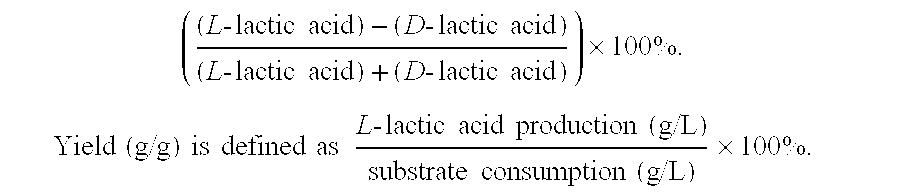Patents
Literature
105results about How to "Appropriately applied" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
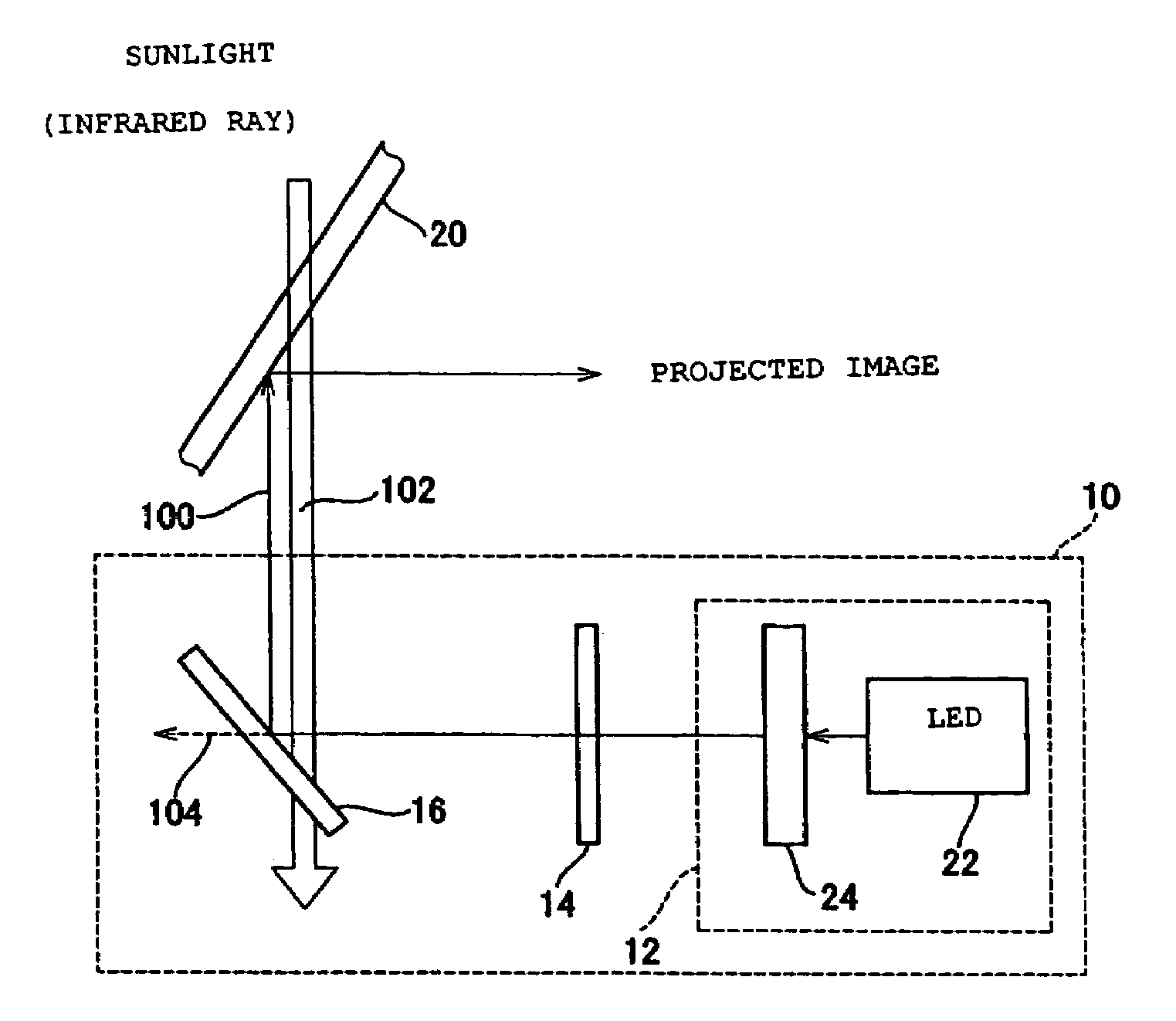
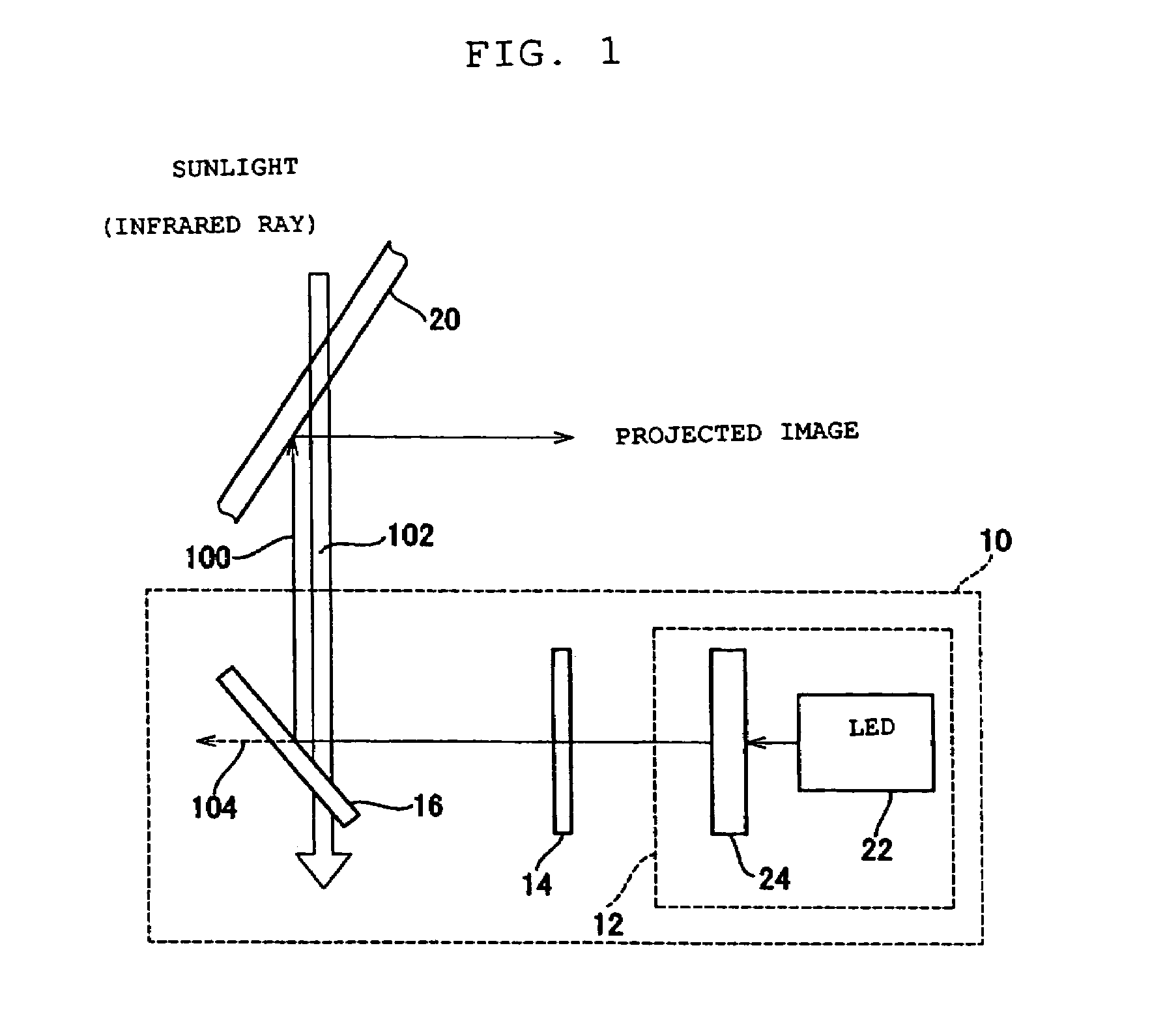
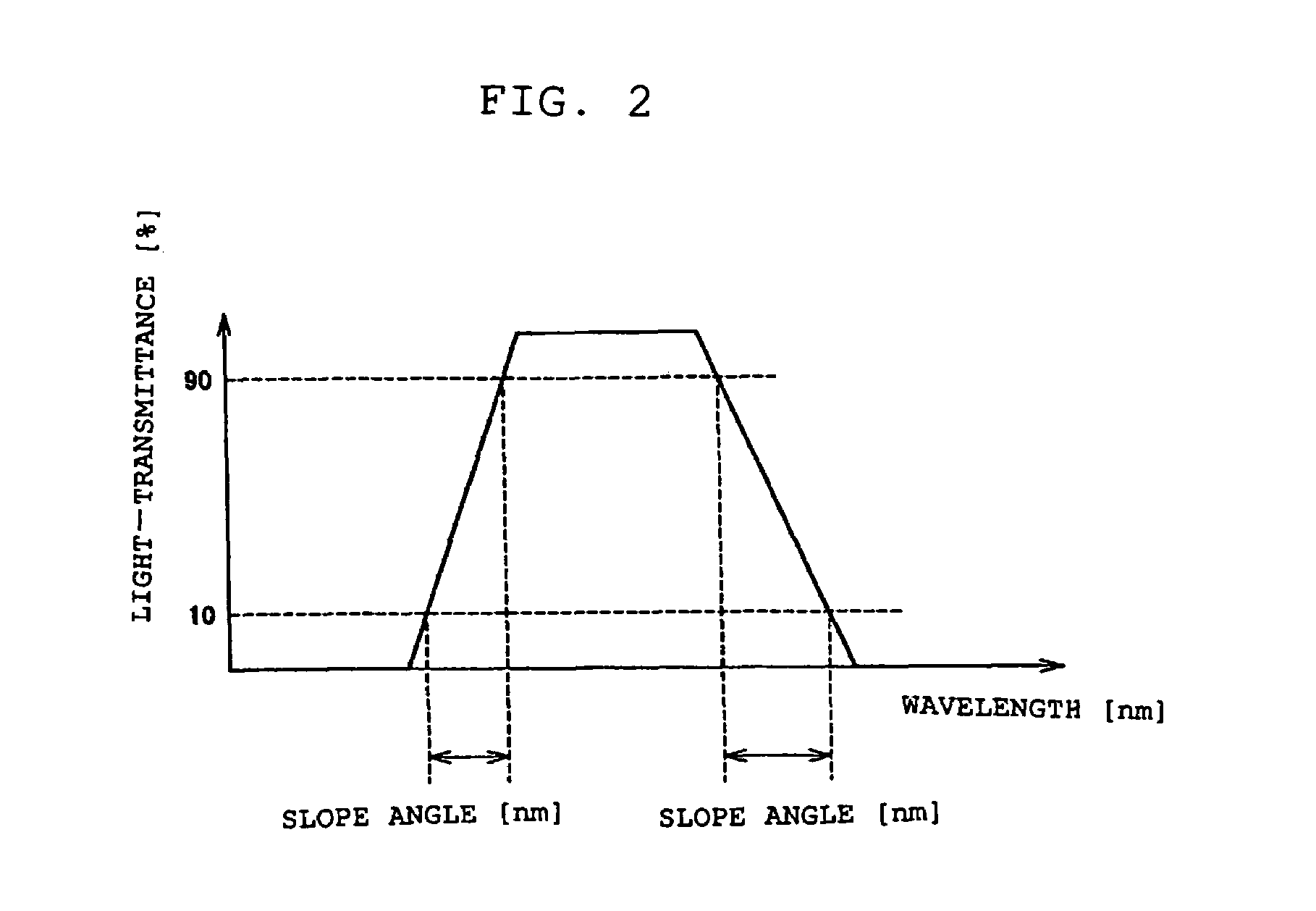
Display device
ActiveUS7320534B2High color purityResists deteriorationShow cabinetsImpedence networksInfraredDisplay device
Disclosed is a display device at a low cost which enhances the color purity of light to be projected, and which resists deterioration due to ambient light such as infrared ray. This display device includes an LED, an optical member for selectively outputting light components, of which wavelength is a predetermined minimum-limit wavelength or longer, from incident light, and a mirror for selectively reflecting light components, of which wavelength is a predetermined maximum-limit wavelength or shorter, from irradiated light. One of the optical member or the mirror receives light directly from the LED, and outputs it to the other. Subsequently, the other receives the light from one of the optical member and the mirror, and outputs it.
Owner:MURAKAMI CORP +1
Lipid-mediated polynucleotide administration to deliver a biologically active peptide and to induce a cellular immune response
InactiveUS7250404B2Short durationFast expressionHydrolasesMicroencapsulation basedLipid formationNucleotide
A method for delivering an isolated polynucleotide to the interior of a cell in a vertebrate, comprising the interstitial introduction of an isolated polynucleotide into a tissue of the vertebrate where the polynucleotide is taken up by the cells of the tissue and exerts a therapeutic effect on the vertebrate. The method can be used to deliver a therapeutic polypeptide to the cells of the vertebrate, to provide an immune response upon in vivo translation of the polynucleotide, to deliver antisense polynucleotides, to deliver receptors to the cells of the vertebrate, or to provide transitory gene therapy.
Owner:VICAL INC +1
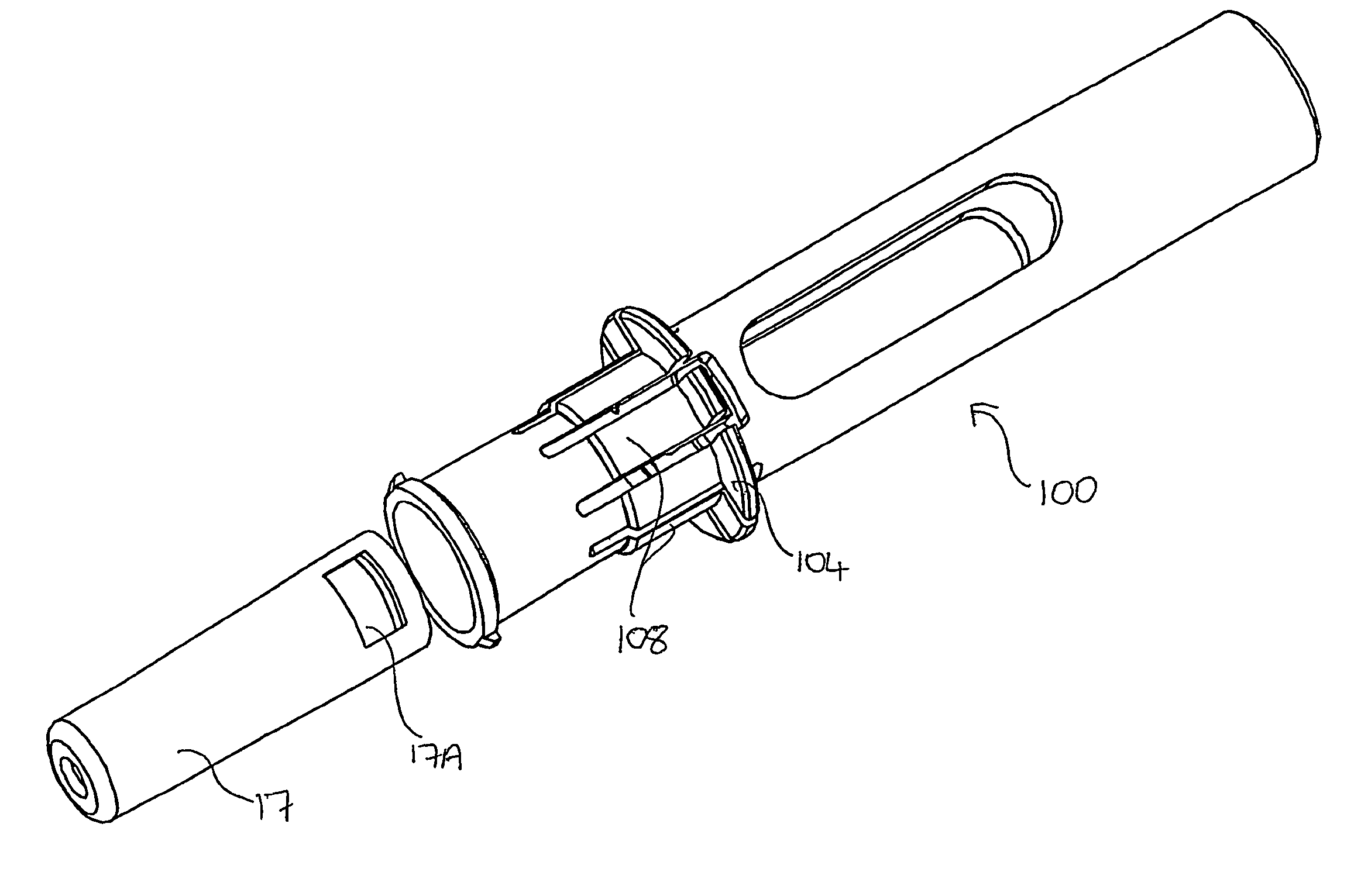
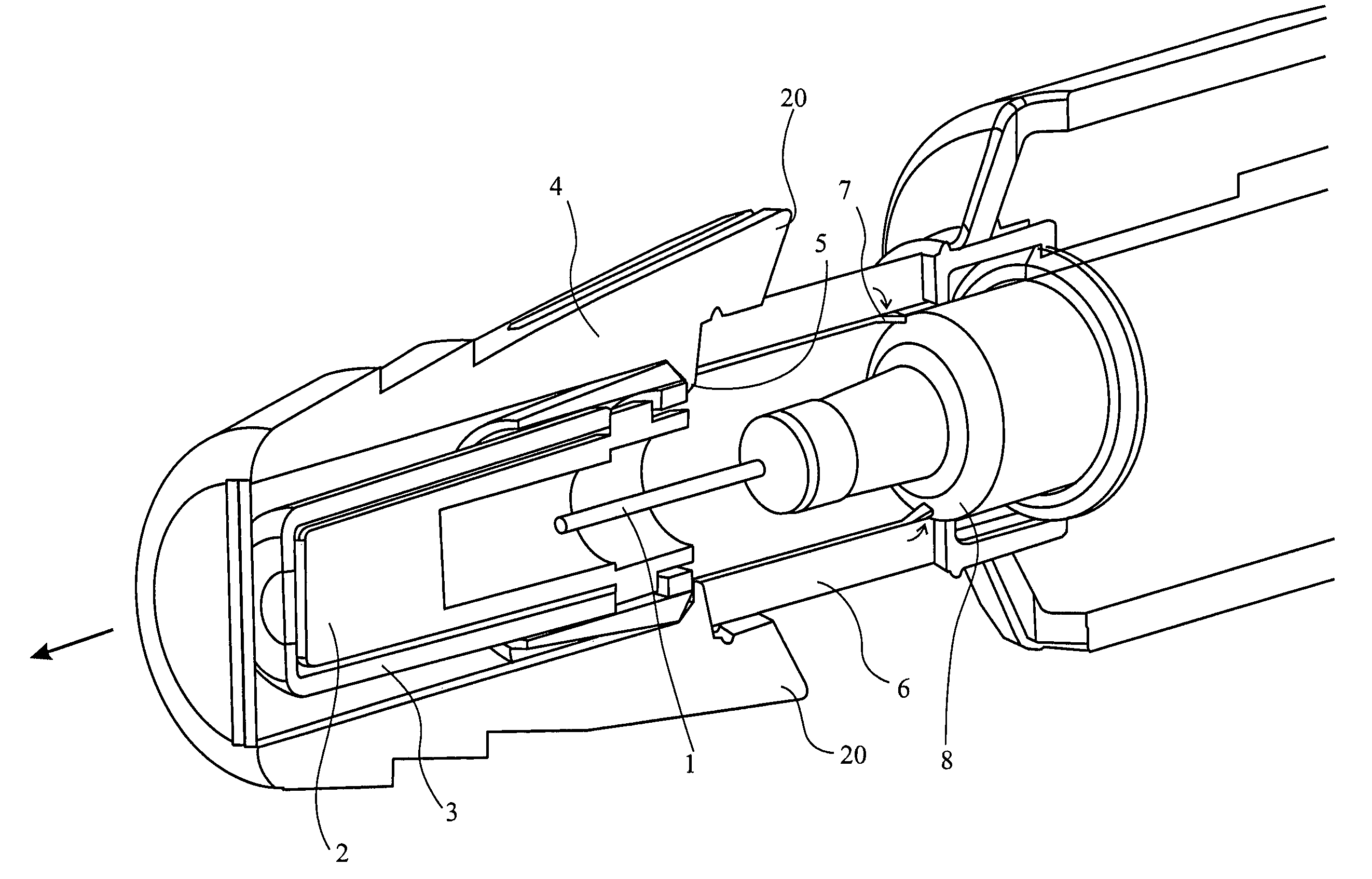
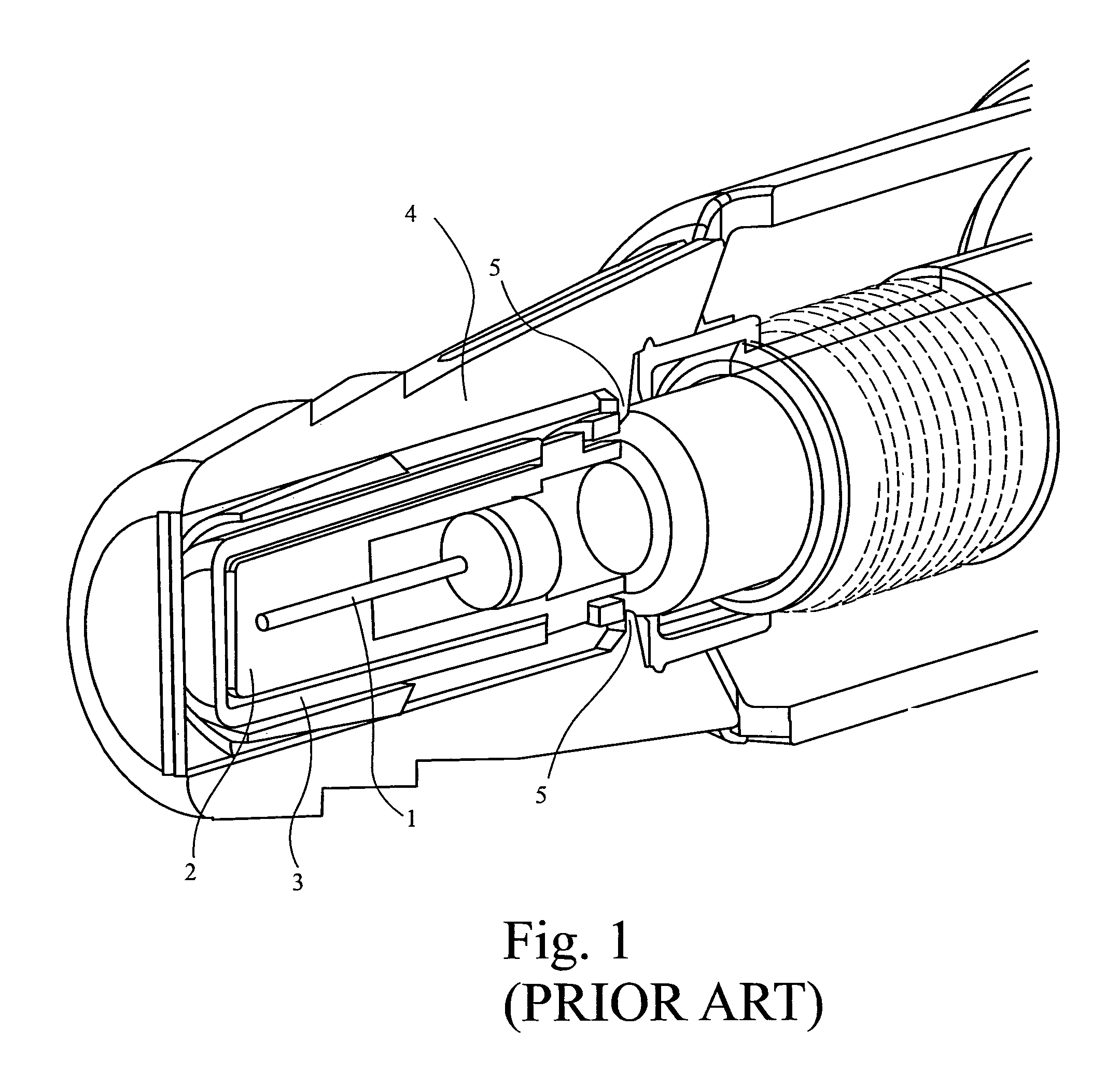
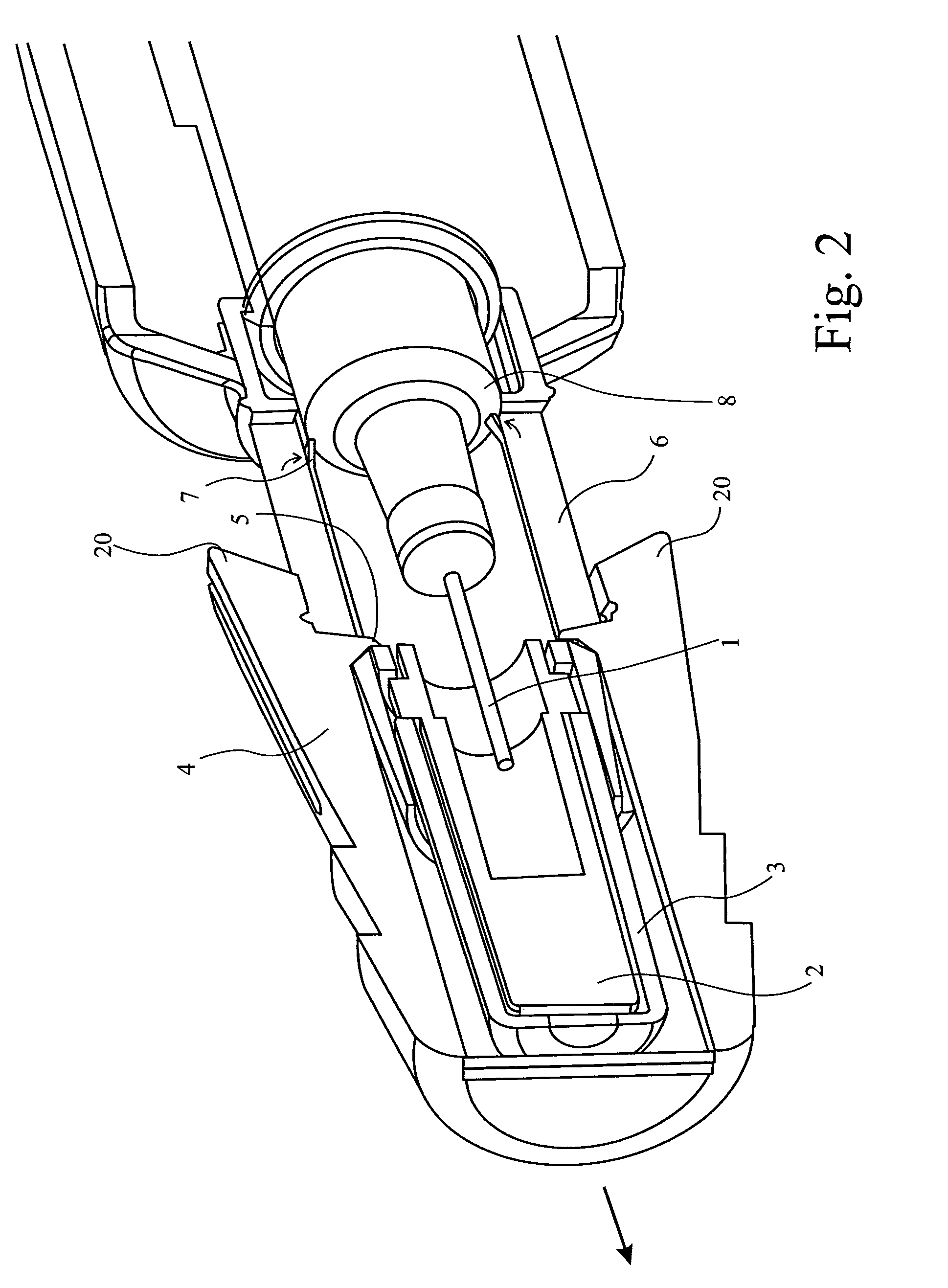
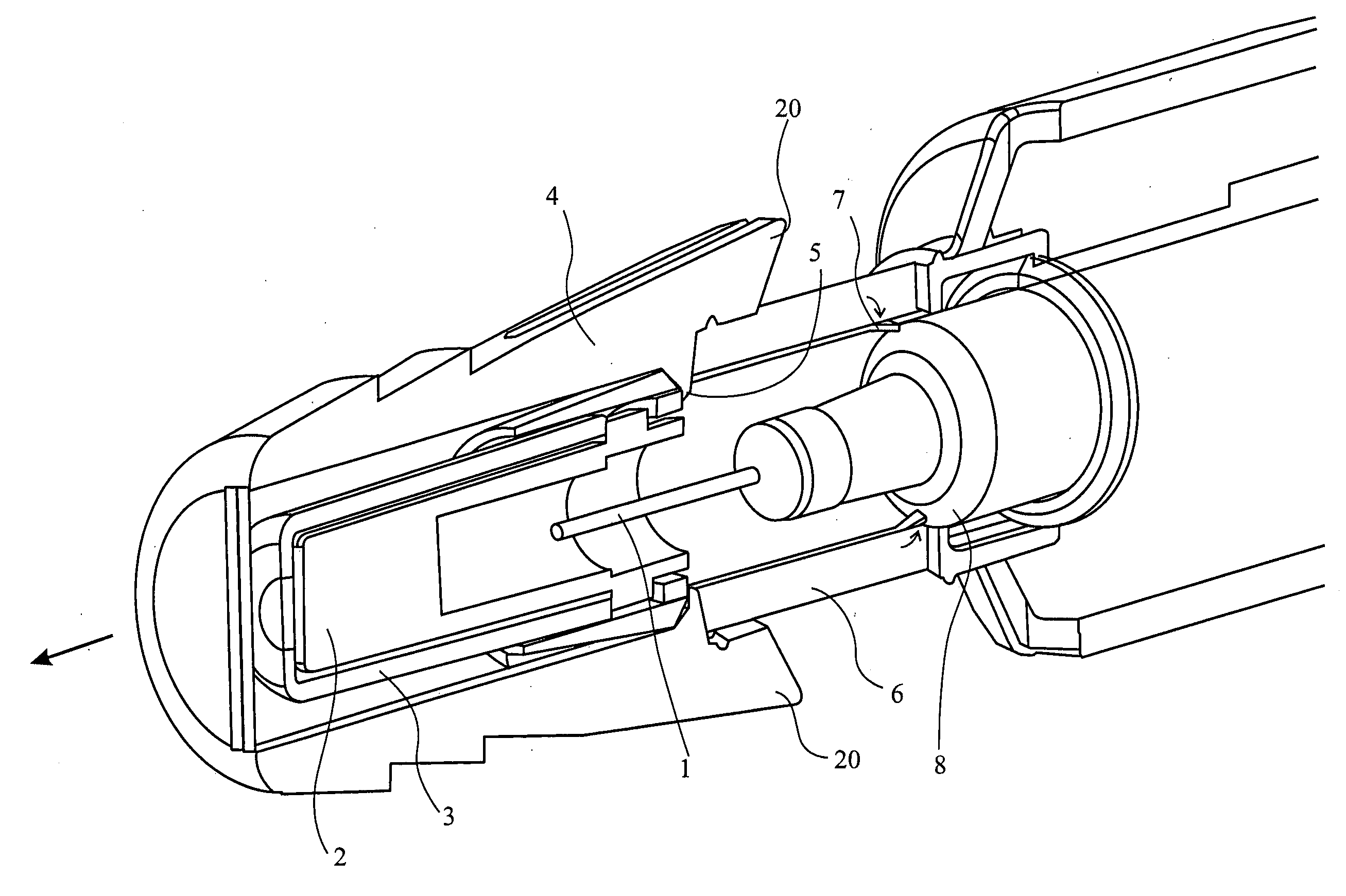
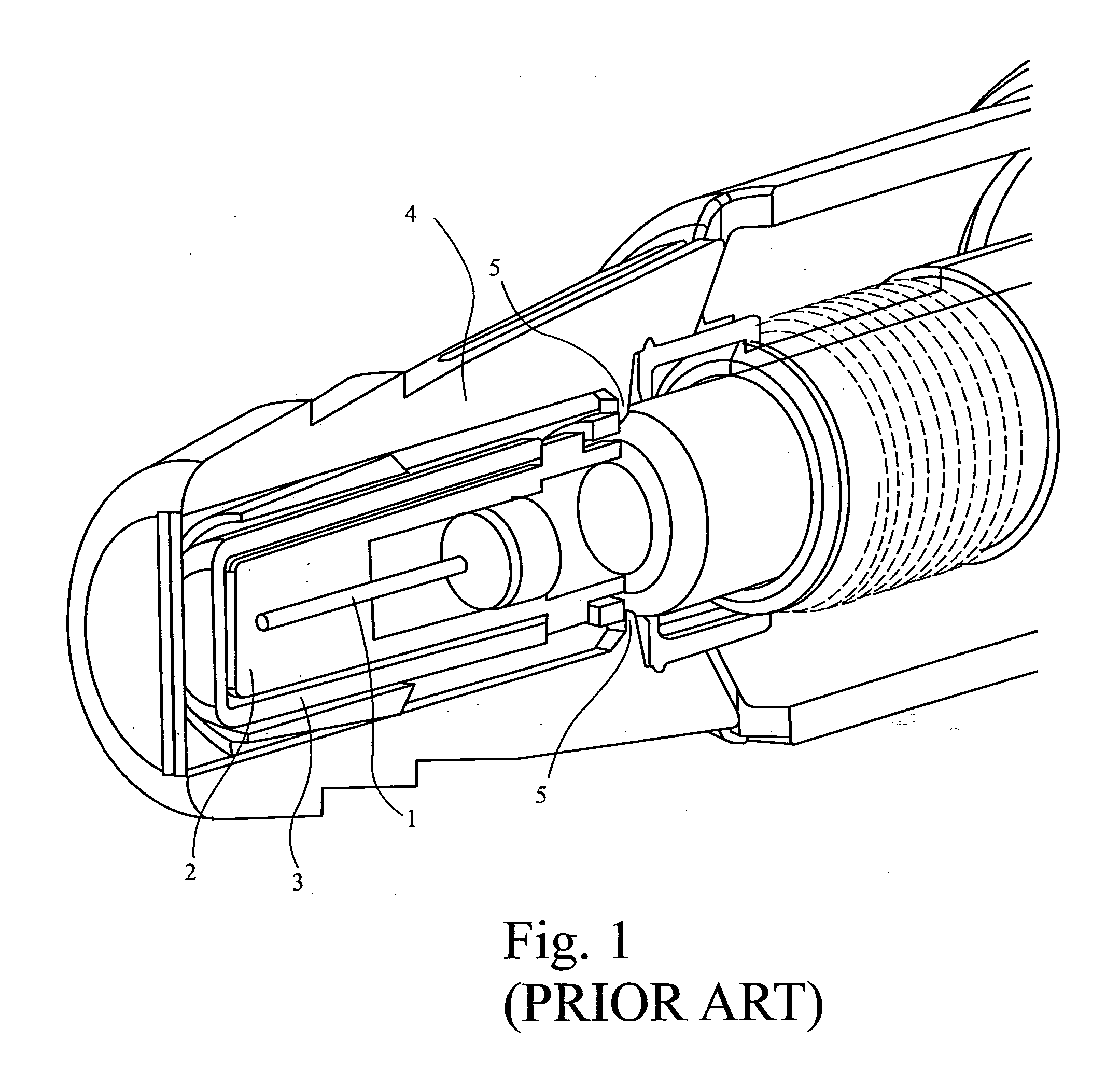
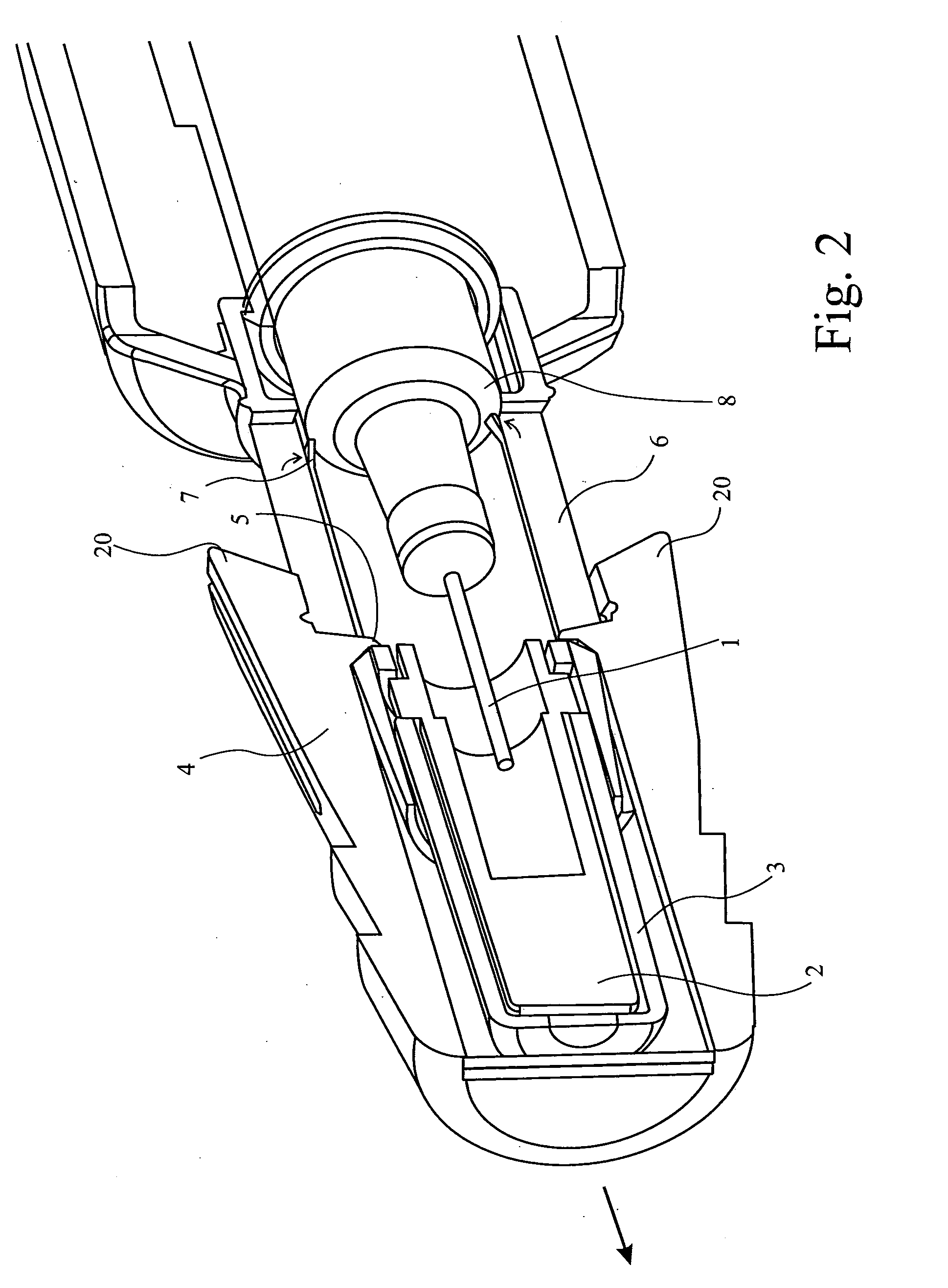
Improved autoinjector supporting the syringe at the front
ActiveUS20100152655A1Eliminate riskCost-effectiveAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesAutoinjectorAxial force
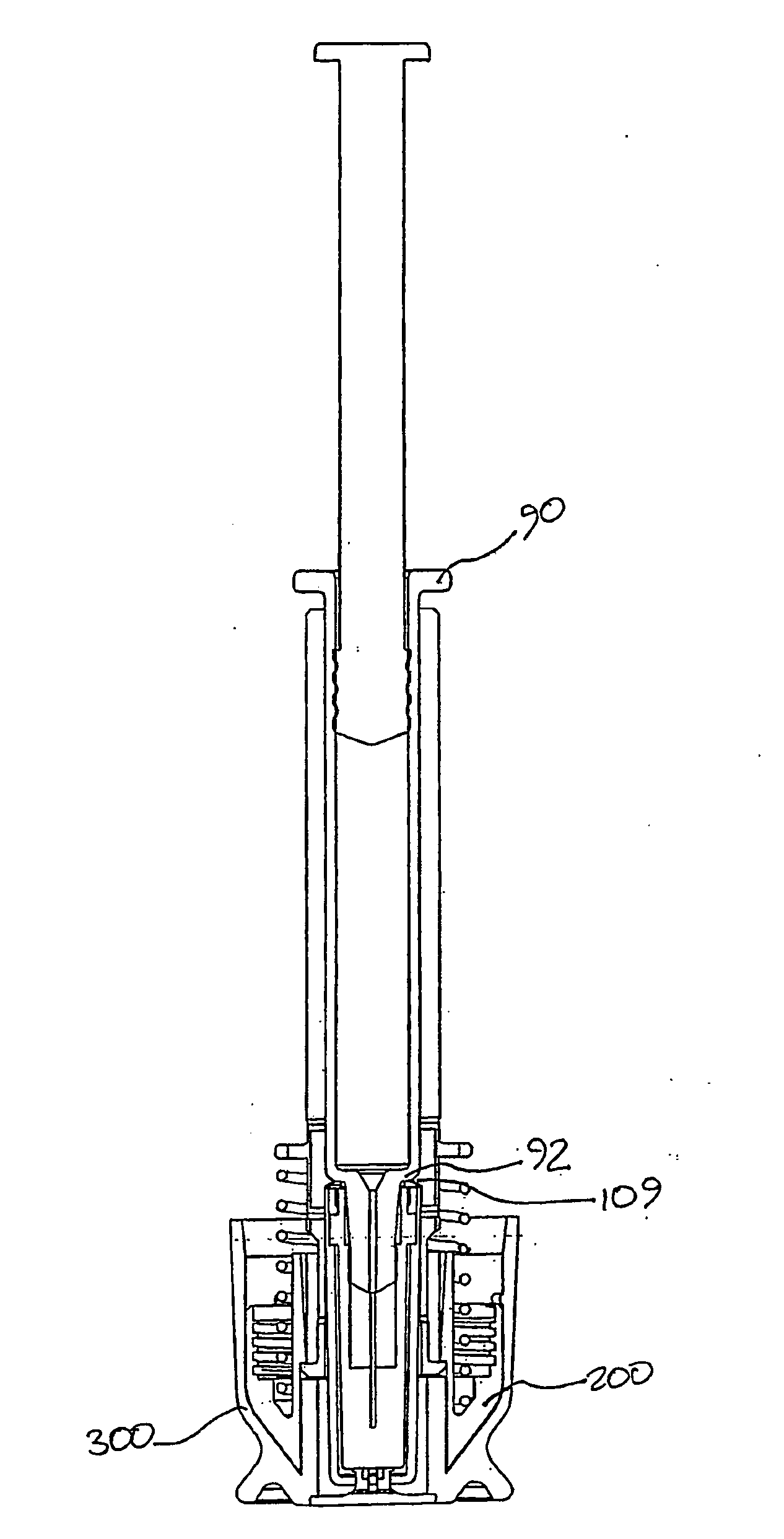
An autoinjector comprising a housing in which can be mounted a syringe comprising a barrel for holding a volume of medicament, a needle at one end of the barrel in fluid communication with the medicament and a plunger axially-moveable in the barrel to a forwardmost position, the autoinjector further comprising a syringe support means for supporting the barrel at an axial location at or forward of the forwardmost position of the plunger and having a reaction surface for the syringe, whereby in use said reaction surface (109) provides an axial compressive force on said barrel when a forward axial force is applied to the plunger.
