Methods and compositions to prevent addiction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
References for Background and Example 1
[0095]1. Zuvekas, S. H., Vitiello, B. & Norquist, G. S. Recent trends in stimulant medication use among U.S. children. Am J Psychiat 163, 579-585 (2006).[0096]2. Olfson, M., Marcus, S. C., Weissman, M. M. & Jensen, P. S. National trends in the use of psychotropic medications by children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41, 514-521 (2002).[0097]3. Brown, R. T., et al. Treatment of attention-deficit / hyperactivity disorder: overview of the evidence. Pediatrics 115, e749-757 (2005).[0098]4. Robbins, T. W. ADHD and addiction. Nat Med 8, 24-25 (2002).[0099]5. Volkow, N. D. Stimulant medications: how to minimize their reinforcing effects? Am J Psychiatry 163, 359-361 (2006).[0100]6. Biederman, J., et al. Is ADHD a risk factor for psychoactive substance use disorders? Findings from a four-year prospective follow-up study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36, 21-29 (1997).[0101]7. Biederman, J., Wilens, T. E., Mick, E., Faraone, S. V. & Spencer, T....
experiment 1
[0124]The following experiments will verify that:
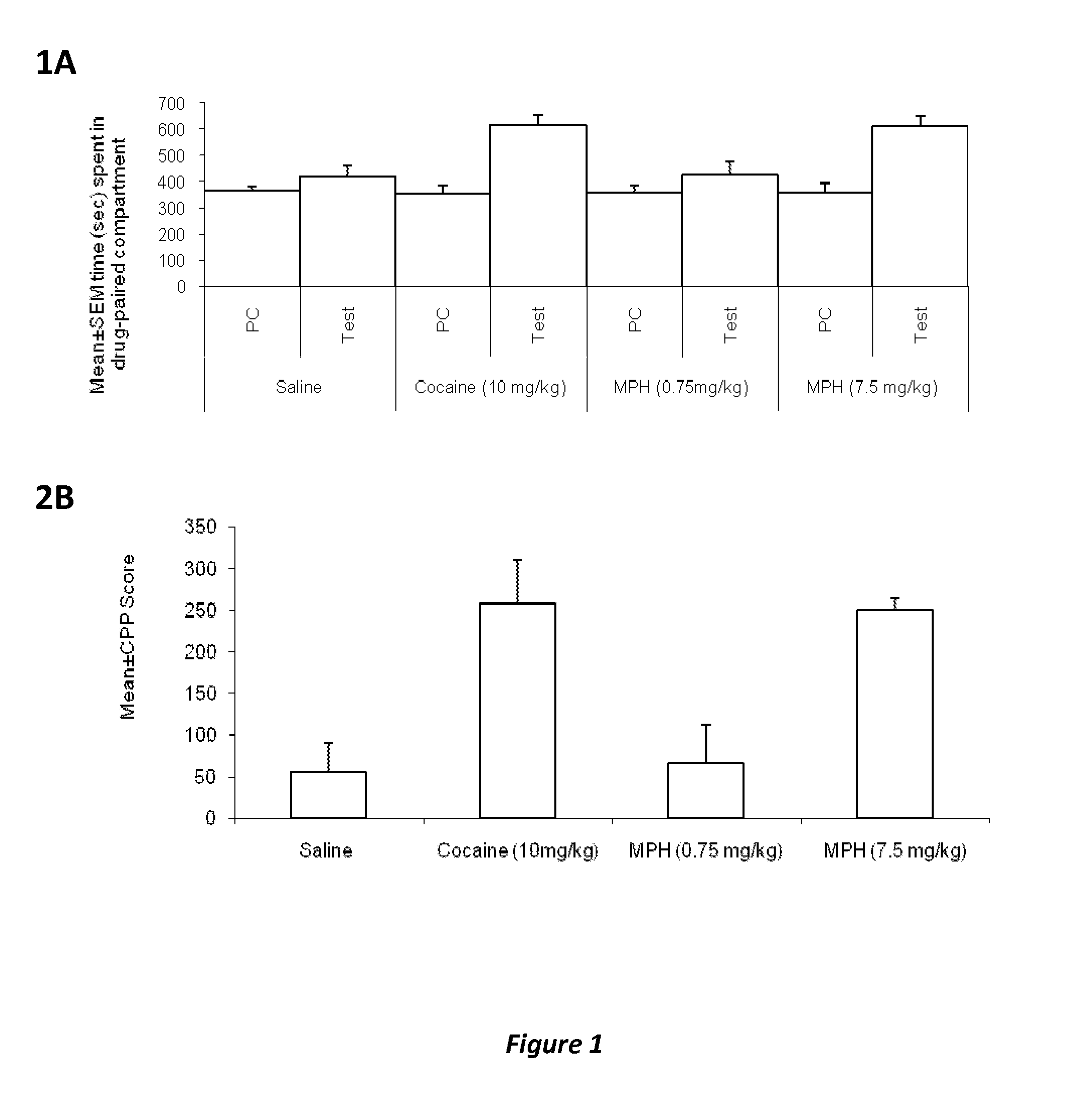
[0125]a) Supra-therapeutic doses of MPH administered to 90-day old (adult) mice produce MPH conditioned place preference (indirect measure of euphoria leading to addiction) whereas therapeutic doses of MPH produce conditioned place aversion (indirect measure of dysphoria leading to aversion)
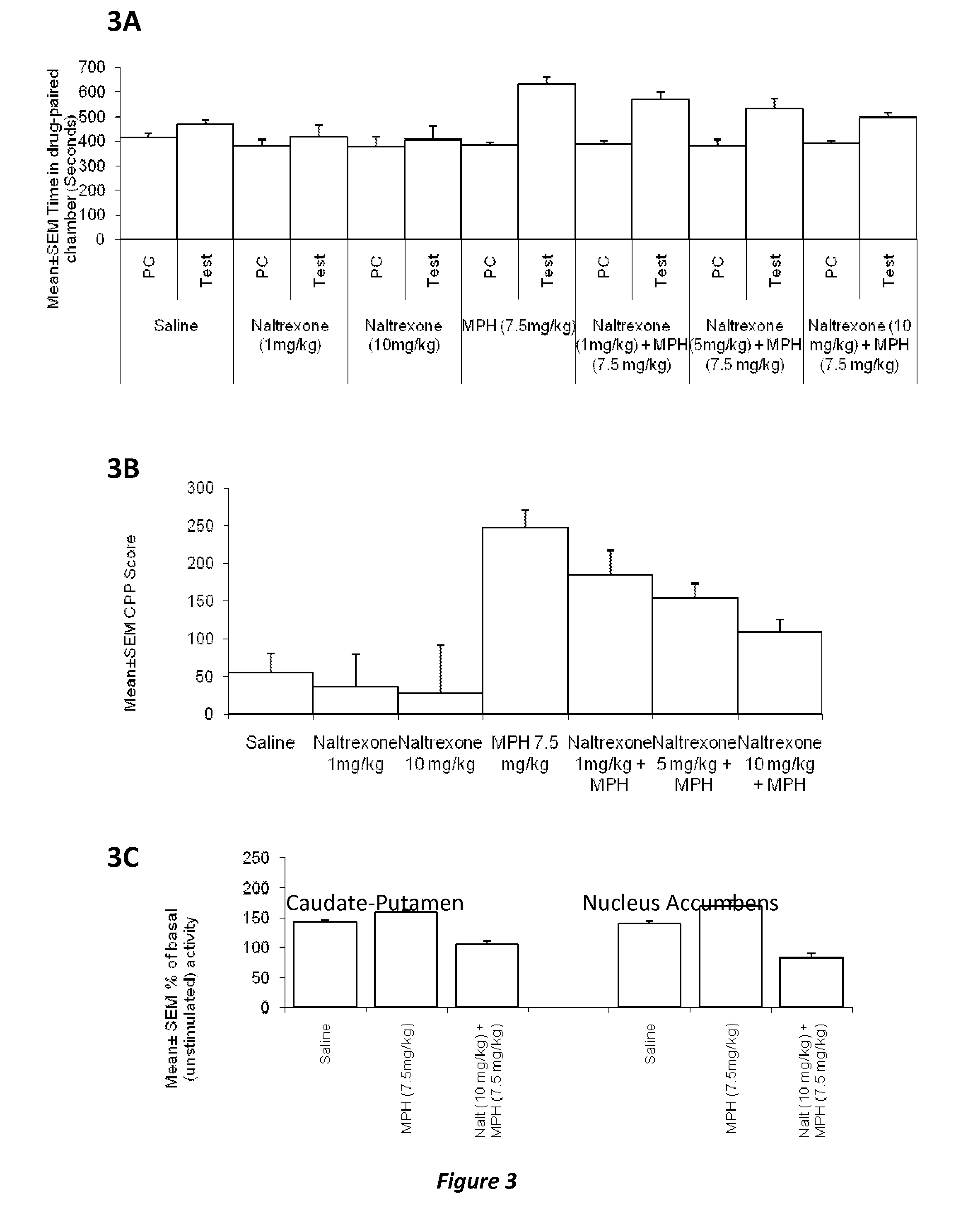
[0126]b) Co-administration of naltrexone, an opioid receptor antagonist, and supra-therapeutic dose of MPH attenuates MPH-induced conditioned place preference whereas co-administration of naltrexone and therapeutic doses of MPH attenuates MPH-induced conditioned place aversion.
