Method and device for predicting a rechargeable battery's lifetime
a rechargeable battery and lifetime technology, applied in the field of methods and devices for predicting the can solve problems such as the end of batteries, and achieve the effect of precise prediction of the end of life of rechargeable batteries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
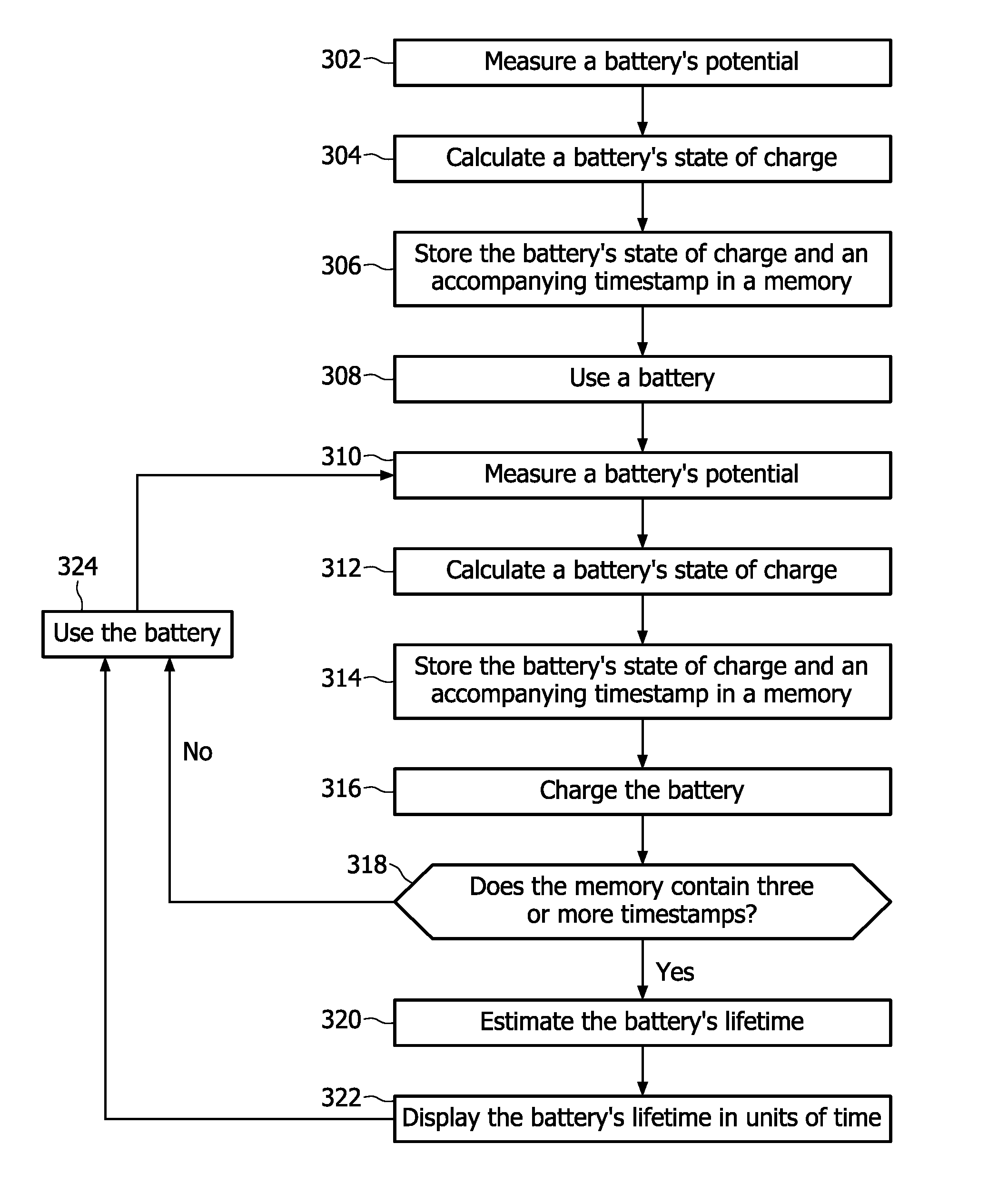
[0039]In a second embodiment according to the invention, the rate of decay for the battery's state of charge is monitored in order to estimate a battery's remaining lifetime. FIG. 3 depicts a flowchart which schematically explains this embodiment. At step 302 the battery's voltage is measured before using the battery employing a voltmeter known per se. During step 302 the battery is operating at substantially small drain currents hence the measured battery's voltage corresponds to a battery's so called equilibrium voltage value which is usually referred to as a battery's EMF. Step 304 contains the determination of a battery's state of charge prior to using the battery on the basis of the battery's voltage measured during step 302 and by employing a look-up table that connects the battery's voltage to the battery's state of charge. Step 306 comprises storing a numerical representation for the battery's maximum capacity and an accompanying timestamp in a memory. Step 308 contains usin...
