shaped intercepting passage for forming a part of the discharge passage and for preventing noise of the blower unit from being transmitted to the exterior. A guide member forming the intercepting passage is disposed at the outside of the blower unit and serves as an acoustic absorber so that noise transmission to the exterior is reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
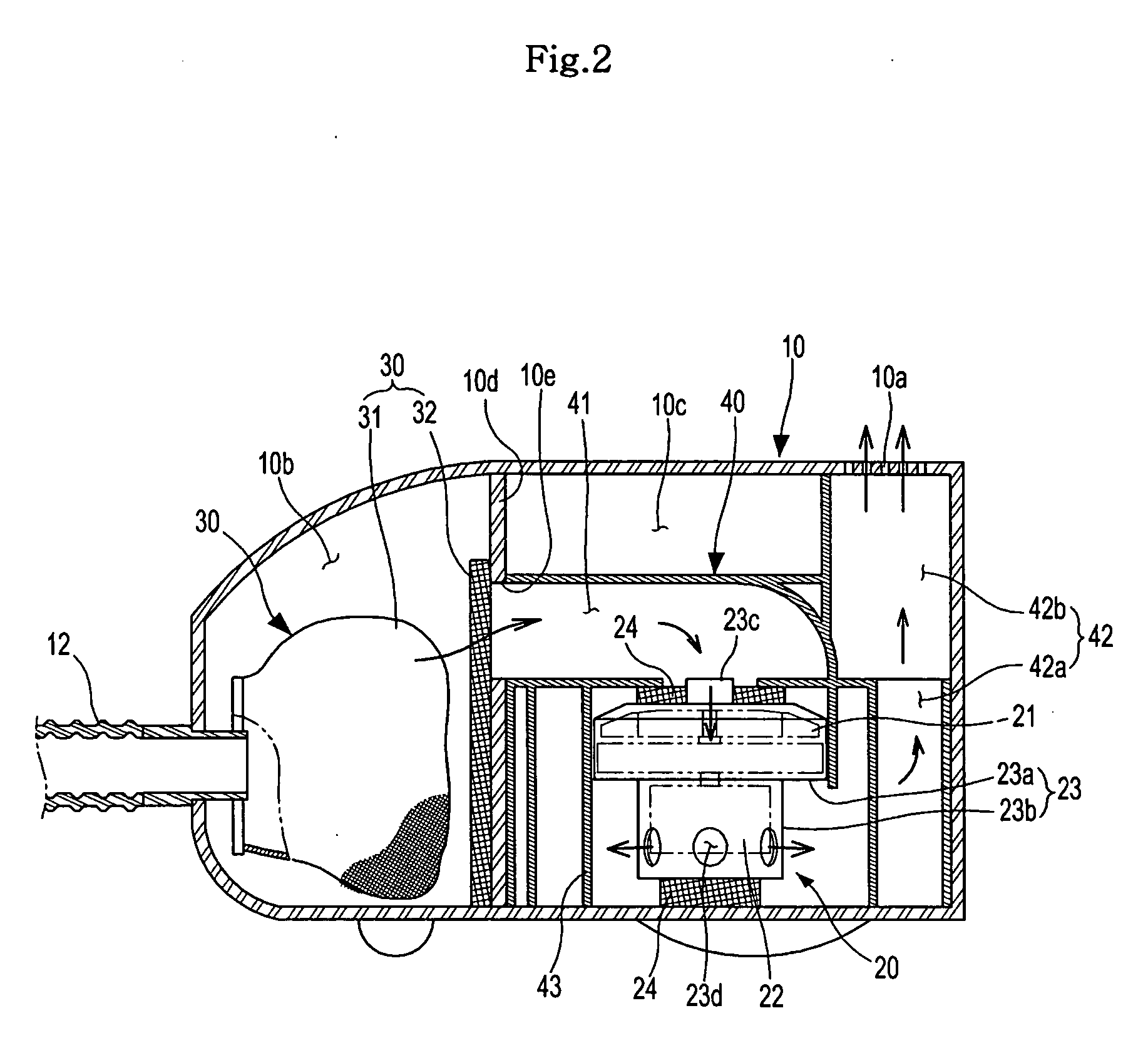
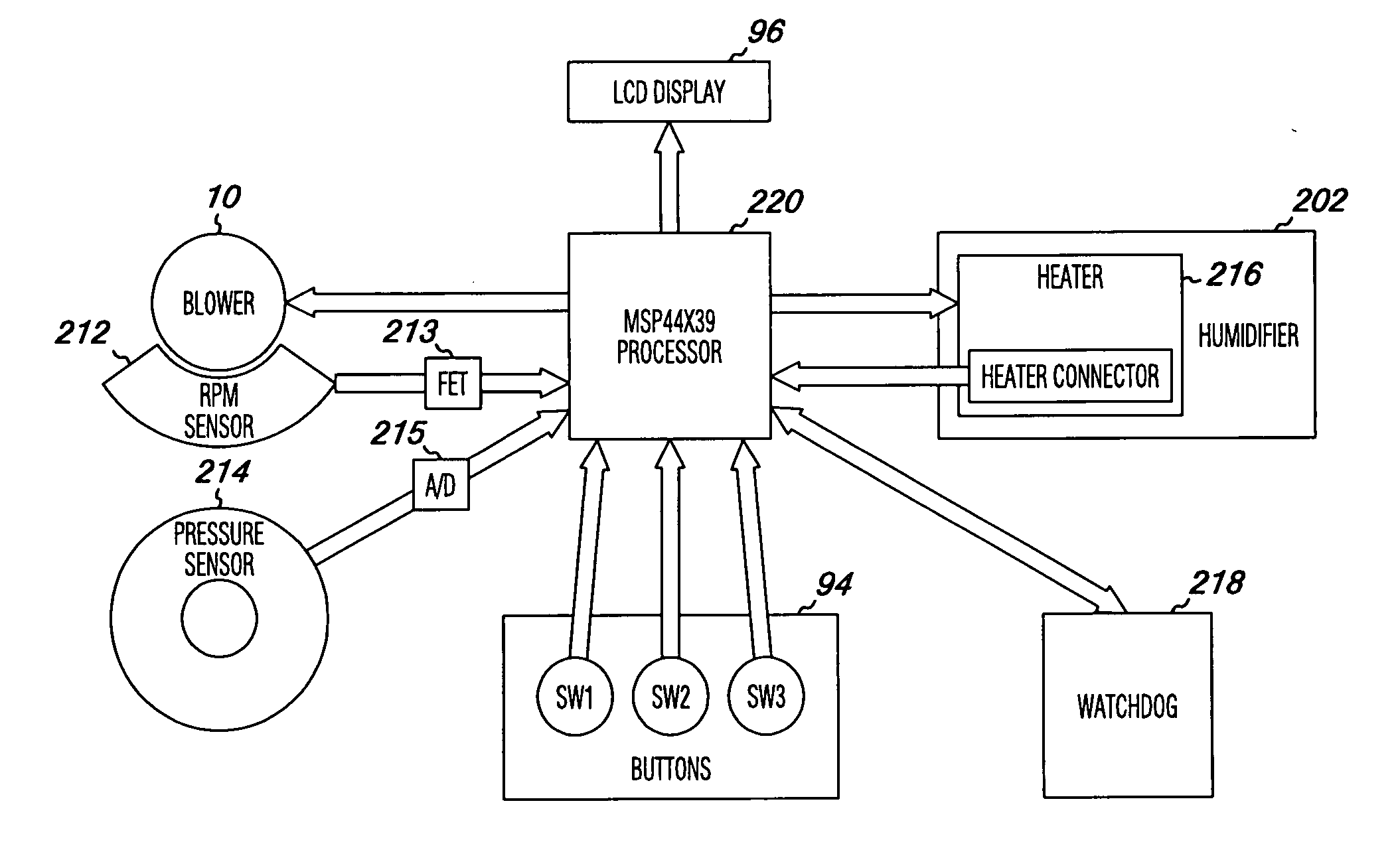
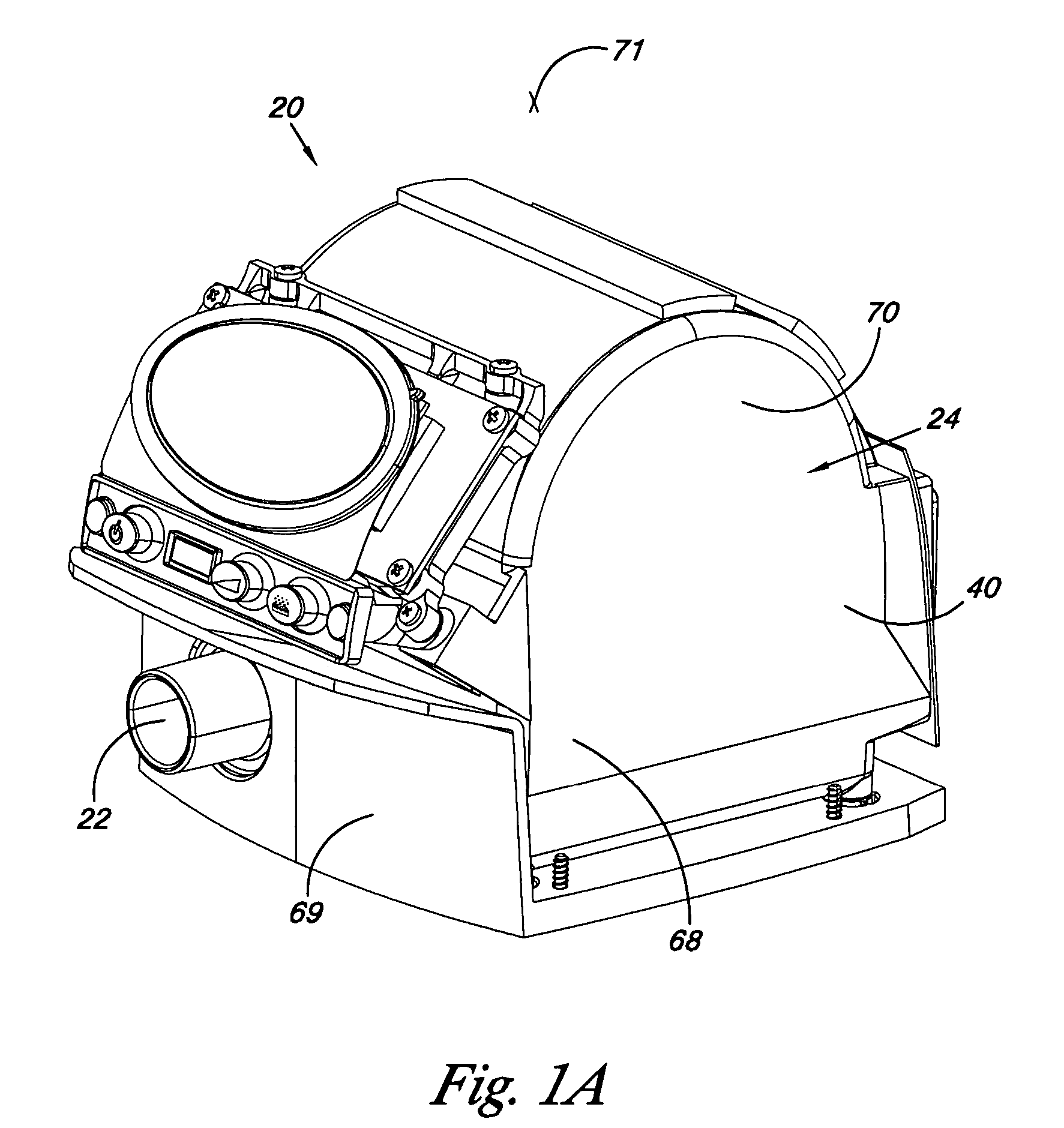
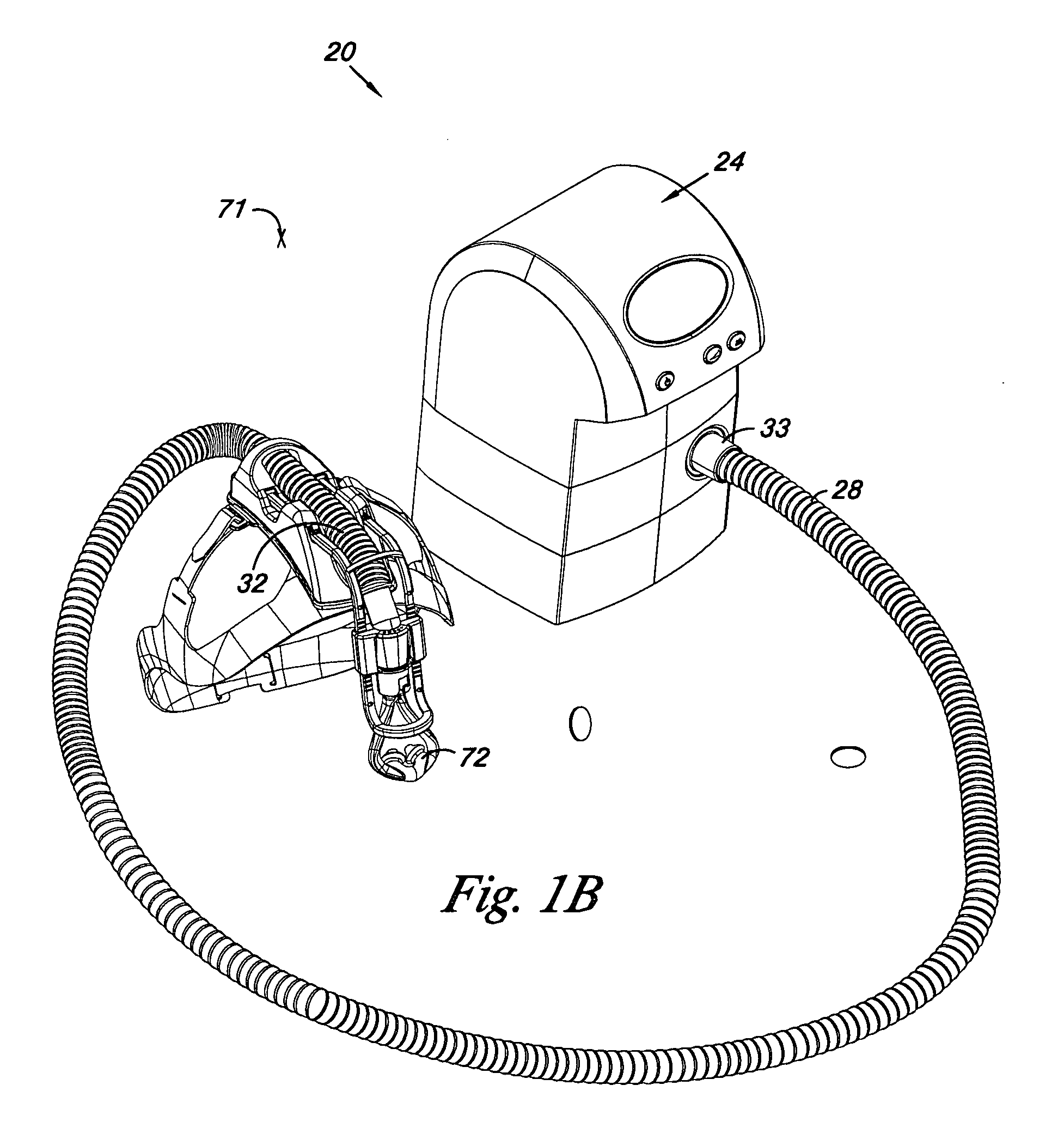
Apparatus for CPAP therapy
InactiveUS20060231097A1Reduce noise transmissionRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSleep apneaDuty cycle
The present invention provides an apparatus for the supply of air for the treatment of sleep apnea. The apparatus of the present invention includes a motor and a fan unit. The motor and fan unit are enclosed in an inner case of flexible foam plastics material. The inner case is configured to contain the motor and the fan unit, and the inner case 48 is generally biased against the motor and the fan unit. The inner case is, in turn, contained within an intermediate case made of rigid material. The intermediate case conforms to and is substantially filled by the inner case such that the inner case is generally biased against the intermediate case. Finally, the intermediate case is contained within an outer case of rigid material. The outer case surrounds the intermediate case. The outer case is generally set apart from the intermediate case so that there is a gap between the intermediate case and the outer case. The inner case, the intermediate case, and the outer case are all interconnected to form a blower housing in a manner that reduces the transmission of noise from the fan unit and from the motor to the external environment to the outer case. The apparatus may also include a humidifier in fluid communication with the volute outlet so as to impart humidity to compressed air or other gasses provided to the patient. The apparatus may include a microcontroller and may be powered by battery. The microcontroller may receive signals from a battery voltage sensor, the motor rate of rotation sensor, and a pressure sensor. The microprocessor may execute an algorithm directed to maintain a constant pressure over a range of battery voltages by regulation of the motor rate of rotation in response to the battery voltage signal and the pressure signal. The control algorithm in the microcontroller may also be arranged to adjust a duty cycle of a heater in the humidifier to adjust the level of humidification provided by the humidifier.
Owner:AEIOMED
Flexible heat sink
InactiveUS7399919B2Reduce shock vibrationReduce noise transmissionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringHeat sink
Provided is a flexible heat sink article comprising a base comprising a polymer and a plurality of polymeric protrusions extending away from the base, each protrusion having a major dimension and a minor dimension. The base comprises thermally conductive particles, and the protrusions comprise non-spherical thermally conductive particles substantially aligned in the direction of the major dimension within the protrusions. A thermal interface material may be provided contiguous with the base. Also provided is a flexible heat sink article comprising a base comprising a polymer and having a first surface and a second surface, a plurality of polymeric protrusions extending away from the first surface of the base, each protrusion having a major and a minor dimension, and a metallic layer contiguous with the second surface of the base, wherein the base and the protrusions comprise thermally conductive particles. Also provided is a method of making a flexible heat sink.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Isolated fuel delivery system
