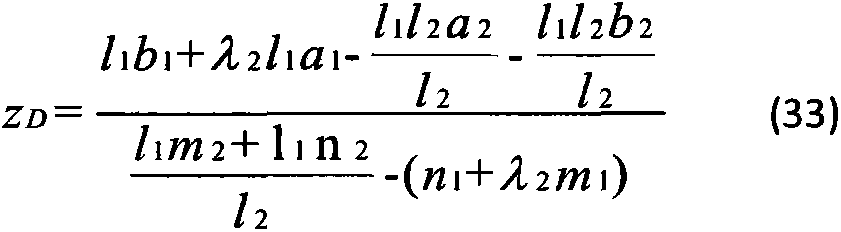Patents
Literature
136 results about "Line of action" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, the line of action of a force F is a geometric representation of how the force is applied. It is the line through the point at which the force is applied in the same direction as the vector F→.
Installation Of Offshore Structures
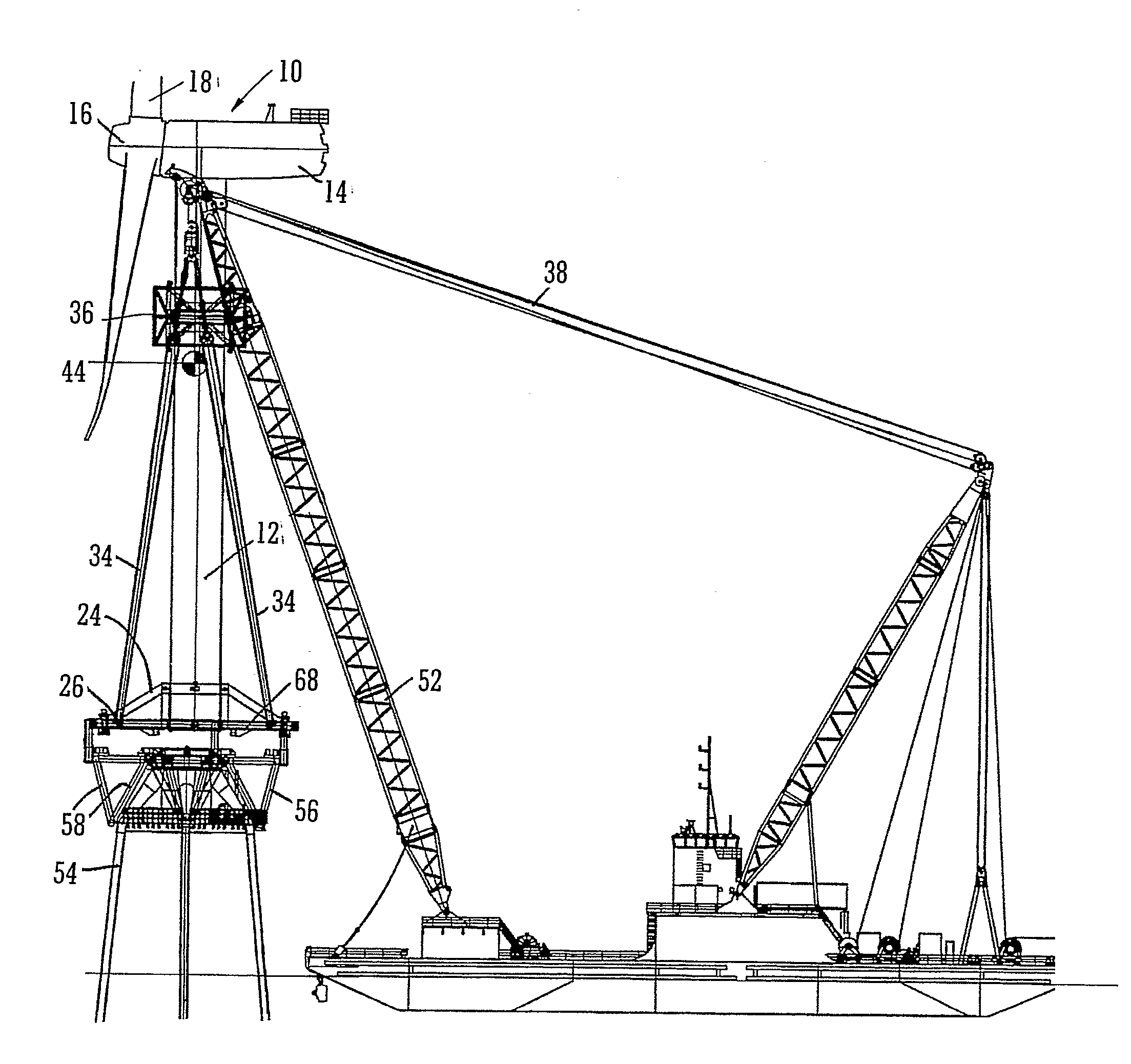
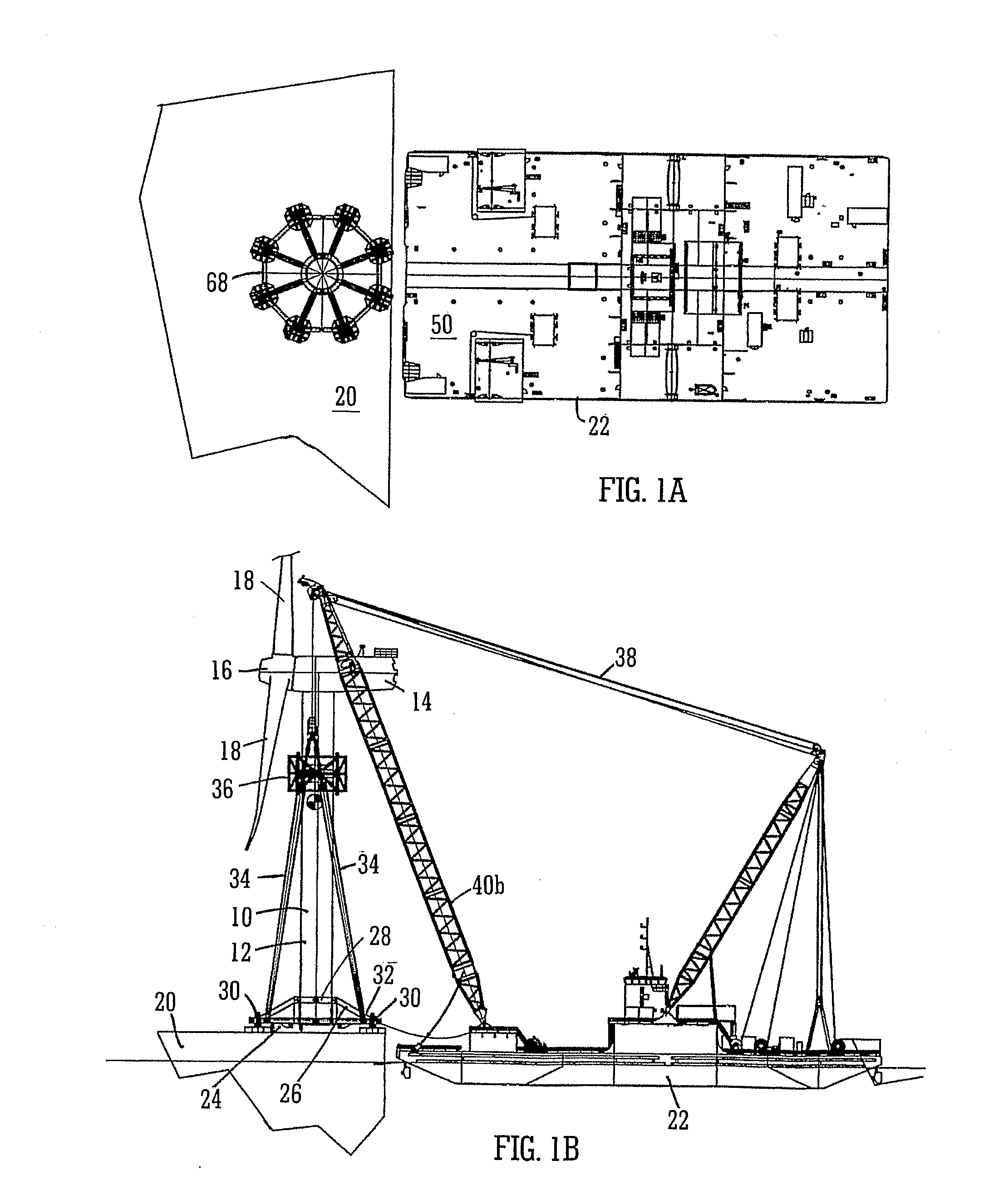
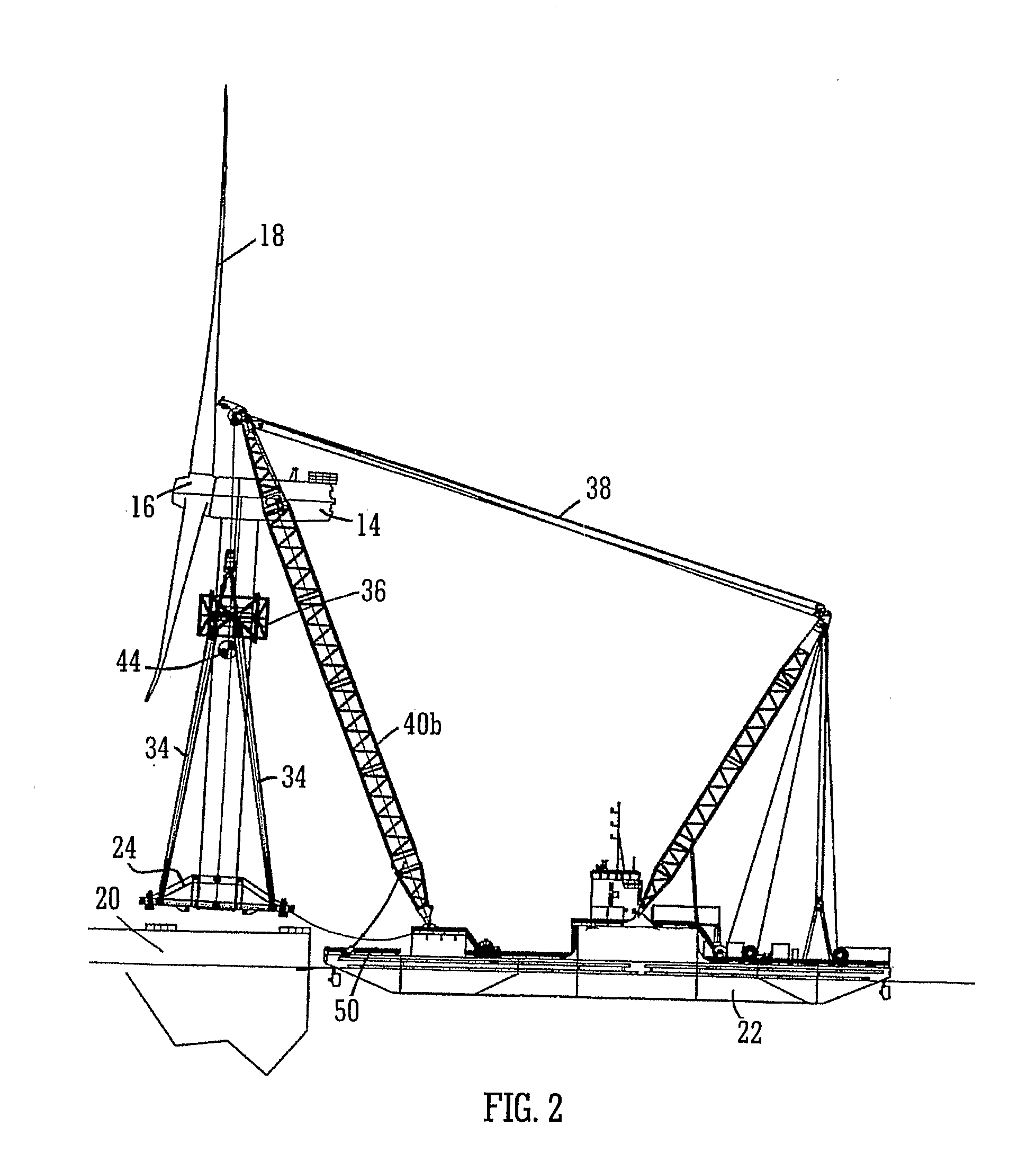
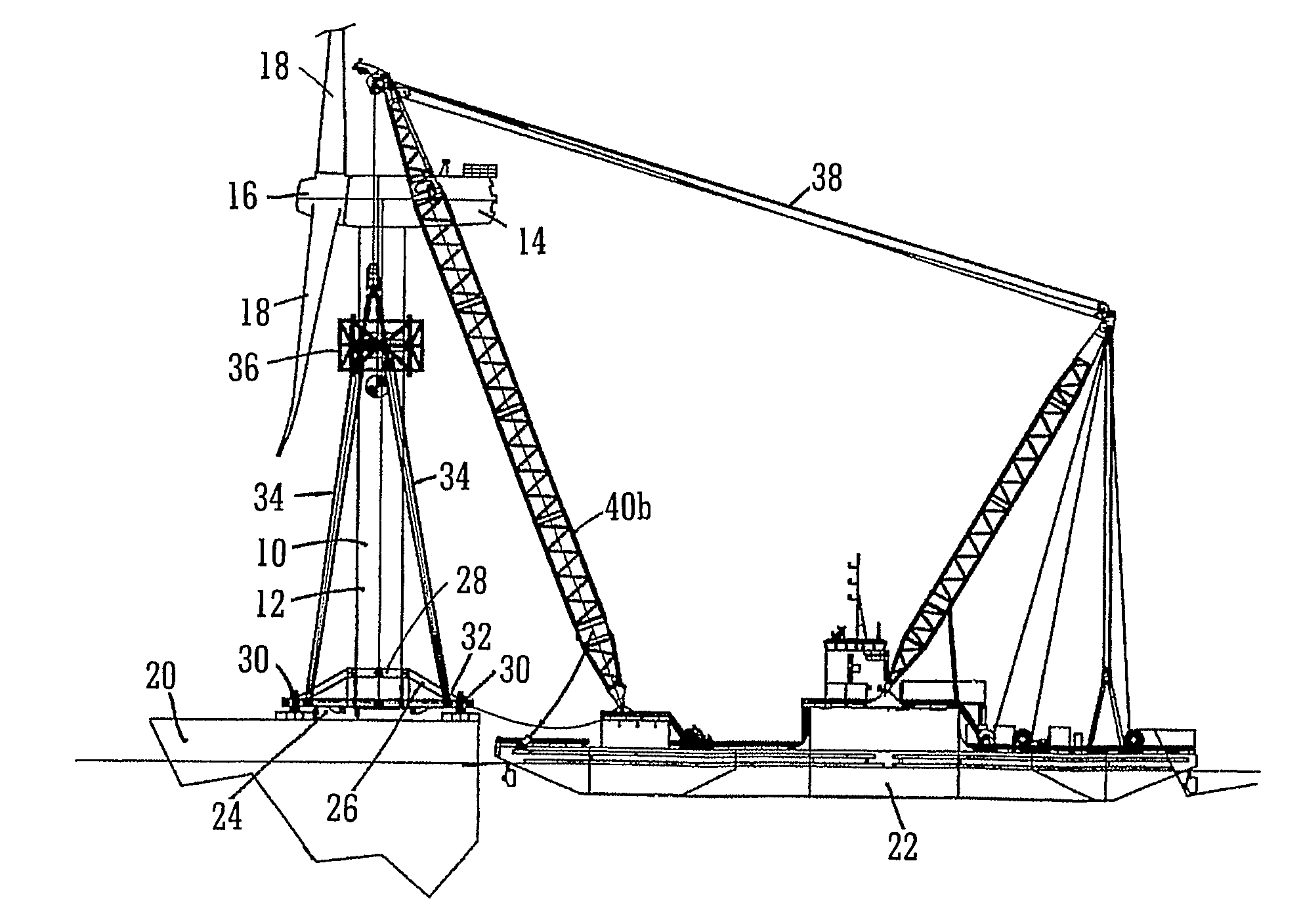
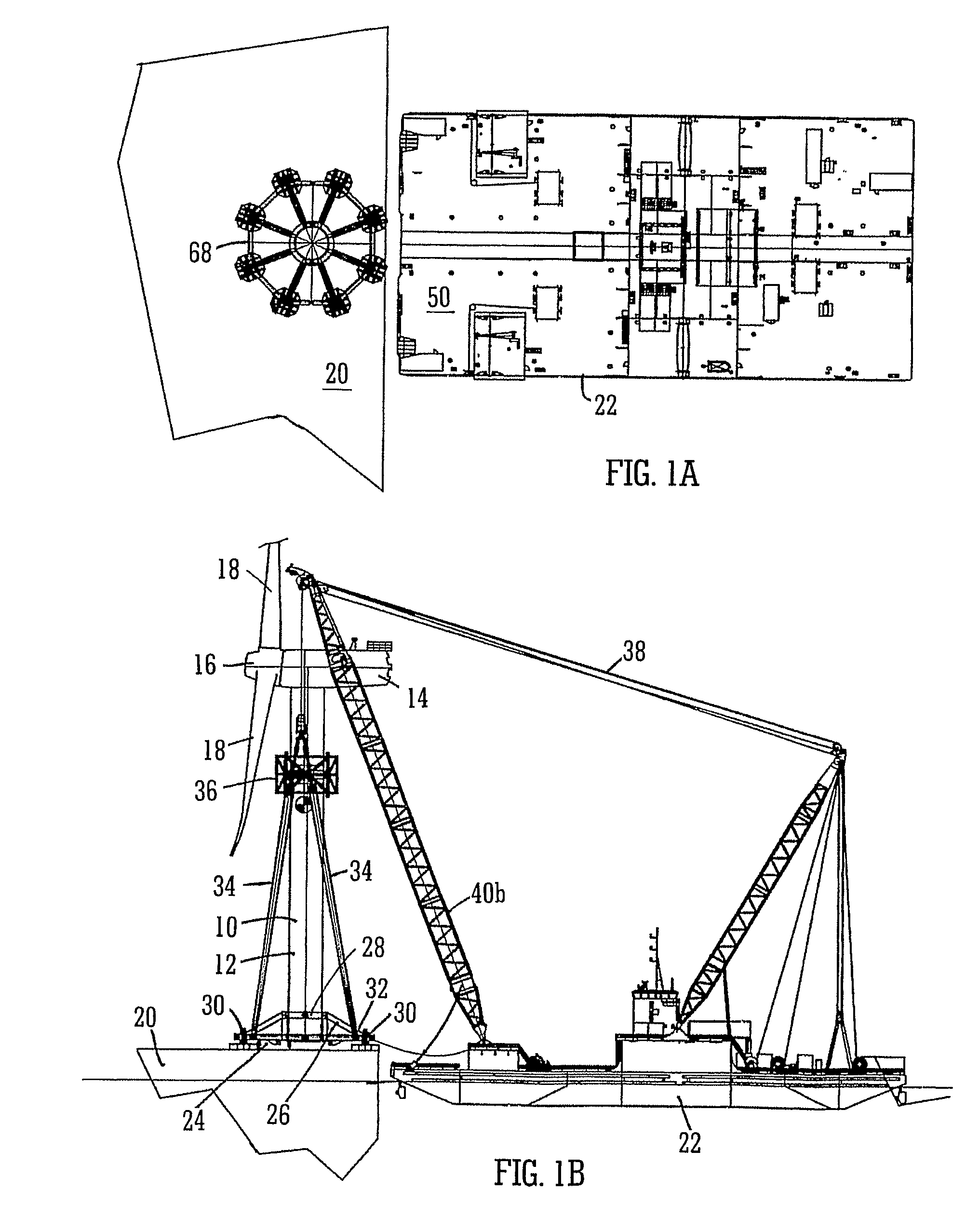
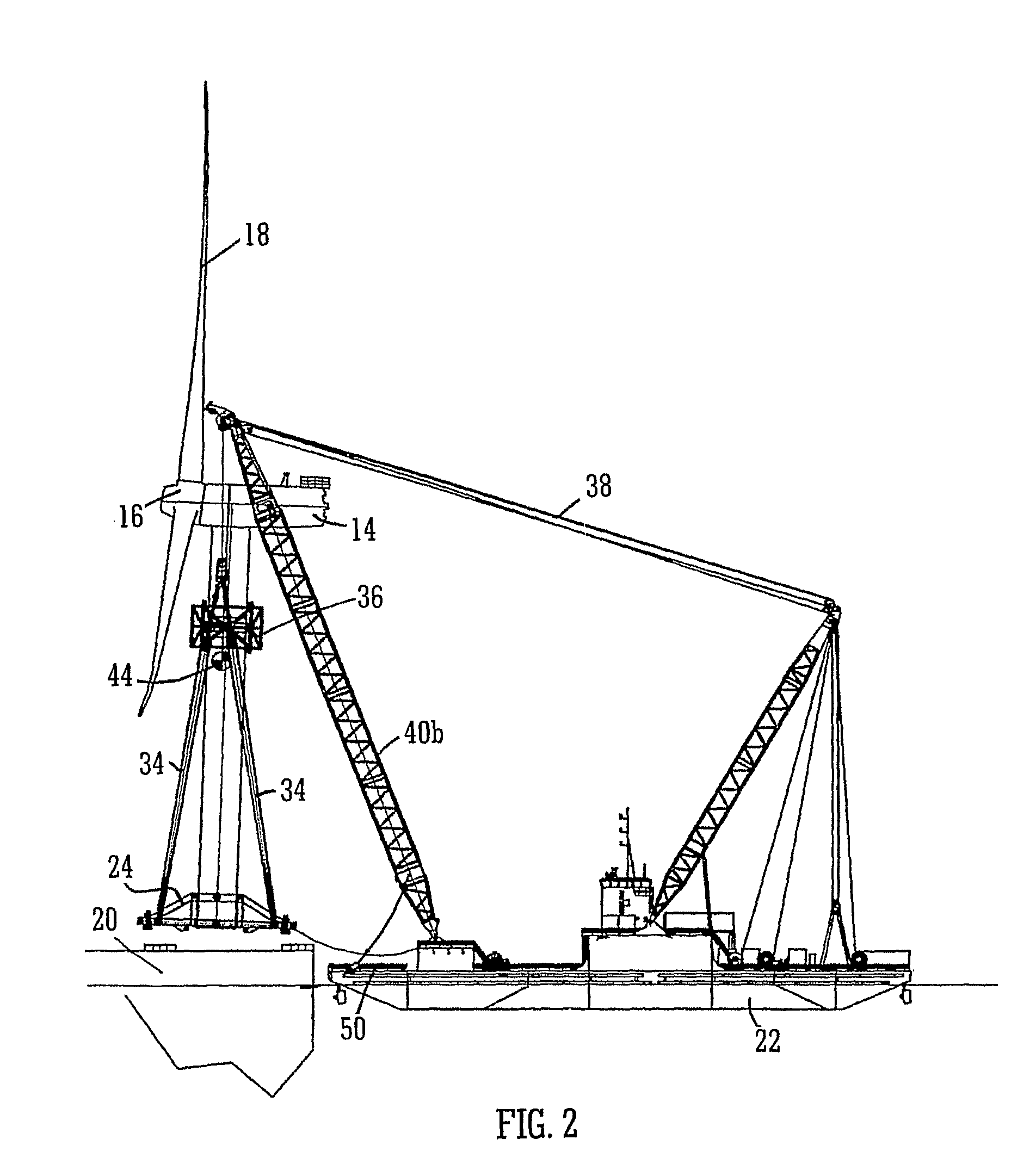
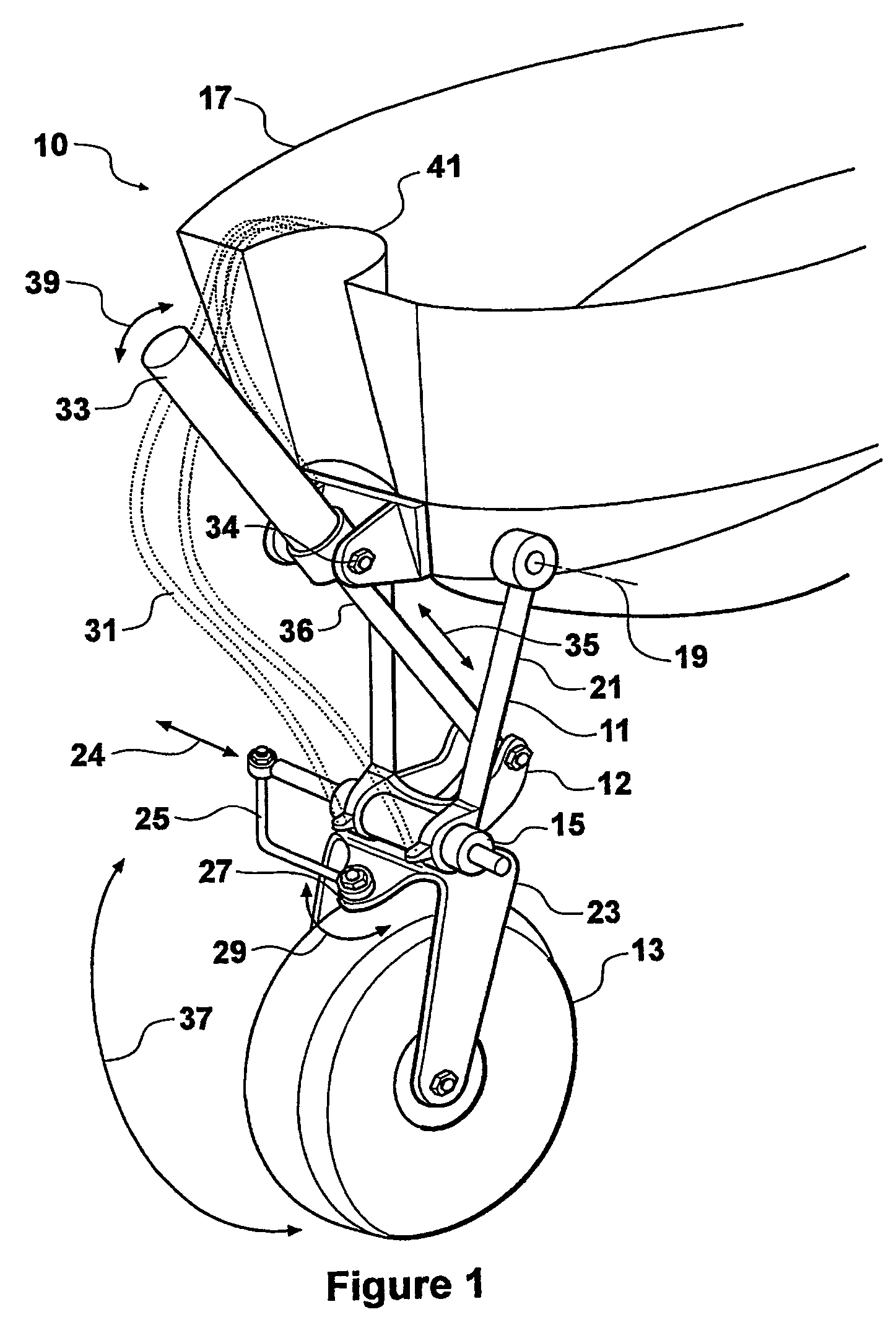
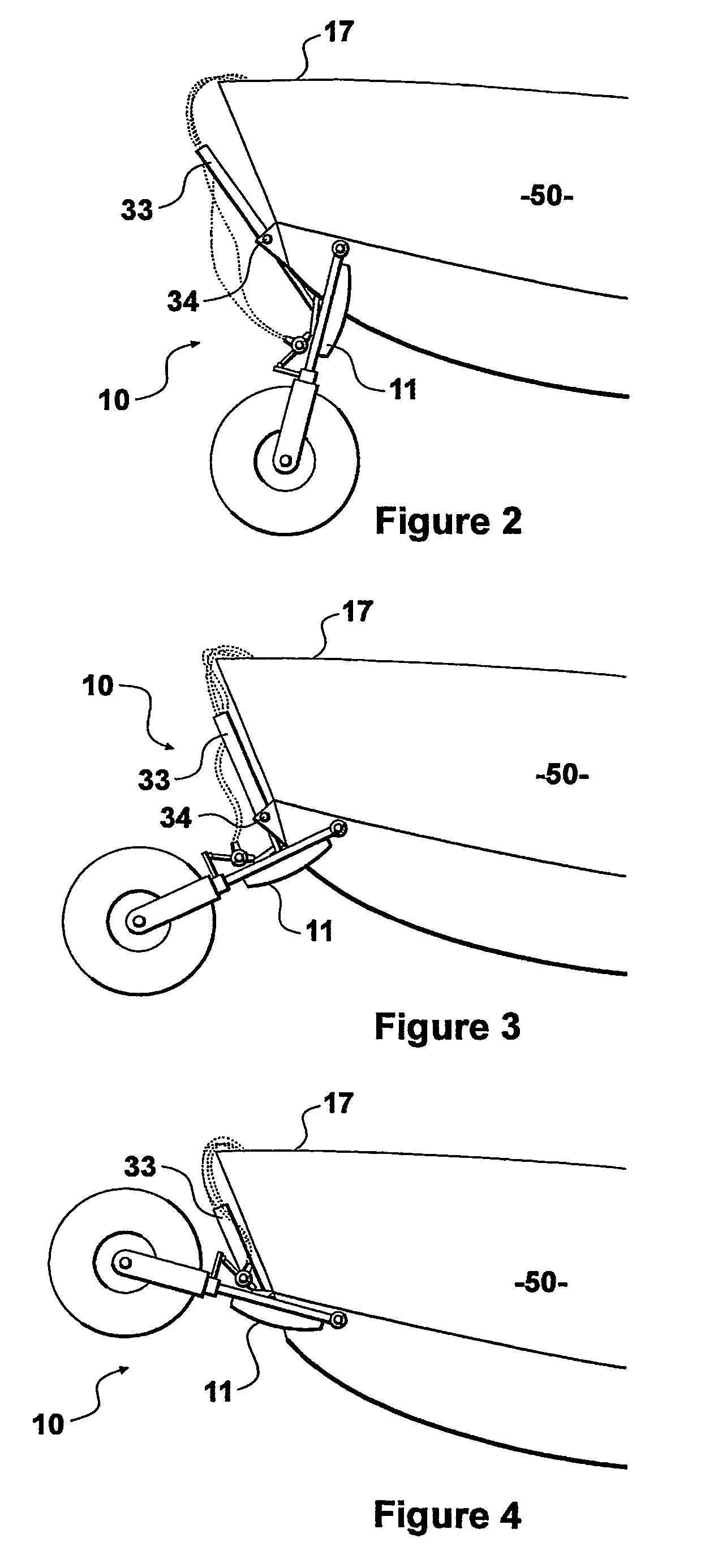
A method and system for transporting an offshore structure such as a wind turbine generator includes a supporting frame in which the offshore structure is assembled on land in an upright configuration. The frame is used for lifting the structure onto a transport vessel, on which it is retained in the upright configuration. At its location of use, the offshore structure is transferred to a pre-prepared foundation. The foundation is provided with a frame which cooperates with the supporting frame. The supporting frame includes a plurality of legs having hydraulically controlled feet. The frame of the foundation includes an equal number of supporting formations on which the feet ultimately rest. The feet are moveable in response to the hydraulic control along a nominally vertical line of action and provide a damping arrangement for the mounting of the offshore structure.