third embodiment
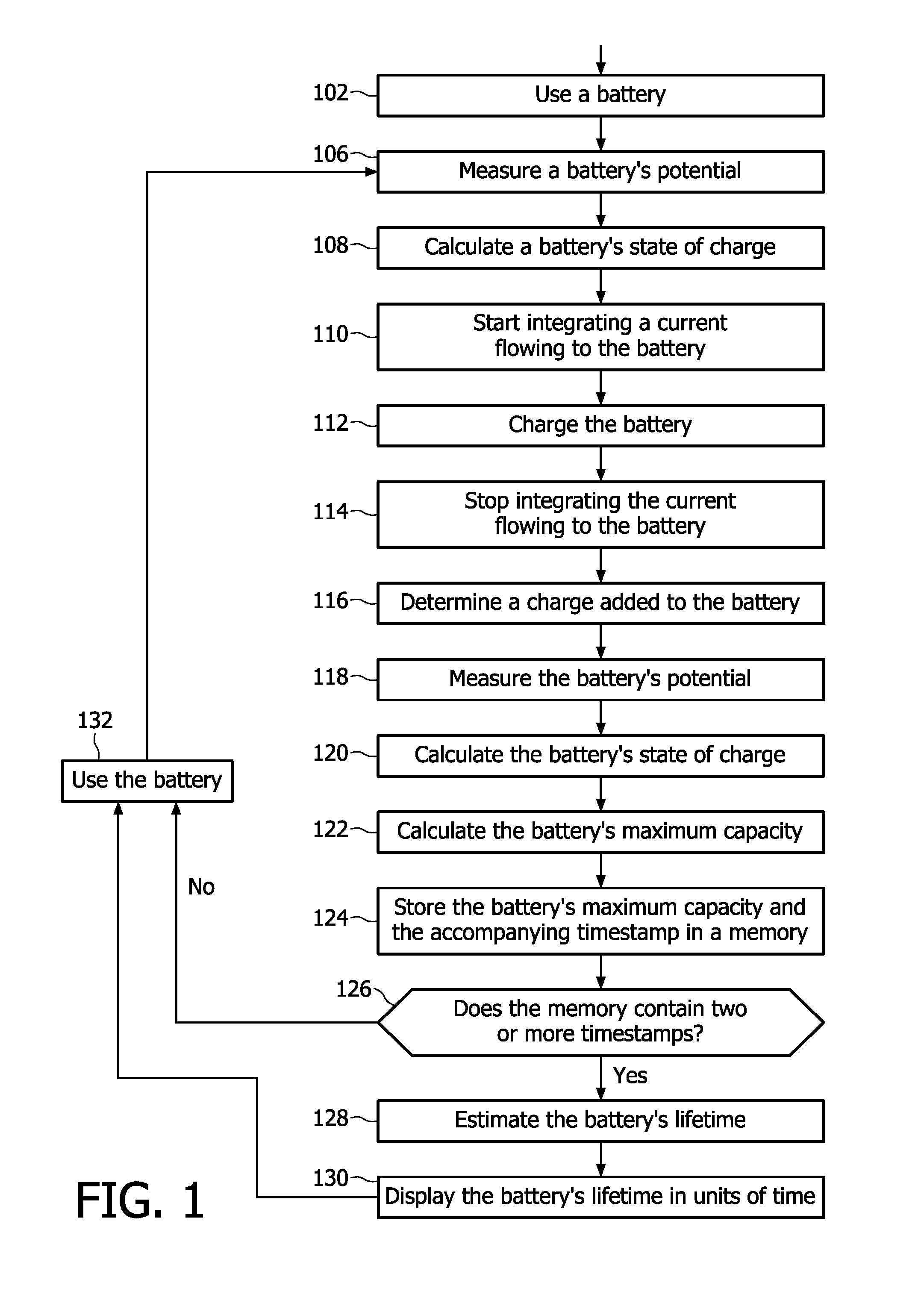
[0044]In a third embodiment according to the invention, time spans between consecutive points of time at which a battery's state of charge decreases from a predetermined maximum level to a predetermined minimum are monitored in order to estimate a battery's remaining lifetime. FIG. 6 depicts a flowchart which schematically explains this embodiment. Step 602 contains using a battery prior to a first instance of charging the battery. At step 604 the battery's state of charge attains the predefined minimum level at which charging is required. Step 606 comprises storing a numerical representation for an accompanying timestamp in a memory. Step 608 comprises charging the battery to the predefined maximum level using a charger known per se. At step 610 the contents of the memory are retrieved employing methods known per se. In case the memory contains three or more data time stamps, a battery's remaining lifetime is estimated at step 612 through a method explained below.