InactiveUS7591246B2Reduce noise transmissionHigh-frequency vibrationNutsLow pressure fuel injectionCylinder headExternal combustion engine
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Fuel injector isolation seat
ActiveUS20070175451A1Reduce noise transmissionHigh-frequency vibrationMachines/enginesSpecial fuel injection apparatusCylinder headAxial force
An isolation seat assembly for a fuel injector that is at least partially disposed within a stepped bore defined by a cylinder head, the stepped bore includes a land. The isolation seat assembly includes a cupped spring washer and an elastomeric ring member disposed between the cupped spring washer and the land. The isolation seat assembly operates to bias the fuel injector away from the land to substantially isolate the fuel injector from the head. The cupped spring washer and elastomeric ring member may be bonded to one another. Additionally, the isolation seat assembly may include a washer member between the elastomeric ring member and the land. The washer member operates to distribute axial forces from the fuel injector to the land. At least a portion of the washer member may be crimped into engagement with the cupped spring washer, thereby capturing the elastomeric ring member therein between.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Air duct for vehicle air conditioning and air conditioner for vehicle
ActiveUS20080032618A1Suppress generationReduce wind roarVehicle seatsAir-treating devicesEngineeringAir conditioning
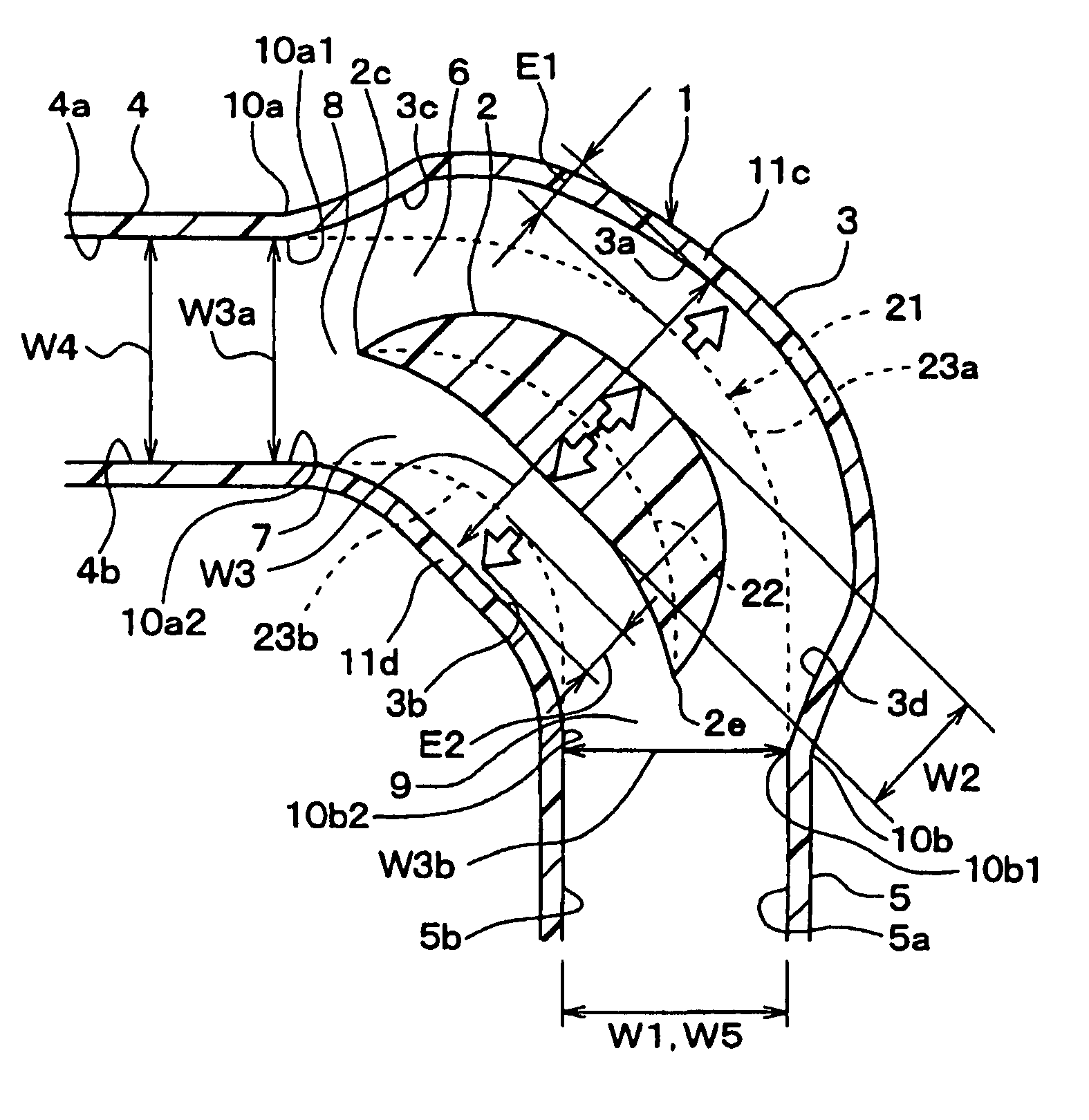
An air duct for vehicle air conditioning, includes a duct body defining a passage, and a passage dividing wall for dividing an interior of the duct body into a first passage and a second passage. In the air duct, the width of the duct body in an arrangement direction of the first and second passages in a bending section is larger than the width of the duct body in upstream-side and downstream side straight sections adjacent to the bending section, so as to increase a passage length difference (L1−L2) between the first passage and the second passage. Accordingly, the air duct has a structure capable of reducing the duct width while obtaining a desired passage length difference between the first passage and the second passage.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Exhaust muffler for internal combustion engines
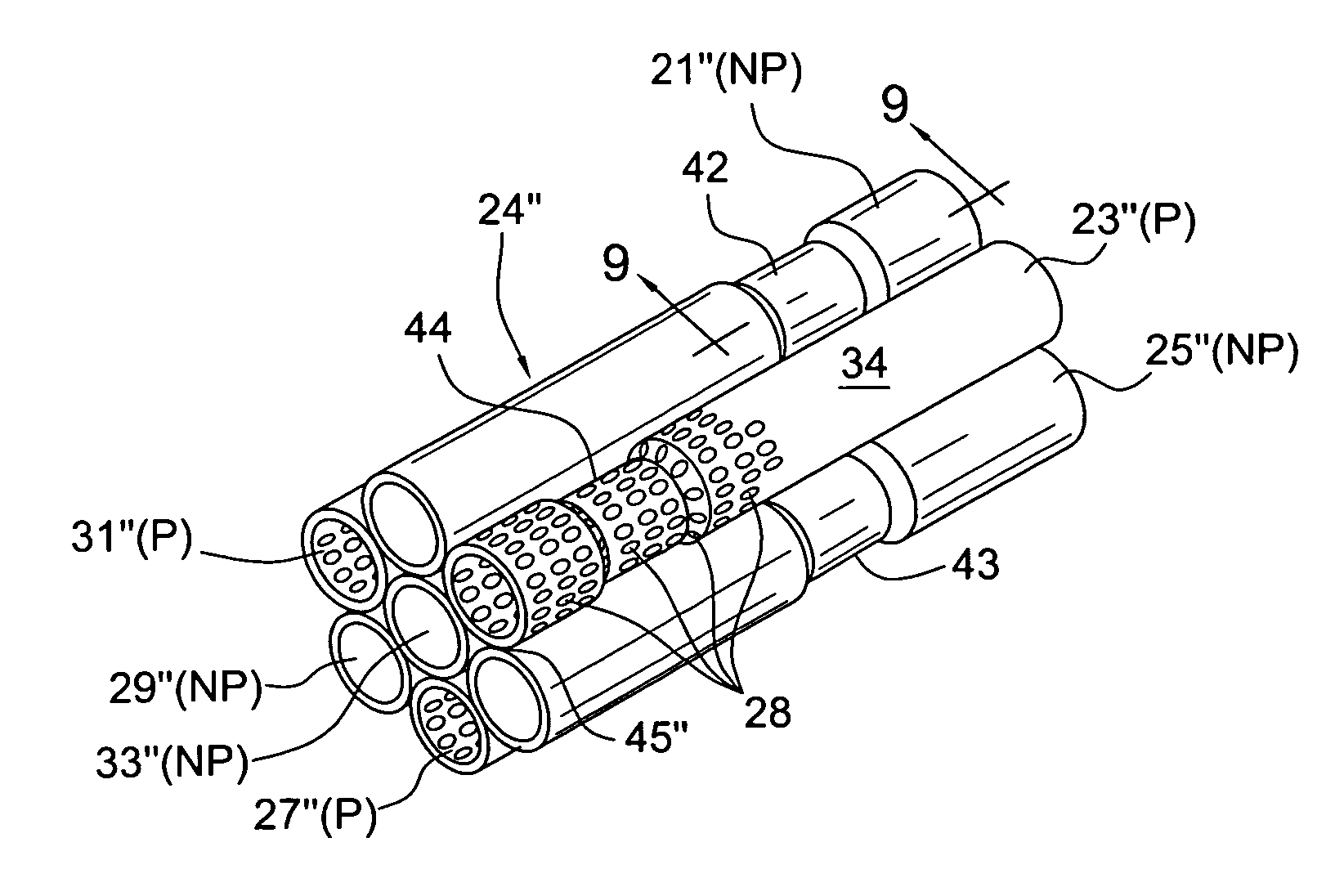
ActiveUS8439159B1Reduce noise transmissionReduce back pressureSilencing apparatusThermometers using physical/chemical changesCombustionEngineering
A new and improved muffler for use particularly with internal combustion engines which utilizes a tube assembly composed of a plurality of laterally nested perforated and non-perforated tubes in direct supporting lateral engagement with each other wherein the perforations provide direct communication of exhaust gases therebetween and wherein the tube assembly is supported at opposite ends by frustoconical entrance and exit collars, the larger ends of the collars being crimped or otherwise secured thereto providing a sealed connection.