Owner:IHC IQIP HLDG BV
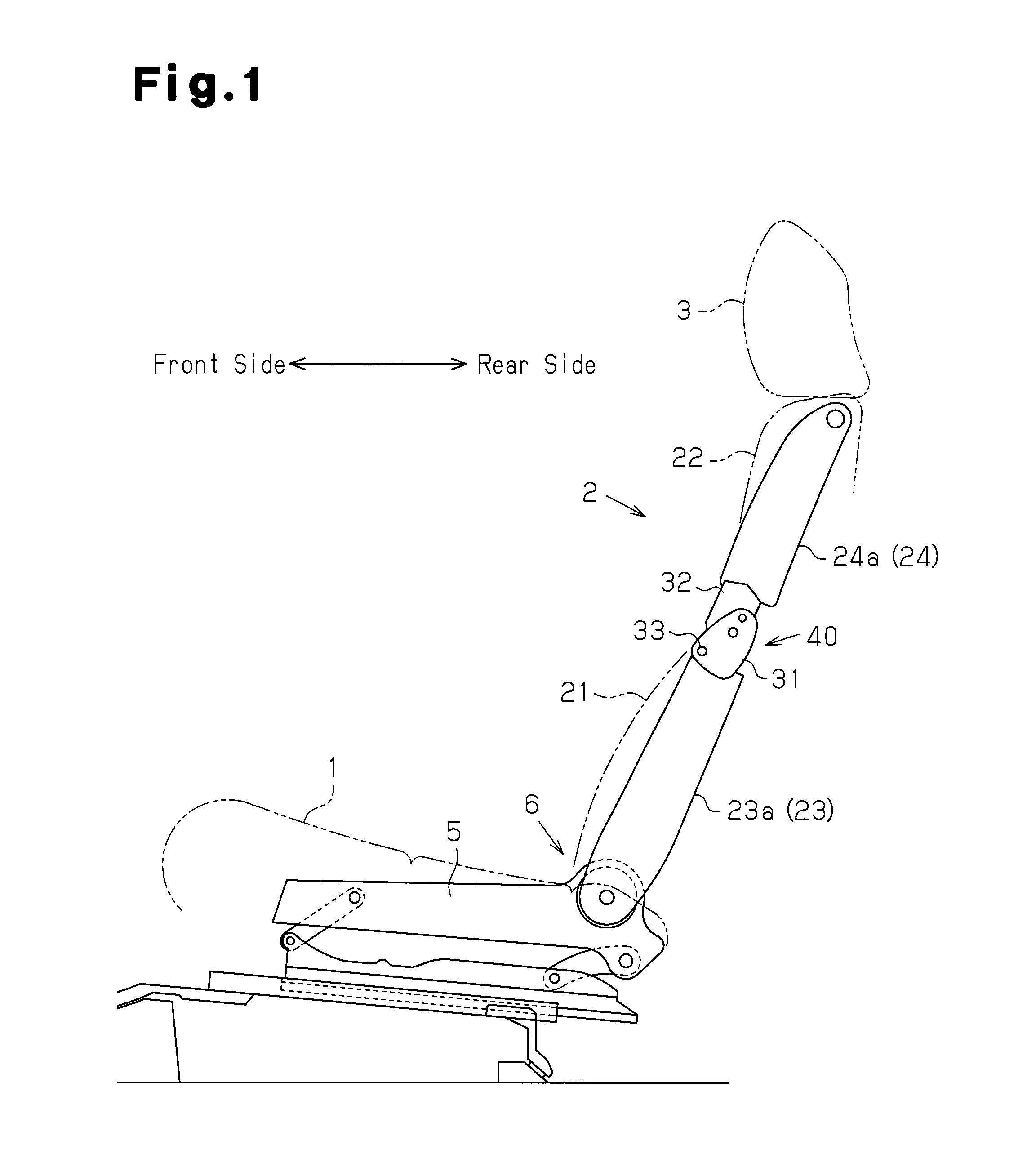
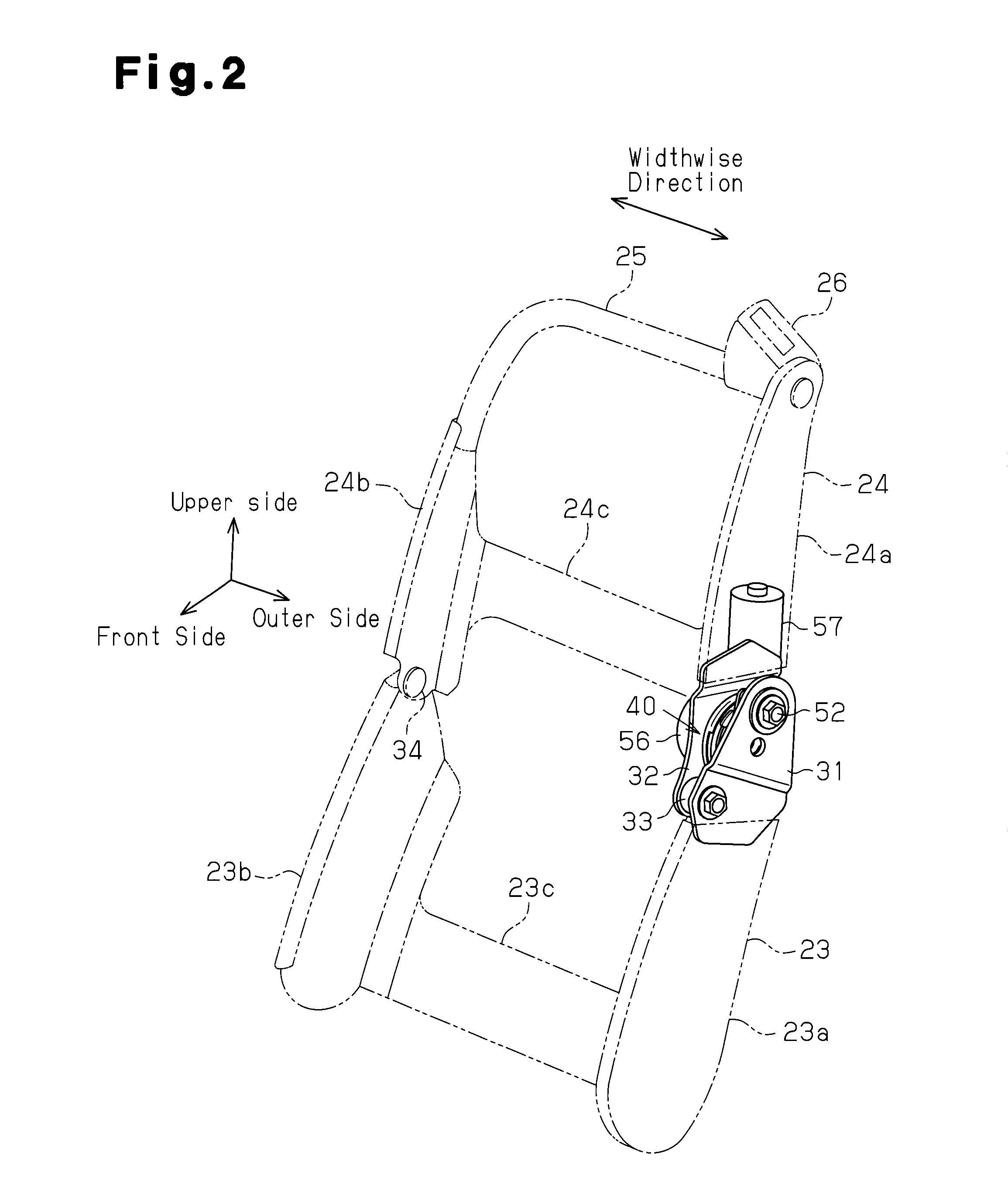
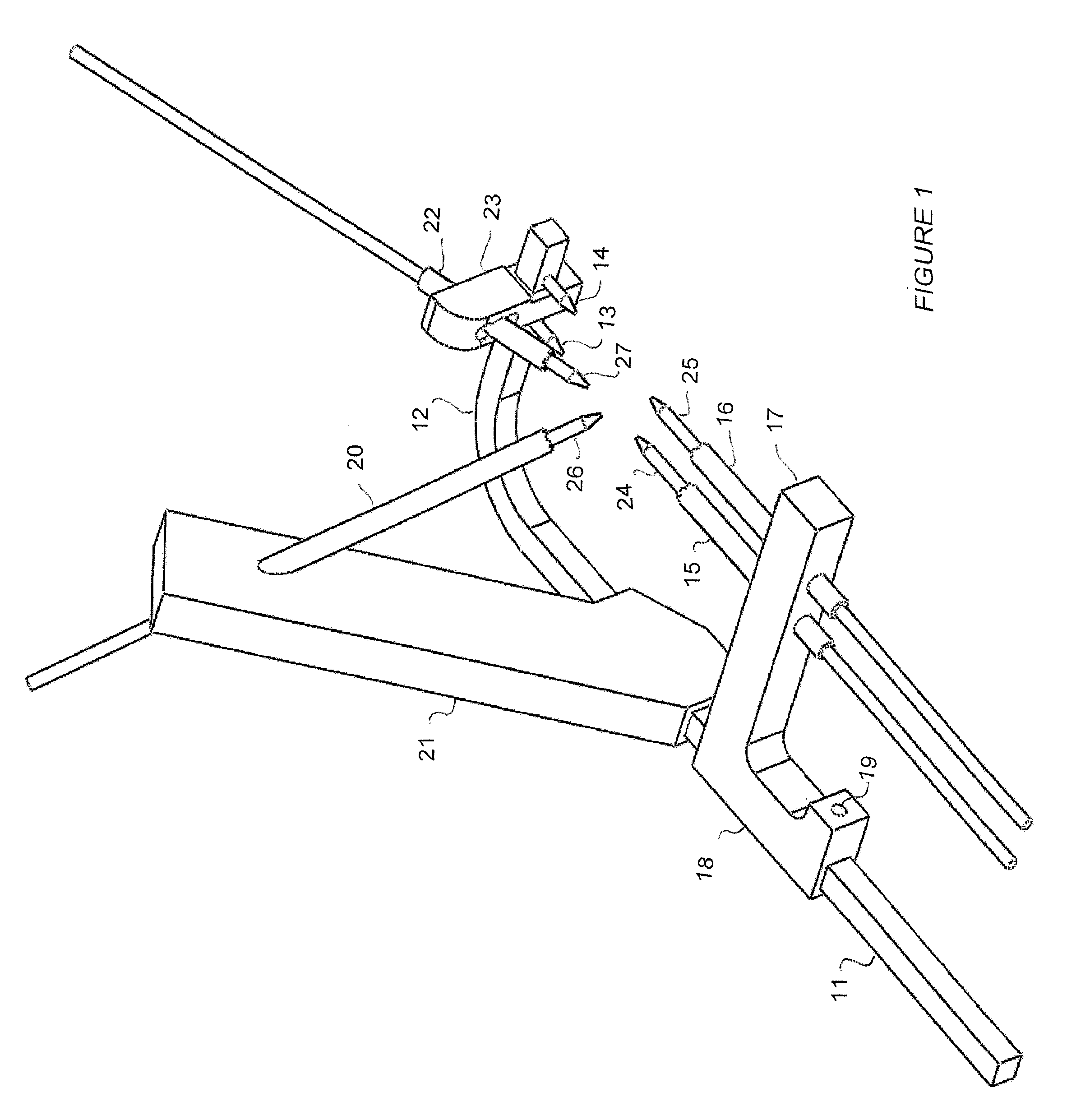
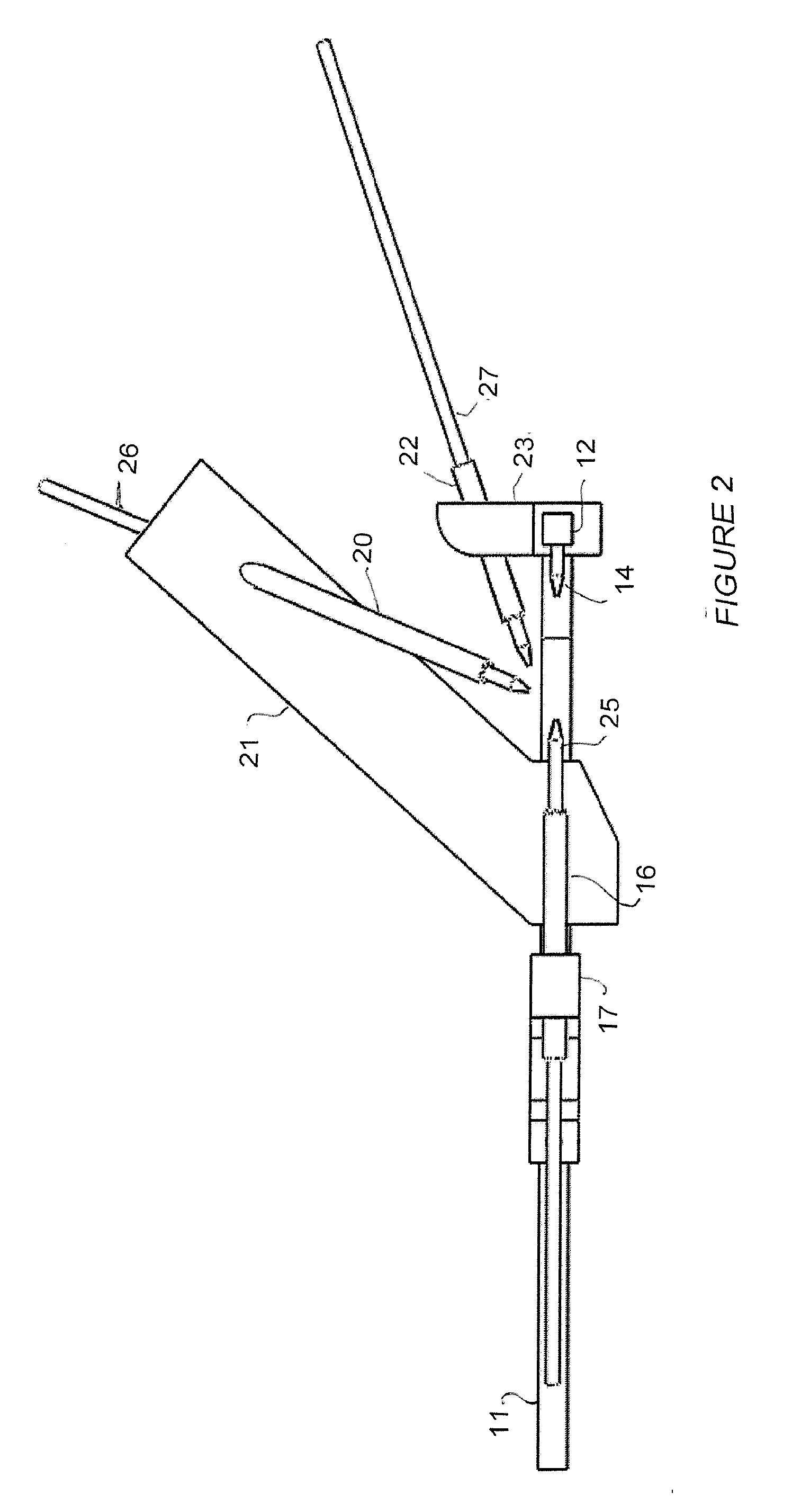
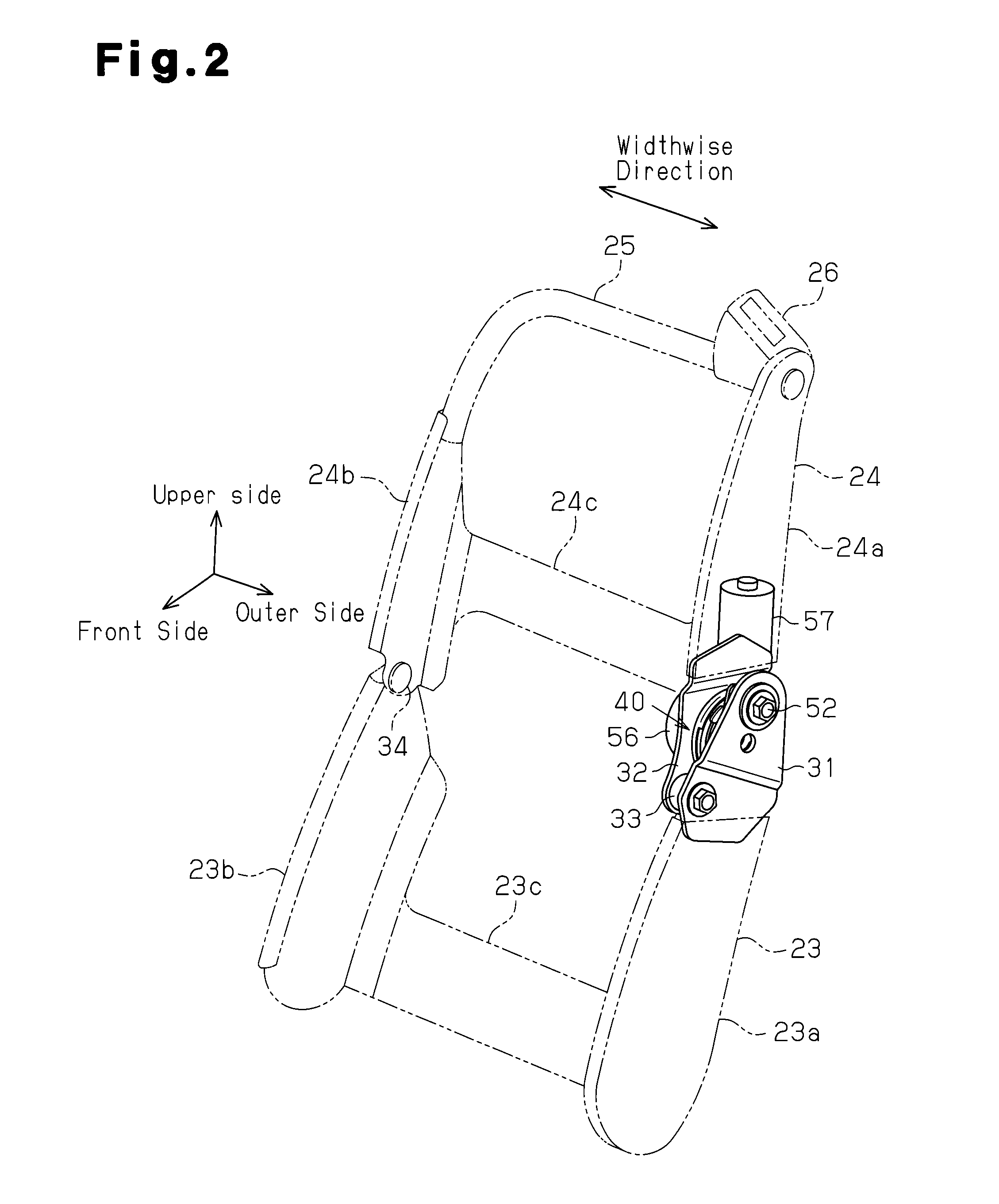
Seat adjustment device, and vehicle seat device with the seat adjustment device
InactiveUS8899683B2Increasing the thicknessHigh strengthOperating chairsSeat framesLine of actionEngineering
A seat adjustment device adjusts the pivoting angle formed by a first seat member and a second seat member. A hinge shaft connects at a first connection point, the first seat member, and the second seat member. An arm section and a connection mechanism are connected at a second connection point. The positions of the axes of the first connection point, the second connection point, and a pivoting section are set in such a manner that, when a load is applied to the front end of either the first seat member or the second seat member, the distance from the second connection point to the axis of the pivoting section is less than the distance from the first connection point to the second connection point with respect to the direction perpendicular to the line of action of a load applied to the second connection point.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Snubbing system for a suspended body
The present invention generally relates to a snubbing or damping system for reducing a shock impact on an isolated body within a shock sensitive device, which may take the form of an inertial measurement unit (IMU). The shock sensitive device includes a housing with an inertial body suspended in an isolated manner within the housing and engaged with the snubbing system. By way of example, the inertial body may take the form of an inertial sensor assembly. Further, the snubbing system may take the form of a plastically deformable snubbing mechanism positioned between the housing and the inertial body along a line of action of the inertial body during an acceleration (e.g. shock) event.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Reciprocating piston engine comprising a rotative cylinder
InactiveUS6928965B2Improve efficiencyRaise the ratioCasingsInternal combustion piston enginesLine of actionMotion transfer
A reciprocating piston engine includes a rotor housing for transferring torque to an engine output drive; a contoured guide element in the rotor housing, having a closed, curvilinearly contoured shape, around which the rotor housing is rotatable; at least one compression unit in the rotor housing, each unit including a piston and a cylinder, with the piston having a straight line of action in a plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the rotor housing; a connecting rod, rigidly coupled to the piston, movable along a path determined by the contoured guide element, for transferring controlled movement specified by the contoured guide element to the piston; and a guide part, joined to the connecting rod, and movable along a separate guide in the rotor housing, with the connecting rod, the piston, and the guide part each performing a single stroke along a straight line in the rotor housing.
Owner:TEUFL ERICH
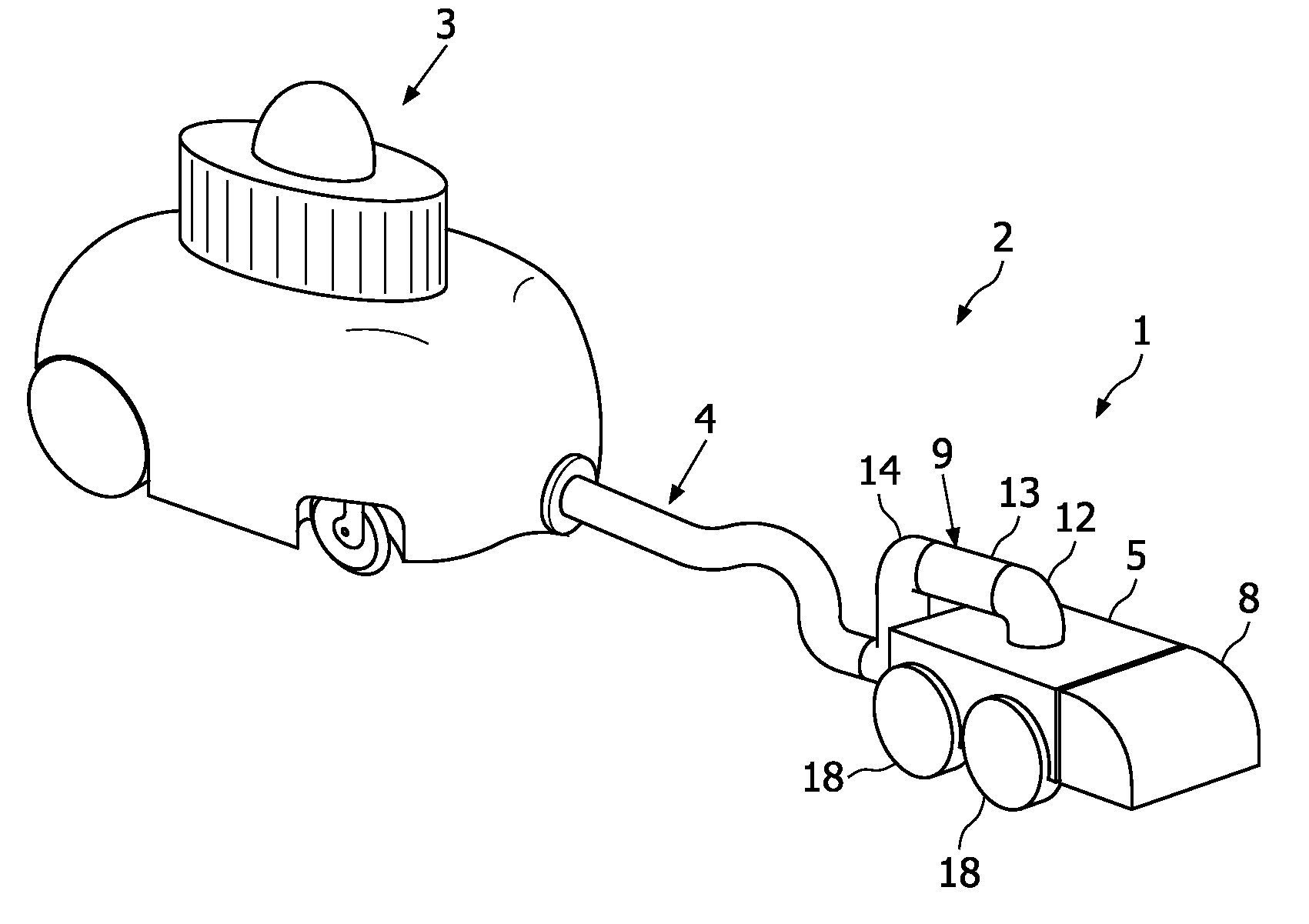
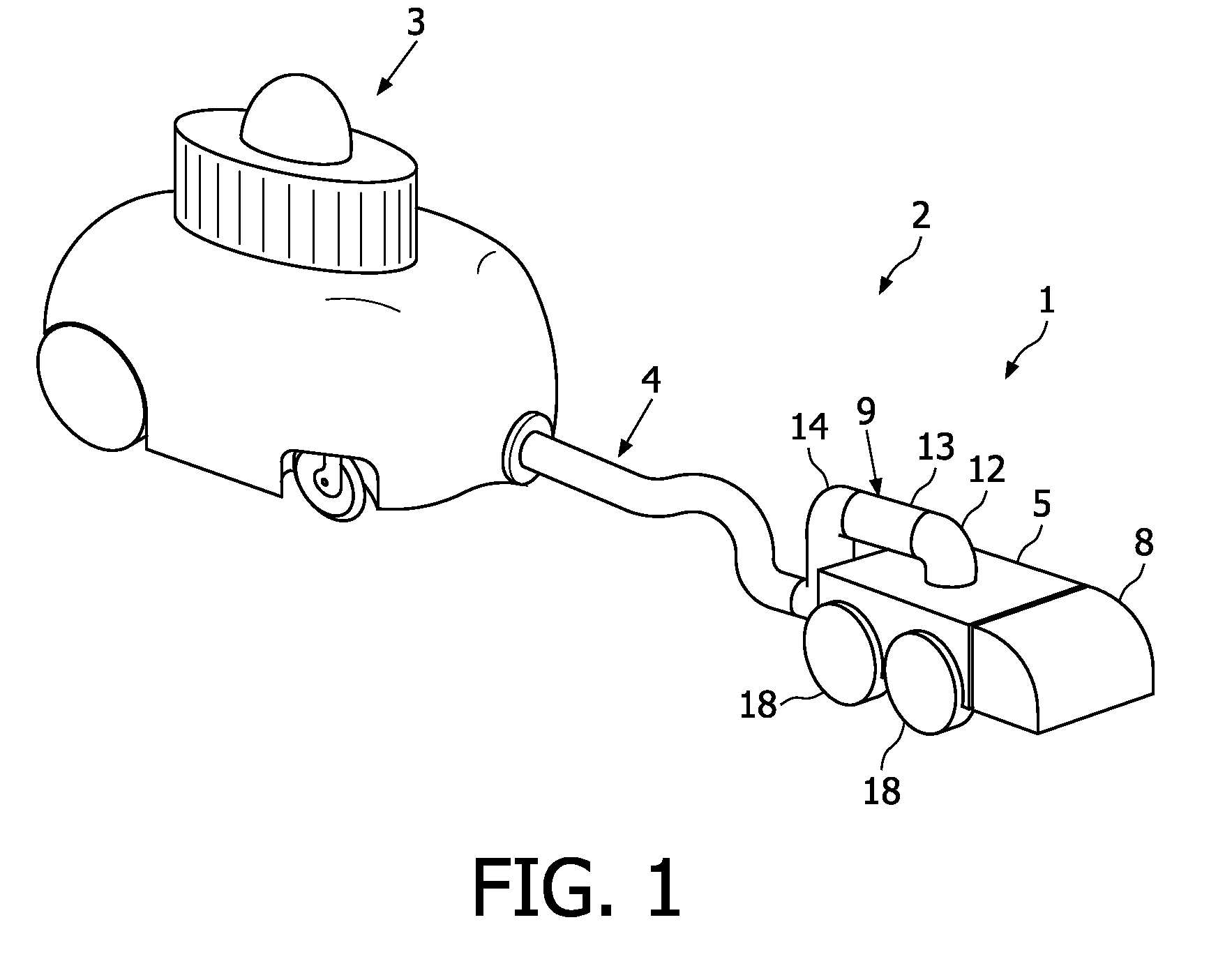
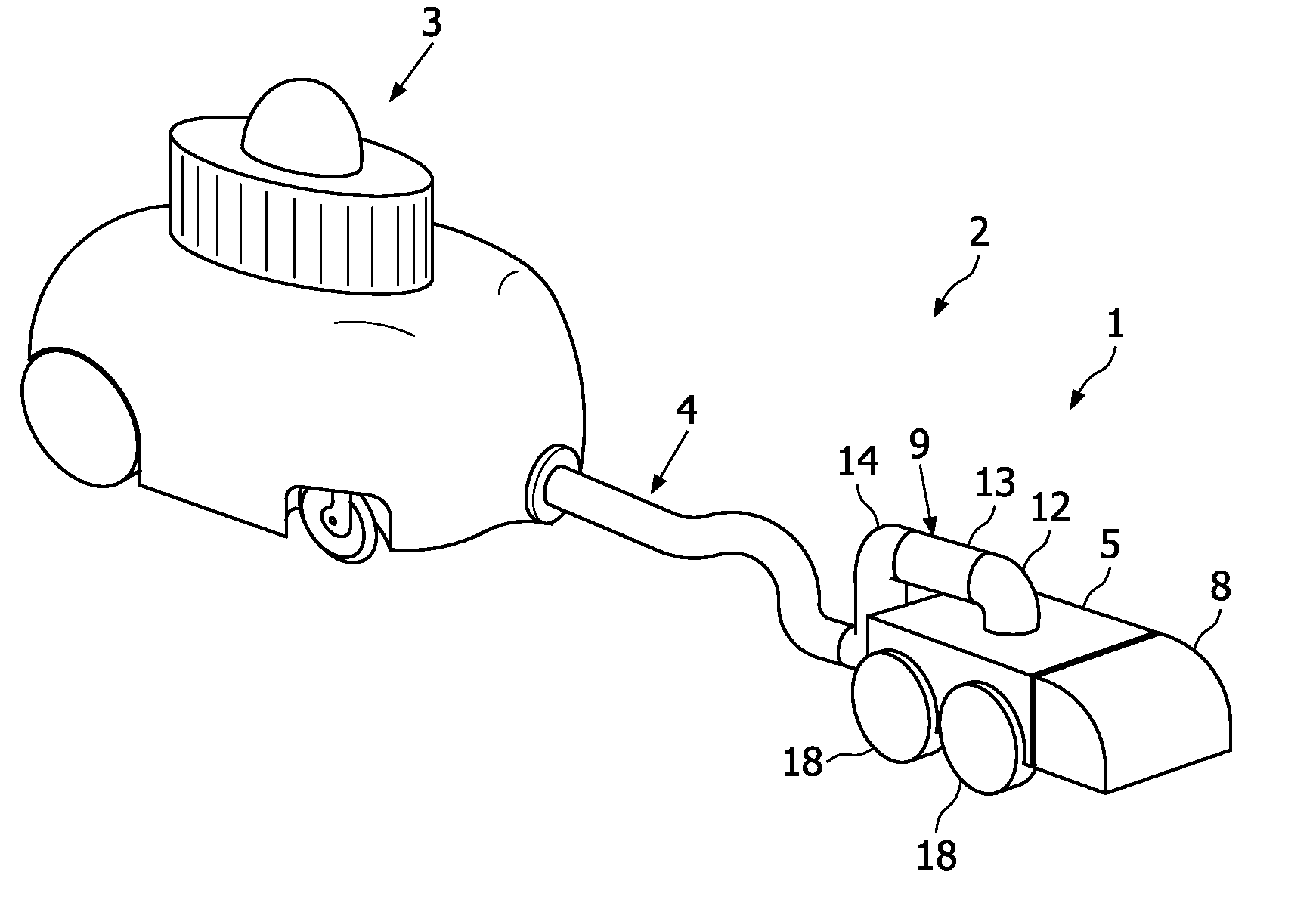
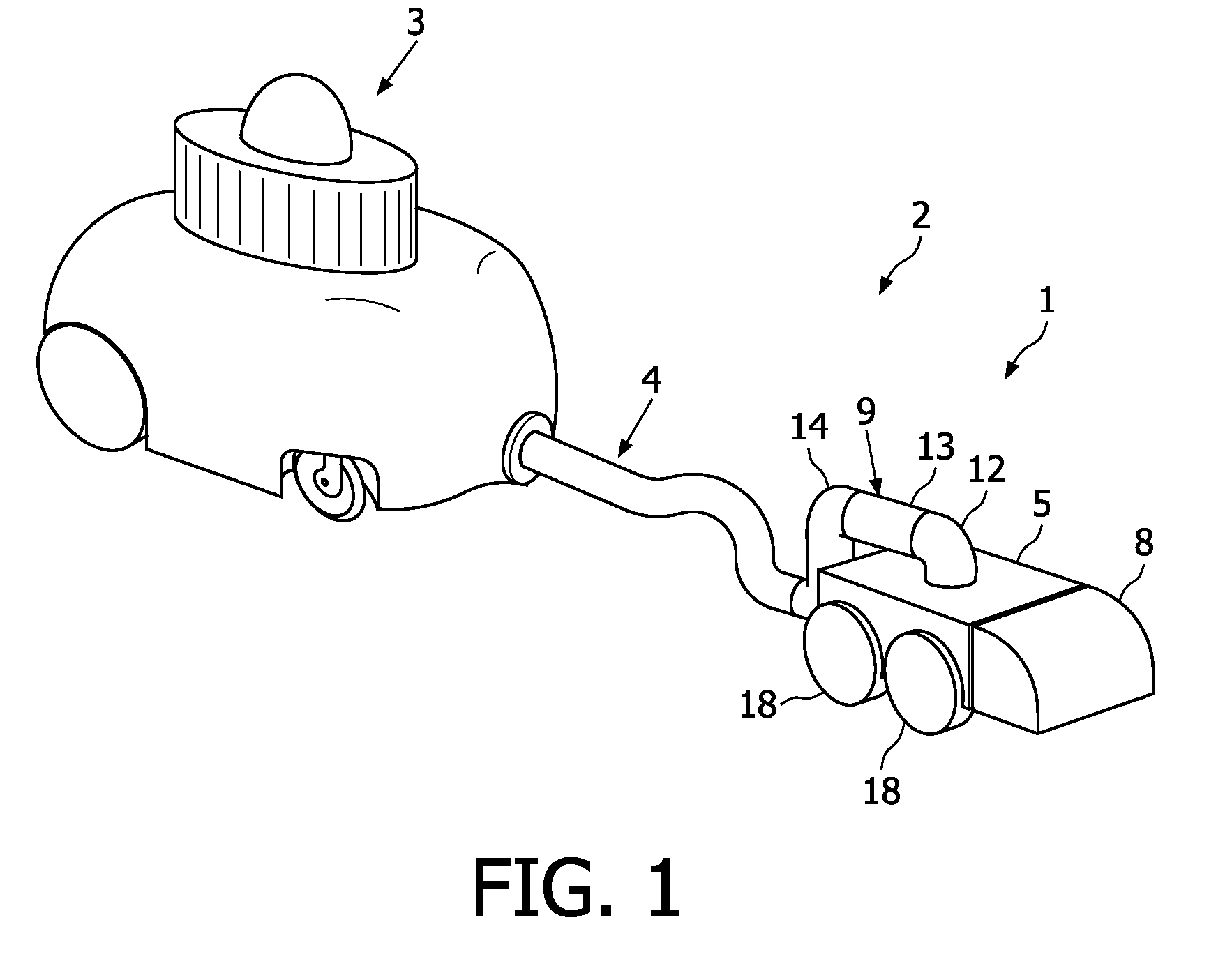
Robotic cleaning head
InactiveUS8136200B2Less maneuverabilityIncrease pressureSuction hosesSuction nozzlesLine of actionChassis
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
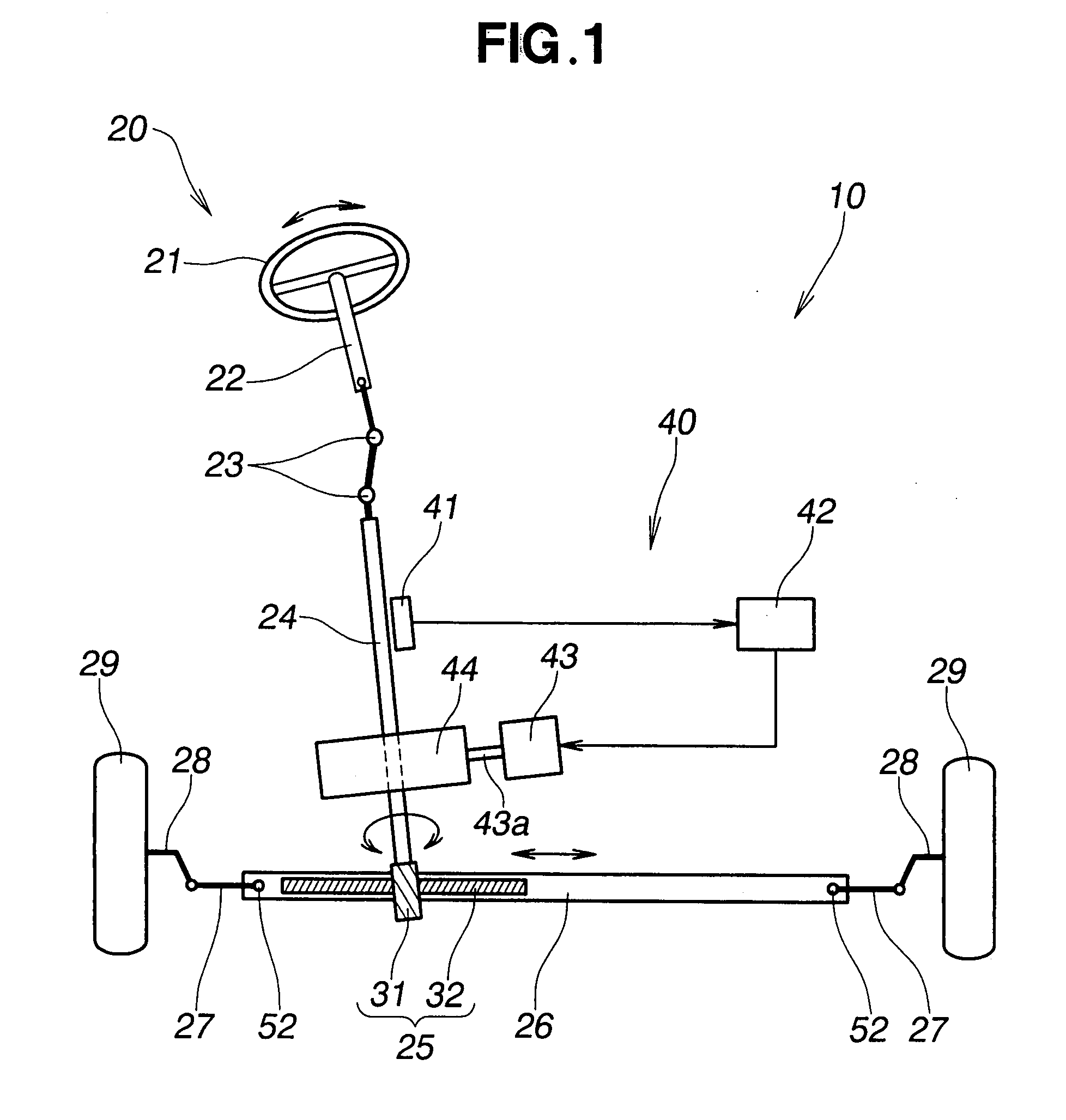
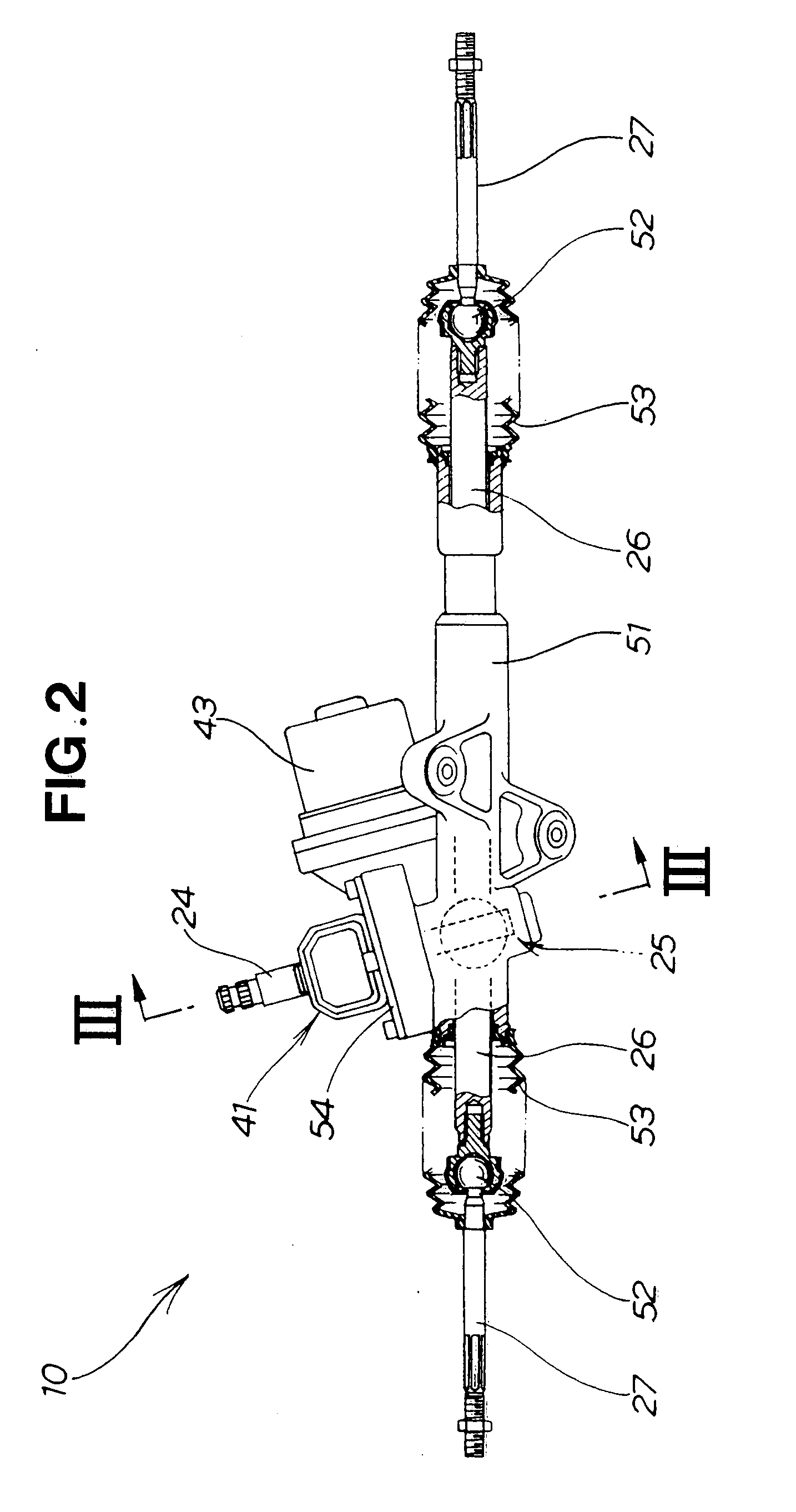
Electric power steering apparatus equipped with worm gear mechanism
InactiveUS20070227279A1Improve transmission efficiencyFavorable steering feelingToothed gearingsPortable liftingElectric power steeringLine of action
