Method for climate control in buildings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
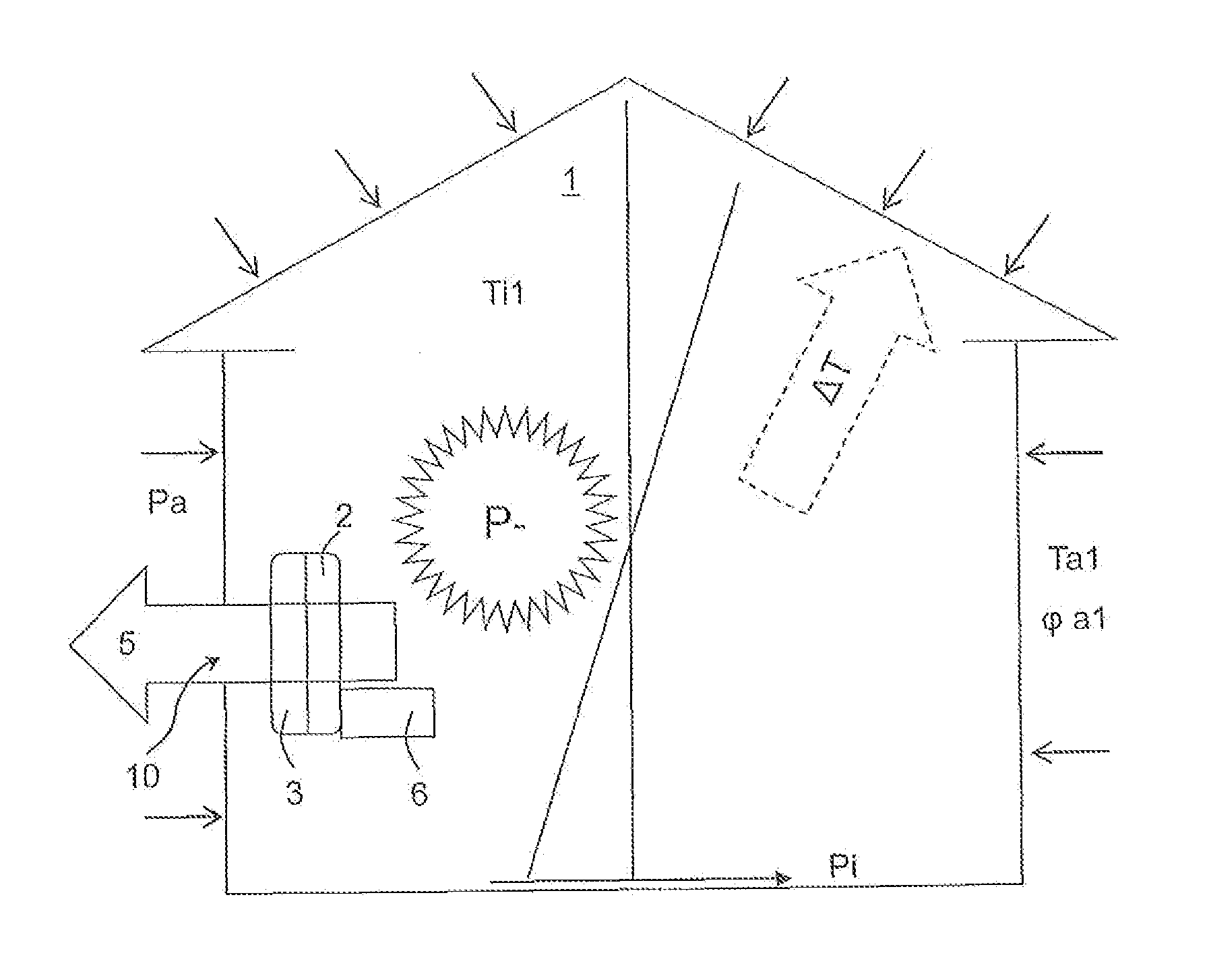
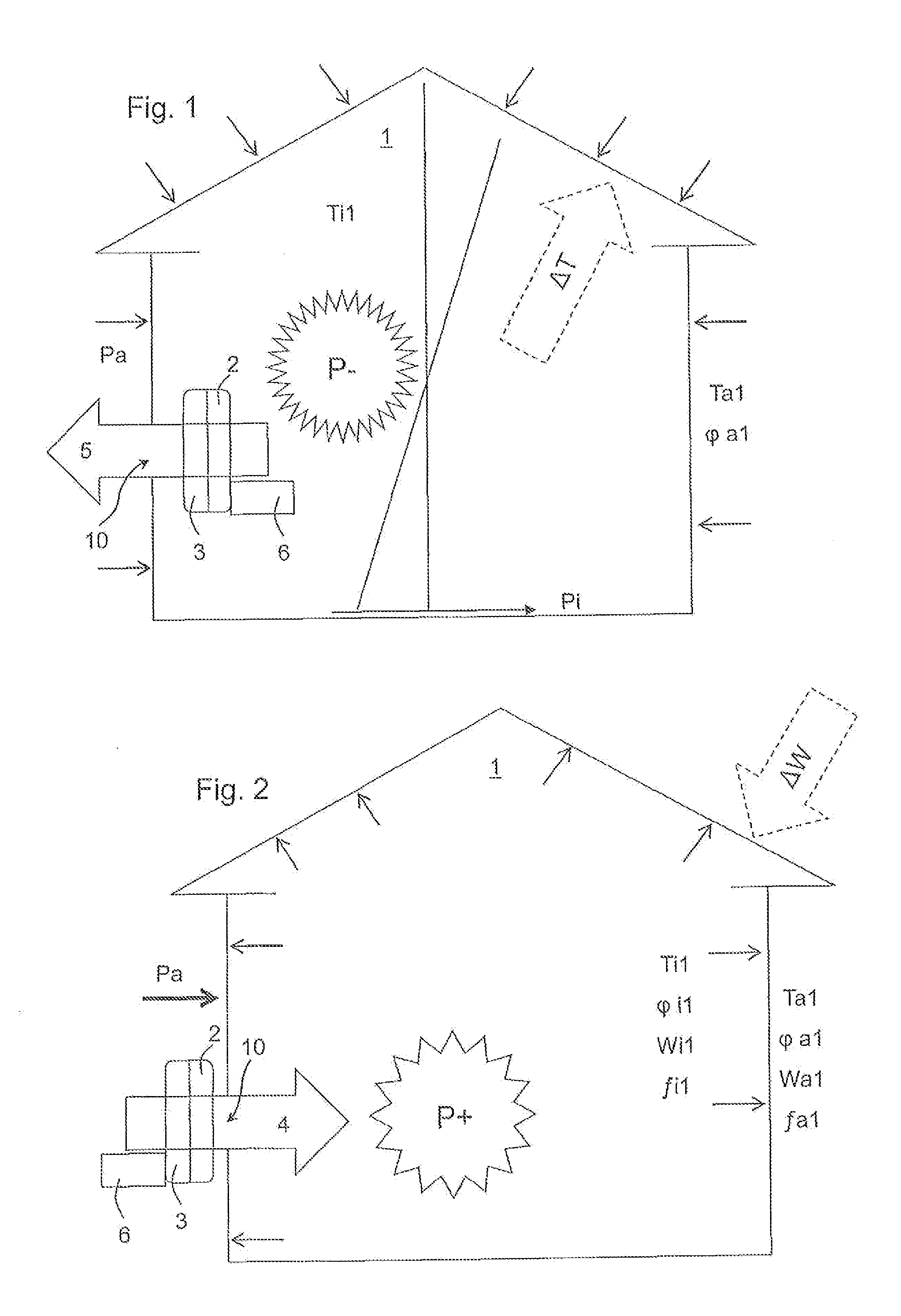
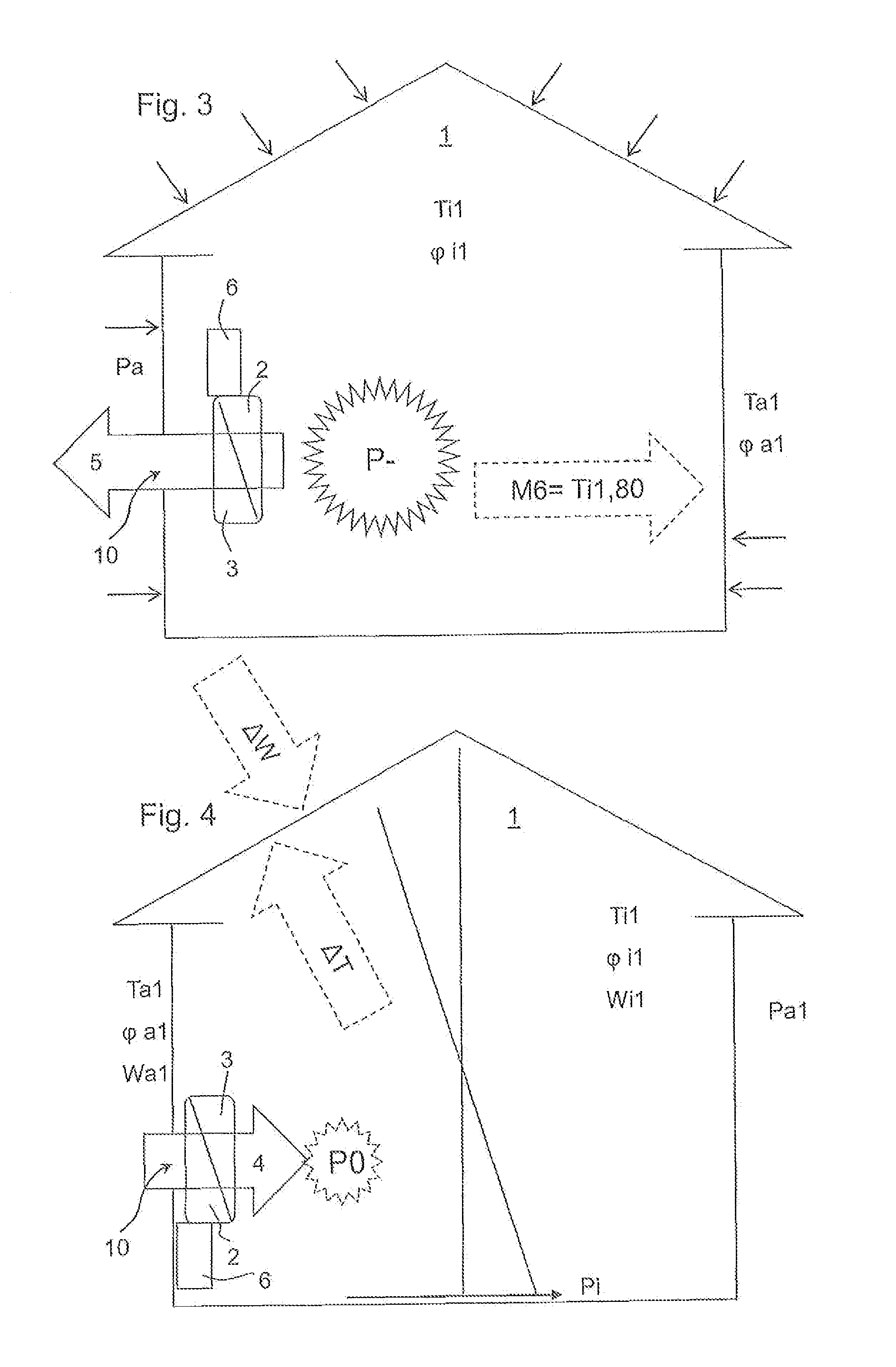
[0054]In practice, a plurality of the afore-described variables are measured directly at a building 1 by means of corresponding sensors or are calculated by means of a corresponding logic in the regulation.
[0055]The following example is to clarify this. Assumption:
Ta = 12°φa = 0.8Ti = 18° C.φ1 = 0.5Building height = 5 mmwind speed = 3 m / s
It follows from this:[0056]1) A partial water vapor pressure difference from outside to inside of 91 Pascal.[0057]2) A pressure drop of the internal building pressure Pi of 1.2 Pascal and an internal building pressure Pi in the lower range of −0.6 Pascal. An overpressure P+ of 5.6 Pascal results through the wind.[0058]3) A temperature drop of 6 Kelvin from the inside to the outside.
[0059]It is to now be determined, how the air flow is to be forced through the ventilation system 2. When considering only the critical relative humidity of 0.8, it can then be determined that the inside air would reach a critical moisture value when passing through the i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com