Owner:SHL MEDICAL AG
Apparatus and method for providing three-dimensional air-touch feedback
InactiveUS20150277610A1Improve spatial resolutionSmall sizeInput/output processes for data processingMobile deviceHuman–computer interaction
Provided are three-dimensional air touch feedback apparatus and method for a mobile apparatus. The present invention provides an air touch feedback apparatus, including: a display unit which outputs a 3D floating image; a touch detecting unit which is disposed at a side edge of a display unit and includes a plurality of sensors to detect a body of a user and receives position information on at least one image object of the 3D floating image from the display unit to determine an air touch position where the body of the user is in contact with the image object; and a feedback providing unit which receives air touch position information from the touch detecting unit and radiates an ultrasonic wave to the air touch position at the side edge of the display unit.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Method and apparatus for mounting
A method and an apparatus for mounting: the method for bonding a plurality of objects to each other, comprising the steps of disposing, apart from each other, a first object, a second object and a holding means therefor, and a backup member having a reference positioning surface in this order, adjusting the parallelism of the second object or the holding means therefor relative to the reference positioning surface, adjusting the parallelism of the first object or the holding means therefor relative to the second object or the holding means therefor, bringing the first object into contact with the second object to temporarily bond both objects to each other, bringing the holding means for the second object into contact with the reference positioning surface of the backup member, and pressing both objects against each other for final bonding, whereby, finally, a highly reliable and accurate bonding state can be achieved.
Owner:TORAY ENG CO LTD +1
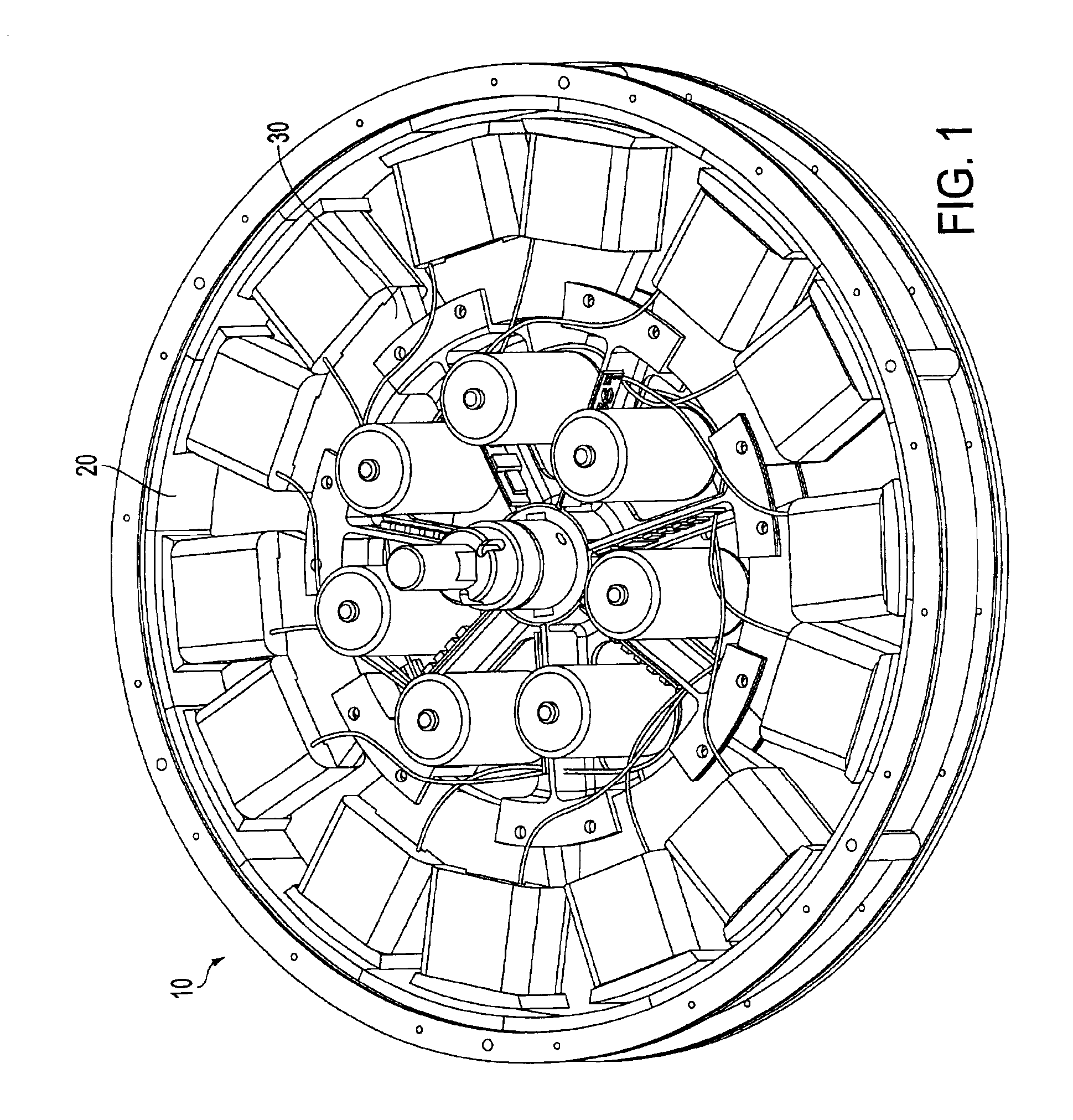
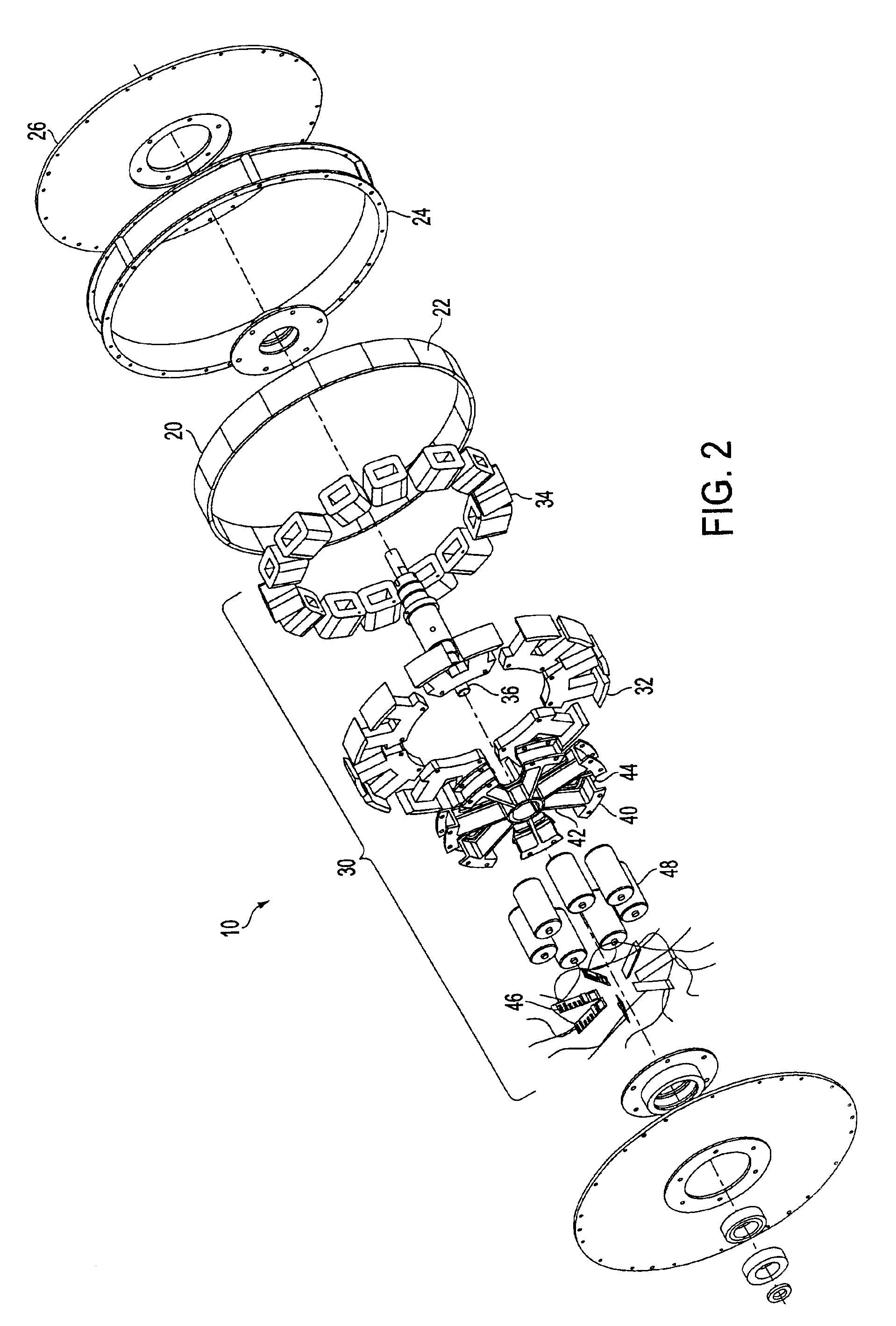
Rotary electric motor having separate control modules for respective stator electromagnets
InactiveUS6927524B2High torqueWide operating rangeAssociation with control/drive circuitsDC motor speed/torque controlElectrical controlDriven element
A rotary brushless electric motor is formed within a cylindrical rotor housing structure that surrounds an annular stator ring. The stator is formed of a plurality of individual power modules and corresponding core segments, each module including electrical control and drive elements supplied by a power source incorporated within the stator. Such parallel architecture provides relatively independently controlled functionality for each module. Each module and stator core segment can be individually installed and removed without disturbing the other units. Should a particular module or stator core segment fail, it can be easily removed for repair or replacement and reinstallation.