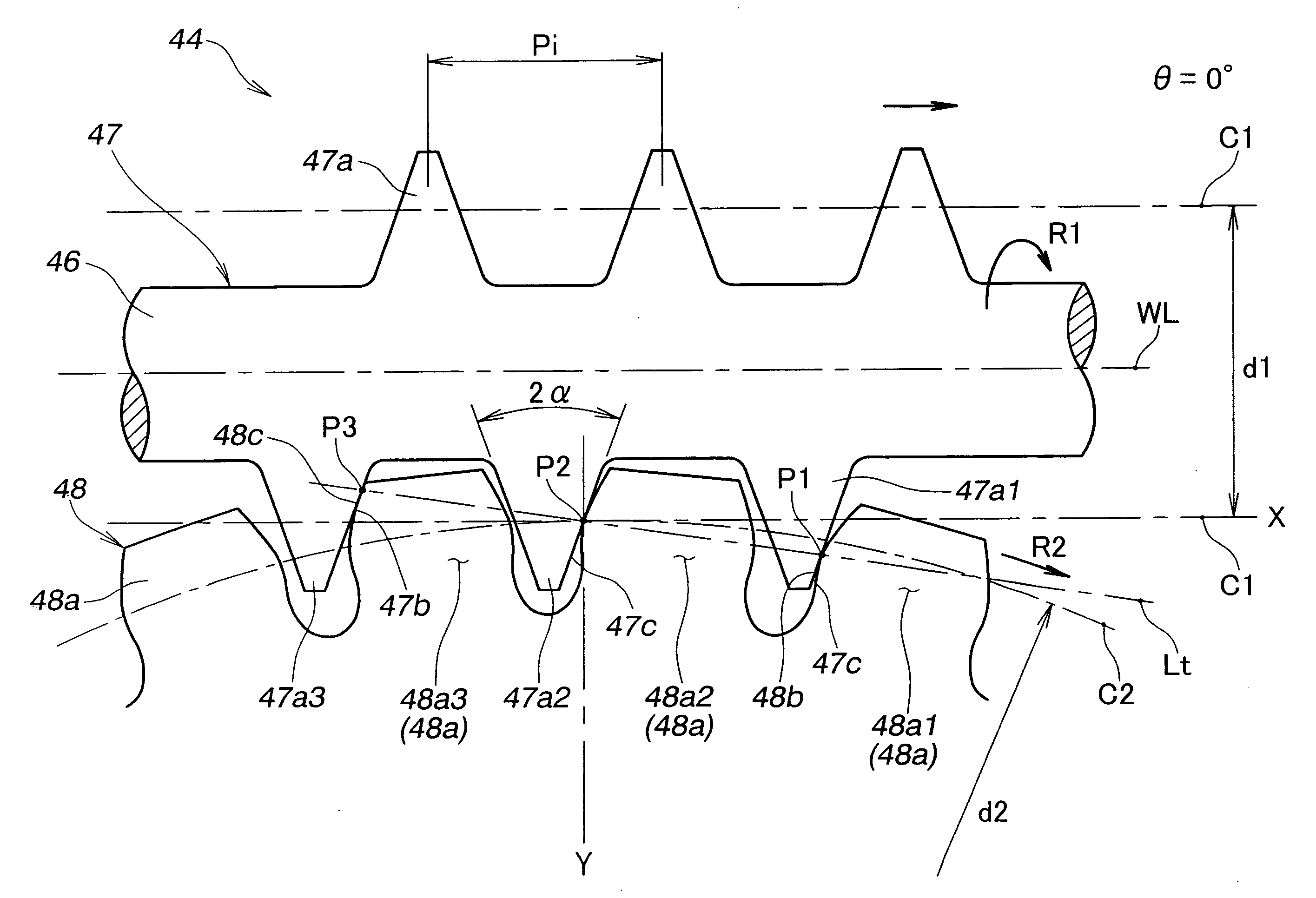
An electric power steering apparatus includes a worm gear mechanism for transmitting the torque generated by an electric motor to a steered road wheel of the vehicle. The worm gear mechanism has a worm gear made of metal and a worm wheel formed of plastic material and meshing with the worm gear. The worm gear has a tooth profile including a dedendum part formed in an involute shape and an addendum part formed in a circular arc shape with a center located on a line of action.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Self-adjusting preload for memory alloy wire
ActiveUS20120187143A1Robust and reliable actuatorIncrease volumeDispensing apparatusNon-mechanical controlsLine of actionOffset distance
A preload mechanism for a memory alloy wire actuator is disclosed that includes a rotating element configured to rotate about a pivot. The rotating element has a first contact point that is configured to couple to the memory alloy wire actuator such that contraction of the memory alloy wire actuator displaces the first contact point such that the rotating element rotates from a first position to a second position. The preload mechanism also includes a bias element with a first end that is coupled to a second contact point of the rotating element and a second end configured to be pinned relative to the pivot. The bias element has a line of action extending from the second end through the first end. The line of action has an offset distance that is the minimum distance between the line of action and the pivot. The offset distance has a first value when the rotating element is in the first position and a second value when the rotating element is the second position, the second value being smaller than the first value.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
Controller for walking assistance device
ActiveUS20090048686A1Reliable controlReduce loadProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesSagittal planeLine of action
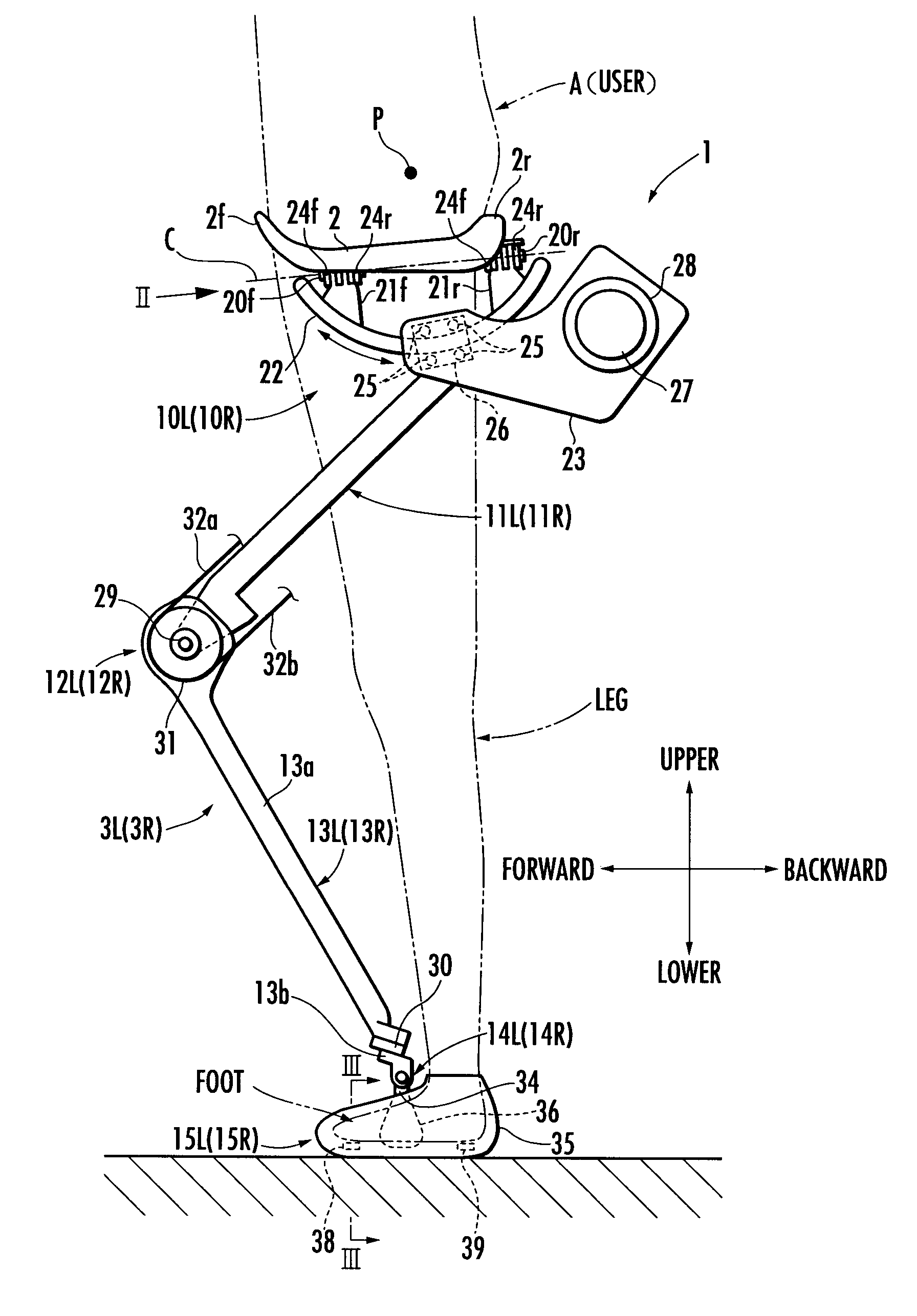
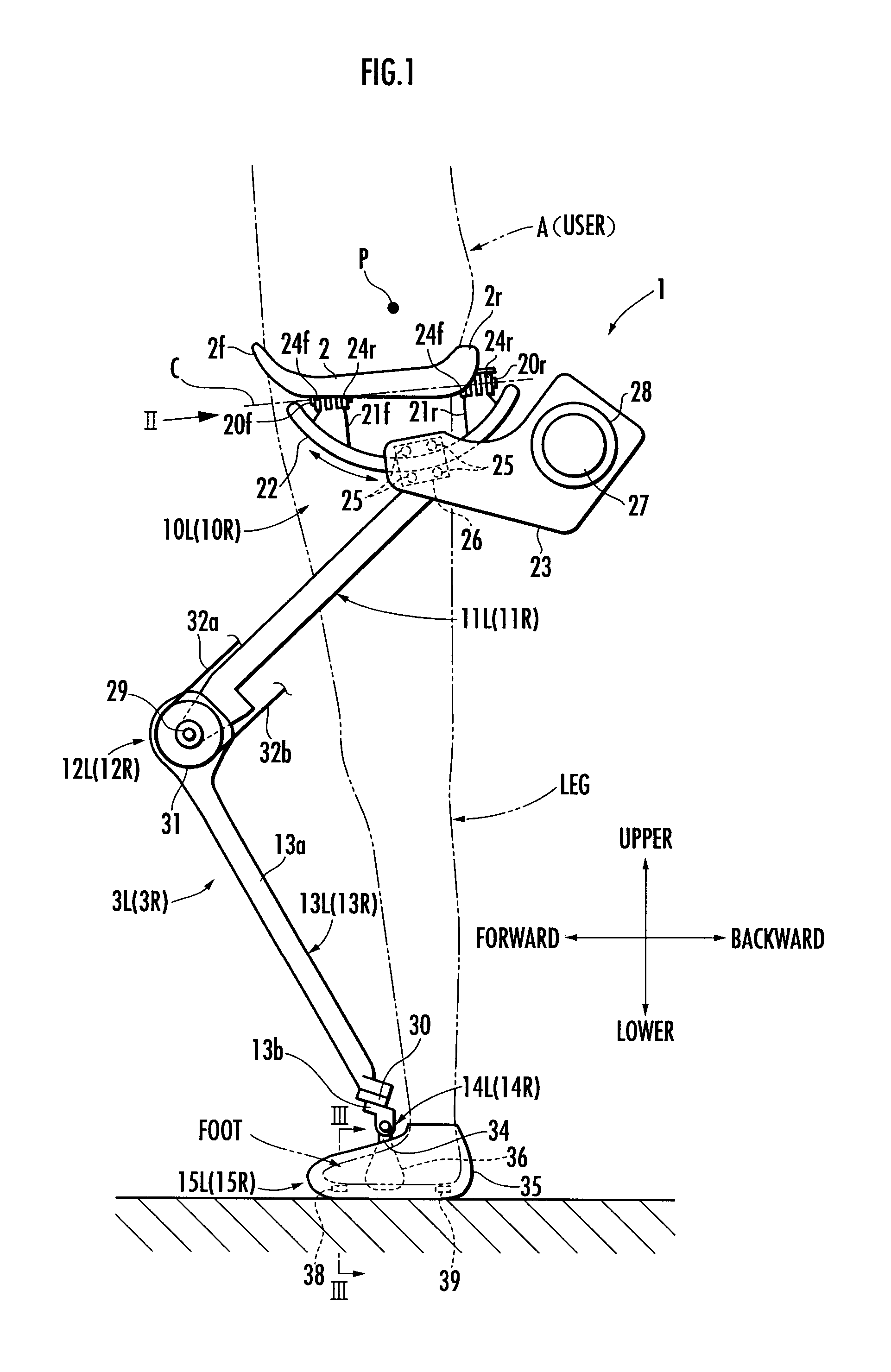
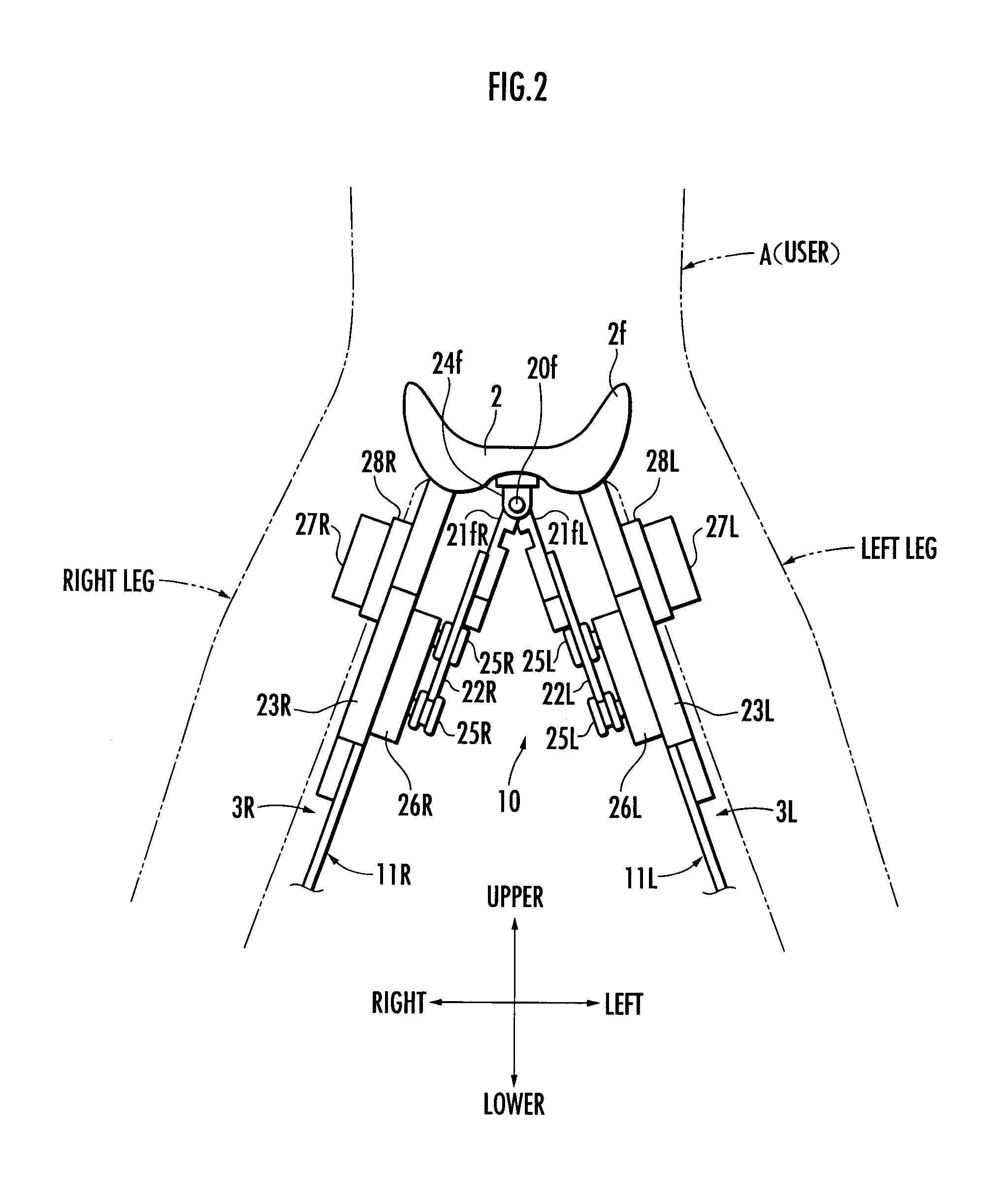
A walking assistance device (1) has a receiving portion (2) which receives a part of the weight of a user (A) applied from above and a pair of left and right leg links (3R, 3L) connected to the receiving portion (2) through first joints (10R, 10L), with foot attachment portions (15R, 15L) at lower ends of the leg links (3R, 3L) attached to the feet of the legs of the user (A), respectively. The leg links (3R, 3L) are connected to the receiving portion (2) in such a way that, when each leg of the user (A) is a standing leg, a line of action of a supporting force transmitted from a third joint (14R, 14L) of the leg link (3R, 3L) to a crus frame (13R, 13L) out of the supporting force acting on the leg link (3R, 3L) from the floor side passes through a specific point (P) located upper than the receiving portion (2) within an anteroposterior width of a contact surface between the receiving portion (2) and the user (A) from the third joint (14R, 14L), viewed in the sagittal plane. Thereby, it is possible to stably apply a desired lifting force for reducing the weight to be borne by the user with his / her legs to the user.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
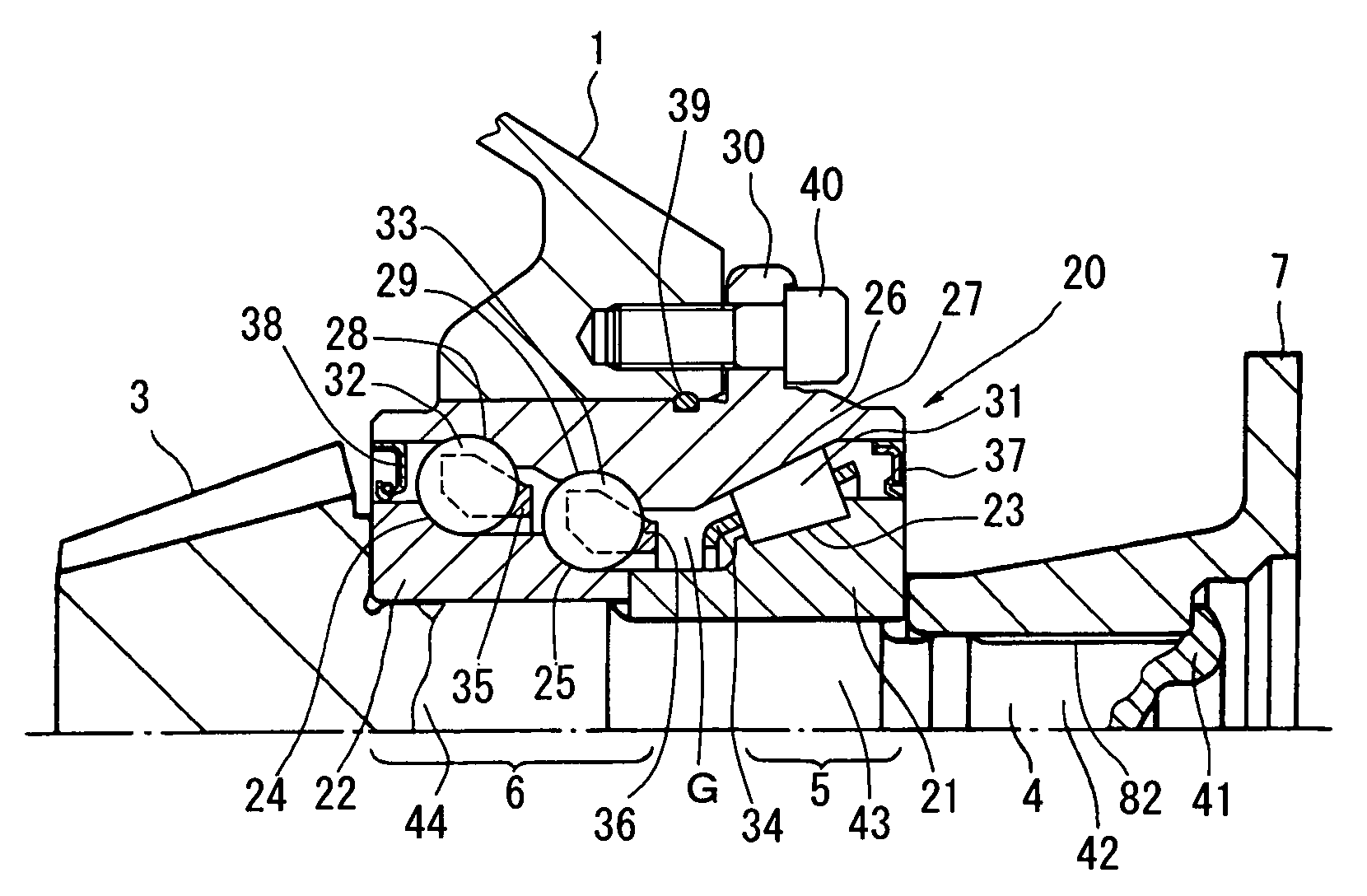
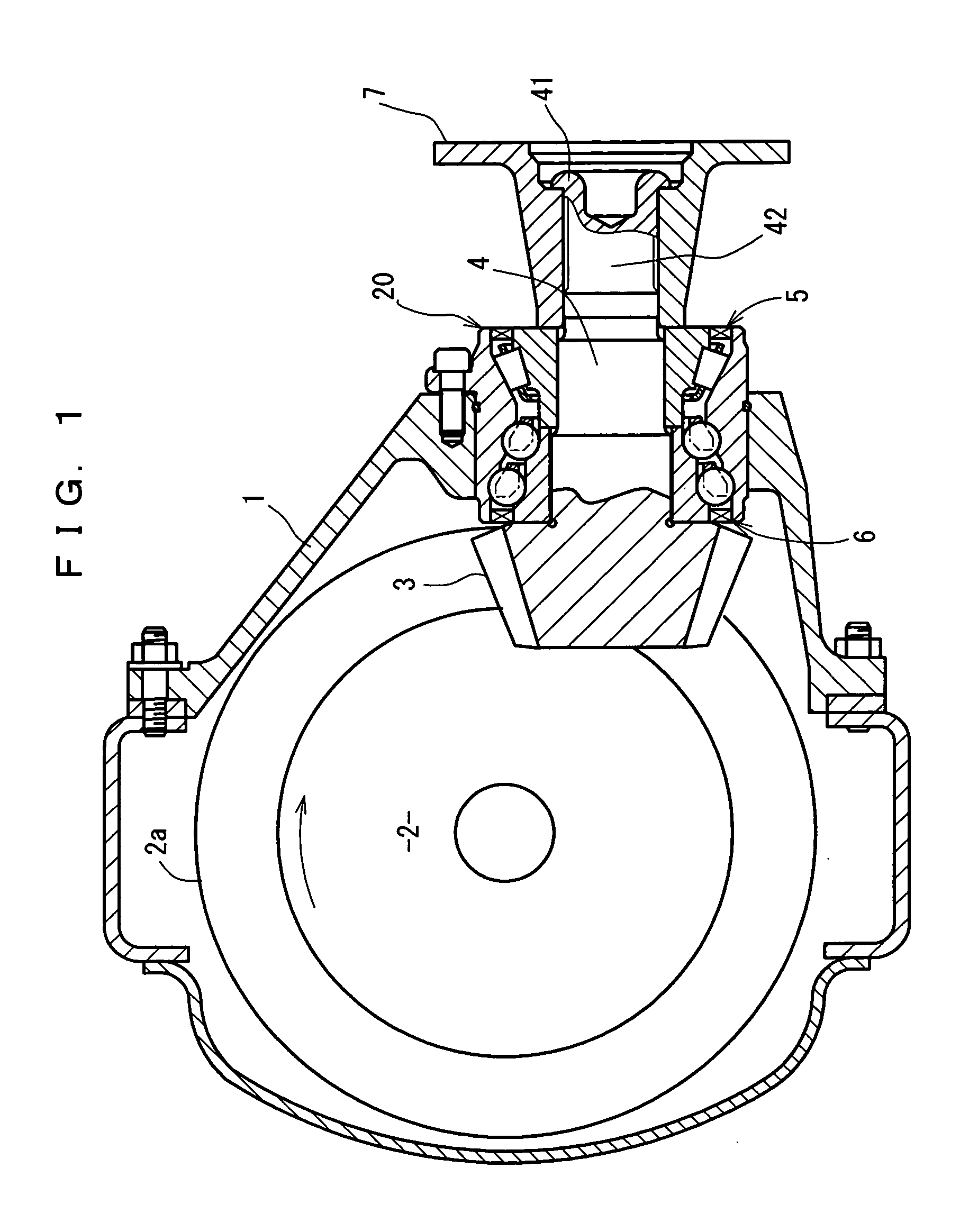
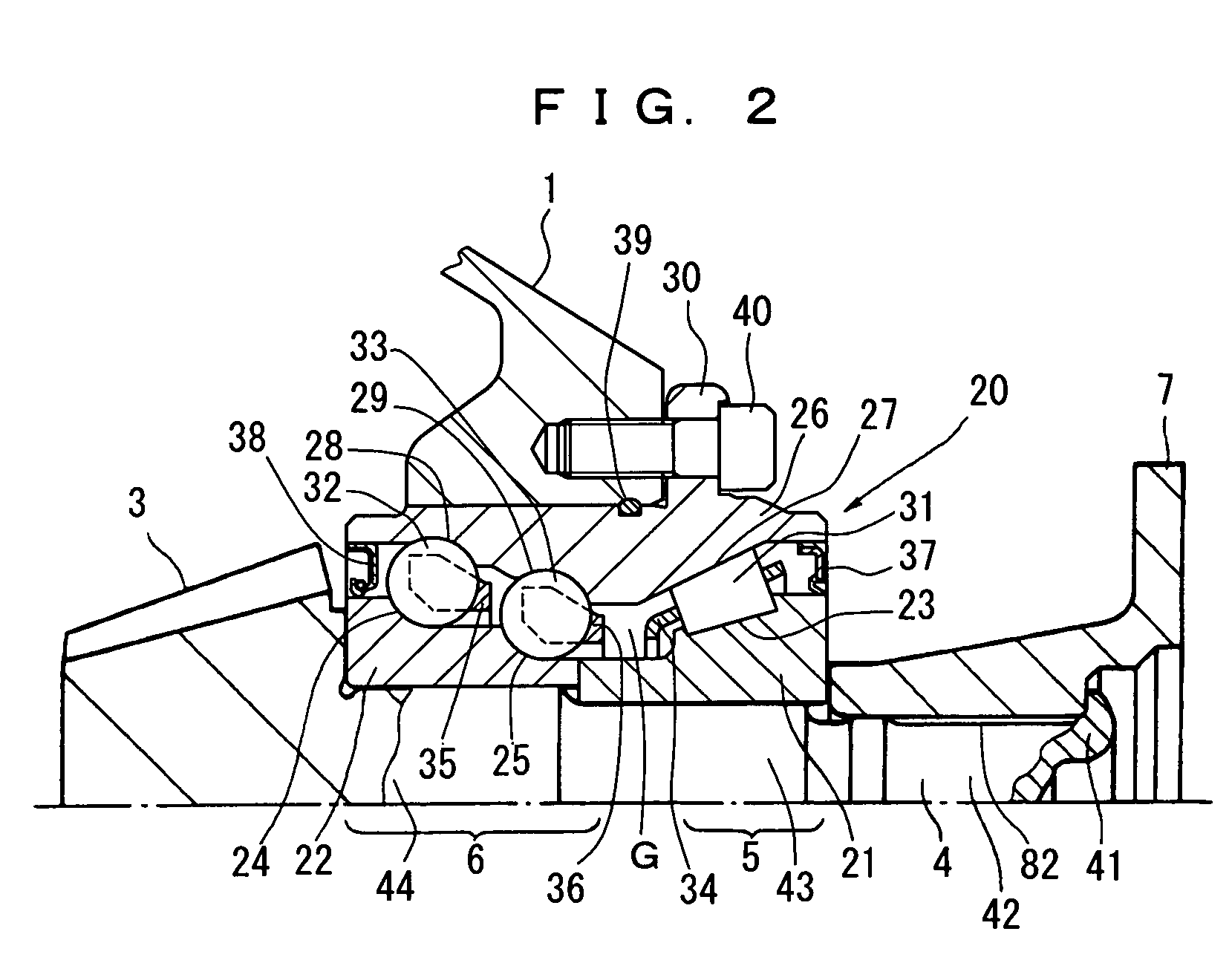
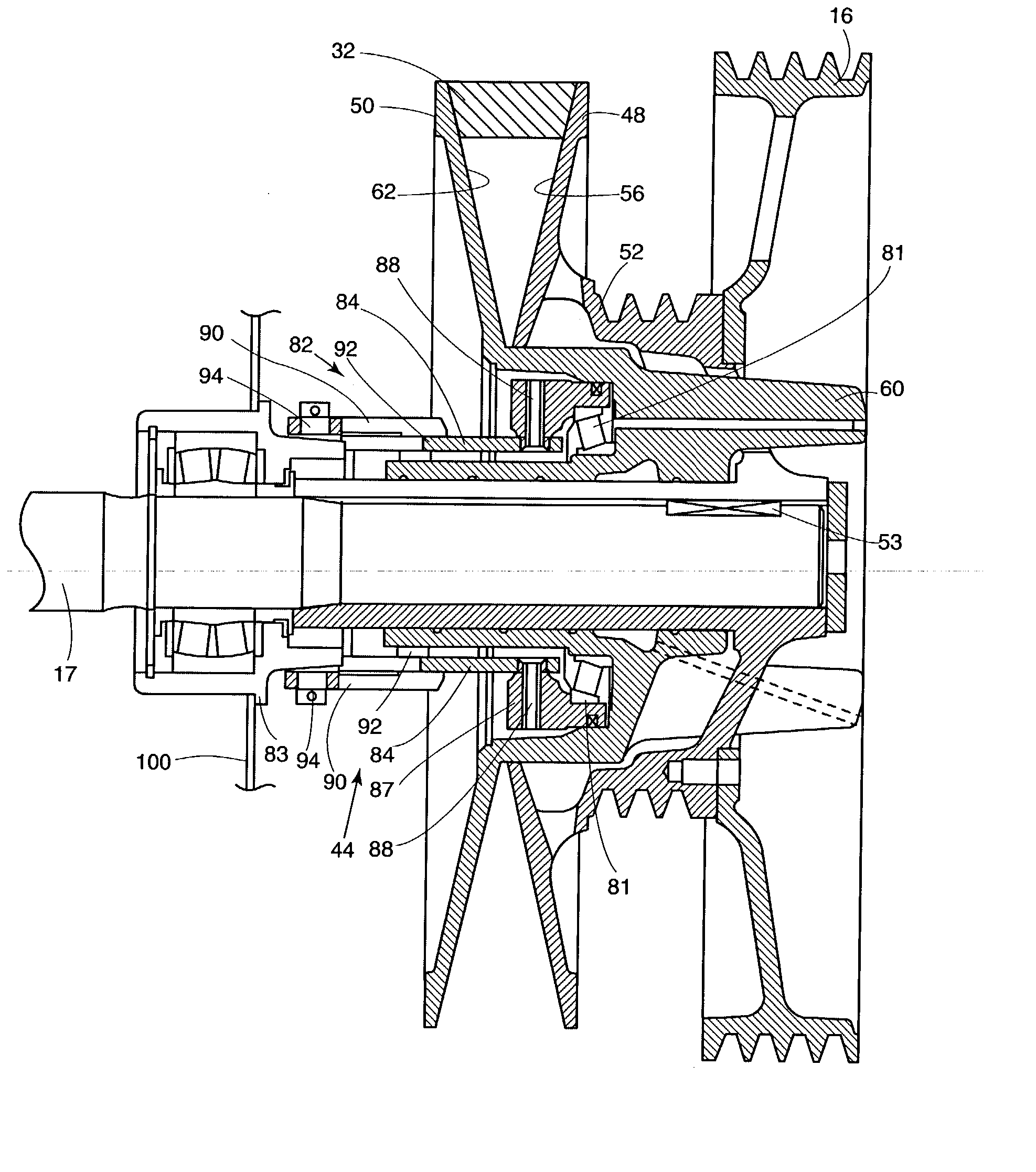
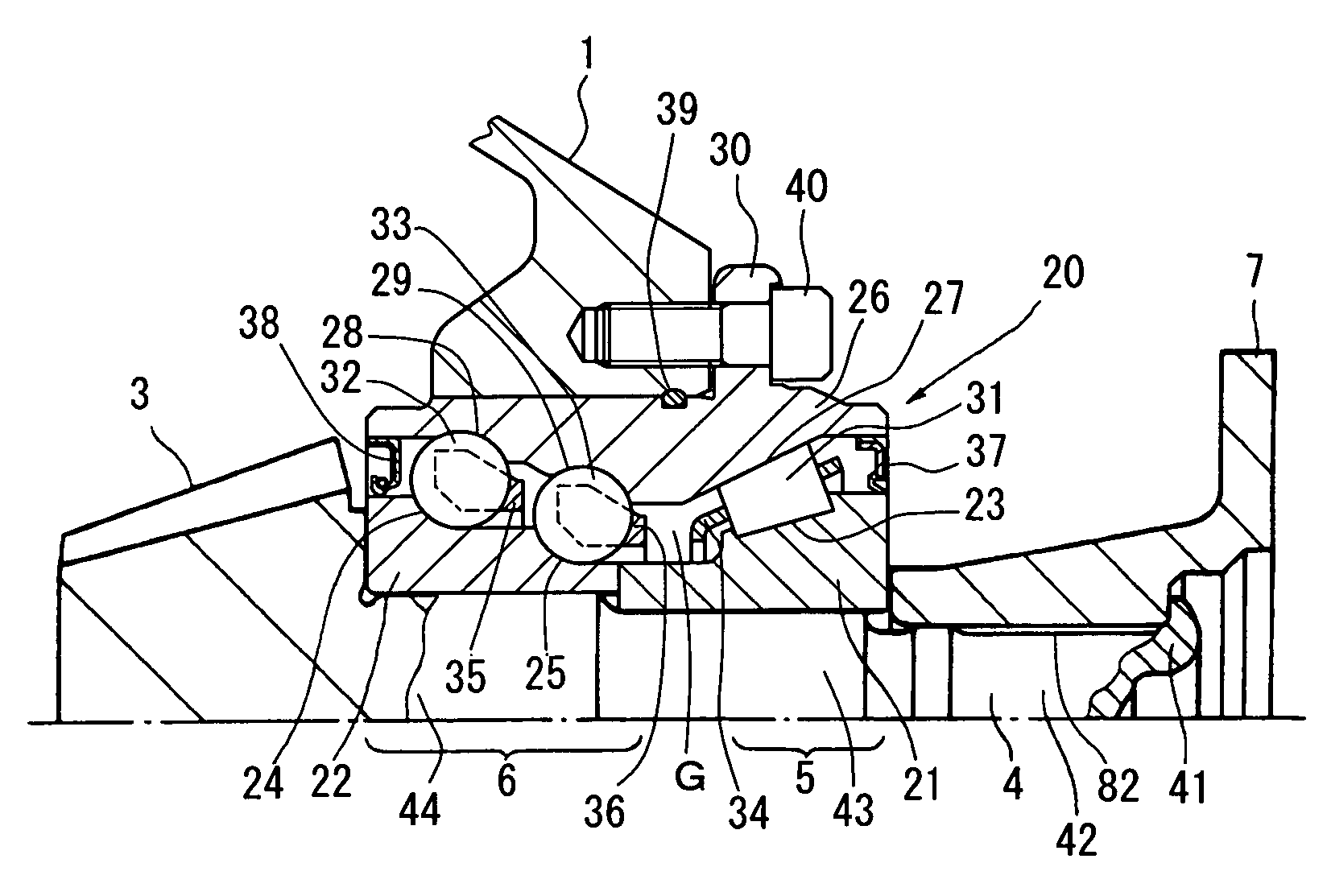
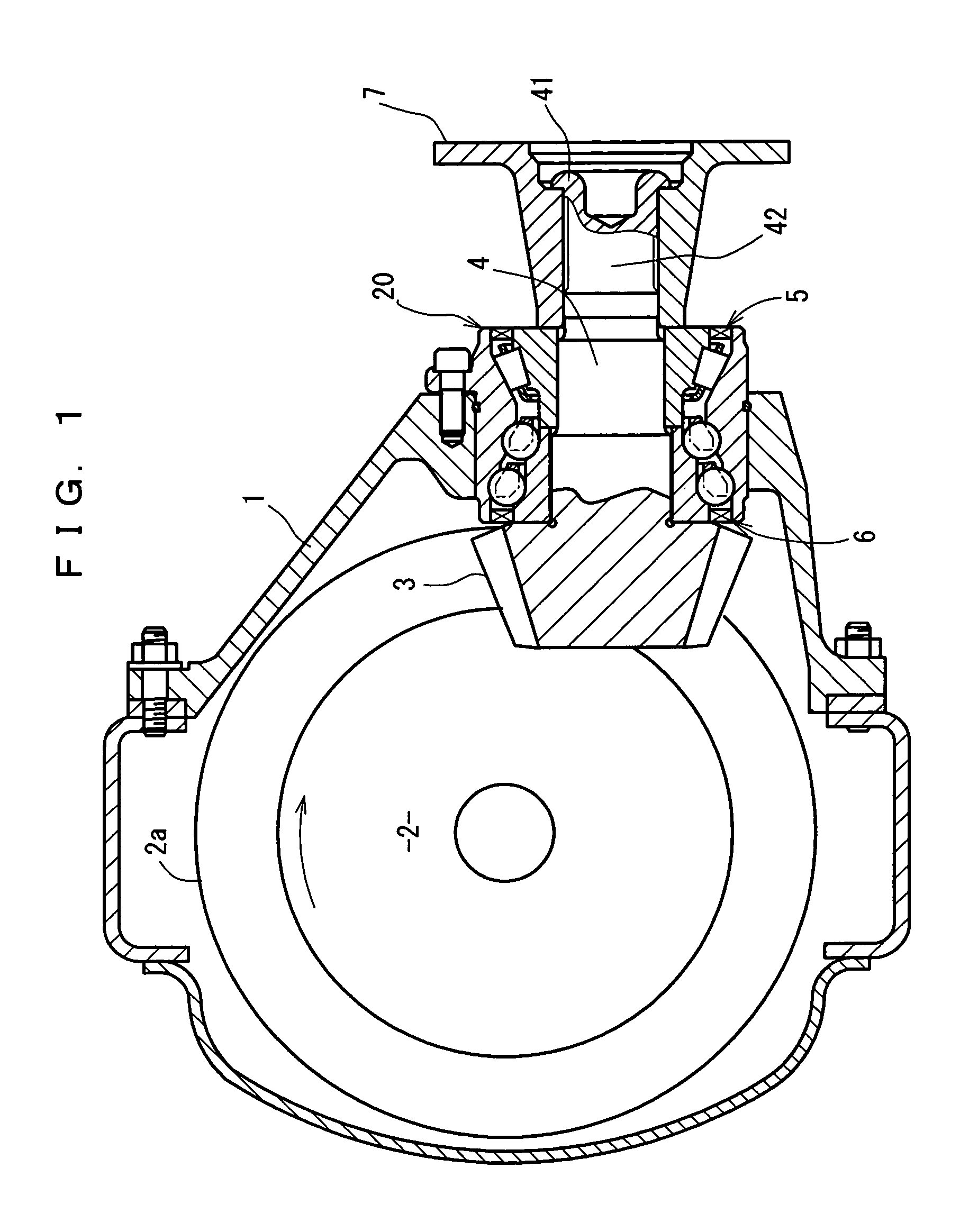
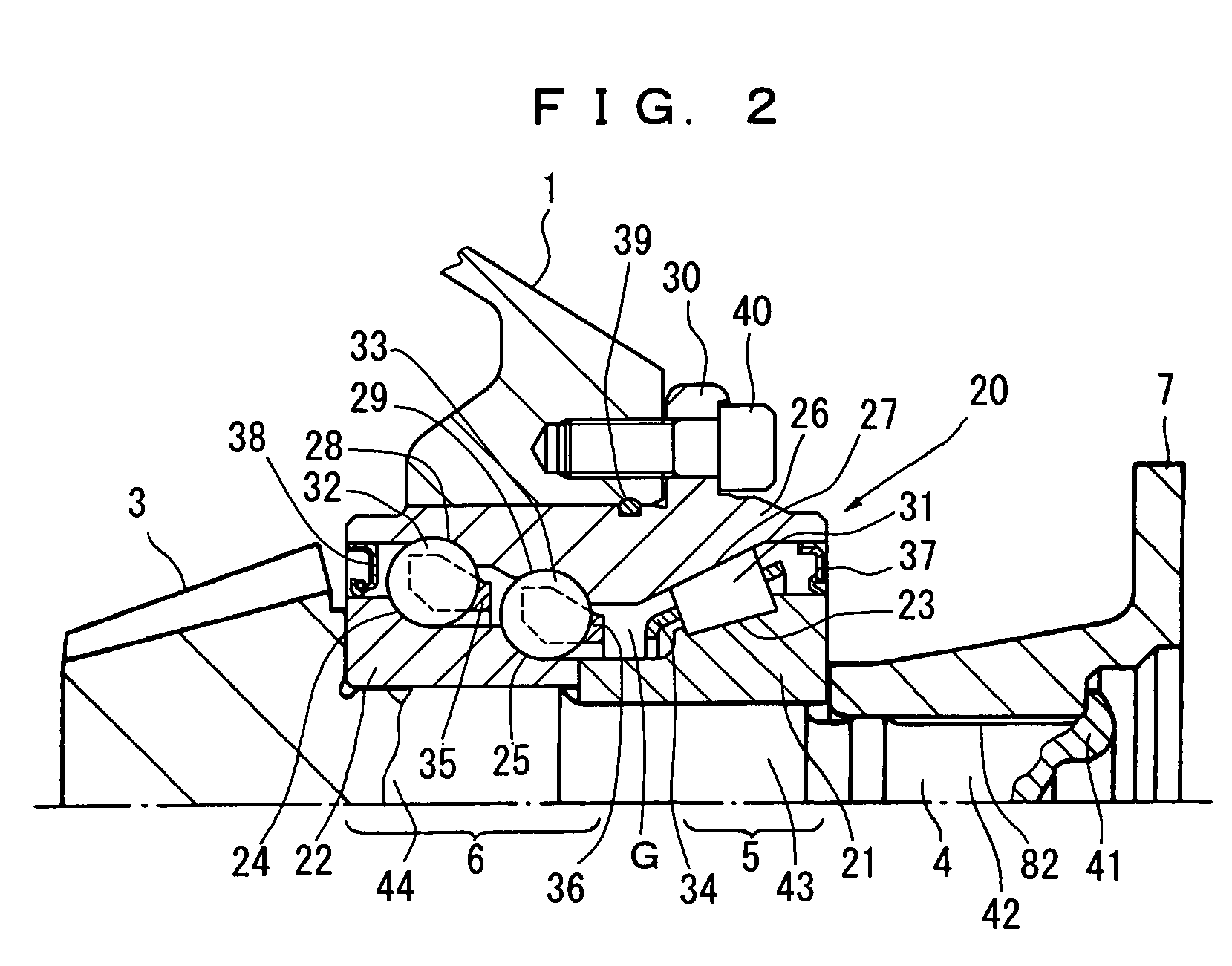
Bearing device for supporting pinion shaft