Owner:BORLA DAVID
Composite Panel with Reinforced Recesses
InactiveUS20080128202A1Low noise transmissionGood strengthConstruction materialWallsElectrical and Electronics engineeringFace sheet
Owner:NASA
Molded and shaped acoustical insulating vehicle panel and method of making the same
ActiveUS20090085378A1Low costImproved and inexpensiveLayered productsVehicle sub-unit featuresVolumetric Mass DensityFibrous composites
A molded and shaped acoustical insulating vehicle panel having a dry-laid needled fibrous composite composed of a first portion of about 50 to 80 percent meltable binder fibers and about 20 to 50 percent stable fibers and having a second portion of about 20 to 50 percent meltable binder fibers and 50 to 80 percent of staple fibers. The meltable binder fibers are in a molded and resolidified state such that the resolidified binder fibers of the first portion form a substantially continuous, semi-impervious, densified skin integrally associated with and bonded to a surface of the first portion. The molded composite is in such a heat and pressure molded state that the composite has over a predominance of its area a density of from about 12 to 22 lbs. / cubic foot (192 to 352 kg / cubic meter) and the panel is sufficiently rigid as to be self-supporting.
Owner:L INT IP HLDG LLC
Operating space with a preferably thermally and acoustically insulating enclosure, and air louver arrangement which cooperates with said operating space
InactiveUS20160096424A1Effective regulationIncrease air circulationCoolant flow controlMachines/enginesWindow shutterEngineering
An operating space, particularly for a motor vehicle, which is bounded by an enclosure, wherewith more than half of the enclosure surface comprises a thermally and acoustically insulating lining material, and / or the enclosure surface is formed from insulating lining material, wherein the enclosure cooperates with an air intake louver system at an intake location that includes an air intake passage opening and at least one air intake louver wherein the intake louver(s) is adjustable between an open or passage position which allows passage of air, wherein the air-permeable flow cross section of the air intake opening is greater, and a closed or blocked position wherein the air-permeable flow cross section of the air intake opening is smaller, so that the amount of air per unit time which is admitted into the operating space through the air intake opening is less than when the at least one air intake louver is in the open position.
Owner:ROECHLING AUTOMOTIVE SE & CO KG
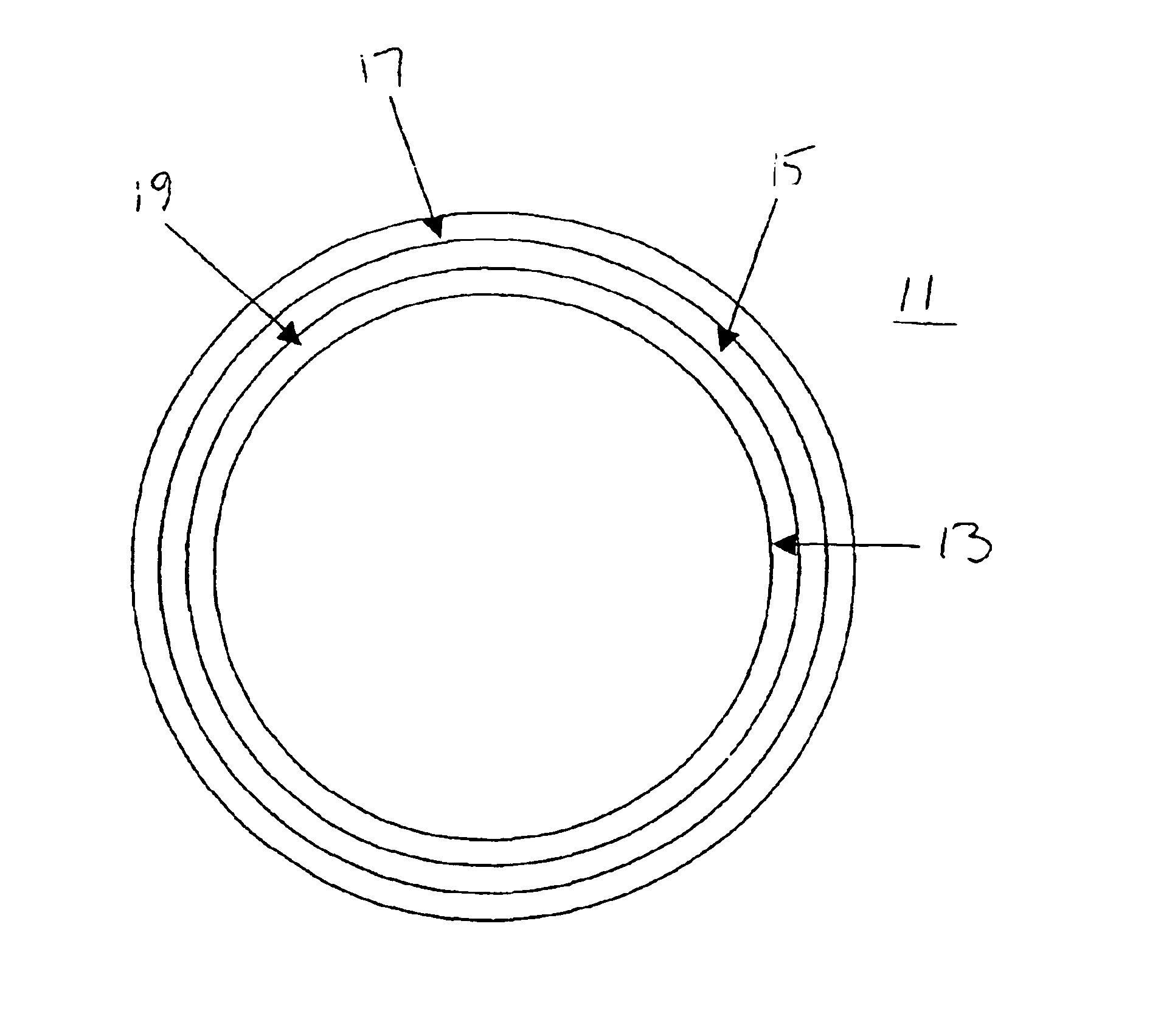
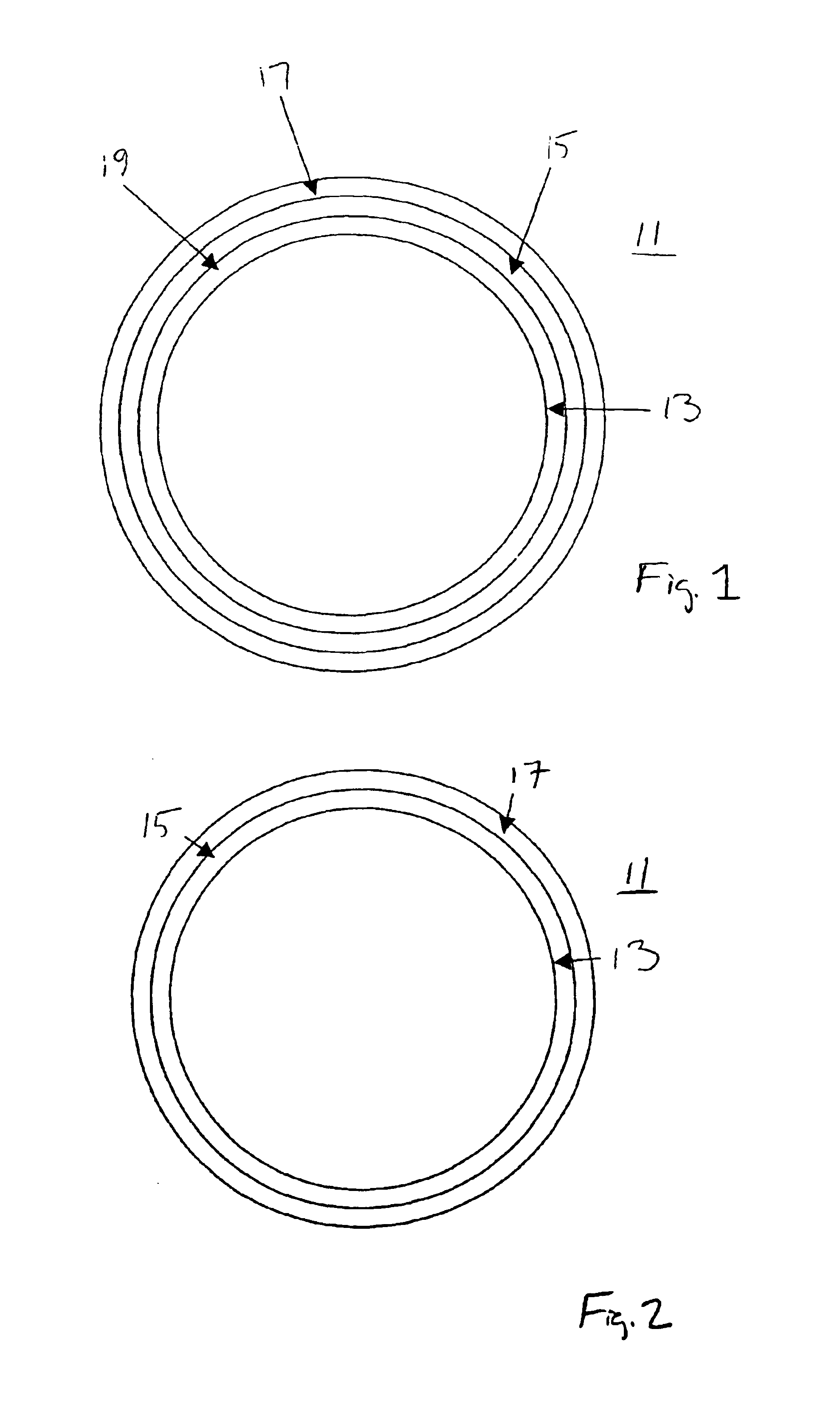
Double Broken Seal Ring
