Prosthetic foot with hybrid layup
a technology of prosthetic feet and hybrid materials, applied in the field of prosthetic feet, can solve the problems of increasing the weight of the foot, increasing the rigidity and thickness of the prosthetic foot, and corresponding increases in stiffness and stiffness, so as to achieve the effect of increasing strength, increasing flexibility or stiffness, and increasing strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020]Embodiments of the invention will now be described with reference to the accompanying figures, wherein like numerals refer to like elements throughout. Although several embodiments, examples and illustrations are disclosed below, it will be understood by those of ordinary skill in the art that the invention described herein extends beyond the specifically disclosed embodiments, examples and illustrations and can include other uses of the invention and obvious modifications and equivalents thereof. The terminology used in the description presented herein is not intended to be interpreted in any limited or restrictive manner simply because it is being used in conjunction with a detailed description of certain specific embodiments of the invention. In addition, embodiments of the invention can comprise several novel features and no single feature is solely responsible for its desirable attributes or is essential to practicing the inventions herein described.
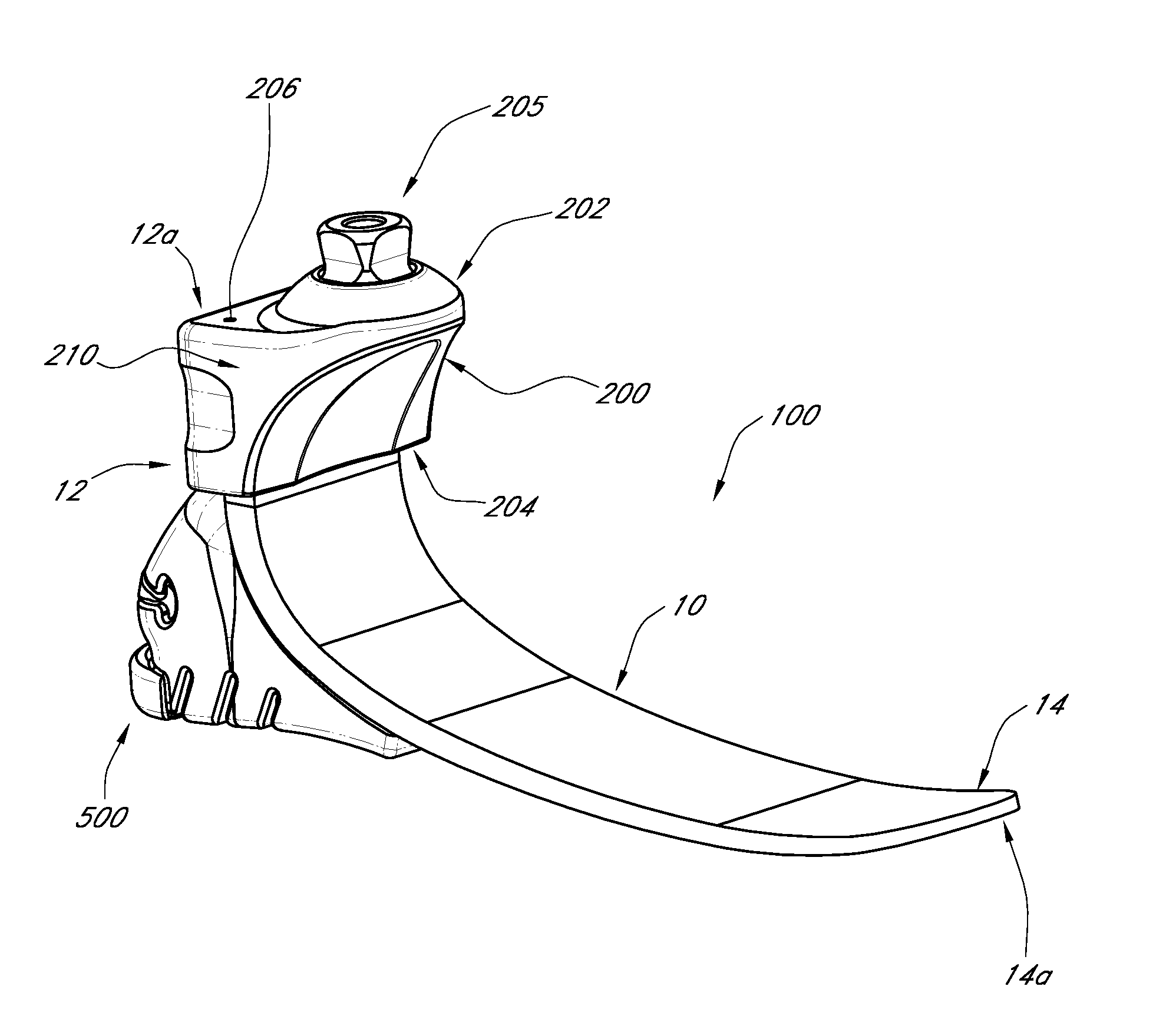
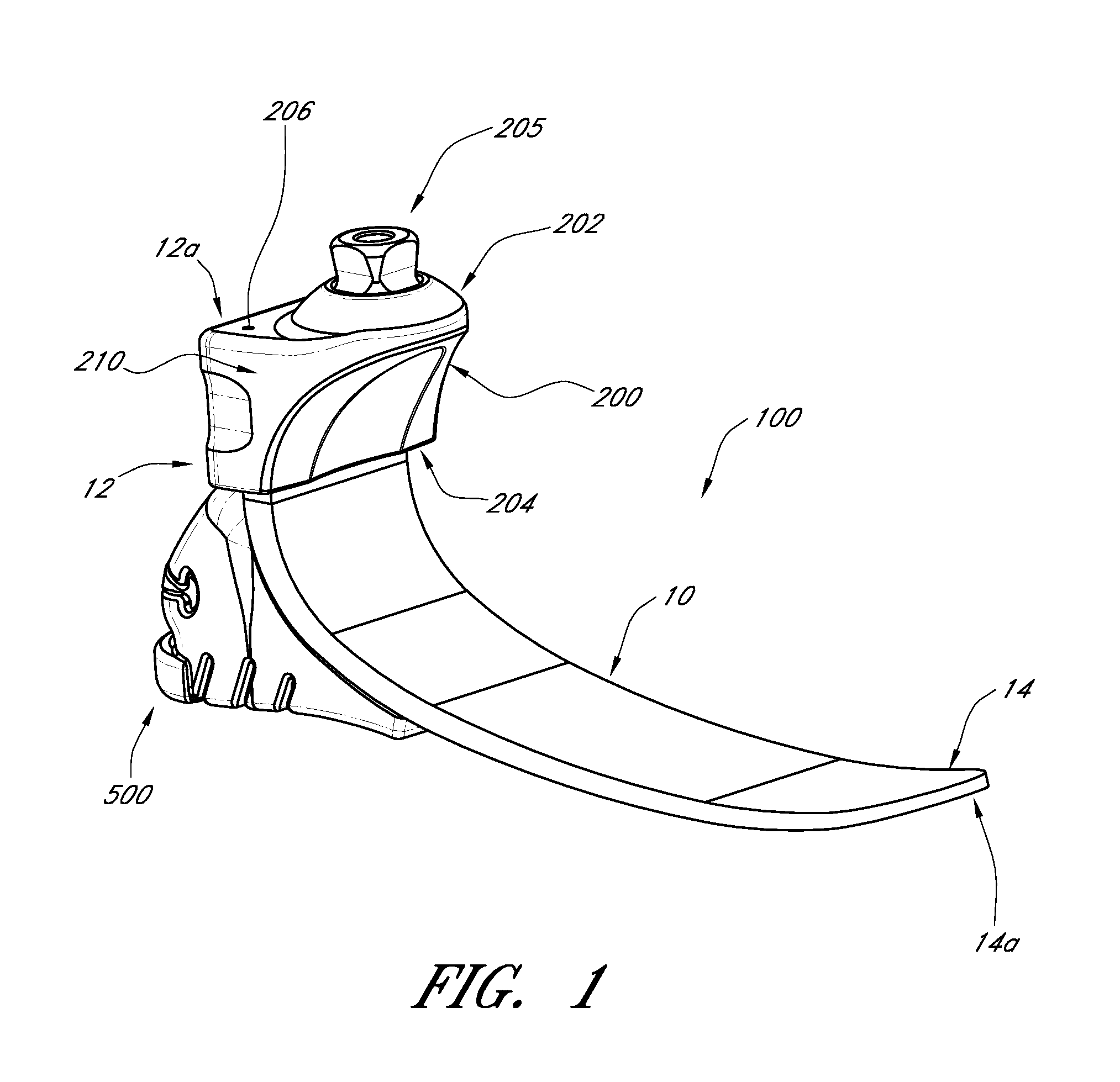
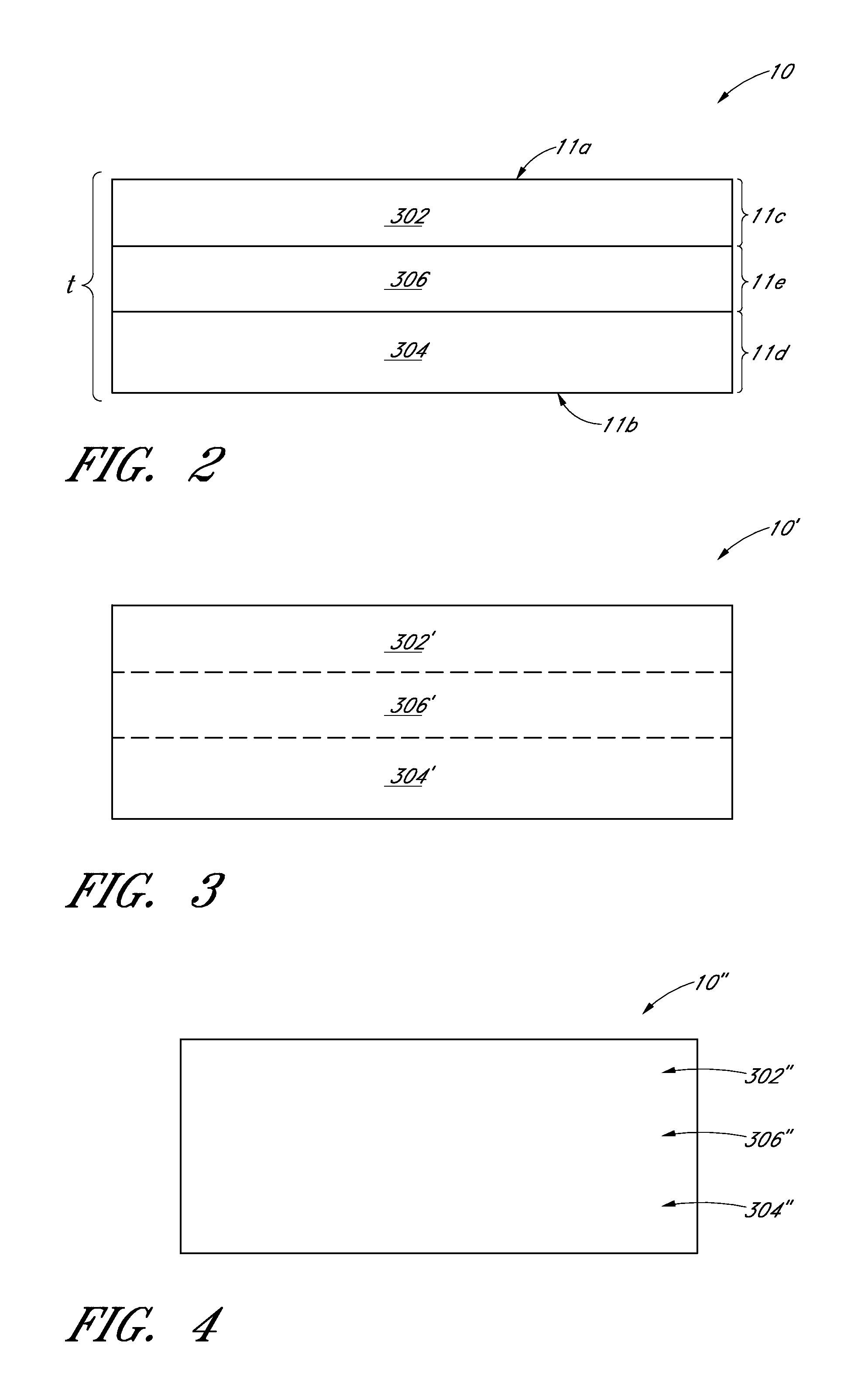
[0021]FIG. 1 illustrat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com