The present invention relates to a bearing device for supporting a pinion shaft so as to freely rotate with respect to a case. The bearing device comprises a first tilt-contact rolling bearing provided on the connecting-flange-side outer peripheral surface of the pinion shaft and a second tilt-contact rolling bearing formed from an angular ball bearing provided on the pinion-gear-side outer peripheral surface of the pinion shaft, wherein lines of action of the first and second tilt-contact rolling bearings intersect with one another on an outer diameter side, the connecting-flange-side end portion of the first tilt-contact rolling bearing and the pinion-gear-side end portion of the second tilt-contact rolling bearing are respectively sealed with seal members, a sealed space between the seal members is infilled with grease, and the connecting flange is fastened in the pinion-gear direction to thereby preload the first and second tilt-contact rolling bearings.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
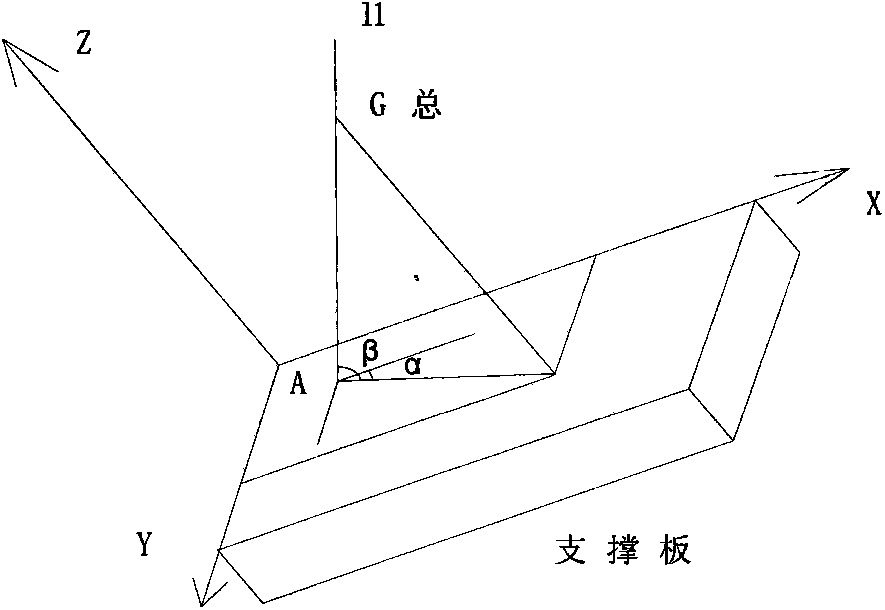
Gravity center measurement instrument based on moment balance principle
InactiveCN103575470AGuaranteed measurement accuracySimple structureStatic/dynamic balance measurementLine of actionRectangular coordinates
Disclosed is a gravity center measurement instrument based on the moment balance principle. The instrument is composed of a supporting plate, six pressure sensors distributed on the periphery of the supporting plate, a mechanical transmission structure, a zooming circuit and a single-chip microcomputer. An intersection point of the gravity vertical of an object to be measured and the supporting plate and the face of the supporting plate is worked out based on the moment balance principle; component force of the G[total] of the supporting plate and the object at each coordinate of a space rectangular coordinate system established on the plate is worked out, and therefore direction vectors of the G[total] are acquired; equations about gravity action lines of the object are worked out based on the space geometry principle; when more equations about the gravity action lines are acquired after the object and the supporting plate rotate to a certain position, the G[total] (x[total], y[total] and z[total]) of the object and the supporting plate is worked out based on the fact that the gravity center passes through all the gravity action lines, and the gravity center G[object] (x[object], y[object] and z[object]) of the object to be measured can be worked out with combination of M[object] and M[plate] based on the fact that G[object], G[plate] and G[total] are located in the same line. In this way, the production of an automatic and computerized instrument which is simple in structure and convenient to operate is achieved on the premise that measurement accuracy in solving the gravity center of the object is guaranteed.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
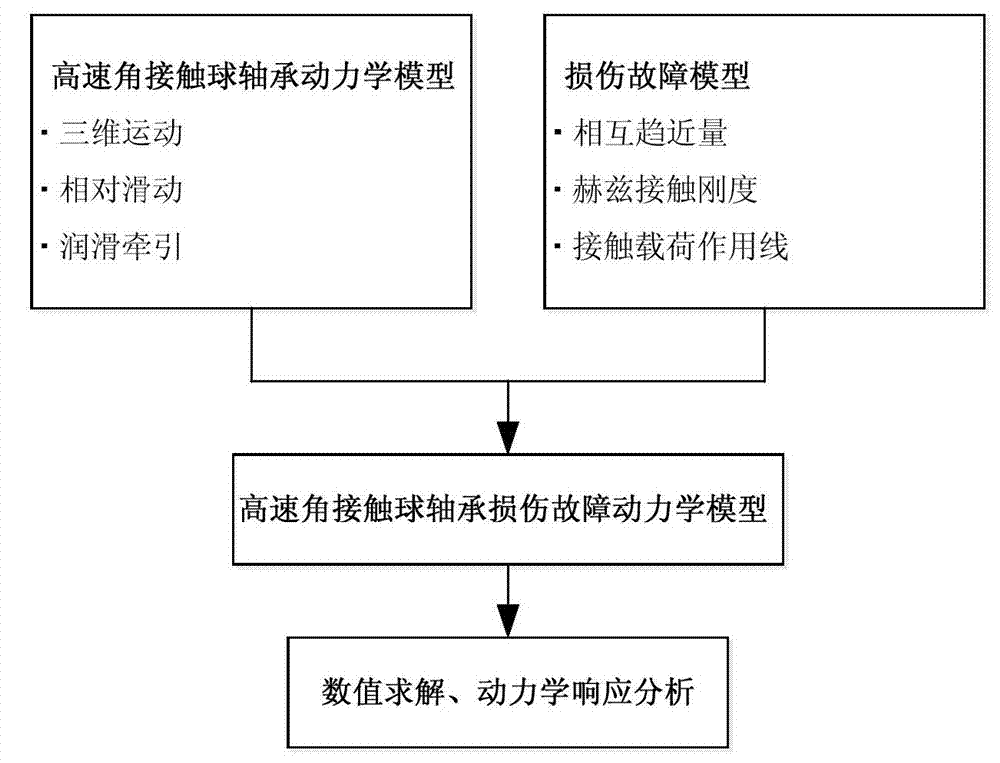
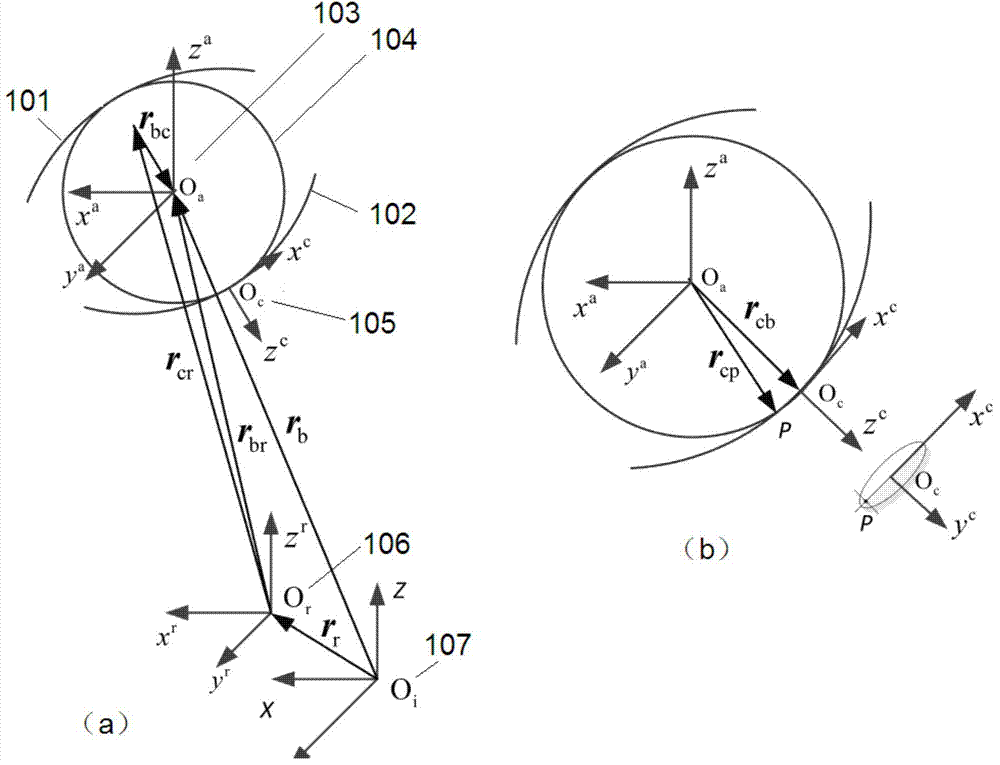
High-speed angular contact ball bearing damage fault dynamic analysis method
The invention discloses a high-speed angular contact ball bearing damage fault dynamic analysis method which is characterized by including the steps of (1) building a high-speed angular contact ball bearing dynamic model, (2) building a high-speed angular contact ball bearing damage fault model, (3) integrating the damage fault model with the high-speed angular contact ball bearing dynamic model to build a high-speed angular contact ball bearing damage fault dynamic model, and (4) carrying out numerical solution to obtain a dynamic response of a bearing under a fault situation and achieving dynamic analysis of a high-speed angular contact ball bearing damage fault. According to the method, three-dimensional motions, relative sliding and lubricating traction effects of the bearing element are taken into consideration, a comprehensive model of the damage fault is built in terms of mutual approach quantity, Hertz contact stiffness and contact load functions, analysis accuracy is improved, and the method for high-speed angular contact ball bearing damage fault dynamic researches is accurate.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