Owner:MATRA MFG & SERVICES
Novel diblock copolymer, preparation method thereof, and method of forming NANO pattern using the same
ActiveUS20130248488A1Promote formationWell formedNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusElectronSoft segment
The present invention relates to a diblock copolymer that may facilitate formation of a finer nano pattern, and be used for manufacture of an electronic device including a nano pattern or a bio sensor, and the like, a method for preparing the same, and a method for forming a nano pattern using the same,The diblock copolymer comprises a hard segment including at least one specific acrylamide-based repeat unit, and a soft segment including at least one (meth)acrylate-based repeat unit.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD +1
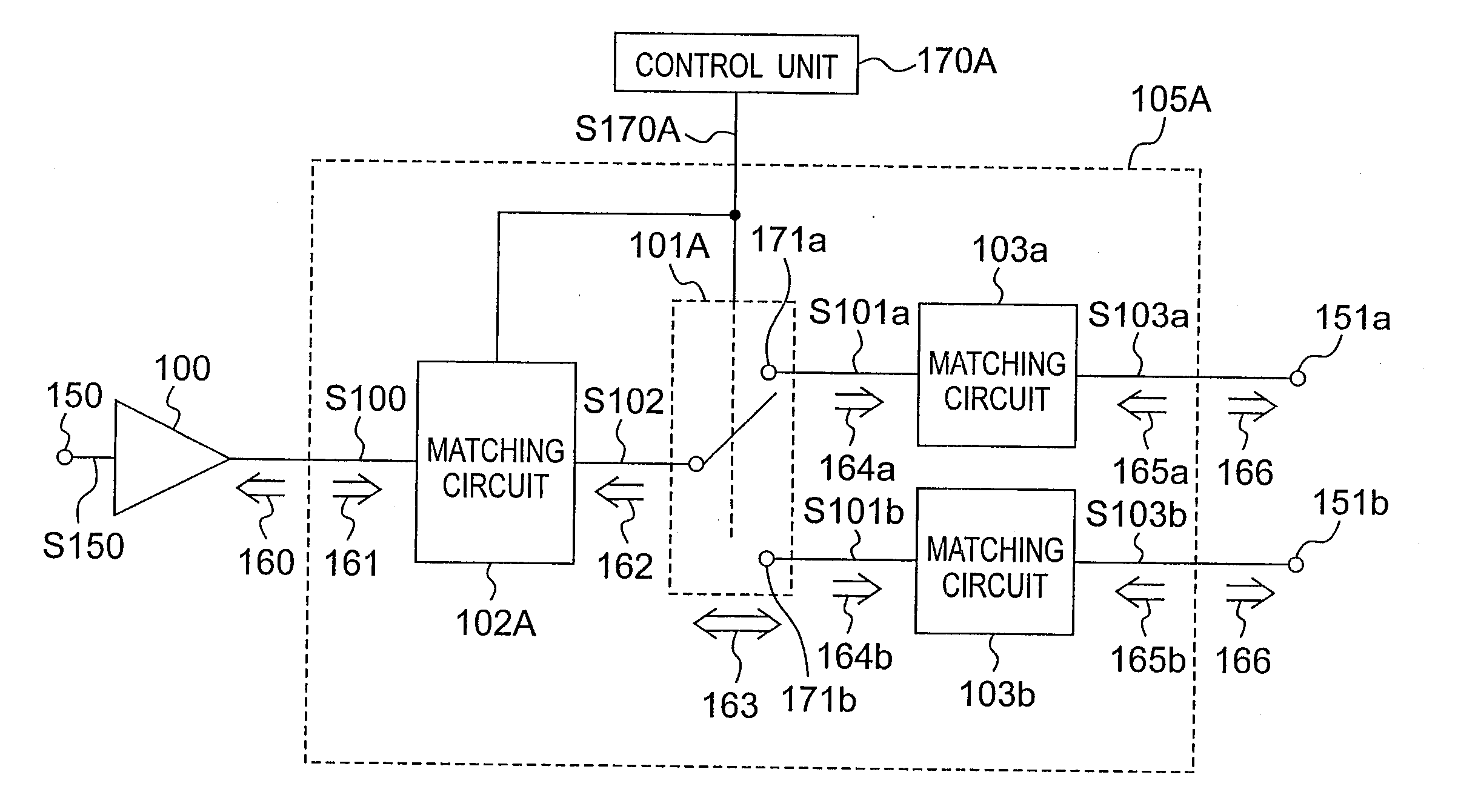
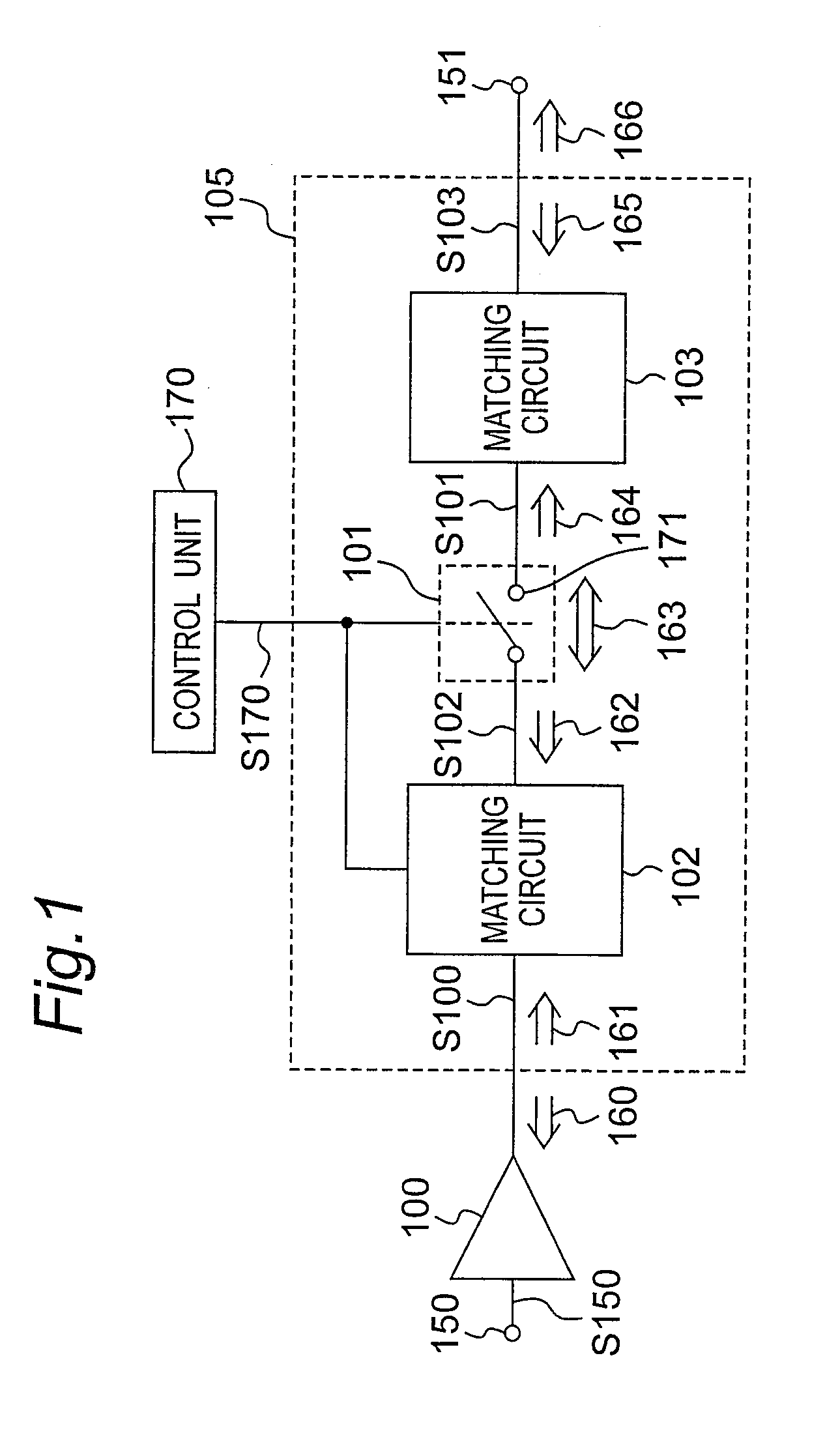
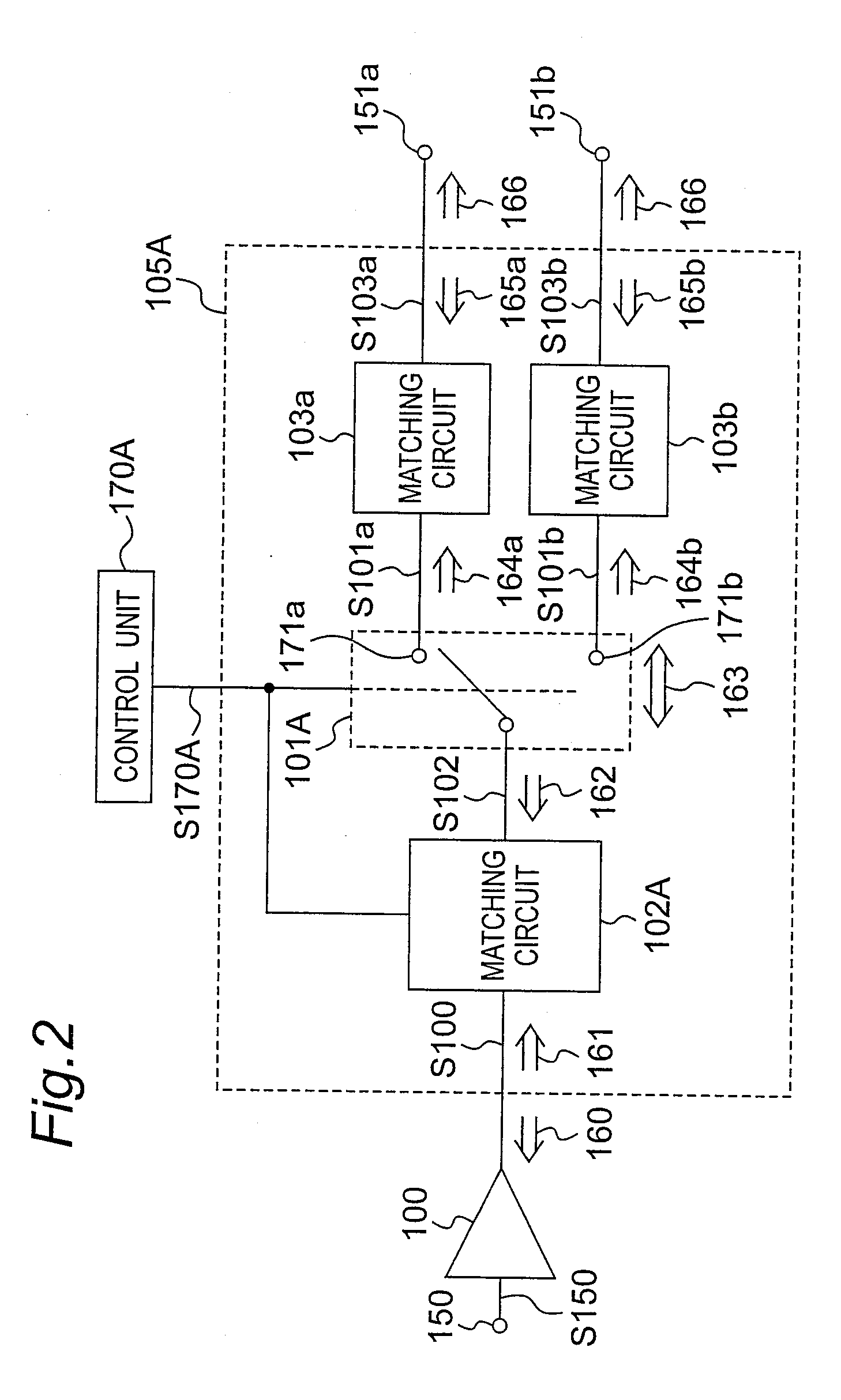
High frequency circuit, semiconductor device, and high frequency power amplification device
InactiveUS20080284539A1Reduce lossesEasy to switchMultiple-port networksHigh frequency amplifiersHigh frequency powerControl signal
A small, high performance, multifunctional high frequency circuit that is multiband and multimode compatible reduces loss from a switch formed on the output side of a final stage amplification unit. The final stage amplification unit power amplifies an input signal and outputs an amplified signal. A first matching circuit impedance converts the amplified signal input thereto at a first input impedance, and outputs a first impedance-converted signal at a first output impedance. A control unit that generates a control signal denoting signal path selection information. A switch unit selects one of at least two signal paths based on the control signal, passes the first impedance-converted signal at an on impedance through the selected path, and outputs the pass signal. A second matching circuit impedance converts a pass signal input thereto at a second input impedance, and outputs a second impedance-converted signal at a second output.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
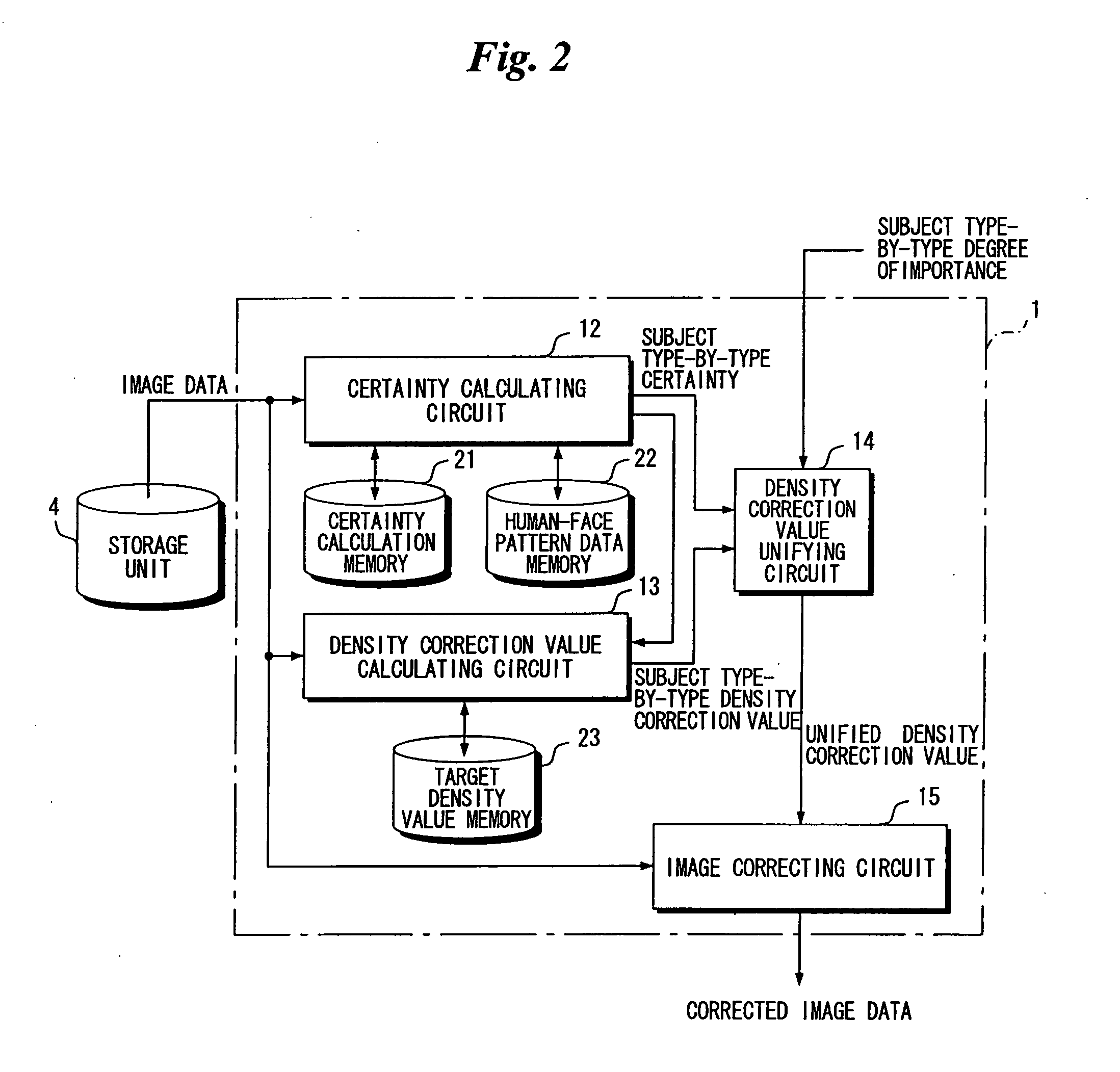
Image Processing Apparatus and Method, and Image Processing Program
ActiveUS20070292038A1Degree of certaintyImprove certaintyImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingAlgorithm
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Autoinjector supporting the syringe at the front
ActiveUS8647299B2Cost-effectiveEasy constructionAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesAxial forceAutoinjector
An autoinjector comprising a housing in which can be mounted a syringe comprising a barrel for holding a volume of medicament, a needle at one end of the barrel in fluid communication with the medicament and a plunger axially-moveable in the barrel to a forwardmost position, the autoinjector further comprising a syringe support means for supporting the barrel at an axial location at or forward of the forwardmost position of the plunger and having a reaction surface for the syringe, whereby in use said reaction surface (109) provides an axial compressive force on said barrel when a forward axial force is applied to the plunger.
Owner:SHL MEDICAL AG
Nanohole structure and method for producing the same, stamper and method for producing the same, magnetic recording medium and method for producing the same, magnetic recording device, and magnetic recording method
InactiveUS20060286345A1Produced easily and economicallyEasy to trackMechanical working/deformationLayered productsHigh densityPorous layer
The object of the present is to provide high-quality magnetic recording media capable of easy tracking, and allowing high-density recording, high-speed recording, and higher capacity without increasing the write-current at magnetic heads. The nanohole structure comprises a metal or metal-compound base material and plural arrays of nanoholes, wherein the plural arrays of nanoholes are respectively arranged into regular alignments, the regular alignments are different between adjacent arrays, and the regular alignments are alternately disposed within the metal or metal-compound base material. The magnetic recording medium according to the present invention comprises a substrate, a porous layer into which plural nanoholes are formed, and a magnetic material within the plural nanoholes, wherein the plural nanoholes are formed in a direction approximately vertical to the plane of the substrate, the porous layer is a nanohole structure according to the present invention
Owner:YAMAGATA FUJITSU
Vehicle behavior control device, and vehicle behavior control method
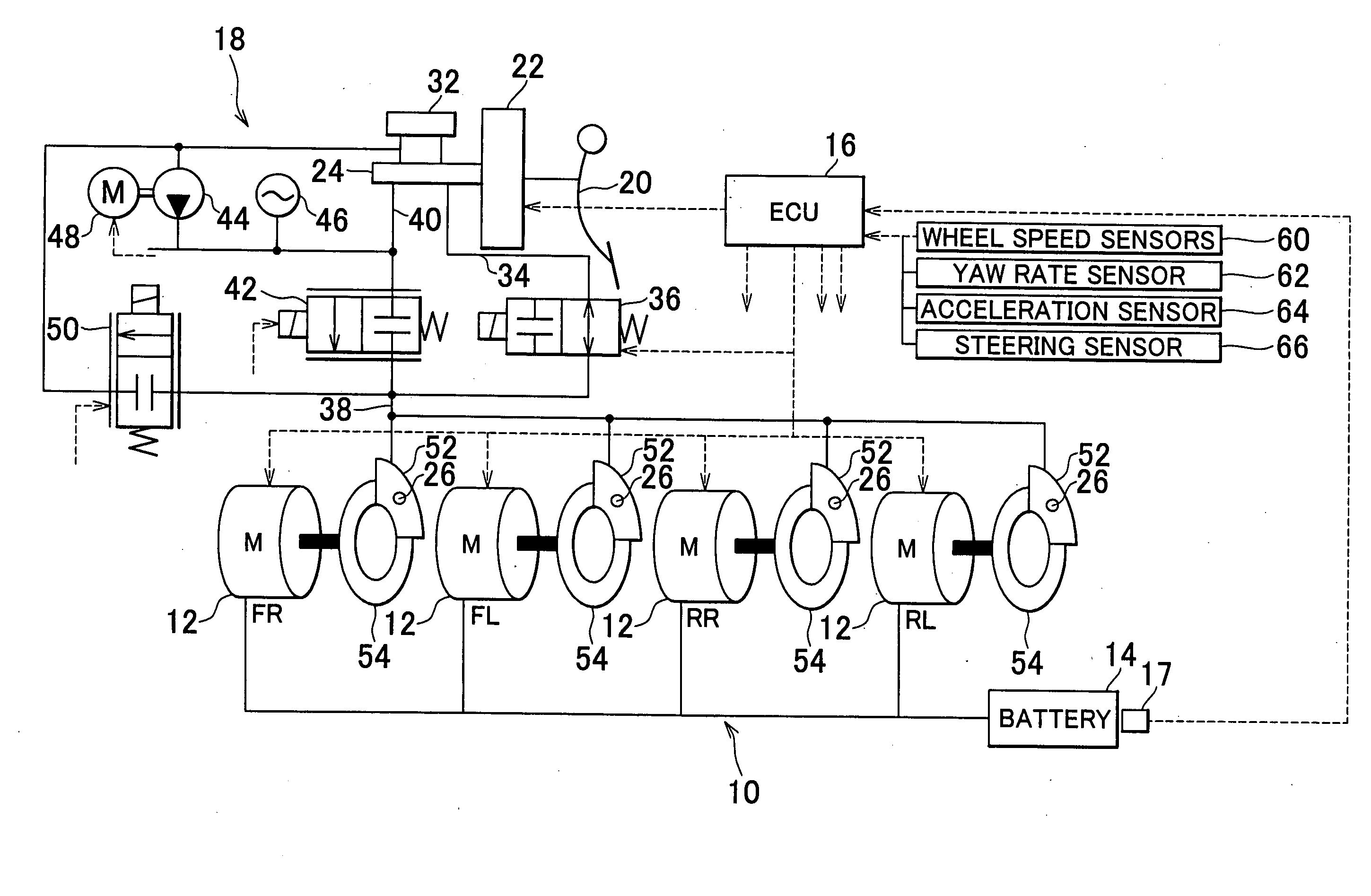
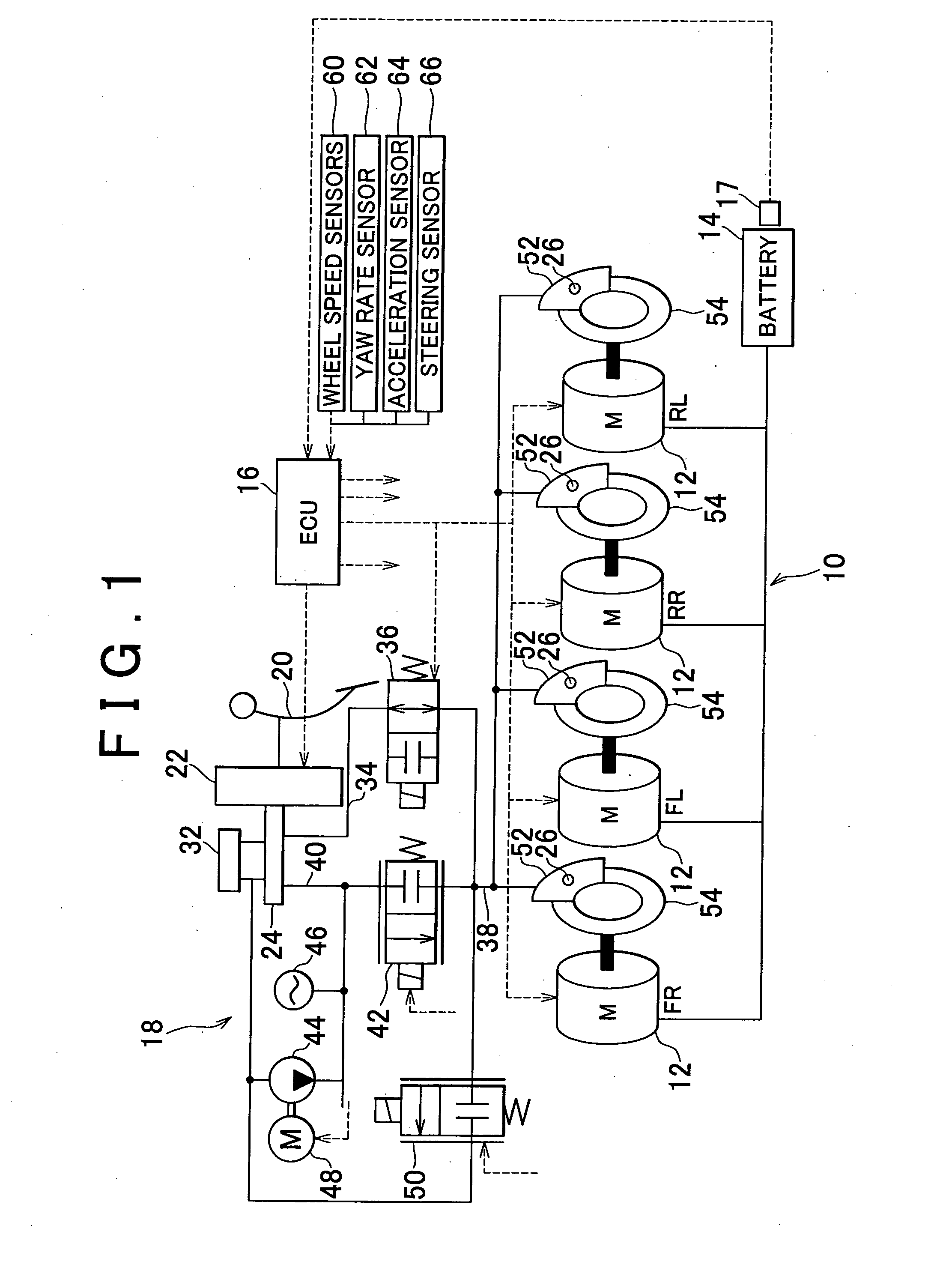
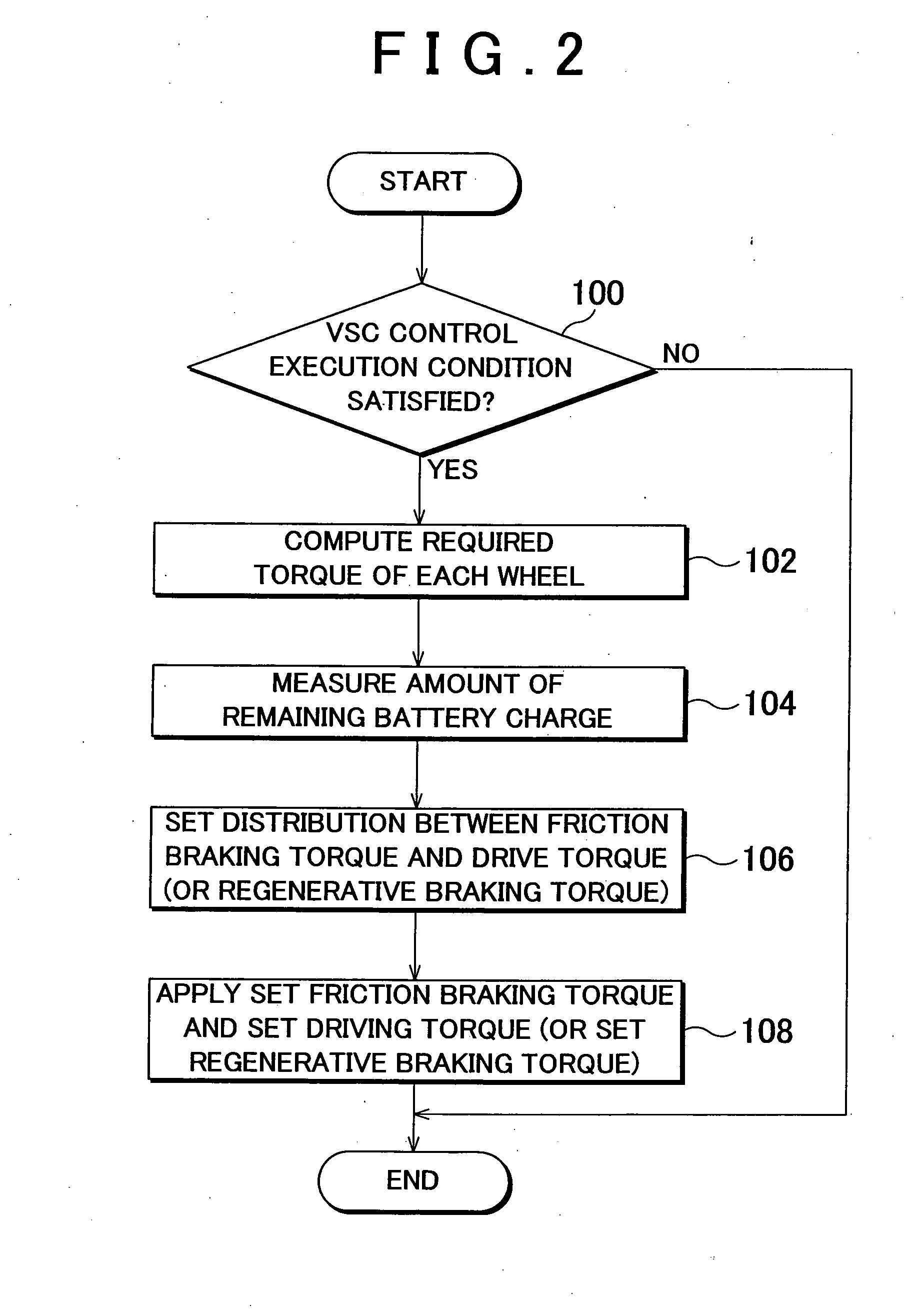
InactiveUS20100292882A1Easy to controlAppropriately appliedHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsBrake torqueVehicle behavior
Required torques that individual wheels are required to generate are computed on the basis of vehicle behavior. With respect to the computed required torque of each wheel, a torque value provided uniformly for the wheels is set as a value of the friction braking torque that the wheel is caused to generate by friction control means (18), and a torque value provided for each wheel independently of each other is set as a value of the driving torque or the regenerative braking torque that the wheel is caused to generate by a corresponding one of electric motors (12) of the wheels. At this time, the amount of remaining charge of a vehicle-mounted battery (14) is measured, and the distribution between the friction braking torque by the friction control means (18) and the driving torque or the regenerative braking torque by each electric motor (12) is altered according to the measured amount of remaining charge.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Autoinjector
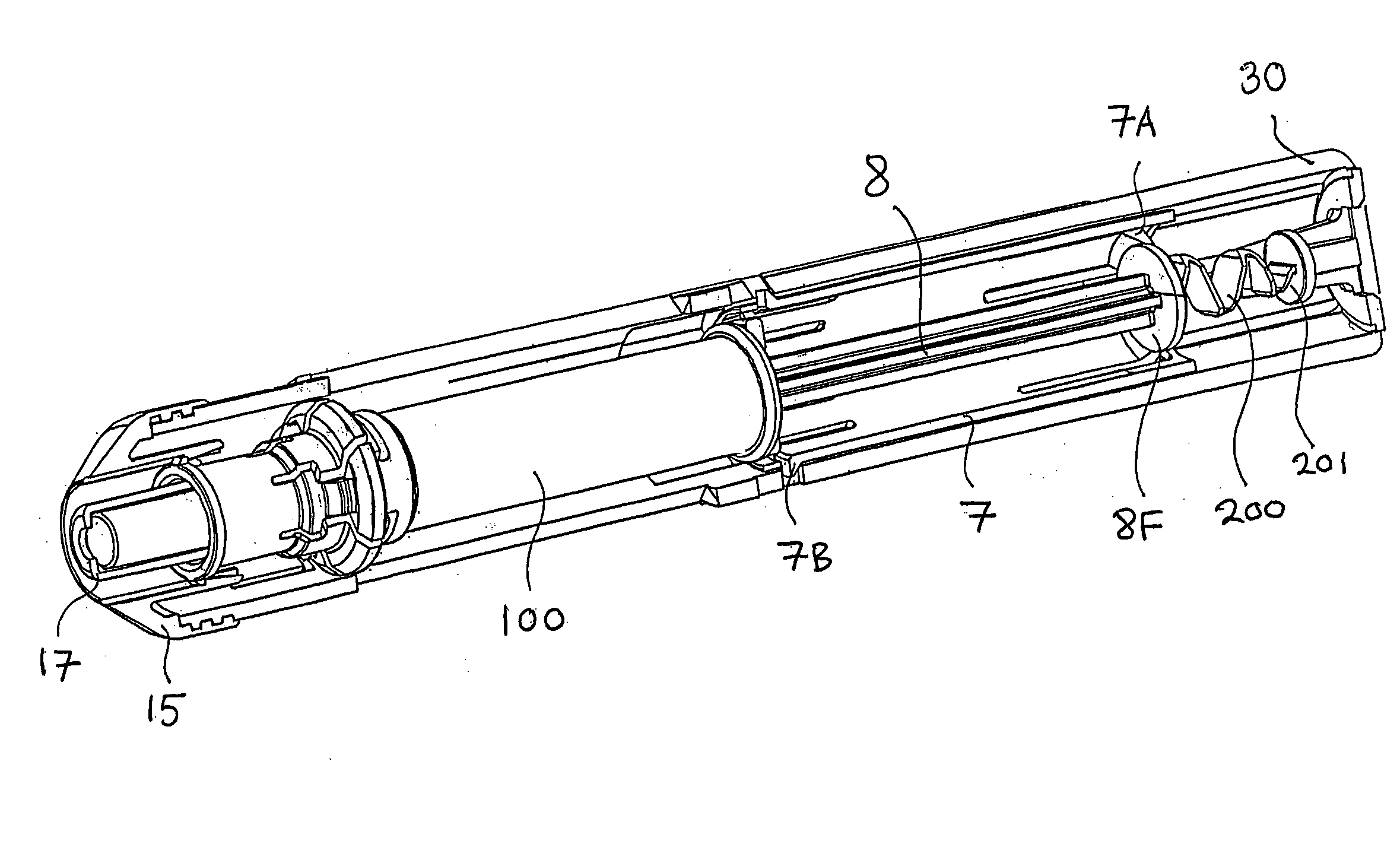
ActiveUS8747357B2Preventing forward axial movement of syringePrevent movementAutomatic syringesMedical devicesAutosamplerAutoinjector
Owner:SHL MEDICAL AG
autoinjector
ActiveUS20110282278A1Reduce complexityCost-effectiveAutomatic syringesMedical devicesAutoinjectorAxial force
An autoinjector comprising an outer housing in which can be mounted a syringe for holding a volume of medicament, the syringe for holding medicament having a needle at one end thereof, a syringe holder for supporting the syringe in an axial position relative to the outer housing, and an intermediate housing at least part of which is located within said outer housing, characterised in that said intermediate housing is provided with a blocking means capable of abutting the syringe or the syringe holder so as to be capable of preventing forward axial movement of the syringe when a forward axial force is applied to said needle before actuation of the autoinjector to deliver an injection, but incapable of preventing forward axial movement of the syringe during actuation of the autoinjector to deliver an injection.