InactiveUS20100084751A1Reduce noise transmissionQuantity minimizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMoisture penetrationEngineering
The amount of signal propagation and moisture penetration and corresponding reliability problems due to moisture penetration degradation in an IC can be reduced by fabricating two seal rings with non-adjacent gaps. In one embodiment, the same effect can be achieved by fabricating a wide seal ring with a channel having offset ingress and egress portions. Either of these embodiments can also have grounded seal ring segments which further reduce signal propagation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Liquid flow proximity sensor for use in immersion lithography
InactiveUS7021119B2Quiet turbulenceReduce noise transmissionVolume/mass flow measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProximity sensorEngineering
An apparatus and method for precisely detecting very small distances between a measurement probe and a surface, and more particularly to a proximity sensor using a constant liquid flow and sensing a liquid mass flow rate within a bridge to detect very small distances. Within the apparatus the use of a flow restrictor and / or snubber made of porous material and / or a liquid mass flow rate controller enables detection of very small distances in the nanometer to sub-nanometer range. A further embodiment wherein a measurement channel of a proximity sensor is connected to multiple measurement branches.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
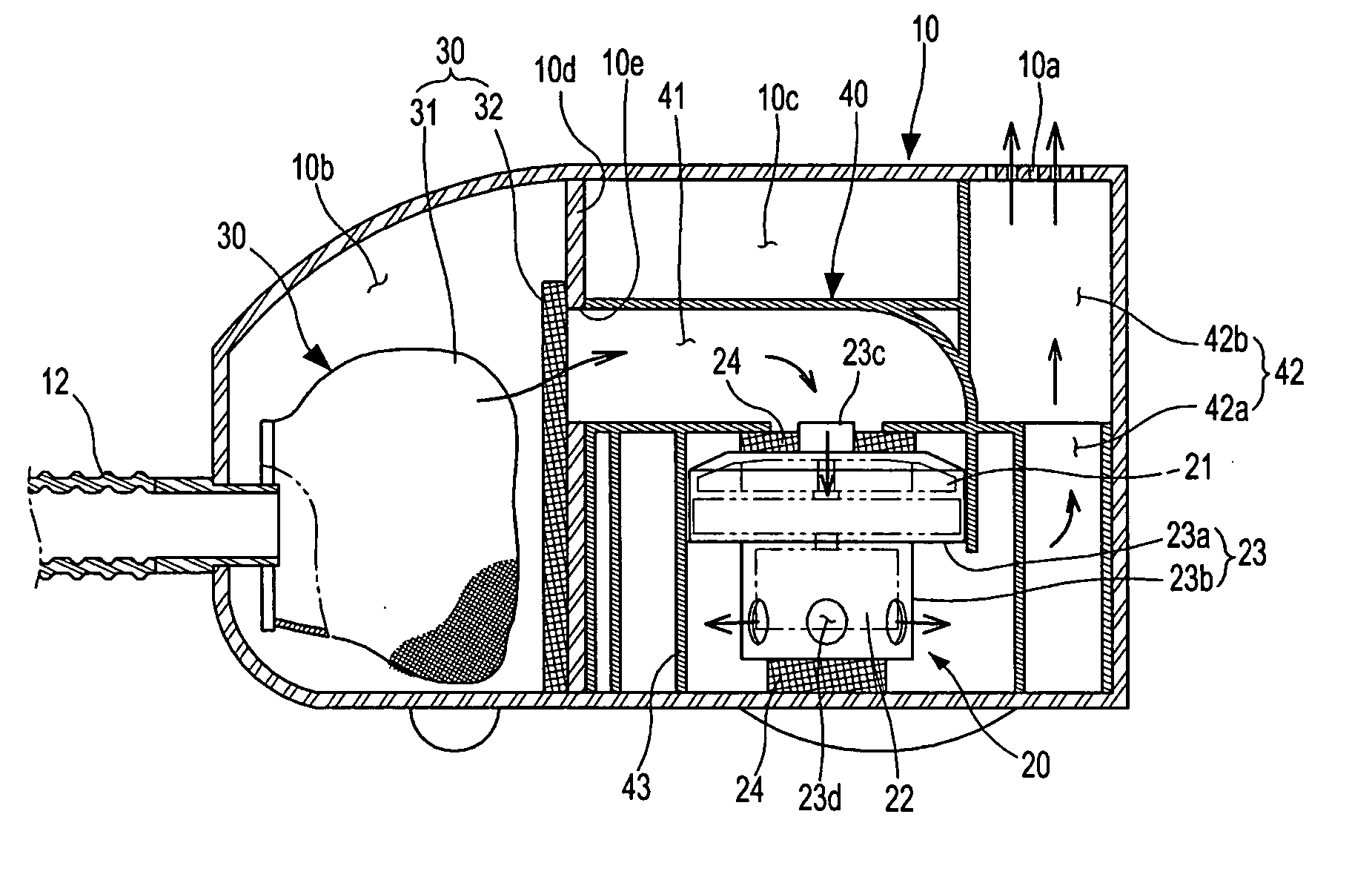
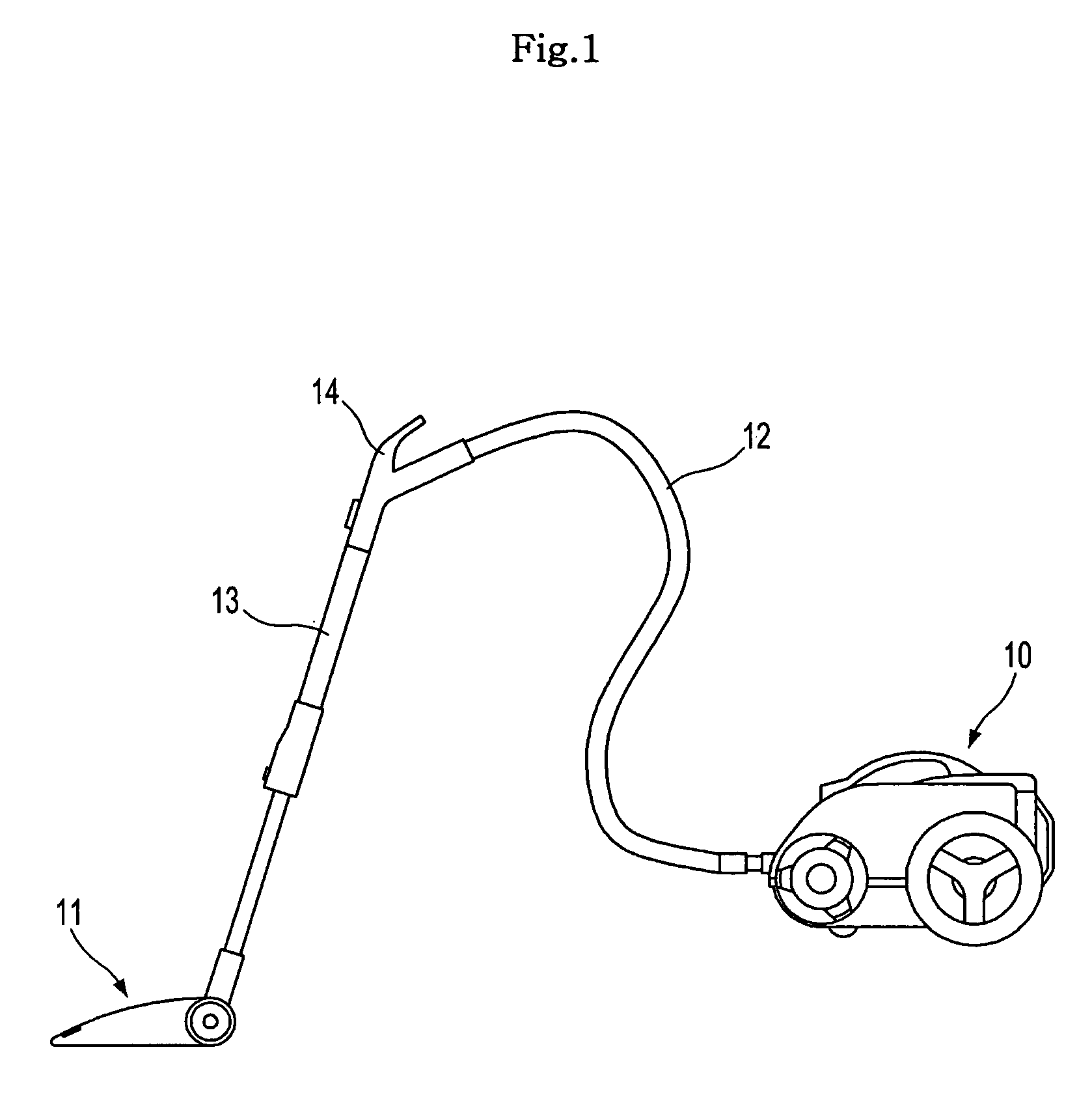
Vacuum cleaner
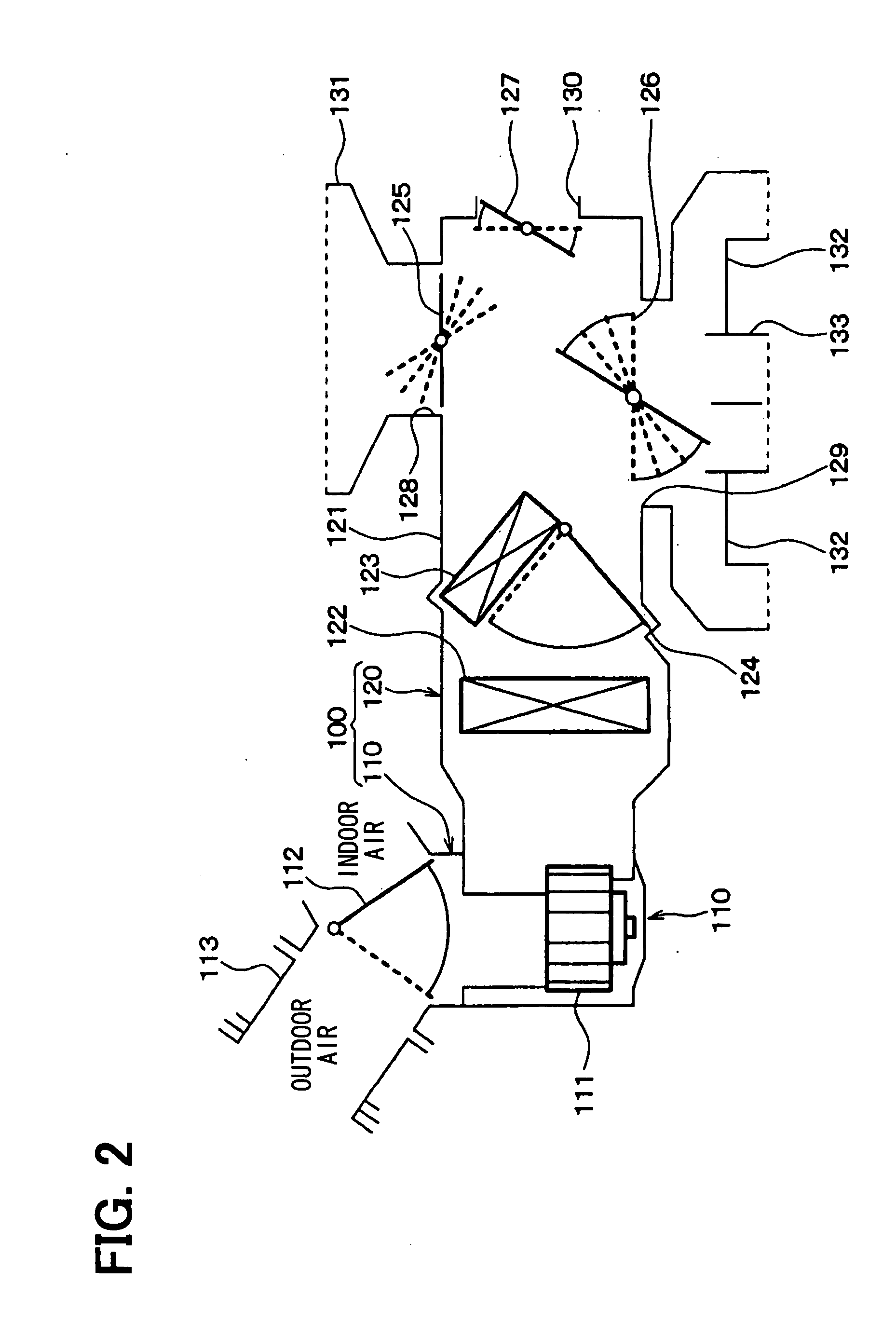
ActiveUS20060260091A1Reduce noise transmissionReduce running noiseBowling gamesCarpet cleanersAerospace engineeringSuction force
A vacuum cleaner is disclosed which comprises a motor chamber for mounting a motor assembly that, generates a suction force at a dust suction port, and a discharge port for guiding an air discharged from the motor chamber to the outside of a cleaner body, wherein the motor chamber comprises an air discharge opening which is in fluid communication with the discharge port; and a path extension member disposed between the motor assembly and the air discharge opening, of which edges are spaced apart from an inner wall of the motor chamber by a predetermined distance, respectively, to thereby form a detour path, and the air discharged from the motor assembly is guided in a circuitous manner by the path extension member so as to be passed through the detour path before reaching the air discharge opening. That assembly effectively reduces noise generated during operation of the motor assembly that is detectable outside of the cleaner body.
