Process and System For Manufacturing Improved Heat Value Solid Fuel From Solid Waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
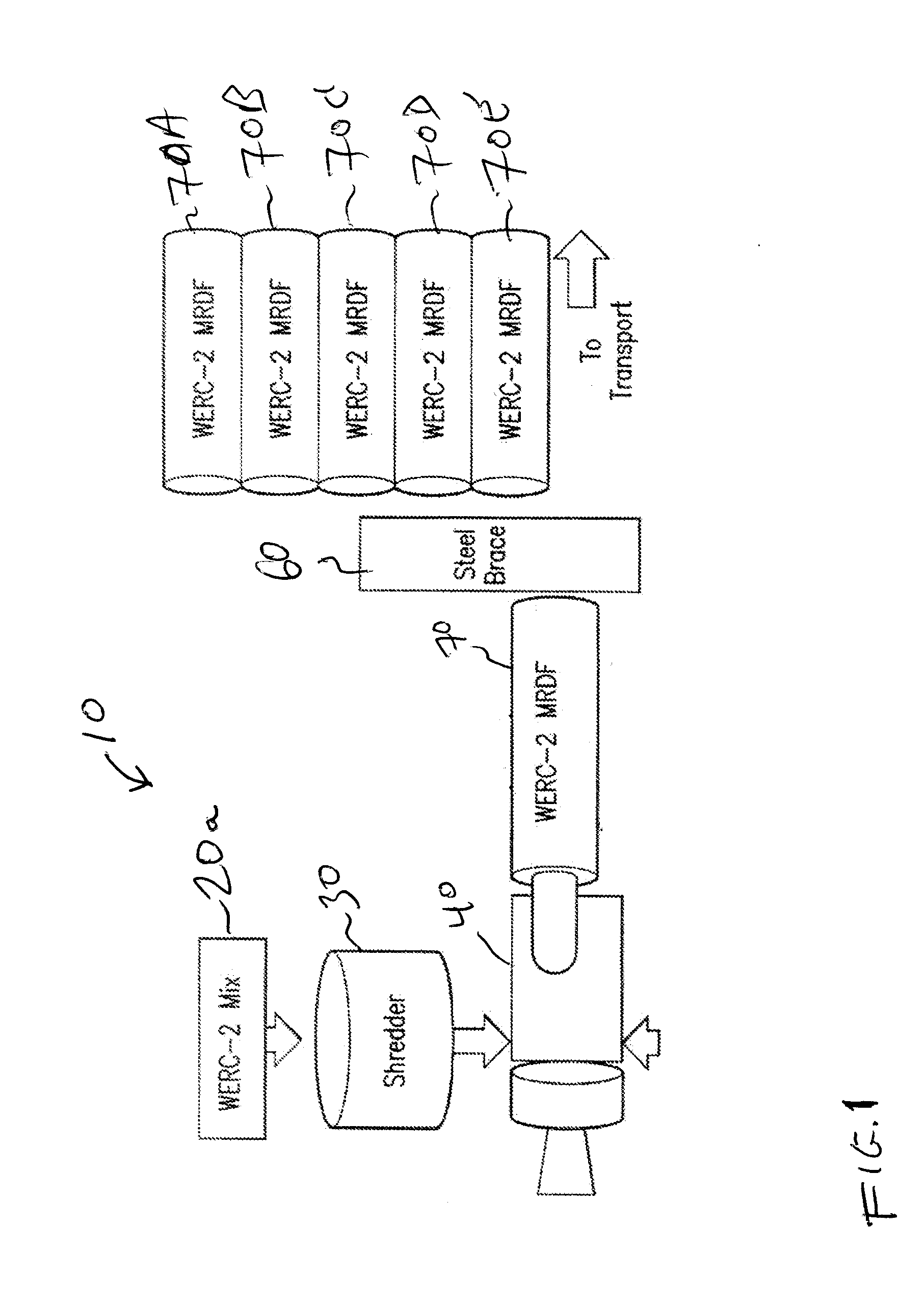
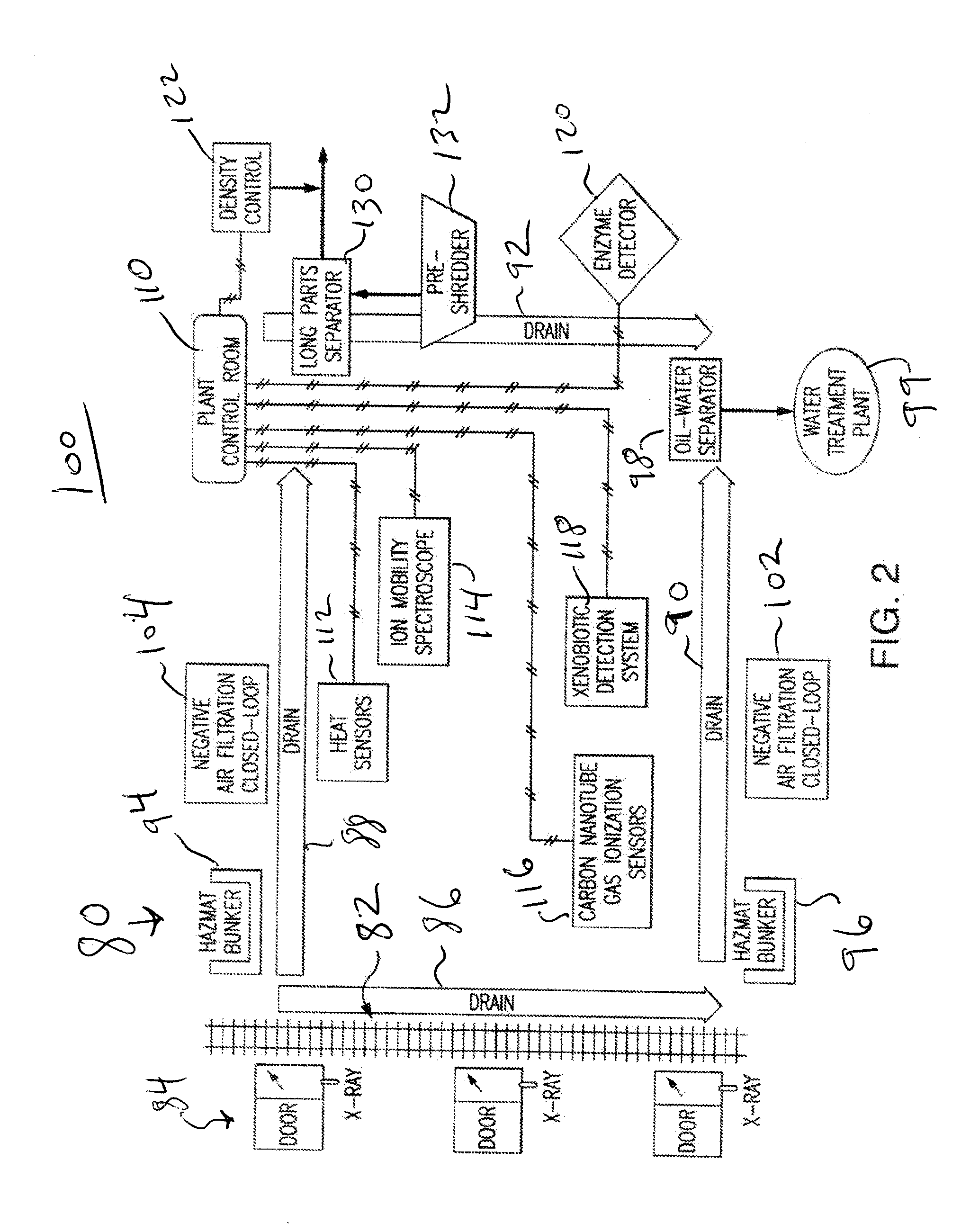
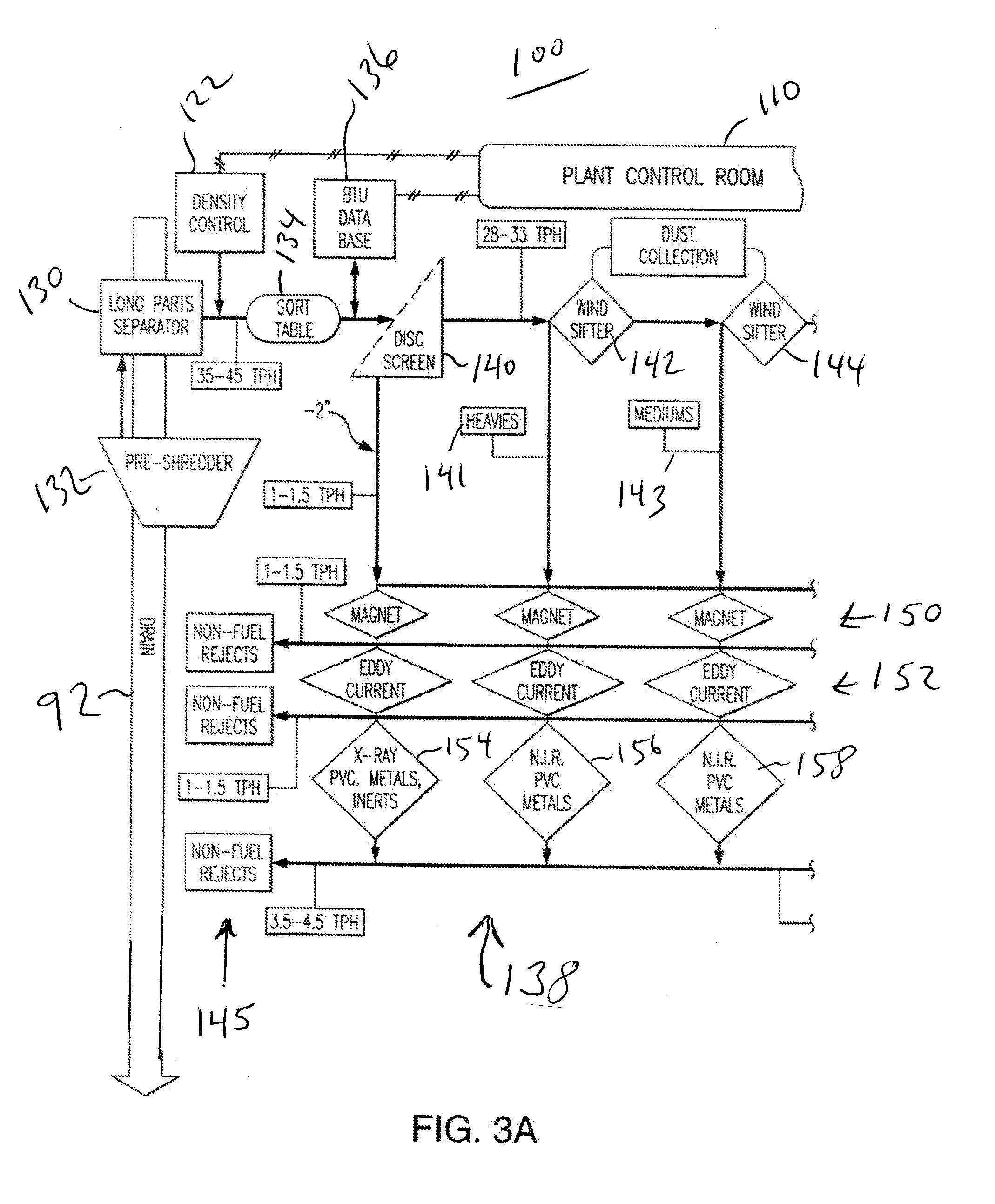
[0027]This invention may be accomplished by a system and method which performs thermodynamic analysis on a waste feedstock stream, adds combustible polymeric material to adjust at least the BTU or other heat value as well as hydrophobic properties, mixes the adjusted feedstock, and then directs the mixed feedstock into at least one product forming machine to produce fuel having a substantially consistent BTU value and other preselected parameters as desired.
[0028]Preferably, the waste stream is initially subjected to a novel process of taking the raw RSW (residential solid waste), commercial solid waste and / or selected MSW (municipal solid waste), as received at a facility. A novel, sophisticated manufacturing process according to the present invention preferably includes: separation, shredding, one or more optional drying steps, dynamic analysis during manufacturing, and a specialized process of adding combustible polymers, to produce a solid fuel. The resultant process preferably ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com