Owner:SHL MEDICAL AG
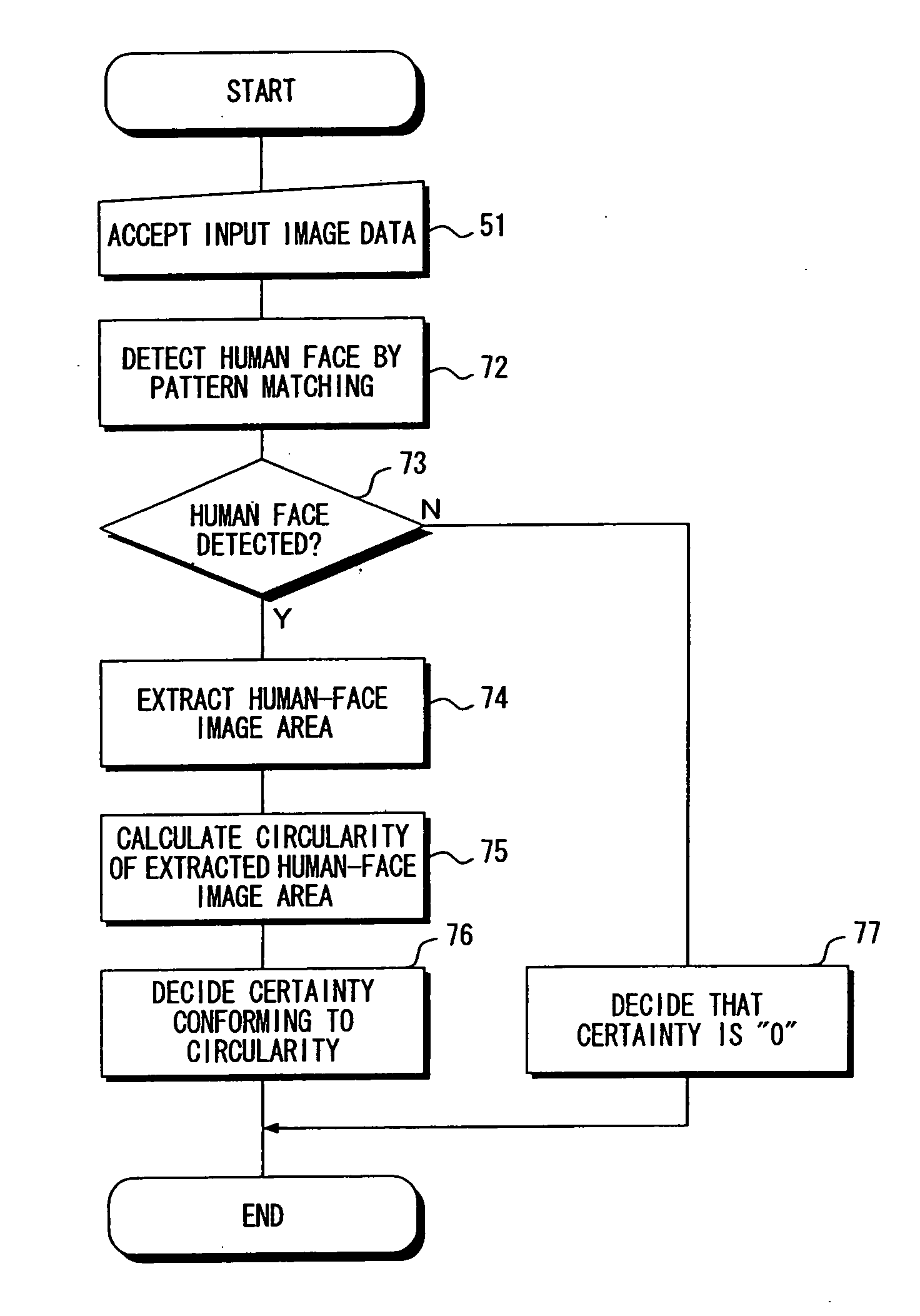
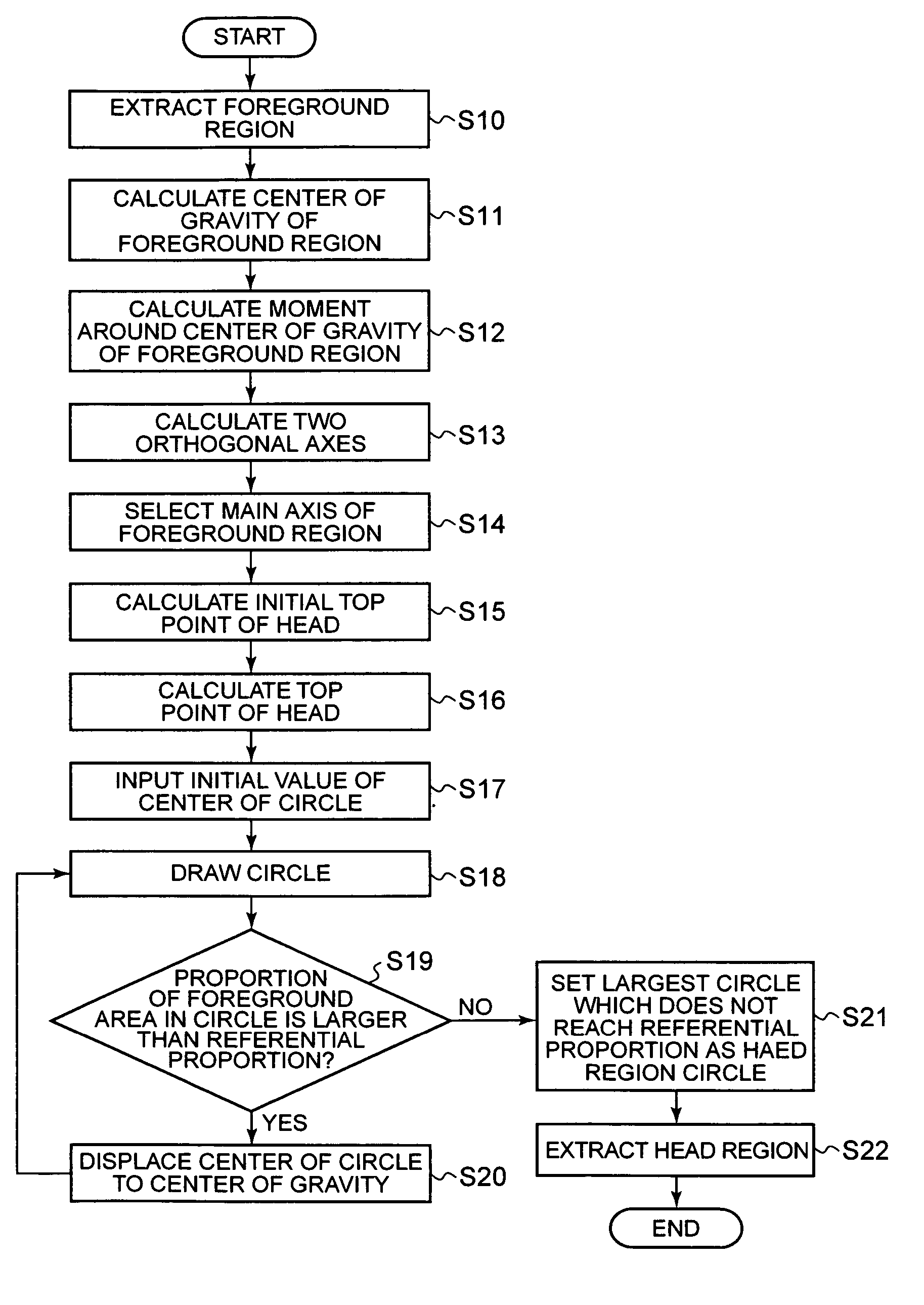
Head detecting apparatus, head detecting method, and head detecting program
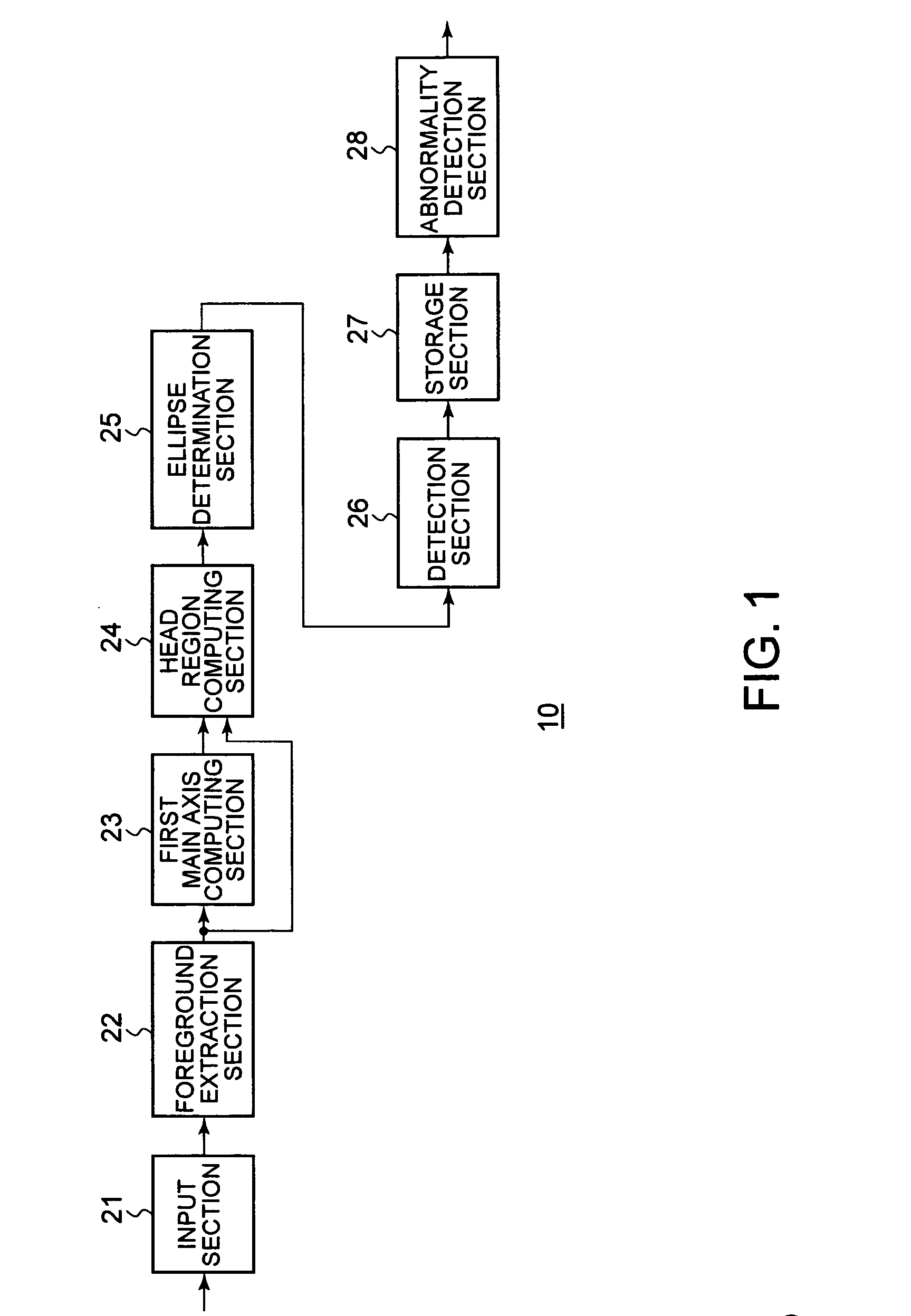
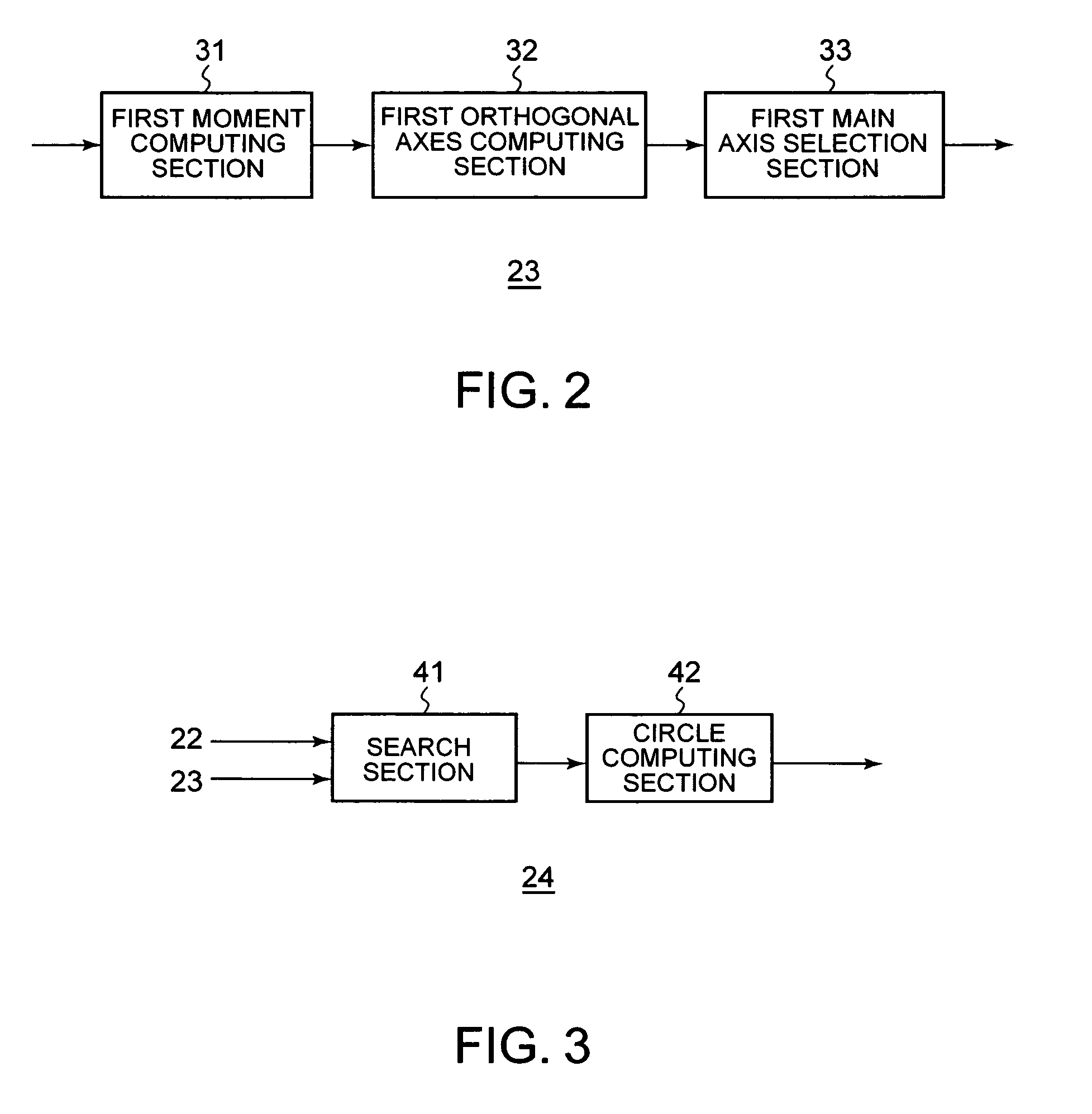
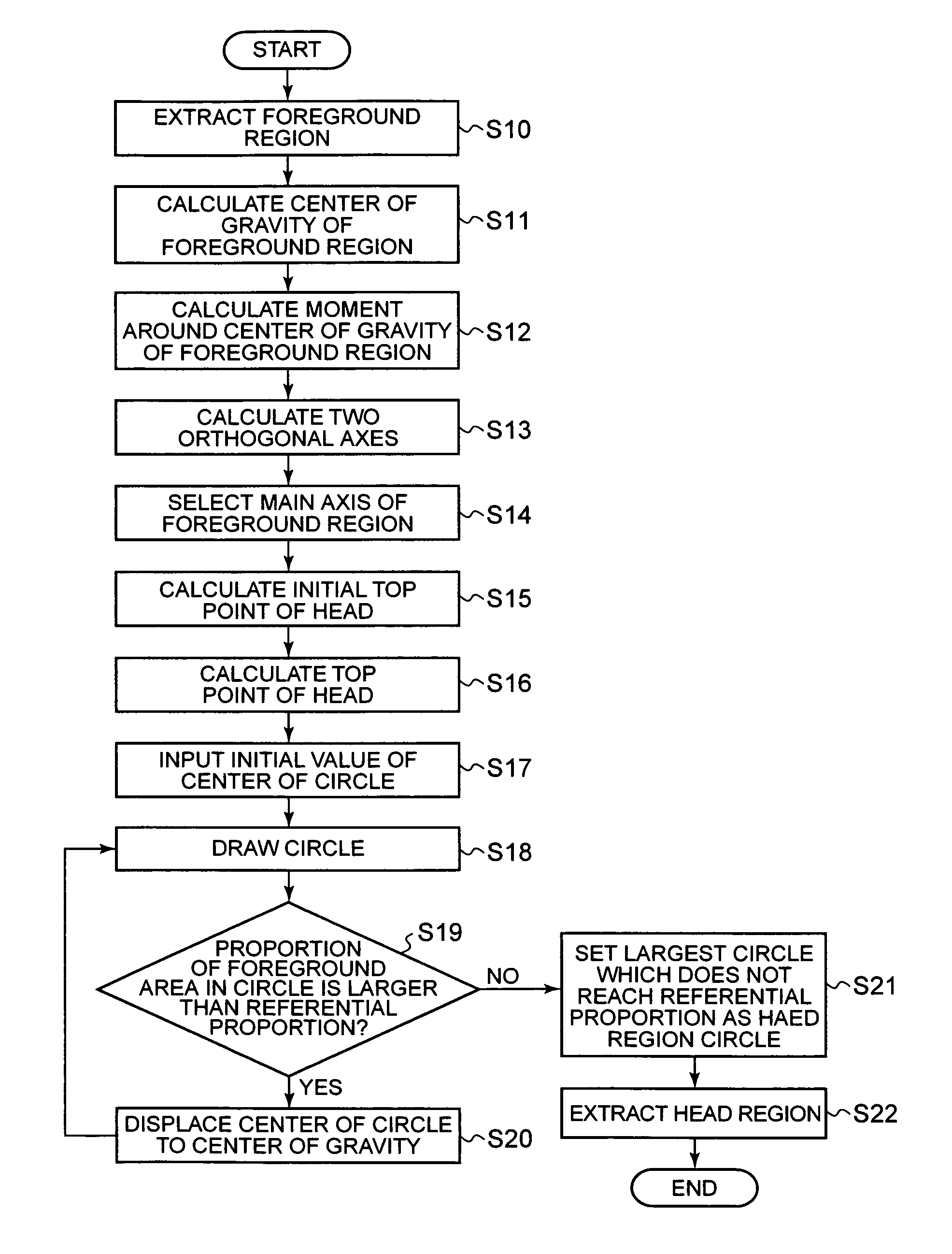
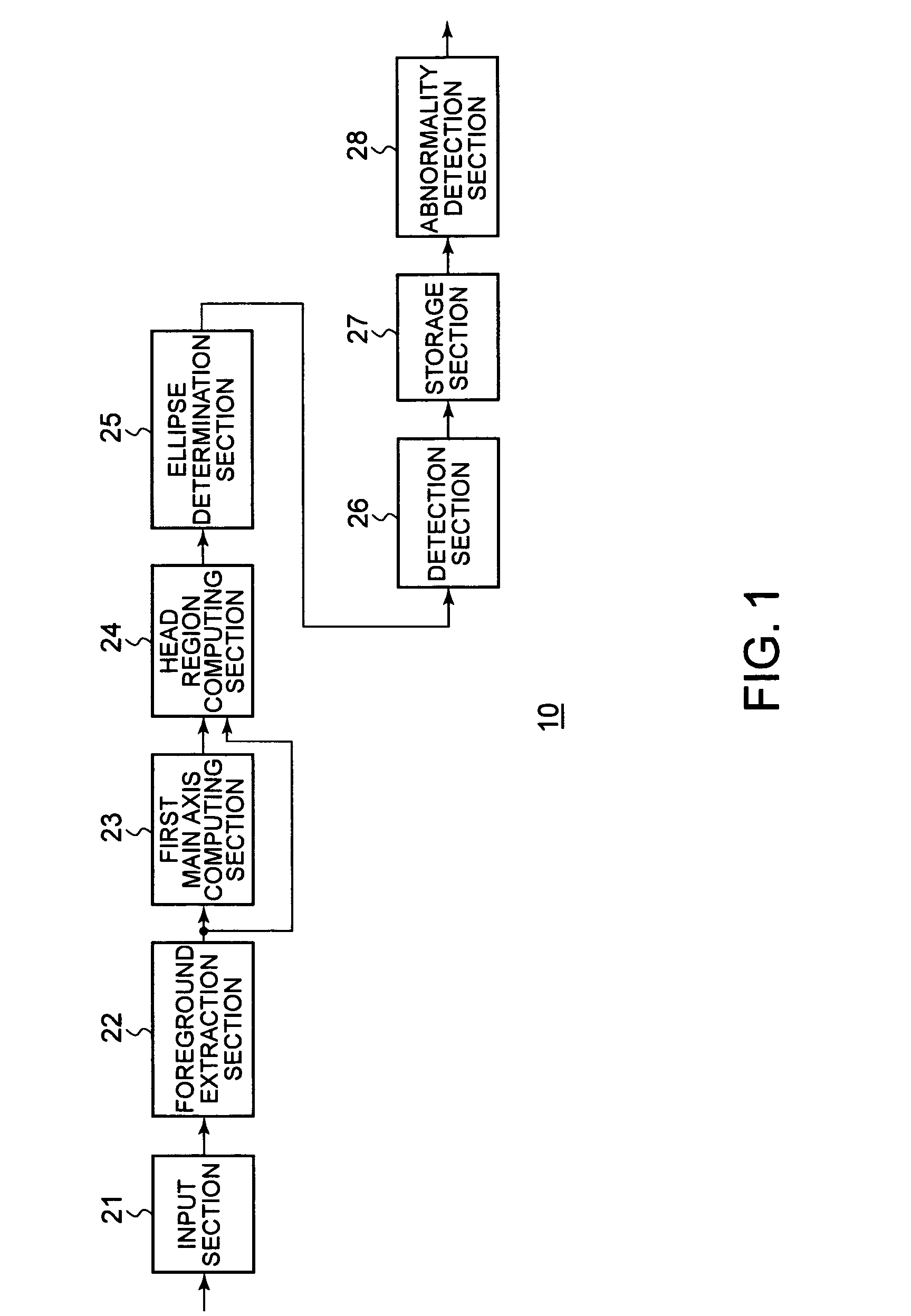
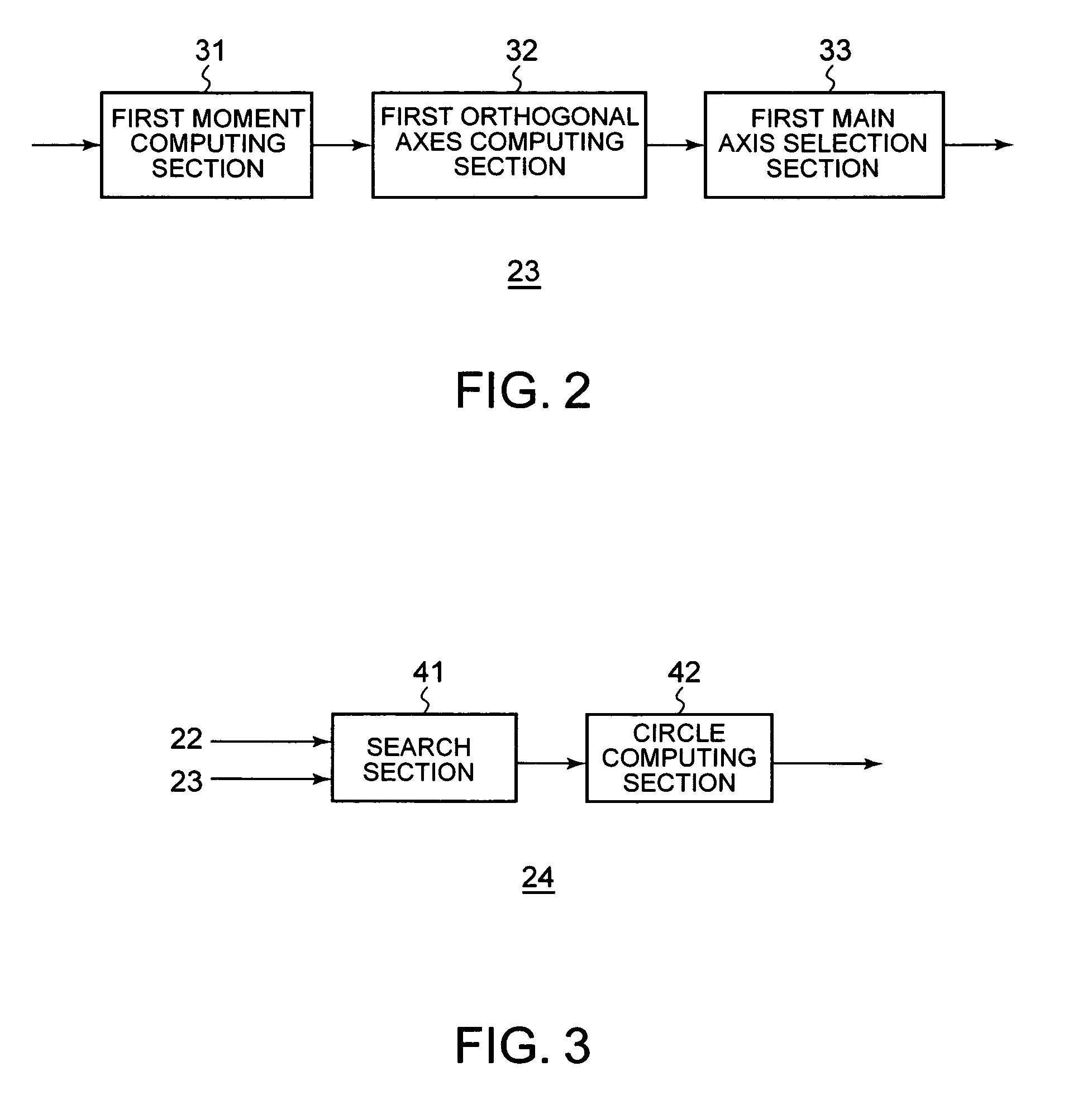
InactiveUS20070160293A1Appropriately appliedColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionEllipse
A head detecting apparatus, including a foreground extraction section for extracting a foreground region in which a person is captured from an input image; a first main axis computing section which includes a first moment computing section for computing a moment around a center of gravity of the foreground region and calculating a main axis of the foreground region based on the moment around the center of gravity of the foreground region; a head computing section for computing a head region included in the foreground region as a part thereof based on the main axis of the foreground region and a shape of the foreground region; and an ellipse determining section for determining an ellipse to be applied to a person's head based on a shape of the head region.