Owner:SAMSUNG GWANGJU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Insulation package and use thereof
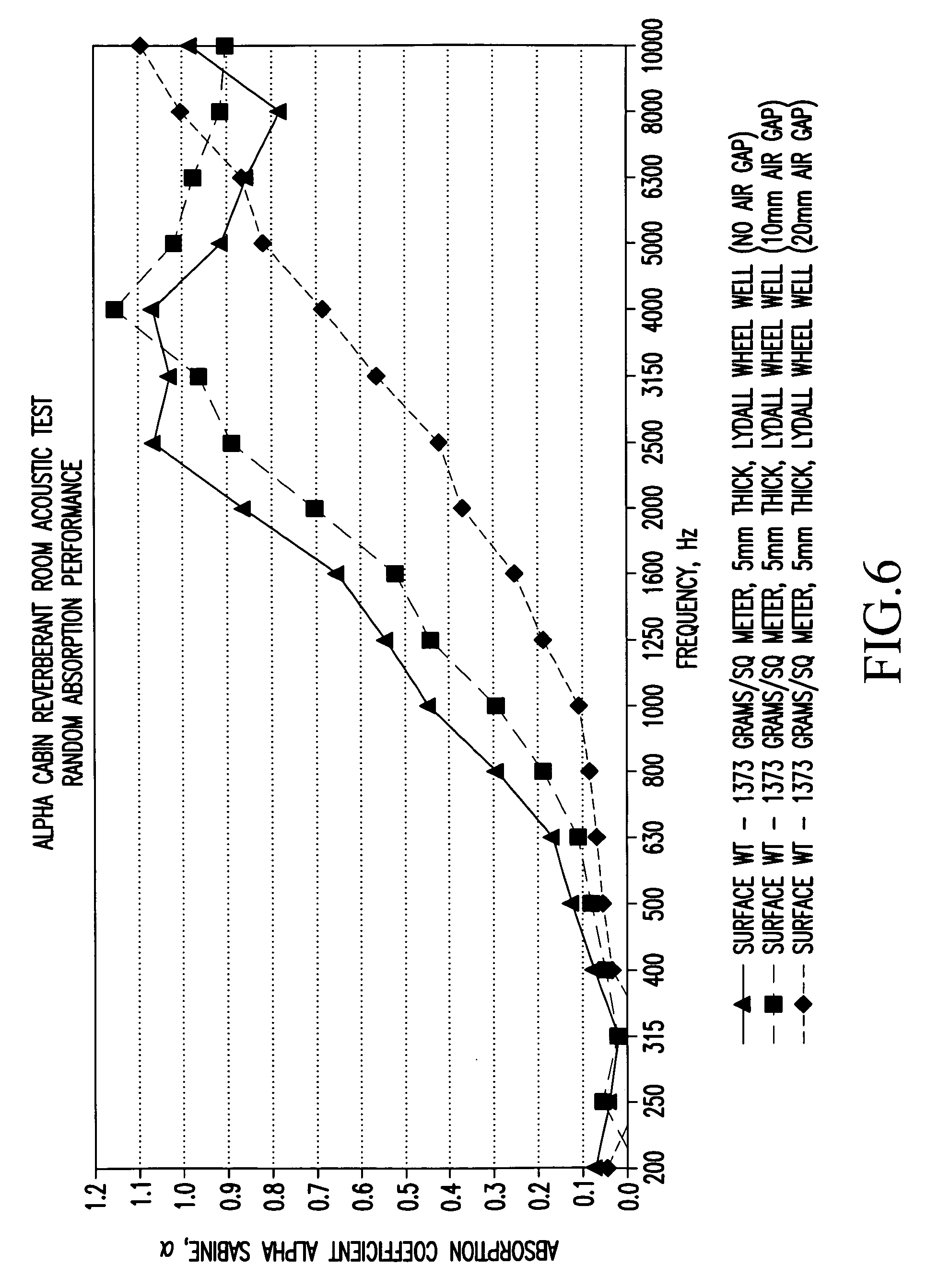
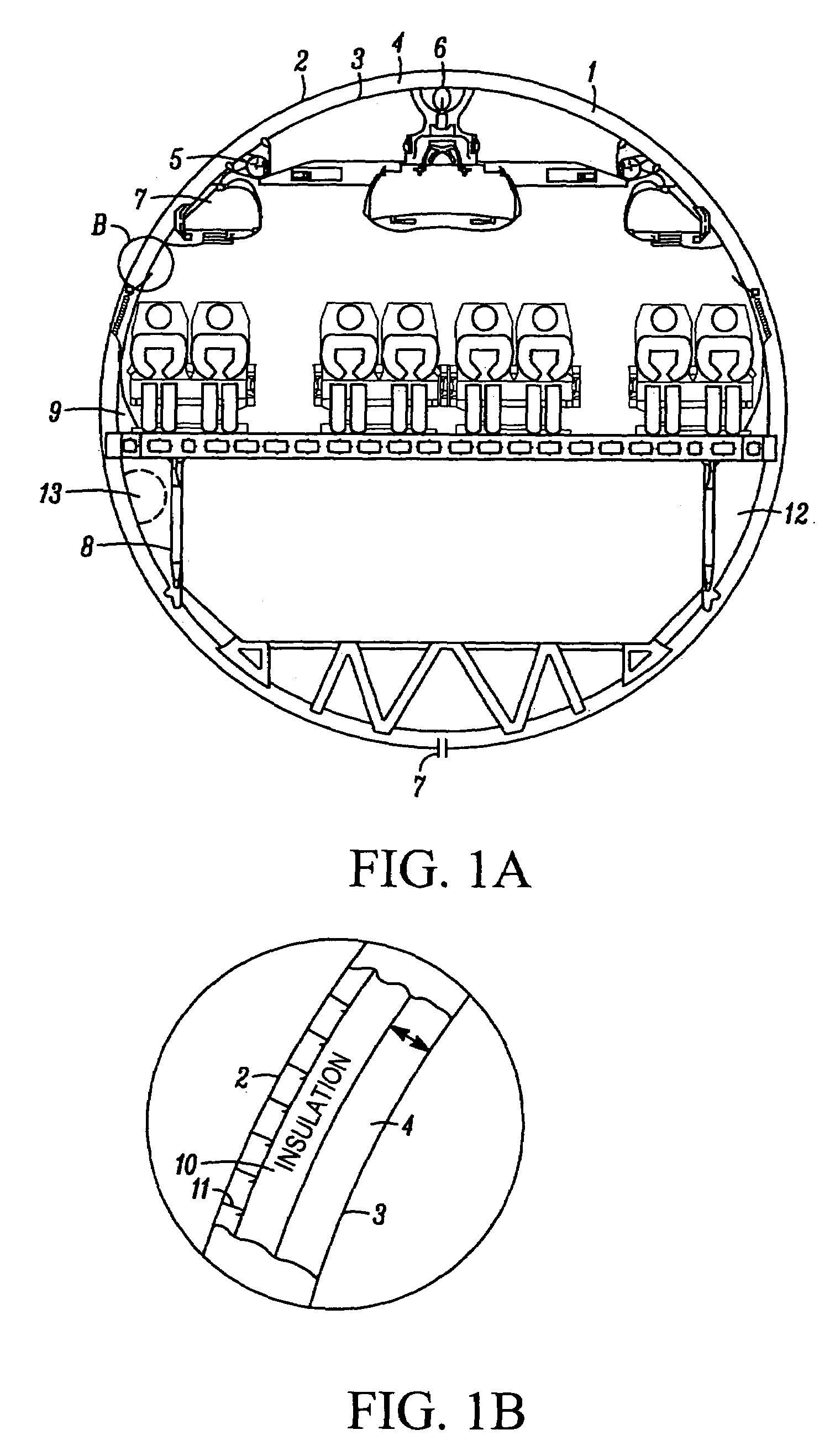
InactiveUS7108227B2Reduce transmission of heatReduce noise transmissionLayered productsFuselage insulationAmbient humidityDiffusion resistance
An insulation package to reduce the transmission of heat and / or noise between the outer skin and the cabin lining of an aircraft composed of an insulating material enclosed by an encapsulating membrane. The encapsulating material has a vapor diffusion resistance (sd value) at least partially dependent on the ambient humidity, and for a gradient of relative humidity across the encapsulating membrane of 3% to 50% it has a vapor diffusion resistance (sd value) of at least 0.8 m and for a gradient of relative humidity across the encapsulating membrane of 50% to 93% it has a maximum vapor diffusion resistance (sd value) of 0.3 m.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Sound jacket for noise reduction in refrigeration apparatus
An insulating jacket for refrigeration system component comprising a closed cell insulation layer comprising an inner and outer surface, an open cell foam layer comprising an inner and outer surface, the inner surface in contact with the outer surface of the closed cell insulation layer, and a sound barrier layer comprising an inner surface in contact with the outer surface of the open cell foam layer.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Removable in-floor storage device
ActiveUS8231164B2Reduce noise transmissionVehicle seatsPassenger spaceEngineeringMechanical engineering
A removable in-floor storage device for a vehicle floorpan well, including a lid assembly have a frame mounted on a floorpan surface about the periphery of the floorpan well so as to define a frame opening, and a lid pivotally mounted on the frame to move from a closed position to an open position allowing access to the frame opening. The storage device further includes a removable storage bin adapted to be received within the frame opening and supported within the frame opening by the frame, to thereby define a storage chamber within the vehicle generally beneath the floorpan surface.
Owner:FCA US
Elevator Cab Ceiling with Dissipative Ventilation Channel
InactiveUS20080190711A1Improve qualityReduce noise transmissionSound producing devicesBuilding liftsResistive elementEngineering
An elevator cab ceiling (22) includes an upper ceiling panel (26), a lower ceiling panel (28), and a ventilation channel (30) extending between the upper ceiling panel (26) and the lower ceiling panel (28). The ventilation channel (30) extends at an oblique angle relative to the upper ceiling panel (26) and separates space between the upper (26) and lower (28) ceiling panels into an upper cavity (32) and a lower cavity (34). A plurality of partitions (36) are formed within at least one of the upper (32) or lower (34) cavities. In one example, an acoustically resistive element (42) extends at least partially along a portion of the ventilation channel (30). The plurality of partitions (36) and the acoustically resistive element (42) cooperate to reduce noise levels transmitted into an elevator cab (10) via the ventilation channel (30).