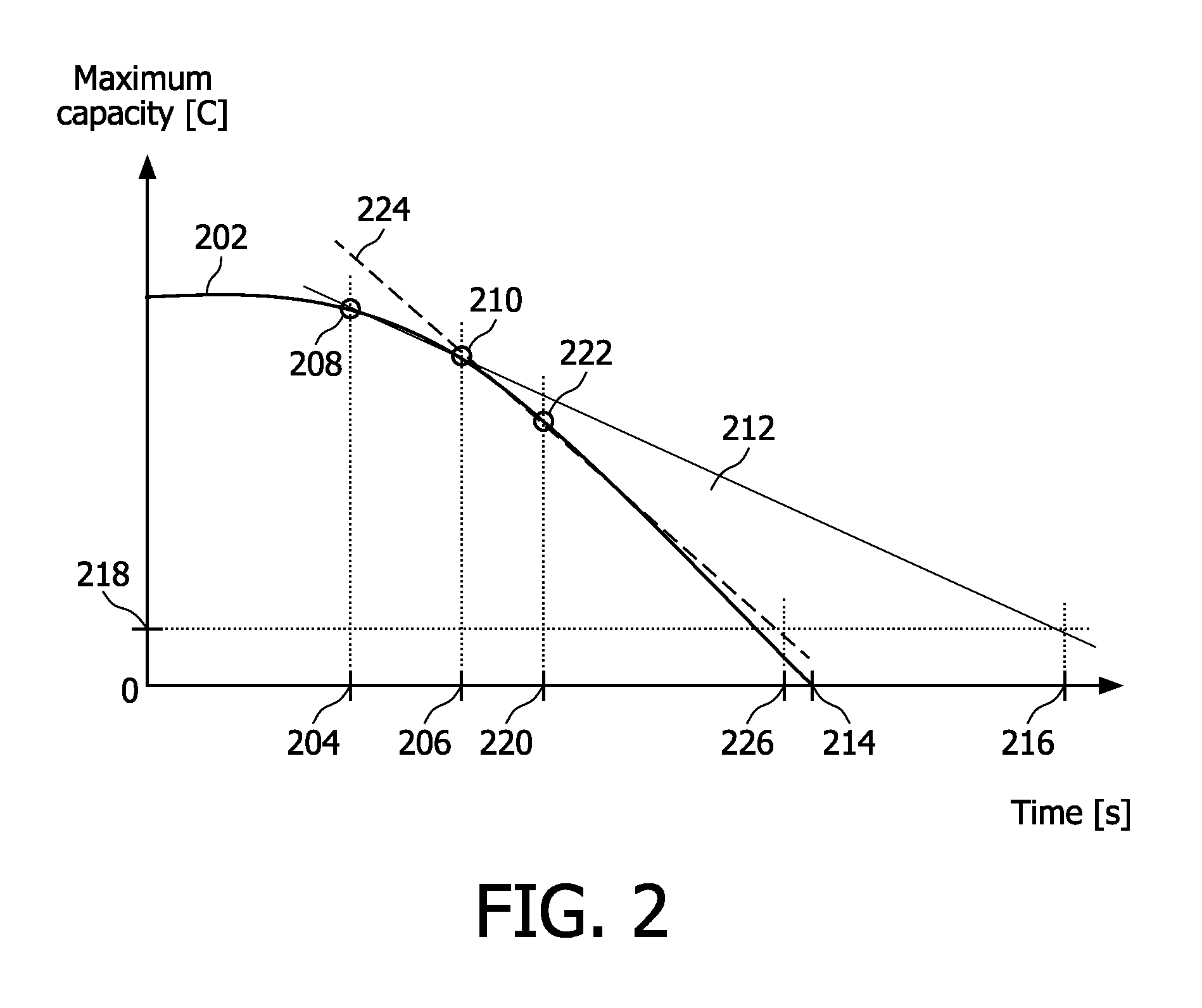
[0045]FIG. 7 schem...
fourth embodiment
[0049]A fourth embodiment according to the invention is a device 902, see FIG. 9 for determining an end of life for a rechargeable battery. The device 902 comprises a battery charger 904 known per se. The device 902 further comprises a provision 906 for monitoring a battery characteristic indicative for battery aging and a provision 908 for estimating a battery's end of life.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com