Sole Structure for a Shoe
a technology for shoe soles and bending resistances, applied in the field of shoe sole structure, can solve the problems of small bending resistance and energy loss of shoes, and achieve the effects of reducing energy loss during running, increasing the amount of restraint easily, and smooth ride feeling during running
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
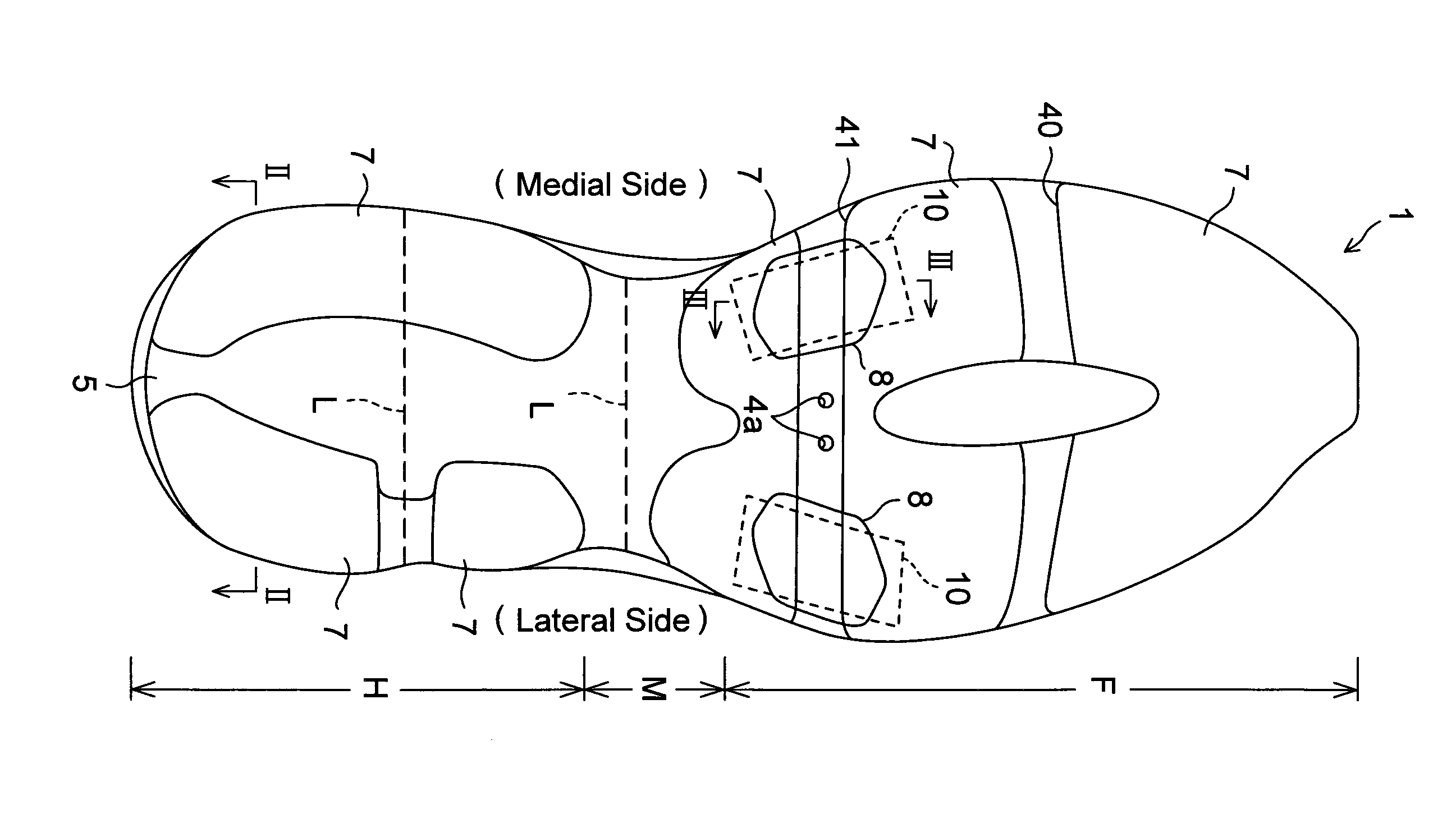
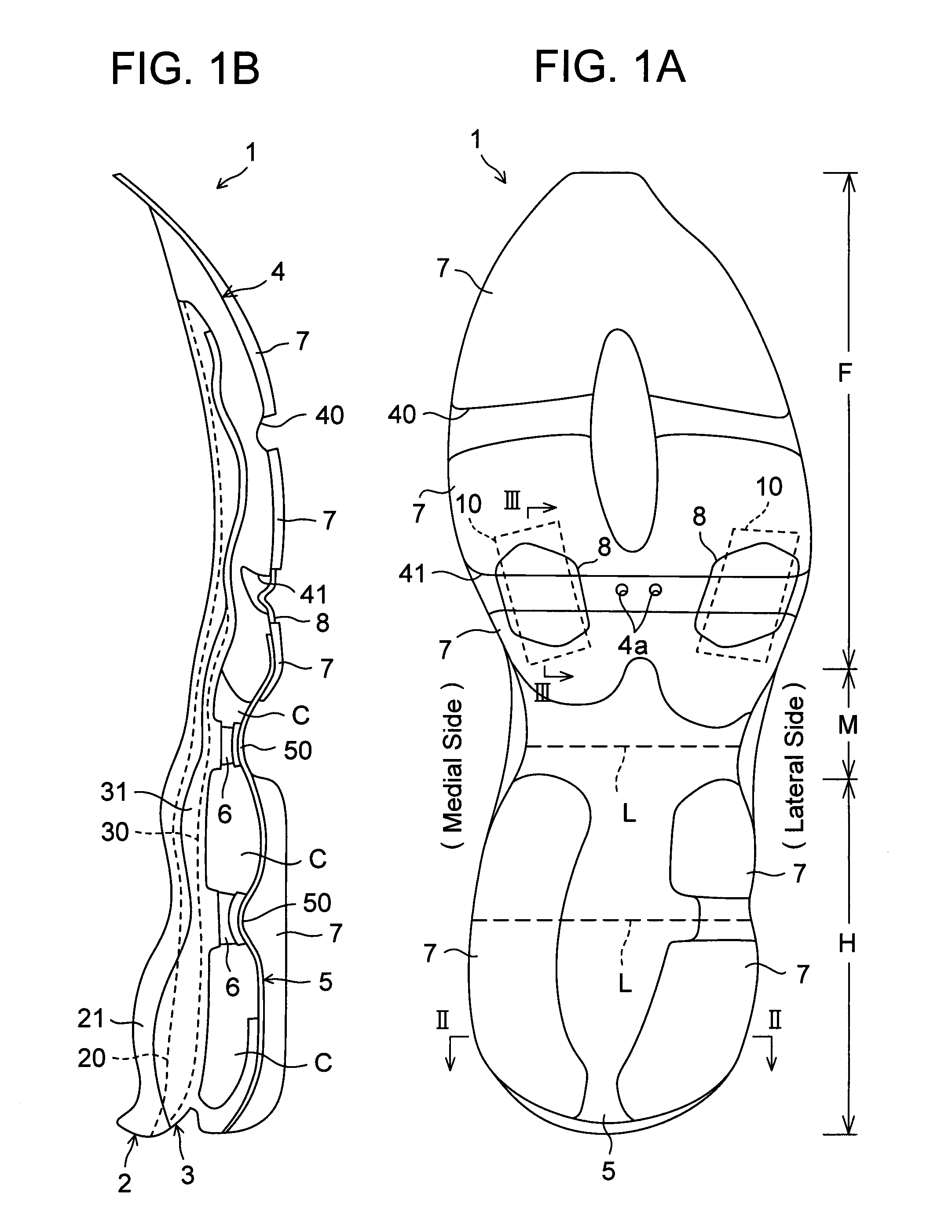
[0110]Referring now to the drawings, FIGS. 1A to 7C show a sole structure or a sole assembly for a shoe according to a first embodiment of the present invention. In these drawings, like reference numbers indicate identical or functionally similar elements.