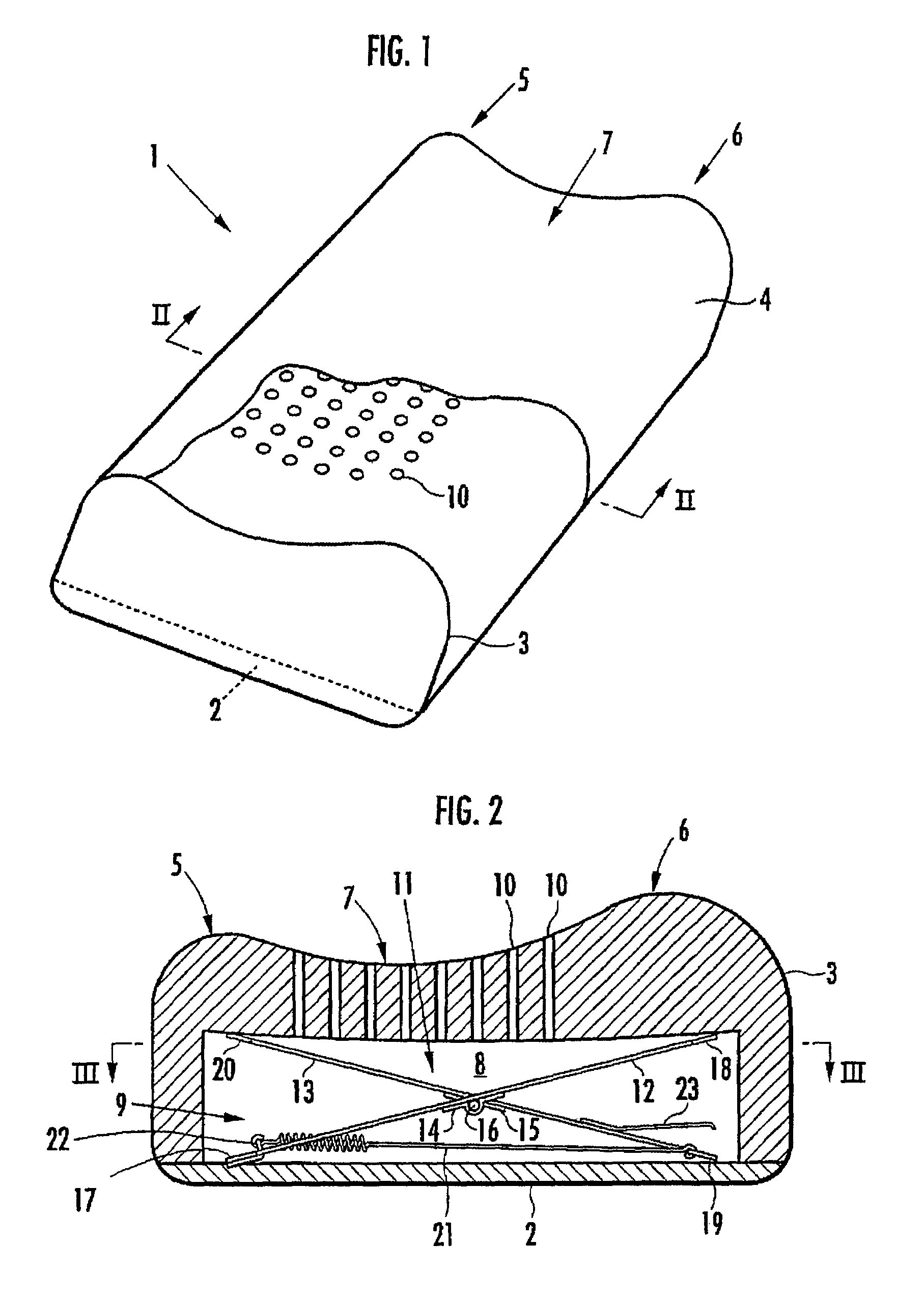
Pillow
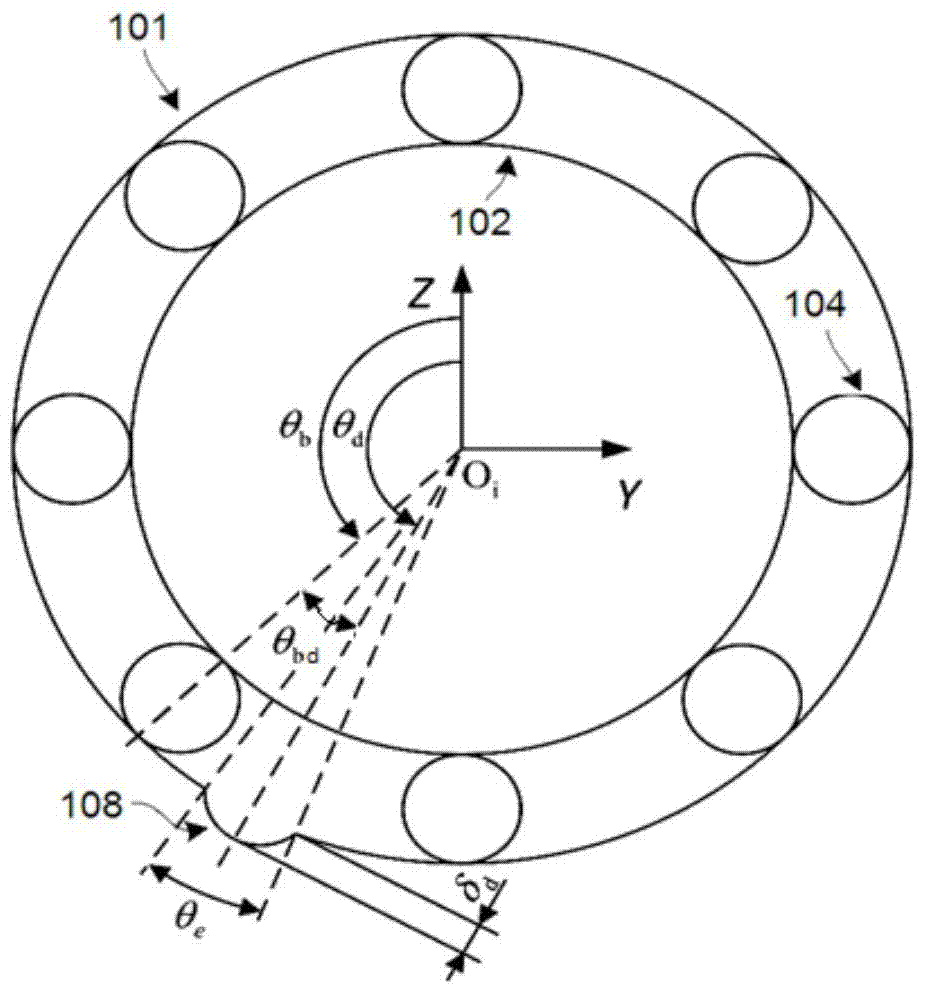
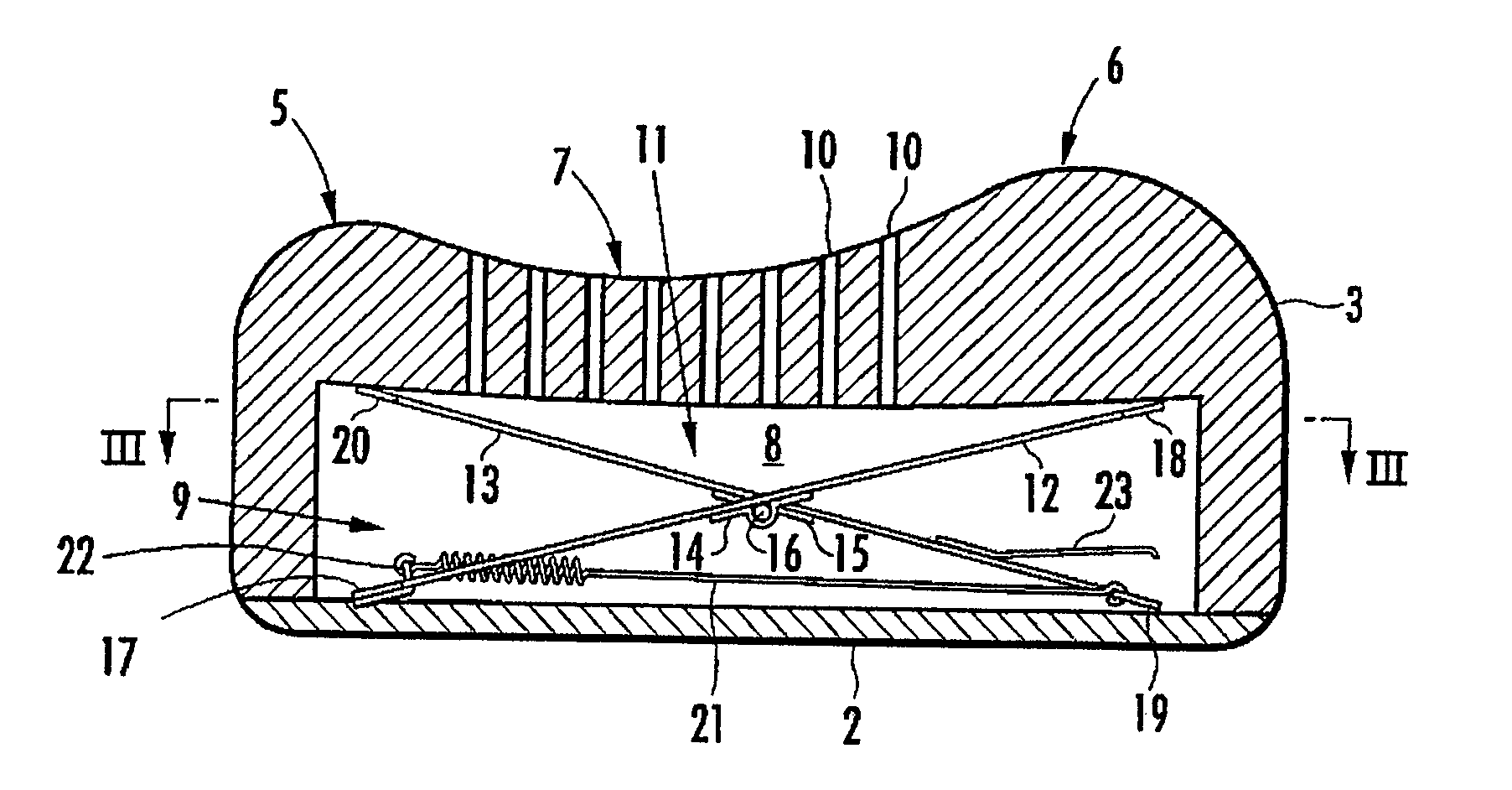
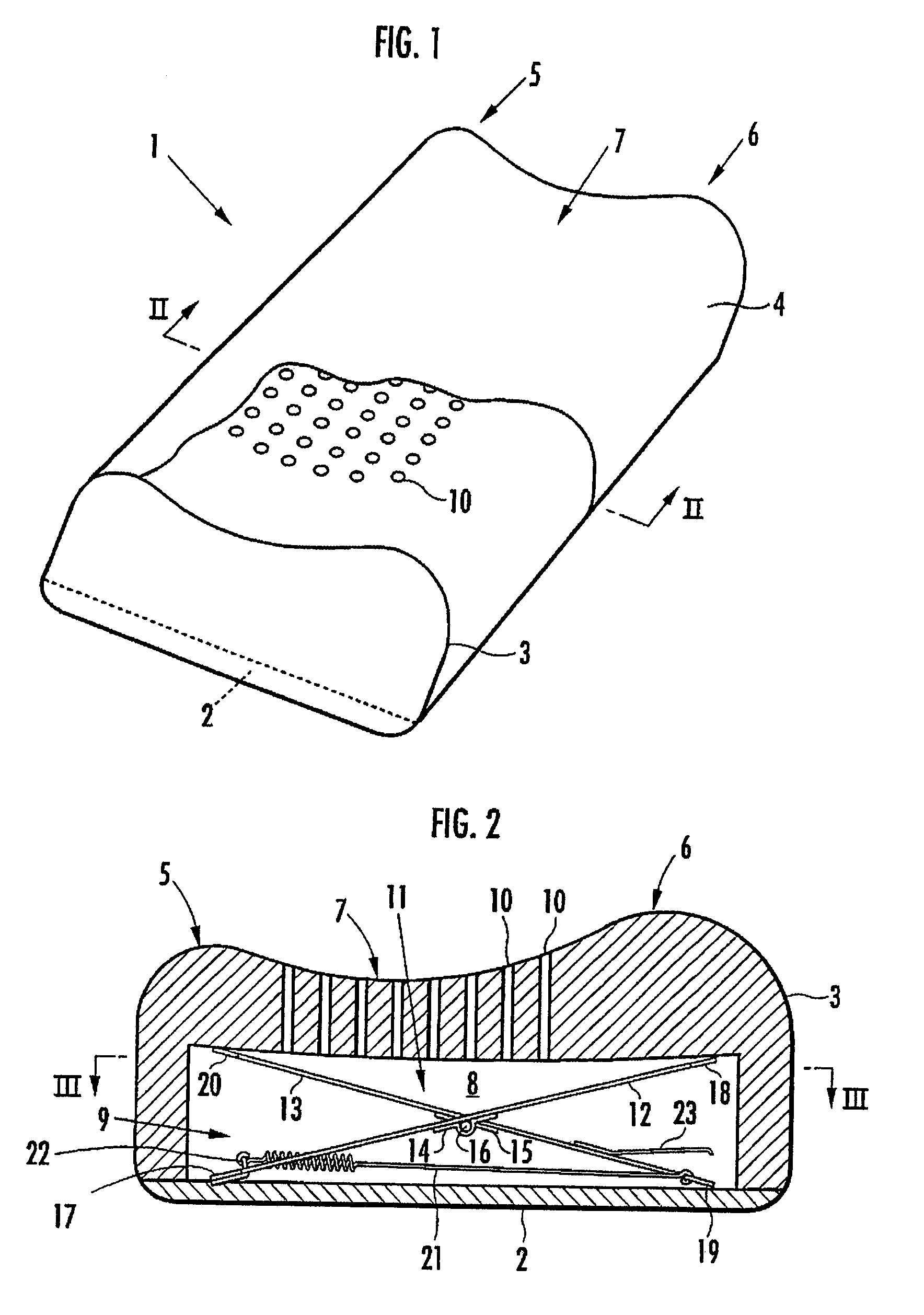
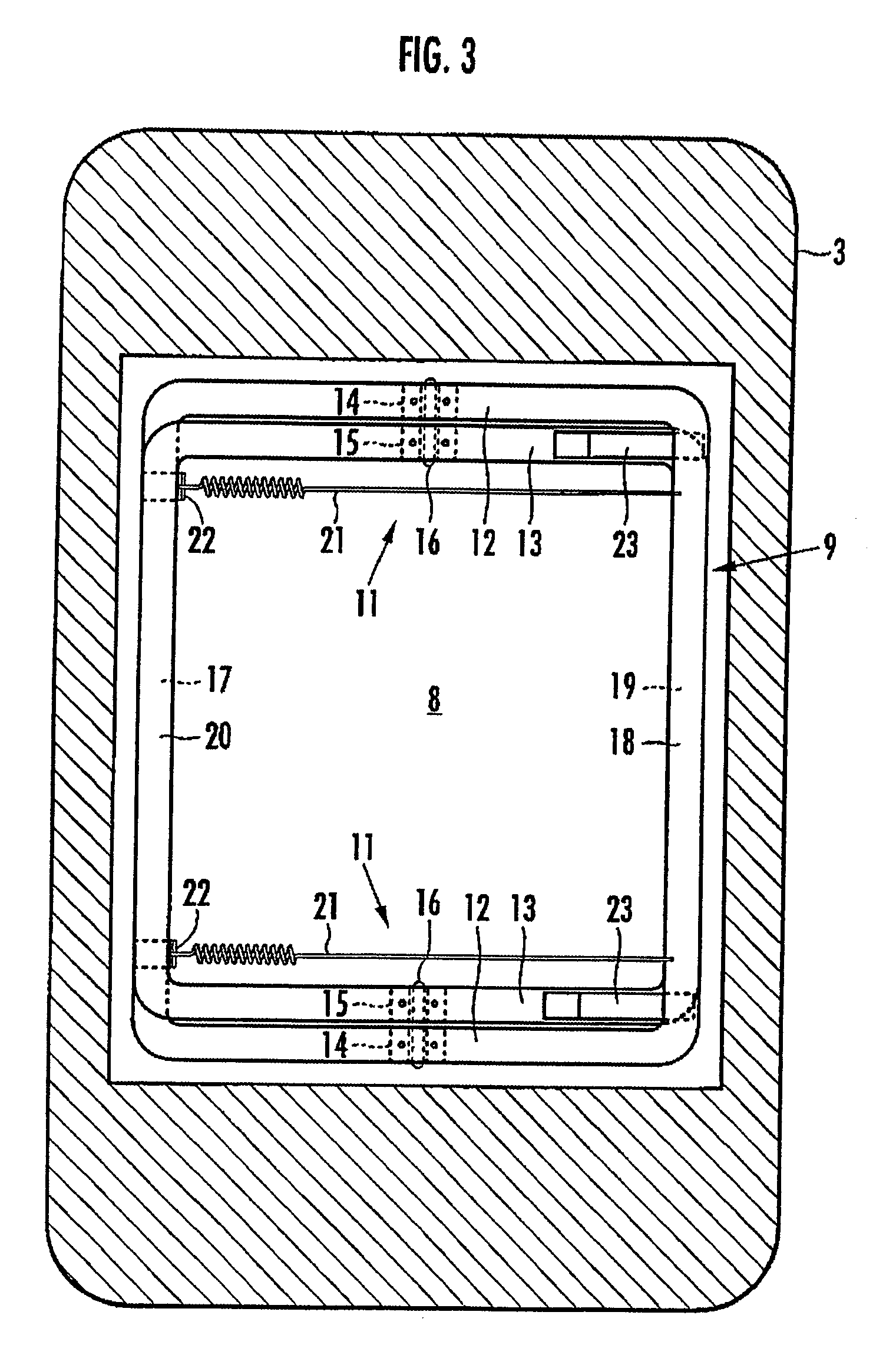
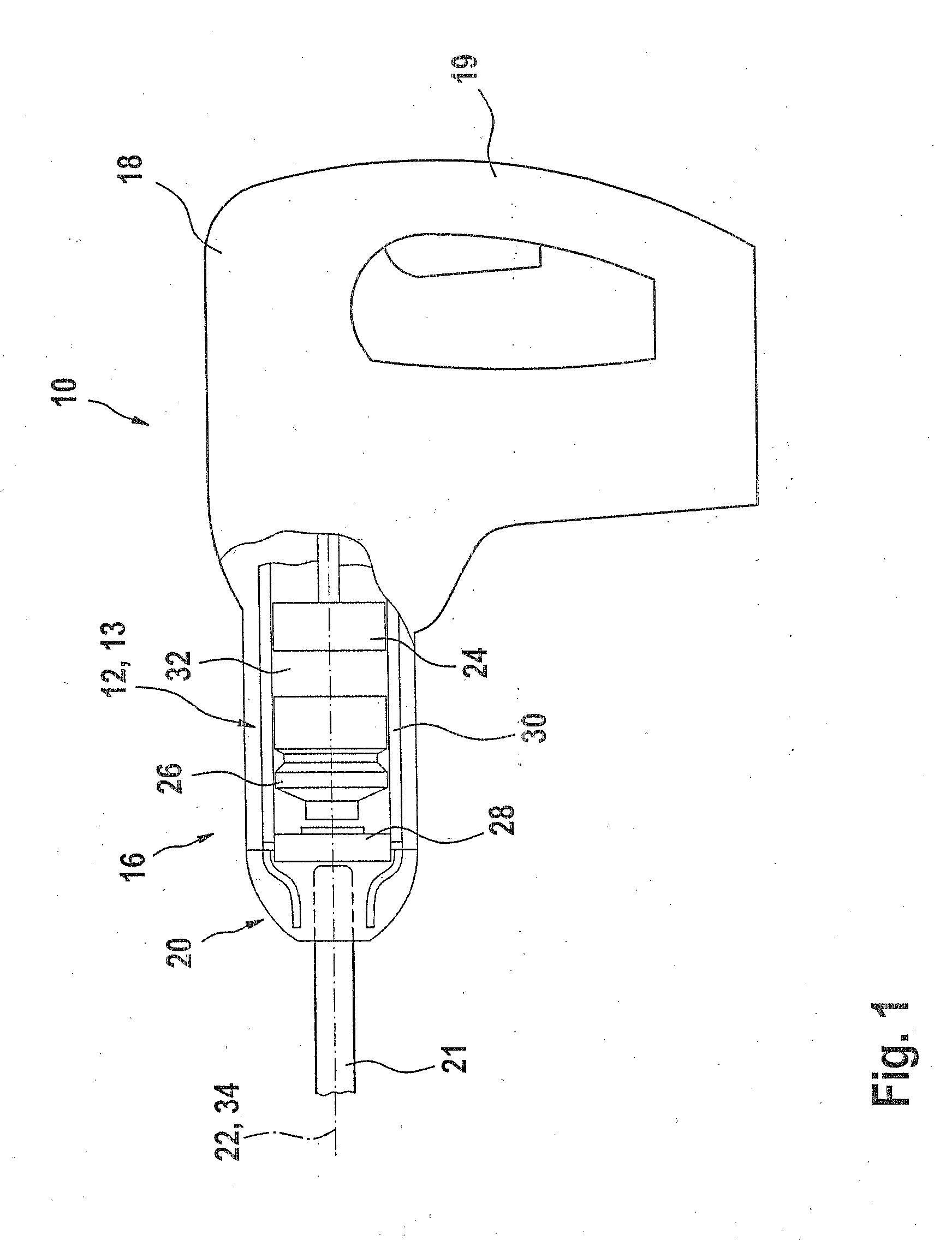
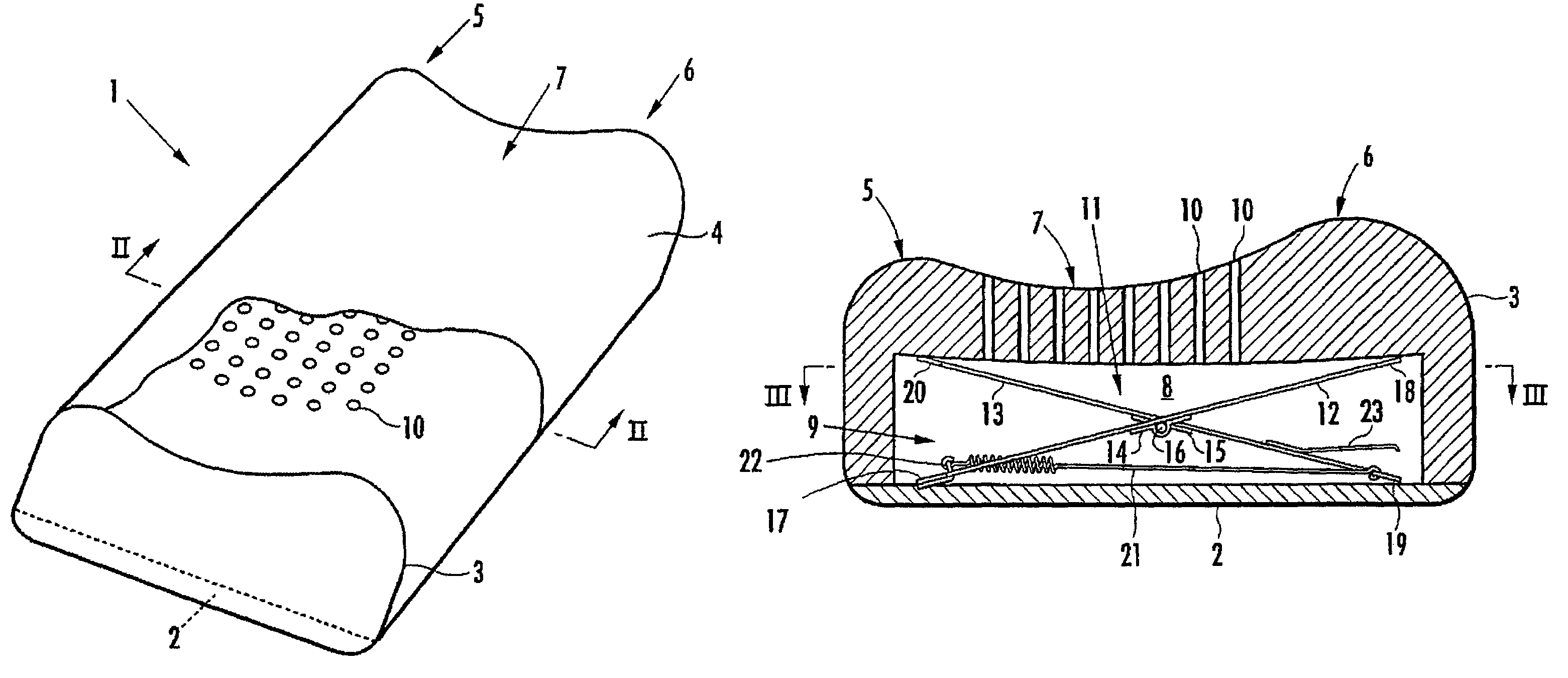
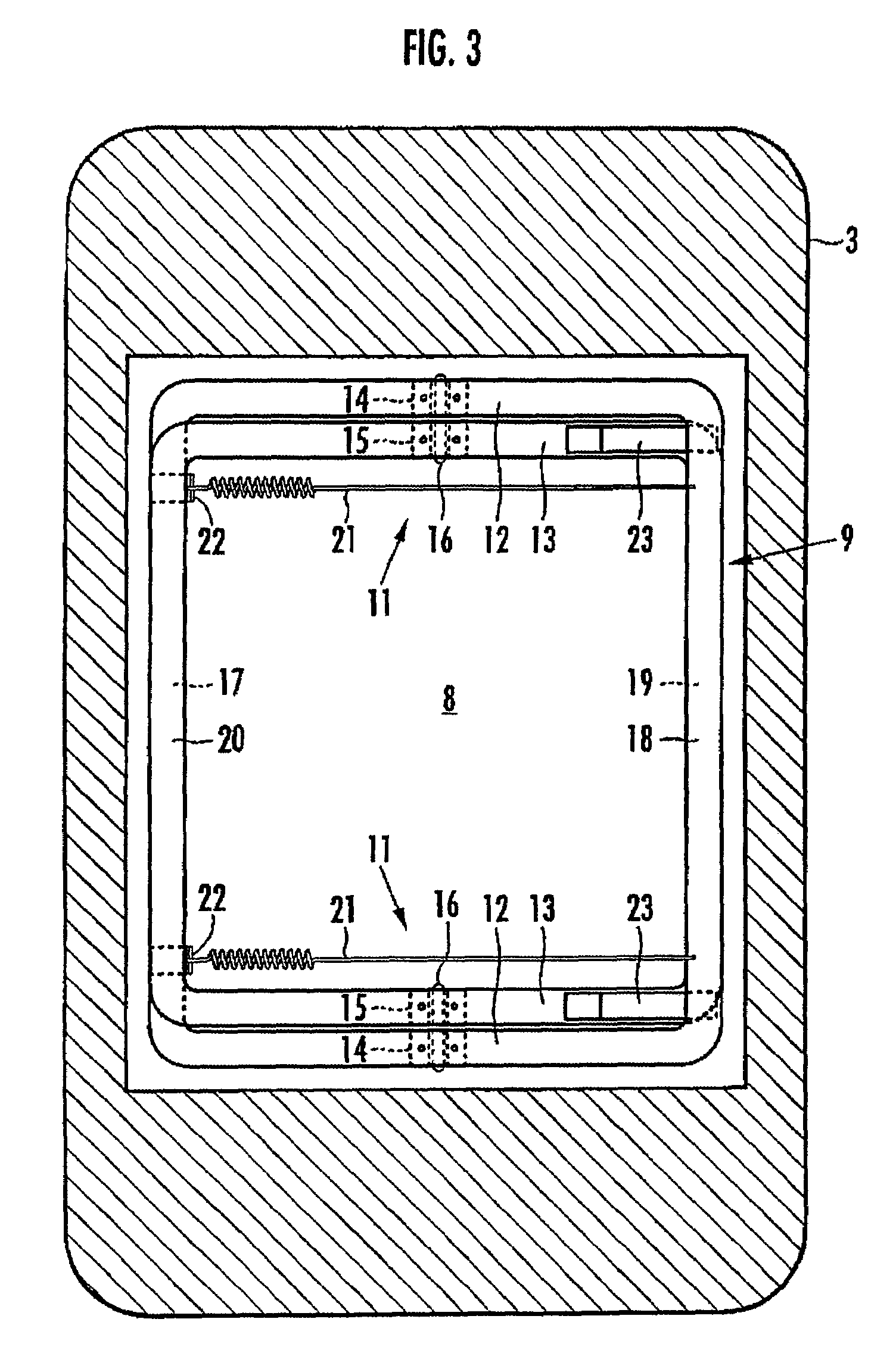
The invention provides a pillow capable of having the height thereof adjusted automatically so that the height of the back of the head of a user in a face-up lying position is slightly higher than his / her back, and also capable of having the height thereof varied automatically between a face-up lying position and a side lying position. A hollow portion 8 having a biasing mechanism 9 disposed therein is formed in a head placement member 3, and when the head is placed face-up on the head placement member 3, the hollow portion 8 is depressed so that the distance between the lowermost portion of the head and the bottom member 2 is in the range of 10 mm to 30 mm. The biasing mechanism has X-shaped links 11 disposed laterally spaced apart in the hollow portion 8. Each X-shaped link is composed by pivotally connecting a first link member 12 slanted upward toward the front and a second link member 13 slanted upward toward the rear by an intermediate link shaft 16. The biasing mechanism further comprises a front-side upper connecting member 18 for connecting the front ends of the first link members of the X-shaped links, a rear-side upper connecting member 20 for connecting the rear ends of the second link members of the X-shaped links, and a spring member 21 providing a spring force for approximating the link members of each X-shaped link in the frontward / rearward direction along a line of action in the frontward / rearward direction with respect to the X-shaped links.
Owner:NAKAYAMA SHINICHIRO
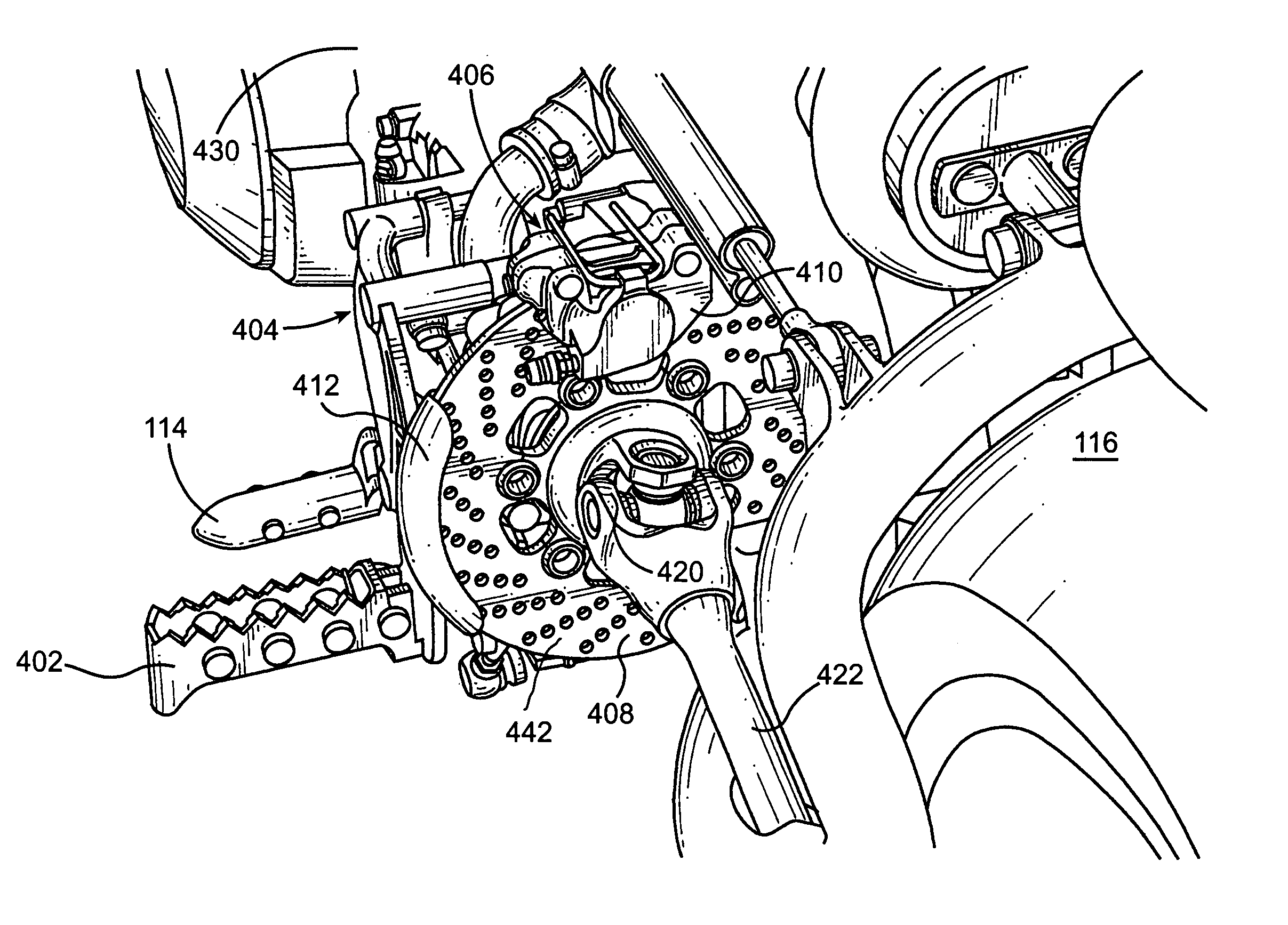
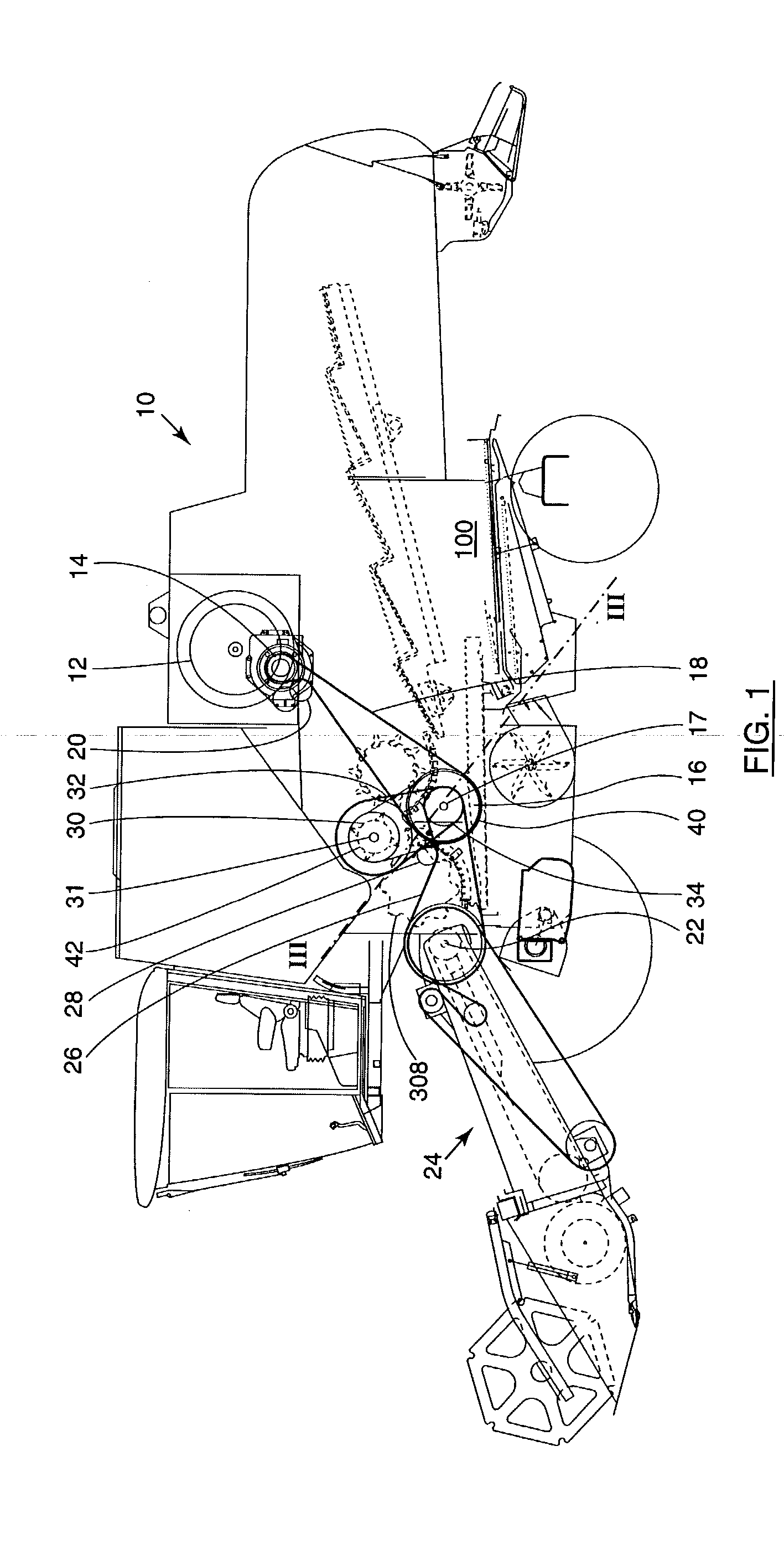
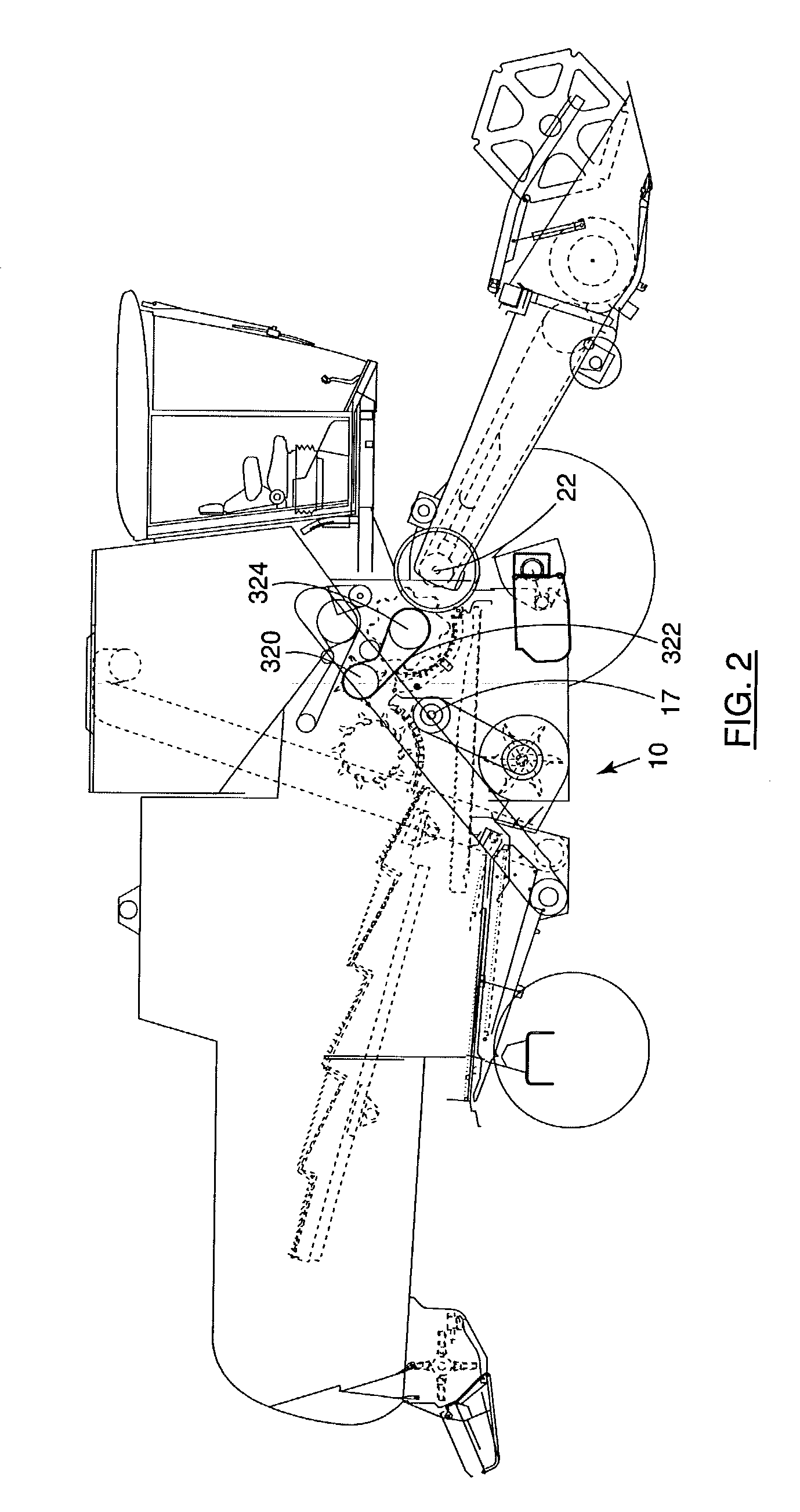
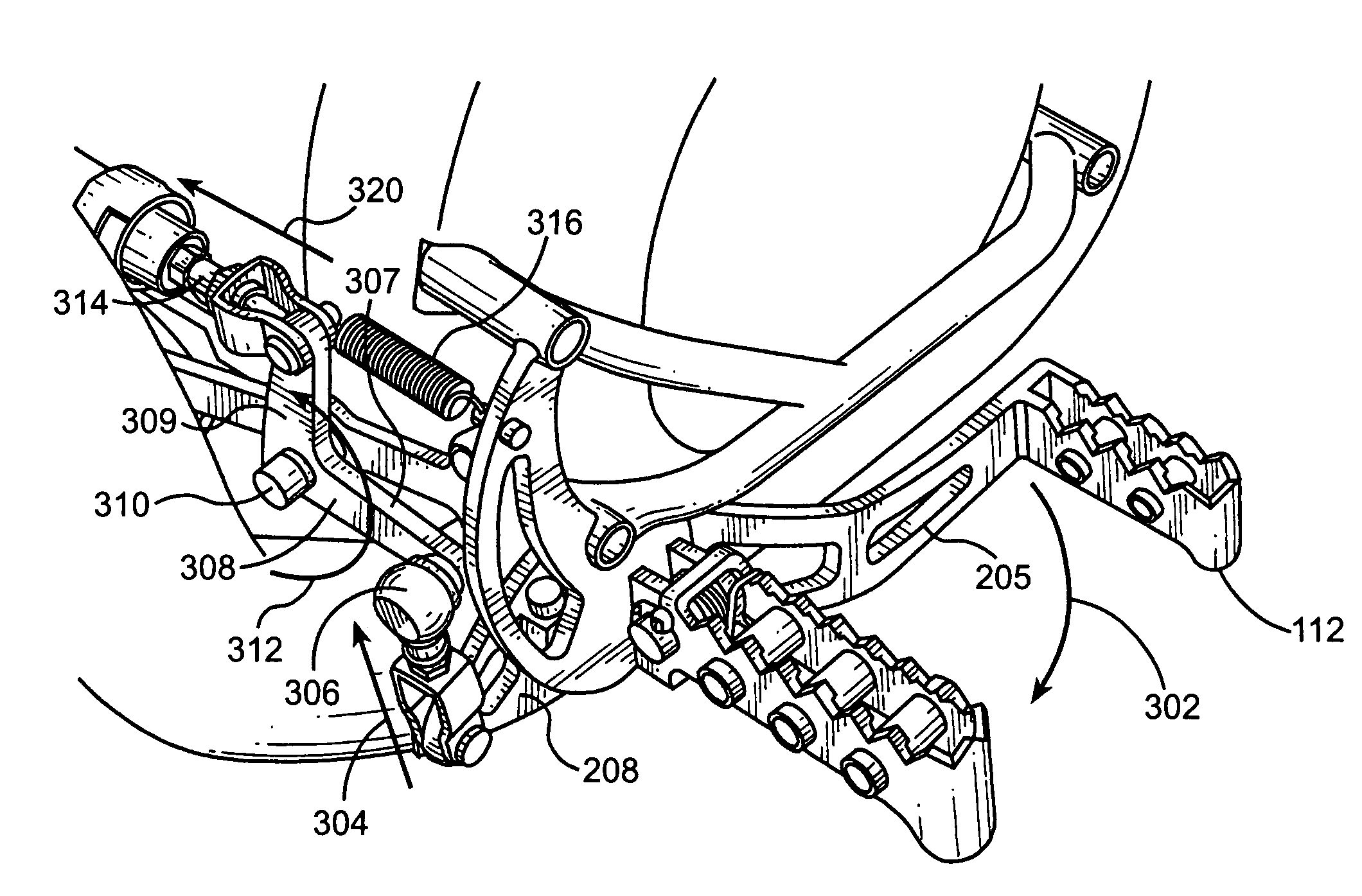
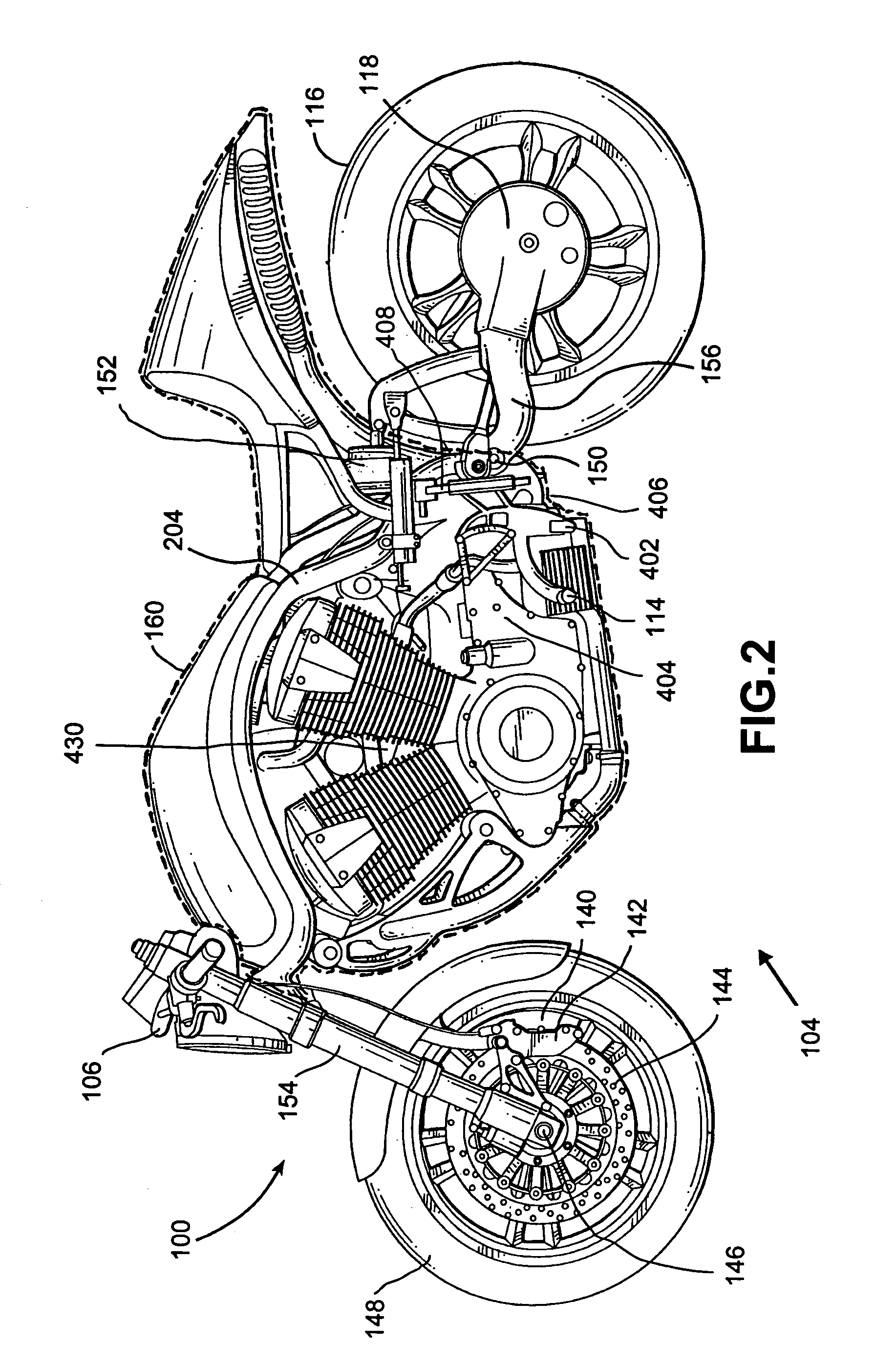
Motorcycle rear disc brake
InactiveUS6923293B1Avoid contactBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesLine of actionEngineering
A motorcycle including a front wheel, a rear wheel, a frame, a seat and handlebars is disclosed. The motorcycle includes a linkage connecting a brake pedal with a caliper. The caliper is located within a body perimeter of the motorcycle. The caliper is adapted to engage a disk and the caliper can have a line of action. The direction of the line of action of the caliper can be different than the axis of rotation of the rear wheel. The linkage can also convert vertical motion into horizontal motion.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
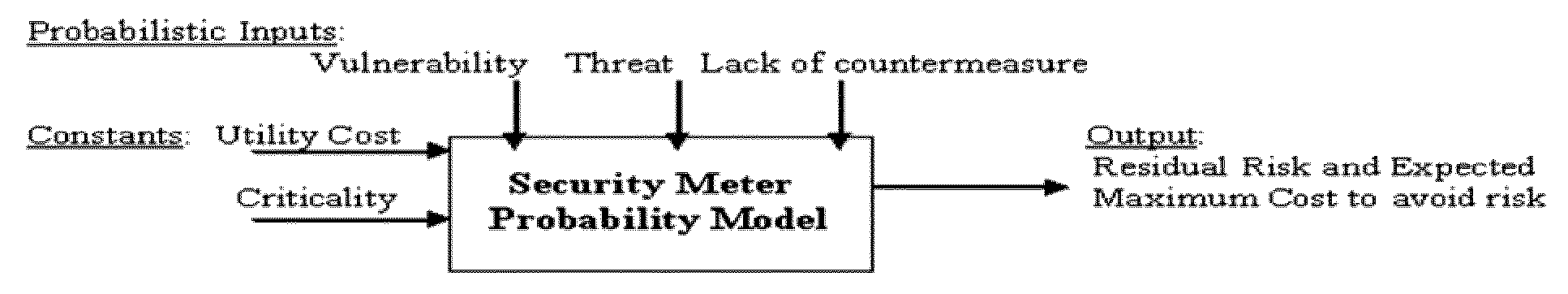
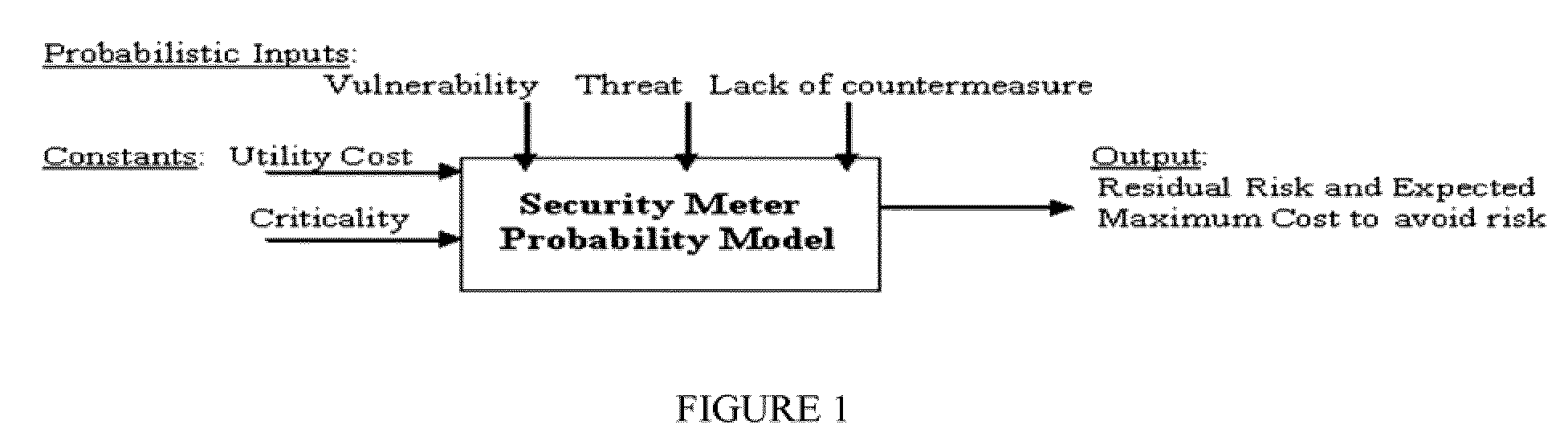
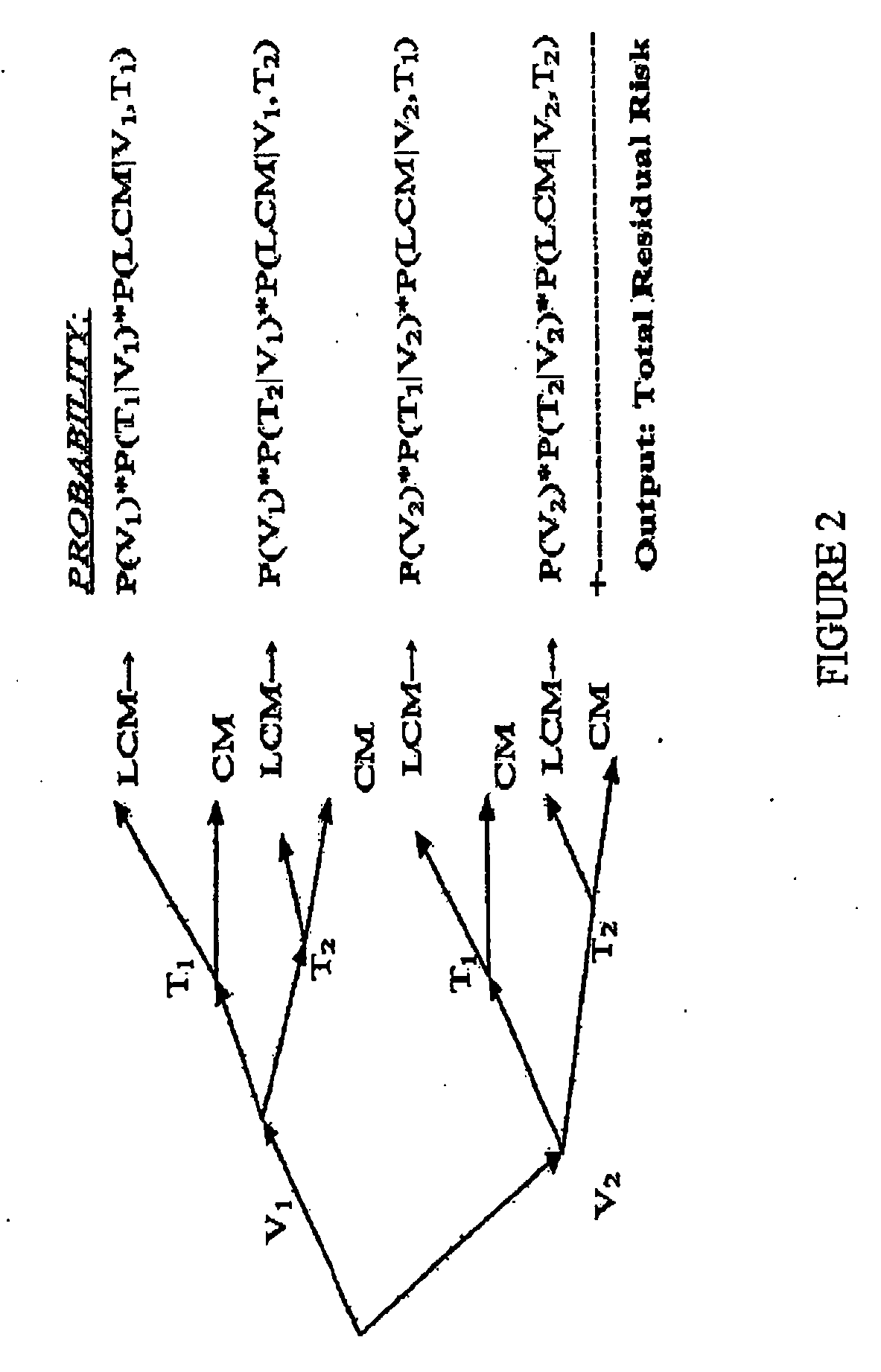
Method of automating security risk assessment and management with a cost-optimized allocation plan