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Wood flooring composed of WPL, base and soundproof layer
InactiveUS7473457B2Improved surface strength and natural textureImprove sound insulationCovering/liningsLighting and heating apparatusWood veneerHigh density
Disclosed herein is a back-grooved laminate wood flooring in which a wood veneer of high pressure resin impregnation laminate (WPL) is laminated on a base selected from a vinyl chloride (PVC) resin layer, on oriented strand board (OSB), a high-density fiberboard (HDF) and a waterproof plywood. More specifically, the back-grooved laminate wood flooring comprises a WPL (20), an adhesive layer (40) and a base (10) (a polyvinyl chloride resin layer, OSB, HDF or waterproof plywood) wherein the WPL (20) includes a base-reinforcing layer (24), a natural veneer layer (23), a resin-impregnated overlay layer (22) and a surface UV coating layer (21) layered in this order from the bottom. The back-grooved laminate wood flooring further exhibits excellent soundproofing performance.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Air duct for vehicle air conditioning and air conditioner for vehicle
ActiveUS8146706B2Reduce noise transmissionReduce noiseVehicle seatsAir-treating devicesEngineeringAir conditioning
An air duct for vehicle air conditioning, includes a duct body defining a passage, and a passage dividing wall for dividing an interior of the duct body into a first passage and a second passage. In the air duct, the width of the duct body in an arrangement direction of the first and second passages in a bending section is larger than the width of the duct body in upstream-side and downstream side straight sections adjacent to the bending section, so as to increase a passage length difference (L1−L2) between the first passage and the second passage. Accordingly, the air duct has a structure capable of reducing the duct width while obtaining a desired passage length difference between the first passage and the second passage.