Owner:IBM CORP
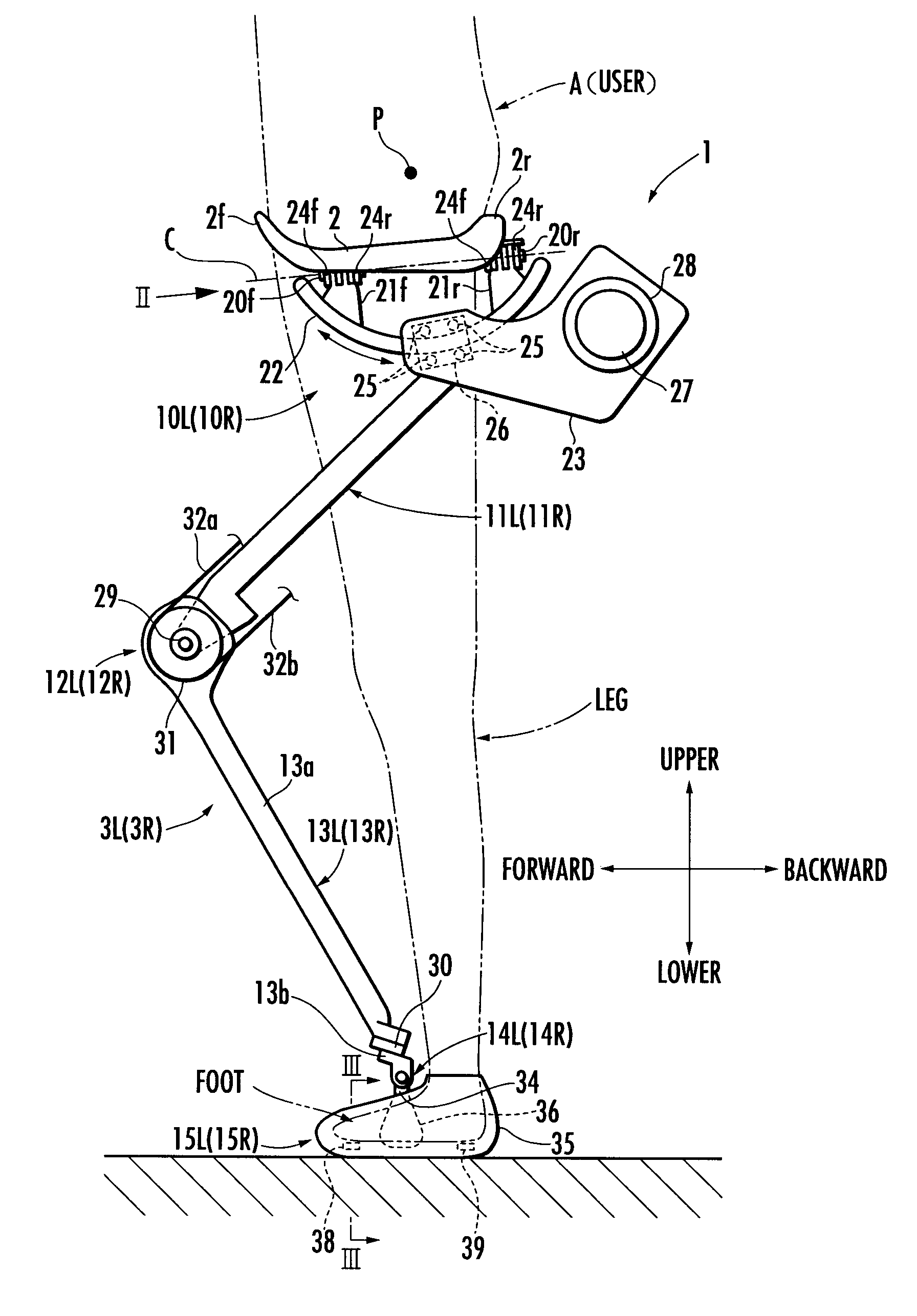
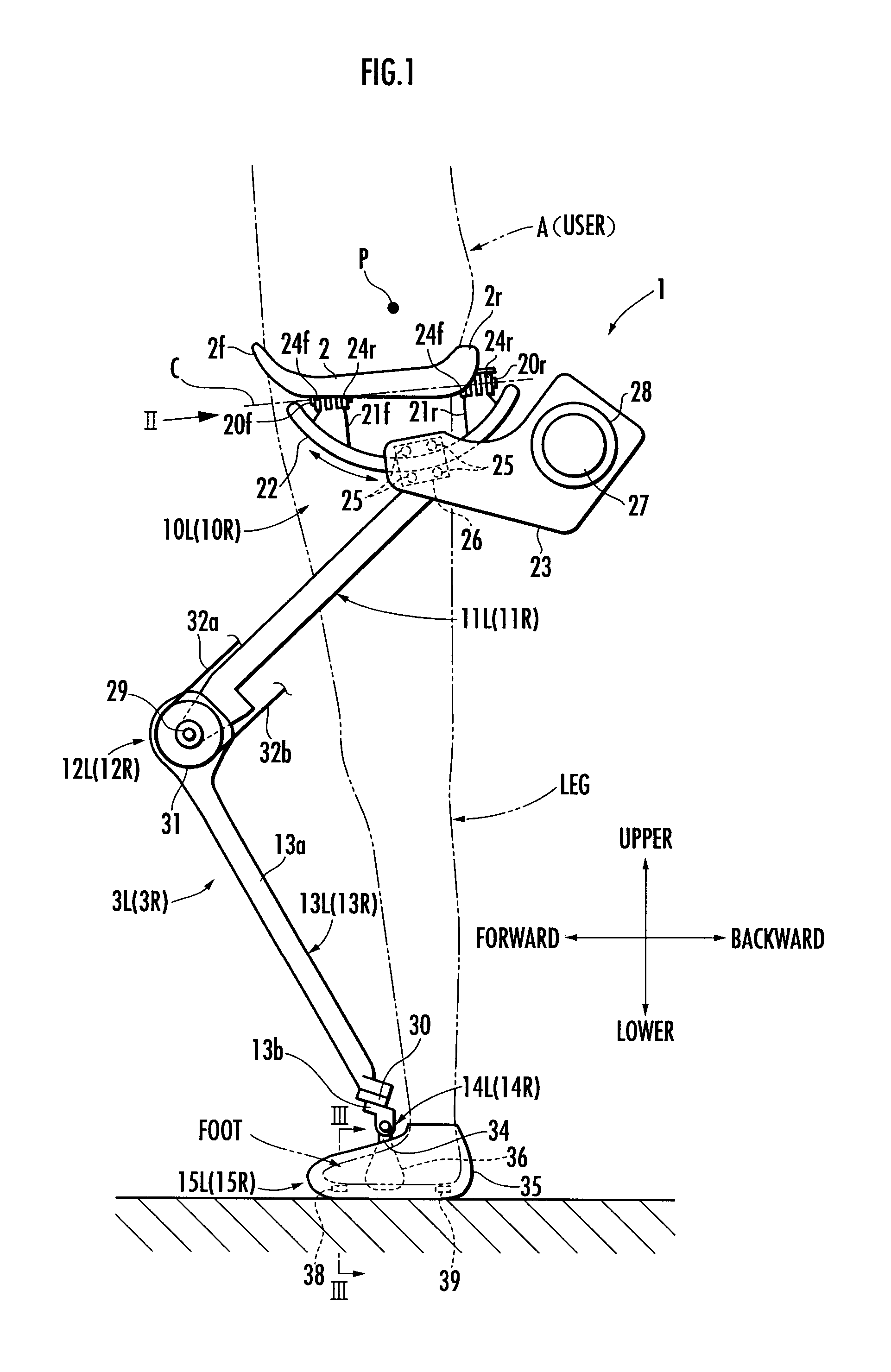
Controller for walking assistance device
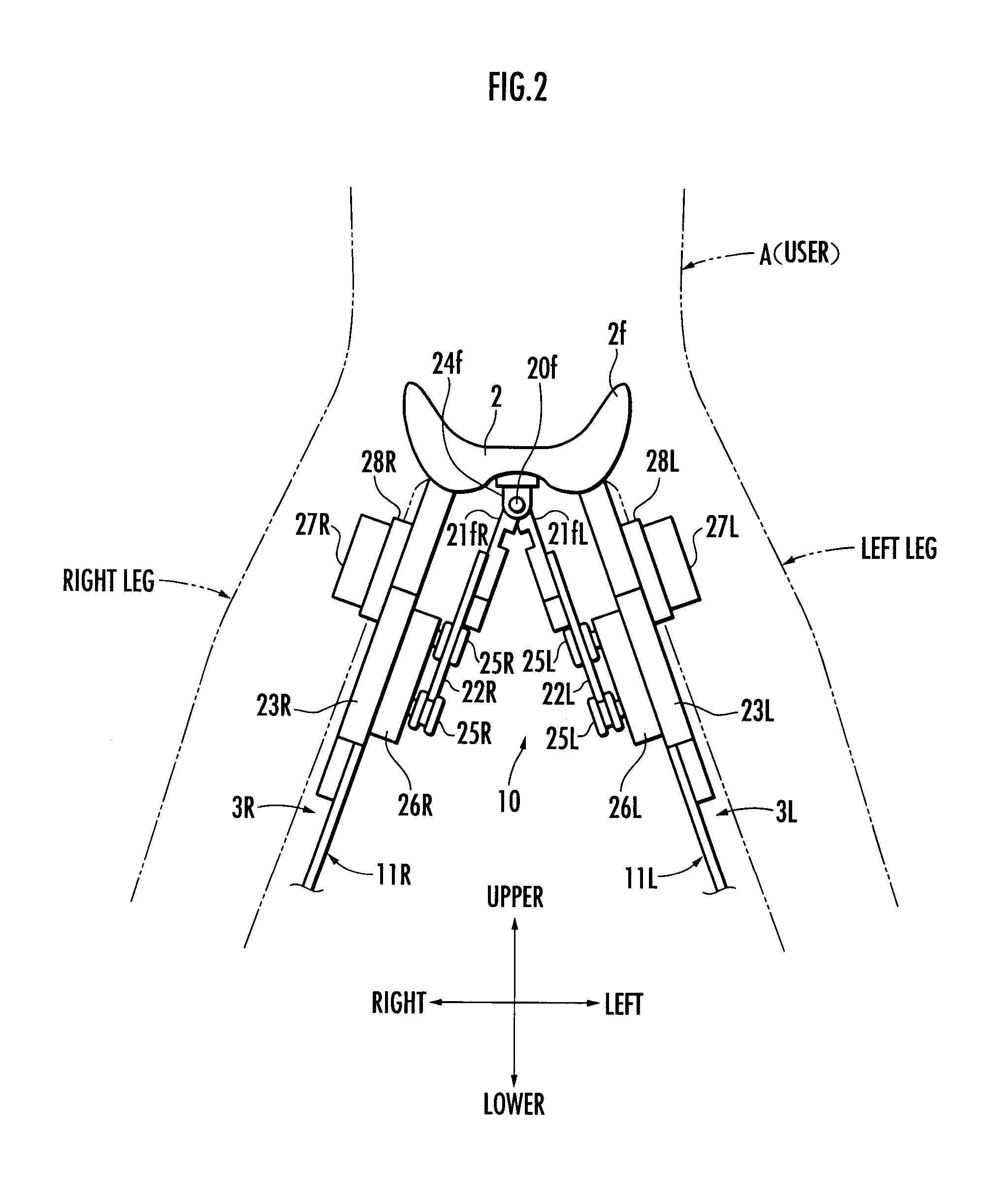
ActiveUS20090048686A1Reliable controlReduce loadProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesSagittal planeLine of action
A walking assistance device (1) has a receiving portion (2) which receives a part of the weight of a user (A) applied from above and a pair of left and right leg links (3R, 3L) connected to the receiving portion (2) through first joints (10R, 10L), with foot attachment portions (15R, 15L) at lower ends of the leg links (3R, 3L) attached to the feet of the legs of the user (A), respectively. The leg links (3R, 3L) are connected to the receiving portion (2) in such a way that, when each leg of the user (A) is a standing leg, a line of action of a supporting force transmitted from a third joint (14R, 14L) of the leg link (3R, 3L) to a crus frame (13R, 13L) out of the supporting force acting on the leg link (3R, 3L) from the floor side passes through a specific point (P) located upper than the receiving portion (2) within an anteroposterior width of a contact surface between the receiving portion (2) and the user (A) from the third joint (14R, 14L), viewed in the sagittal plane. Thereby, it is possible to stably apply a desired lifting force for reducing the weight to be borne by the user with his / her legs to the user.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Illumination Device Comprising A Phosphor Arrangement And A Laser
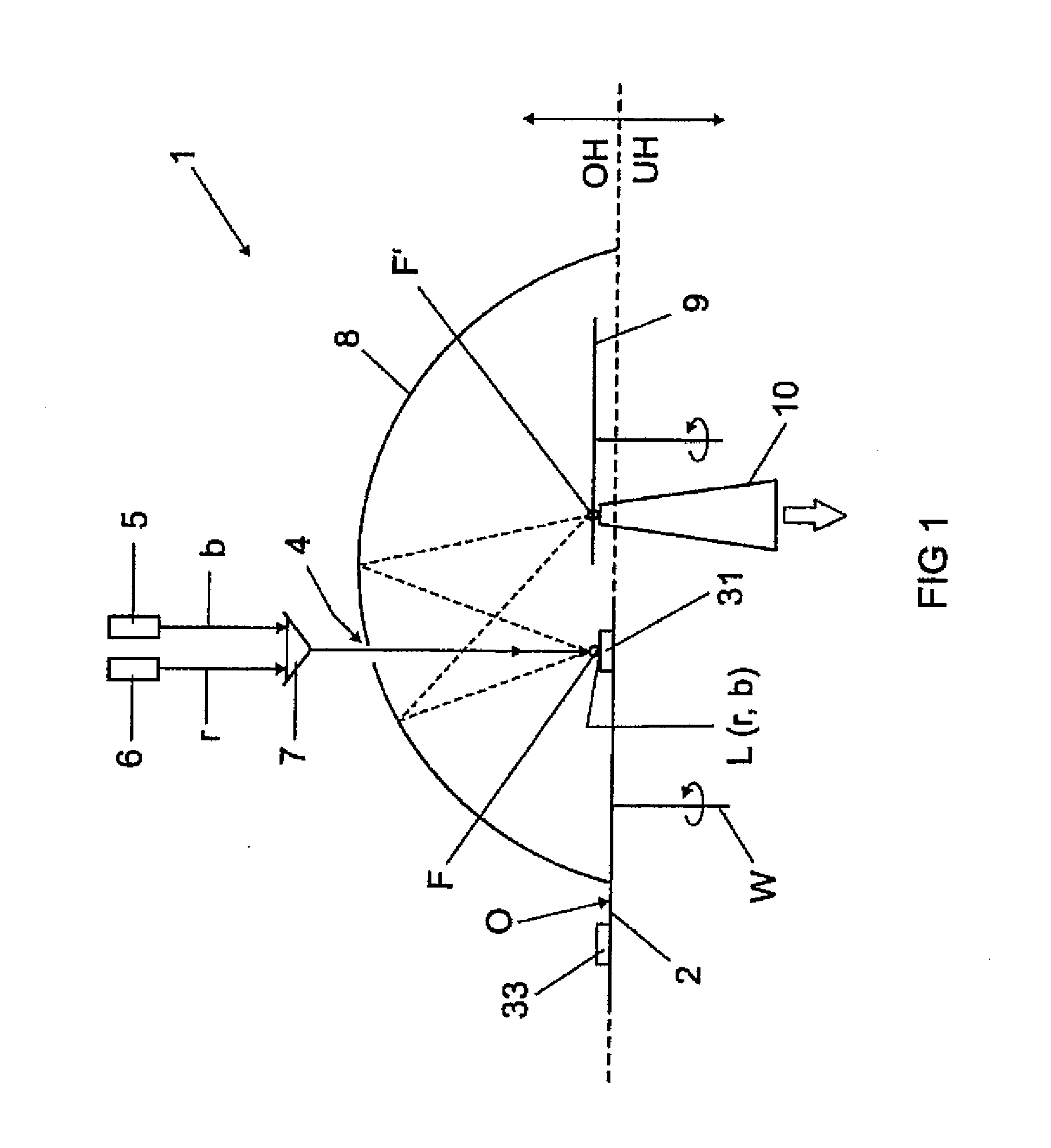
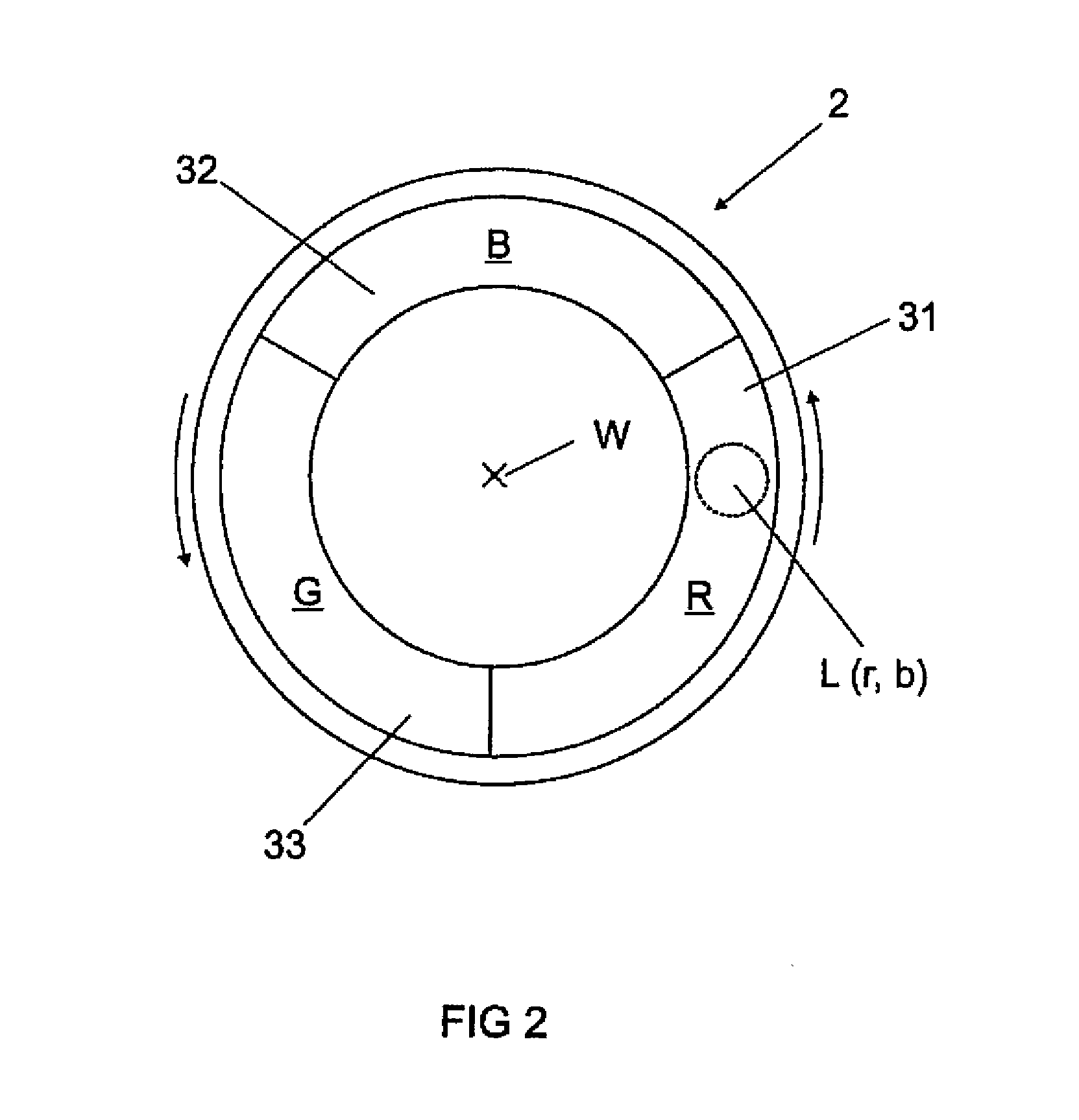
InactiveUS20150167907A1Increase luminous fluxIncrease brightnessLight source combinationsVehicle headlampsPhosphorEffect light
A lighting device comprising a phosphor arrangement (2) having a phosphor region; (31-33), a first laser (5) for irradiating a part of the phosphor region (31-33) with a first laser radiation; wherein the phosphor region (31-33) comprises at least one phosphor which can be irradiated by the first laser radiation and re-emits said first laser radiation at least partly in a manner wavelength-converted into colored light having a first light color; a second laser (6) configured for emitting a second laser radiation having a second light color, wherein the second light color of the second laser radiation is identical in color to the first light color of the wavelength-converted colored light; and wherein the lighting device is configured to simultaneously emit the second laser radiation and the wavelength-converted colored light of identical color emitted by the phosphor.
Owner:OSRAM GMBH
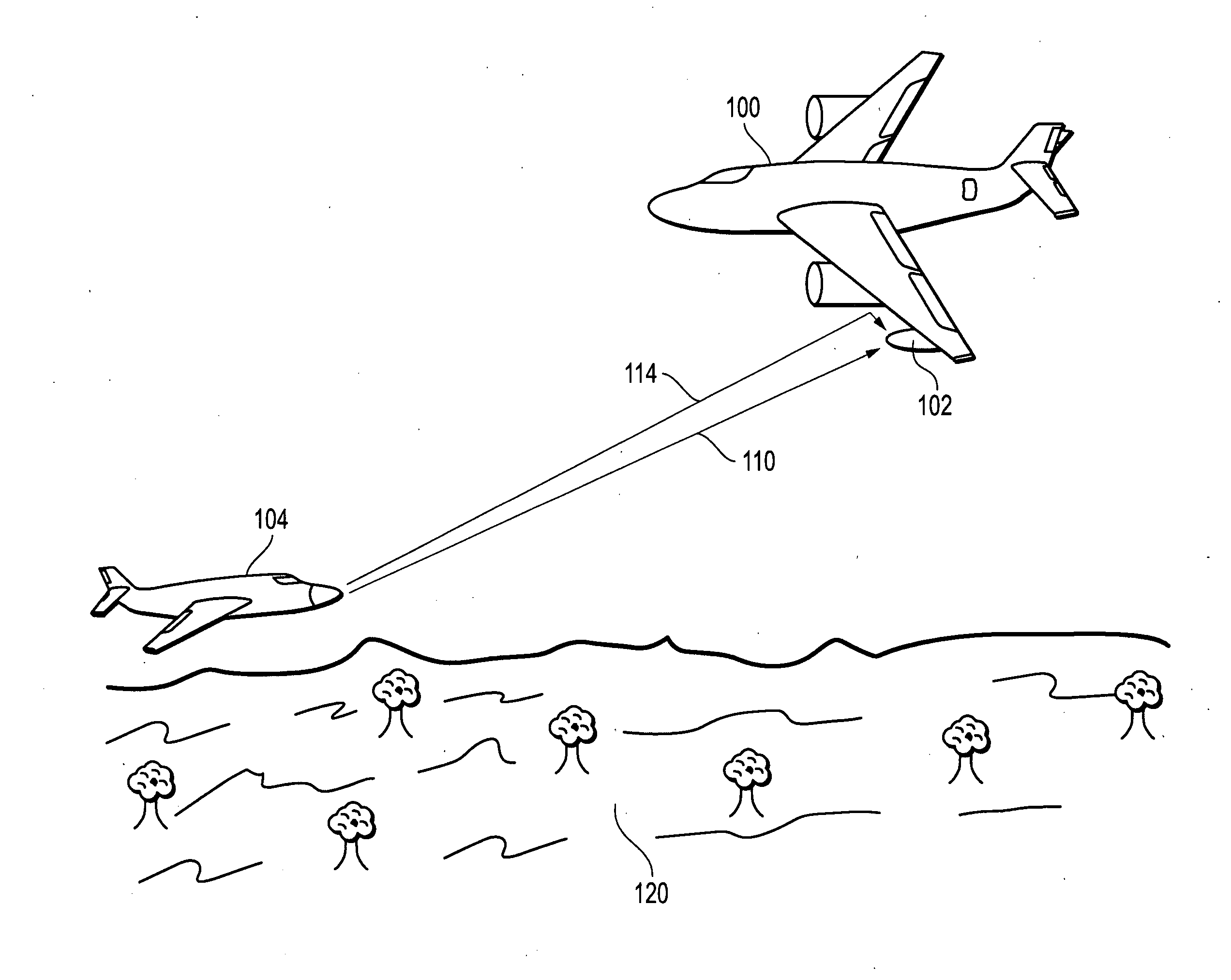
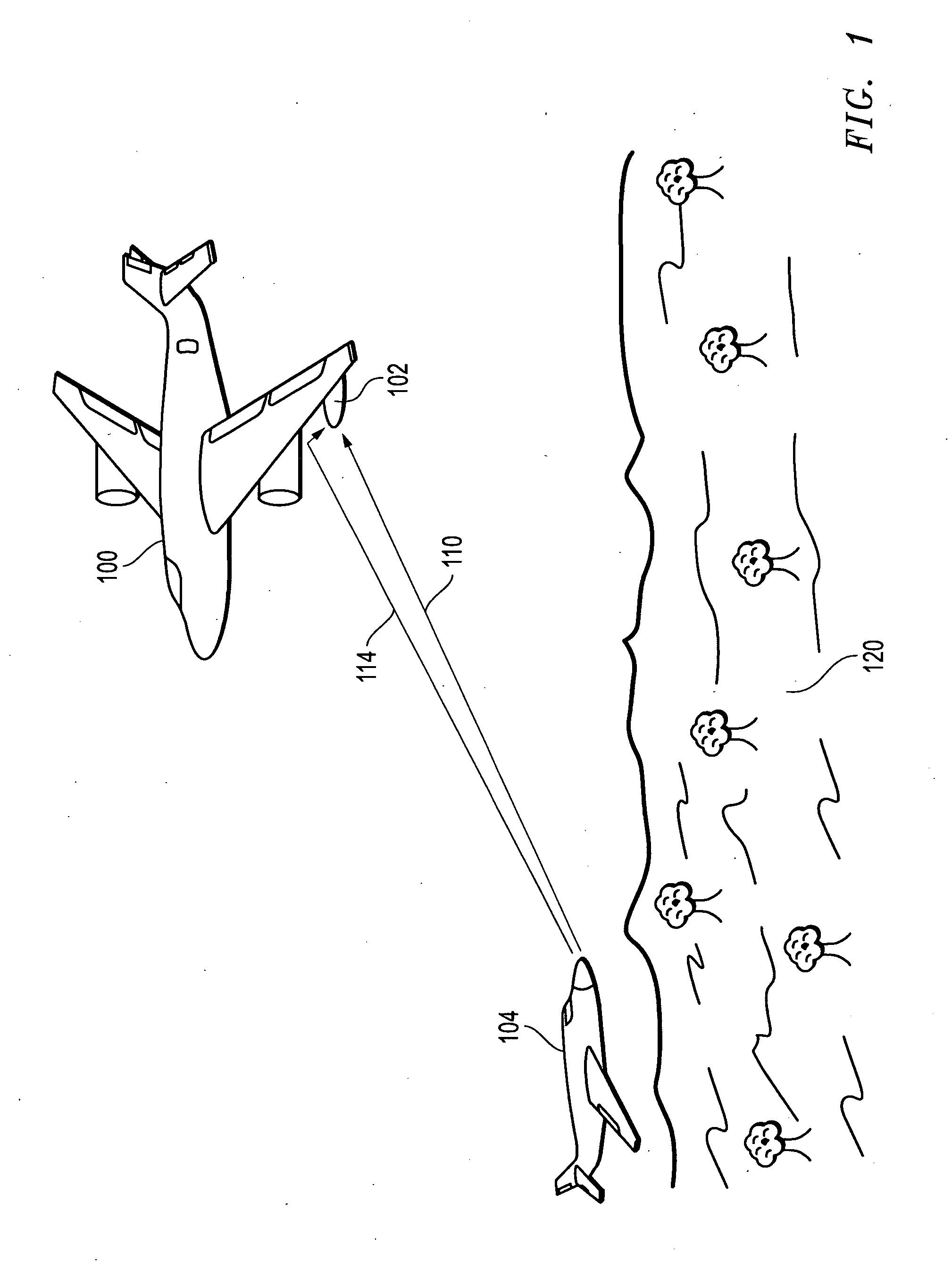
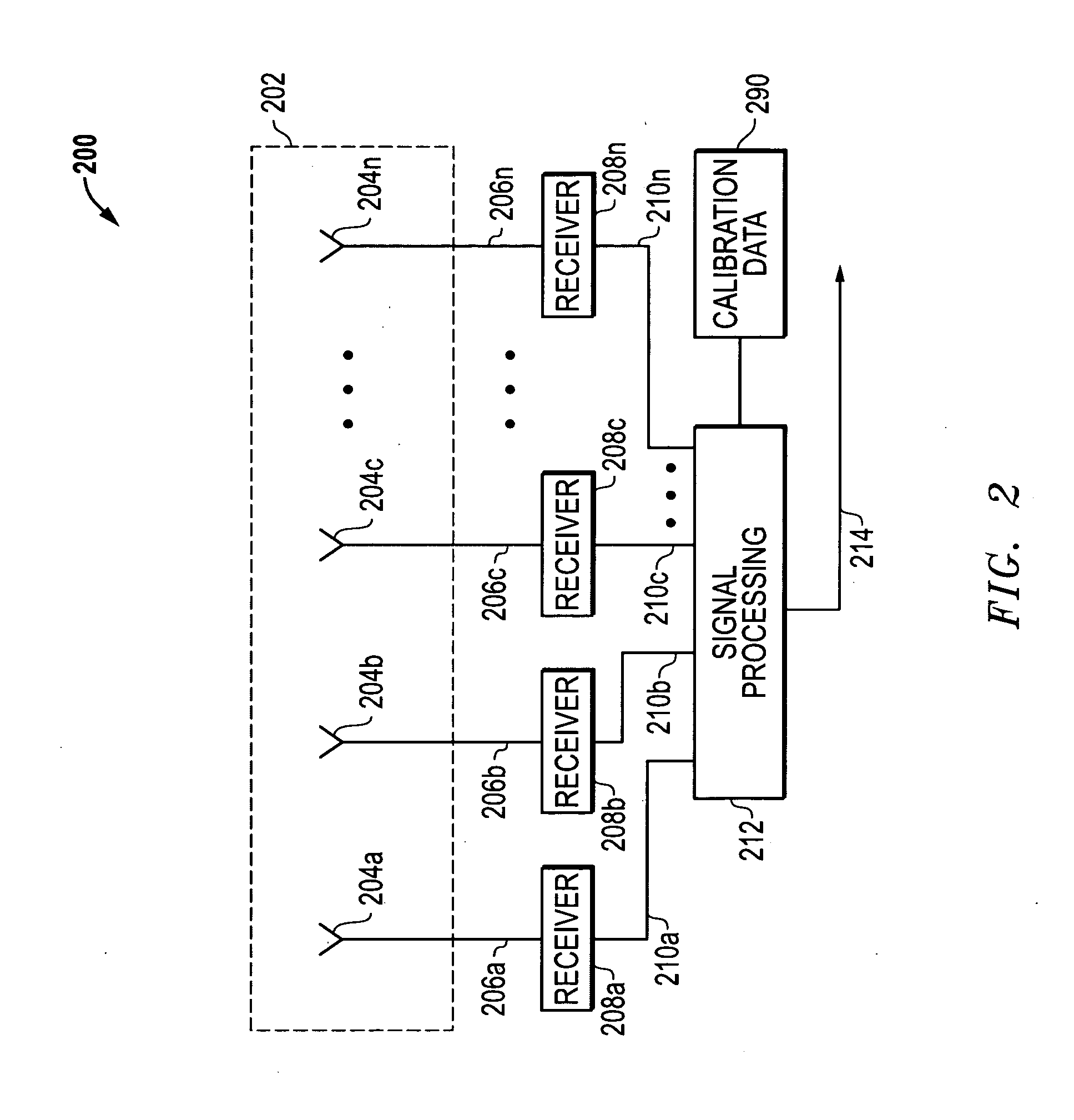
Systems and methods for resolving interferometric angle-of-arrival ambiguities due to local multipath reflections
InactiveUS20110260911A1Accelerated settlementReduce adverse effectsRadio wave finder detailsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHypothesisPhase difference
Interferometric angle-of-arrival (AOA) ambiguities due to local multipath reflections are resolved by measuring the received phase differences of one or more pairs of antenna elements of the interferometer array, constructing hypotheses from unwrapped phase pairs that correspond to potential AOA solutions, and selecting the hypothesis that most likely represents the true AOA of the signal emitter based on processed unwrapped data that has been corrected through the application of a priori calibration terms selected on the bases of the candidate hypotheses.