A method of automating security risk assessment and management and corrective feedback with a cost-optimized allocation plan is disclosed. The method, operable in a computer system, includes presenting an on-line survey questionnaire and receiving, in response to the on-line survey questionnaire, a user-provided answer. The method further includes extracting data from the computer system and calculating, in response to the user-provided answer and the extracted data, a security risk. The method also includes producing, in response to the security risk, the cost-optimized allocation plan. The data and the user-provided answer are recorded in a data repository. The cost-optimized allocation plan is produced using a game-theoretical approach. The cost-allocation allocation plan includes changes to break even a cost differential of an expected cost of loss (ECL), and further assigns realistic market-oriented mitigation costs to each line of action for the user's computer or system.
Owner:SAHINOGLU MEHMET
Installation of offshore structures
A method and system for transporting an offshore structure such as a wind turbine generator includes a supporting frame in which the offshore structure is assembled on land in an upright configuration. The frame is used for lifting the structure onto a transport vessel, on which it is retained in the upright configuration. At its location of use, the offshore structure is transferred to a pre-prepared foundation. The foundation is provided with a frame which cooperates with the supporting frame. The supporting frame includes a plurality of legs having hydraulically controlled feet. The frame of the foundation includes an equal number of supporting formations on which the feet ultimately rest. The feet are moveable in response to the hydraulic control along a nominally vertical line of action and provide a damping arrangement for the mounting of the offshore structure.
Owner:IHC HOLLAND NV
Hand-held power tool, particularly a drilling and/or chisel hammer, having a damper unit
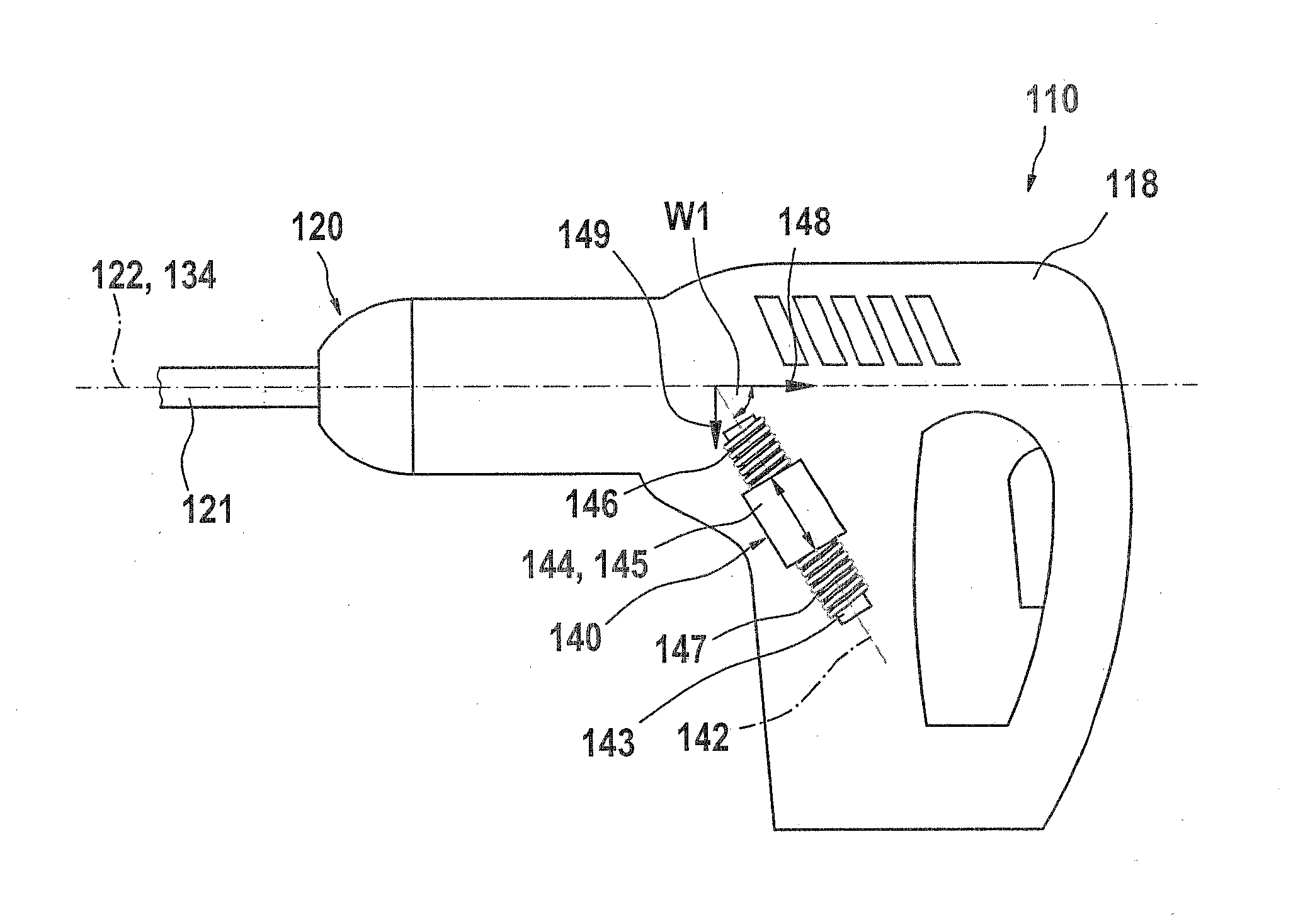
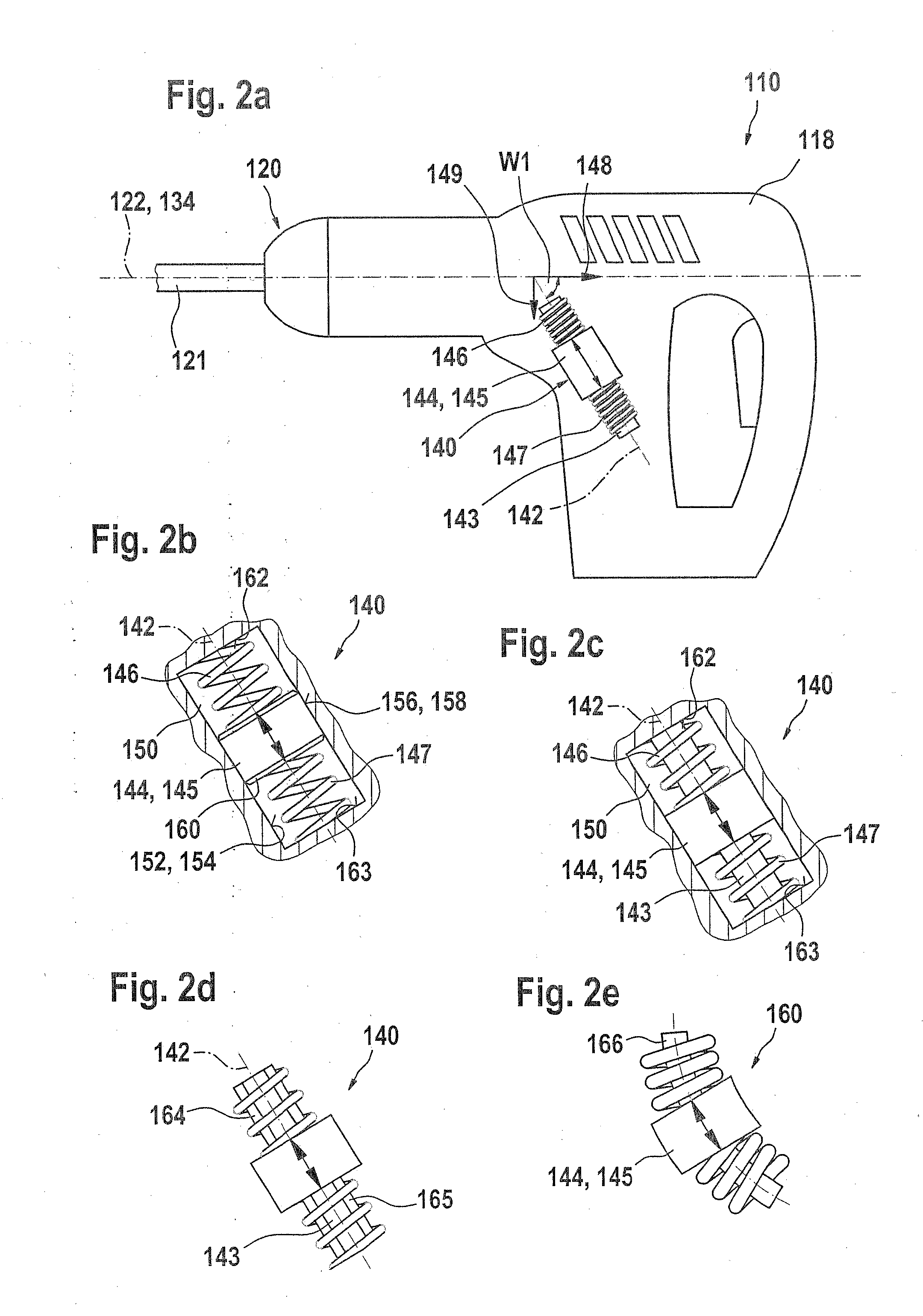
InactiveUS20100307783A1Reduce oscillationSimple structurePortable percussive toolsPortable power-driven toolsLine of actionChisel
A hand-held power tool, in particular an impact driver, an impact drill, or a rotary hammer, is proposed, which has a drive unit and / or output with at least one line of action, which produces at least oscillations along the line of action. In order to reduce these oscillations, the hand-held power tool is equipped with at least one vibration absorber unit. The vibration absorber unit has at least one mobile vibration absorbing element, which has at least one degree of freedom of movement. This degree of freedom of movement encloses at least one angle not equal to zero with the line of action.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Motor with linear actuators
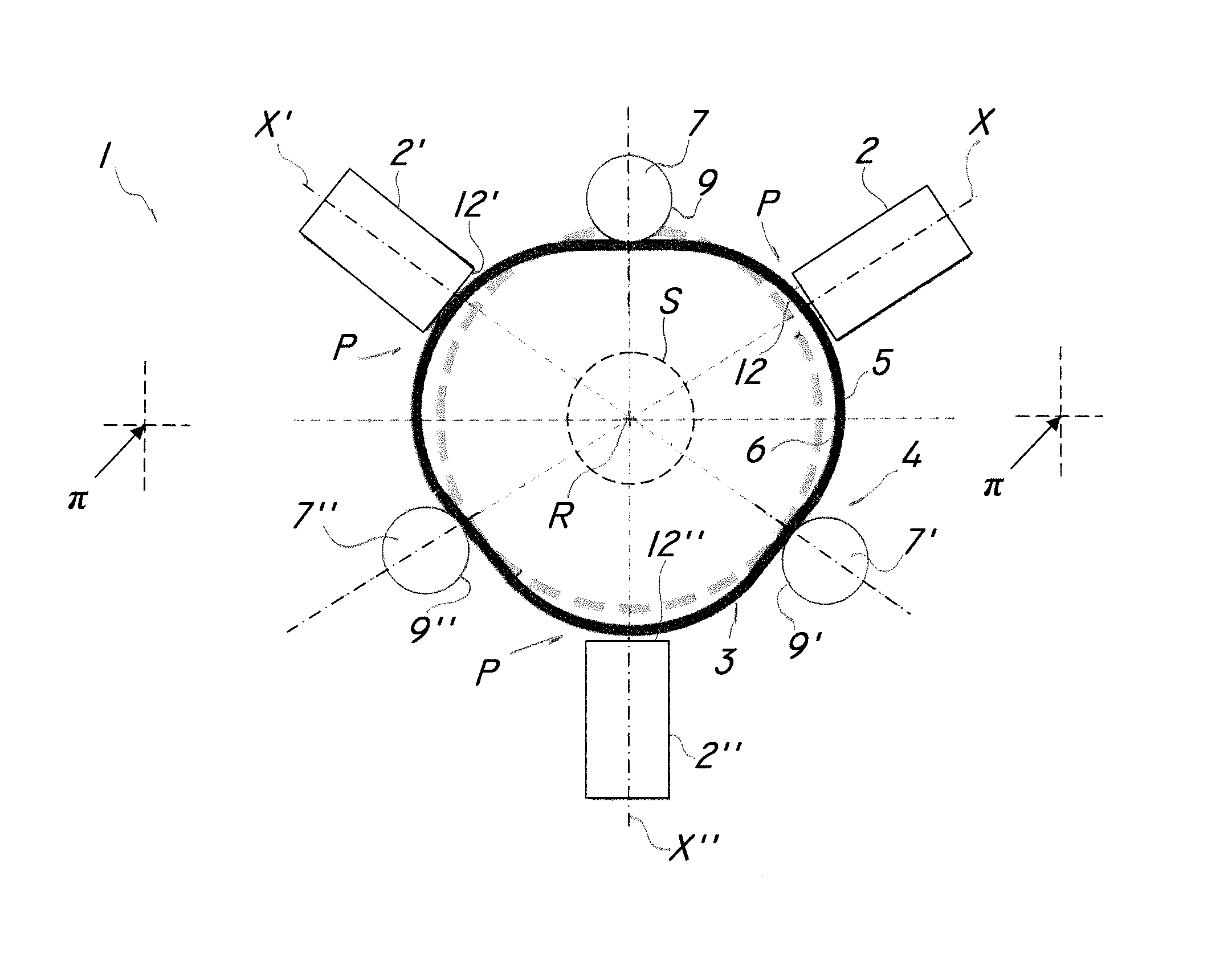
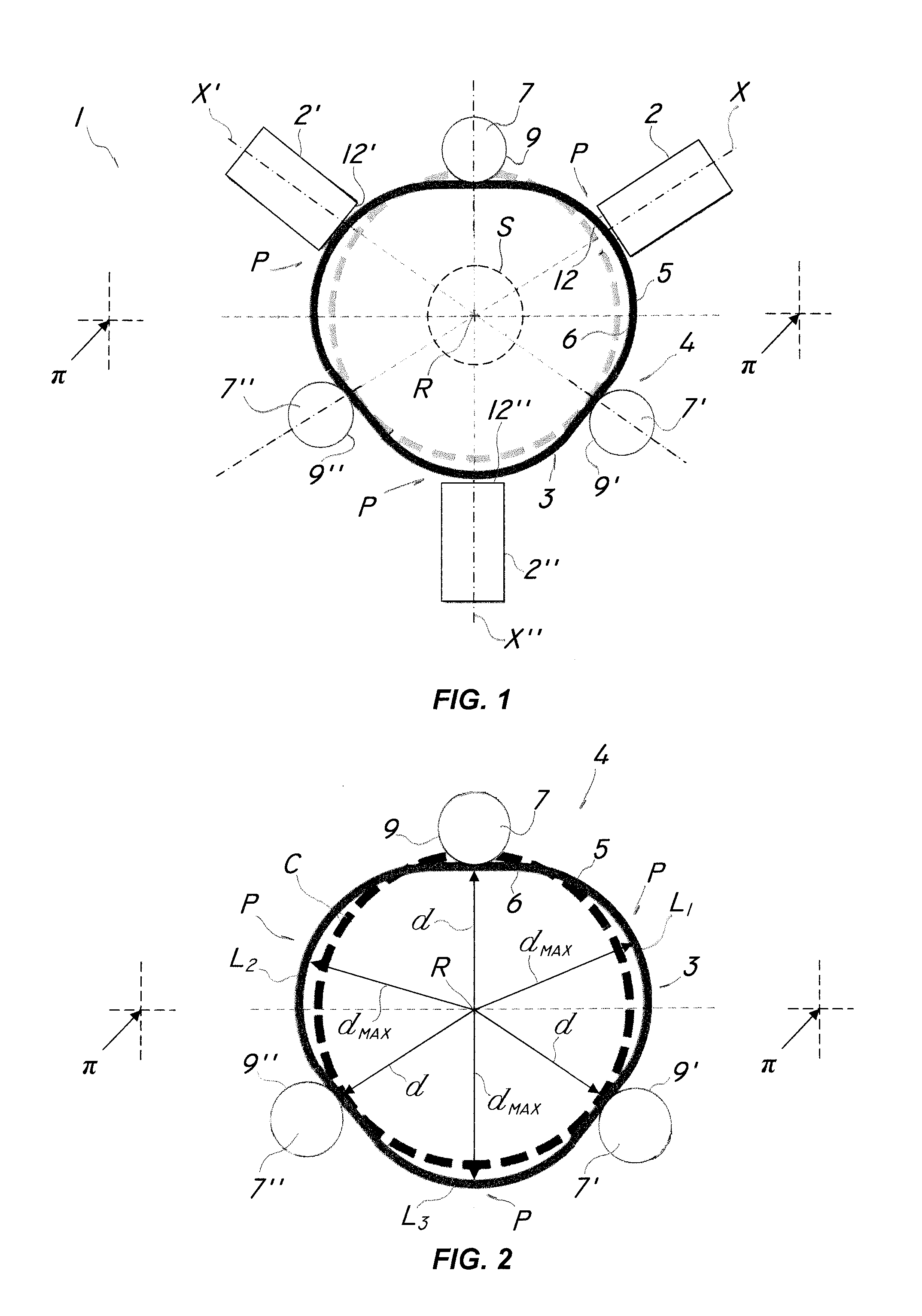
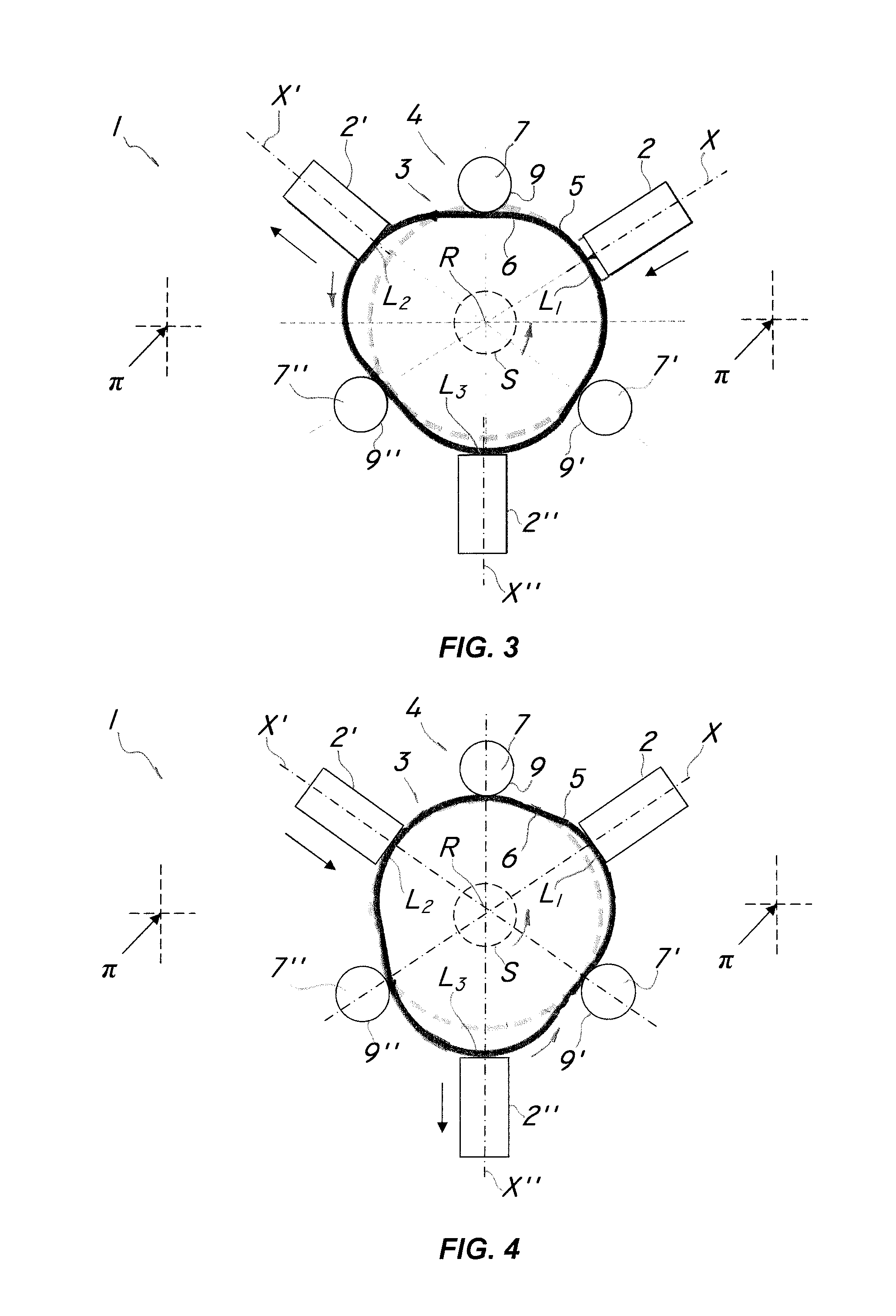
InactiveUS20150167801A1Improve efficiencyIncrease torqueFlexible wall reciprocating enginesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLine of actionDrive shaft
A motor powered by linear actuators comprises a base plane in which a plurality of linear actuators (2, 2′, 2″, 20) operate by reciprocating along respective lines of action (X, X′, X″), an elastic conversion member (3, 30) which is adapted to move in the plane and suitable to be connected to a drive shaft (S). The linear actuators (2, 2′, 2″, 20) are operatively connected with the conversion member (3, 30) for converting the reciprocating motion of the linear actuators (2, 2′,2″, 20) into a substantially continuous motion of the conversion member (3, 30). The motor also comprises stationary constraint means (4, 40) which are adapted to selectively interact with the conversion member (3, 30) to locally deform it and / or promote sliding and movement thereof the plane about a predetermined axis or in a predetermined direction in response to the action of the linear actuators (2, 2′, 2″, 20).