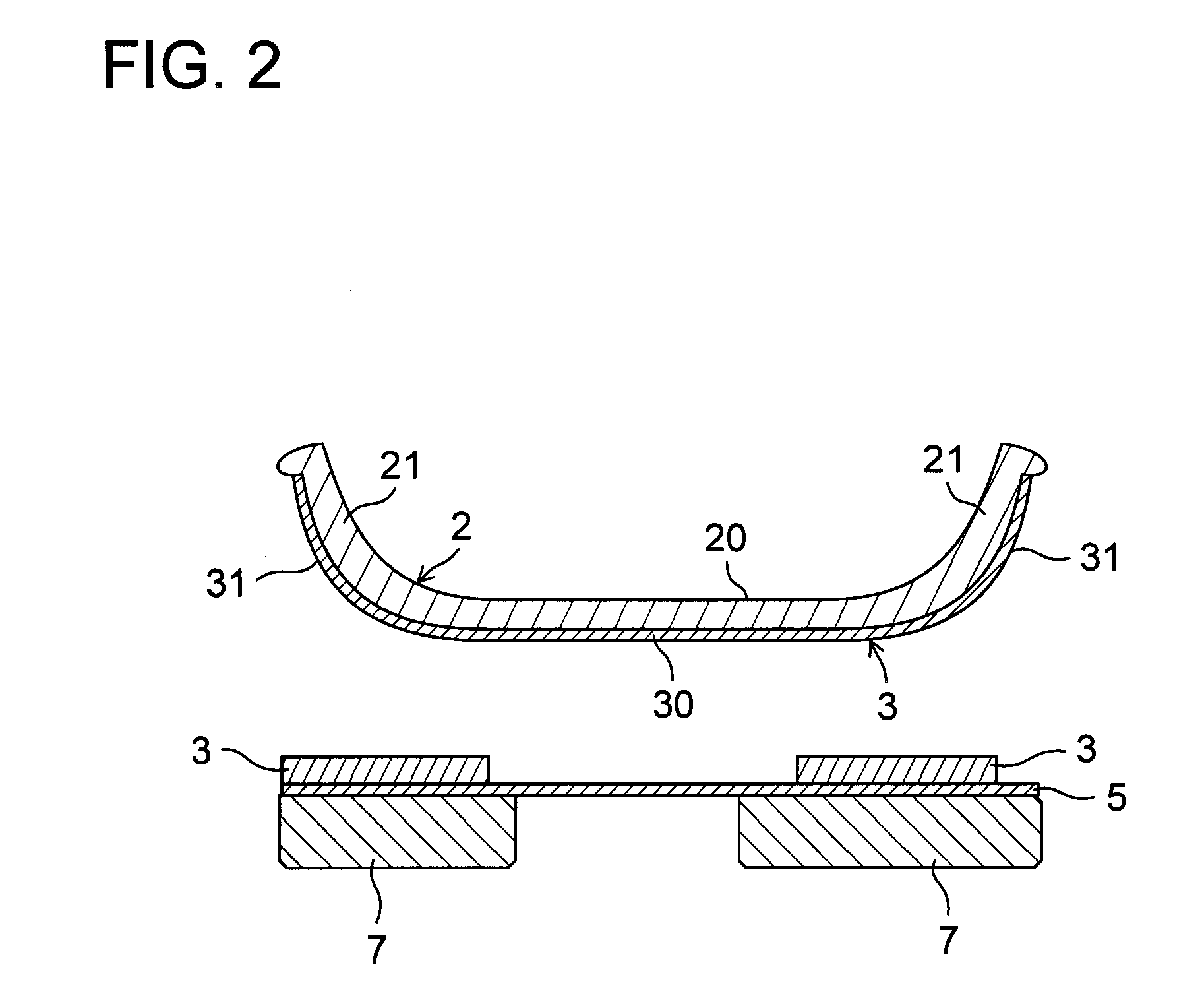
[0111]As shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B, a sole structure 1 for a shoe comprises an upper midsole 2 formed of a soft elastic material and extending longitudinally from a heel region H through a midfoot region M to a forefoot region F of the shoe, an upper plate 3 formed of a hard elastic material, fixedly attached to the bottom of the upper midsole 2 and extending longitudinally from the heel region H through the midfoot region M to the forefoot region F of the shoe, a lower midsole 4 formed of a soft elastic material, fixedly attached to the bottom of the upper plate 3 and disposed mainly at the forefoot region F of the shoe, and a lower plate 5 of hard elasticity which extends longitudinally mainly from the heel region H to the midfoot...
second embodiment
[0169]In the first embodiment, the groove 41 formed on the lower midsole 4 has an inverted V-shape in cross section but the present invention is not limited to such an example. The cross sectional shape of the groove 41 may be inverted U-shaped or circular shaped. Any suitable shape can be adopted as long as the groove 41 opens to the ground contact side. In all cases, the sole bends around the bottom of the groove of an inverted V-shape, inverted U-shape, circular shape or any other shape as the bending or flex point during bending of the sole.
[0170]In any of the cases where the groove 41 has a different shape in cross section, the bending restriction member 10 disposed in the groove 41 has the upwardly protruding bent portion 10a, which is not fixedly attached to the bottom of the groove 41. Preferably, the bending restriction member 10 is not fixed to the sidewall of the groove 41 either and located away from the sidewall of the groove 41.
third embodiment
[0171]In the first embodiment, the bending restriction member 10 has an inverted V-shape in longitudinal section but the present invention is not limited to such an example. The longitudinal sectional shape of the bending restriction member 10 may be inverted U-shaped or circular shaped. Any suitable shape can be adopted in accordance with the cross sectional shape of the groove 41.
[0172]Also, as shown in FIG. 8, the bending restriction member may have a downwardly protruding bent portion 10′a in a V-shape or U-shape. In this case, an elastic cover member 8′ that covers the downwardly protruding bent portion 10′a of the bending restriction member 10′ from below also has a downwardly protruding bent shape along the bent shape of the bending restriction member 10′. In FIG. 8, reference numbers similar to those of the first embodiment indicate identical or functionally similar elements.
[0173]In this case, in the beginning stage of bending of the sole, the bending restriction member 10′...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com