Method and program for identifying errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
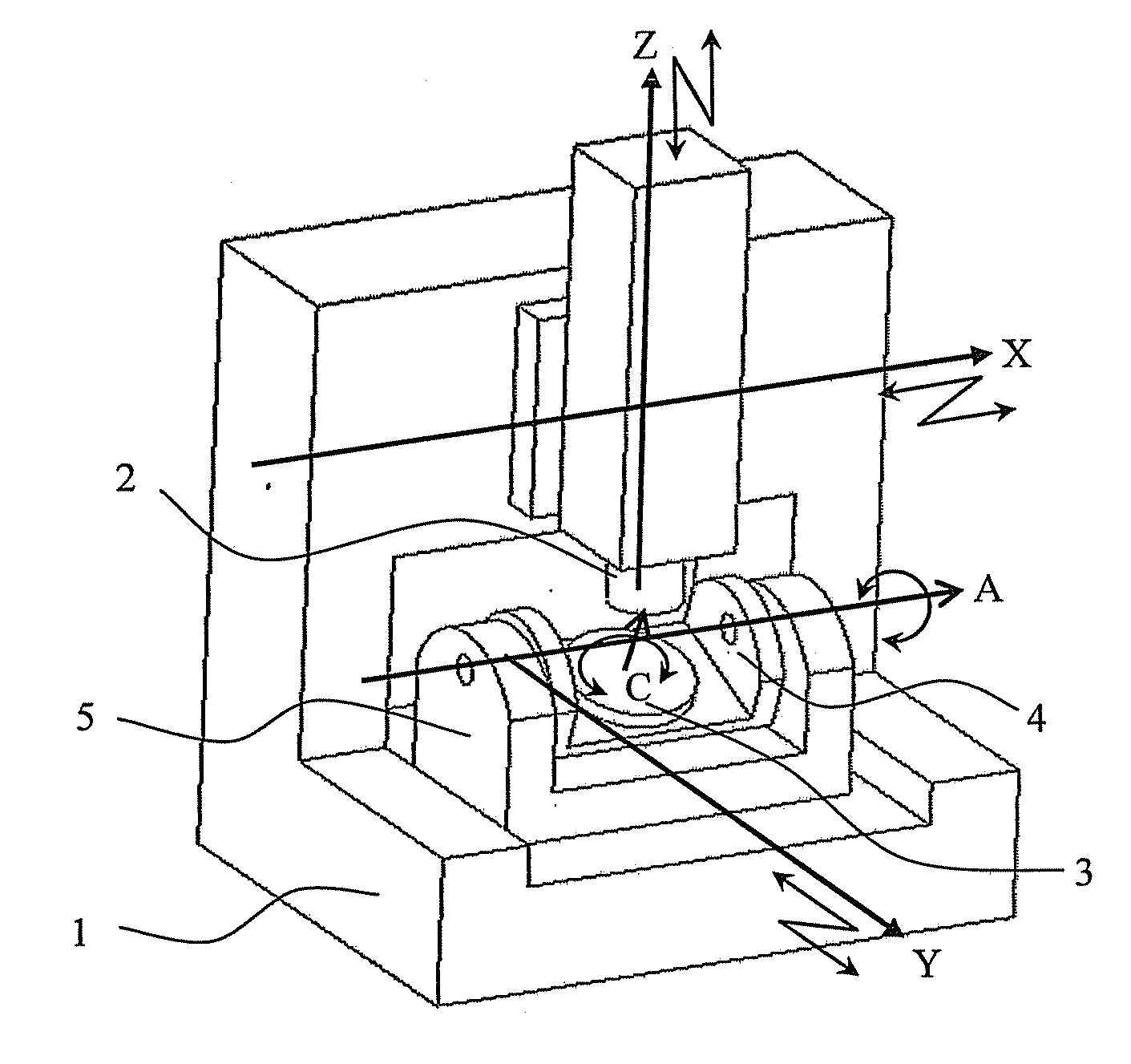
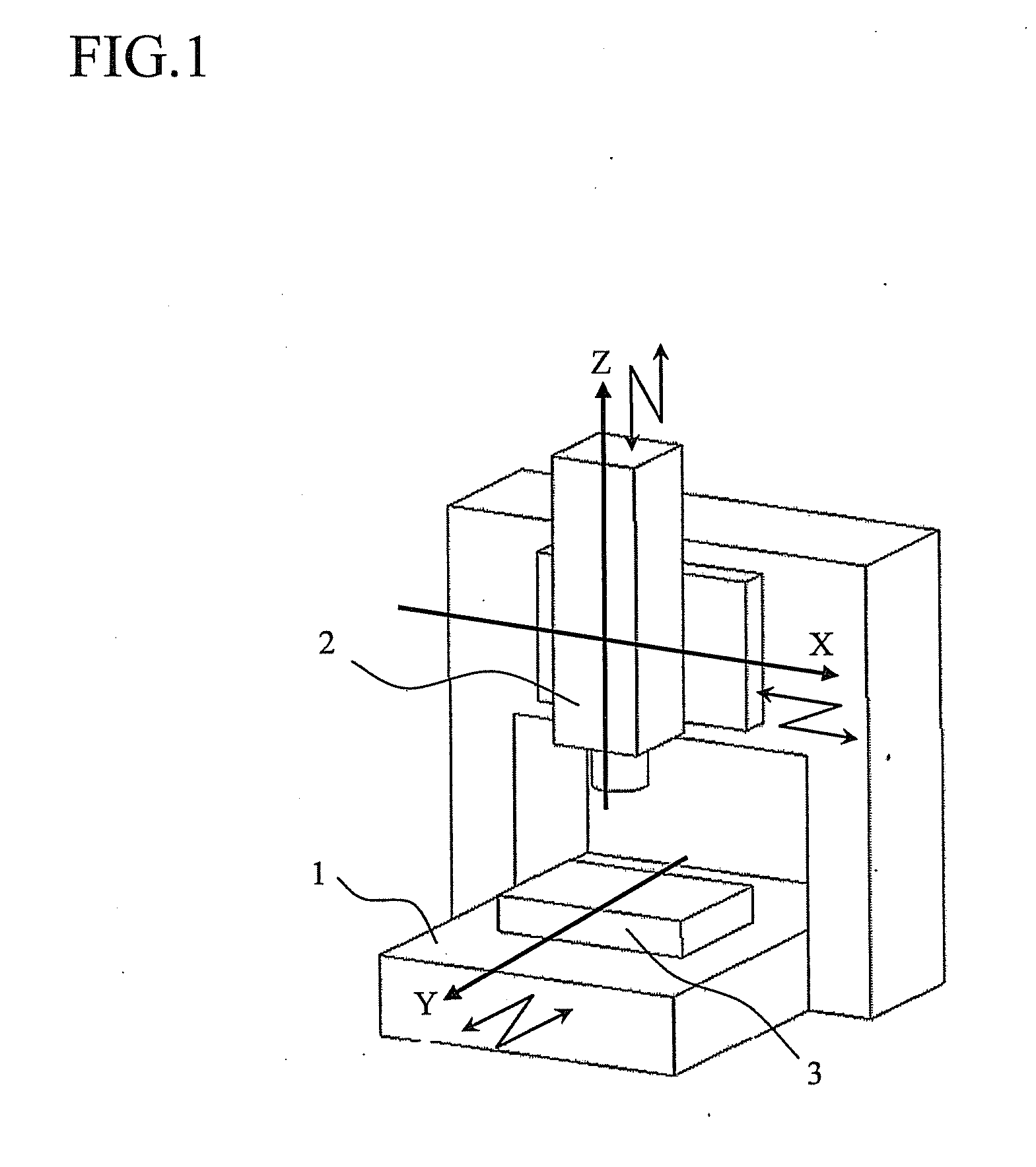
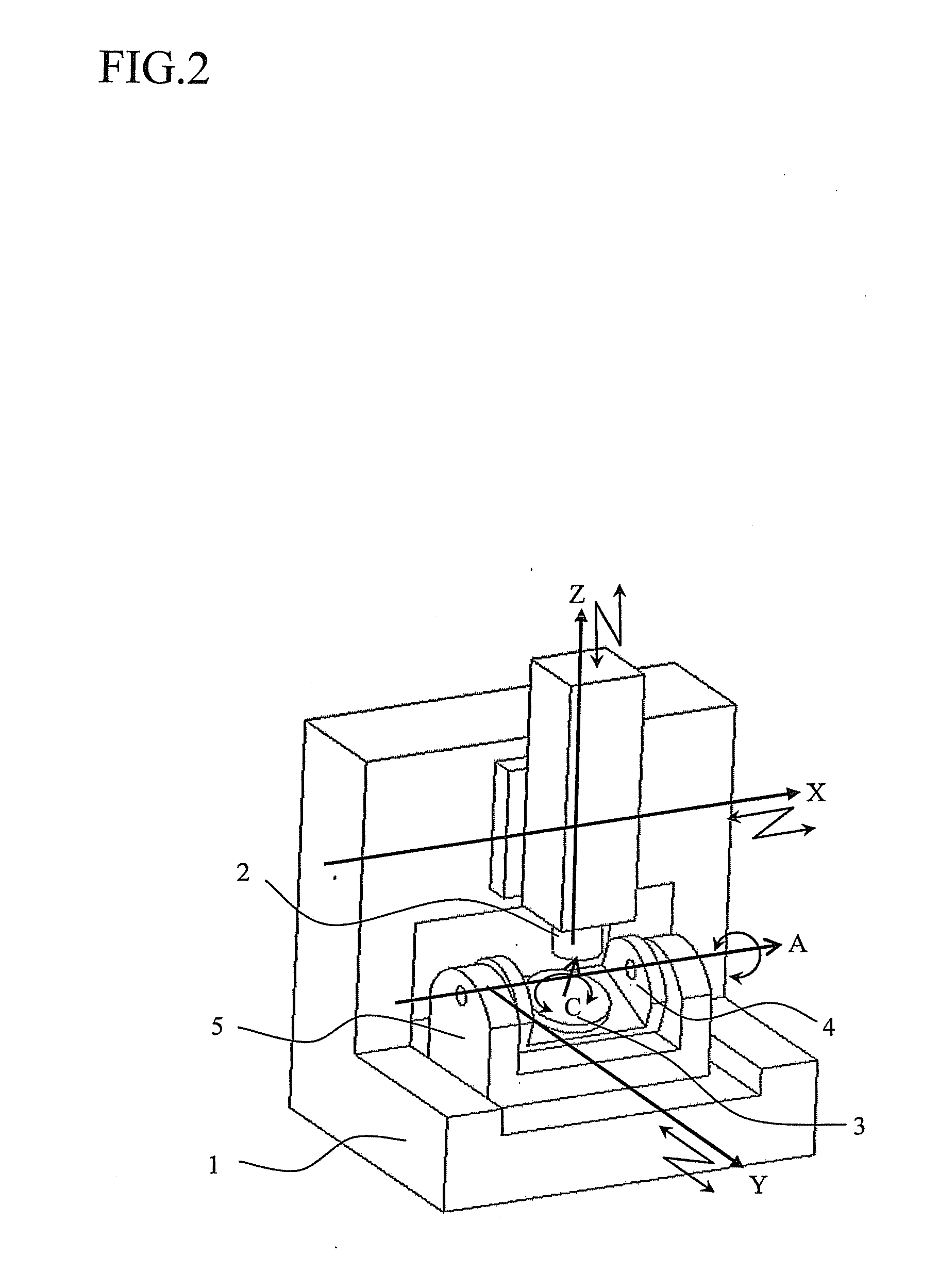
With reference to the accompanying drawings where necessary, a method for identifying errors of a five-axis control machining center shown in FIG. 2, which is one exemplary embodiment of the present invention, using a computer (i.e., controller (not shown)) will be described below. The computer may be a numerical controlling device for the five-axis machine, a separate computer connected to the numerical controlling device, or the combination thereof. It is to be noted that the present invention is not limited to the following specific embodiment.
First, geometric errors will be described. A total of six component error parameters (i.e., δx, δy, δz, α, β, γ) are defined as geometric errors; that is, relative translational errors in three directions and relative rotational errors in three directions between the axes. In the case of the five-axis machine as shown in FIG. 2, axes are related from the workpiece to the tool in the order of the C-axis, the A-axis, the Y-axis, the X-axis, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com