Owner:PHI DRIVE
Tibiotalar arthrodesis guide
ActiveUS20130030446A1Improve stabilityAccurate and repeatable insertionProsthesisFastenersTibiaAnkle bone
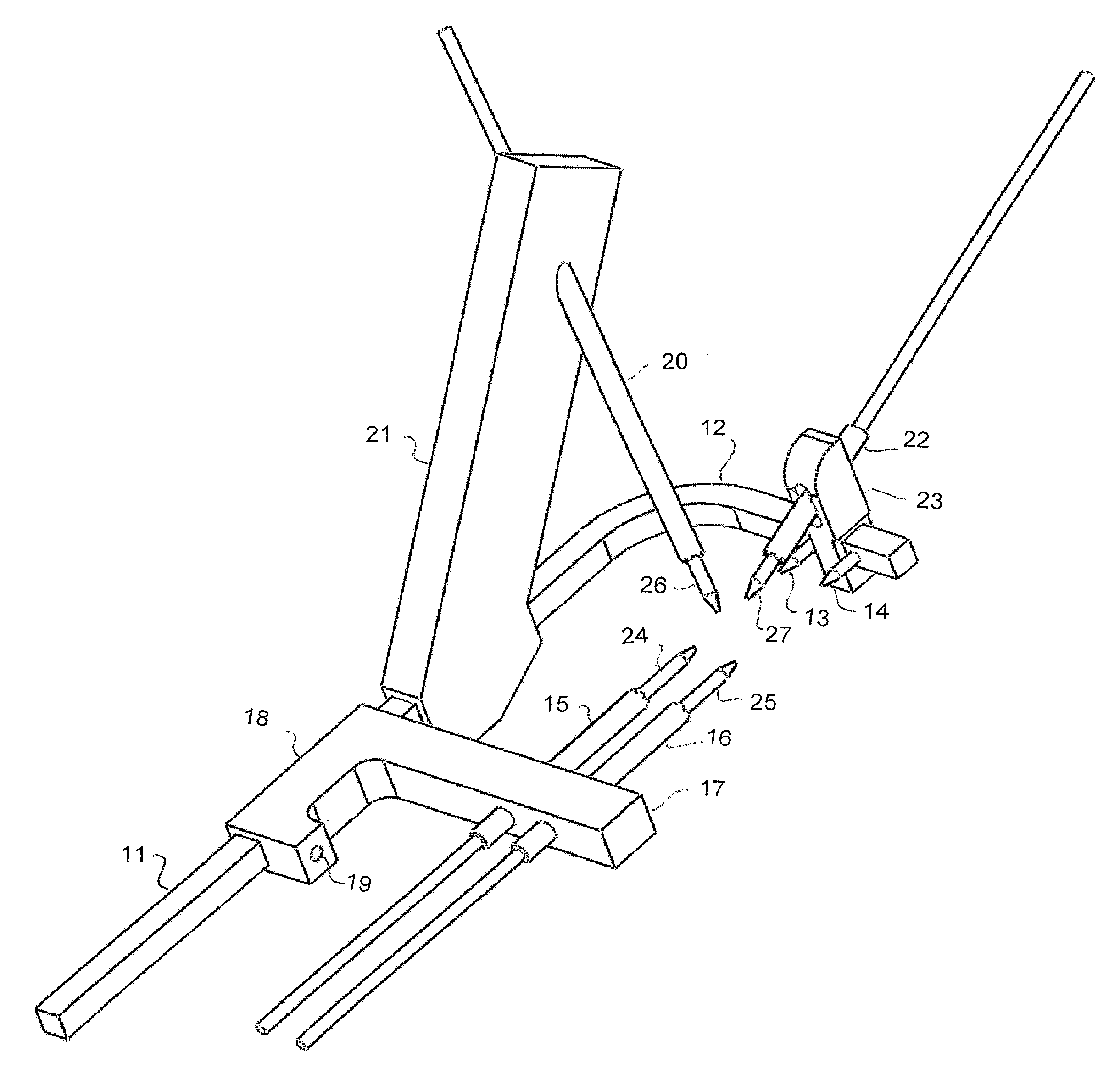
A Tibiotalar Arthrodesis Guide (TAG) used for fusion of the talus to the tibia is comprised of several basic components. The main component is a straight guide post upon which other components can slide. A curved arm is featured at the end of the straight guide post, featuring points at the ends which serve as indicators of the pins' exit sites based upon the lines of action of the parallel pins. The parallel guide cylinders are positioned on a movable arm which translates superiorly and inferiorly on the guide post of the handle, allowing a surgeon to adjust the device for varying ankle sizes. A “home-run” pin guide cylinder for a home-run guide pin is oriented superiorly and at an angle to the parallel guide cylinders. Using a similar concept as the parallel guide cylinders, the “home-run” guide is also attached to a movable arm that can translate inferiorly and superiorly along the main guide post. A medial guide cylinder for a medial guide pin passes through one of a plurality of holes in a vertical guide arm. The surgeon has the flexibility to utilize either the “home-run” or medial pins, depending on the needs of the patient and preference of the surgeon and, in either case, the “home-run” and medial pin pass between the two parallel pins.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
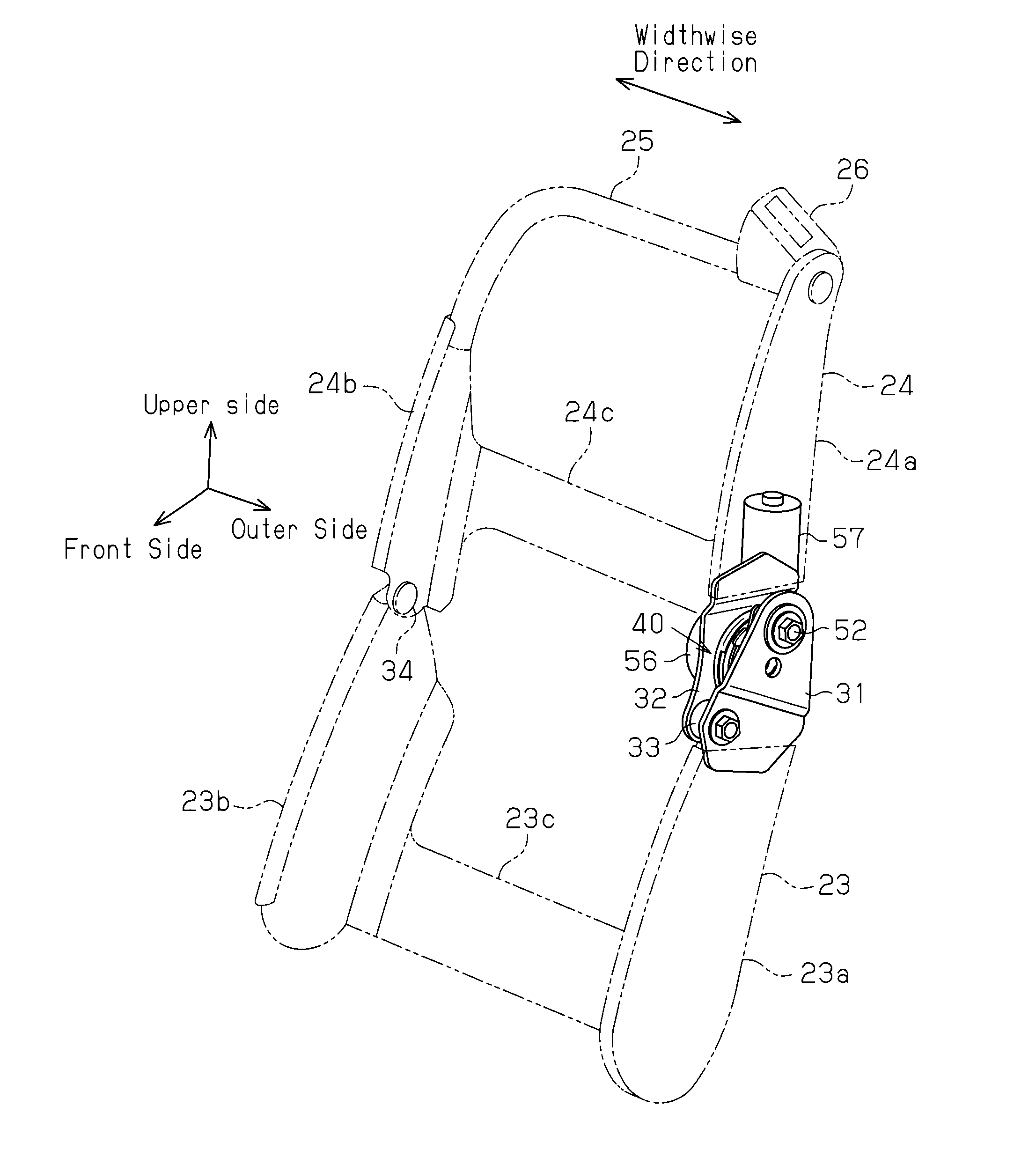
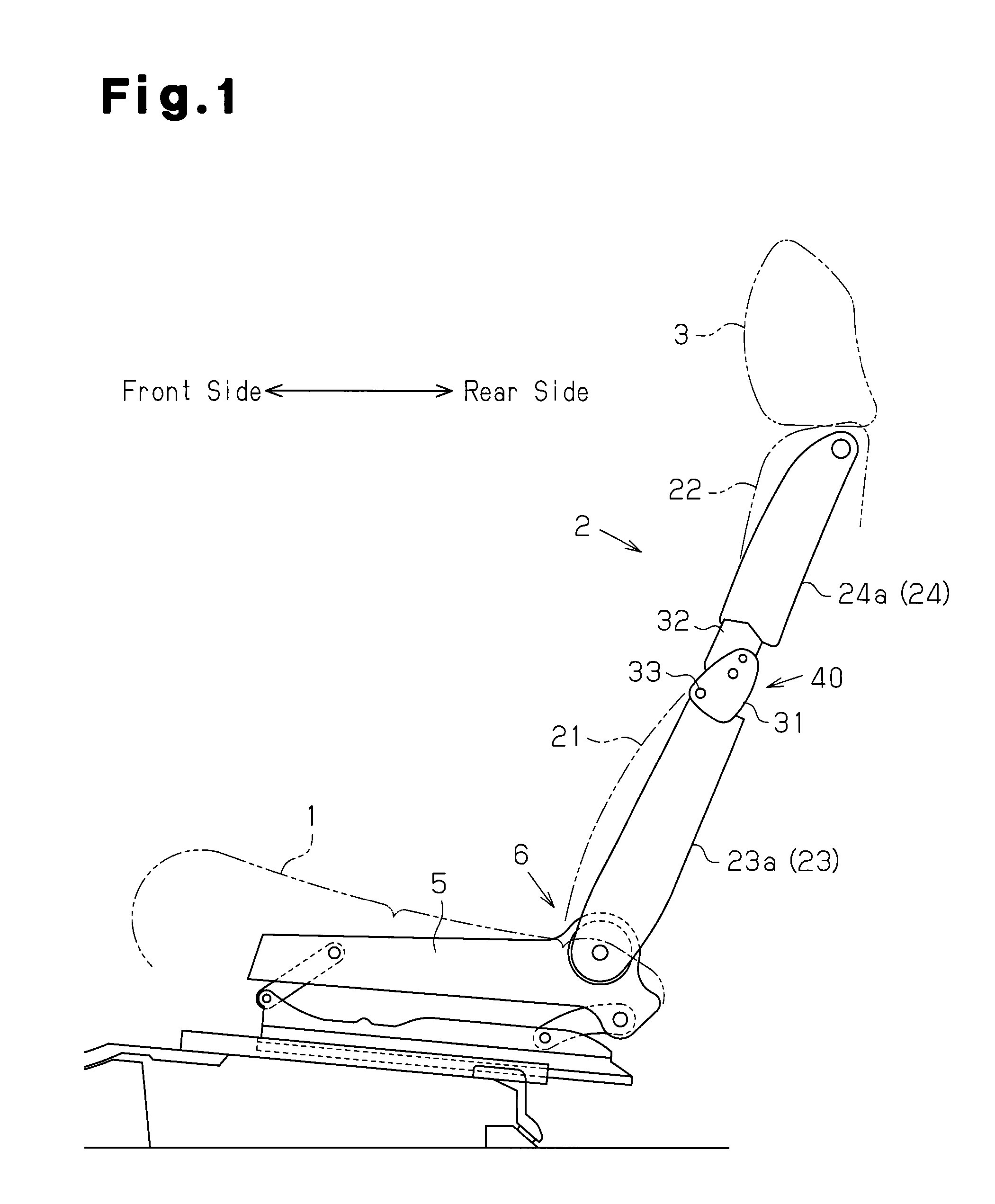
Seat adjustment device, and vehicle seat device with the seat adjustment device
InactiveUS20130300174A1High strengthIncreasing the thicknessFurniture partsSeating furnitureLine of actionEngineering
A seat adjustment device adjusts the pivoting angle formed by a first seat member and a second seat member. A hinge shaft connects at a first connection point, the first seat member, and the second seat member. An arm section and a connection mechanism are connected at a second connection point. The positions of the axes of the first connection point, the second connection point, and a pivoting section are set in such a manner that, when a load is applied to the front end of either the first seat member or the second seat member, the distance from the second connection point to the axis of the pivoting section is less than the distance from the first connection point to the second connection point with respect to the direction perpendicular to the line of action of a load applied to the second connection point.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
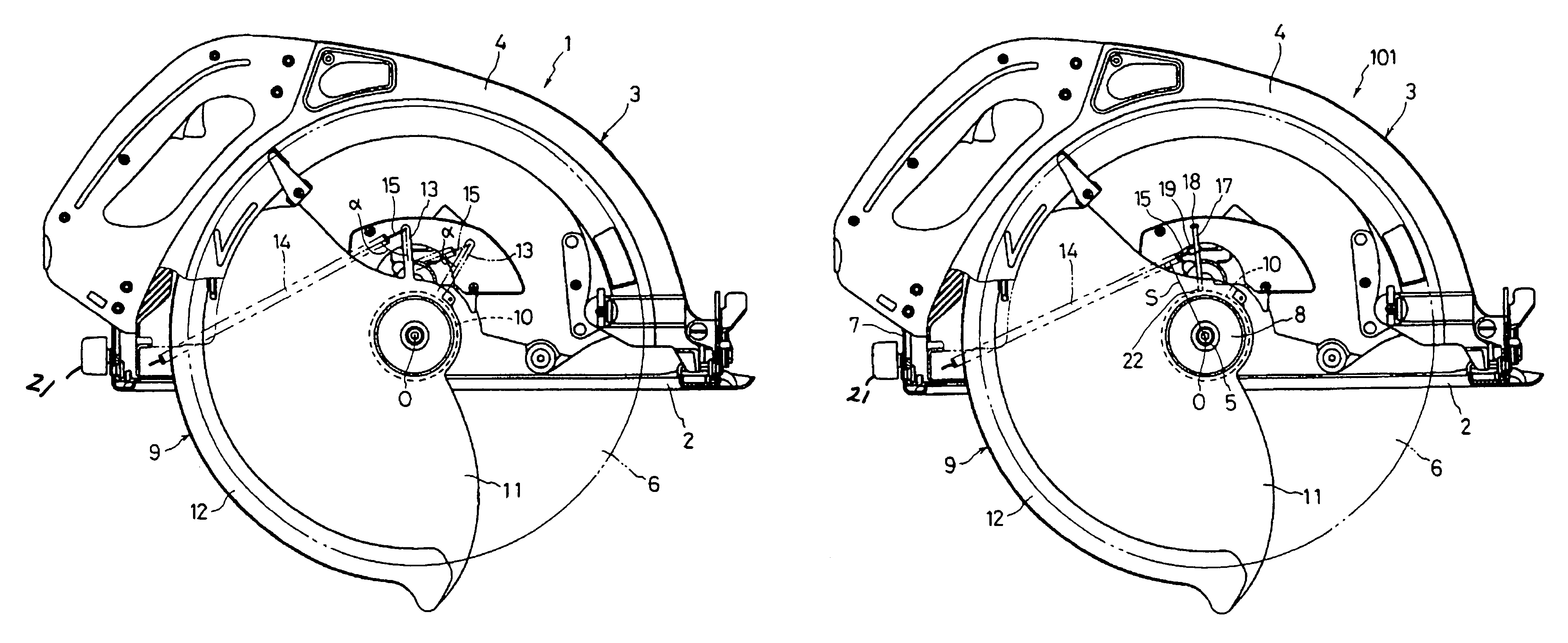
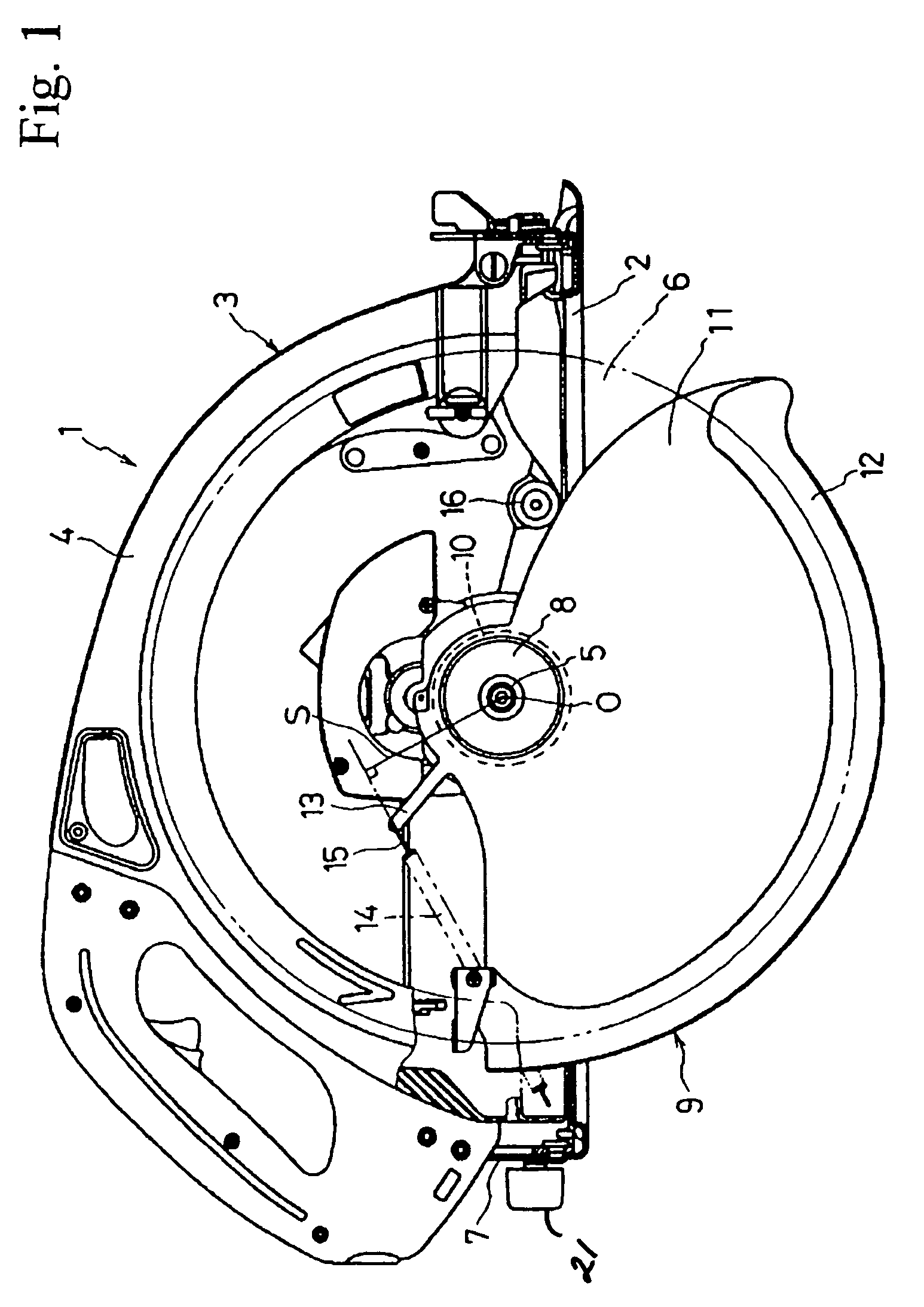
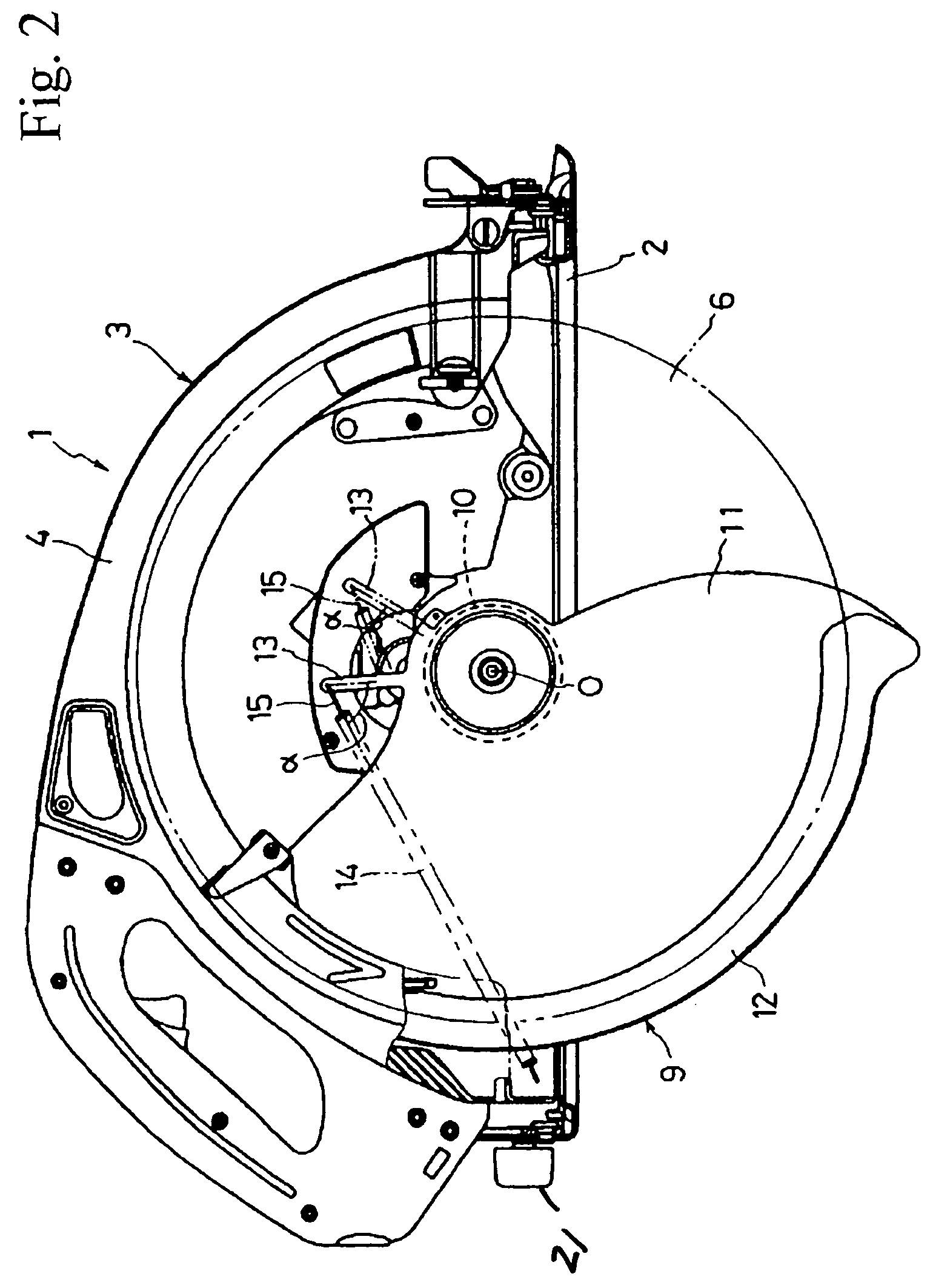
Circular saw with an improved lower blade guard
InactiveUS7089671B2Avoid accidental rotationWithout compromising handling comfortMetal sawing devicesMetal sawing accessoriesLine of actionCircular saw
A circular saw (1) includes a base plate (2) and a saw blade assembly (3) including a lower blade guard (9) for covering a saw blade (6). The blade guard includes a sleeve portion (10) rotatably fitted on a bearing box (8) coupled to the saw blade assembly and a sectoral portion (11) extending radially from the sleeve portion in the rear of the blade. A connecting bar (13) projects radially rearward from the sectoral portion. A spring (14) is stretched between the top of the connecting bar (13) and a lower rear portion of an upper blade guard (4) close to the base plate. When not in use, torque, generated as the product of the spring's tensile force and the perpendicular distance (S) from the line of action or the force to the axis of rotation (O), rotates the blade guard to a closed position.
Owner:MAKITA CORP
Decanting centrifuge with vibration isolation
A centrifuge has a rotor for receiving a disposable processing unit. The centrifuge is configured such that the motor is attached to an enclosure and the enclosure is supported on a base. The connection between the base and the enclosure is a vibration isolator, and the isolator is positioned such that its effective line of action aligns with the effective plane of rotation of the rotor. In accordance with another feature of the invention, the processing units are held in a decanting position by a decant ring that moves vertically but does not rotate. The ring engages the top of the processing unit during decant and the abrasion is minimal.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Retractable leg assembly for amphibious vehicle
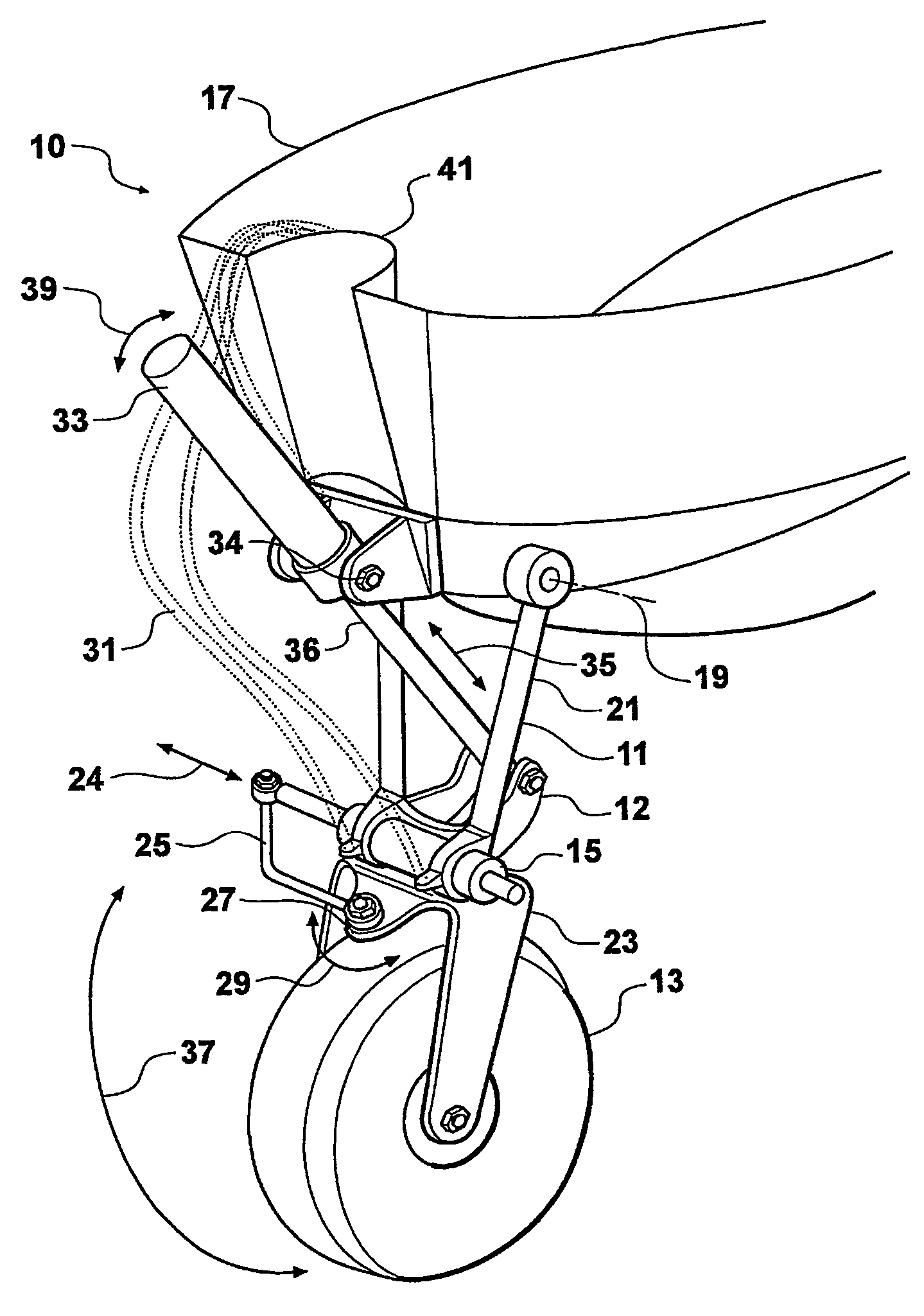
Leg assembly (10) for an amphibious vehicle comprises leg (11) and hydraulic ram (33) each pivotally mounted, above the waterline, externally to hull (17). The line of action of ram (33) is such that it is optimal (eg less than 30 DEG) with respect to the tangent to the arc of travel of leg (11) when it is lowered or raised. Leg (11) carries wheel (13) which may be swivelled for steering using hydraulic linear actuator (15). Assembly (10) is compact, light, yet capable of lifting the vehicle off the ground.