Owner:L 3 COMM INTEGRATED SYST
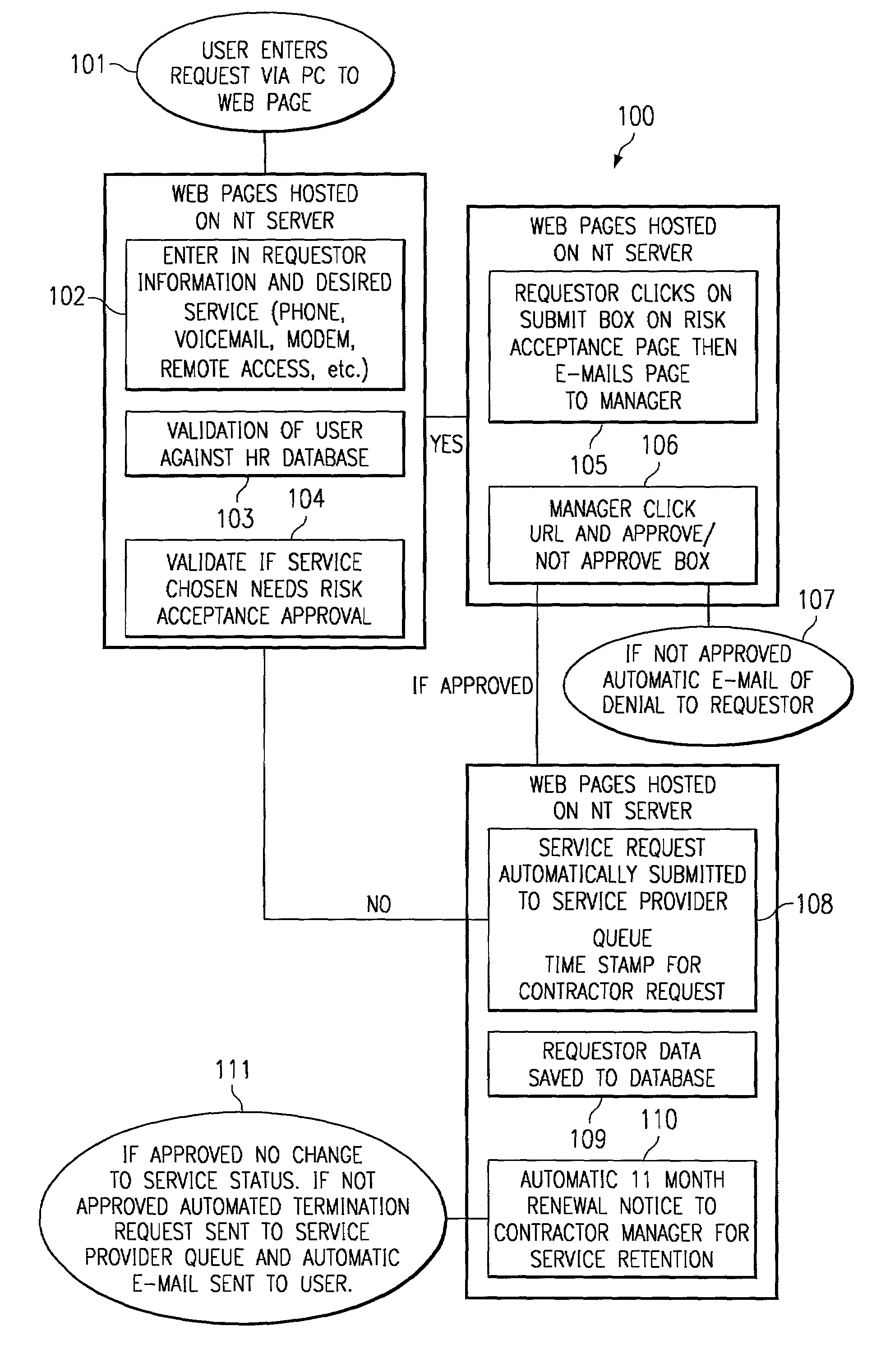
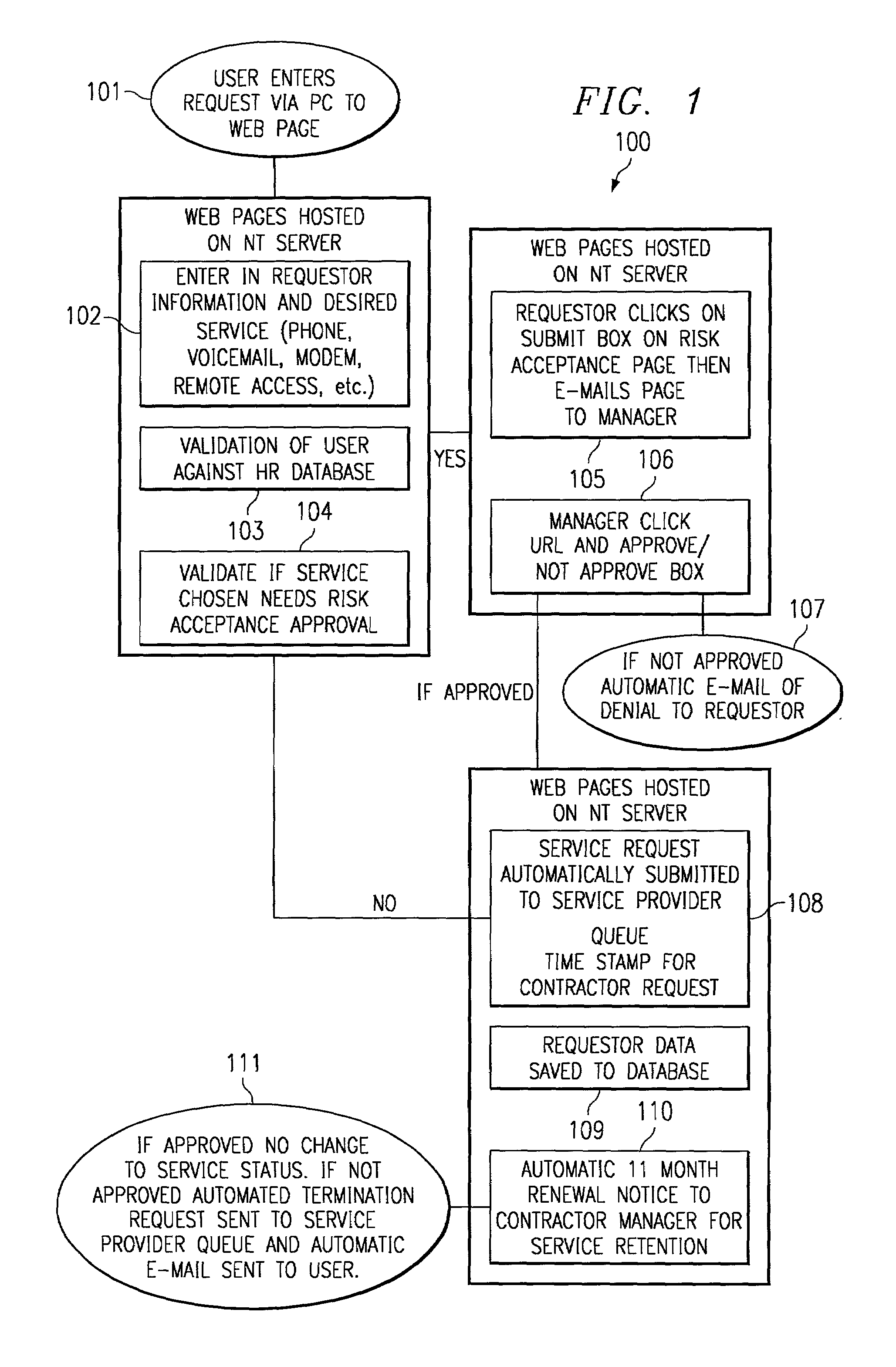
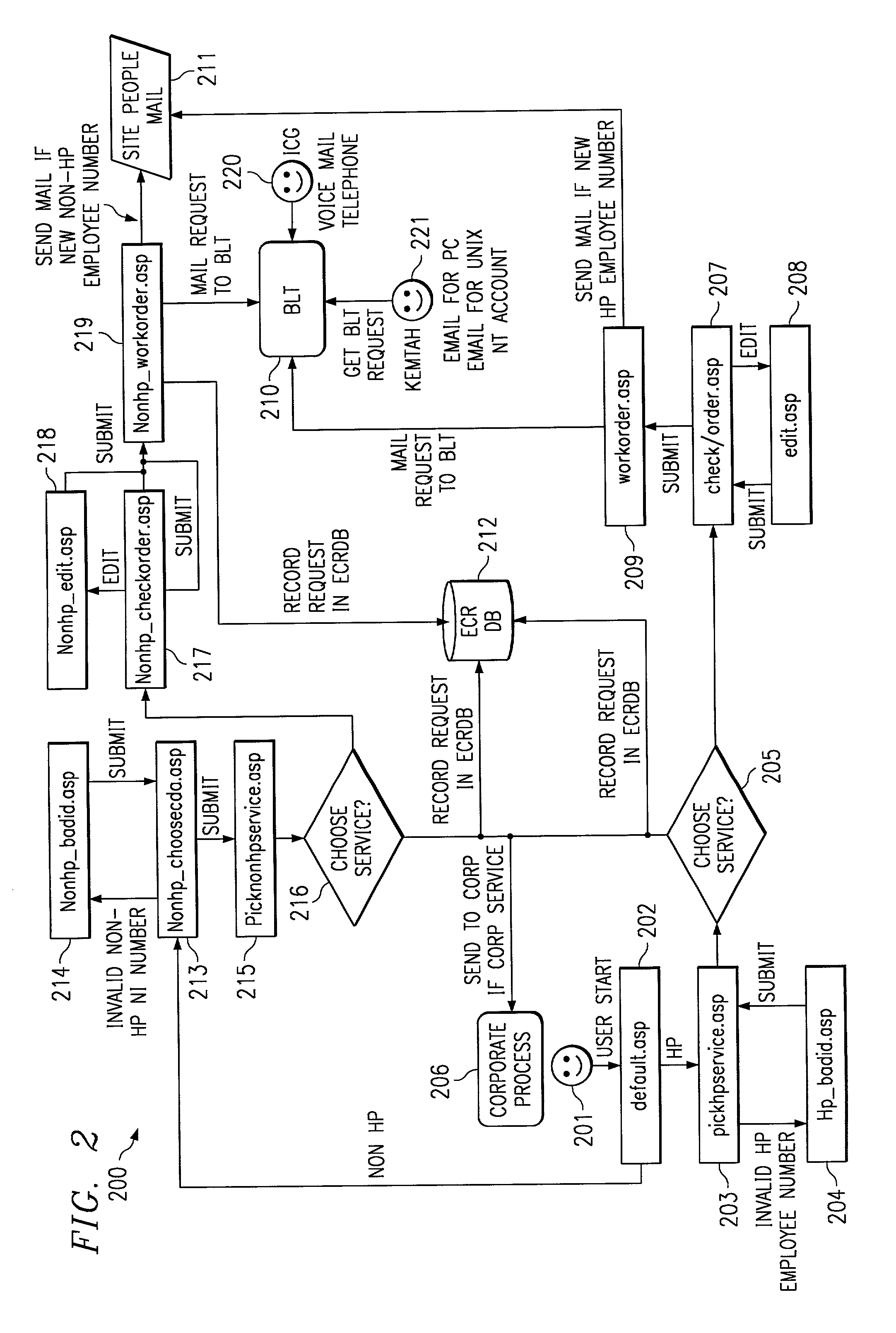
System and method for efficient processing of service requests
ActiveUS6941475B1Quality assuranceQuick changeFinanceDigital data processing detailsComputer networkLogistics management
A method and system for efficient processing of service requests requires a user to access the system and identify himself / herself. The user can then enter a request for a service. The identity and access to the requested service is then validated against an enterprise database. At this time, the need for risk acceptance approval is also carried out. If necessary, the user and manager are then queried for risk acceptance approval. If approved, the request is time-date stamped and forwarded to a service provider. User and request data are saved to a business logistics tracking database. If necessary, the user's manager is notified when renewal of the service is required, prior to expiration of the service. If the renewal is approved the service is then renewed.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP +1
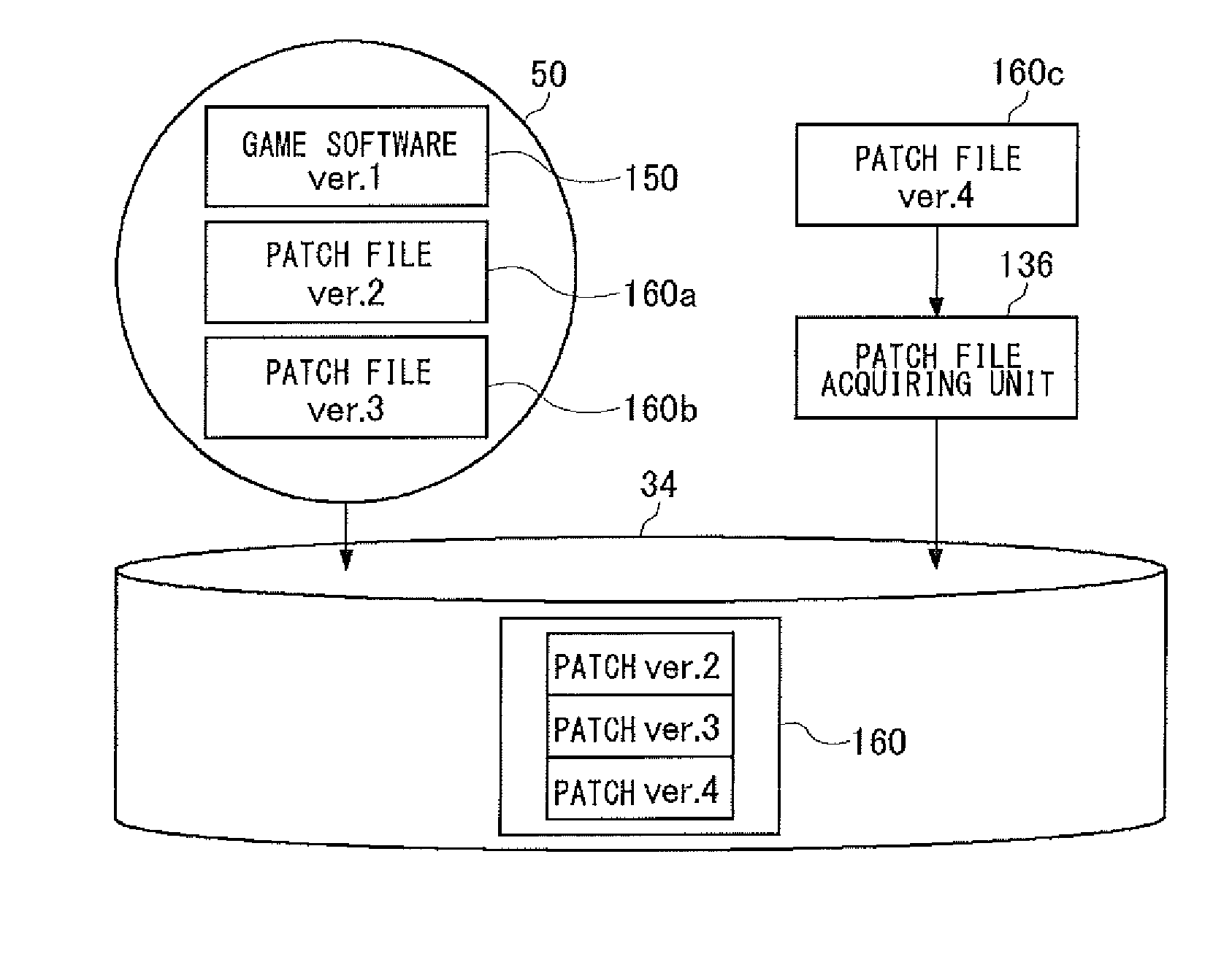
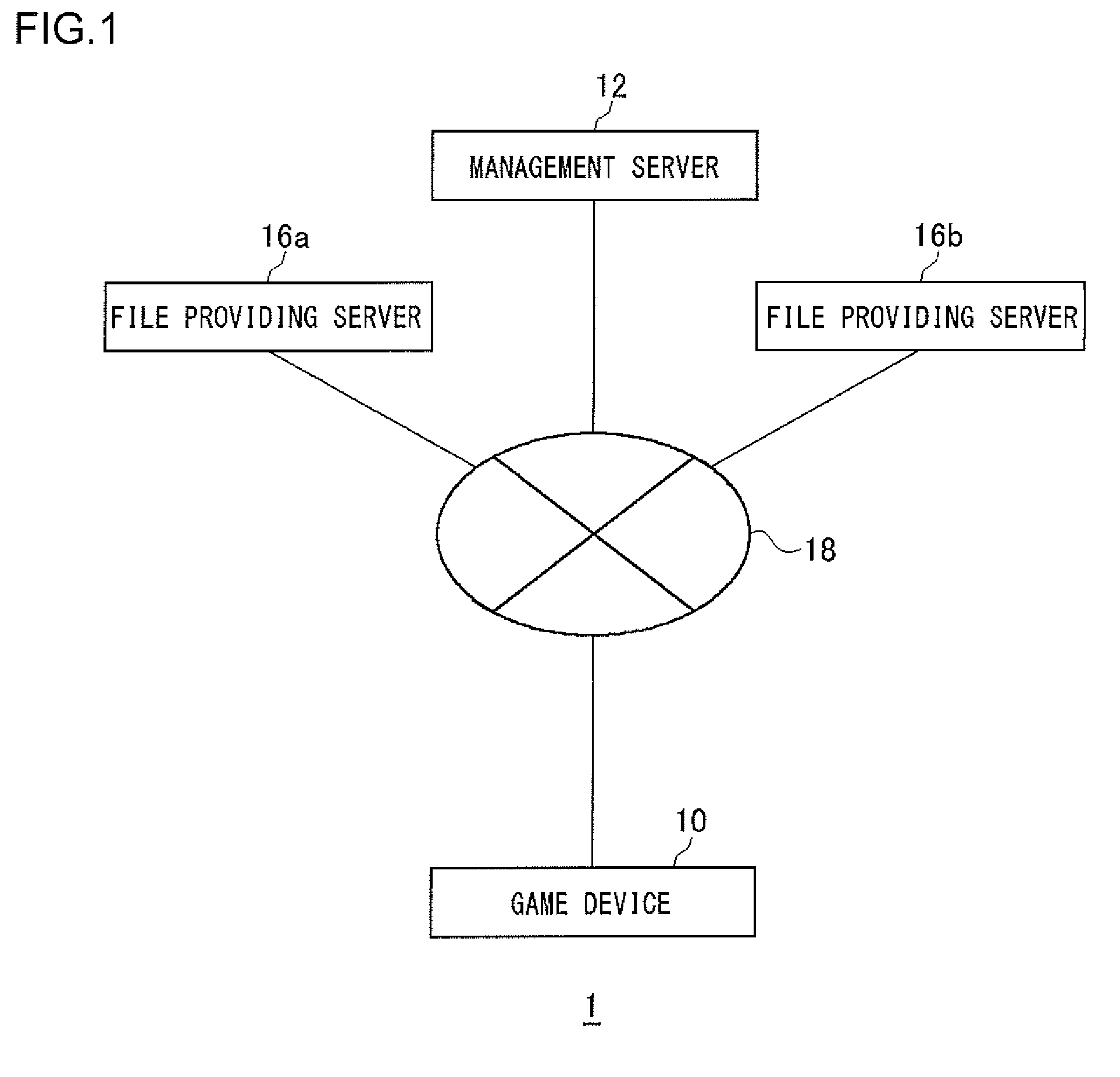
Information Processing Apparatus
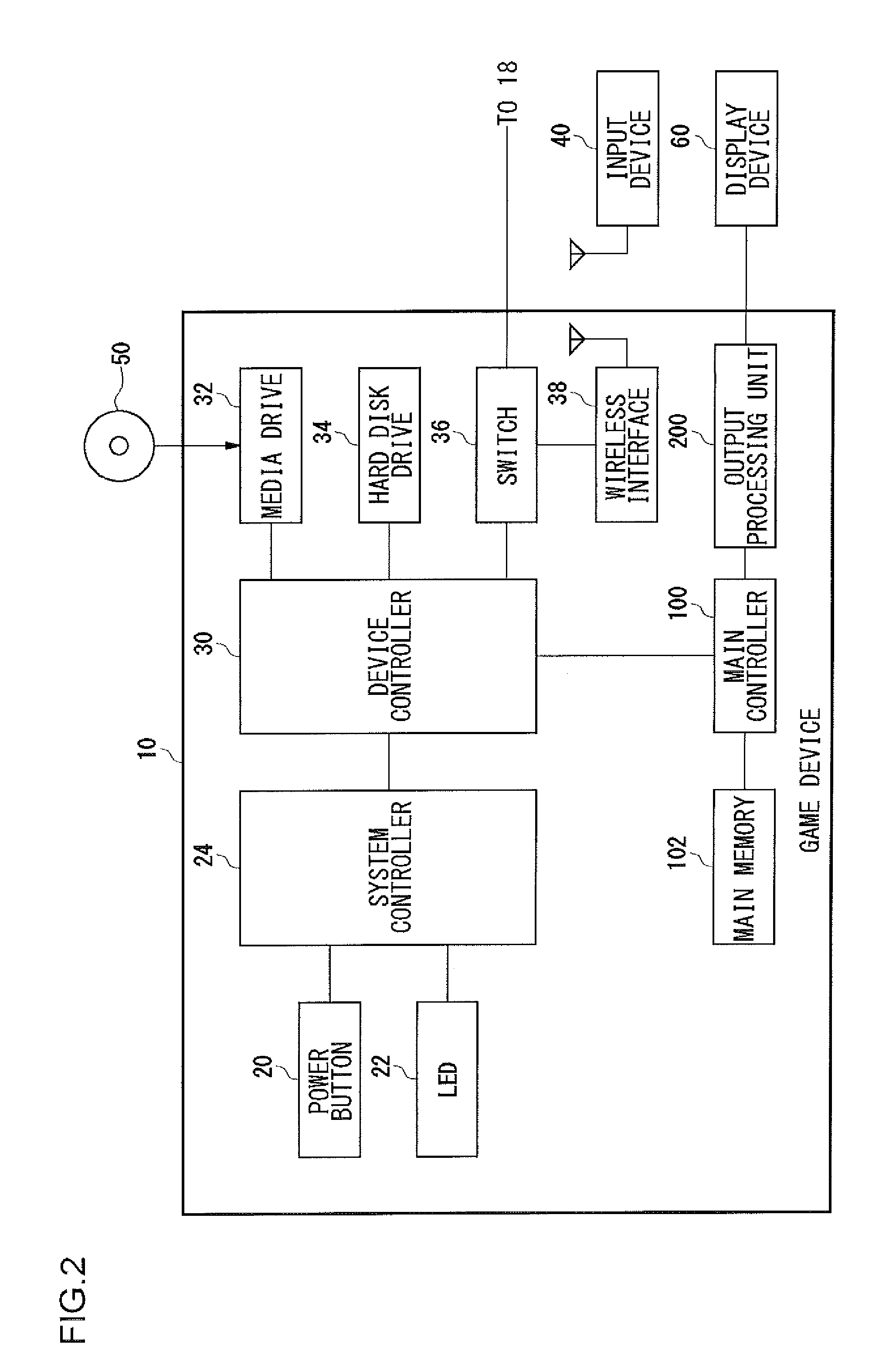
ActiveUS20110055821A1Appropriately appliedProgram loading/initiatingVideo gamesInformation processingApplication software
If a ROM medium is mounted on a media drive and a request for executing an application is received from an input device, a read controlling unit controls the media drive so that the media drive reads out a patch file from the ROM media and installs the patch file on a hard disk drive. After the patch file is installed, an execution processing unit applies the installed patch file and activates the game software.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Autoinjector
ActiveUS20100130930A1Eliminate riskCost-effectiveAutomatic syringesIntravenous devicesAutoinjectorBiomedical engineering
An autoinjector comprising an outer housing in which is mounted a syringe, the autoinjector further comprising an inner housing intermediate the outer housing and the syringe and an energy source in communication with said inner housing, wherein the inner housing is moveable by the energy source between three positions, namely a first position in. which the inner housing is in communication with the barrel such that, in use, the plunger and barrel are moveable axially so as to move at least part of said needle out of the outer housing; a second position in which the inner housing is in communication with the plunger but not the barrel such that, in use, said plunger is moveable axially into said barrel so as to expel medicament through the needle; and a third position in which the inner housing is in communication with neither the plunger nor the barrel such that, in use, the plunger and barrel are able to retract in order to retract the needle into the outer housing, characterised in that the plunger includes biasing means for axially biasing the barrel, before activation of the energy source, to a position forward of the part of the inner housing which acts on the barrel in said first position.