Owner:DENSO CORP
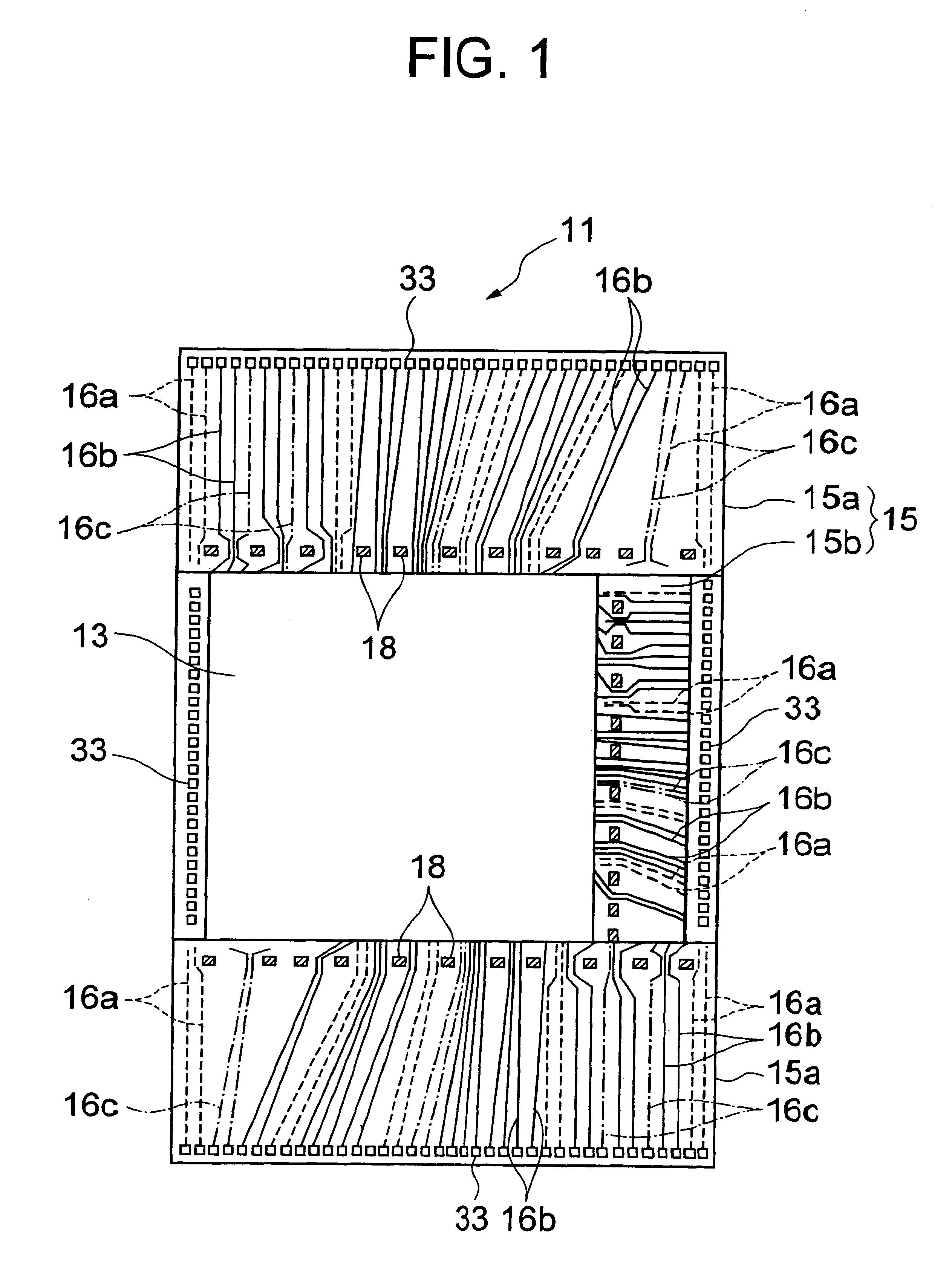
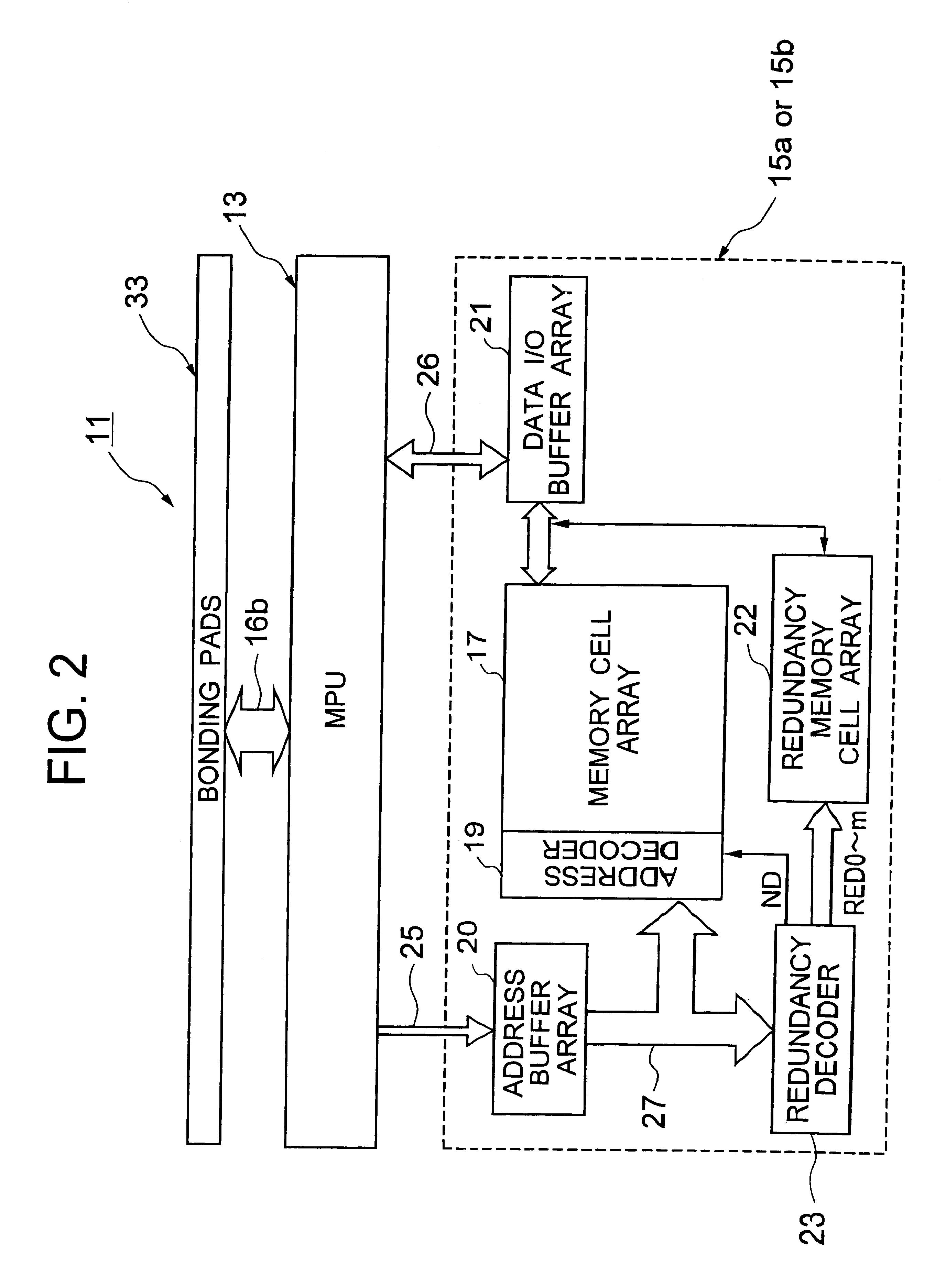
Semiconductor integrated circuit having a MPU and a DRAM cache memory
InactiveUS6378118B1Reduce noise transmissionPotential fluctuationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDram cacheComputer science
A large scale semiconductor integrated circuit, implemented on a chip, includes an MPU and a DRAM cache memory including a plurality of DRAM macro blocks located around the MPU. The DRAM macro block has a redundancy function for which a plurality of fuses are disposed for cut-out by laser beams. The lower metallic layers implement source lines for power and ground to the DRAM macro blocks, whereas a topmost metallic layer implements source lines for the MPU. The topmost metallic layer circumvents areas of the chip where portions of a metallic layer constituting fuses for implementing the redundancy function are located.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
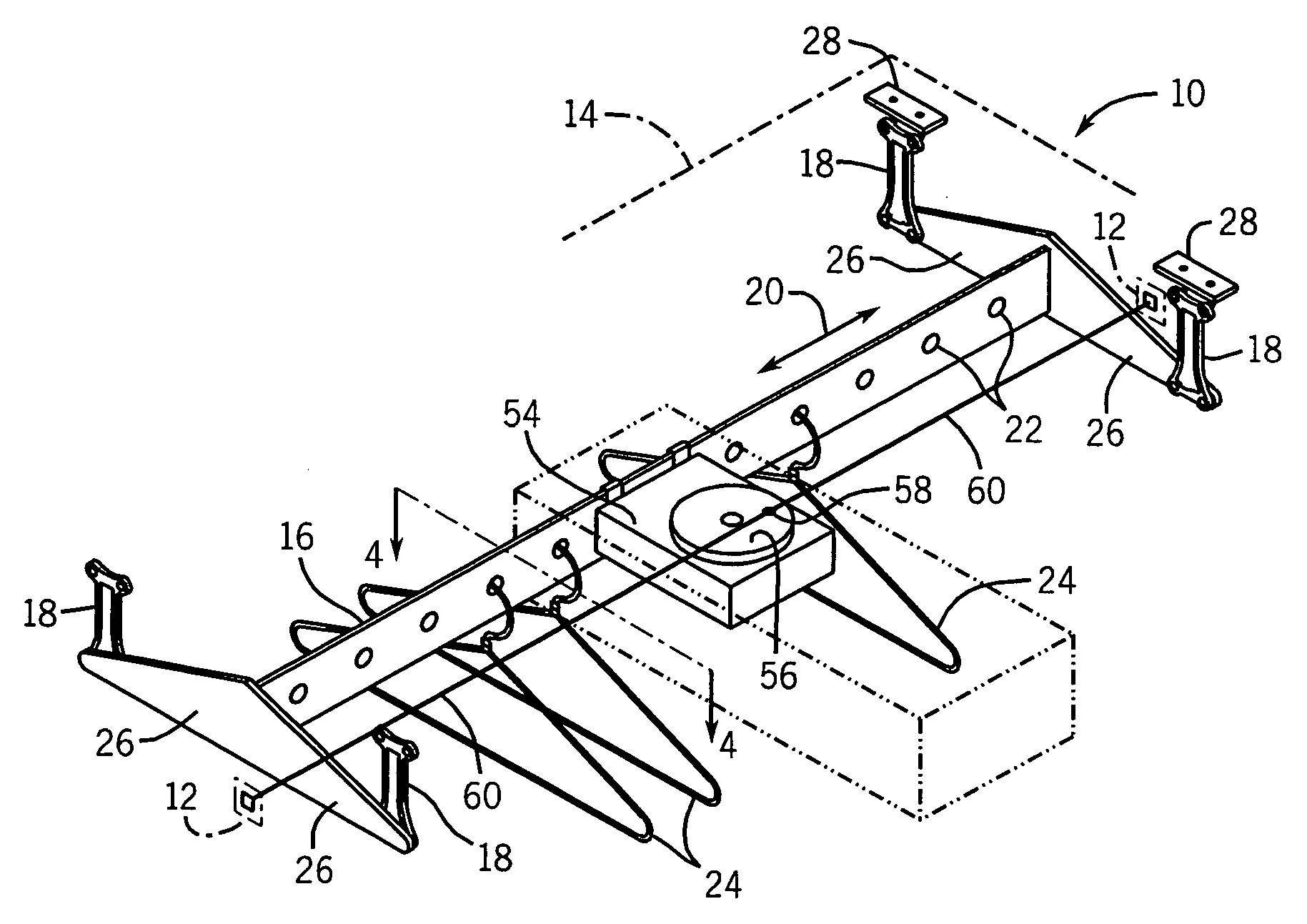
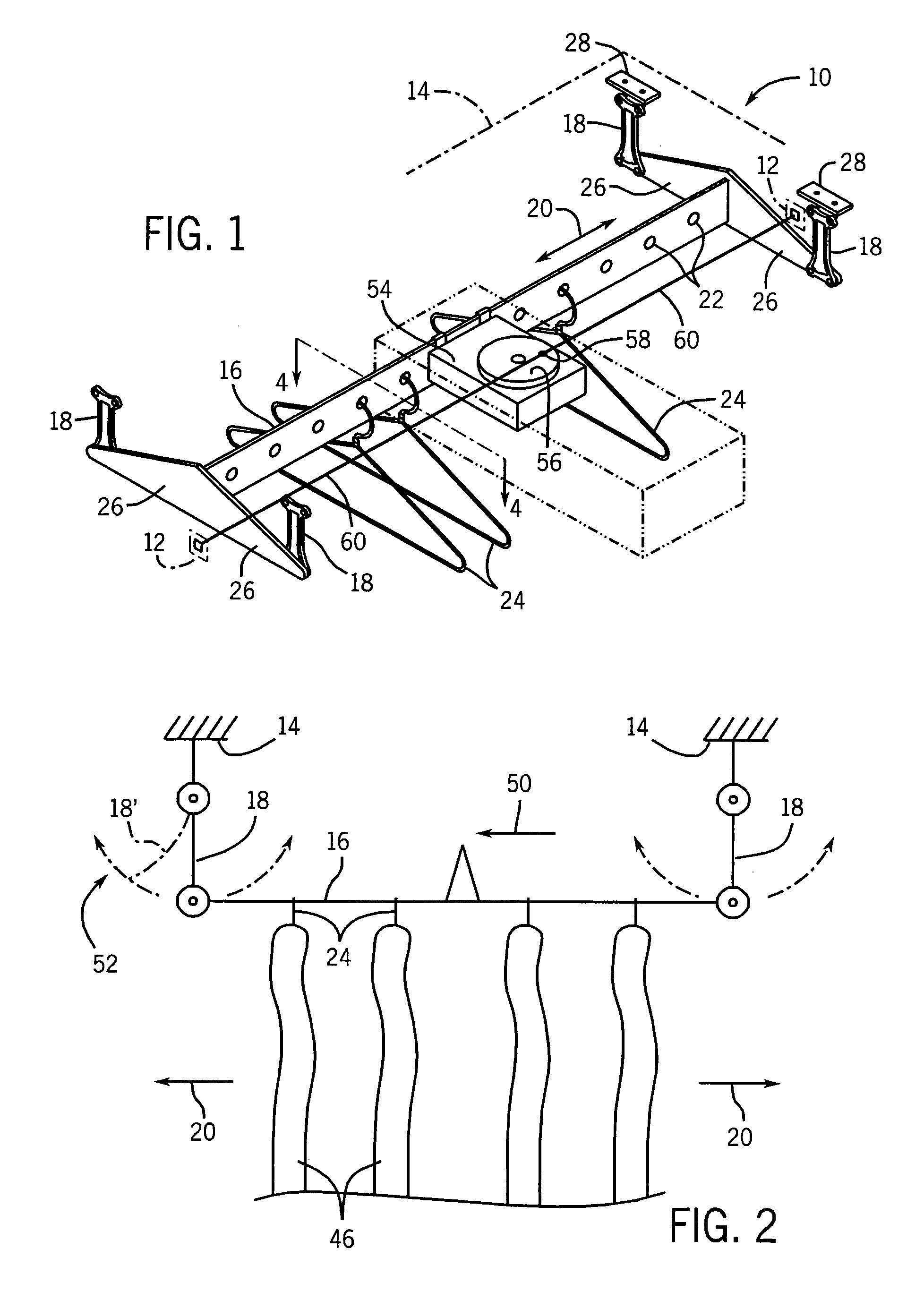
Agitator for removing wrinkles from clothing
An agitator mechanism for a clothes finishing cabinet provides a pendulum mounted hanger bar that may reciprocate under the application of a periodic force by an actuator without rigid connection between the cabinet housing and the hanger bar. Quiet operation is obtained by mounting an actuator motor directly on the hanger bar to be isolated by sound absorbing hanger support materials.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Nuclear spin tomographic radiography equipment with damping plate
