Hydraulic Fracturing Process for Deviated Wellbores
a hydraulic fracturing and wellbore technology, applied in drinking water installation, borehole/well accessories, construction, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of hydraulic fracture stimulation, high cost of hydraulic fracture equipment and wellbore intervention equipment, and high cost of use of isolation or diversion means at each stage, so as to improve the volume of stimulated reservoirs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
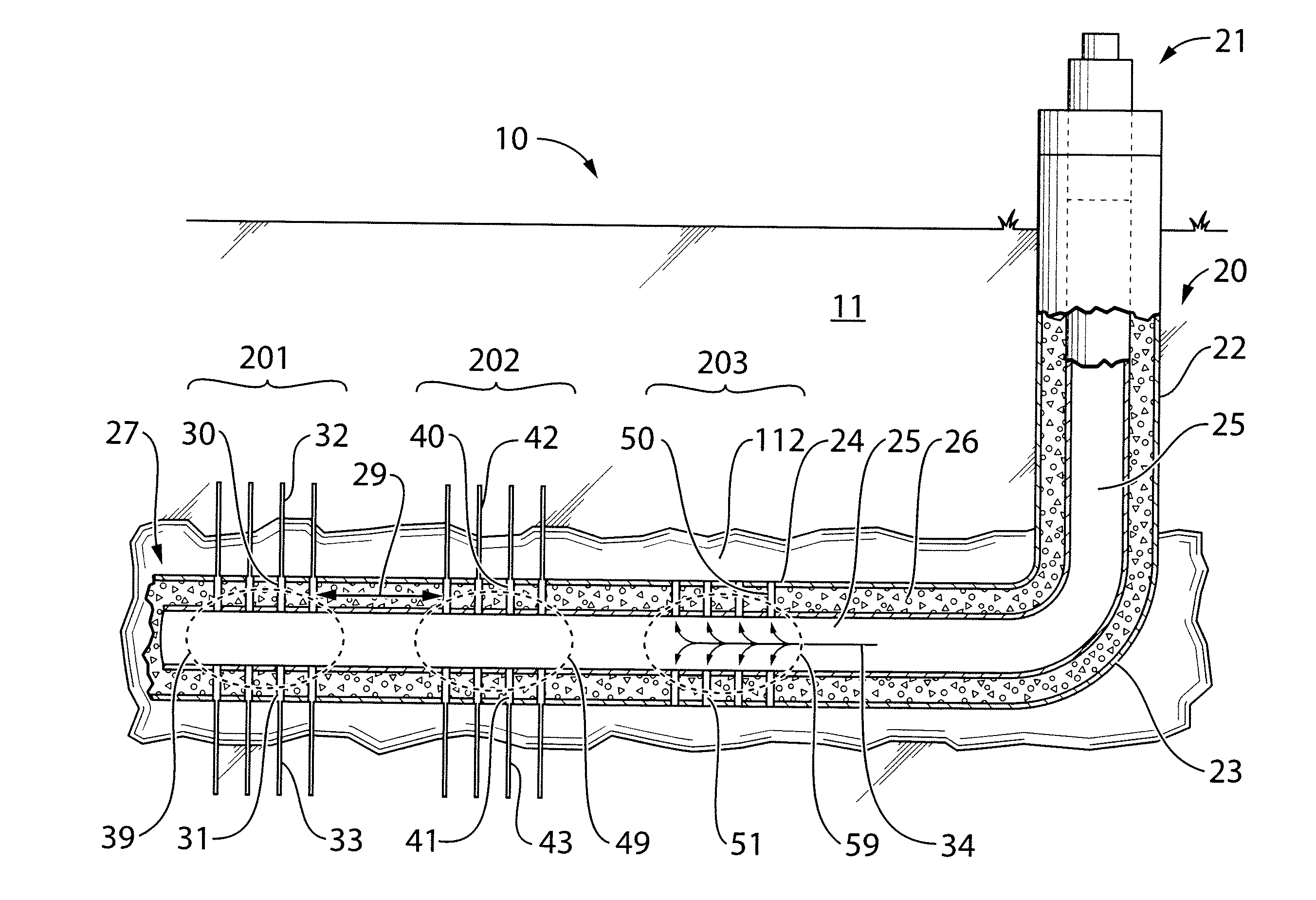
