Use of dynamic bounded regions to improve the scalability of decentralised online environments
a dynamic bounded region and online environment technology, applied in the field of information networks, can solve the problems of high data rate, large data volume, and high resource consumption of multi-user networks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
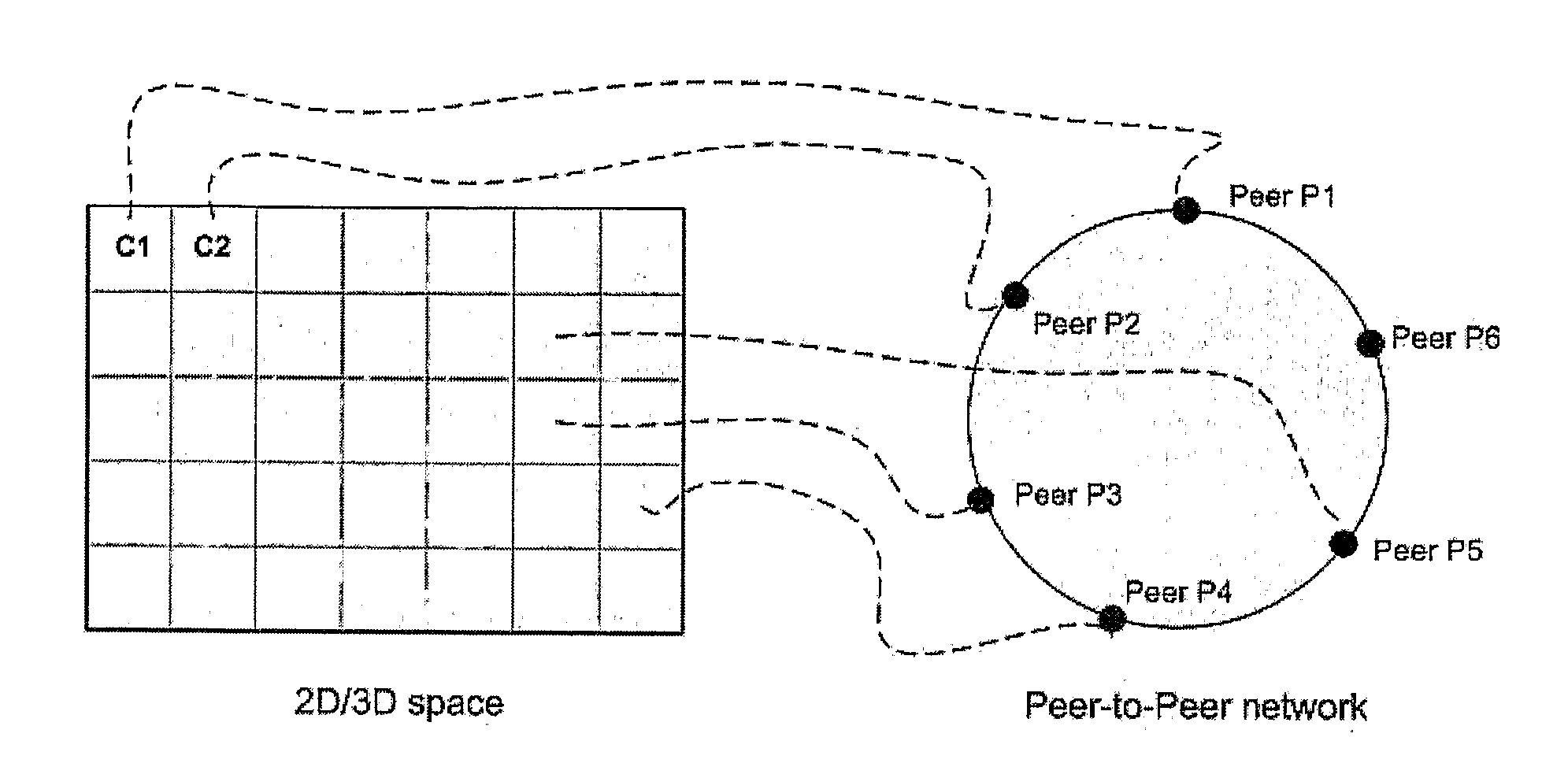
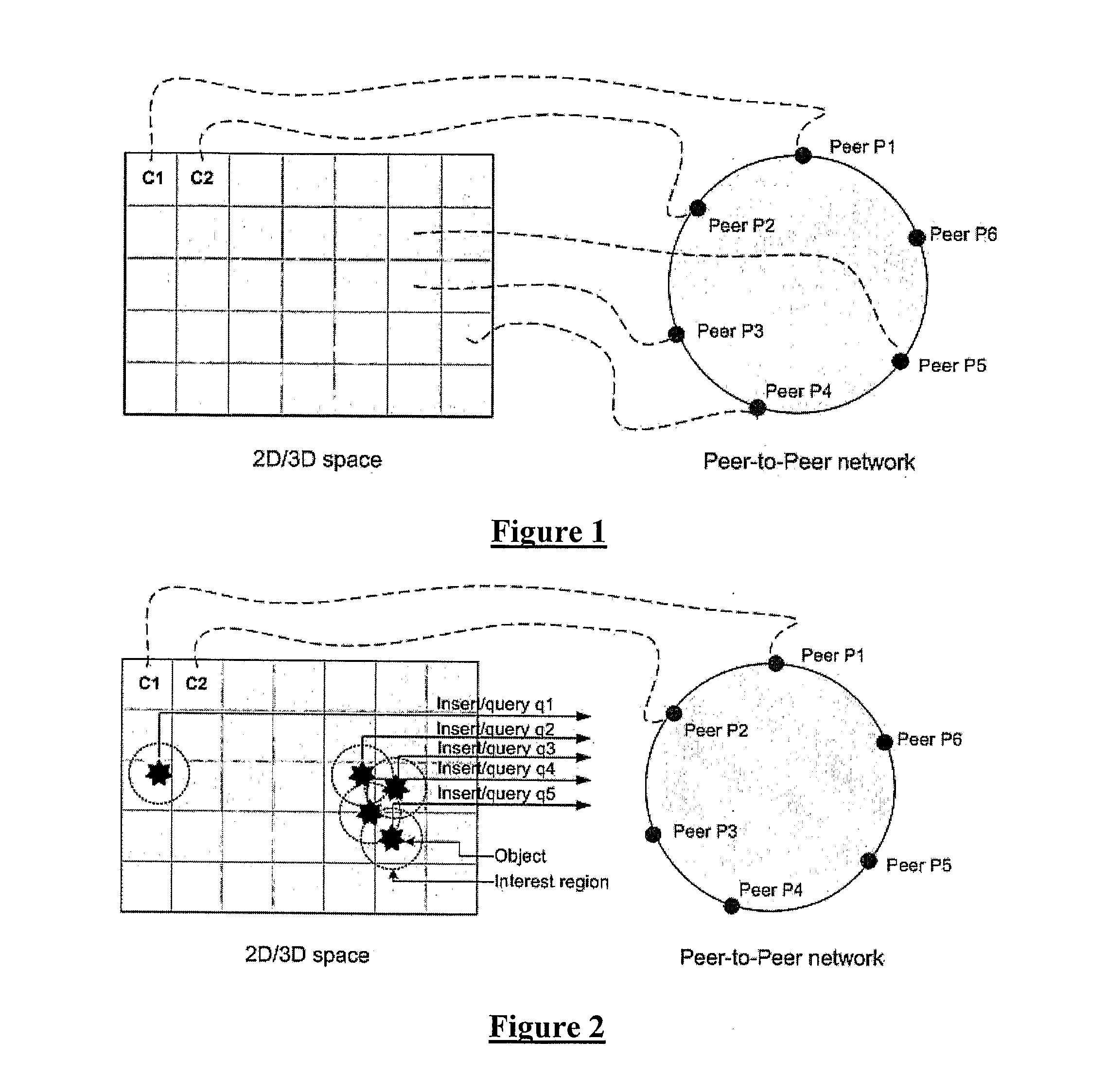
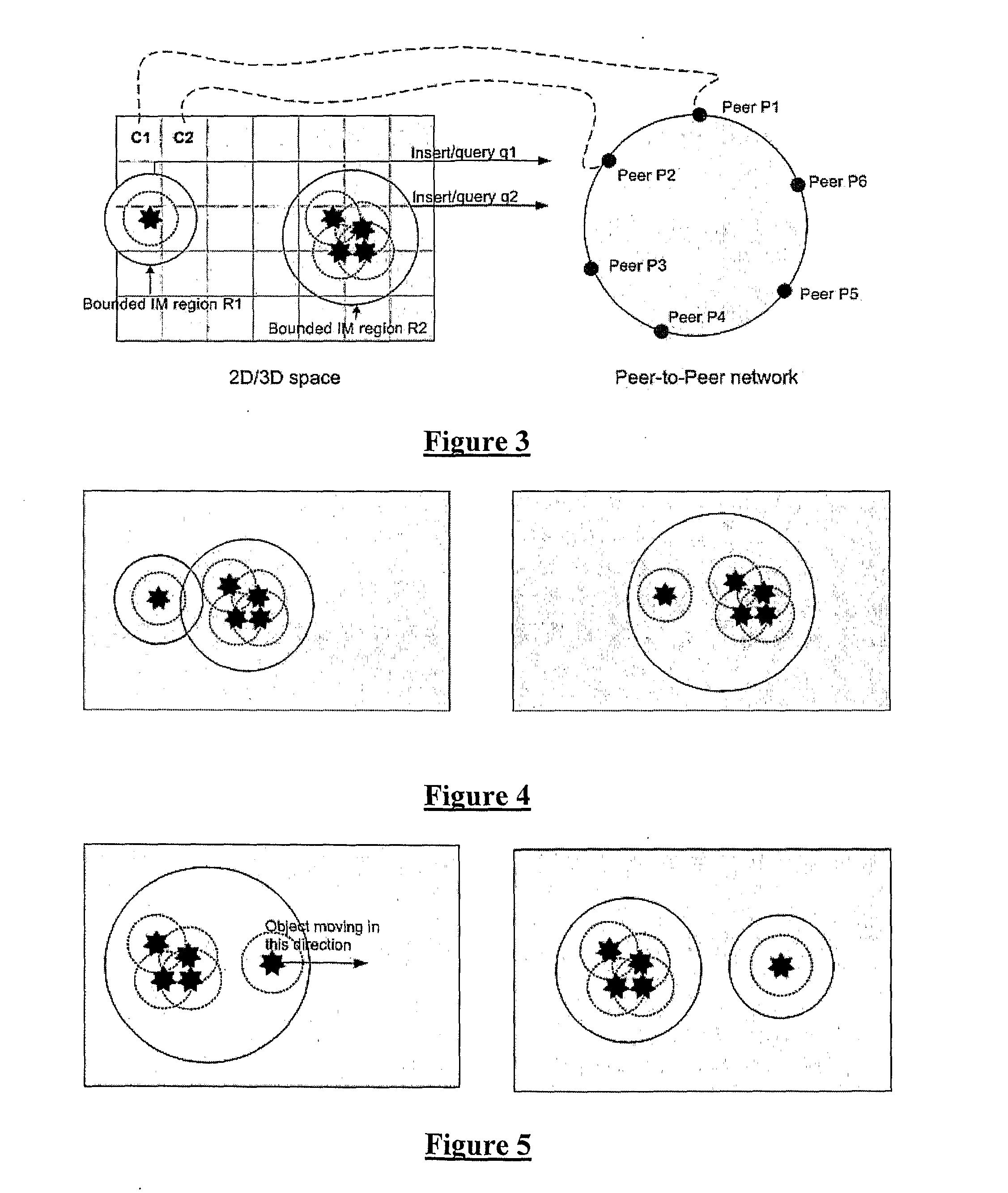
The embodiment of the invention described in the following relates to a peer-to-peer platform for deploying massively multi-player online games (MMOG). The present embodiment improves the scalability of decentralised MMOGs. Notably, the present embodiment provides for a bounded interest management (IM) service as an additional layer between the objects and the distributed hash table (DHT).
The present invention recognises that decentralised architectures for deploying an online environment may be used to avoid the problems of centralized gaming servers. As decentralized architectures use a peer-to-peer network to manage the MMO, there is no central point of failure and the platform can theoretically scale to a greater number of users. The present invention particularly recognises that when using a structured peer-to-peer network there exists additional overhead in maintaining a distributed hash table (DHT). A DHT is necessary in such architectures as it provides reliability and consi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com