Phototherapy Device Thermal Control Apparatus and Method
a technology of thermal control apparatus and phototherapy device, which is applied in the field of thermal control apparatus and method, can solve the problems of discharging heat into, affecting the efficiency of phototherapy devices, so as to reduce or eliminate the problems or disadvantages associated with them
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
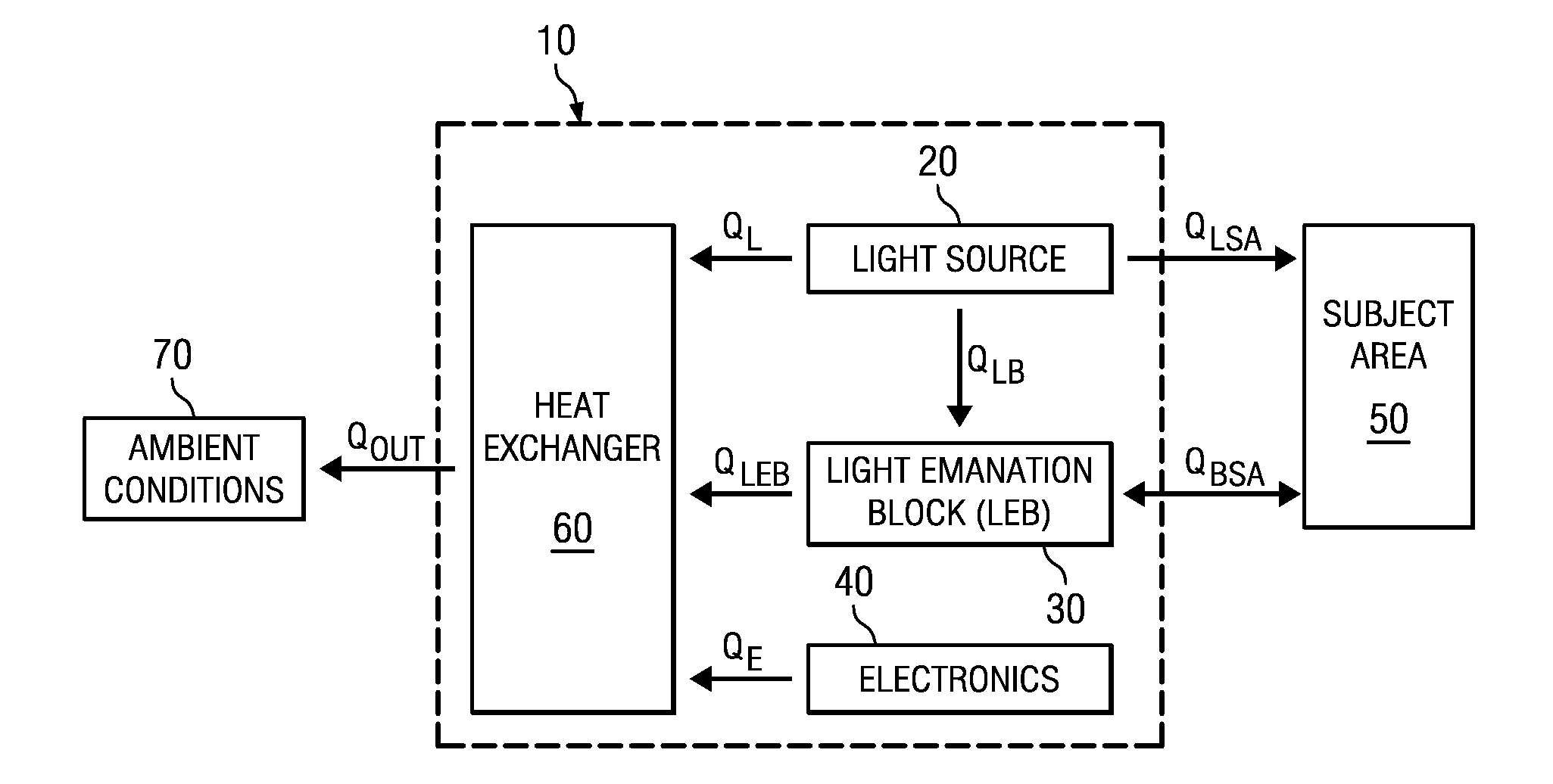
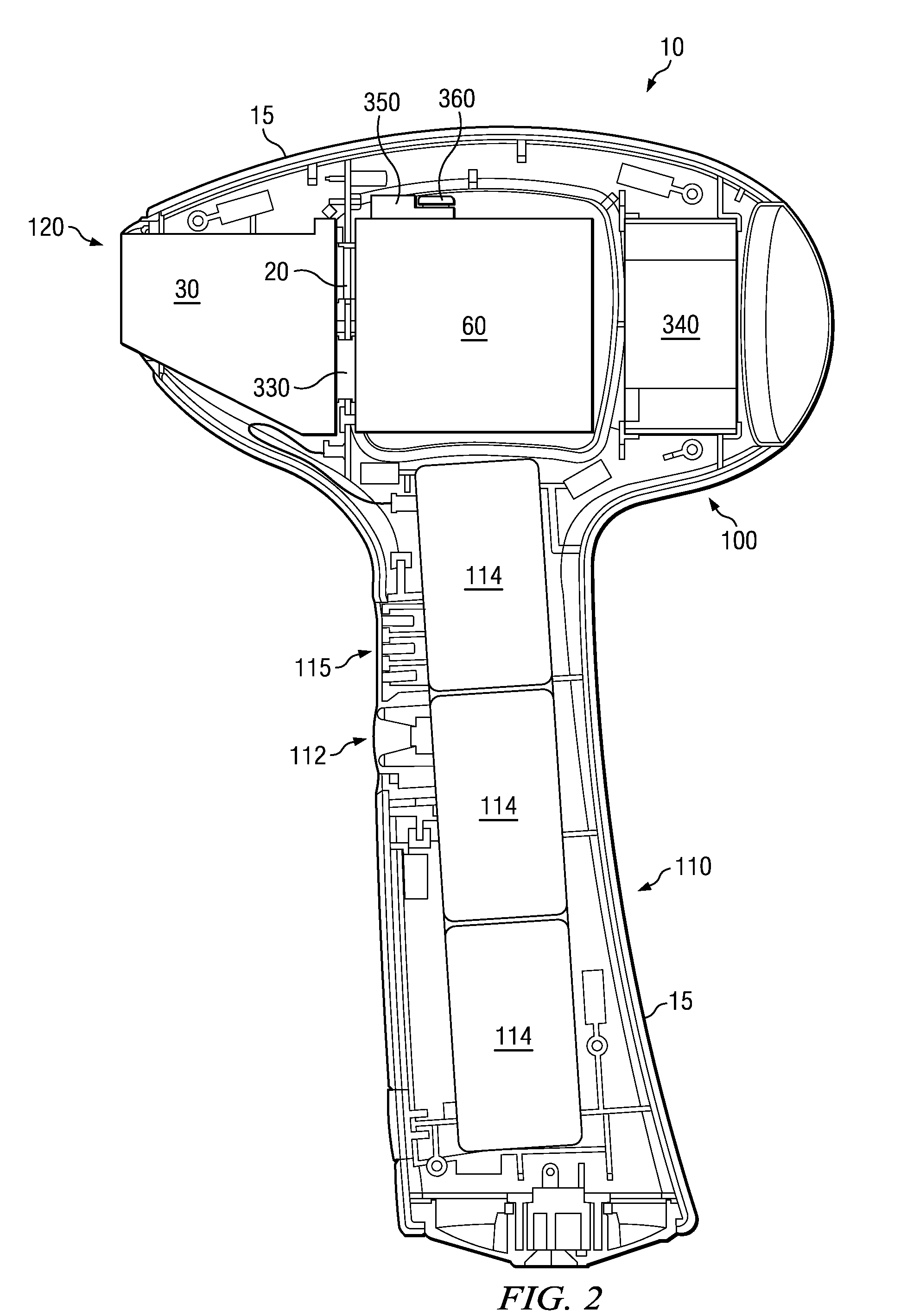
[0097]Initial pulse repetition frequency is one light pulse every two seconds. The device detects that a thermal limit threshold has been reached (e.g., sensed device tip temperature reaches a set point of approximately 37° C.). The pulse repetition frequency is then reduced to one light pulse every 2.5 seconds until either the condition is alleviated (e.g., tip temperature drops below the 37° C. set point) or a second thermal trigger is reached (e.g., tip temperature drops to a specified level). At such time, pulse repetition frequency is increased to greater than one light pulse every 2.5 seconds.
example 2
[0098]Initial pulse repetition frequency is one light pulse every two seconds. The device detects that a thermal limit may be reached (e.g., sensed device tip temperature is increasing toward or is near approximately 37° C.). The pulse repetition frequency is then reduced, or device operation suspended, as necessary to avoid establishment of the thermal limit condition. When a lower thermal trigger of 34° C. is sensed, pulse repetition frequency is increased again to one light pulse every two seconds.
[0099]Laser diode bars typically may be about 50% efficient at normal baseline operating temperatures. Thus, by way of example, for a laser diode bar at 25° C., a forty watt (40 W) electrical input results in about a twenty watt (20 W) optical output and a twenty watt (20 W) thermal output. At higher temperatures, though, laser diode bars are less efficient. For example, for a laser diode bar at 42° C., a forty watt (40 W) electrical input produces a sixteen watt (16 W) optical output a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com