Owner:SEALEGS INT
Anti-vibration actuator and lens unit/camera equipped therewith
InactiveCN101799612AAvoid oversizingGreat driving forceTelevision system detailsPrintersCamera lensLine of action
To provide an anti-vibration actuator with which a high drive force can be obtained without increasing size. The present invention is an anti-vibration actuator, including a fixed portion, a movable portion, movable portion support means, first drive means having a first drive magnet and coil; second drive means having a second drive magnet and coil; third drive means having a third drive magnet and coil; first, second, and third position detection elements for detecting the positions of each drive magnet; and a control portion for moving the movable portion to a specified position; wherein the first and second position detection elements are disposed within a region diagonally opposed to the region in which the third drive means is positioned, from among four regions partitioned by the lines of action of the drive forces of the first and second drive means.
Owner:TAMRON
Compression coil spring device having discontinuous support structure
InactiveUS20050051937A1Minimize changesSpring force can be minimizedWound springsLine of actionContact pressure
In a compression coil spring device, suitable for use in a strut wheel suspension system, including a coil wire wound into a coil having an end turn, the end turn is adapted to be supported by a spring seat at one or a plurality of discrete points. This can be accomplished either by providing a plurality of projections on the coil wire along the length of the coil wire of the end turn or by providing a plurality of projections for supporting the end turn at one or a plurality of discrete points of the spring seat. Thus, the spring demonstrates a same property with regard to the centroid of contact pressure or line of action of the spring force, and the spring constant without regard to the spring load as long as the spring end is supported by the same discrete contact point or points. In other words, the changes in the number of effective turns depending on the magnitude of the load can be minimized so that the relationship between the load and compression stroke can be made substantially linear, and the change in the angle of the axis of the spring force can be minimized. Also, in the above structure, the end turn contacts the spring seat only at the predetermined projections, and this minimizes the variation in the spring property, frictional resistance between the contacting members and bending moment relating to individual coil springs.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
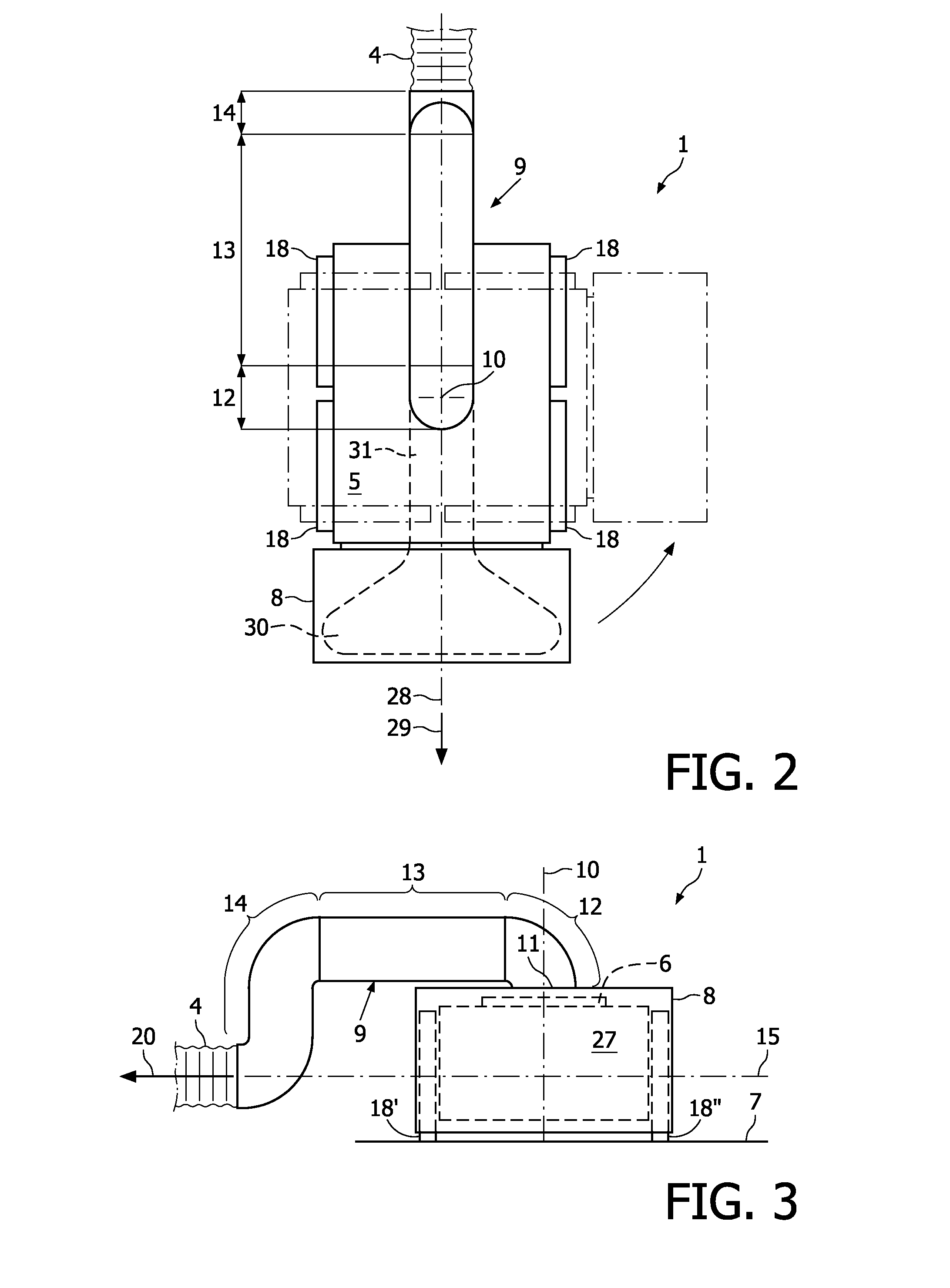
Robotic cleaning head
InactiveUS20100050366A1Less maneuverabilityIncrease pressureSuction hosesSuction nozzlesLine of actionEngineering
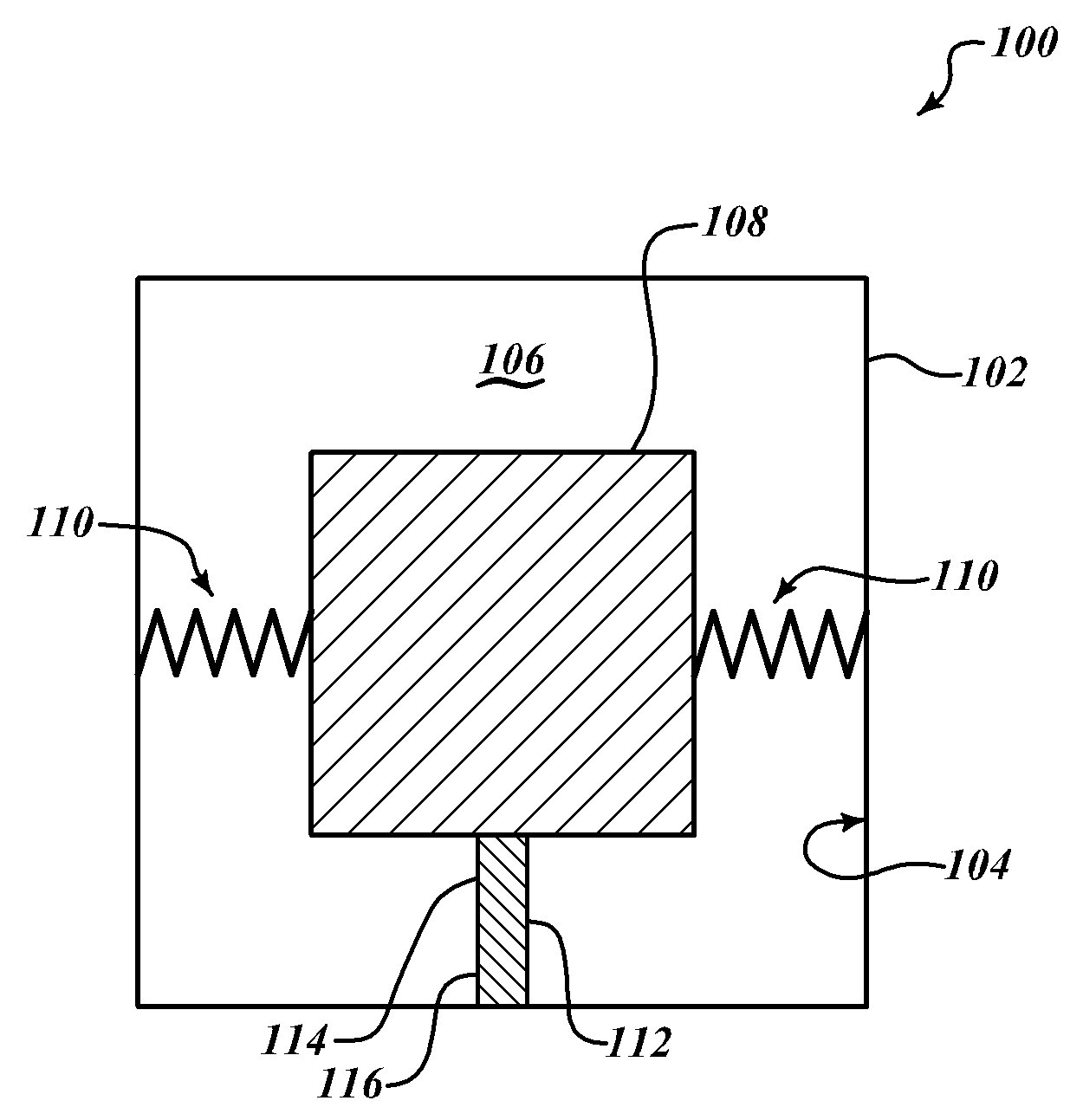
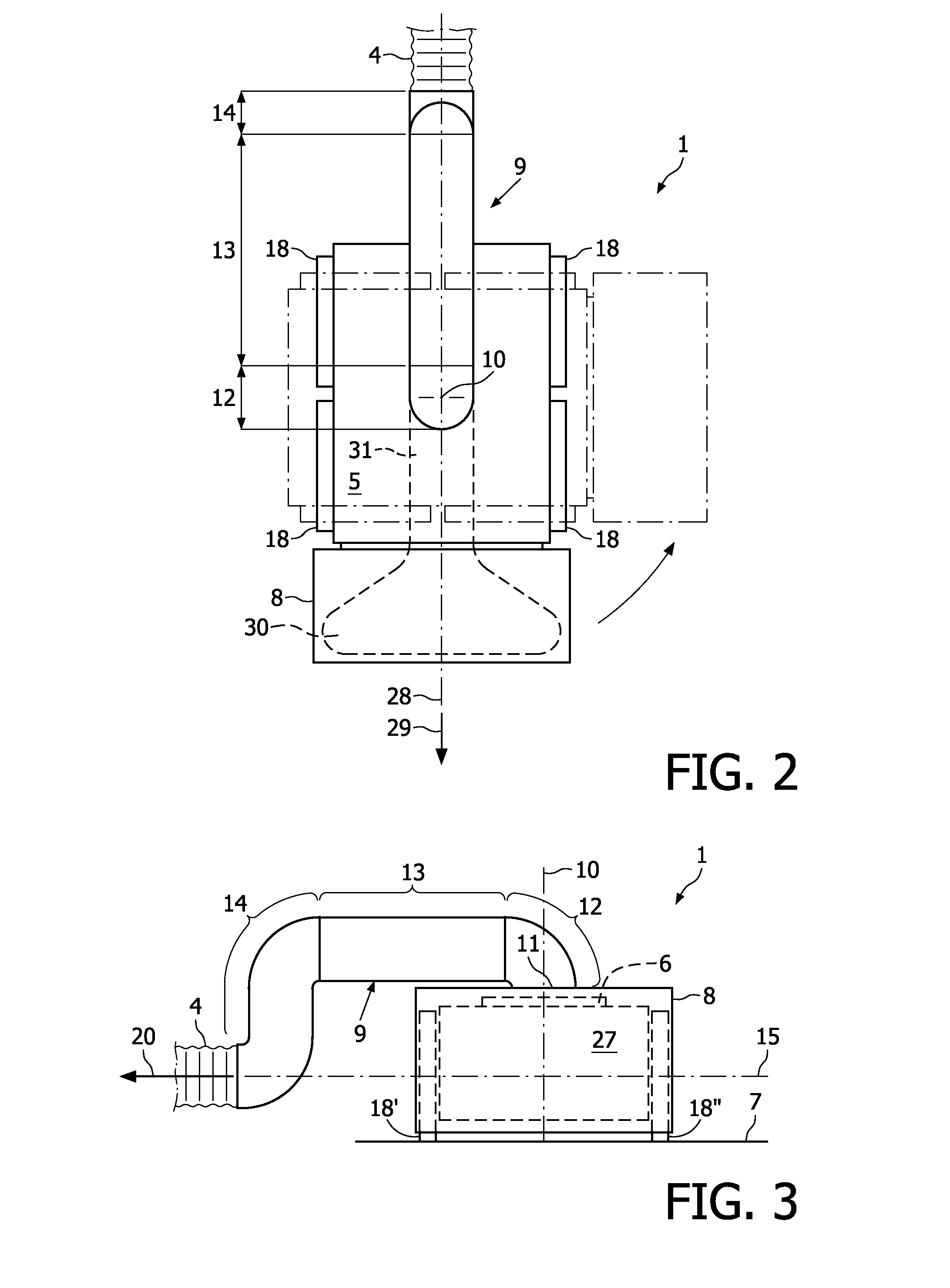
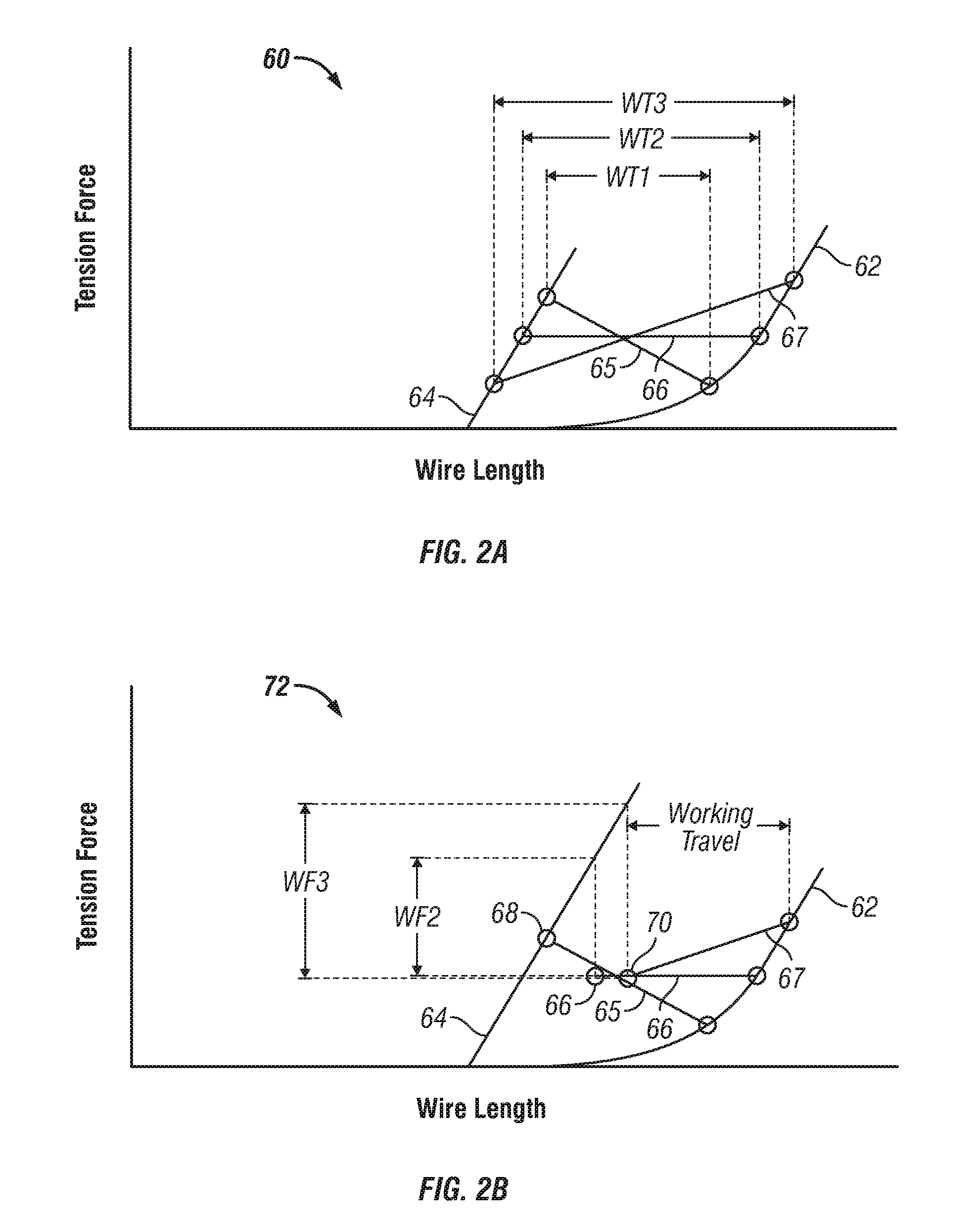
A robotic cleaning head (1; 101) for use as part of an autonomous vacuum cleaning system (2) including a canister unit (3) and a hose assembly (4; 104) connecting the cleaning head (1; 101) to the canister unit (3). The cleaning head (3) has a chassis (5; 105), a drive system (6; 18; 27), a vacuum cleaning nozzle (8; 108) and a conduit (9; 109). The conduit (9; 109) communicates with an air passage bound by the cleaning nozzle (8; 108). It is suspended pivotable about a pivot axis (10; 110) and includes an inlet (11; 111) provided on top of said chassis (5; 105), and an elbow section (12; 112) downstream of the inlet (11; 111), and the conduit (9; 109) is suspended and shaped such that a line of action (15; 115) of a tension force (20; 120) exerted by the hose assembly (4; 104) onto the chassis (5; 105), via the conduit (9; 109) to which the hose assembly (4; 104) is connected, extends spaced below a downstream end of the elbow section (12; 112).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Utility machinery and associated control arrangements
A power transmission device for utility machinery is disclosed, the device including: a) a sleeve supporting a first sheave member having a first face; b) a hub received through said sleeve and moveable axially in relation thereto, said hub supporting a second sheave member having a second face that opposes said first face such that said first and second faces define therebetween a groove adapted to receive a belt and relative axial movement between said sleeve and said hub being adapted to vary at least one of pitch diameter and grip imparted to said belt from said sheaves; and c) an actuator mechanism adapted, through control of relative axial displacement between said sleeve and said hub, to vary at least one of said pitch and grip, said actuator mechanism comprising a control rod disposed substantially perpendicularly to the line of action of said axial displacement and connected to said hub through a link mechanism, said control rod being adapted to rotate and said link mechanism being adapted to translate rotation of said control rod into linear movement for relative axial displacement of said hub.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
Linkage for motorcycle brake
A motorcycle including a front wheel, a rear wheel, a frame, a seat and handlebars is disclosed. The motorcycle includes a linkage connecting a brake pedal with a caliper. The caliper is located within a body perimeter of the motorcycle. The caliper is adapted to engage a disk and the caliper can have a line of action. The direction of the line of action of the caliper can be different than the axis of rotation of the rear wheel. The linkage can also convert vertical motion into horizontal motion.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Bearing device for supporting pinion shaft
The present invention relates to a bearing device for supporting a pinion shaft so as to freely rotate with respect to a case. The bearing device comprises a first tilt-contact rolling bearing provided on the connecting-flange-side outer peripheral surface of the pinion shaft and a second tilt-contact rolling bearing formed from an angular ball bearing provided on the pinion-gear-side outer peripheral surface of the pinion shaft, wherein lines of action of the first and second tilt-contact rolling bearings intersect with one another on an outer diameter side, the connecting-flange-side end portion of the first tilt-contact rolling bearing and the pinion-gear-side end portion of the second tilt-contact rolling bearing are respectively sealed with seal members, a sealed space between the seal members is infilled with grease, and the connecting flange is fastened in the pinion-gear direction to thereby preload the first and second tilt-contact rolling bearings.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Self-locking roller cam for hose and pipe coupling
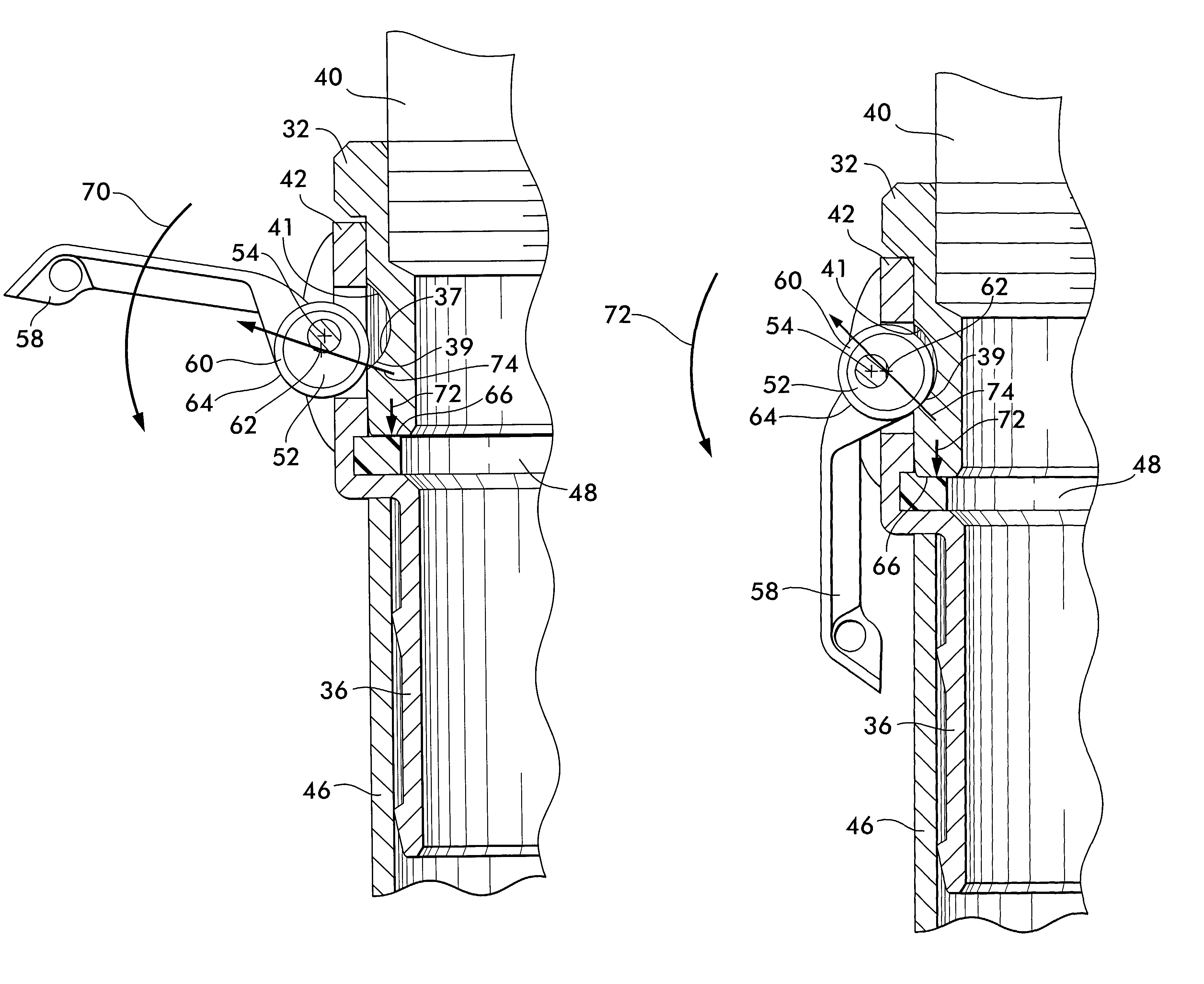
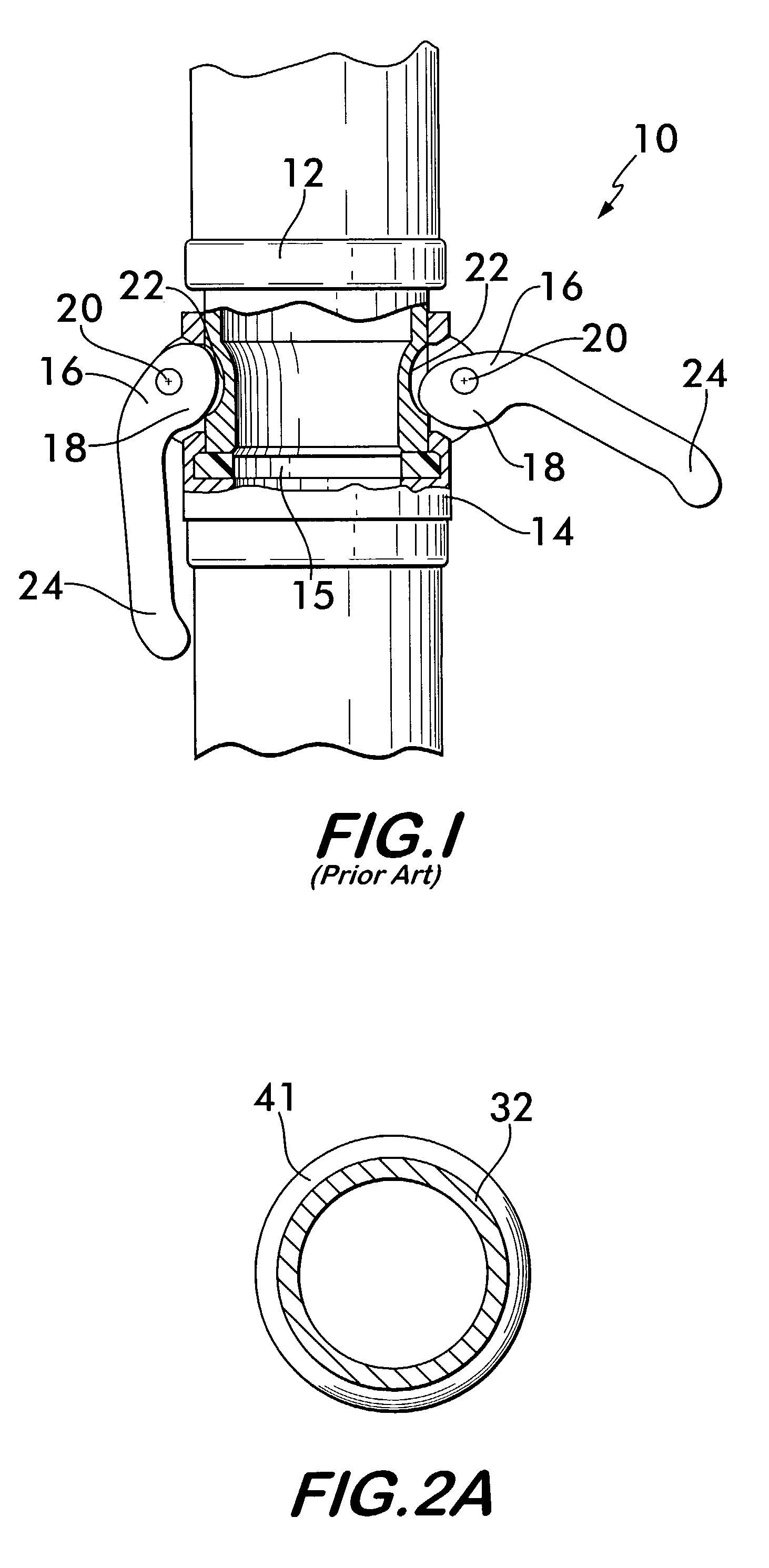
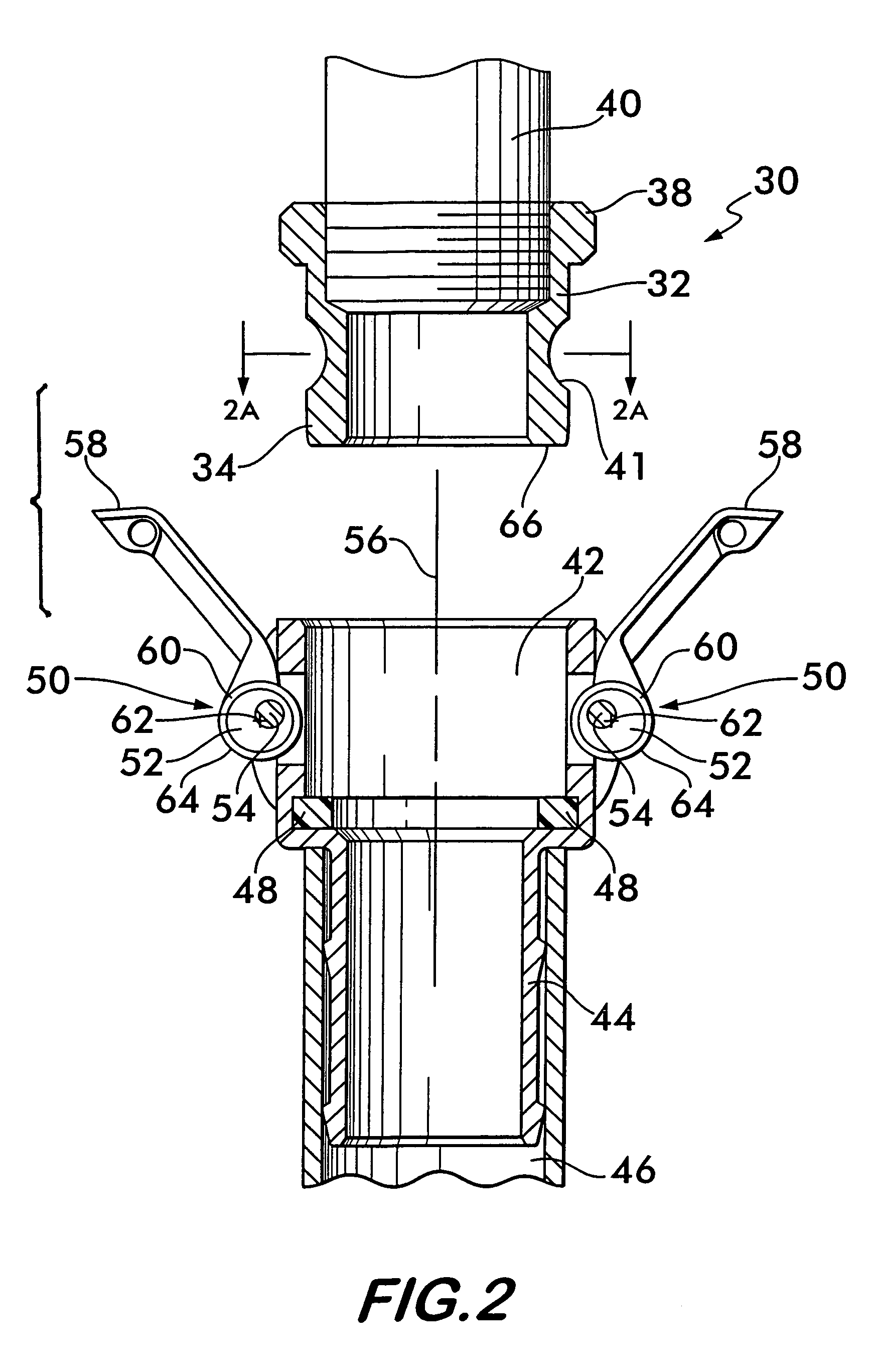
InactiveUS7543857B2Reduce frictionReduced actuation forcePipe elementsCouplingsLine of actionCoupling
A coupling for joining conduits together is disclosed, the coupling having male and female fitting portions held in engagement by a self-locking roller cam positioned on the female portion. The roller cam has a cam body rotatable about an axis offset from the center of the cam body. An annular roller surrounds the cam body and is rotatable relatively to it. An outwardly facing surface on the roller engages an opposing concave surface on the male portion of the coupling. Reaction forces between the roller and the opposing surface operate along a line of action initially positioned to one side of the offset axis to create a torque opposing rotation of the cam into engagement with the opposing concave surface. Further forced rotation of the cam into engagement with the opposing concave surface causes the line of action of the reaction force to shift to an opposite side of the offset axis thereby creating a torque which causes rotation of the cam body into engagement with the opposing concave surface to retain the male fitting portion within the female fitting portion.
Owner:VICTAULIC
Pillow
The invention provides a pillow capable of having the height thereof adjusted automatically so that the height of the back of the head of a user in a face-up lying position is slightly higher than his / her back, and also capable of having the height thereof varied automatically between a face-up lying position and a side lying position. A hollow portion 8 having a biasing mechanism 9 disposed therein is formed in a head placement member 3, and when the head is placed face-up on the head placement member 3, the hollow portion 8 is depressed so that the distance between the lowermost portion of the head and the bottom member 2 is in the range of 10 mm to 30 mm. The biasing mechanism has X-shaped links 11 disposed laterally spaced apart in the hollow portion 8. Each X-shaped link is composed by pivotally connecting a first link member 12 slanted upward toward the front and a second link member 13 slanted upward toward the rear by an intermediate link shaft 16. The biasing mechanism further comprises a front-side upper connecting member 18 for connecting the front ends of the first link members of the X-shaped links, a rear-side upper connecting member 20 for connecting the rear ends of the second link members of the X-shaped links, and a spring member 21 providing a spring force for approximating the link members of each X-shaped link in the frontward / rearward direction along a line of action in the frontward / rearward direction with respect to the X-shaped links.
Owner:NAKAYAMA SHINICHIRO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com