Owner:SHL MEDICAL AG
Wide range fluid leak detector and flow meter
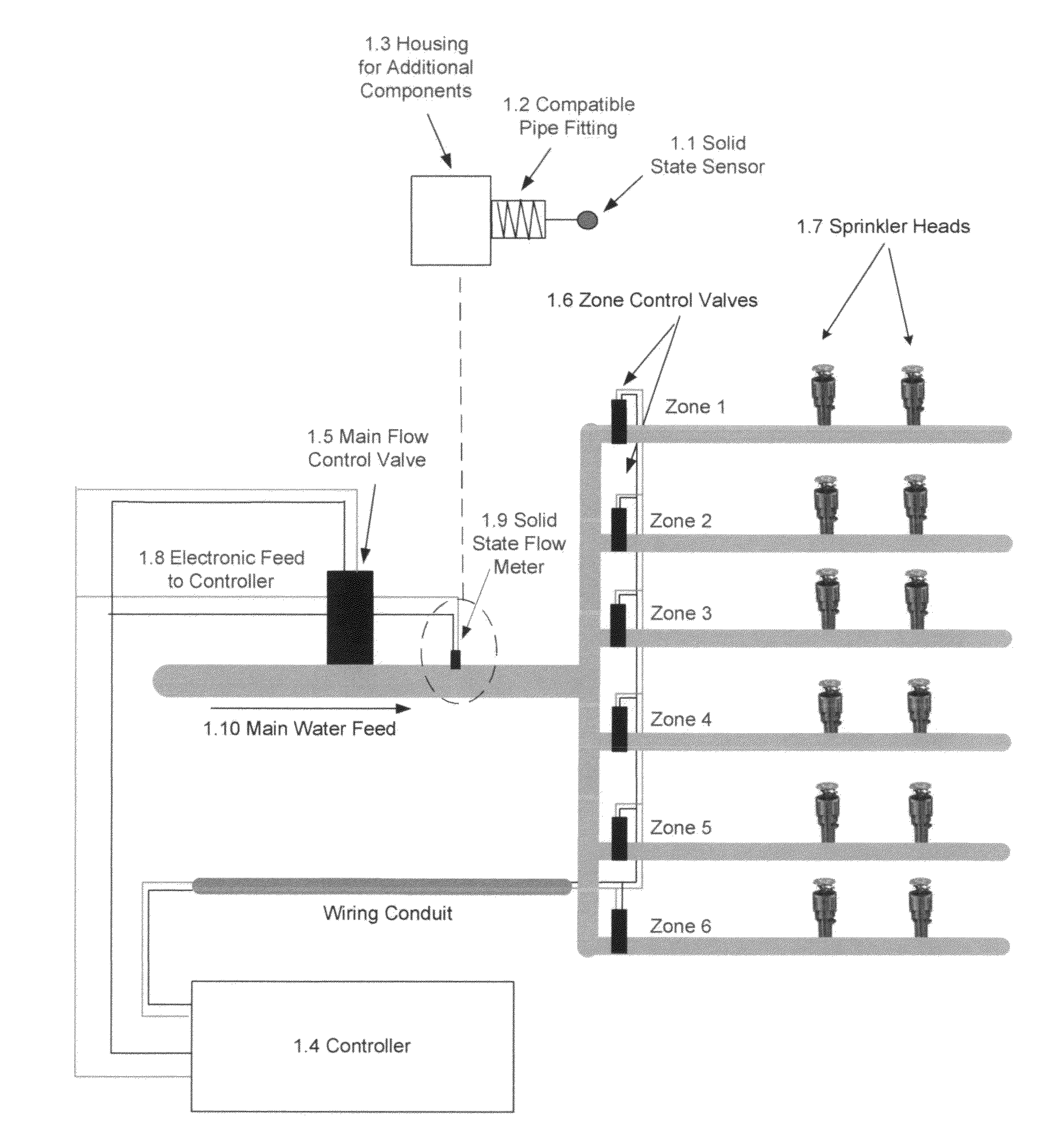
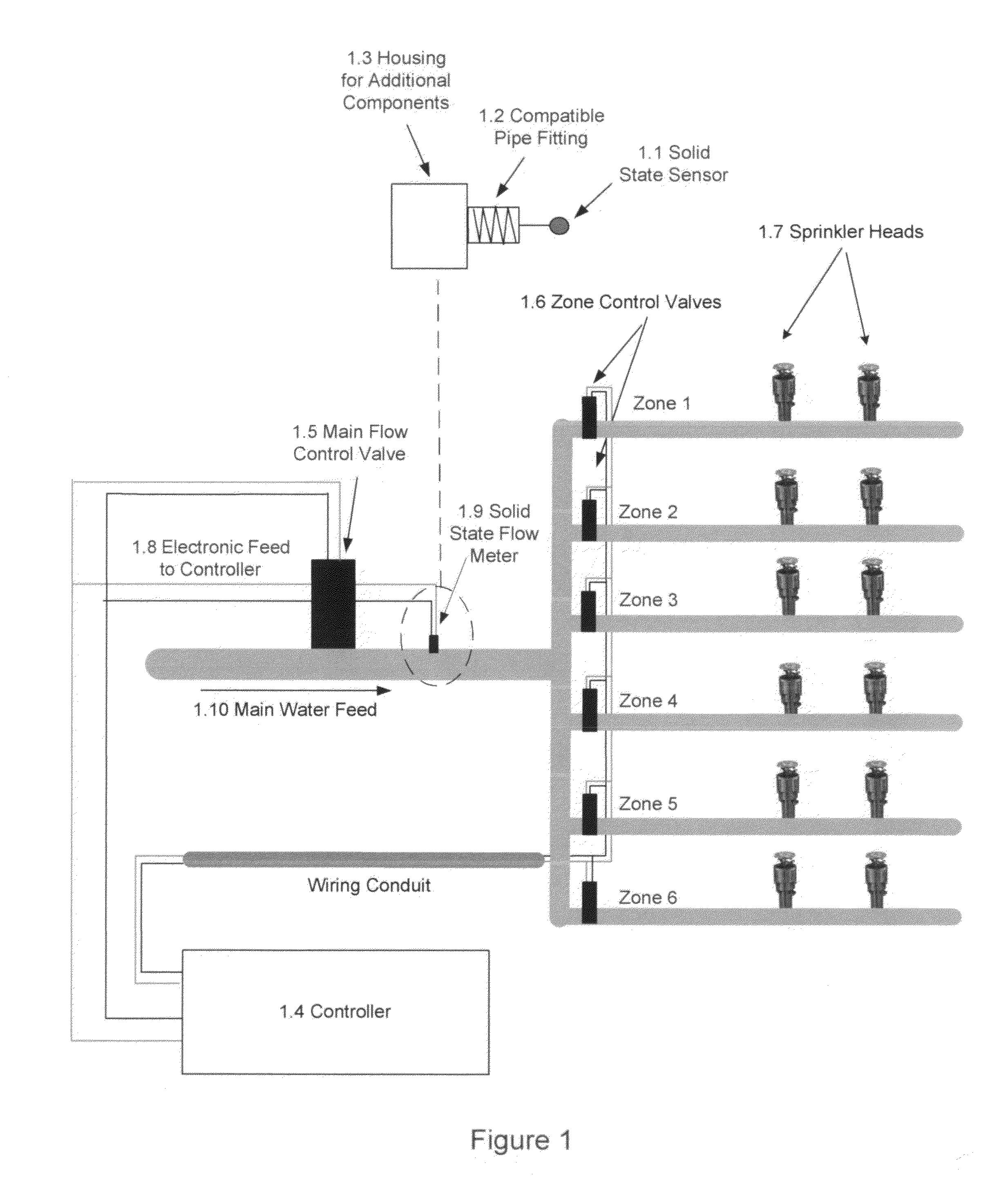
InactiveUS20110302995A1Low costReduce wasteDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateCost sensitiveNarrow range
A flowmeter is provided with a solid-state sensor technology for increasing the accuracy and efficiency of fluid flow monitoring and leak detection in the irrigation industry and other cost-sensitive flow-critical applications. The device can monitor and detect usage of fluids such as water more accurately and economically than presently possible to help eliminate waste and ensure correct billing. Measurement can be over an optimized narrow range or can be automatically switched to cover consecutive ranges from leakage to gross fluid conduit faults. With its minimal component count, ease of assembly, independence from the specifics of its housing, low maintenance needs, and its interchangeability this device can serve a wide range of metering needs from low end leak monitoring to standard flow measurement.
Owner:LEBEAU LAWRENCE W +1
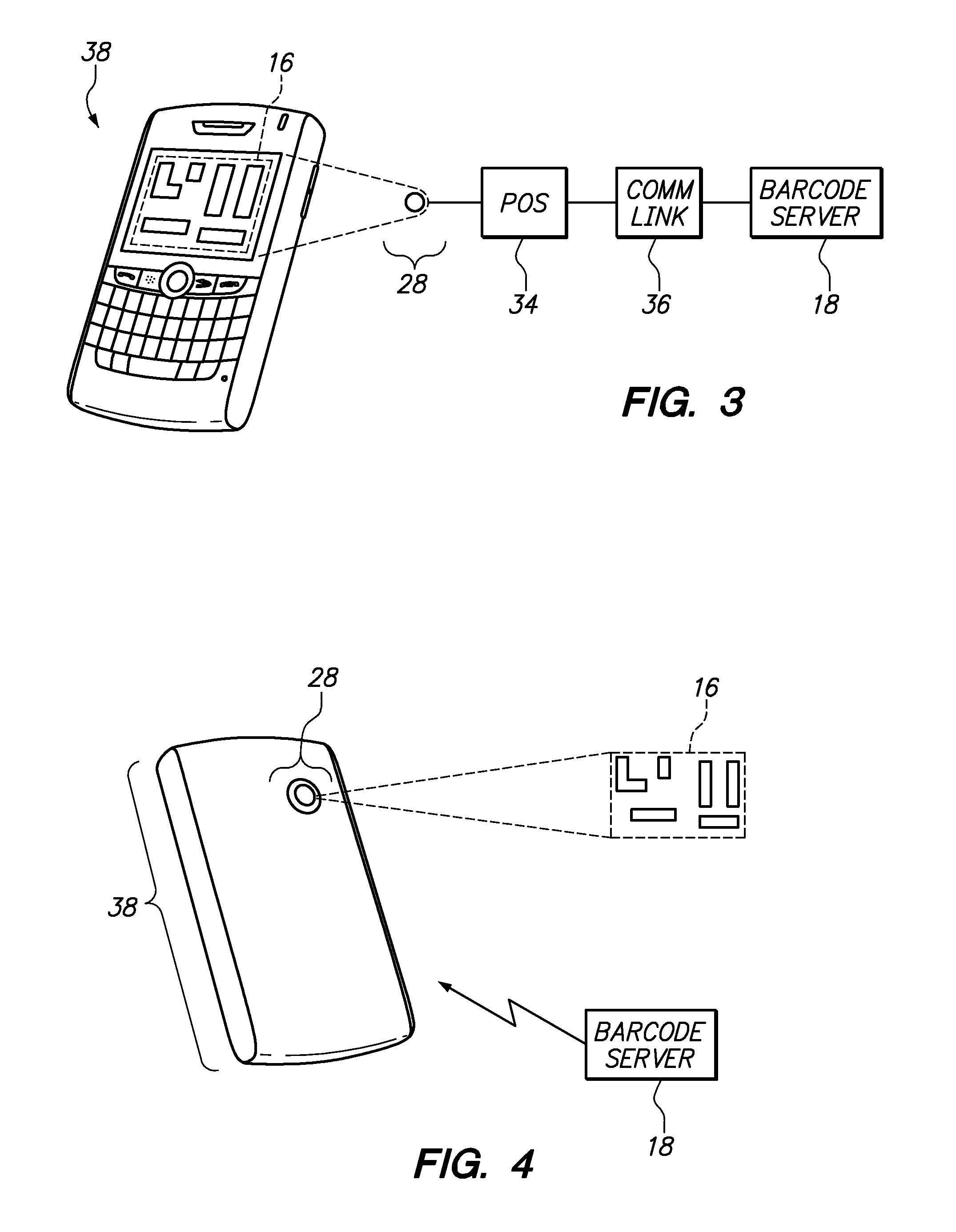
Online barcode directory and systems for facilitating transactions utilizing the same
InactiveUS20110226850A1Facilitate a rewards programAppropriately appliedInput/output for user-computer interactionPayment architectureElectronic systemsPassword
An online directory of people, businesses and products which is accessible by a user is described herein. Each person, business or product may be associated with a unique visual identifier such as a barcode which facilitates transactions between the parties. Moreover, the barcode may be an electronic barcode which can be displayed on a user's phone and scanned by a camera of the other party's electronic system. It is contemplated that the electronic barcode may be displayed only after entering a password on the user's mobile phone.
Owner:UNGOS JAY +1
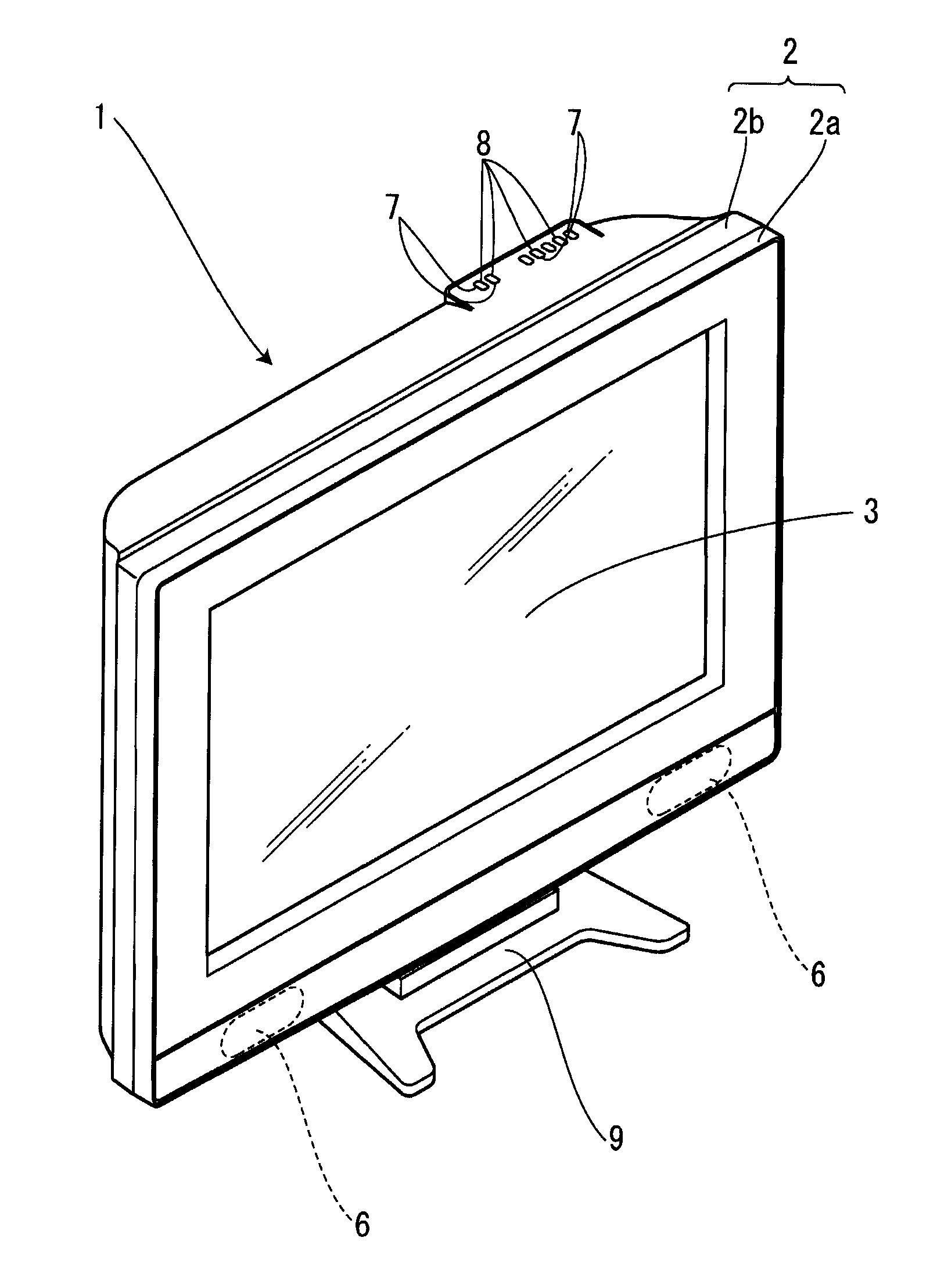
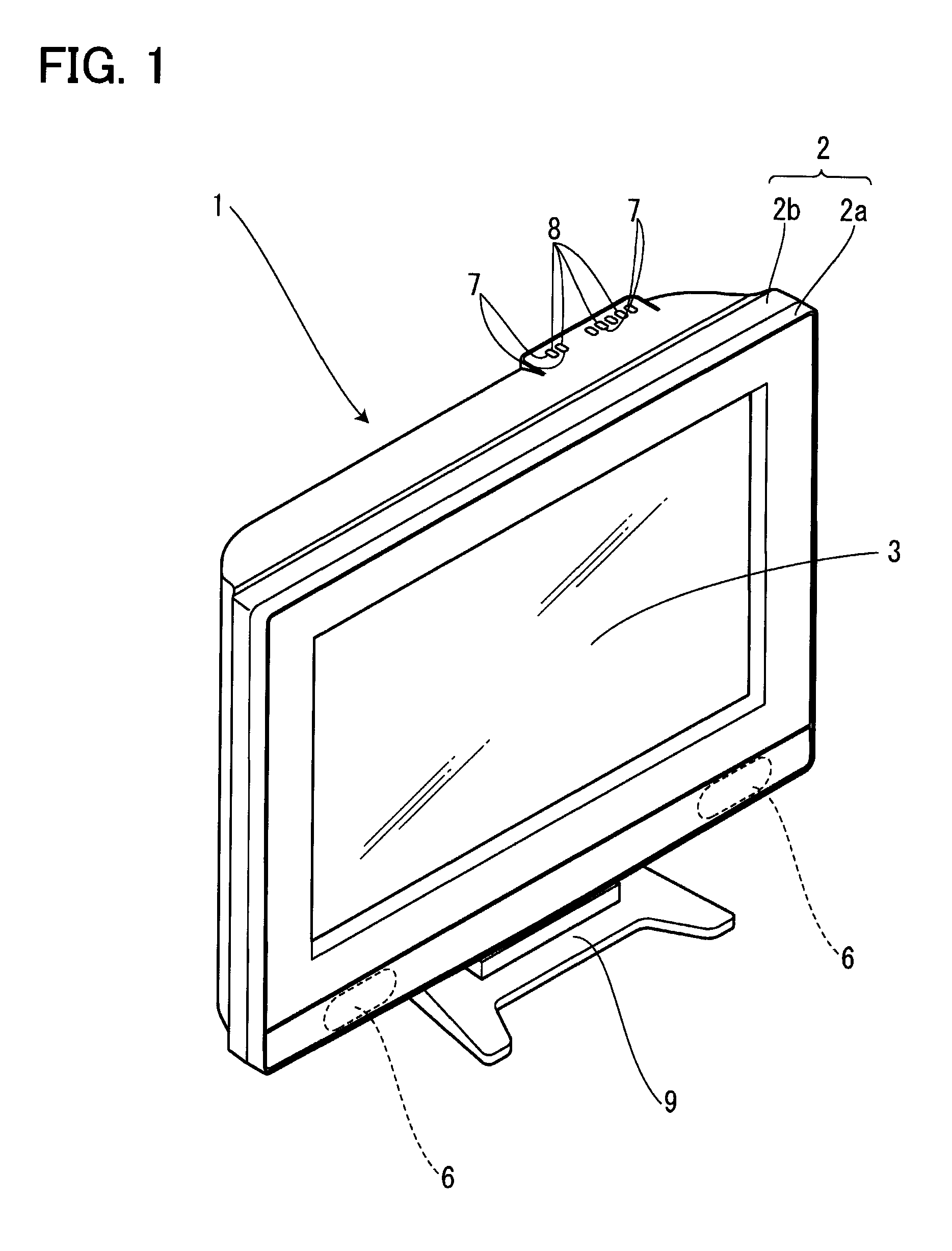
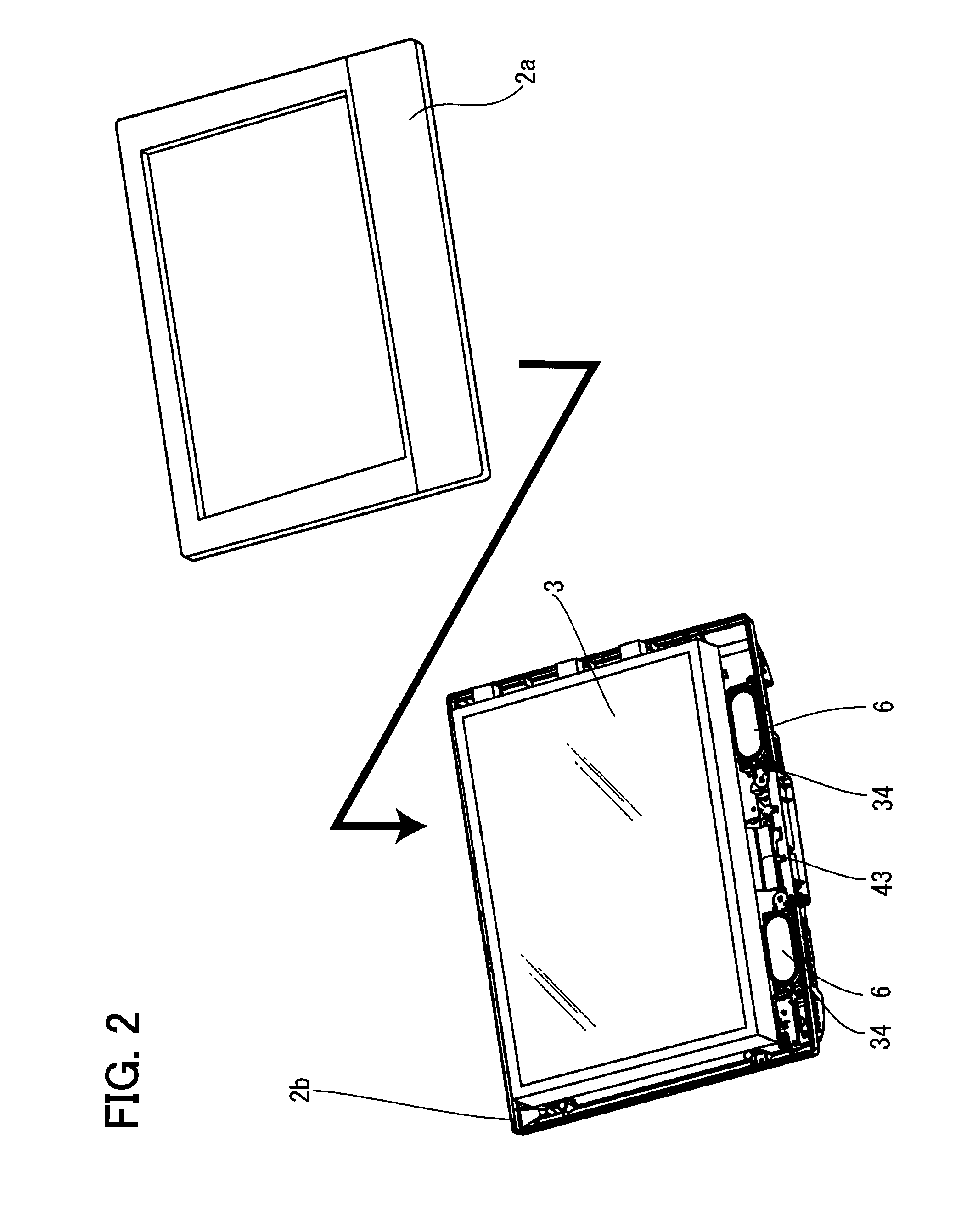
Display device
InactiveUS20090168321A1Facilitates product inspection and maintenanceAppropriately appliedTelevision system detailsMagnetic/electric field screeningProduct inspectionDisplay device
The present invention provides a display device that facilitates product inspection and maintenance. A button section is mounted to a back cabinet, and a power-source circuit board is fitted into a circuit-board fitting slit. Furthermore, the power-source circuit board is locked and fixed by a first circuit-board locking claw, and a main circuit board is locked and fixed by a second circuit-board locking claw. A speaker integrally assembled in a speaker holder is locked and fixed by a speaker locking claw, and thereafter a display panel is caused to be held by a display panel standing holding portion in a standing manner. The wire connection work of a display panel, each of the circuit boards, and the like is performed, the display panel is brought down and placed on a display panel placement portion, a front cabinet is mounted, and a leg portion is mounted to a leg-portion mounting portion.