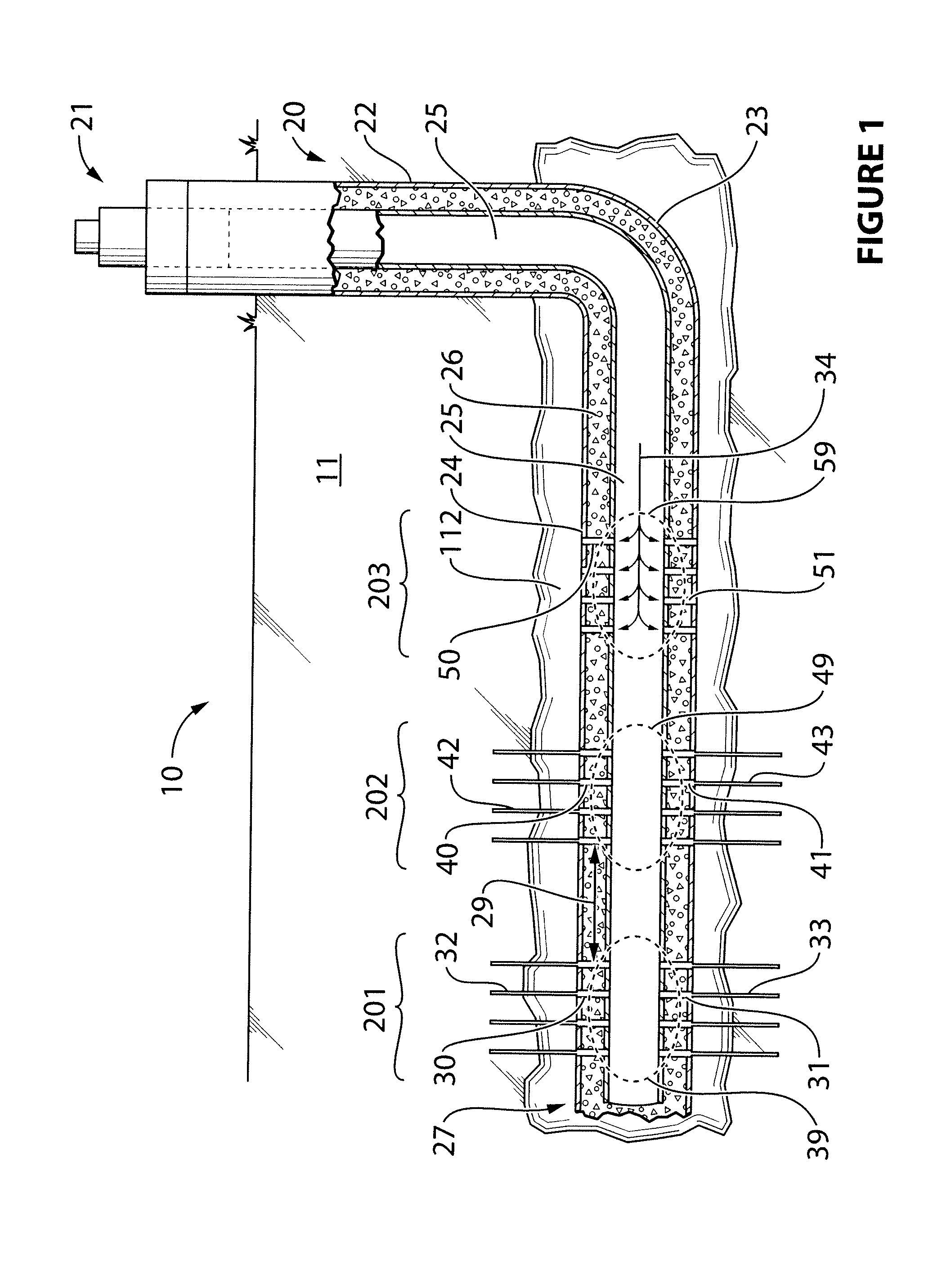
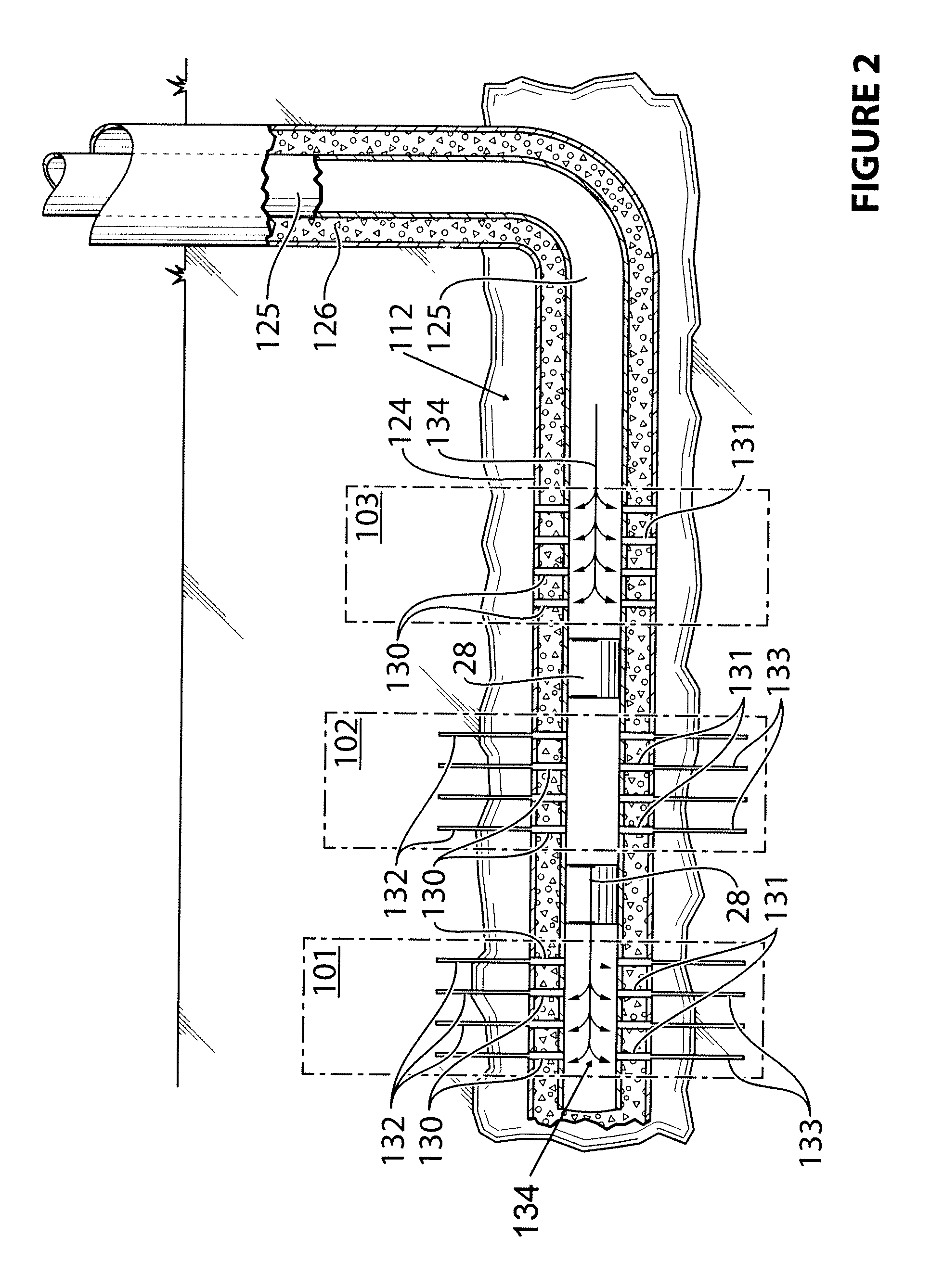
[0149]In the following example, traditional “Plug and Perf” was performed, followed by the method of the present invention, in a horizontal wellbore with a casing, to assess the viability thereof. Referring now to FIG. 4, the following was conducted:
[0150]Stages 101, 102, 103 up to 300 were created using the prior art technology “Plug and Perf” and then fractured with use of a plug 28 between each of the stages.
[0151]Upon completion of fracturing stage 300, a plug 28 was introduced into the wellbore 124. Wellbore 124 has a casing 125 which is cemented 126. Stage 201 was perforated 230 and 231 and fractured 232 and 233, followed by the perforation 241, 240, 251, 250 and fracturing 242, 243, 252, 253 of stages 202 and 203. R / A tracer was pumped (not shown) in stages 202 and 203 during fracturing. Three tracers were used: 1 Isotopes in test stage 202 and 2 Isotopes in test stage 203. A finding of 2 Isotopes of R / A material in these stages, indicated perforations in all stages and confi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com