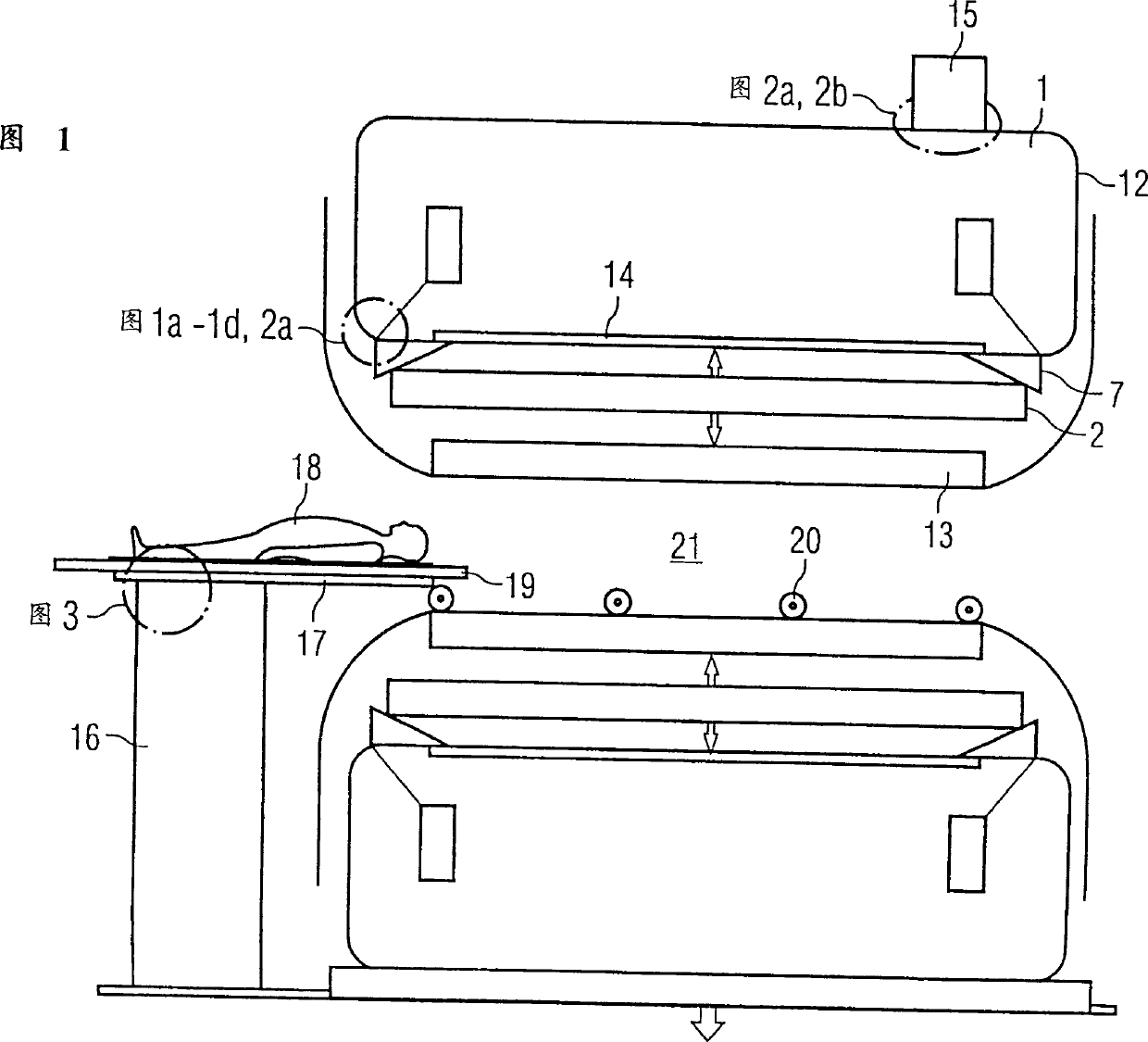
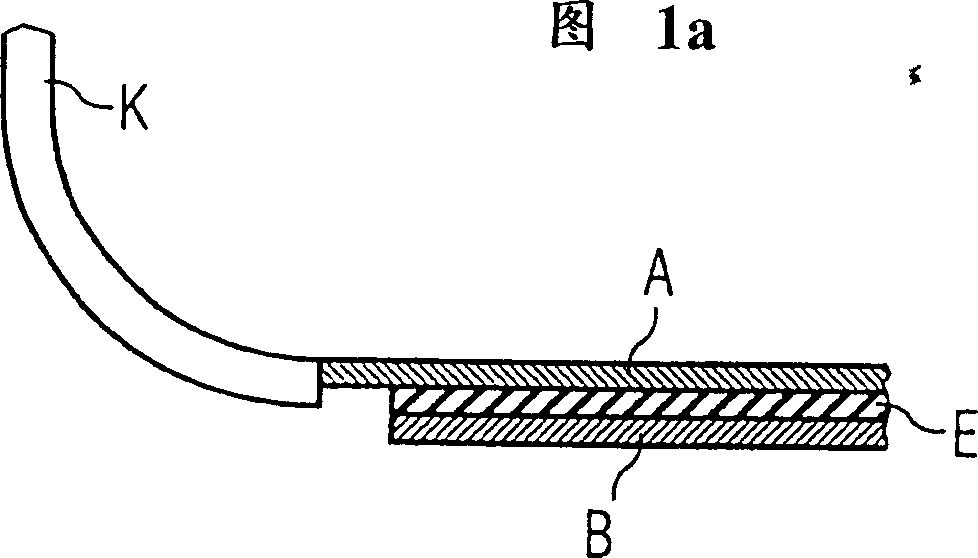
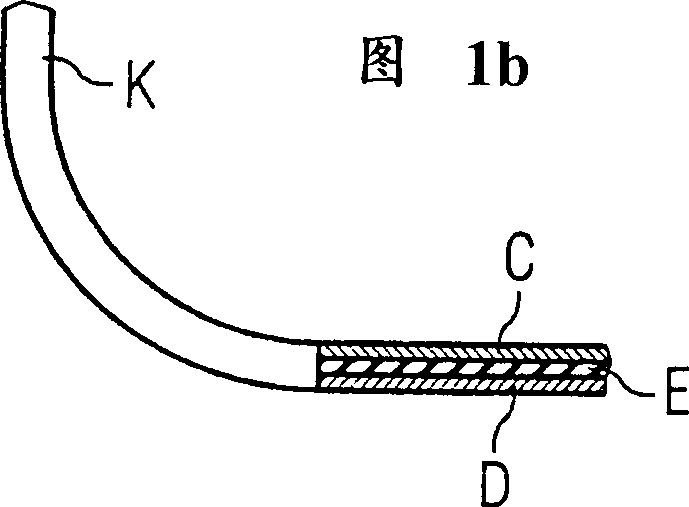
InactiveCN1399141AQuality is not affectedAvoid damageElectromagnets without armaturesTransformers/inductances noise dampingSpinsPatient diagnosis
The invention relates to a nuclear spin tomographic radiography method (synonym: magnetic resonance imaging method, that is MRT) which is used for patient diagnosis in medicine. The invention especially relates to a nuclear spin tomographic radiography device to reduce vibration of components which constitute a magnetic resonance imaging equipment and reduce propagating paths of noise. This magnetic resonance imaging equipment includes a static magnetic field magnet (1), enclosed by a magnet container (12) for enclosing and bordering an inner space (21) and an inclined magnetic field coil system (2) disposed in this inner space (21). Silencing laminated plate structures (A-E-B, C-E-D) is provided on the inside surface (14) of the magnet container (12) for bordering this inner space (21). Consequently, acoustic vibrations, generated when the inclined magnetic coil system (2) is switched, are absorbed.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Soundproofing material
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
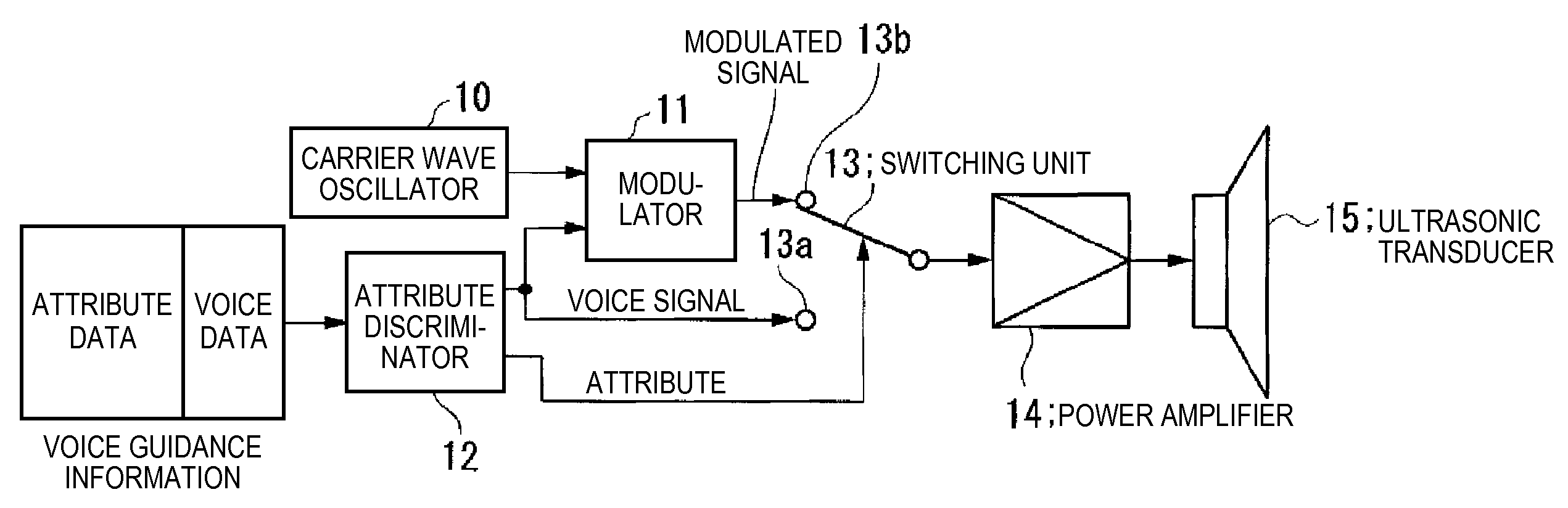
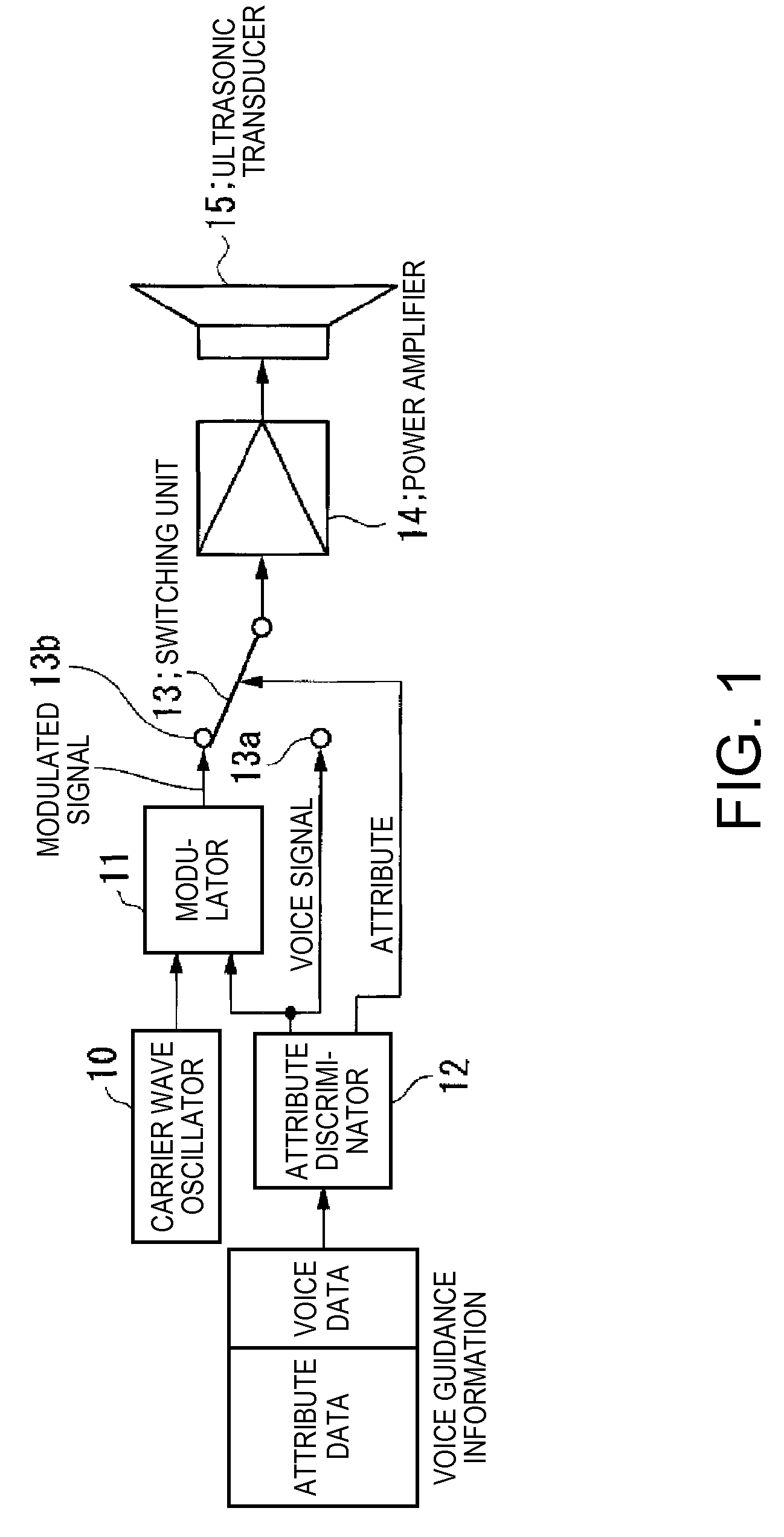
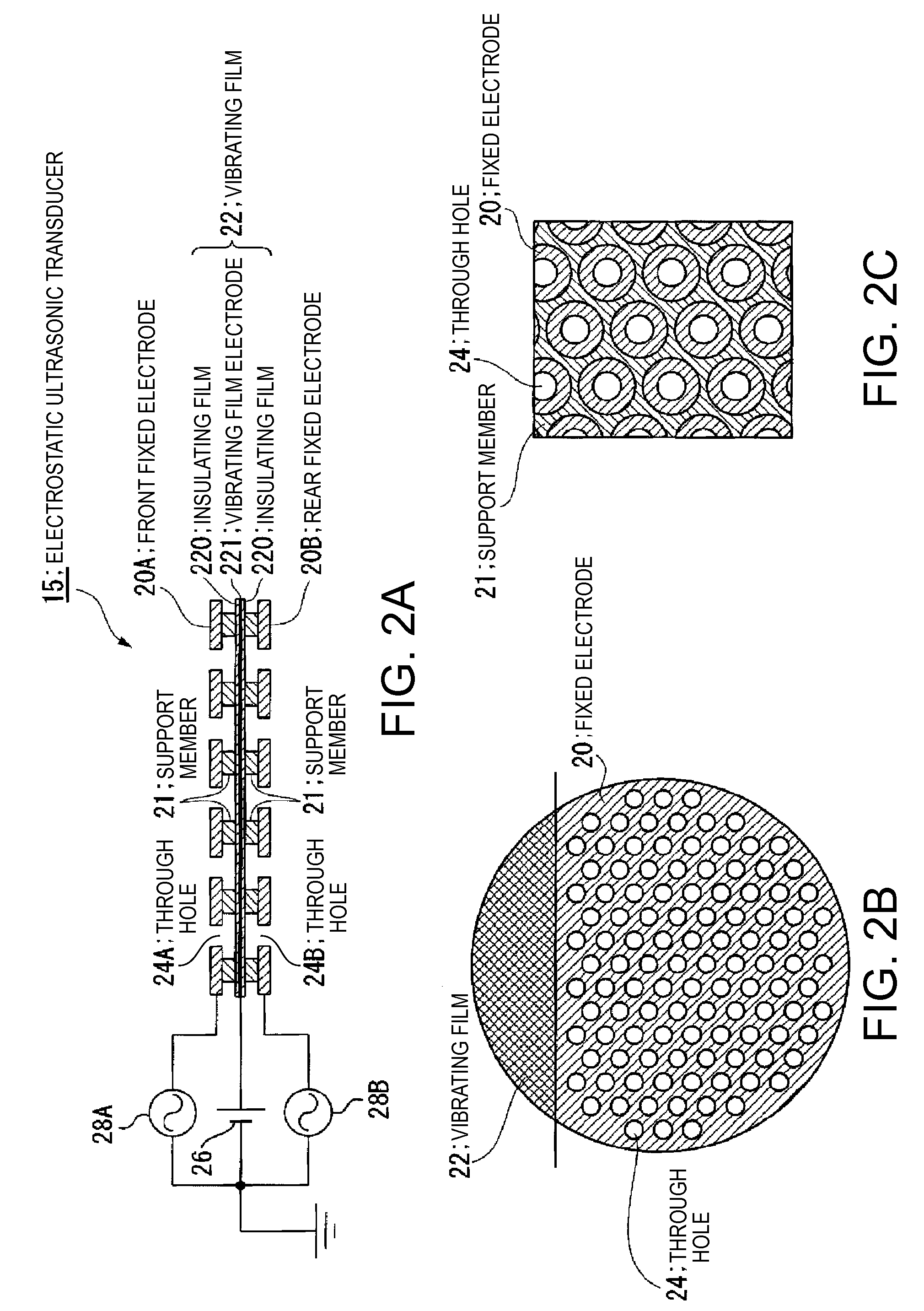
Guiding device and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS20070217616A1Low directivity soundImprove directivityNear-field transmissionSubstation/switching arrangement detailsEmbedded system
A guiding device controls the directivity of a sound that is reproduced from a speaker in accordance with an attribute of contents.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com