Owner:ORION ELECTRIC CO LTD
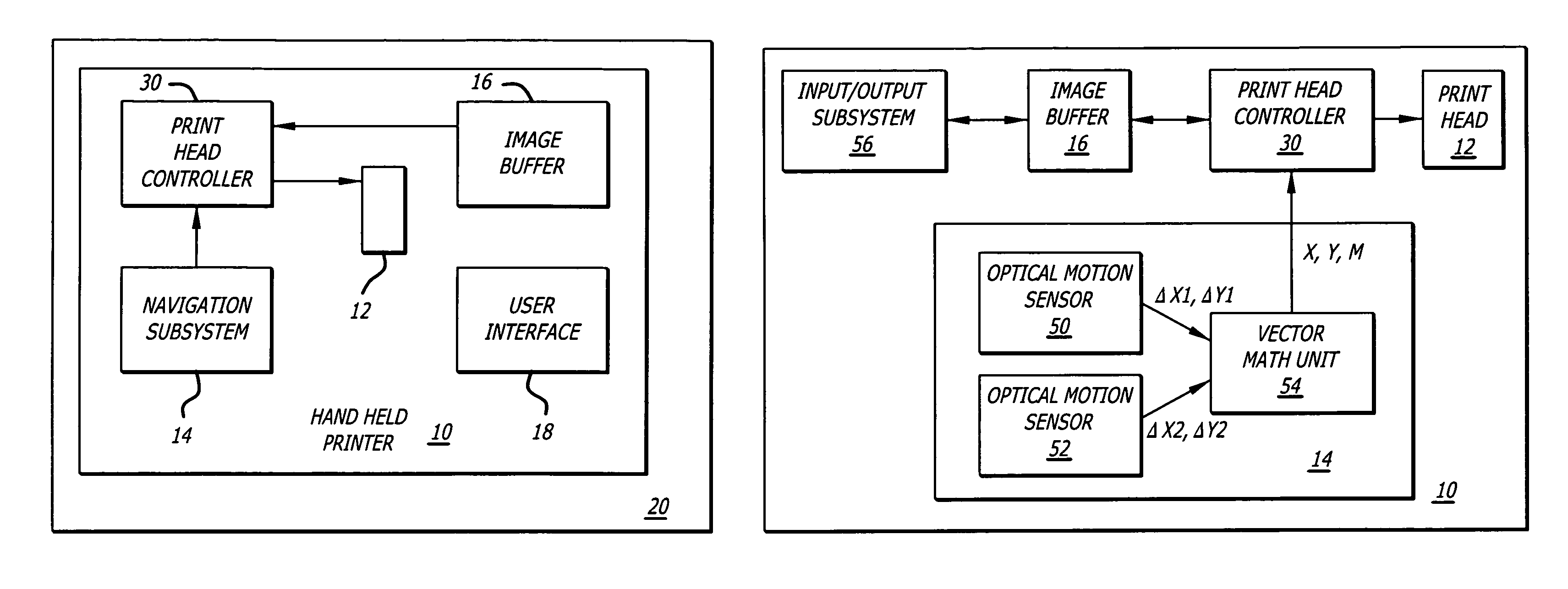
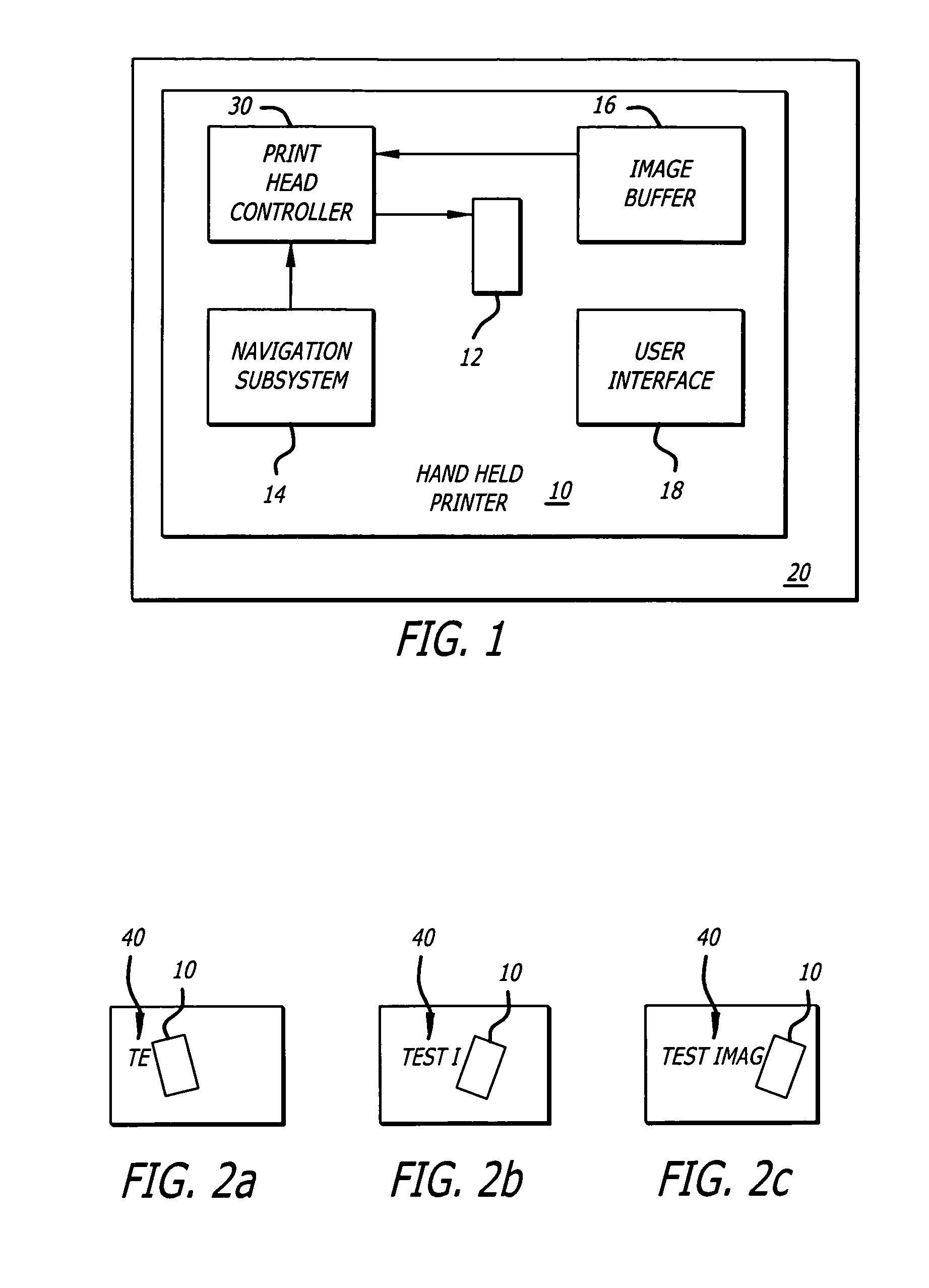
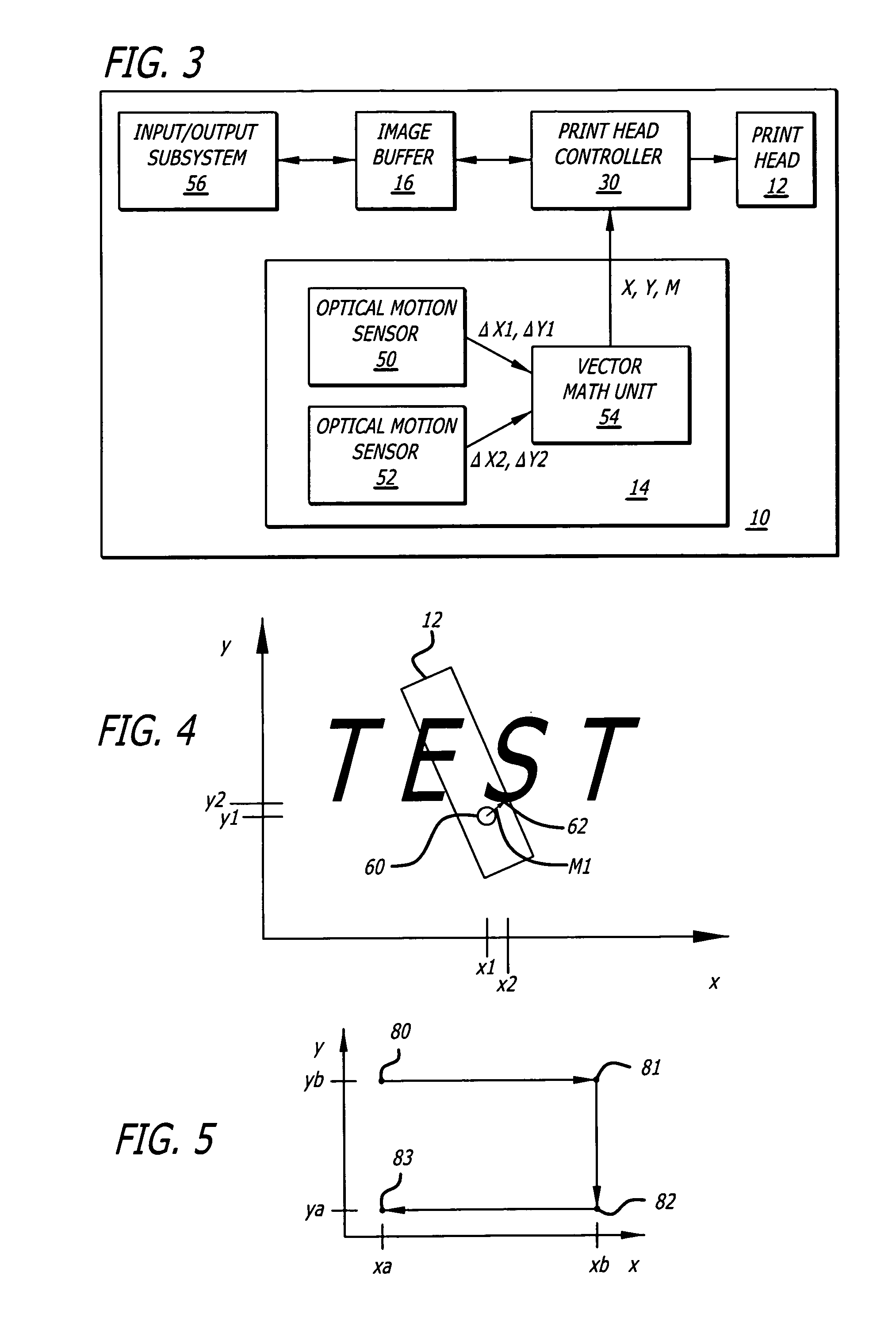
Handheld printer
A handheld printer that provides an appropriate application of ink to a print medium without a bulky and complex mechanical system for positioning a print head with respect to the print medium. A handheld printer according to the present teachings includes a navigation subsystem that tracks a motion of the handheld printer with respect to a printing surface and a print head controller that causes a print head to fire ink drops onto the printing surface in response to the motion and in response to an image contained in an image buffer.
Owner:MARVELL INT TECH
Bacillus coagulans strains and their applications in l-lactic acid production
ActiveUS20130143286A1High level of lactic acid production abilityLow costBacteriaFermentationXyloseIndustrial waste
The invention is concerned with the strains of B. coagulans for lactic acid production and the related methods, in which the carbon sources are pentose or hexose or the agricultural or industrial wastes containing pentose or hexose or a mixture of both. According to the invention, the highest amount of L-lactic acid produced from glucose is 173 g / L, the optical purity is over 99%, the yield is up to 0.98, and the productivity is up to 2.4 g / L per hour. The highest amount of L-lactic acid produced from xylose is 195 g / L, the optical purity is over 99%, the yield is up to 0.98, and the productivity is up to 2.7 g / L per hour. The highest amount of L-lactic acid produced from reducing sugars in xylitol byproducts is 106 g / L, the optical purity is over 99%, and the productivity is up to 2.08 g / L per hour. The B. coagulans strains XZL4 (DSM No. 23183) and XZL9 (DSM No. 23184) of the invention can directly utilize various reducing sugars in xylitol byproducts to produce high amounts of L-lactic acid, which improves the production efficiency at low costs, and the strains are, thus, appropriate for industrial productions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Head detecting apparatus, head detecting method, and head detecting program
InactiveUS7450737B2Appropriately appliedColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionEllipse
A head detecting apparatus, including a foreground extraction section for extracting a foreground region in which a person is captured from an input image; a first main axis computing section which includes a first moment computing section for computing a moment around a center of gravity of the foreground region and calculating a main axis of the foreground region based on the moment around the center of gravity of the foreground region; a head computing section for computing a head region included in the foreground region as a part thereof based on the main axis of the foreground region and a shape of the foreground region; and an ellipse determining section for determining an ellipse to be applied to a person's head based on a shape of the head region.
Owner:IBM CORP
Pediatric adapter for transillumination
ActiveUS7841751B2Improve abilitiesAppropriately appliedMechanical apparatusDiagnostics using lightPediatric patientTransillumination
Owner:MULANI NIZAR A
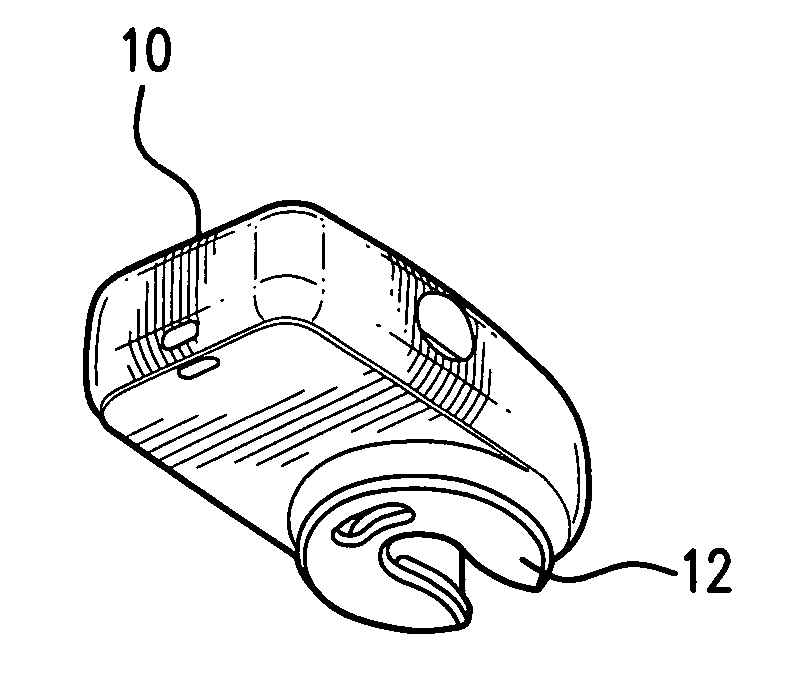
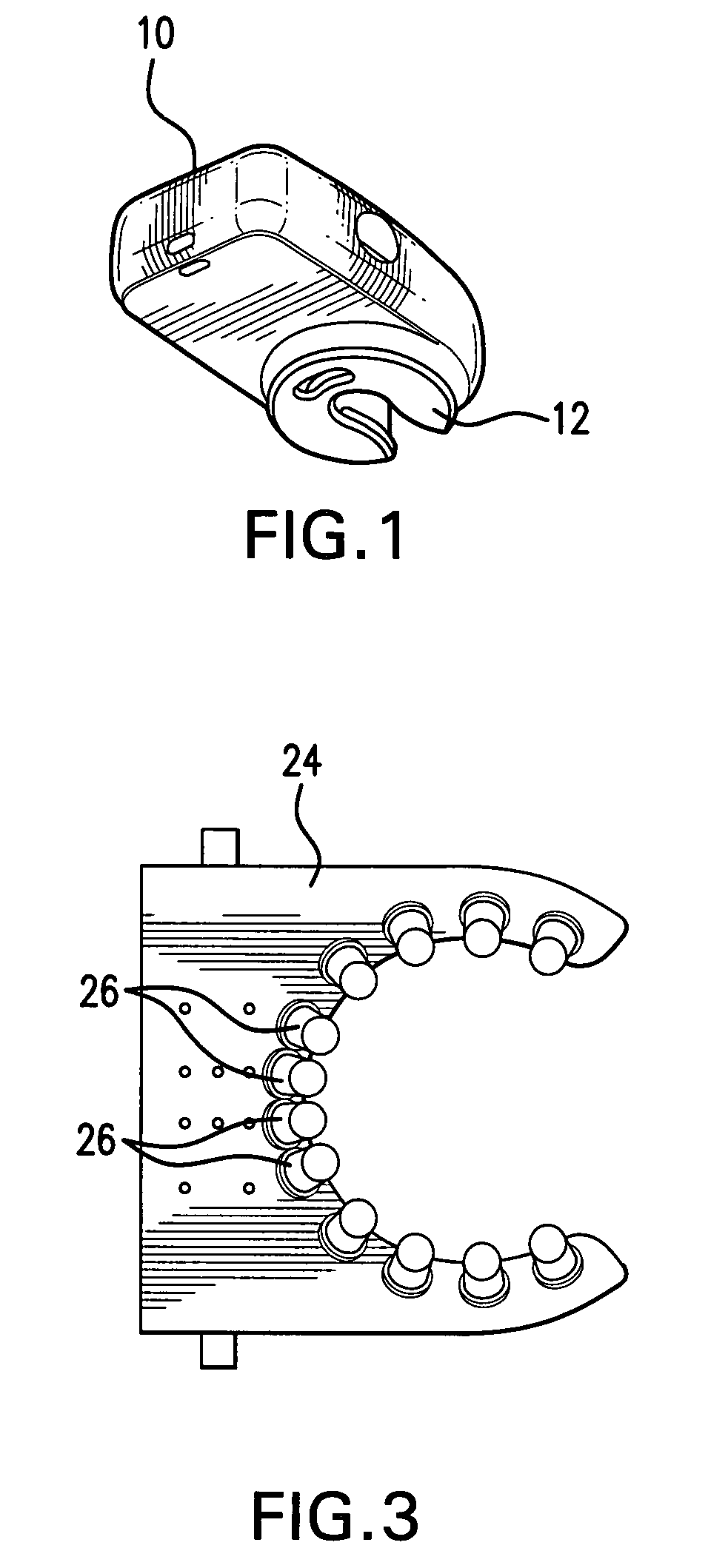
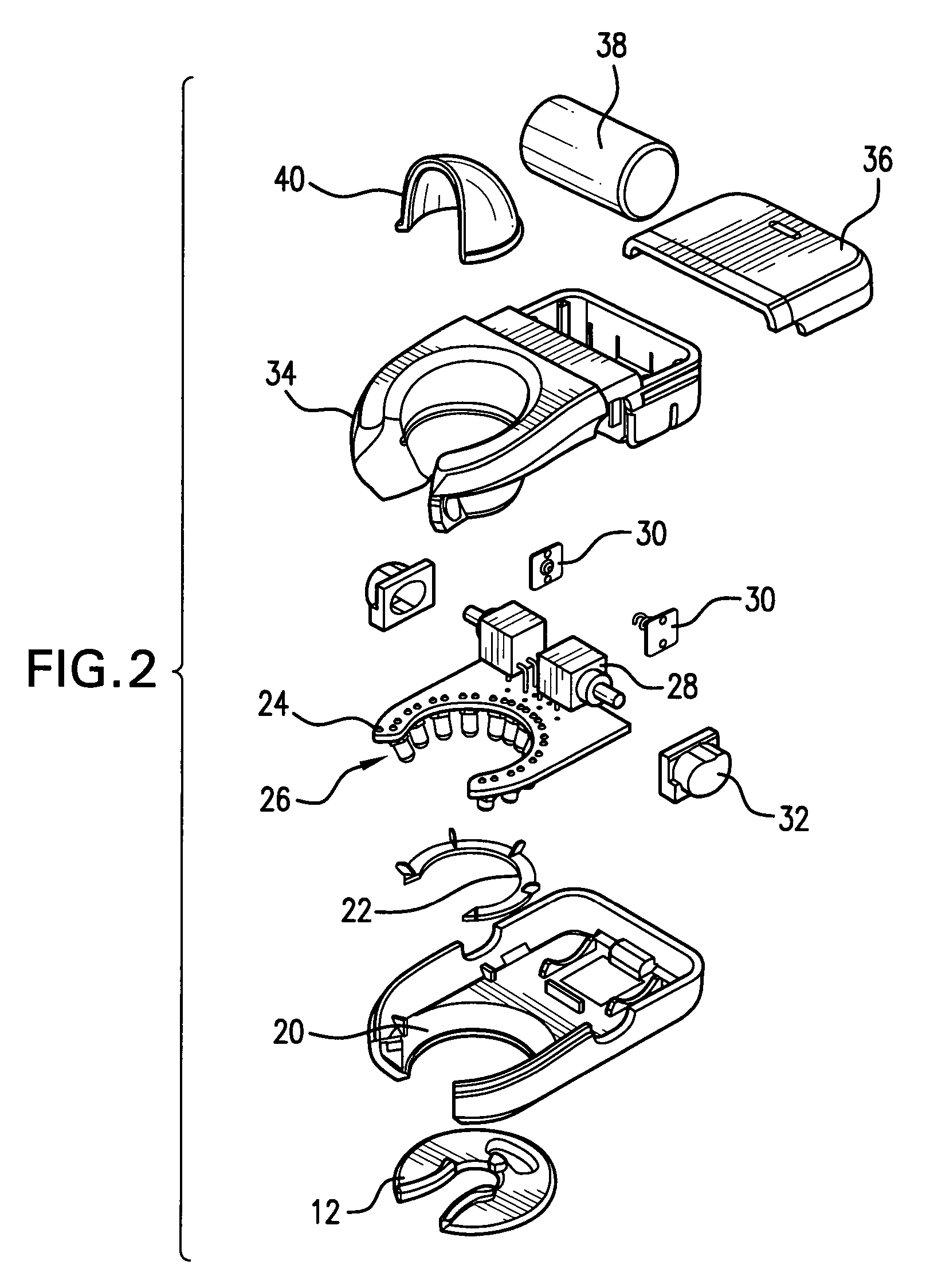
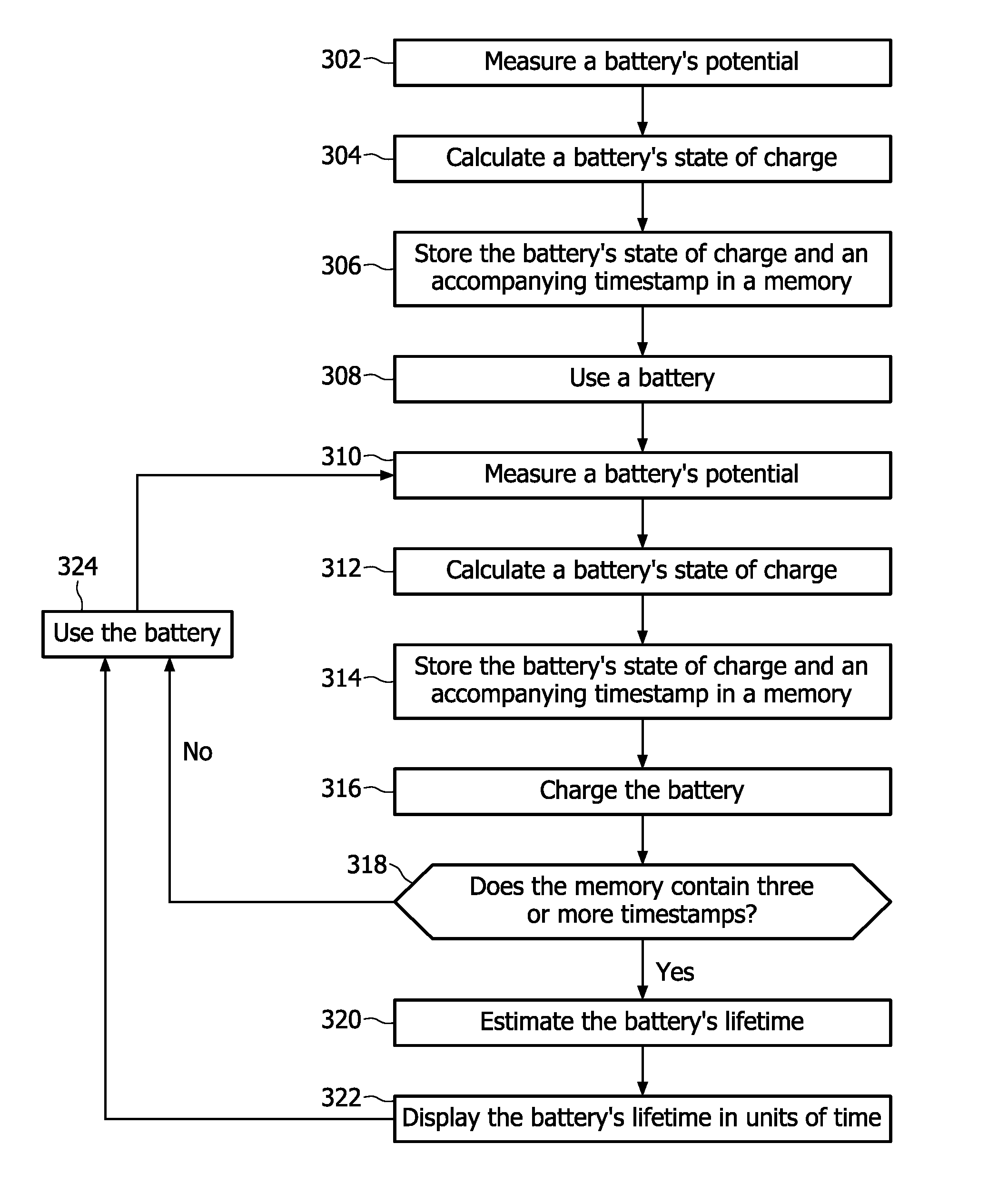
Method and device for predicting a rechargeable battery's lifetime
InactiveUS20110029265A1Accurate predictionAppropriately appliedBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingBattery degradationRechargeable cell
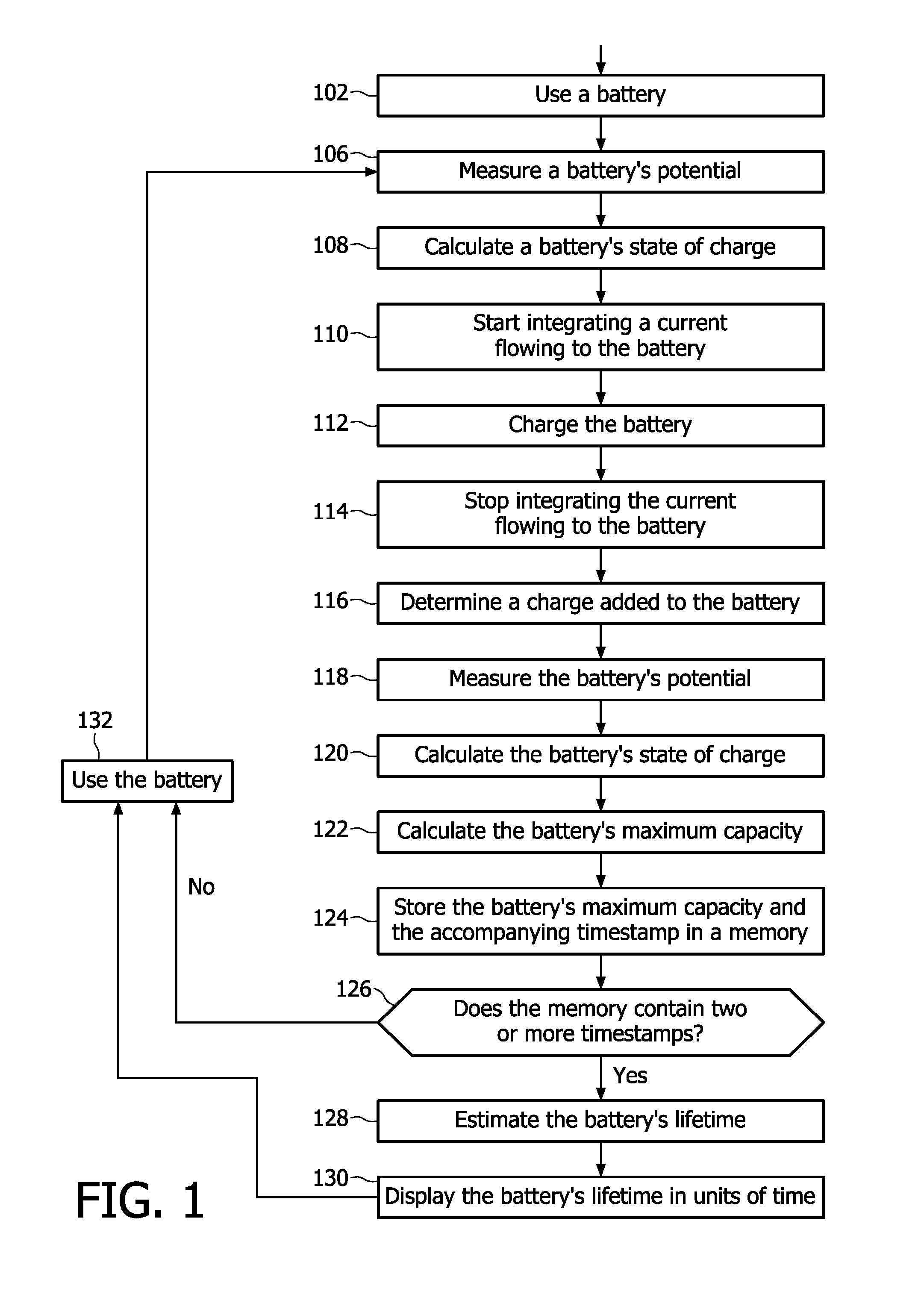
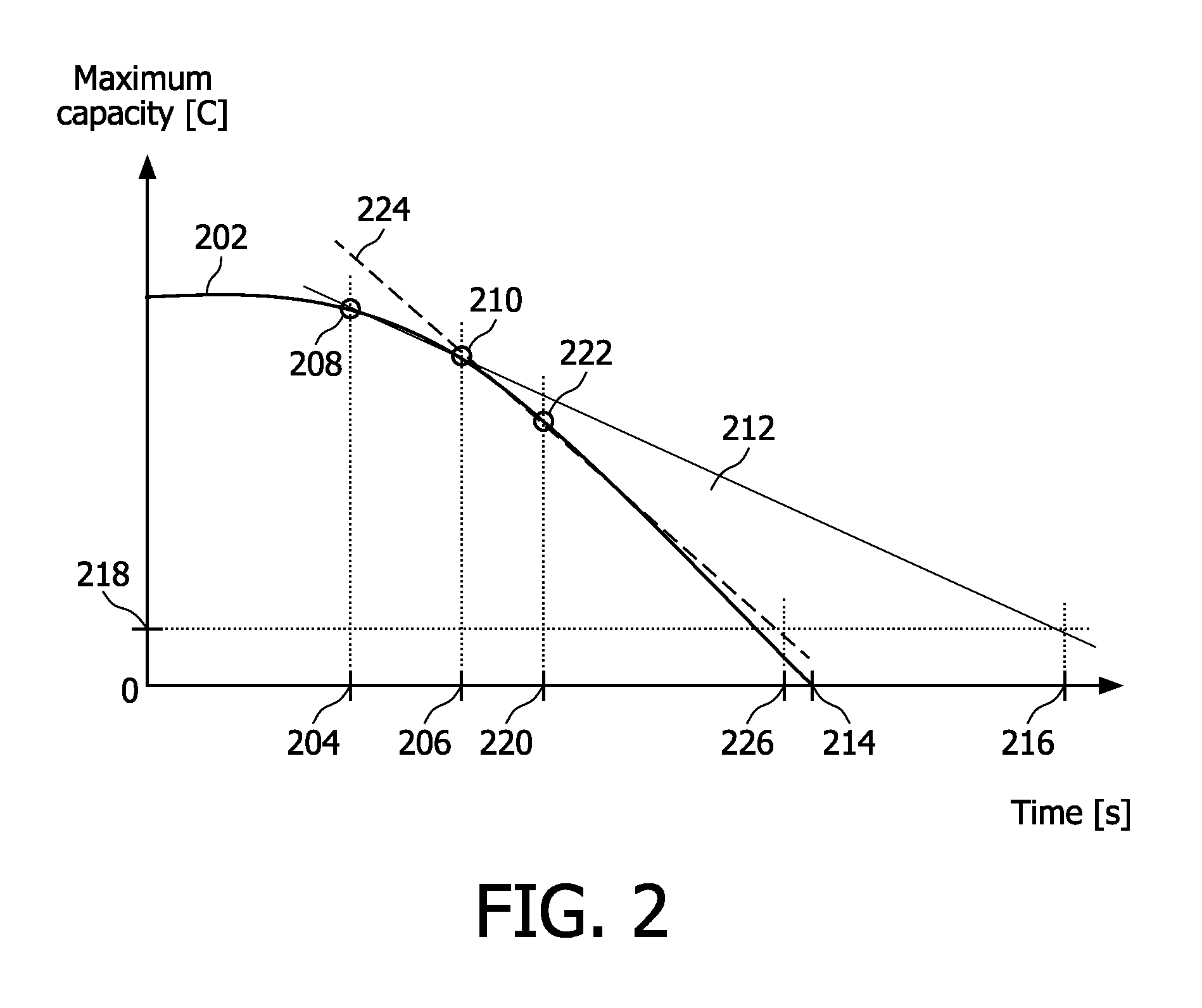
A method is disclosed for determining an end of life for a rechargeable battery comprising the steps of using the battery (102), charging the battery (112) and making an estimation of a battery's life-time (128), characterized by monitoring a battery characteristic indicative for battery aging (122).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Bumper Structure
InactiveUS20080203742A1Easy to detectAvoid deformationPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementBumpersDetection performanceHead-on collision
In a bumper, a touch sensor and a load detection sensor detect a load applied to the bumper in the event of a head-on collision, when pressed by an absorber. The touch sensor and the load detection sensor are provided in front of reinforced portions of a front wall of a bumper reinforcement. The touch sensor is provided in front of the load detection sensor with a load transfer plate interposed the touch sensor and the load detection sensor. In addition, in the event of a head-on collision, deformation of the front wall is suppressed by the reinforced portions and the load is appropriately applied to the touch sensor and the load detection sensor, and the load is appropriately applied from the touch sensor to the load detection sensor. Thus, the detection performance of the touch sensor and the load detection sensor can be stabilized.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com