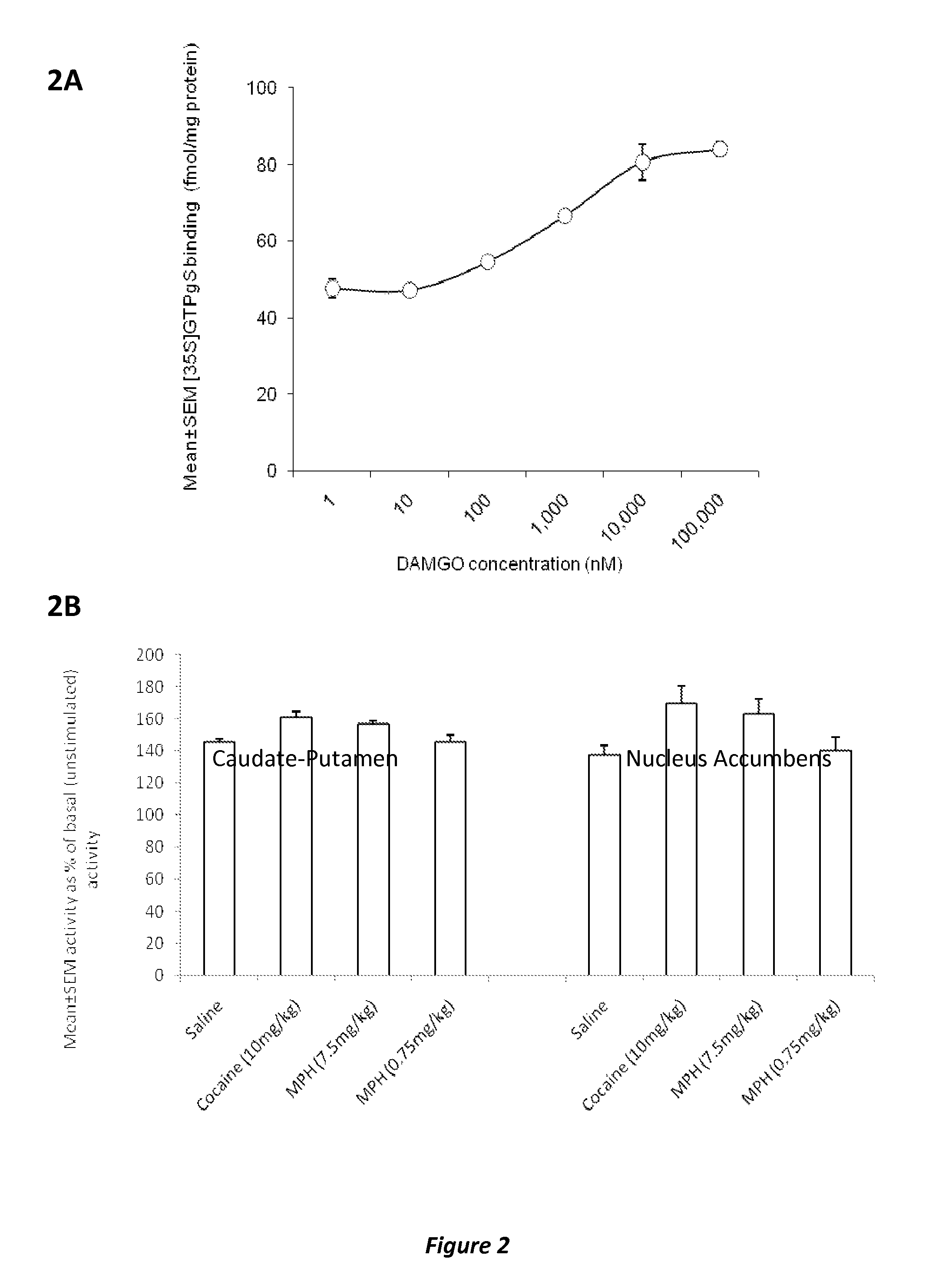
[0127]c) MPH-induced conditioned place preference correlates with upregulation of mu or delta opioid receptor activity whereas MPH-induced conditioned place aversion correlates with upregulation of kappa opioid receptor activity in the striatum. Naltrexone-MPH co-administration attenuates both types of changes in opioid receptor activity observed when MPH is administered alon...
experiment 2
[0134]The following experiment will show that naltrexone-MPH co-administration does not adversely influence the effects of MPH on attentional mechanisms in a 2-choice serial reaction time test. The effects of MPH alone versus naltrexone+MPH on operant extinction learning will also be compared. Each of the analyses will be performed following twice daily, short-term (5 days) or long-term (35 days) drug administration.
[0135]0.75 mg / kg MPH plus 5 or 10 mg / kg naltrexone (these doses were effective in Preliminary studies) will be used. Behavioral analyses will be performed in collaboration with and under the direct supervision of Dr. Jean-Cosme Dodart. The principal assay will be the 2-CSRT assay recently developed in Dr. Dodart's lab (Dillon et al., 2009). This is a novel attention task that overcomes some of the limitations of the other attentional task used in rodents, the 5-CSRT task. The 5-CSRT requires an average training period of 3-4 months for normal rodents (i.e. rats or mice) ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com